
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 215-226.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210707
• Reviews and Special Topics • Next Articles
WANG Jingying1,2, ZHAO Guangxin1,2, QIU Guankai1,2, FANG Jun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-20
Revised:2021-09-06
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
FANG Jun
王婧莹1,2, 赵广欣1,2, 邱冠凯1,2, 方军1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
方军
基金资助:WANG Jingying, ZHAO Guangxin, QIU Guankai, FANG Jun. Advances in Research on the Modification of the Heading Date Genes in Rice by Phosphorylation and Ubiquitination Pathways[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 215-226.
王婧莹, 赵广欣, 邱冠凯, 方军. 水稻抽穗期途径基因的磷酸化、泛素化研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 215-226.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210707
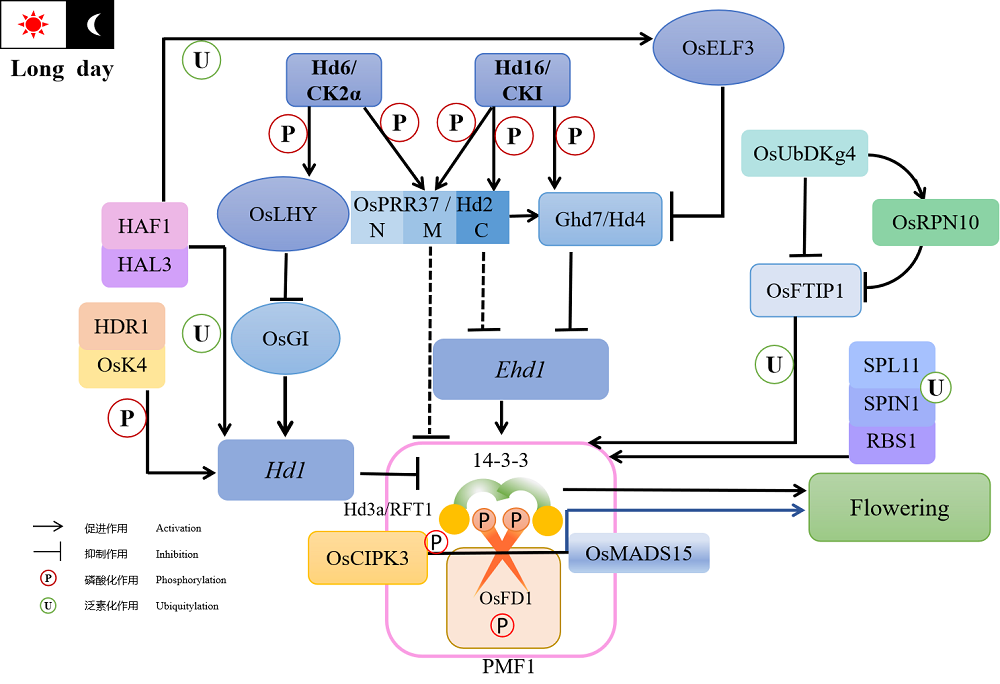
Fig. 1. Phosphorylation and ubiquitylation regulation network of rice flowering under long daylight condition. In the above content, only OsFD1 and HAF1 proteins have the function affecting heading date under SD conditions, and their regulatory pathways are not clear, so they are not shown in the diagram.
