
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 532-540.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9055
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chunquan ZHU, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Zhigang BAI, Jie HUANG, Qingduo LIANG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG*( )
)
Received:2019-05-13
Revised:2019-07-31
Online:2019-11-10
Published:2019-11-10
Contact:
Junhua ZHANG
朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华*( )
)
通讯作者:
张均华
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chunquan ZHU, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Zhigang BAI, Jie HUANG, Qingduo LIANG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Hydrogen Sulfide Enhancing Phosphorus Absorption and Transportation in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 532-540.
朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华. 硫化氢提高水稻磷吸收转运的生理和分子机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 532-540.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9055
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward (5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsPT1 | AGCGTTCGGGTTCCTGTA | CGTTCTTGATGCCGATCC |
| OsPT2 | GACGAGACCGCCCAAGAAG | TTTTCAGTCACTCACGTCGAGAC |
| OsPT3 | GTGCTCATGGTGGTGTGCT | GAGCCAGAACCGGAAGAAG |
| OsPT4 | GGAGAAGGCTGACGAGGTC | CCCATGGCGTCTCAAAAA |
| OsPT5 | GGCGAGAACGAAATGGAG | GACGGTCTGCCTGTAGGAGT |
| OsPT6 | TATAACTGATCGATCGAGACCAGAG | TGGATAGCCAGGCCAGTTATATATC |
| OsPT7 | GCTTCCTCCTCACCTTCCTT | TTCTCCCGTGACATCTCCTC |
| OsPT8 | AGAAGGCAAAAGAAATGTGTGTTAAAT | AAAATGTATTCGTGCCAAATTGCT |
| OsPT9 | CATAGGCTTGTCATCCTTTGG | CACTGTAAATAAATCCGCGTTTC |
| OsPT10 | GAGCTCGCACCTCAGCAT | GAGTTCACTCACACGGAGACC |
| OsPT12 | AAATCGAGGTGGAGGAGGAG | CGAGAAGAGGCCGTAGTCC |
| OsHistone | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
Table 1 Sequence of primers used in present study.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward (5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsPT1 | AGCGTTCGGGTTCCTGTA | CGTTCTTGATGCCGATCC |
| OsPT2 | GACGAGACCGCCCAAGAAG | TTTTCAGTCACTCACGTCGAGAC |
| OsPT3 | GTGCTCATGGTGGTGTGCT | GAGCCAGAACCGGAAGAAG |
| OsPT4 | GGAGAAGGCTGACGAGGTC | CCCATGGCGTCTCAAAAA |
| OsPT5 | GGCGAGAACGAAATGGAG | GACGGTCTGCCTGTAGGAGT |
| OsPT6 | TATAACTGATCGATCGAGACCAGAG | TGGATAGCCAGGCCAGTTATATATC |
| OsPT7 | GCTTCCTCCTCACCTTCCTT | TTCTCCCGTGACATCTCCTC |
