
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 82-91.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240111
杨传铭1,2,4, 王立志2,4, 张喜娟2,4, 杨贤莉2,4, 王洋洋1,2,4, 侯本福1,2,4, 崔士泽2,4, 李青超3, 刘凯4, 马瑞5, 冯延江6, 来永才4, 李红宇1,*( ), 姜树坤2,3,4,*(
), 姜树坤2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-29
修回日期:2024-04-20
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2025-01-14
通讯作者:
*email: shukunjiang@haas.cn;基金资助:
YANG Chuanming1,2,4, WANG Lizhi2,4, ZHANG Xijuan2,4, YANG Xianli2,4, WANG Yangyang1,2,4, HOU Benfu1,2,4, CUI Shize2,4, LI Qingchao3, LIU Kai4, MA Rui5, FENG Yanjiang6, LAI Yongcai4, LI Hongyu1,*( ), JIANG Shukun2,3,4,*(
), JIANG Shukun2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-29
Revised:2024-04-20
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2025-01-14
Contact:
*email: shukunjiang@haas.cn;摘要:
【目的】低温冷害是影响水稻生长发育,进而造成不同程度减产的主要气象灾害之一。挖掘鉴定耐冷基因,选育耐冷品种,是解决水稻低温冷害最简单、直接和有效的手段之一。【方法】利用丽江新团黑谷/沈农265衍生的包含144个株系的重组自交系群体,通过人工气候室进行苗期耐冷性鉴定。结合全基因组重测序构建的包含2828个bin标记的高密度遗传图谱,进行苗期耐冷性QTL定位和互作分析。【结果】利用完备区间作图法共检测到4个苗期耐冷QTL,分别定位于水稻的1、8、10和12号染色体上,单个QTL的表型贡献率为5.33%~19.86%。其中,qCTS1、qCTS10和qCTS12的增效等位基因来源于强耐冷亲本丽江新团黑谷,qCTS8的增效等位基因来源于沈农265。主效QTL qCTS12定位在12号染色体的15.98 Mb-16.37 Mb之间,物理图谱区间为396.67 Kb。qCTS1定位在1号染色体的9.20 Mb-9.50 Mb间,物理图谱区间为299.85 kb。qCTS8定位在8号染色体的26.09 Mb-26.15 Mb之间,物理图谱区间为55.05 Kb。qCTS10定位在10号染色体的11.13 Mb-11.21 Mb间,物理图谱区间为85.82 kb。进一步分析发现,除qCTS1-qCTS8之间存在负向互作外,其余QTL间的互作表现为加性效应。【结论】利用丽江新团黑谷和沈农265的重组自交系群体,结合包含2818个bin标记的遗传图谱,共检测到4个苗期耐冷QTL,其中3个QTL的增效等位基因来自强耐冷地方品种丽江新团黑谷。可为耐冷分子设计育种提供有用的基因资源,同时为阐明水稻苗期耐冷的遗传和分子机制提供参考。
杨传铭, 王立志, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王洋洋, 侯本福, 崔士泽, 李青超, 刘凯, 马瑞, 冯延江, 来永才, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 基于高密度遗传图谱的粳稻苗期耐冷QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 82-91.
YANG Chuanming, WANG Lizhi, ZHANG Xijuan, YANG Xianli, WANG Yangyang, HOU Benfu, CUI Shize, LI Qingchao, LIU Kai, MA Rui, FENG Yanjiang, LAI Yongcai, LI Hongyu, JIANG Shukun. Analysis of QTL Controlling Cold Tolerance at Seedling Stage by Using a High-Density SNP Linkage Map in japonica Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 82-91.