| [1] | Izawa T. Adaptation of flowering-time by natural and artificial selection in Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 58: 3091-3097. |
| [2] | Tsuji H, Tamaki S, Komiya R, Shimamoto K. Florigen and the photoperiodic control of flowering in rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1: 25-35. |
| [3] | Fujino K, Sekiguchi H. Mapping of QTLs conferring extremely early heading in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2005, 111: 393-398. |
| [4] | Fornara F A, de Montaigu A, Coupland G. SnapShot: Control of flowering in Arabidopsis[J]. Cell, 2010, 141: 550. |
| [5] | Masahiro Y, Takuji S. Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1997, 35: 145-153. |
| [6] | Hayama R, Yokoi S, Tamaki S, Masahiro Y, Ko S. Adaptation of photoperiodic control pathways produces short-day flowering in rice[J]. Nature, 2003, 422: 719-722. |
| [7] | Kardailsky I, Shukla V K, Ahn J H, Dagenais N, Christensen S K, Nguyen J T, Chory J, Harrison M J, Weigel D. Activation tagging of the floral inducer FT[J]. Science, 1999, 286: 1962-1965. |
| [8] | Hayama R, Izawa T, Shimamoto K. Isolation of rice genes possibly involved in the photoperiodic control of flowering by a fluorescent differential display method[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 2002, 43: 494-504. |
| [9] | Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T. Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 12: 2473-2484. |
| [10] | Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Tang W J, Wang L, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40: 761-767. |
| [11] | Doi K, Izawa T, Fuse T, Yamanouchi U, Kubo T, Shimatani Z, Yano M, Yoshimura A. Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers shortday promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1[J]. Genes & Development, 2004, 18: 926-936. |
| [12] | Nardini M, Gnesutta N, Donati G, Gatta R, Forni C, Fossati A, Vonrhein C, Moras D, Romier C, Bolognesi M, Mantovani R. Sequence-specific transcription factor NF-Y displays histone-like DNA binding and H2B-like ubiquitination[J]. Cell, 2013, 152: 132-143. |
| [13] | Thirumurugan T, Ito Y, Kubo, T, Serizawa A, Kurata N. Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2008, 279: 279-289. |
| [14] | Petroni K, Kumimoto R W, Gnesutta N, Calvenzani V, Fornari M, Tonelli C, Ben F, Mantovani R. The promiscuous life of plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors[J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 4777-4792. |
| [15] | Du A P, Tian W, Wei M G, Yan W, He H, Zhou D, Huang X, Li S G, Ouyang X H. The DTH8-Hd1 module mediates day-length-dependent regulation of rice flowering[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10: 948-961. |
| [16] | Goretti D, Martignago D, Landini M, Brambilla V, Gómez-Ariza J, Gnesutta N, Galbiati F, Collani S, Takagi H, Terauchi R, Mantovani R, Fornara F. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms limit heading date 1(Hd1) function to adapt rice to high latitudes[J]. PloS Genetics, 2017, 13: e1006530. |
| [17] | Shen C C, Liu H Y, Guan Z Y, Yan J J, Zheng T, Yan W H, Wu C Y, Zhang Q F, Yin P, Xing Y Z. Structural Insight into DNA Recognition by CCT/NF-YB/YC Complexes in Plant Photoperiodic Flowering[J]. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(11): 3469-3484. |
| [18] | Gnesutta N, Kumimoto R W, Swain S, Chiara M, Siriwardana C, Horner D S, Ben F Holt 3rd, Mantovani R. CONSTANS imparts DNA sequence specificity to the histone fold NF-YB/NF-YC dimer. Plant Cell, 2017, 29: 1516-1532. |
| [19] | 刘静, 李亚超, 周梦岩, 吴鹏飞, 马祥庆. 植物蛋白质翻译后修饰组学研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37 (1): 67-76 |
| Liu J, Li Y C, Zhou M Y, Wu P F, Ma X Q. Advances in posttranslational modification of plant proteins[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(1): 67-76. | |
| [20] | Withers J, Dong X N. Post-translational regulation of plant immunity[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2017, 38: 124-132. |
