
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 238-246.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6156 238
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yusong LÜ1,#, Yunfeng XIE1,2,#, Zhonghua SHENG1, Yawen WU1, Shaoqing TANG1, Peisong HU1, Xiangjin WEI1,*( )
)
Received:2016-11-24
Revised:2017-02-06
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-05-10
Contact:
Xiangjin WEI
吕育松1,#, 谢耘丰1,2,#, 圣忠华1, 邬亚文1, 唐绍清1, 胡培松1, 魏祥进1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
魏祥进
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yusong LÜ, Yunfeng XIE, Zhonghua SHENG, Yawen WU, Shaoqing TANG, Peisong HU, Xiangjin WEI. Morphological and Molecular Genetic Analysis of a Dwarf and Small Grain Rice Variety Xiaoxiang’ai[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 238-246.
吕育松, 谢耘丰, 圣忠华, 邬亚文, 唐绍清, 胡培松, 魏祥进. 矮秆小粒水稻潇湘矮的形态学与分子遗传学分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 238-246.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6156 238
| 引物 Marker name | 前引物序列 Forward(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RM18408 | GGCACTCTGGTTCCTCAATGG | TCTGTATCATCAACGGCAACTCC |
| RM5140 | GGCACTCGTATTTCTCAACTTCTCC | GGGTGTATCAGGAGTACAGGTTGC |
| RM18457 | ATCCTCCACCGCTCAAGAACACG | CGAGGCCATTCATCGAACAAAGC |
| RM18402 | TTATGAGGCAGCCCGTAATGTTGC | GCAGCGGTGTCAACAGCTTCC |
| RM18450 | AAGGCTCCATGGTTGGTTGC | CGATGGACAGACAGTGTGTAGTGG |
| F78 | GGGACGAATTCTTTTCGATTAC | CGTGGACCAATTTTGGTAACTG |
| F79 | AATTATTCCACTATGCACATGT | ATTTTCTTCCATCGCCTCTTGC |
| F81 | GTAAACTATCGACTTGCTATGT | ACTAGTGCAGACTGTTTTCCTG |
| F82 | AGATGATTGGATGAGAATTTAA | ACCCAGAAACCATCTAGTAATT |
| F84 | GGGTGGCTCCTTACGACATTAC | TTTCATATTTTAGCGGTGCTCT |