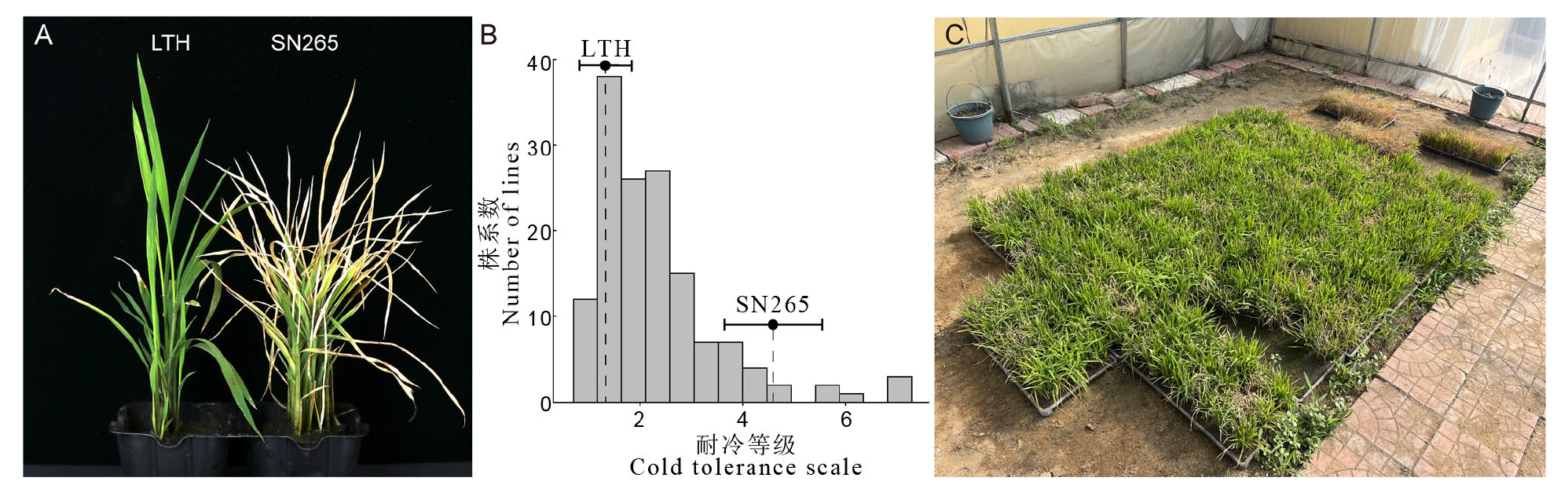
图2 丽江新团黑谷(LTH)、沈农265(SN265)及二者衍生的重组自交系群体苗期耐冷表型和等级分布 A:丽江新团黑谷和沈农265苗期冷处理恢复第7日的表型比较;B:重组自交系群体的苗期耐冷等级分布;C:重组自交系群体在苗期低温处理后的表现(恢复第7日)。LTH表示丽江新团黑谷,SN265表示沈农265。
Fig. 2. Cold tolerant phenotypes of LTH and SN265 and distribution of cold tolerance scales in LTH/SN265 RILs at seedling stage A, Comparison of phenotypes between LTH and SN265 after cold treatment after 7 days of recovery at the seedling stage; B, Distribution of cold tolerance scales at the seedling stage in LTH/SN265 RILs; C, Phenotypes of LTH/SN265 RILs after cold treatment at seedling stage (after 7 days of recovery). LTH, Lijiang Xintuan Heigu; SN265, Shennong 265.