| [21] | Zhou S R, Zhu S S, Cui S, Hou H G, Wu H Q, Hao B Y, Cai L, Xu Z, Liu L L, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Wan J M. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of heading date in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2021, 230: 943-956. |
| [22] | Millar A H, Heazlewood J L, Giglione C, Holdsworth M J, Bachmair A, Schulze W X. The scope, functions, and dynamics of posttranslational protein modifications[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 119-151. |
| [23] | Ruan B J, Dai P, Wang W, Sun J, Zhang W, Zhen Y, Yang J. Progress on post-translational modification of proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2014, 7: 1027-1037 |
| [24] | Garrett R H. 生物化学. 影印版[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. |
| Garrett R H. Photocopy[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005. | |
| [25] | 孙大业, 马力耕. 细胞信号转导[M]. 第2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 350-355. |
| Sun D, Ma L. Cell Signal Transduction[M]. Version 2. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 350-355. | |
| [26] | Hanks S K, Quinn A M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: Identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 1991, 200: 38-62. |
| [27] | Gross S D, Anderson R A. Casein kinase: I. Spatial organization and positioning of a multifunctional protein kinase family[J]. Cell Signal, 1998, 10: 699-711. |
| [28] | Knippschild U, Gocht A, Wolff S, Huber N, Löhler J, Stöter M. The casein kinase1 family: Participation in multiple cellular processes in eukaryotes. Cell Signal, 2005, 17(6): 675-689 |
| [29] | Tan S T, Dai C, Liu H T, Xue H W. Arabidopsis casein kinase1 proteins CK1.3 and CK1.4 phosphorylate cryptochrome2 to regulate blue light signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2013, 25: 2618-2632. |
| [30] | Daniel X, Sugano S, Tobin E M. CK2 phosphorylation of CCA1 is necessary for its circadian oscillator function in Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2004, 101: 3292-3297. |
| [31] | Ogiso E, Takahashi Y, Sasaki T, Yano M, Izawa T. The role of Casein Kinase II in flowering time regulation has diversified during evolution[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152: 808-820. |
| [32] | Dai C, Xue H W. Rice early flowering1, a CKI, phosphorylates DELLA protein SLR1 to negatively regulate gibberellin signalling[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2010, 29: 1916-1927. |
| [33] | Kwon C T, Koo B H, Kim D, Yoo S C, Paek N C. Casein Kinases I and 2α Phosphorylate Oryza sativa pseudo-response regulator 37 (OsPRR37) in photoperiodic flowering in rice[J]. Molecules and Cells, 2014: 1029-1032. |
| [34] | Murakami M, Matsushika A, Ashikari M, Yamashino T, Mizuno T. Circadian-associated rice pseudo response regulators (OsPRRs): Insight into the control of flowering time[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2005, 69: 410-414. |
| [35] | Koo B H, Yoo S C, Park J W, Kwon C T, Lee B D, An G, Zhang Z Y, Li J J, Li Z Z, Paek N C. Natural variation in OsPRR37 regulates heading date and contributes to rice cultivation at a wide range of latitudes[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6: 1877-1888. |
| [36] | Gao H, Jin M, Zheng X M, Chen J, Yuan D Y, Xin Y Y, Wang M Q, Huang D Y, Zhang Z, Zhou K N, Sheng P K, Ma J, Ma W W, Deng H F, Jiang L, Liu S J, Wang H Y, Wu C Y, Yuan L P, Wan J M. Days to heading 7, a major quantitative locus determining photoperiod sensitivity and regional adaptation in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 2014, 111: 16337-16342. |
| [37] | Weng X Y, Wang L, Wang J, Hu Y, Du H, Xu C G, Xing Y Z, Li X H, Xiao J H, Zhang Q F. Grain number, plant height, and heading date7 is a central regulator of growth, development, and stress response[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164: 735-747. |
| [38] | Huang H D, Lee T Y, Tseng S W, Horng J T. KinasePhos: A web tool for identifying protein kinase-specific phosphorylation sites[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33: W226-W229. |