| F85 | CCTCGACCCACTGCATCATCAG | TGGTCGGTCTCCTCCCTCTTCA |
| F86 | CAGTATTCGAGTAAGTTCACAA | CCTCGCCCCTATTCATCCTCTT |
Table 1 Primers for mapping in the study.
| 引物 Marker name | 前引物序列 Forward(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RM18408 | GGCACTCTGGTTCCTCAATGG | TCTGTATCATCAACGGCAACTCC |
| RM5140 | GGCACTCGTATTTCTCAACTTCTCC | GGGTGTATCAGGAGTACAGGTTGC |
| RM18457 | ATCCTCCACCGCTCAAGAACACG | CGAGGCCATTCATCGAACAAAGC |
| RM18402 | TTATGAGGCAGCCCGTAATGTTGC | GCAGCGGTGTCAACAGCTTCC |
| RM18450 | AAGGCTCCATGGTTGGTTGC | CGATGGACAGACAGTGTGTAGTGG |
| F78 | GGGACGAATTCTTTTCGATTAC | CGTGGACCAATTTTGGTAACTG |
| F79 | AATTATTCCACTATGCACATGT | ATTTTCTTCCATCGCCTCTTGC |
| F81 | GTAAACTATCGACTTGCTATGT | ACTAGTGCAGACTGTTTTCCTG |
| F82 | AGATGATTGGATGAGAATTTAA | ACCCAGAAACCATCTAGTAATT |
| F84 | GGGTGGCTCCTTACGACATTAC | TTTCATATTTTAGCGGTGCTCT |
| F85 | CCTCGACCCACTGCATCATCAG | TGGTCGGTCTCCTCCCTCTTCA |
| F86 | CAGTATTCGAGTAAGTTCACAA | CCTCGCCCCTATTCATCCTCTT |
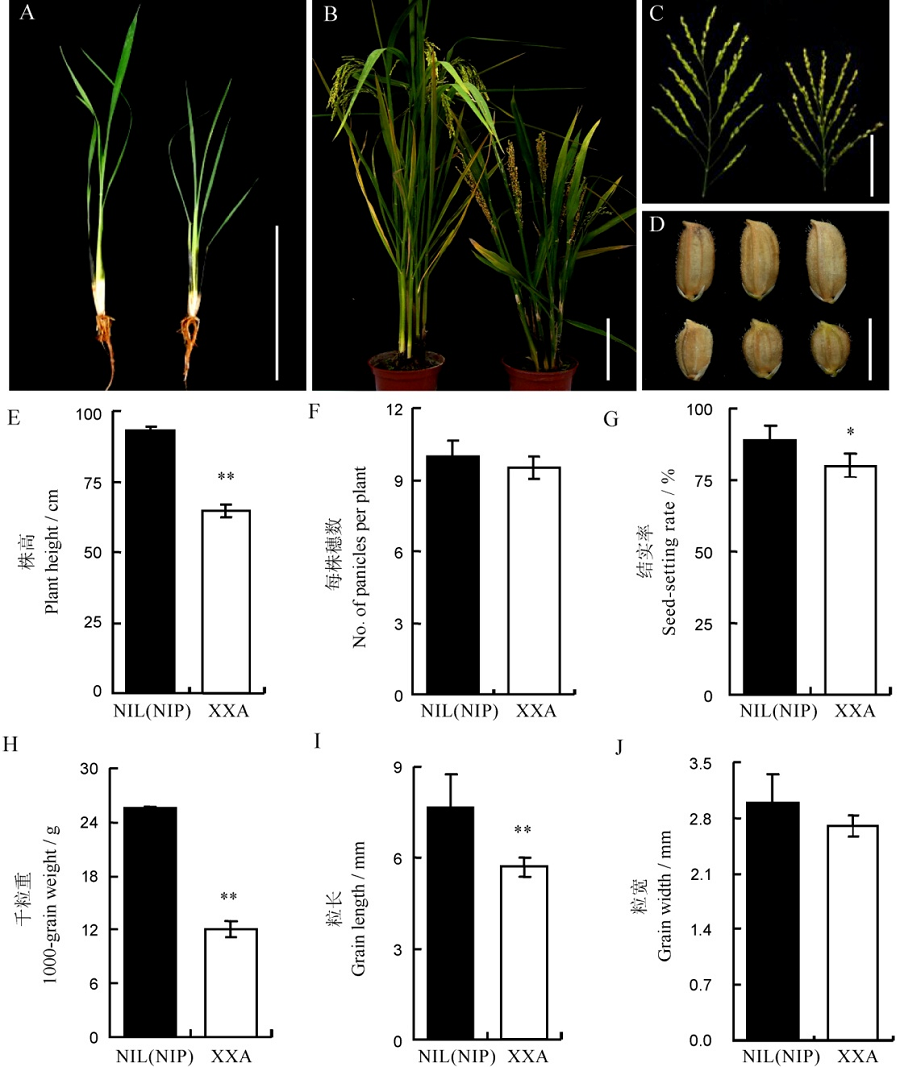
Fig. 1. Phenotype analysis of XXA and NIL(NIP). A, 5-weeks-old seedlings of NIL(NIP)(left) and XXA(right); B, Phenotypes of NIL(NIP) and XXA plants at the mature stage in paddy field; C, Comparison of main panicles between NIL(NIP) and XXA at the mature stage; D, Grain size of NIL(NIP) and XXA at the mature stage; E-J, Plant height(E), number of panicles per plant(F), seed setting rate(G), 1,000-grain weight(H), grain length(I) and grain width(J) between NIL(NIP) and XXA. Bar=10 cm in Figures A, B and C; Bar=5 mm in Figure D. Data in E-J are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the Student’s t-test(*P<0.05, **P<0.01).