| OsPT8 | AGAAGGCAAAAGAAATGTGTGTTAAAT | AAAATGTATTCGTGCCAAATTGCT |
| OsPT9 | CATAGGCTTGTCATCCTTTGG | CACTGTAAATAAATCCGCGTTTC |
| OsPT10 | GAGCTCGCACCTCAGCAT | GAGTTCACTCACACGGAGACC |
| OsPT12 | AAATCGAGGTGGAGGAGGAG | CGAGAAGAGGCCGTAGTCC |
| OsHistone | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
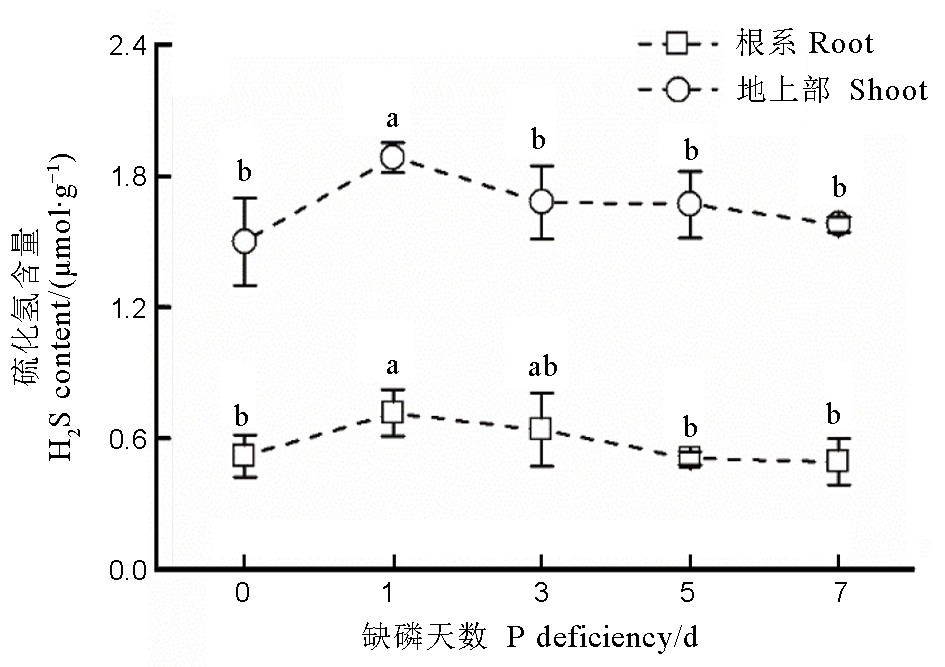
Fig. 1. Content of H2S in rice root and shoot under different phosphorus deficient durations. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters stand for significant difference at P < 0.05. The P concentration in the nutrient solution is 18 mmol/L under P deficient conditions.
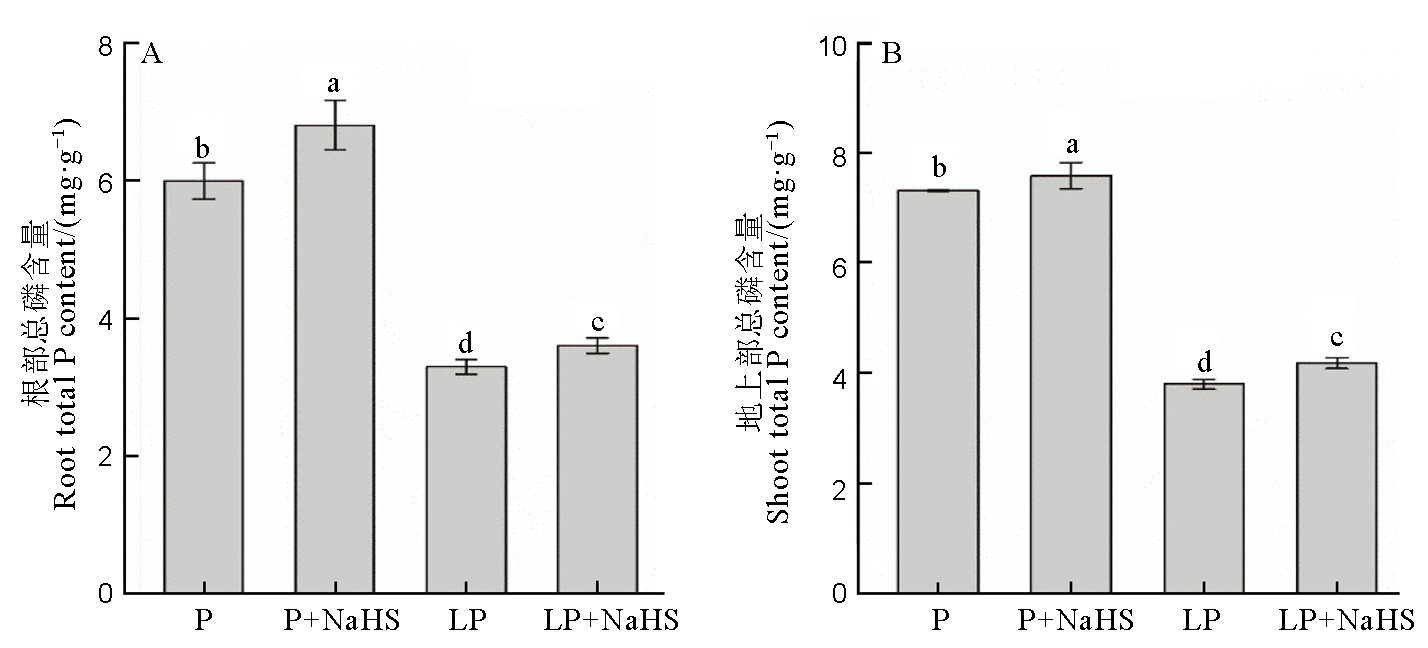
Fig. 2. Available P and total P contents in rice roots and shoots. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the columns mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, P concentration of 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
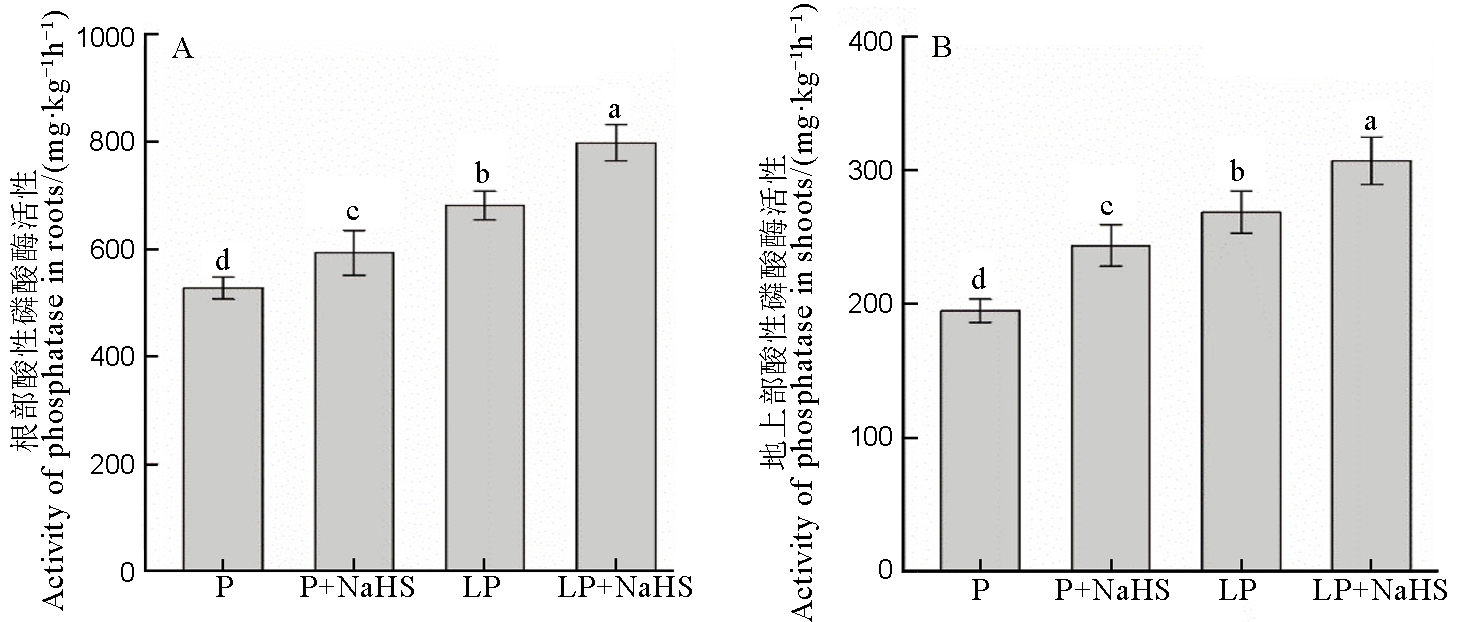
Fig. 3. Activites of acid phosphatase in rice roots and shoots. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the columns are significantly different at P < 0.05. P, P concentration of 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L.