| [39] | Li X F, Liu H Z, Wang M Q, Liu H L, Tian X J, Zhou W J, Lü T X, Wang Z Y, Chu C C, Fang J, Bu Q Y. Combinations of Hd2 and Hd4 genes determine rice adaptability to Heilongjiang Province, northern limit of China[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2015, 57: 698-707. |
| [40] | Cho L H, Yoon J, Pasriga R, An G. Homodimerization of Ehd1 is required to induce flowering in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(4): 2159-2171. |
| [41] | Thelander M, Nilsson A, Olsson T, Johansson M, Girod P A, Schaefer D G, Zrÿd J P, Ronne H. 1 interacting proteins with homologues in vascular plants[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 64: 559-573. |
| [42] | Sun X H, Zhang Z G, Wu J X, Cui X A, Feng D, Wang K, Xu M, Zhou L, Han X, Gu X F, Lu T G. The Oryza sativa regulator HDR1 associates with the kinase OsK4 to control photoperiodic flowering[J]. PloS Genetics, 2016, 12(3): e1005927. |
| [43] | Lu C A, Lin C C, Lee K W, Chen J L, Huang L F, Ho S L, Liu H J, Hsing Y I, Yu S M. The SnRK1A protein kinase plays a key role in sugar signaling during germination and seedling growth of rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19: 2484-2499. |
| [44] | Thelander M, Olsson T, Ronne H. Snf1-related protein kinase 1 is needed for growth in a normal daynight light cycle[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2004, 23: 1900-1910. |
| [45] | Emanuelle S, Hossain M I, Moller I E, Pedersen H L, Allison M L, van de Meene, Doblin M S, Koay A, Oakhill J S, Scott J W, Willats W G T, Kemp B E, Bacic A, Gooley P R, Stapleton D I. SnRK1 from Arabidopsis thaliana is an atypical AMPK[J]. The Plant Journal, 2015, 82: 183-192. |
| [46] | Komiya R, Ikegami A, Tamaki S, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K. Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice[J]. Development, 2008, 135: 767-774. |
| [47] | Tamaki S,. Matsuo S, Wong H L, Yokoi S J, Shimamoto K. Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice[J]. Science, 2007, 316: 1033-1036. |
| [48] | Taoka K, Ohki I, Tsuji H, Furuita K, Hayashi K, Yanase T, Yamaguchi M, Nakashima C, Purwestri Y A, Tamaki S, Ogaki Y, Shimada C, Nakagawa A, Kojima C, Shimamoto K. 14-3-3 proteins act as intracellular receptors for rice Hd3a florigen[J]. Nature, 2011, 476: 332-335. |
| [49] | Zhao J, Chen H Y, Ren D, Tang H W, Qiu R, Feng J L, Long Y M, Niu B X, Chen D P, Zhong T Y, Liu Y G, Guo J X. Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) and Heading date 3a (Hd3a)/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 (RFT1) control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. New Phytologist, 2015, 208(3): 936-948. |
| [50] | Peng Q, Zhu C M, Liu T, Zhang S, Feng S J, Wu C Y. Phosphorylation of OsFD1 by OsCIPK3 promotes the formation of RFT1-containing florigen activation complex for long-day flowering in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(7): 1135-1148. |
| [51] | Peng Y B, Hou F X, Bai Q, Xu P Z, Liao Y X, Zhang H Y, Gu C J, Deng X S, Wu T, Chen X Q, Ali A, Wu X J. Rice calcineurin B-like protein interacting protein kinase 31 (OsCIPK31) is involved in the development of panicle apical spikelets[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1661. |
| [52] | 彭强. 蛋白激酶PMF1调控水稻抽穗期的分子机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| Peng Q. Molecular mechanism of protein kinase PMF1 regulating rice heading hate in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [53] | Stone S L. Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in plant response to abiotic stress[J]. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2019, 343: 65-110. |
| [54] | Yu F F, Xie Q. Ubiquitination modification precisely modulates the ABA signaling pathway in plants[J]. Hereditas, 2017, 39(8): 692-706. |
| [55] | McClellan A J, Laugesen S H, Ellgaard L. Cellular functions and molecular mechanisms of non-lysine ubiquitination[J]. Open Biology, 2019, 9(9): 190147. |
