
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 67-81.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.231111
梁楚炎1,2, 曾维2, 王洁冰1,3, 叶靖2, 巫明明2, 翟荣荣2, 张小明2, 张恒木3,*( ), 叶胜海2,*(
), 叶胜海2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-14
修回日期:2024-03-04
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2025-01-14
通讯作者:
*email: zhhengmu@tsinghua.org.cn;基金资助:
LIANG Chuyan1,2, ZENG Wei2, WANG Jiebing1,3, YE Jing2, WU Mingming2, ZHAI Rongrong2, ZHANG Xiaoming2, ZHANG Hengmu3,*( ), YE Shenghai2,*(
), YE Shenghai2,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-14
Revised:2024-03-04
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2025-01-14
Contact:
*email: zhhengmu@tsinghua.org.cn;摘要:
【目的】探明浙粳99优良穂型的形成机制,为水稻穗型发育机制研究及其育种应用提供科学依据。【方法】利用EMS诱变浙粳99获得短穗小粒突变体,借助分子标记获得连锁区间,采用RNA-Seq及DNA测序确定候选基因,并利用激光共聚焦显微镜观察突变基因的亚细胞定位。使用转录组测序的方法对该突变体的基因表达情况进行分析。【结果】Ossp3与浙粳99在株型、穗型以及粒型上均存在差异。该突变表型由候选基因Os02g0450000发生碱基插入引起。亚细胞定位结果显示该基因产物定位于细胞核。Ossp3幼穗出现329个差异表达基因(DEG),主要分布在1、3和4号染色体上,KEGG富集分析显示,这些差异表达基因主要集中在植物激素信号转导途径、MARK信号通路-植物等生物学过程。相关基因表达分析显示进化上保守的植物特异性基因OsSP3通过MAPK信号通路或与bZIP转录因子作用影响生长素、细胞分裂素含量及其对应信号途径,实现对稻穗发育的调控。【结论】优良穗型品种浙粳99 Os02g0450000基因突变会产生短穗小粒的表型,其生物学功能通过核定位实现,RNA-Seq分析表明该突变基因可能通过影响生长素与细胞分裂素信号通路协同调控稻穗的生长发育,同时很可能通过与OsbZIP47直接或间接作用调控粒型。
梁楚炎, 曾维, 王洁冰, 叶靖, 巫明明, 翟荣荣, 张小明, 张恒木, 叶胜海. 一个浙粳99短穗小粒突变体的鉴定及转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 67-81.
LIANG Chuyan, ZENG Wei, WANG Jiebing, YE Jing, WU Mingming, ZHAI Rongrong, ZHANG Xiaoming, ZHANG Hengmu, YE Shenghai. Characterization and Transcriptome Analysis of a Mutant with Short Panicle and Small Grain from Zhejing 99[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 67-81.
| 引物名称 Name | 引物序列 Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| OsSP3-F1 | ATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGGAGGA |
| OsSP3-R1 | TTACACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAAC |
| OsSP3-F2 | AACACGGGGGACTTTGCAACATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGG |
| OsSP3-R2 | GACAGAGCTAGTTACATTACACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAACT |
| OsSP3-F3 | GGGGCCTGGGGTACCCATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGG |
| OsSP3-R3 | CGCCCTTGCTCACGTCGACCACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAACT |
表1 引物信息
Table 1. Information of primers
| 引物名称 Name | 引物序列 Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| OsSP3-F1 | ATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGGAGGA |
| OsSP3-R1 | TTACACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAAC |
| OsSP3-F2 | AACACGGGGGACTTTGCAACATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGG |
| OsSP3-R2 | GACAGAGCTAGTTACATTACACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAACT |
| OsSP3-F3 | GGGGCCTGGGGTACCCATGTCGACGGCCGCCAAGG |
| OsSP3-R3 | CGCCCTTGCTCACGTCGACCACTGAGGAGCGCTCCAAACT |
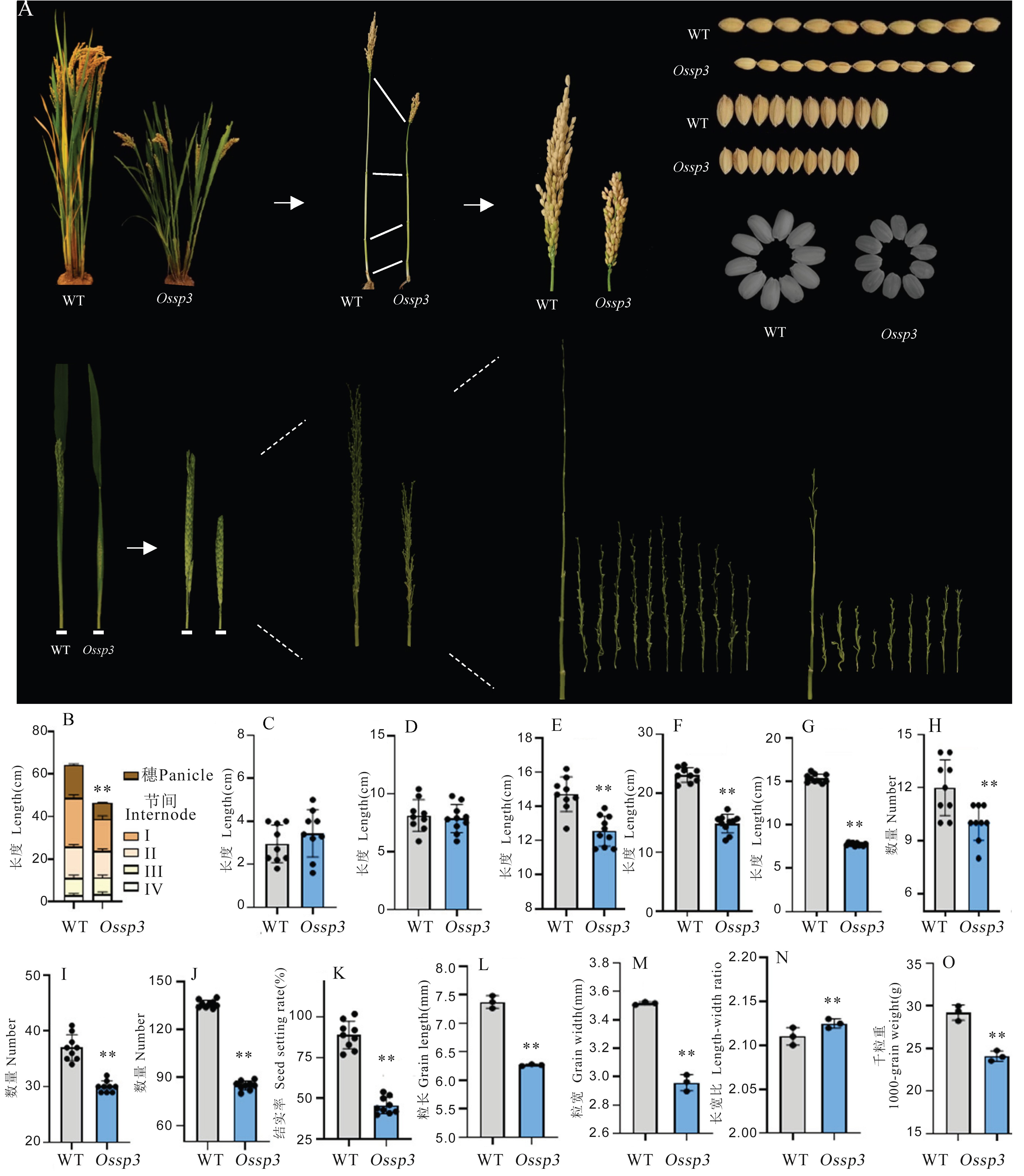
图1 Ossp3突变体的表型鉴定 A: WT与Ossp3成熟期植株、抽穗早期稻穗、成熟期稻粒;B: 株高;C: 第4节节间长;D: 第3节节间长;E: 第2节节间长;F: 第1节节间长;G: 穗长;H: 一次枝梗数;I: 二次枝梗数;J: 每穗粒数;K: 结实率;L: 粒长;M: 粒宽; N: 长宽比;O: 千粒重。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic identification of Ossp3 mutant A, Mature plants, early heading rice panicles, mature rice grains of WT and Ossp3; B, Plant height; C, Length of internode Ⅳ; D, Length of internode Ⅲ; E, Length of internode Ⅱ; F, Length of internode Ⅰ; G, Panicle length; H, Number of primary branches; I, Number of secondary branches ; J, Grain number per panicle; K, Seed setting rate; L, Grain length; M, Grain width; N, Length-width ratio; O, 1000-grain weight.