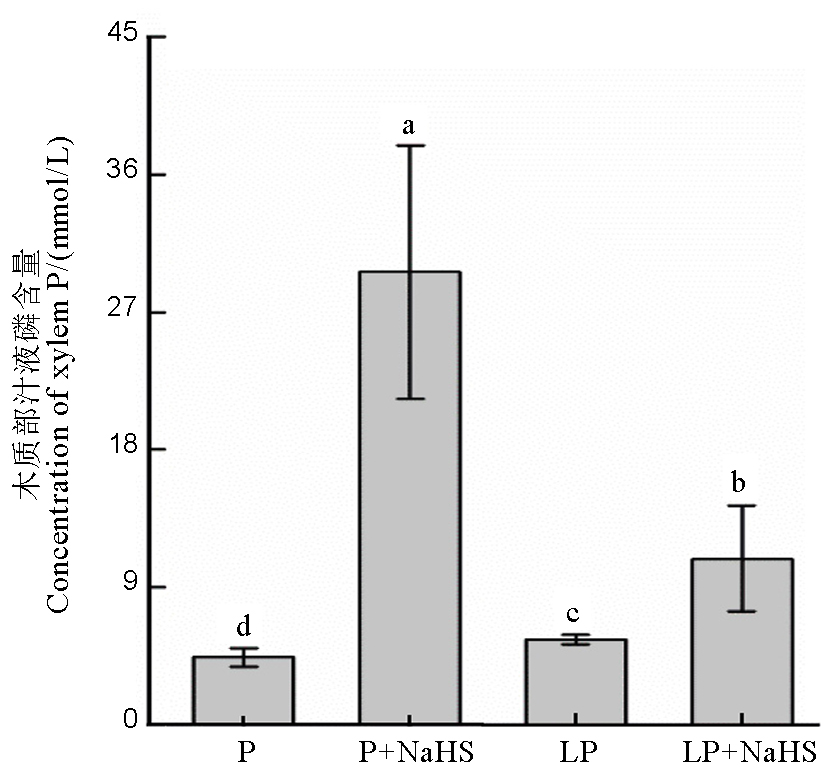
Fig. 4. Xylem P concentration in rice. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
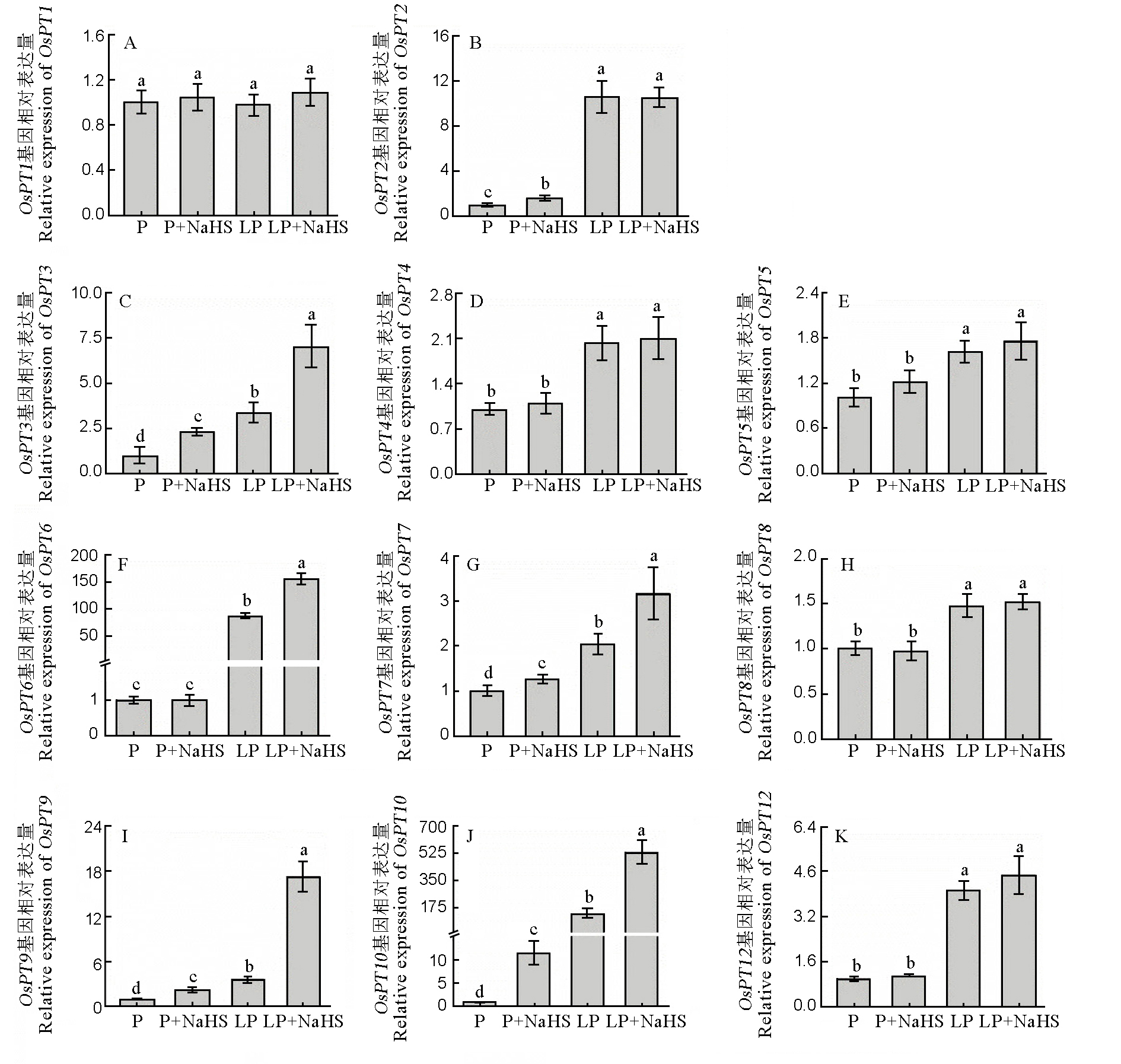
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of P transporter genes. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
| 酶的名称 Enzyme name | 部位 Position | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 3.39±0.08 d | 3.89±0.39 c | 6.21±0.88 b | 10.74±1.24 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 35.82±2.61 d | 49.44±5.17 c | 63.32±5.00 b | 73.20±2.62 a | |
| 过氧化物酶 Peroxidase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 837.56±35.96 d | 1300.92±74.56 c | 1852.22±160.51 b | 2601.40±94.97 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 1745.27±346.02 d | 2649.98±178.02 c | 5070.26±639.59 b | 7627.11±688.69 a | |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 Ascorbate peroxidase/(μmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 0.17±0.04 c | 0.47±0.10 b | 0.45±0.08 b | 0.62±0.07 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 0.26±0.06 d | 0.45±0.04 c | 0.65±0.09 b | 0.92±0.22 a | |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(nmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 10.56±0.16 d | 12.90±0.14 c | 17.51±0.28 b | 22.79±1.83 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 7.08±2.44 d | 23.23±3.88 c | 36.30±4.57 b | 63.21±16.26 a | |
Table 2 Activities of antioxidant enzymes in rice roots and shoots.