| QTL | Chr. | 峰值位置a Peak position a (Mb) | 峰值标记 Peak marker | QTL区间 QTL interval | LOD值 LOD value | 表型 贡献率 Phenotypic variation explained (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | 增效等位基因来源 Positive allele donor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物理图谱 Physical location (Mb) | 定位区间 Location interval(kb) | ||||||||
| qCTS1 | 1 | 9.23 | Bin01-072 | 9.20-9.50 | 299.85 | 4.35 | 5.33 | −0.37 | LTH |
| qCTS8 | 8 | 26.10 | Bin08-220 | 26.05-26.15 | 55.05 | 4.42 | 5.59 | 0.36 | SN265 |
| qCTS10 | 10 | 11.20 | Bin10-149 | 11.13-11.21 | 85.82 | 7.07 | 9.04 | −0.46 | LTH |
| qCTS12 | 12 | 16.02 | Bin12-103 | 15.98-16.37 | 396.67 | 13.82 | 19.86 | −0.69 | LTH |
表1 利用丽江新团黑谷/沈农265的重组自交系群体检测苗期耐冷QTL
Table 1. QTL controlling cold tolerance at seedling stage identified in LTH/SN265 RILs
| QTL | Chr. | 峰值位置a Peak position a (Mb) | 峰值标记 Peak marker | QTL区间 QTL interval | LOD值 LOD value | 表型 贡献率 Phenotypic variation explained (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | 增效等位基因来源 Positive allele donor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物理图谱 Physical location (Mb) | 定位区间 Location interval(kb) | ||||||||
| qCTS1 | 1 | 9.23 | Bin01-072 | 9.20-9.50 | 299.85 | 4.35 | 5.33 | −0.37 | LTH |
| qCTS8 | 8 | 26.10 | Bin08-220 | 26.05-26.15 | 55.05 | 4.42 | 5.59 | 0.36 | SN265 |
| qCTS10 | 10 | 11.20 | Bin10-149 | 11.13-11.21 | 85.82 | 7.07 | 9.04 | −0.46 | LTH |
| qCTS12 | 12 | 16.02 | Bin12-103 | 15.98-16.37 | 396.67 | 13.82 | 19.86 | −0.69 | LTH |
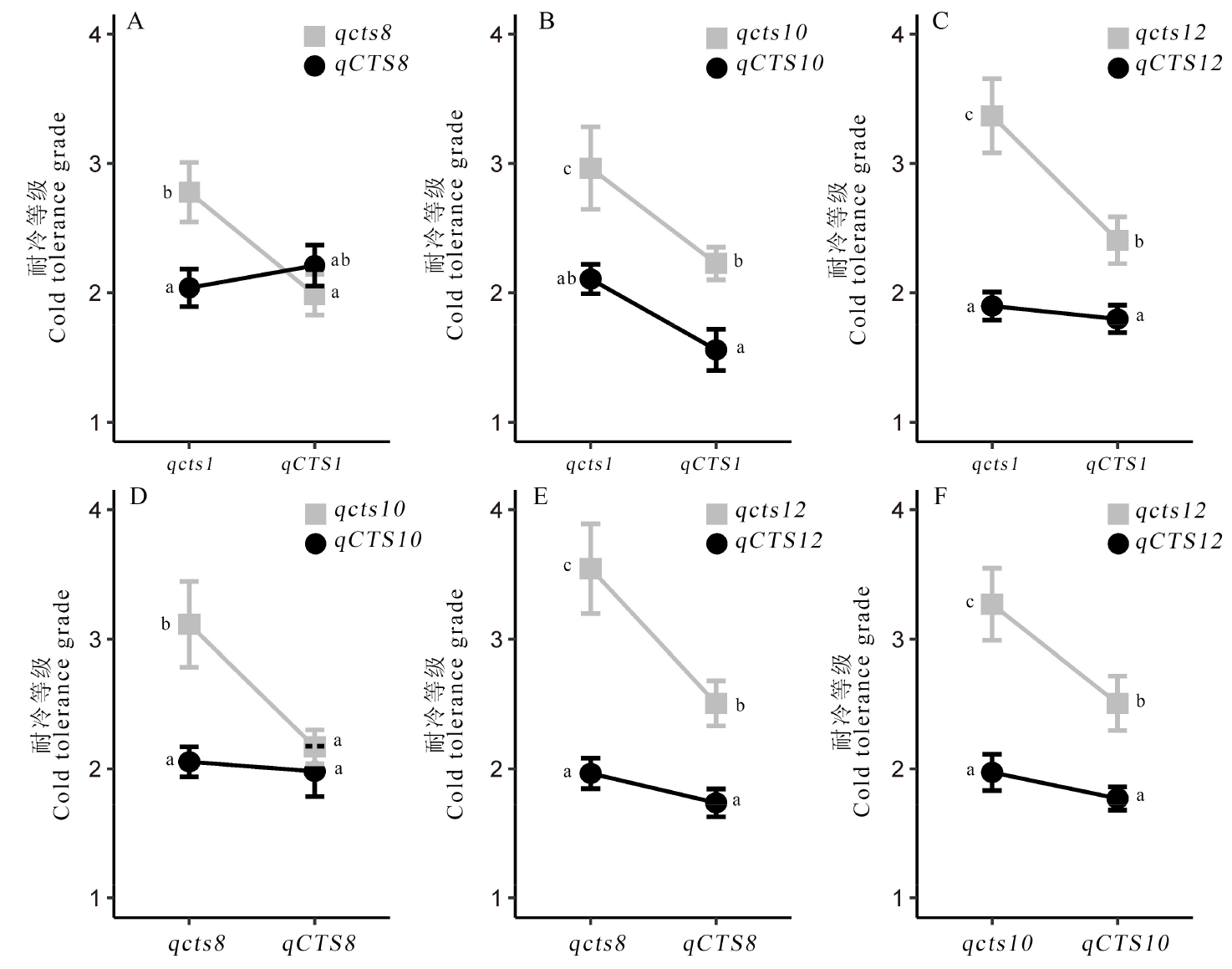
图4 鉴定的4个苗期耐冷QTL间的互作分析 CTS表示耐冷的等位基因型;cts表示不耐冷的等位基因型。
Fig. 4. Interaction analysis of four QTLs for cold tolerance at seedling stage CTS denotes cold tolerant allele genotype; cts denotes the cold susceptible allelic genotype.
| [1] | Shi H, Li Y, Jie Y, Shen G, Xiao D, Ye Y, De F, Shao K. Super hybrid rice breeding in China: Achievements and prospects[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2007, 49(6): 805-810. |
| [2] | Saito K, Miura K, Nagano K, Hayano S Y, Araki H, Kato A. Identification of two closely linked quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance on chromosome 4 of rice and their association with anther length[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2001, 103(6): 862-868. |
| [3] | Cruz R P D, Sperotto R A, Cargnelutti D, Adamski J M, Terra T D F, Fett J. Avoiding damage and achieving cold tolerance in rice plants[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2013, 2(2): 96-119. |
| [4] | Sthapit B R, Witcombe J R. Inheritance of tolerance to chilling stress in rice during germination and plumule greening[J]. Crop Science, 1998, 38(3): 660-665. |
| [5] | Zhu Y, Chen K, Mi X, Chen T, Ali J, Ye G, Xu J, Li Z. Identification and fine mapping of a stably expressed QTL for cold tolerance at the booting stage using an interconnected breeding population in rice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0145704. |
| [6] | Fujino K, Sekiguchi H, Sato T, Kiuchi H, Nonoue Y, Takeuchi Y, Ando T, Lin Y S, Yano M. Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling low-temperature germinability in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2004, 108(5): 794-799. |