| 组合 Combination | F1正常表型植株 Number of normal plants in F1 | F2 | χ2(3:1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总株数 Total plant number | 正常表型植株 Normal plants | 突变表型植株 Mutant plants | |||||
| Ossp3/WT | 5 | 355 | 265 | 90 | 0.0117 | ||
表2 Ossp3的遗传分析
Table 2. Genetic analysis of Ossp3 mutant
| 组合 Combination | F1正常表型植株 Number of normal plants in F1 | F2 | χ2(3:1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总株数 Total plant number | 正常表型植株 Normal plants | 突变表型植株 Mutant plants | |||||
| Ossp3/WT | 5 | 355 | 265 | 90 | 0.0117 | ||
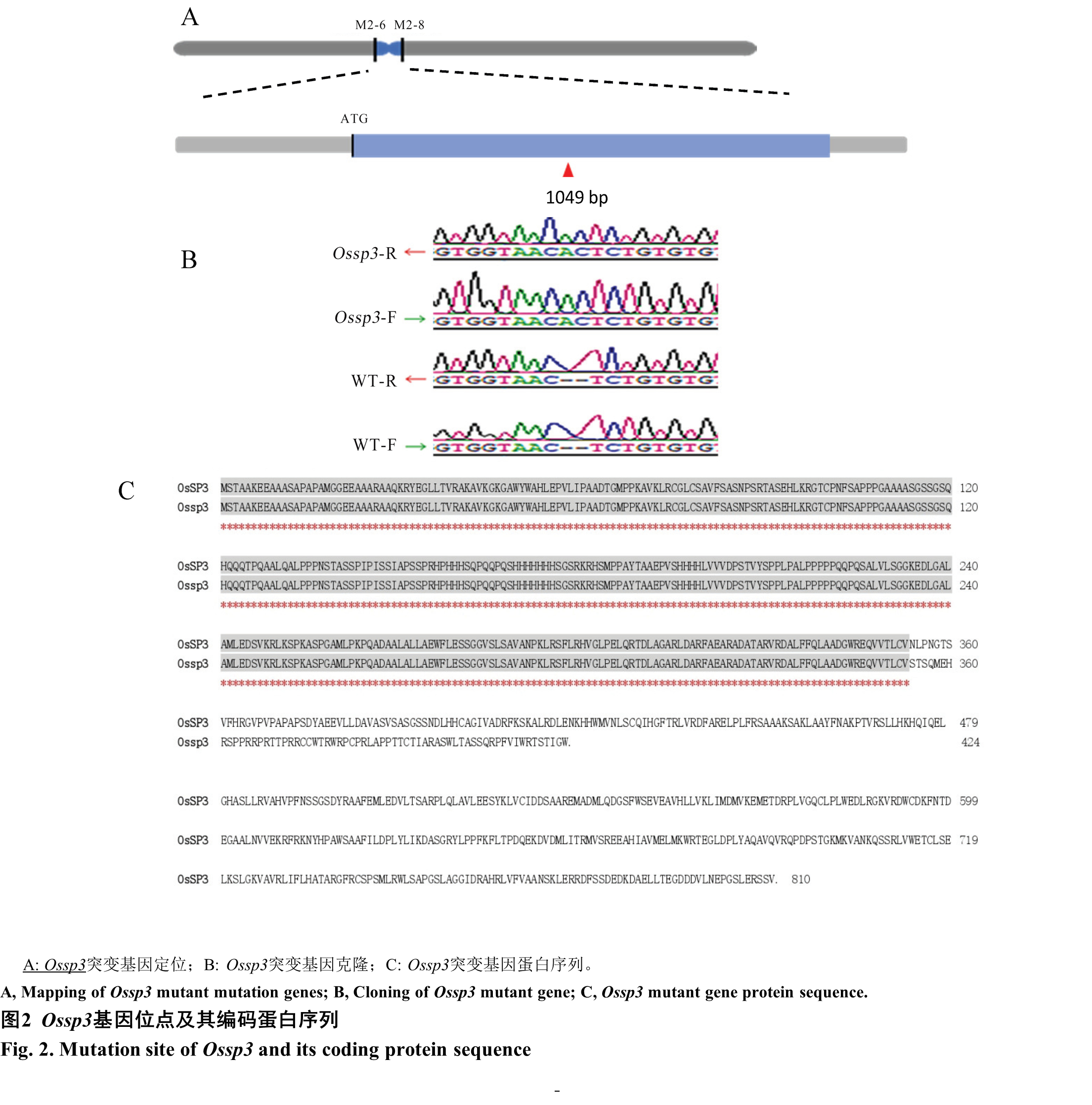
图2 Ossp3基因位点及其编码蛋白序列 A: Ossp3突变基因定位;B: Ossp3突变基因克隆;C: Ossp3突变基因蛋白序列。
Fig. 2. Mutation site of Ossp3 and its coding protein sequence A, Mapping of Ossp3 mutant mutation genes; B, Cloning of Ossp3 mutant gene; C, Ossp3 mutant gene protein sequence.