| 酶的名称 Enzyme name | 部位 Position | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 3.39±0.08 d | 3.89±0.39 c | 6.21±0.88 b | 10.74±1.24 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 35.82±2.61 d | 49.44±5.17 c | 63.32±5.00 b | 73.20±2.62 a | |
| 过氧化物酶 Peroxidase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 837.56±35.96 d | 1300.92±74.56 c | 1852.22±160.51 b | 2601.40±94.97 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 1745.27±346.02 d | 2649.98±178.02 c | 5070.26±639.59 b | 7627.11±688.69 a | |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 Ascorbate peroxidase/(μmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 0.17±0.04 c | 0.47±0.10 b | 0.45±0.08 b | 0.62±0.07 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 0.26±0.06 d | 0.45±0.04 c | 0.65±0.09 b | 0.92±0.22 a | |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(nmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 10.56±0.16 d | 12.90±0.14 c | 17.51±0.28 b | 22.79±1.83 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 7.08±2.44 d | 23.23±3.88 c | 36.30±4.57 b | 63.21±16.26 a | |
| 参数 Parameter | 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total length/cm | 234.77±6.63 c | 262.77±2.27 b | 269.38±5.49 b | 309.72±8.28 a |
| 总表面积Total surface area/cm2 | 31.18±1.00 c | 35.60±1.12 b | 35.76±0.69 b | 45.37±3.63 a |
| 平均直径Average diagram/cm | 0.42±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a |
| 根系总体积Root volume/cm3 | 0.35±0.01 c | 0.39±0.01 b | 0.39±0.00 b | 0.45±0.03 a |
| 根尖数Root tip number | 448.0±15.0 d | 392.0±20.0 c | 549.0±5.3 b | 639.7±23.2 a |
Table 3 Root development parameters in rice.