| [7] | Xu M, Ye X, Wang W, Wei C, Zhang J, Tu J. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a high threshold and low temperature-sensitive mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at the seedling stage[J]. Euphytica, 2015, 203(1): 71-82. |
| [8] | Satoh T, Tezuka K, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Satoh Nagasawa N, Ueda K, Sakurai K, Watanabe A, Takahashi H, Akagi H. Identification of QTLs controlling low-temperature germination of the East European rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety Maratteli[J]. Euphytica, 2016, 207(2): 245-254. |
| [9] | Najeeb S, Ali J, Mahender A, Pang Y, Zilhas J, Murugaiyan V, Vemireddy L, Li Z. Identification of main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for low-temperature stress tolerance germination- and early seedling vigor-related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2020, 40(1): 10. |
| [10] | Lou Q, Chen L, Sun Z, Xing Y, Li J, Xu X, Mei H, Luo L. A major QTL associated with cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Euphytica, 2007, 158(1): 87-94. |
| [11] | Koseki M, Kitazawa N, Yonebayashi S, Maehara Y, Wang Z, Minobe Y. Identification and fine mapping of a major quantitative trait locus originating from wild rice, controlling cold tolerance at the seedling stage[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2010, 284(1): 45-54. |
| [12] | Kim S M, Suh J P, Lee C K, Lee J H, Kim Y G, Jena K K. QTL mapping and development of candidate gene-derived DNA markers associated with seedling cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2014, 289(3): 333-343. |
| [13] | 曹慧敏, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 翟来圆, 姜树坤, 郑天清, 邱先进, 徐建龙. 利用双向导入系和重组自交系定位和挖掘水稻苗期耐冷QTL和有利等位基因[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(10): 2633-2642. |
| Cao H M, Yang X L, Wang L Z, Zhai L Y, Jiang S K, Zheng T Q, Qiu X J, Xu J L. QTL identification and favorable allele mining of cold tolerance at seedling stage by reciprocal introgression and recombinant inbred line populations in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2633-2642. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 吴爱婷, 宋佳谕, 胡涛, 刘思彤, 高继平, 黄丽湘, 高银隆, 赵明辉. 超级稻沈农265苗期耐冷性QTL定位[J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(8): 1477-1482. |
| Wu A T, Song J Y, Hu T, Liu S T, Gao J P, Huang L X, Gao Y L, Zhao M H. QTLs mapping for cold tolerance at seedling stage in super rice variety Shennong 265[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(8): 1477-1482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 彭强, 张大双, 吴健强, 王际凤, 黄培英, 朱速松. 水稻苗期耐冷性的QTL定位分析[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2015, 43(5): 11-13. |
| Peng Q, Zhang D S, Wu J Q, Wang J F, Huang P Y, Zhu S S. QTL analysis of cold-tolerance at seedling stage in rice[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(5): 11-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 刘欣, 覃宝祥, 曾伟, 王永亮, 王君, 江祈贵, 陈保善, 罗继景. 水稻苗期耐冷相关性状QTLs的初步定位[J]. 分子植物育种, 2015, 13(5): 968-976. |