| 变异位点 Mutation site | SNP/InDel | 参考基因组碱基 Reference genome bases | 样品wt碱基 Sample wt base | 样品sp3碱基 Sample sp3 base | 候选基因 Candidate gene | 原因 Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17287987 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 同义突变GGT/GGC→Gly |
| 17489881 | SNP | C | C | T | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为T |
| 18059754 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 18121601 | SNP | C | C | A | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为A |
| 19270791 | SNP | T | T | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 19309819 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 20348604 | SNP | G | G | A | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为A |
| 14683027 | InDel | A | A | AAC | 是Yes | 移码突变 |
表3 连锁区间内候选位点
Table 3. Candidate loci within the linkage interval
| 变异位点 Mutation site | SNP/InDel | 参考基因组碱基 Reference genome bases | 样品wt碱基 Sample wt base | 样品sp3碱基 Sample sp3 base | 候选基因 Candidate gene | 原因 Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17287987 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 同义突变GGT/GGC→Gly |
| 17489881 | SNP | C | C | T | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为T |
| 18059754 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 18121601 | SNP | C | C | A | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为A |
| 19270791 | SNP | T | T | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 19309819 | SNP | A | A | G | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为G |
| 20348604 | SNP | G | G | A | 否No | 其他参考基因组碱基为A |
| 14683027 | InDel | A | A | AAC | 是Yes | 移码突变 |
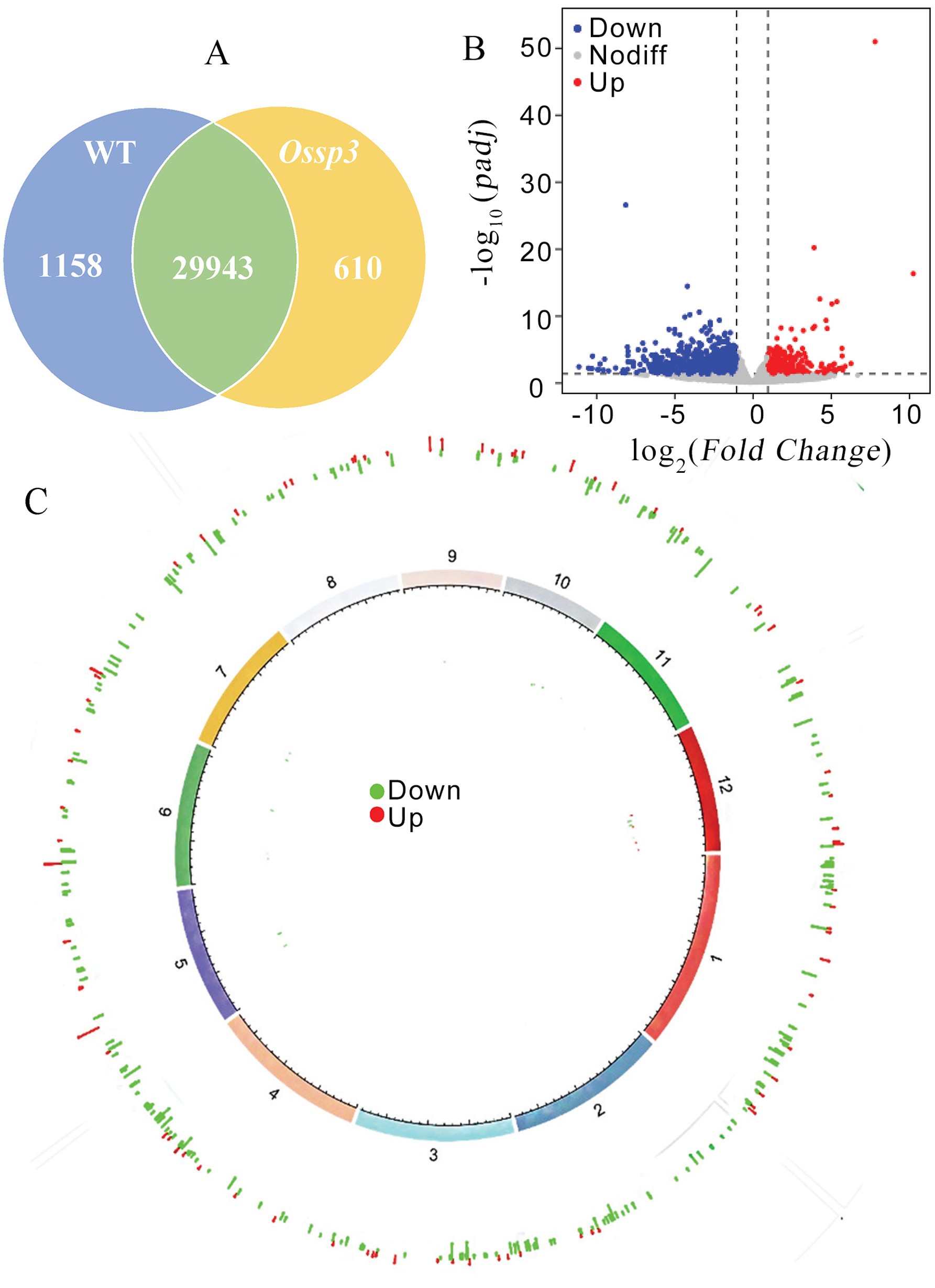
图5 Ossp3与浙粳99的差异表达基因分析 A: 共表达维恩图;B: 差异表达基因火山图;C: 差异表达基因组圈图。
Fig. 5. Analysis of differentially expressed genes between Ossp3 and Zhejing 99 A, Coexpression Venn diagram; B, Differentially expressed gene volcano map; C, Genome circus of differentially expressed gene.