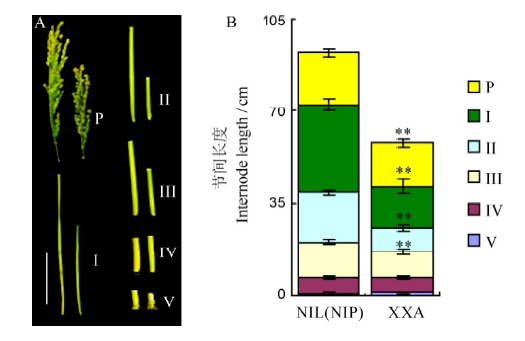
Fig. 2. The internode and panicle length comparison in XXA and NIL(NIP). A, Differences in panicles and internode length for NIL(NIP)(left) and XXA(right) plants. P, Panicle. Those from I to V indicate the corresponding internodes from the top to bottom, bar = 15 cm; B, Internode and young panicle length analysis of NIL(NIP) and XXA at the heading stage. Data in B are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the t-test(**P<0.01).
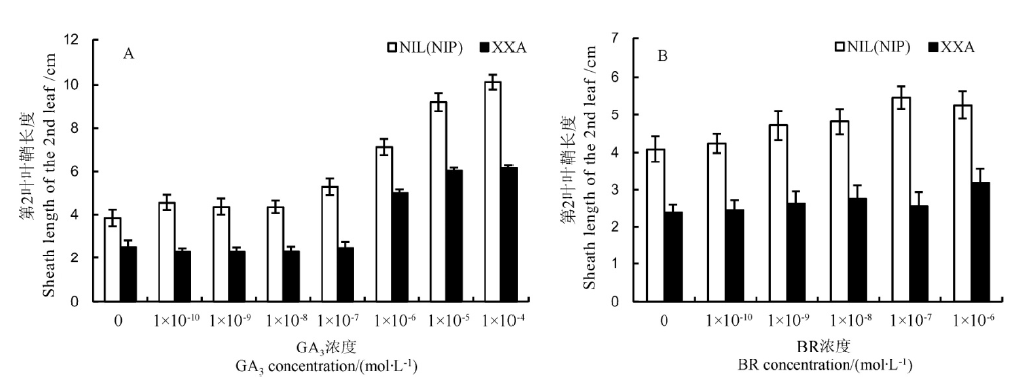
Fig. 3. Elongation of the second leaf sheath in response to gibberellin(A) and brassinolide(B) in NIL(NIP) and XXA plants. Data in A, B are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates.
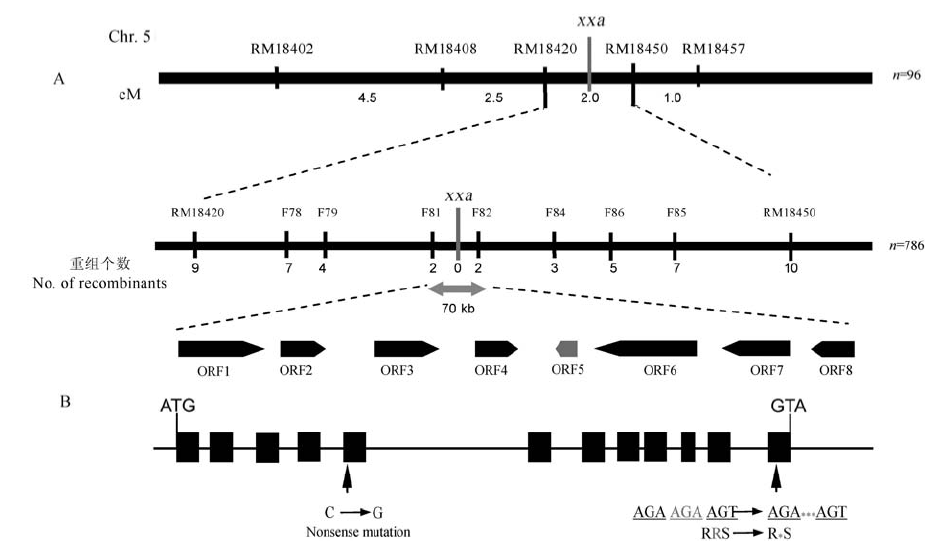
Fig. 4. Fine mapping and positional cloning of the candidate gene. A, Fine mapping of the xxa gene; B, The structure of candidate gene LOC_Os05g26890 and the mutation sites in XXA. Black arrows show 1-bp nonsense mutation in the 5th exon and a 3-bp deletion that resulted in a lysine deletion in the 12th exon of D1.