| Liu X, Qin B X, Zeng W, Wang Y L, Wang J, Jiang Q G, Chen B S, Luo J J. Preliminary mapping the QTLs for cold tolerant-associated traits in the seedling stage of rice[J], Molecular Plant Breeding, 2015, 13(5): 968-976. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Mao D, Xin Y, Tan Y, Hu X, Bai J, Liu Z, Yu Y, Li L, Peng C, Fan T, Zhu Y, Guo Y, Wang S, Lu D, Xiang Y, Yuan L, Chen C. Natural variation in the HAN1 gene confers chilling tolerance in rice and allowed adaptation to a temperate climate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(9): 3494-3501. |
| [18] | Liu F, Xu W, Song Q, Tan L, Liu J, Zhu Z, Fu Y, Su Z, Sun C. Microarray-assisted fine-mapping of quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(3): 757-767. |
| [19] | Zhao J, Zhang S, Dong J, Yang J, Yang T, Mao X, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu B. A novel functional gene associated with cold tolerance at the seedling stage in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1141-1148. |
| [20] | Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D, Xiao J, Guo X, Xu S, Niu Y, Jin J, Zhang H, Xu X, Li L, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(6): 1209-1221. |
| [21] | Xia C, Liang G, Chong K, Xu Y. The COG1-OsSERL2 complex senses cold to trigger signaling network for chilling tolerance in japonica rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 3104. |
| [22] | Feng J, Li Z, Luo W, Liang G, Xu Y, Chong K. COG2 negatively regulates chilling tolerance through cell wall components altered in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2023, 136: 19. |
| [23] | Liu D, Luo S, Li Z, Liang G, Guo Y, Xu Y, Chong K. COG3 confers the chilling tolerance to mediate OsFtsH2-D1 module in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2024, online. |
| [24] | Li Z, Wang B, Luo W, Xu Y, Wang J, Xue Z, Niu Y, Cheng Z, Ge S, Zhang W, Zhang J, Li Q, Chong K. Natural variation of codon repeats in COLD11 endows rice with chilling resilience[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(1): eabq5506. |
| [25] | 姜树坤, 王立志, 杨贤莉, 李波, 母伟杰, 董世晨, 车韦才, 李忠杰, 迟力勇, 李明贤, 张喜娟, 姜辉, 李锐, 赵茜, 李文华. 基于高密度SNP遗传图谱的粳稻芽期耐低温QTL鉴定[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(8): 1174-1184. |
| Jiang S K, Wang L Z, Yang X L, Li B, Mu W J, Dong S C, Che W C, Li Z J, Chi L Y, Li M X, Zhang X J, Jiang H, Li R, Zhao Q, Li W H. Detection of QTLs controlling cold tolerance at bud bursting stage by using a high-density SNP linkage map in japonica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1174-1184. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations[J]. The Crop Journal, 2015, 3(3): 269-283. |
| [27] | McCouch S R. Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1(1): 72-84. |
| [28] | Yang L, Liu H, Zhao H, Wang J, Sun J, Zheng H, Lei L, Zou D. Mapping quantitative trait loci and meta-analysis for cold tolerance in rice at booting stage[J]. Euphytica, 2019, 215: 89. |
| [29] | 周勇, 王中德, 陶亚军, 缪军, 高云, 魏伟, 梁国华. 水稻苗期耐冷性相关QTLqCTS3-1的鉴定和分子定位[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2013, 29(6): 1181-1186. |