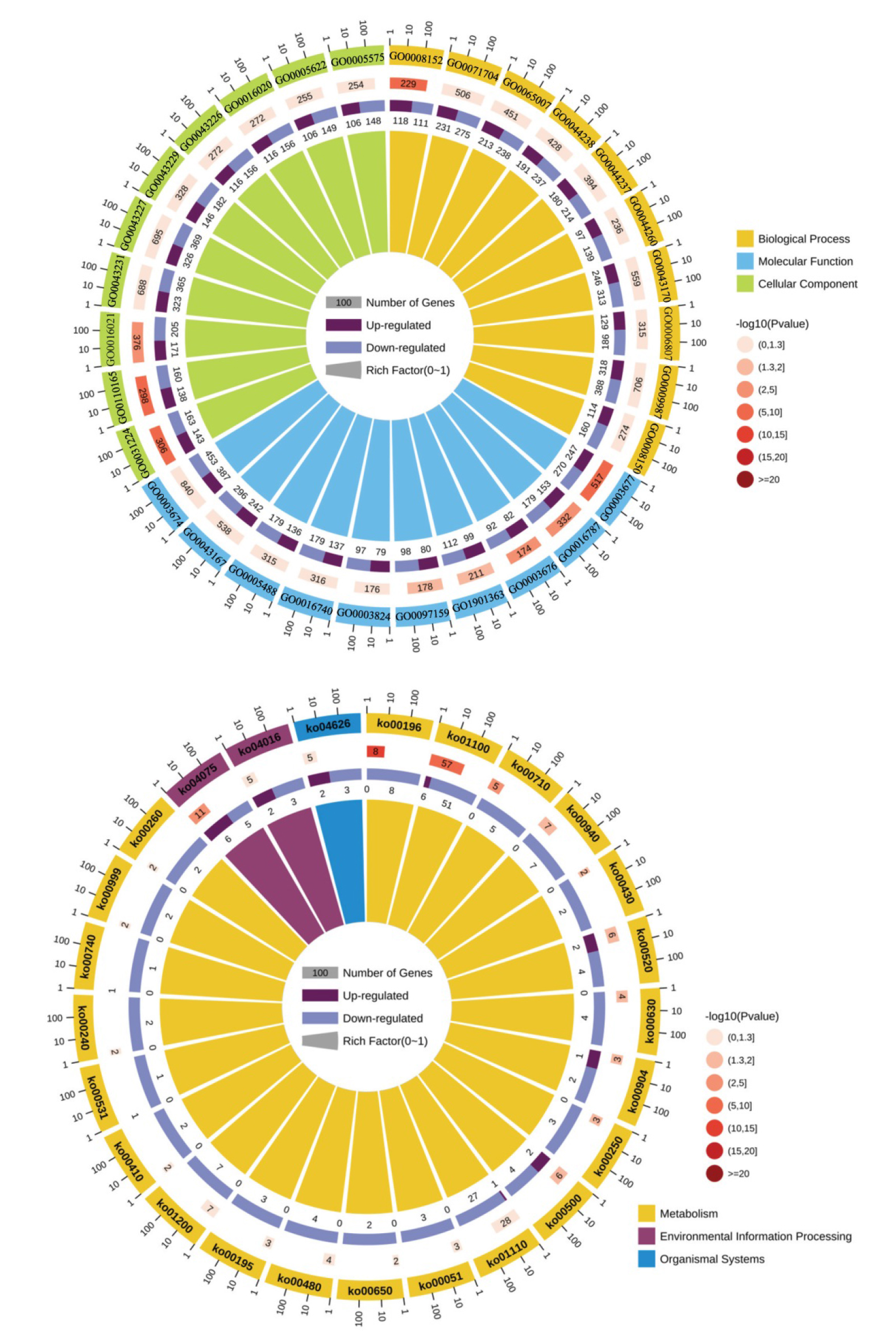
图6 差异表达基因在GO富集三大类基因前10条及在KEGG富集基因数前25条通路
Fig. 6. Top 10 genes in each of the top three categories of GO enrichment for differentially expressed genes and top 25 pathways in KEGG enrichment
| GO: ID | GO条目 GO term | 基因数Number | GO ID | GO条目 GO term | 基因数 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0008150 | Biological process | 179 | GO:0043231 | Intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | 94 |
| GO:0009987 | Cellular process | 144 | GO:0043227 | Membrane-bounded organelle | 94 |
| GO:0008152 | Metabolic process | 141 | GO:0016020 | Membrane | 81 |
| GO:0071704 | Organic substance metabolic process | 127 | GO:0031224 | Intrinsic component of membrane | 70 |
| GO:0044238 | Primary metabolic process | 118 | GO:0016021 | Integral component of membrane | 63 |
| GO:0044237 | Cellular metabolic process | 117 | GO:0003674 | Molecular function | 189 |
| GO:0006807 | Nitrogen compound metabolic process | 90 | GO:0005488 | Binding | 119 |
| GO:0043170 | Macromolecule metabolic process | 86 | GO:0003824 | Catalytic activity | 104 |
| GO:0044260 | Cellular macromolecule metabolic process | 75 | GO:1901363 | Heterocyclic compound binding | 81 |
| GO:0065007 | Biological regulation | 61 | GO:0097159 | Organic cyclic compound binding | 81 |
| GO:0005575 | Cellular component | 183 | GO:0043167 | Ion binding | 55 |
| GO:0110165 | Cellular anatomical entity | 182 | GO:0016787 | Hydrolase activity | 45 |
| GO:0005622 | Intracellular anatomical structure | 110 | GO:0003676 | Nucleic acid binding | 42 |
| GO:0043229 | Intracellular organelle | 97 | GO:0003677 | DNA binding | 37 |
| GO:0043226 | Organelle | 97 | GO:0016740 | Transferase activity | 35 |
表4 差异表达基因在GO富集三大类中基因数前10条目
Table 4. Top 10 entries in each of the three major classifications of GO enrichment for differentially expressed genes
| GO: ID | GO条目 GO term | 基因数Number | GO ID | GO条目 GO term | 基因数 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0008150 | Biological process | 179 | GO:0043231 | Intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | 94 |
| GO:0009987 | Cellular process | 144 | GO:0043227 | Membrane-bounded organelle | 94 |
| GO:0008152 | Metabolic process | 141 | GO:0016020 | Membrane | 81 |
| GO:0071704 | Organic substance metabolic process | 127 | GO:0031224 | Intrinsic component of membrane | 70 |
| GO:0044238 | Primary metabolic process | 118 | GO:0016021 | Integral component of membrane | 63 |
| GO:0044237 | Cellular metabolic process | 117 | GO:0003674 | Molecular function | 189 |
| GO:0006807 | Nitrogen compound metabolic process | 90 | GO:0005488 | Binding | 119 |
| GO:0043170 | Macromolecule metabolic process | 86 | GO:0003824 | Catalytic activity | 104 |
| GO:0044260 | Cellular macromolecule metabolic process | 75 | GO:1901363 | Heterocyclic compound binding | 81 |
| GO:0065007 | Biological regulation | 61 | GO:0097159 | Organic cyclic compound binding | 81 |
| GO:0005575 | Cellular component | 183 | GO:0043167 | Ion binding | 55 |
| GO:0110165 | Cellular anatomical entity | 182 | GO:0016787 | Hydrolase activity | 45 |
| GO:0005622 | Intracellular anatomical structure | 110 | GO:0003676 | Nucleic acid binding | 42 |
| GO:0043229 | Intracellular organelle | 97 | GO:0003677 | DNA binding | 37 |
| GO:0043226 | Organelle | 97 | GO:0016740 | Transferase activity | 35 |
| ID | KEGG条目 KEGG term | 基因数Number | ID | KEGG条目 KEGG term | 基因数Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ko01100 | Metabolic pathways | 57 | ko00904 | Diterpenoid biosynthesis | 3 |
| ko01110 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 28 | ko00250 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 3 |
| ko04075 | Plant hormone signal transduction | 11 | ko00051 | Fructose and mannose metabolism | 3 |
| ko00196 | Photosynthesis - antenna proteins | 8 | ko00195 | Photosynthesis | 3 |
| ko00940 | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 7 | ko00430 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 2 |
| ko01200 | Carbon metabolism | 7 | ko00650 | Butanoate metabolism | 2 |
| ko00520 | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 6 | ko00410 | beta-Alanine metabolism | 2 |
| ko00500 | Starch and sucrose metabolism | 6 | ko00240 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 2 |
| ko00710 | Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 5 | ko00999 | Biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites | 2 |
| ko04016 | MAPK signaling pathway - plant | 5 | ko00260 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 2 |
| ko04626 | Plant-pathogen interaction | 5 | ko00531 | Glycosaminoglycan degradation | 1 |
| ko00630 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 4 | ko00740 | Riboflavin metabolism | 1 |
| ko00480 | Glutathione metabolism | 4 |
表5 差异表达基因在KEGG富集基因数前25条通路
Table 5. Top 25 entries in KEGG enrichment for differentially expressed genes
| ID | KEGG条目 KEGG term | 基因数Number | ID | KEGG条目 KEGG term | 基因数Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ko01100 | Metabolic pathways | 57 | ko00904 | Diterpenoid biosynthesis | 3 |
| ko01110 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 28 | ko00250 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 3 |
| ko04075 | Plant hormone signal transduction | 11 | ko00051 | Fructose and mannose metabolism | 3 |
| ko00196 | Photosynthesis - antenna proteins | 8 | ko00195 | Photosynthesis | 3 |
| ko00940 | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 7 | ko00430 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 2 |