| F1组合 Combination of F1 | 总植株数 Total No. of plants | 正常植株数 No. of half-dwarfing plants | 矮秆小粒植株数 No. of dwarfing plants | 理论比 Expressed ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本晴/潇湘矮 Nipponbare/XXA | 3223 | 2341 | 782 | 3:1 | 0.078 |
| 热研1号/潇湘矮 Reyan 1/XXA | 2964 | 2249 | 725 | 3:1 | 0.420 |
| 0248/潇湘矮 0248/XXA | 3744 | 2812 | 932 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
| Y01/潇湘矮 Y01/XXA | 3416 | 2560 | 856 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
Table 2 Segregation of combination Nipponbare/XXA , Reyan 1/XXA, 0248/XXA and Y01/XXA.
| F1组合 Combination of F1 | 总植株数 Total No. of plants | 正常植株数 No. of half-dwarfing plants | 矮秆小粒植株数 No. of dwarfing plants | 理论比 Expressed ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本晴/潇湘矮 Nipponbare/XXA | 3223 | 2341 | 782 | 3:1 | 0.078 |
| 热研1号/潇湘矮 Reyan 1/XXA | 2964 | 2249 | 725 | 3:1 | 0.420 |
| 0248/潇湘矮 0248/XXA | 3744 | 2812 | 932 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
| Y01/潇湘矮 Y01/XXA | 3416 | 2560 | 856 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
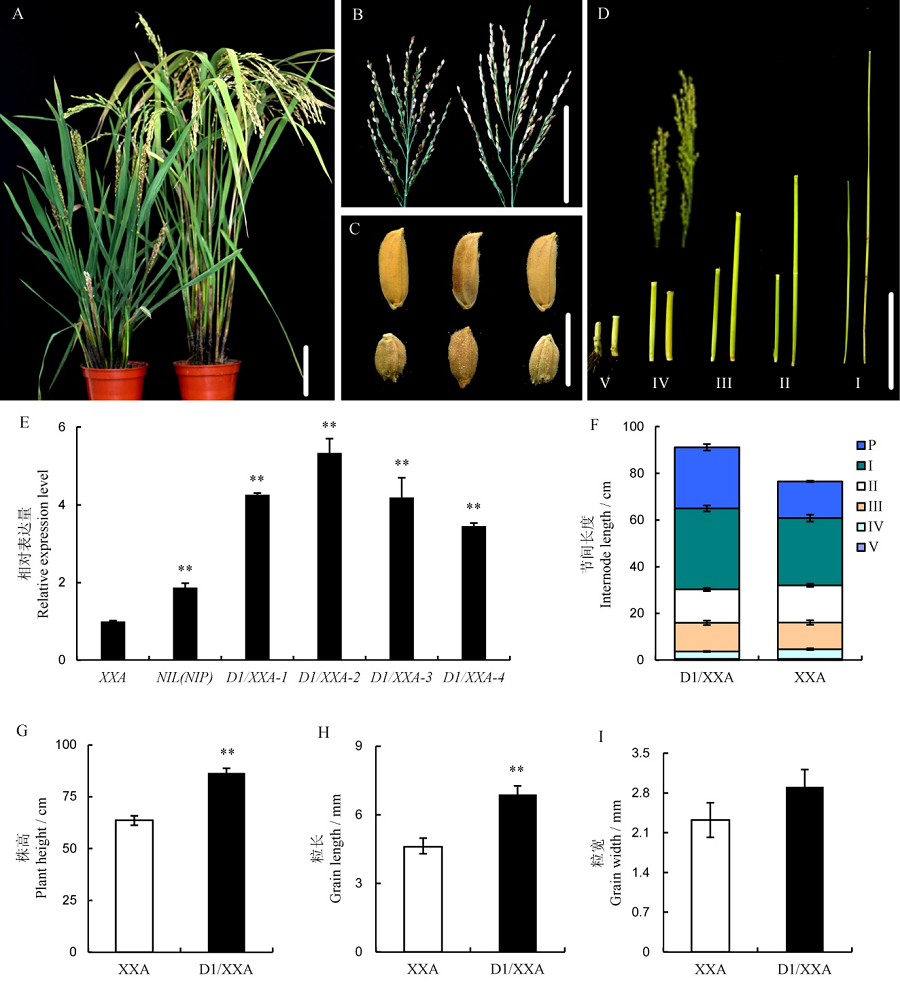
Fig. 5. Phenotype analysis of complementary plants(D1/XXA). A-D, Phenotypes of the complementary plants of D1/XXA-1(right) and XXA(left) at harvesting time, including plant type(A), panicle(B), grain size(C) and internode(D) of D1/XXA-1 and XXA; E, Relative expression levels of D1 gene in XXA and D1/XXA lines. F-I, Internode length(F), plant height(G), grain length(H) and grain width(I) of D1/XXA-1 and XXA(Bar=10 cm in A, B and D; Bar=5 mm in C). Data in E are shown as Mean±SD from 3 individual replicates. Data in F-I are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the Student’s t-test(*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
| [1] | Khush G S.Green revolution: the way forward.Nat Rev Genet, 2001, 2(10): 815-822. |
| [2] | Hu C H.Evaluation of breeding semidwarf rice by induced mutation and hybridization.Euphytica, 1973, 22: 562-574. |
| [3] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice.Nature, 2002, 416: 701-702. |
| [4] | Peng J, Richards D E, Hartley N M, Murphy G P, Devos K M, Flintham J E, Beales J, Fish L J, Worland A J, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape J W, Gale M D, Harberd N P.“Green revolution” genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators.Nature, 1999, 400: 256-261. |
| [5] | 张云辉, 张所兵, 林静, 汪迎节, 方先文. 水稻株高基因克隆及功能分析的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30: 1-7. |
| Zhang Y H, Zhang S B, Fang X W, Lin J, Wang Y J, Fang X W.Research progress on cloning and functional analysis of plant height genes in rice(Oryza sativa L.).Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2014, 30: 1-7.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Fujioka S, Yokota T.Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2003, 54: 137-164. |