| Zhou Y, Wang Z D, Tao Y J, Miu J, Gao Y, Wei W, Liang G H. Identification and mapping of a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) qCTS3-1 controlling cold tolerance in rice seedling[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 29(6): 1181-1186. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Jiang N, Shi S, Shi H, Khanzada H, Wassan G, Zhu C, Peng X, Yu Q, Chen X, He X, Fu J, Hu L, Xu J, Ouyang L, Sun X, Zhou D, He H, Bian J. Mapping QTL for seed germinability under low temperature using a new high-density genetic map of rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1223. |
| [31] | Dai L, Lin X, Ye C, Ise K, Saito K, Kato A, Xu F, Yu T, Zhang D. Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling cold tolerance at the reproductive stage in Yunnan landrace of rice, Kunmingxiaobaigu[J]. Breeding Science, 2004, 54(3): 253-258. |
| [32] | Shirasawa S, Endo T, Nakagomi K, Yamaguchi M, Nishio T. Delimitation of a QTL region controlling cold tolerance at booting stage of a cultivar, ‘Lijiangxintuanheigu’, in rice, Oryza sativa L[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2012, 124(5): 937-946. |
| [33] | Endo T, Chiba B, Wagatsuma K, Kenichi S, Ando T, Shomura A, Mizubayashi T, Ueda T, Yamamoto T, Nishio T. Detection of QTLs for cold tolerance of rice cultivar ‘Kuchum’ and effect of QTL pyramiding[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2016, 129(3): 631-640. |
| [34] | 杨树明, 王荔, 曾亚文, 杜娟, 普晓英, 杨涛. 粳稻丽江新团黑谷近等基因系孕穗期耐冷性指标性状的遗传分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(1): 7-11. |
| Yang S M, Wang L, Zeng Y W, Du J, Pu X Y, Yang T. Genetic analysis on cold toleance characteristics at booting stage in the near-isogenic lines from japonica rice Lijiangxintuanheigu[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2013, 28(1): 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 刘友发. 超级杂交稻Y两优2号萌发期和芽期的耐冷性QTL定位研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2019. |
| Liu Y F. QTL mapping of cold tolerance in the germination period and bud bursting period of super hybrid rice Y Liangyou 2[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 韩龙植, 乔永利, 曹桂兰, 张媛媛, 安永平, 芮钟斗, 高熙宗. 水稻生长早期耐冷性QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(2): 122-126. |
| Han L Z, Qiao Y L, Cao G L, Zhang Y Y, An Y P, Rui Z D, Gao X Z. QTL analysis on cold tolerance during early growth period in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(2): 122-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Andaya V C, Mackill D J. Mapping of QTLs associated with cold tolerance during the vegetative stage in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(392): 2579-2585. |
| [38] | 刘晓, 巩迎军, 董彦君, 林冬枝. 一个水稻苗期耐冷性的主效QTL精细定位研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(22): 62-66. |
| Liu X, Gong Y J, Dong Y J, Lin D Z. Study on fine mapping of a major QTL for cold tolerance at seedling stage of rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(22): 62-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Jiang L, Xun M, Wang J, Wan J. QTL analysis of cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombination inbred lines[J]. Journal of Cereal Science. 2008, 48(1): 173-179. |
| [40] | Baruah A R, Ishigo-Oka N, Adachi M, Oguma Y, Tokizono Y, Onishi K, Sano Y. Cold tolerance at the early growth stage in wild and cultivated rice[J]. Euphytica, 2009, 165(3): 459-470. |