| ko01200 | Carbon metabolism | 7 | ko00650 | Butanoate metabolism | 2 |
| ko00520 | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 6 | ko00410 | beta-Alanine metabolism | 2 |
| ko00500 | Starch and sucrose metabolism | 6 | ko00240 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 2 |
| ko00710 | Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 5 | ko00999 | Biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites | 2 |
| ko04016 | MAPK signaling pathway - plant | 5 | ko00260 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 2 |
| ko04626 | Plant-pathogen interaction | 5 | ko00531 | Glycosaminoglycan degradation | 1 |
| ko00630 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 4 | ko00740 | Riboflavin metabolism | 1 |
| ko00480 | Glutathione metabolism | 4 |
| ID | 基因符号 Symbol | 注释 Innovation | 表型 Phenotype | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os03g0180800 | OsJAZ9; OsTIFY11a | TIFY家族基因 (茉莉酸信号通路基因) | 过表达导致脱落酸(ABA)和茉莉酸(JA)水平升高,降低了叶片宽度和气孔密度。RNAi导致缺水胁迫更敏感,植株茎部的生长只有野生型的60%[ | −3.79 |
| Os09g0111100 | OsCYCD3 | D型细胞周期蛋白 | 敲除突变体分支数量减少,腋生分生组织和茎尖分生组织(SAM)活性受到损害[ | 1.16 |
| Os06g0696600 | 糖基水解酶家族 | 未知 | −3.26 | |
| Os11g0141900 | OsNH5.1; OsBOP2 | NPR1类似基因; BOP基因 | 过表达促进叶鞘发育、抑制叶片发育。基因冗余控制小穗器官发育,护颖更长[ | 1.58 |
| Os01g0382400 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.00 | |
| Os02g0200900 | F-box蛋白; E3泛素连接酶 | OsEBF2与OsEIL1互作,过表达增强褐飞虱抗性,抗性机制通过抑制乙烯应答因子基因的表达来降低乙烯含量[ | −1.30 | |
| Os03g0322700 | OsbZIP29 | bZIP转录因子 | bZIP转录因子从开花到穗和种子发育不同阶段,存在特异和共表达模式[ | 2.41 |
| Os06g0265400 | OsbZIP47 | bZIP转录因子 | 突变体粒宽和粒重增加,过表达籽粒变窄[ | 1.40 |
| Os04g0691100 | OsSAPK5 | 应激活化蛋白激酶 | OsSAPK5能被高渗透胁迫激活[ | −1.05 |
| Os10g0191300 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.78 | |
| Os11g0221000 | OsIAA27 | OsAux/IAAs家族基因 (生长素信号通路基因) | 未知 | −1.41 |
表6 富集在植物激素信号转导途径的11个差异基因
Table 6. Eleven differentially expressed genes enriched in plant hormone signaling pathways
| ID | 基因符号 Symbol | 注释 Innovation | 表型 Phenotype | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os03g0180800 | OsJAZ9; OsTIFY11a | TIFY家族基因 (茉莉酸信号通路基因) | 过表达导致脱落酸(ABA)和茉莉酸(JA)水平升高,降低了叶片宽度和气孔密度。RNAi导致缺水胁迫更敏感,植株茎部的生长只有野生型的60%[ | −3.79 |
| Os09g0111100 | OsCYCD3 | D型细胞周期蛋白 | 敲除突变体分支数量减少,腋生分生组织和茎尖分生组织(SAM)活性受到损害[ | 1.16 |
| Os06g0696600 | 糖基水解酶家族 | 未知 | −3.26 | |
| Os11g0141900 | OsNH5.1; OsBOP2 | NPR1类似基因; BOP基因 | 过表达促进叶鞘发育、抑制叶片发育。基因冗余控制小穗器官发育,护颖更长[ | 1.58 |
| Os01g0382400 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.00 | |
| Os02g0200900 | F-box蛋白; E3泛素连接酶 | OsEBF2与OsEIL1互作,过表达增强褐飞虱抗性,抗性机制通过抑制乙烯应答因子基因的表达来降低乙烯含量[ | −1.30 | |
| Os03g0322700 | OsbZIP29 | bZIP转录因子 | bZIP转录因子从开花到穗和种子发育不同阶段,存在特异和共表达模式[ | 2.41 |
| Os06g0265400 | OsbZIP47 | bZIP转录因子 | 突变体粒宽和粒重增加,过表达籽粒变窄[ | 1.40 |
| Os04g0691100 | OsSAPK5 | 应激活化蛋白激酶 | OsSAPK5能被高渗透胁迫激活[ | −1.05 |
| Os10g0191300 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.78 | |
| Os11g0221000 | OsIAA27 | OsAux/IAAs家族基因 (生长素信号通路基因) | 未知 | −1.41 |
| ID | 基因符号 Symbol | 注释 Innovation | 表型 Phenotype | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0382400 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.00 | |
| Os01g0699400 | OsMKKK55 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶激酶 | osmkkk55/62/70三突变体的种子小,叶角直立[ | −6.00 |
| Os02g0200900 | OsEBF2 | F-box蛋白 | 过表达增强褐飞虱抗性,农艺性状不变,敲除对褐飞虱敏感[ | −1.30 |
| Os04g0691100 | OsSAPK5 | 应激活化蛋白激酶 | OsSAPK5能被高渗透胁迫激活[ | −1.05 |
| Os10g0191300 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.78 |
表7 富集在MAPK信号通路的5个差异基因
Table 7. Five differentially expressed genes enriched in MAPK signaling pathway - plant
| ID | 基因符号 Symbol | 注释 Innovation | 表型 Phenotype | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0382400 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.00 | |
| Os01g0699400 | OsMKKK55 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶激酶 | osmkkk55/62/70三突变体的种子小,叶角直立[ | −6.00 |
| Os02g0200900 | OsEBF2 | F-box蛋白 | 过表达增强褐飞虱抗性,农艺性状不变,敲除对褐飞虱敏感[ | −1.30 |
| Os04g0691100 | OsSAPK5 | 应激活化蛋白激酶 | OsSAPK5能被高渗透胁迫激活[ | −1.05 |
| Os10g0191300 | SCP样细胞外蛋白 | 未知 | 4.78 |
| ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2(Fold Change) | ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0813100 | OsbZIP09 | 0.17 | Os04g0559800 | OsMKKK10 | 0.10 |
| Os06g0601500 | OsbZIP48 | −0.18 | Os02g0787300 | OsMKK4 | 0.13 |
| Os07g0686100 | OsbZIP62 | 0.82 | Os05g0115800 | OsMKP1 | 0.08 |
| Os06g0162800 | OsMADS5 | 0.30 | Os06g0154500 | OsMAPK6 | −0.01 |
| Os03g0753100 | OsMADS34 | 0.05 | Os01g0699500 | OsMKKK70 | −1.88 |
| Os04g0411400 | RCN4 | 2.61 | Os03g0786400 | DST | −0.358 |
| Os12g0601300 | OsIAA30 | −0.70 | Os06g0203800 | OsER1 | 0.45 |
| Os03g0187500 | OsAFB6 | 0.36 | Os06g0157700 | Hd3a | 2.53 |
| Os01g0625900 | OsOFP2 | 0.46 | Os06g0157500 | RFT1 | FPKM=0 |
| Os04g0442300 | OsRR1 | 0.87 | Os09g0540800 | OsbZIP77 | 2.48 |
| Os10g0463400 | Ehd1 | FPKM=0 | Os08g0430500 | Gf14 | −0.27 |
| Os01g0197700 | Gn1a | 0.32 | Os05g0489700 | OsbZIP42 | 0.16 |
表8 互作调控网络内基因log2(Fold Change)值
Table 8. log2(Fold Change) value of genes in the interaction regulatory network
| ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2(Fold Change) | ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2(Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0813100 | OsbZIP09 | 0.17 | Os04g0559800 | OsMKKK10 | 0.10 |
| Os06g0601500 | OsbZIP48 | −0.18 | Os02g0787300 | OsMKK4 | 0.13 |
| Os07g0686100 | OsbZIP62 | 0.82 | Os05g0115800 | OsMKP1 | 0.08 |
| Os06g0162800 | OsMADS5 | 0.30 | Os06g0154500 | OsMAPK6 | −0.01 |