| 参数 Parameter | 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total length/cm | 234.77±6.63 c | 262.77±2.27 b | 269.38±5.49 b | 309.72±8.28 a |
| 总表面积Total surface area/cm2 | 31.18±1.00 c | 35.60±1.12 b | 35.76±0.69 b | 45.37±3.63 a |
| 平均直径Average diagram/cm | 0.42±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a |
| 根系总体积Root volume/cm3 | 0.35±0.01 c | 0.39±0.01 b | 0.39±0.00 b | 0.45±0.03 a |
| 根尖数Root tip number | 448.0±15.0 d | 392.0±20.0 c | 549.0±5.3 b | 639.7±23.2 a |
| [1] | Marschner H.Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 2nd edn. Boston, MA, USA: Academic Press, 1995. |
| [2] | Vance C P, Uhde-Stone C, Allan D L.Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource.New Phytol, 2003, 157: 423-447. |
| [3] | Shen J B, Yuan L X, Zhang J L, Li H G, Bai Z H, Chen X P, Zhang W F, Zhang F S.Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156: 997-1005. |
| [4] | Holford I.Soil phosphorus: its measurement, and its uptake by plants.Soil Res, 1997, 35: 227-240. |
| [5] | Lynch J P, Brown K M.Topsoil foraging-an architectural adaptation of plants to low phosphorus availability.Plant Soil, 2001, 237: 225-237. |
| [6] | Steingrobe B, Schmid H, Claassen N.Root production and root mortality of winter barley and its implication with regard to phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil, 2001, 237: 239-248. |
| [7] | Clarkson D T, Nutrient interception and transport by root systems. Physiological processes limiting plant productivity, London: Butterworths, 1981: 307-330. |
| [8] | Bolan N, Elliott J, Gregg P, Weil S.Enhanced dissolution of phosphate rocks in the rhizosphere.Biol Fert Soils, 1997, 24: 169-174. |
| [9] | Otani T, Ae N, Tanaka H.Phosphorus (P) uptake mechanisms of crops grown in soils with low P status: Ⅱ. Significance of organic acids in root exudates of pigeonpea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 1996, 42: 553-560. |
| [10] | Theodorou M E, Plaxton W C.Metabotic adaptations of plant respiration to nutrional phosphate deprivation.Plant physiol, 1993, 101: 339-344. |
| [11] | Miller S S, Liu J Q, Allan D L, Menzhuber C J, Fedorova M, Vance C P.Molecular control of acid phosphatase secretion into the rhizosphere of proteoid roots from phosphorus-stressed white lupin. Plant Physiol, 2001, 127: 594-606. |
| [12] | Zhu C Q, Zhu X F, Hu A Y,., Wang C, Wang B, Shen R F.Differential effects of nitrogen forms on cell wall phosphorus remobilization are mediated by nitric oxide, pectin content, and phosphate transporter expression. Plant Physiol, 2016. 171: 1407-1417. |
| [13] | Chapin L J, Jones M L.Ethylene regulates phosphorus remobilization and expression of a phosphate transporter (PhPT1) during petunia corolla senescence. J Exp Bot, 2009, 60: 2179-2190. |
| [14] | Wang B, Tang X, Cheng L, Zhang A Z, Zhang W H, Zhang F S, Liu J Q, Cao Y, Allan D L, Vance C P, Shen J B.Nitric oxide is involved in phosphorus deficiency -induced cluster-root development and citrate exudation in white lupin. New Phytol, 2010, 187: 1112-1123. |
| [15] | Li L, Rose P, Moore P.K. Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling.Ann Rev Pharmaco Toxicol, 2011, 51: 169-187. |
| [16] | Zhang H, Tan Z Q, Hu L Y, Wang S H, Luo J P, Jones R L.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in germinating wheat seedlings.J Integ Plant Biol, 2010, 52: 556-567. |
| [17] | Zhang H, Tang J, Liu X P, Wang Y, Yu W, Peng W Y, Fang F, Ma D F, Wei Z J, Hu L Y.Hydrogen sulfide promotes root organogenesis in Ipomoea batatas, Salix matsudana and Glycine max. J Integ Plant Biol, 2009, 51: 1086-1094. |