| [56] | Dittmar G, Winklhofer K F. Linear Ubiquitin Chains: Cellular Functions and Strategies for Detection and Quantification[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2019, 7: 915. |
| [57] | Fennell L M, Rahighi S, Ikeda F. Linear ubiquitin chain-binding domains[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2018, 285 (15): 2746-2761. |
| [58] | Wang F, Shi Y G. Progress in structural biology of 26S proteasome[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2014, 44: 965-974. |
| [59] | Pickart C M, Eddins M J. Ubiquitin: Structures, functions, mechanisms[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2004, 1695: 55-72. |
| [60] | Chen L Y, Hellmann H. Plant 3E ligases: Flexible enzymes in a sessile world[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(5): 1388-1404. |
| [61] | Vierstra R D. The ubiquitin-26S proteasome system at the nexus of plant biology[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2009, 10: 385-397. |
| [62] | Yang Y, Fu D, Zhu C M, He Y Z, Zhang H J, Liu T, Li X H, Wu C Y. The RING-finger ubiquitin ligase HAF 1 mediates Heading date 1degradation during photoperiodic flowering in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2015, 27: 2455-2468. |
| [63] | Stone S L, Hauksdóttir H, Troy A, Herschleb J, Kraft E, Callis J. Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2005, 137(1): 13-30. |
| [64] | Feltham R, Bettjeman B, Budhidarmo R, Mace P D, Shirley S, Condon S M, Chunduru S K, McKinlay M A, Vaux D L, Silke J, Day C L. Smac mimetics activate the E3 ligase activity of cIAP1 protein by promoting RING domain dimerization[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286: 17015-17028. |
| [65] | Zagotta M T, Hicks K A, Jacobs C I, Young J C, Hangarter R P, Meeks-Wagner D R. The Arabidopsis ELF3 gene regulates vegetative photomorphogenesis and the photoperiodic induction of flowering[J]. The Plant Journal, 1996, 10: 691-702. |
| [66] | Covington M F, Panda S, Liu X L, Strayer C A, Wagner D R, Kay S A. ELF3 modulates resetting of the circadian clock in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13: 1305-1315. |
| [67] | Fowler S, Lee K, Onouchi H, Samach A, Richardson K, Morris B, Coupland G, Putterill J. GIGANTEA: A circadian clock-controlled gene that regulates photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis and encodes a protein with several possible membrane-spanning domains[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1999, 18: 4679-4688. |
| [68] | Suarez-Lopez P, Wheatley K, Robson F, Onouchi H, Valverde F, Coupland G. CONSTANS mediates between thecircadian clock and the control of flowering in Arabidopsis[J]. Nature, 2001, 410(6832): 1116-1120. |
| [69] | Yang Y, Peng Q, Chen G X, Li X H, Wu C Y. OsELF3 is involved in circadian clock regulation for promoting flowering under long-day conditions in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6: 202-215. |
| [70] | Matsubara K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Hori K, Ebana K, Ando T, Yano M. Natural variation in Hd17, a homolog of Arabidopsis ELF3 that is involved in rice photoperiodic flowering[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 2012, 53: 709-716. |
| [71] | Kay S A, Keith B, Shinozaki K, Chua N H. The sequence of the rice phytochrome gene[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1989, 17(7): 2865-2866. |
| [72] | Sheerin D J, Menon C, Oven-Krockhaus S Z, Enderle B, Zhu L, Johnen P, Schleifenbaum F, Stierhof Y D, Huq E, Hiltbrunner A. Light-activated Phytochrome A and B interact with members of the SPA family to promote photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis by reorganizing the COP1/SPA complex[J]. Plant Cell, 2015, 27(1): 189-201. |
| [73] | Weng X Y, Wang L, Wang J, Hu Y, Du H, Xu C G, Xing Y Z, Li X H, Xiao J H, Zhang Q F. Grain Number, Plant Height, and Heading Date7is a central regulator of growth, development, and stress response[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164: 735-747. |