| [7] | Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Sato Y, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.The gibberellin signaling pathway is regulated by the appearance and disappearance of SLENDER RICE1 in nuclei.Plant Cell, 2002, 14: 57-70. |
| [8] | Hirano K1, Asano K, Tsuji H, Kawamura M, Mori H, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M. Characterization of the molecular mechanism underlying gibberellin perception complex formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2010, 22: 2680-2696. |
| [9] | Smith S M, Waters M T.Strigolactones: Destruction- dependent perception?Curr Biol, 2012, 22: 924-927. |
| [10] | Monna L1, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: Rice “green revolution gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis.DNA Res, 2002, 9: 11-17. |
| [11] | Spielmeyer W, Ellis M H, Chandler P M.Semidwarf(sd-1), “green revolution” rice, contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99: 9043-9048. |
| [12] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow T Y, Hsing Y I, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M.GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature, 2005, 437: 693-698. |
| [13] | Izawa Y, Takayanagi Y, Inaba N, Abe Y, Minami M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Ohki S, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y.Function and expression pattern of the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in rice.Plant Cell Physiol, 2010, 51: 271-281. |
| [14] | Kamei T, Matozaki T, Sakisaka T.Coendocytosis of cadherin and c-Met coupled to disruption of cell-cell adhesion in MDCK cells-regulation by Rho, Rac and Rab small G proteins.Oncogene, 1999, 18: 6776-6784. |
| [15] | Wu Y, Fu Y, Zhao S, Gu P, Zhu Z, Sun C, Tan L.CLUSTERED PRIMARY BRANCH 1, a new allele of DWARF11, controls panicle architecture and seed size in rice.Plant Biotechnol J, 2016, 14: 377-386. |
| [16] | Tong H, Liu L, Jin Y, Du L, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice.Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 2562-2577. |
| [17] | Shi Z.Characterization and cloning of SMALL GRAIN 4, a novel DWARF11 allele that affects brassinosteroid biosynthesis in rice.Chin Sci Bull, 2015, 60: 905-915. |
| [18] | Zhou F, Lin Q, Zhu L, Ren Y, Zhou K, Shabek N, Wu F, Mao H, Dong W, Gan L, Ma W, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen W, Chu J, Yan C, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Zhai H, Wu C, Wang H, Zheng N, Wan J.D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling.Nature, 2013, 504(7480): 406-410. |