| [18] | García-Mata C, Lamattina L.Hydrogen sulphide, a novel gasotransmitter involved in guard cell signalling. New Phytol, 2010, 188: 977-984. |
| [19] | Wang B L, Shi L, Li Y X, Zhang W H.Boron toxicity is alleviated by hydrogen sulfide in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings. Planta, 2010, 231: 1301-1309. |
| [20] | Li Z G, Ding X J,. Du P F.Hydrogen sulfide donor sodium hydrosulfide-improved heat tolerance in maize and involvement of proline. J Plant Physiol, 2013, 170: 741-747. |
| [21] | 朱春权, 朱晓芳, 沈仁芳. 硫化氢促进缺磷条件下水稻根系细胞壁磷的再利用. 土壤, 2018, 50: 51-58. |
| Zhu C Q, Zhu X F, Shen R F.Hydrogen sulfide promote rice (Oryza sativa) cell wall P remobilization under P starvation condition. Soils, 2018 50: 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Zhang H, Ye Y K, Wang S H, Luo J P, Tang J, Ma D F.Hydrogen sulfide counteracts chlorophyll loss in sweetpotato seedling leaves and alleviates oxidative damage against osmotic stress. Plant Growth Reg, 2009, 58: 243-250. |
| [23] | Chang C, Hu Y S, Zhu Y, Ma G, Xu G H.Proton pump OsA8 is linked to phosphorus uptake and translocation in rice.J Exp Bot, 2009, 60: 557-565. |
| [24] | Toshiaki T, Hiroshi S.Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of several crop species under phosphorus -deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 1991, 37: 129-140. |
| [25] | Beauchamp C, Fridovich I.Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels.Anal Biochem, 1971, 44: 276-287. |
| [26] | Dhindsa R S, Plumbdhindsa P, Thorpe T A. leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exper Bot, 1981, 32: 93-101. |
| [27] | Nakano Y, Asada K.Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts.Plant Cell Physiol, 1981, 22: 867-880. |
| [28] | Chen J, Wang W H, Wu F H, You C Y, Liu T W, Dong X J, He J X, Zheng H L.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Soil, 2013, 362: 301-318. |
| [29] | Che J, Yamaji N, Shao J F, Ma J F.Silicon decreases both uptake and root-to-shoot translocation of manganese in rice.J Exp Bot, 2016, 67: 1535-1544. |
| [30] | Zhang H, Xue Y H, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H.Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with shoot growth in “super”rice. Field Crops Res, 2009, 113: 31-40. |
| [31] | Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J, Fan X R, Xin W J, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q R, Wu P, Miller A J.Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1; 2 and OsPht1; 6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation.Plant J, 2009, 57: 798-809. |
| [32] | Jia H, Ren H, Gu M, Zhao J N, Sun S B, Zhang X, Chen J Y, Wu P, Xu G H.The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1; 8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156: 1164-1175. |
| [33] | Liu F, Wang Z, Ren H, Shen C, Li Y, Ling H Q, Wu C, Lian X, Wu P.OsSPX1 suppresses the function of OsPHR2 in the regulation of expression of OsPT2 and phosphate homeostasis in shoots of rice.Plant J, 2010, 62: 508-517. |
| [34] | Wang X, Wang Y, Piñeros M A, Wang Z, Wang W, Li C, Wu Z, Kochian LV, Wu P.Phosphate transporters OsPHT1;9 and OsPHT1;10 are involved in phosphate uptake in rice.Plant Cell Environ, 2014, 37: 1159-1170. |
| [35] | Xia J, Yamaji N, Ma J F.A plasma membrane-localized small peptide is involved in rice aluminum tolerance.Plant J, 2013, 76: 345-55. |
| [36] | Zhou J, Jiao F C, Wu Z C, Li Y Y, Wang X M, He X W, Zhong W Q, Wu P.OsPHR2 is involved in phosphate- starvation signaling and excessive phosphate accumulation in shoots of plants. Plant Physiol, 2008, 146: 1673-1686. |