| Os03g0753100 | OsMADS34 | 0.05 | Os01g0699500 | OsMKKK70 | −1.88 |
| Os04g0411400 | RCN4 | 2.61 | Os03g0786400 | DST | −0.358 |
| Os12g0601300 | OsIAA30 | −0.70 | Os06g0203800 | OsER1 | 0.45 |
| Os03g0187500 | OsAFB6 | 0.36 | Os06g0157700 | Hd3a | 2.53 |
| Os01g0625900 | OsOFP2 | 0.46 | Os06g0157500 | RFT1 | FPKM=0 |
| Os04g0442300 | OsRR1 | 0.87 | Os09g0540800 | OsbZIP77 | 2.48 |
| Os10g0463400 | Ehd1 | FPKM=0 | Os08g0430500 | Gf14 | −0.27 |
| Os01g0197700 | Gn1a | 0.32 | Os05g0489700 | OsbZIP42 | 0.16 |
| [1] | Sun C, Wang Y, Yang X, Tang L, Wan C, Liu J, Chen C, Zhang H, He C, Liu C, Wang Q, Zhang K, Zhang W, Yang B, Li S, Zhu J, Sun Y, Li W, Zhou Y, Wang P, Deng X. MATE transporter GFD1 cooperates with sugar transporters, mediates carbohydrate partitioning and controls grain-filling duration, grain size and number in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21(3): 621-634. |
| [2] | Li X, Zhang R C, Chen G, Xie J X, Xiao Z W, Cao F B, Izhar A, Anas I, Abdul W, Huang M, Chen J N. Increasing grain weight and yield stability by increasing pre-heading non-structural carbohydrate reserves per spikelet in short-growth duration rice[J]. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(6): 1912-1920. |
| [3] | 刘坚, 陶红剑, 施思, 叶卫军, 钱前, 郭龙彪. 水稻穗型的遗传和育种改良[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(2): 227-234. |
| Liu J, Tao H J, Shi S, Ye W J, Qian Q, Guo L B. Genetics and breeding improvement for panicle type in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(2): 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Lu H, Shi Z Y. Molecular research progress of rice panicle development[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(2): 111-121. |
| [5] | Itoh J I, Nonomura K I, Ikeda K, Yamaki S, Inukai Y, Yamagishi H, Kitano H, Nagato Y. Rice plant development: From zygote to spikelet[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2005, 46(1): 23-47. |
| [6] | Mehra P, Pandey B K, Verma L, Prusty A, Singh A P, Sharma S, Malik N, Bennett M J, Parida S K, Giri J, Tyagi A K. OsJAZ11 regulates spikelet and seed development in rice[J]. Plant Director, 2022, 6(5): e401. |
| [7] | Gao S, Fang J, Xu F, Wang W, Chu C. Rice HOX12 regulates panicle exsertion by directly modulating the expression of ELONGATED UPPERMOST INTERNODE1[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(3): 680-695. |
| [8] | 曾维, 郭铧艳, 叶胜海, 朱国富, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 巫明明, 吕华良, 张小明. 水稻穗型相关基因定位和育种利用研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22(6): 2052-2059. |
| Zeng W, Guo H Y, Ye S H, Zhu G F, Zhai R R, Ye J, Wu M M, Lü H L, Zhang X M. Research progress on rice panicle type related gene mapping and breeding utilization[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024, 22(6): 2052-2059. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Huang L, Hua K, Xu R, Zeng D, Wang R, Dong G, Zhang G, Lu X, Fang N, Wang D, Duan P, Zhang B, Liu Z, Li N, Luo Y, Qian Q, Yao S, Li Y. The LARGE2-APO1/APO2 regulatory module controls panicle size and grain number in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2021, 33(4): 1212-1228. |
| [10] | Zhang D, Zhang M, Wang Y, Liang J. RGB1 regulates rice panicle architecture and grain filling through monitoring cytokinin level in inflorescence meristem and grain abscisic acid level during filling stage[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(4): 317-321. |
| [11] | Huang Y, Bai X, Luo M, Xing Y. Short Panicle 3 controls panicle architecture by upregulating APO2/RFL and increasing cytokinin content in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2019, 61(9): 987-999. |
| [12] | He Q, Yang L, Hu W, Zhang J, Xing Y Z. Overexpression of an auxin receptor OsAFB6 significantly enhanced grain yield by increasing cytokinin and decreasing auxin concentrations in rice panicle[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 14051. |
| [13] | Guo T, Lu Z Q, Shan J X, Ye W W, Dong N Q, Lin H X. ERECTA1 acts upstream of the OsMKKK10- OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to control spikelet number by regulating cytokinin metabolism in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(9): 2763-2779. |
| [14] | Hake A A, Ballichatla S, Barbadikar K M, Magar N, Dutta S, Gokulan C G, Awalellu K, Patel H K, Sonti R V, Phule A S, Varma E P, Ayeella P G, Vamshi P, Sundaram R M, Maganti S M. Combined strategy employing MutMap and RNA-seq reveals genomic regions and genes associated with complete panicle exsertion in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2023, 43(9): 69. |
| [15] | Niu F, Liu M, Dong S, Dong X, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chu H, Hu Z, Ma F, Yan P, Lan D, Zhang J, Zhou J, Sun B, Zhang A, Hu J, Zhang X, He S, Cui J, Yuan X, Yang J, Cao L, Luo X. RNA-seq transcriptome analysis and evolution of OsEBS, a gene involved in enhanced spikelet number per panicle in rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(12): 10303. |
| [16] | Liang W, Hu F, Qi W, Zhao C G, Chen T, Wang C, Lü Y, Zhang Y. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of GS3 near-isogenic lines during panicle development in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2022, 13: 857143. |
| [17] | Ke S, Liu X J, Luan X, Yang W, Zhu H, Liu G, Zhang G, Wang S. Genome-wide transcriptome profiling provides insights into panicle development of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Gene, 2018, 675: 285-300. |