| [74] | Zheng T H, Sun J, Zhou S R, Chen S H, Lu J, Cui S, Tian Y L, Zhang H, Cai M H, Zhu S S, Wu M M, Wang Y H, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Wang H Y, Wan J M. Post-transcriptional regulation of Ghd7 protein stability by phytochrome and OsGI in photoperiodic control of flowering in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 224: 306-320. |
| [75] | Itoh H, Nonoue Y, Yano M, Izawa T. A pair of floral regulators sets critical day length for Hd3a florigen expression in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010, 42: 635-638. |
| [76] | Andrés F, Galbraith D W, Talón M, Domingo C. Analysis of PHOTOPERIOD SENSITIVITY5 sheds light on the role of phytochromes in photoperiodic flowering in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 151(2): 681-690. |
| [77] | Kircher S, Gil P, Kozma-Bognár L, Fejes E, Speth V, Muller T H, Bauer D, Adám E, Schäfer E, Nagy F. Nucleocytoplasmic partitioning of the plant photoreceptors phytochrome A, B, C, D, and E is regulated differentially by light and exhibits a diurnal rhythm[J]. Plant Cell, 2002, 14: 1541-1555. |
| [78] | Liu L, Liu C, Hou X L, Xi W Y, Shen L S, Tao Z, Wang Y, Yu H. FTIP1 is an essential regulator required for florigen transport[J]. PloS Biology, 2012, 10: e1001313. |
| [79] | Song S Y, Chen Y, Liu L, Wang Y W, Bao S J, Zhou X, Norman Teo Z W, Mao C Z, Gan Y B, Yu H. OsFTIP1-mediated regulation of florigen transport in rice is negatively regulated by the ubiquitin-like domain kinase OsUbDKg4[J]. Plant Cell, 2017, 29: 491-507. |
| [80] | Liu L, Zhu Y, Shen L H, Yu H. Emerging insights into florigen transport[J]. Plant Biology, 2013, 16: 607-613. |
| [81] | Galvão R, Kota U, Soderblom E, Goshe M, Boss W. Characterization of a new family of protein kinases from Arabidopsis containing phosphoinositide 3/4-kinase and ubiquitin-like domains[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2008, 409: 117-127. |
| [82] | Balla A, Balla T. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases: Old enzymes with emerging functions[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2006, 16(7): 351-361. |
| [83] | Fruman D A, Meyers R E, Cantley L C. Phosphoinositide kinases[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 1998, 67: 481-507. |
| [84] | Lucas J I, Arnau V, Marin I. Comparative genomics and protein domain graph analyses link ubiquitination and RNA metabolism[J]. Molecular Biology, 357(1): 9-17. |
| [85] | Liu J L, Li W, Ning Y S, Shirsekar G, Cai Y H, Wang X L, Dai L Y, Wang Z L, Liu W D, Wang G L. The U-box E3 ligase SPL11/PUB13 is a convergence point of defense and flowering signaling in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 160(1): 28-37. |
| [86] | Zeng L R, Park C H, Venu R C, Gough J, Wang G L. Classification, expression pattern, and E3 ligase activity assay of rice U-box-containing proteins[J]. Molecular Plant, 2008, 1(5): 800-815. |
| [87] | Vernet C, Artzt K. STAR, a gene family involved in signal transduction and activation of RNA[J]. Trends in Genetics, 1997, 13(12): 479-484. |
| [88] | Vega-Sa´nchez M E, Zeng L, Chen S B, Leung H, Wang G L. SPIN1, a K homology domain protein negatively regulated and ubiquitinated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SPL11, is involved in flowering time control in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(6): 1456-1469. |
| [89] | Lorković Z J, Barta A. A Genome analysis: RNA recognition motif (RRM) and K homology (KH) domain RNA-binding proteins from the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30: 623-635. |
| [90] | Cai Y H, Vega-Sa´nchez M E, Park C H, Bellizzi M, Guo Z J, Wang G L. RBS1, an RNA binding protein, interacts with SPIN1 and is involved in flowering time control in rice[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(1): e87258. |
| [91] | Sun C H, Chen D, Fang J, Wang P G, Deng X J, Chu C C. Understanding the genetic and epigenetic architecture in complex network of rice flowering pathways[J]. Protein Cell, 2014, 5(12): 889-898. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||