| [37] | Li H, Guo L, Tao C, Yang L M, Wang X Z.Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 gene family. Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 4236-4251. |
| [38] | Paszkowski U, Kroken S, Roux C, Briggs SP.Rice phosphate transporters include an evolutionarily divergent gene specifically activated in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis.PNAS, 2002, 99: 13324-13329. |
| [39] | Zhu C Q, Zhang J H, Sun L M, Zhu L F, Abliz B, Hu W J, Zhong C, Bai Z G, Sajid H, Cao X C, Jin Q Y.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity via decreasing apoplast and symplast Al contents in rice. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9. |
| [40] | Dracup M N H, Barrett-Lennard E G, Greenway H, Robson, A D. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on phosphatase activity of cell walls from roots of subterranean clover. J Exp Bot, 1984, 35: 466-480. |
| [41] | 庞欣, 张福锁, 李春俭. 部分根系供磷对黄瓜根系和幼苗生长及根系酸性磷酸酶活性影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2000, 26: 153-158. |
| Pang X, Zhang F S, Li C J.Effect of the part of P-supply roots on cucumber seedling growth, P concentration in shoot and root and secreted acid phosphatase activity by root.Acta Phytophysiol Sin, 2000, 26: 153-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 樊明寿, 徐冰, 王艳. 缺磷条件下玉米根系酸性磷酸酶活性的变化. 中国农业科技导报, 2001, 3: 33-36. |
| Fan M S, Xu B, Wang Y.Acid phosphatase activities of intact roots and ground root tissues of maize grown in high P or low P nutrient solution.Rev China Agric Sci Technol, 2001, 3: 33-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 张丽梅, 郭再华, 张琳, 贺立源. 缺磷对不同耐低磷玉米基因型酸性磷酸酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21: 898-910. |
| Zhang L M, Guo Z H, Zhang L, He L Y.Effect of phosphate deficiency on acid phosphatase activities of different maize genotypes tolerant to low-P stress.J Plant Nutr Fert, 2015, 21: 898-910. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 黄宇, 张海伟, 徐芳森. 植物酸性磷酸酶的研究进展. 华中农业大学学报, 2008, 27: 148-154. |
| Huang Y, Zhang H W, Xu F S.Research progress on plant acid phosphatase.J Huazhong Agric Univ, 2008, 27: 148-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Seo H M, Jung Y, Song S, Kim Y, Kwon T, Kim D H, Jeung S J, Yi Y B, Yi G, Nam M H.Increased expression of OsPT1, a high-affinity phosphate transporter, enhances phosphate acquisition in rice. Biotechnol Let, 2008, 30: 1833-1838. |
| [46] | Zhang F, Sun Y, Pei W, Jain A, Sun R, Cao Y, Wu X, Jiang T, Zhang L, Fan X.Involvement of OsPht1;4 in phosphate acquisition and mobilization facilitates embryo development in rice. Plant J, 2015, 82: 556-569. |
| [47] | Sun S, Gu M, Cao Y, Huang X P, Zhang X, Ai P H, Zhao J N, Fan X R, Xu G H.A constitutive expressed phosphate transporter, OsPht1;1, modulates phosphate uptake and translocation in phosphate-replete rice. Plant Physiol, 2012, 159: 1571-1581. |
| [48] | Suzuki N. Suzuki N, Miller G, Morales J, Shulaev V, Torres M A, Mittler R.Respiratory burst oxidases: The engines of ROS signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2011, 14: 691-699. |
| [49] | Marques A T, Santos S P, Rosa M G, Rodrigues M A, Abreu I A, Frazão C, Romão C V.Expression, purification and crystallization of MnSOD from Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Crystall, 2014, 70: 669-672. |
| [50] | Ward J T, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Salt D E, Raghothama K G.The effect of iron on the primary root elongation of Arabidopsis during phosphate deficiency. Plant Physiol, 2008, 147: 1181-1191. |
| [51] | Bates T R, Lynch J P.Root hairs confer a competitive advantage under low phosphorus availability. Plant Soil, 2001, 236: 243-250. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||