| [18] | Guo H, Mendrikahy J N, Xie L, Deng J, Lu Z, Wu J, Li X, Shahid M Q, Liu X. Transcriptome analysis of neo-tetraploid rice reveals specific differential gene expressions associated with fertility and heterosis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40139. |
| [19] | 叶胜海. 常规晚粳稻品种浙粳 99[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2017, 58(3): 552. |
| Ye S H. Conventional late japonica rice variety Zhegeng 99[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 58(3): 552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 王俊梅, 叶胜海, 翟荣荣, 余鹏, 朱国富, 金庆生, 张小明. 耐草甘膦水稻种质资源的创制和鉴定[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(03): 432-439. |
| Wang J M, Ye S H, Zhai R R, Yu P, Zhu G F, Jin Q S, Zhang X M. Greation and identification of glyphosate-tolerant rice germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(3): 432-439. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 项聪英, 蔡年俊, 李静, 羊健, 陈剑平, 张恒木. 一个水稻小热休克蛋白基因的克隆和鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 587-592. |
| Xiang C Y, Cai N J, Li J, Yang J, Chen J P, Zhang H M. Cloning and characterization of a small heat shock protein (SHSP) gene in rice plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 587-592. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 刘继云, 叶胜海, 李小华, 赵小燕, 尚海漩, 纪现军, 邓晓梅, 陈萍萍, 金庆生, 张小明. 一个水稻矮秆窄叶突变体的鉴定和基因定位[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2014, 26(1): 7-13. |
| Liu J Y, Ye S H, Li X H, Zhao X Y, Shang H X, Ji X J, Deng X M, Chen P P, Jin Q S, Zhang X M. Identification and gene mapping of a dwarf narrow leaf mutant in rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2014, 26(1): 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Jiang S H, Zhou H, Lin D Z, Dong Y J, Ye S H, Zhang X M. Identification and gene mapping of a thermo-sensitive leaf-color mutant at seeding in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(04): 359-364. |
| [24] | 齐盼盼, 郭留明, 李静, 吕明芳, 袁正杰, 张恒木. 水稻TAF12b基因cDNA克隆及其分子特性鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 577-586. |
| Qi P P, Guo L M, Li Jing, Lü M F, Yuan Z J, Zhang H M. cDNa cloning and molecular characterization of OsTAF12b gene in Oryza sativa[J]. Chinese Journal oF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 577-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Li H, Sun H, Jiang J, Sun X, Tan L, Sun C. TAC4 controls tiller angle by regulating the endogenous auxin content and distribution in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(1): 64-73. |
| [26] | Huang Y, Dong H, Mou C, Wang P, Hao Q, Zhang M, Wu H, Zhang F, Ma T, Miao R, Fu K, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Chen C, Tong Q, Wang Z, Zhou S, Liu X, Liu S, Tian Y, Jiang L, Wan J M. Ribonuclease H-like gene SMALL GRAIN2 regulates grain size in rice through brassinosteroid signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(10): 1883-1900. |
| [27] | Wu H, Ye H, Yao R, Zhang T, Xiong L. OsJAZ9 acts as a transcriptional regulator in jasmonate signaling and modulates salt stress tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2015, 232: 1-12. |
| [28] | Singh A P, Mani B, Giri J. OsJAZ9 is involved in water-deficit stress tolerance by regulating leaf width and stomatal density in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 162: 161-170. |
| [29] | Ohyama A, Tominaga R, Toriba T, Tanaka W. D-type cyclin OsCYCD3;1 is involved in the maintenance of meristem activity to regulate branch formation in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2022, 270: 153634. |
| [30] | Toriba T, Tokunaga H, Shiga T, Nie F, Naramoto S, Honda E, Tanaka K, Taji T, Itoh J I, Kyozuka J. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes temporally and developmentally regulate the sheath to blade ratio of rice leaves[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 619. |
| [31] | Chern M, Bai W, Ruan D, Oh T, Chen X, Ronald P C. Interaction specificity and coexpression of rice NPR1 homologs 1 and 3 (NH1 and NH3), TGA transcription factors and Negative Regulator of Resistance (NRR) proteins[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 461. |
| [32] | Ma F, Li Z, Wang S, Li K, Tang F, Jia J, Zhao Q, Jing P, Yang W, Hua C, Han H, Xu J, Sun R, Zhang J, Han R, Liu X, Fan S, Gu L, Xu K, Li L. The F-box protein OsEBF2 confers the resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilparvata lugens Stål)[J]. Plant Science, 2023, 327: 111547. |
| [33] | Nijhawan A, Jain M, Tyagi A K, Khurana J P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 146(2): 333-350. |
| [34] | Hao J, Wang D, Wu Y, Huang K, Duan P, Li N, Xu R, Zeng D, Dong G, Zhang B, Zhang L, Inzé D, Qian Q, Li Y H. The GW2-WG1-OsbZIP47 pathway controls grain size and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(8): 1266-1280. |
| [35] | Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Minami H, Kagaya Y, Hattori T. Differential activation of the rice sucrose nonfermenting1-related protein kinase2 family by hyperosmotic stress and abscisic acid[J]. The Plant Cell, 2004, 16(5): 1163-1177. |
| [36] | Liu Z, Mei E, Tian X, He M, Tang J, Xu M, Liu J, Song L, Li X, Wang Z, Guan Q, Xu Q, Bu Q. OsMKKK70 regulates grain size and leaf angle in rice through the OsMKK4-OsMAPK6-OsWRKY53 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(12): 2043-2057. |
| [37] | Chen Y, Li X Y. Research progress in genetic regulation of rice panicle architecture[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(1): 19-29. |
| [38] | Kieber J J, Schaller G E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development[J]. Development, 2018, 145(4): dev149344. |