| [41] | Wang Z, Wang F, Zhou R, Wang J, Zhang H. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance during the germination and seedling stages in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Euphytica, 2011, 181(3): 405-413. |
| [42] | Yang L, Wang J, Han Z, Lei L, Liu H, Zheng H, Xin W, Zou D. Combining QTL-seq and linkage mapping to fine map a candidate gene in qCTS6 for cold tolerance at the seedling stage in rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 278. |
| [43] | Kim S J, Jeong J H, An G, Kim S. Characterization of a drought-responsive gene, OsTPS1, identified by the T-DNA Gene-Trap system in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2005, 48(4): 371-379. |
| [44] | Jia M, Luo N, Meng X, Song X. OsMPK4 promotes phosphorylation and degradation of IPA1 in response to salt stress to confer salt tolerance in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2022, 49(8): 766-775. |
| [45] | 胡莹, 王奕众. 水稻RIL群体苗期耐冷性QTL分析[J]. 武汉植物学研究, 2005, 23(3): 211-215. |
| Hu Y, Wang Y Z. Mapping of QTL controlling seedling cold tolerance using recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2005, 23(3): 211-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 屈婷婷, 陈立艳, 章志宏, 胡中立, 李平, 朱英国. 水稻籼粳交DH群体苗期耐冷性基因的分子标记定位[J]. 武汉植物学研究, 2003, 21(5): 385-389. |
| Qu T T, Chen L Y, Zhang Z H, Hu Z L, Li P, Zhu Y G. Molecular mapping of genes conferring cold tolerance at seedling stage using doubled haploid lines from an indica-japonica cross in rice[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2003, 21(5): 385-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | Han L, Qiao Y, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Cao G, Kim J, Lee K, Koh H. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cold response of seedling vigor traits in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2007, 34(3): 239-246. |
| [48] | 胡苗, 孙志忠, 孙学武, 谭炎宁, 余东, 刘瑞芬, 袁贵龙, 丁佳, 袁定阳. 利用高密度SNP标记定位水稻粒形相关QTL[J]. 杂交水稻, 2015, 30(5): 54-58. |
| Hu M, Sun Z Z, Sun X W, Tan Y N, Yu D, Liu R F, Yuan G L, Ding J, Yuan D Y. Mapping of rice grain shape relevant QTLs using high-density SNP markers[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2015, 30(5): 54-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 张健, 杨靖, 王豪, 李冬秀, 杨瑰丽, 黄翠红, 周丹华, 郭涛, 陈志强, 王慧. 基于高密度遗传图谱定位水稻籽粒大小相关性状QTL[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(2): 225-238. |
| Zang J, Yang J, Wang H, Li D X, Yang G L, Huang C H, Zhou D H, Guo T, Chen Z Q, Wang H. QTL mapping for grain size related traits based on a high-density map in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(2): 225-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | Yu H, Xie W, Wang J, Xing Y, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, Zhang Q. Gains in QTL detection using an ultra-high density SNP map based on population sequencing relative to traditional RFLP/SSR markers[J]. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(3): e17595. |
| [51] | Gao Z, Zhao S, He W, Qian Q. Dissecting yield-associated loci in super hybrid rice by resequencing recombinant inbred lines and improving parental genome sequences[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(35): 14492-14497. |