| [19] | Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G, Liu H, Chen F, Wang L, Meng X, Liu G, Yu H, Yuan Y, Yi W, Zhao L, Ma H, He Y, Wu Z, Melcher K, Qian Q, Xu H E, Wang Y, Li J.DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice.Nature, 2013, 504: 401-405. |
| [20] | Huang N, Courtois B, Khush G S.Association of quantitative trait loci for plant height with major dwarfing genes in rice.Heredity, 1996, 77: 130-137. |
| [21] | Moncada P, Martínez C P, Borrero J.Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment.Theor Appl Genet, 2002, 102: 41-52. |
| [22] | 罗炬, 邵高能, 魏祥进, 陈明亮, 唐绍清, 焦桂爱, 谢黎虹, 胡培松. 一个控制水稻株高QTL qPH3的遗传分析. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 417-422. |
| Luo J, Shao G N, Wei X J, Chen M L, Tang S Q, Jiao Q A, Xie L H, Hu P S.Genetic analysis of a QTL qPH3 for plant height in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(4): 417-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 余应弘, 吴云天, 曾翔, 袁隆平. 水稻矮秆小粒突变体潇湘矮的特征特性及其遗传鉴定. 杂交水稻, 2007, 22(6): 67-70. |
| Yu Y H, Wu Y T, Zeng X, Yuan L P.Characterization and genetic studies on dwarf rice mutant Xiaoxiangai with small grains.Hybrid Rice, 2007, 22(6): 67-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 郑贵朝, 胡事君. 提高水稻愈伤组织植株再生能力几种方法的评价. 杂交水稻, 2005, 20(2): 54-57. |
| Zheng C G, Hu S J.Evaluation of some culture methods for enhancing plant regeneration ability of rice callus.Hybrid Rice, 2005, 20(2): 54-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A.Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant gene Dwarf 1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96: 10284-10289. |
| [26] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujisawa Y, Kobayashi M.Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97: 11638-11643. |
| [27] | Hartweck L M, Olszewski N E.Rice GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 is a gibberellin receptor that illuminates and raises questions about GA signaling.Plant Cell, 2006, 18: 278-282. |
| [28] | Choe S, Dilkes B P, Gregory B D, Ross A S, Yuan H, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tanaka A, Yoshida S, Tax F E, Feldmann K A.The Arabidopsis dwarf 1 mutant is defective in the conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol, 1999, 119: 897-907. |
| [29] | Ferrero-Serrano A, Assmann S M.The alpha-subunit of the rice heterotrimeric G protein, RGA1, regulates drought tolerance during the vegetative phase in the dwarf rice mutant d1.J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(11): 3433-3443. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||