| [52] | Liu H, Niu Y, Gonzalez-Portilla P J, Zhou H, Wang L, Zuo T, Qin C, Tai S, Jansen C, Shen Y, Lin H, Lee M, Ware D, Zhang Z, Lubberstedt T, Pan G. An ultra-high-density map as a community resource for discerning the genetic basis of quantitative traits in maize[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 1078. |
| [53] | Song W, Wang B, Hauck A L, Dong X, Li J, Lai J. Genetic dissection of maize seedling root system architecture traits using an ultra-high density bin-map and a recombinant inbred line population[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2016, 58(3): 266-279. |
| [54] | Zou G, Zhai G, Feng Q, Song Y, Wang A, Zhao Q, Shao J, Zhang Z, Han B, Tao Y. Identification of QTLs for eight agronomical important traits using an ultra-high-density map based on SNPs generated from high-throughput sequencing in sorghum under contrasting photoperiods[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(15): 5451-5462. |
| [55] | 董骥驰, 杨靖, 郭涛, 陈立凯, 陈志强, 王慧. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻抽穗期QTL定位[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6): 938-946. |
| Dong J C, Yang J, Guo T, Chen L K, Chen Z Q, Wang H. QTL mapping for heading date in rice using high-density bin map[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 938-946. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 邵雅芳, 朱大伟, 郑欣, 牟仁祥, 章林平, 陈铭学. 2002−2022长三角地区粳稻品质发展状况和地域差异性分析 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 264-276. |
| [2] | 随晶晶, 赵桂龙, 金欣, 卜庆云, 唐佳琦. 水稻孕穗期耐冷调控的分子及生理机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 1-10. |
| [3] | 刘俊峰, 牟静怡, 赵红艳, 郭诗梦, 李漪濛, 梁超, 周婵婵, 王术, 黄元财. 施氮方式与行距配置对不同穗型粳稻品种产量和氮素利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 672-684. |
| [4] | 姚姝, 陈涛, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 梁文化, 赫磊, 路凯, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 管菊, 王才林, 张亚东. 江淮稻区不同类型粳稻品种外观及蒸煮食味品质特征比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 709-718. |
| [5] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [7] | 肖乐铨, 李雷, 戴伟民, 强胜, 宋小玲. 转cry2A*/bar基因水稻与杂草稻杂交后代的苗期生长特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 347-358. |
| [8] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [9] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [10] | 姚姝, 赵春芳, 陈涛, 路凯, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 梁文化, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 低谷蛋白半糯型粳稻营养品质与蒸煮食味品质特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [11] | 裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [12] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [13] | 刘进, 崔迪, 余丽琴, 张立娜, 周慧颖, 马小定, 胡佳晓, 韩冰, 韩龙植, 黎毛毛. 水稻苗期耐热种质资源筛选及QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 259-268. |
| [14] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 姊妹系间杂交快速培育优良食味半糯粳稻新品种的育种效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 455-465. |
| [15] | 王孟佳, 殷敏, 褚光, 刘元辉, 徐春梅, 章秀福, 王丹英, 陈松. 长江中下游双季晚粳稻产量、生育时期及温光资源配置的生态性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 475-486. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||