| [39] | Lavy M, Estelle M. Mechanisms of auxin signaling[J]. Development, 2016, 143(18): 3226-3229. |
| [40] | Ciura J, Kruk J. Phytohormones as targets for improving plant productivity and stress tolerance[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2018, 229: 32-40. |
| [41] | Wang C, Zhu C, Zhou Y, Xiong M, Wang J, Bai H, Lu C, Zhang C, Liu Q, Li Q. OsbZIP09, a unique OsbZIP transcription factor of rice, promotes rather than suppresses seed germination by attenuating abscisic acid pathway[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(4): 358-367. |
| [42] | Brambilla V, Martignago D, Goretti D, Cerise M, Somssich M, de Rosa M, Galbiati F, Shrestha R, Lazzaro F, Simon R, Fornara F. Antagonistic transcription factor complexes modulate the floral transition in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(11): 2801-2816. |
| [43] | Burman N, Bhatnagar A, Khurana J P. OsbZIP48, a HY5 transcription factor ortholog, exerts pleiotropic effects in light-regulated development[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(2): 1262-1285. |
| [44] | Cui R, Han J, Zhao S, Su K, Wu F, Du X, Xu Q, Chong K, Theissen G, Meng Z. Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. The Plant Journal, 2010, 61(5): 767-781. |
| [45] | Zhu W, Yang L, Wu D, Meng Q, Deng X, Huang G, Zhang J, Chen X, Ferrándiz C, Liang W, Dreni L, Zhang D. Rice SEPALLATA genes OsMADS5 and OsMADS34 cooperate to limit inflorescence branching by repressing the TERMINAL FLOWER1-like gene RCN4[J]. The New Phytologist, 2022, 233(4): 1682-1700. |
| [46] | Zhang Y, Yu H, Liu J, Wang W, Sun J, Gao Q, Zhang Y, Ma D, Wang J, Xu Z, Chen W. Loss of function of OsMADS34 leads to large sterile lemma and low grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2016, 36(11): 147. |
| [47] | Kobayashi K, Maekawa M, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Kyozuka J. PANICLE PHYTOMER2 (PAP2), encoding a SEPALLATA subfamily MADS-box protein, positively controls spikelet meristem identity in rice[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(1): 47-57. |
| [48] | Schmitz A J, Begcy K, Sarath G, Walia H. Rice Ovate Family Protein 2 (OFP2) alters hormonal homeostasis and vasculature development[J]. Plant Science, 2015, 241: 177-188. |
| [49] | Cho L H, Yoon J, Tun W, Baek G, Peng X, Hong W J, Mori I C, Hojo Y, Matsuura T, Kim S R, Kim S T, Kwon S W, Jung K H, Jeon J S, An G. Cytokinin increases vegetative growth period by suppressing florigen expression in rice and maize[J]. The Plant Journal, 2022, 110(6): 1619-1635. |
| [50] | Endo-Higashi N, Izawa T. Flowering time genes Heading date 1 and Early heading date 1 together control panicle development in rice[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(6): 1083-1094. |
| [51] | Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S Y, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles E R, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5735): 741-745. |
| [52] | Yeh S Y, Chen H W, Ng C Y, Lin C Y, Tseng T H, Li W H, Ku M S B. Down-regulation of cytokinin oxidase 2 expression increases tiller number and improves rice yield[J]. Rice, 2015, 8(1): 36. |
| [53] | Duan P, Rao Y, Zeng D, Yang Y, Xu R, Zhang B, Dong G, Qian Q, Li Y H. SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 77(4): 547-557. |
| [54] | Guo T, Chen K, Dong N Q, Shi C L, Ye W W, Gao J P, Shan J X, Lin H X. GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4- OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(4): 871-888. |
| [55] | Huang X Y, Chao D Y, Gao J P, Zhu M Z, Shi M, Lin H X. A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control[J]. Genes & Development, 2009, 23(15): 1805-1817. |
| [56] | Li S, Zhao B, Yuan D, Duan M, Qian Q, Tang L, Wang B, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang J, Sun J, Liu Z, Feng Y Q, Yuan L, Li C. Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(8): 3167-3172. |
| [57] | Liu S, Hua L, Dong S, Chen H, Zhu X, Jiang J E, Zhang F, Li Y, Fang X, Chen F. OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production[J]. The Plant Journal, 2015, 84(4): 672-681. |
| [58] | Kaneko-Suzuki M, Kurihara-Ishikawa R, Okushita- Terakawa C, Kojima C, Nagano-Fujiwara M, Ohki I, Tsuji H, Shimamoto K, Taoka K I. TFL1-like proteins in rice antagonize rice FT-like protein in inflorescence development by competition for complex formation with 14-3-3 and FD[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2018, 59(3): 458-468. |
| [59] | Cai M, Zhu S, Wu M, Zheng X, Wang J, Zhou L, Zheng T, Cui S, Zhou S, Li C, Zhang H, Chai J, Zhang X, Jin X, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Lei C, Ren Y, Lin Q, Guo X, Zhao L, Wang J, Zhao Z, Jiang L, Wang H, Wan J. DHD4, a CONSTANS-like family transcription factor, delays heading date by affecting the formation of FAC complex in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(2): 330-343. |
| [60] | Zhang M, Zhang S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(2): 301-341. |
| [61] | He N, Zhan G, Huang F, Abou-Elwafa S F, Yang D. Fine mapping and cloning of a major QTL qph12, which simultaneously affects the plant height, panicle length, spikelet number and yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 878558. |
| [1] | 冯涛, 张朝阳, 黄新妮, 王月, 钟旭志, 冯志明, 刘欣, 左示敏, 欧阳寿强. Osa-miR166i-3p介导活性氧积累途径正调控水稻纹枯病抗性 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 187-196. |
| [2] | 童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576. |
| [3] | 伏荣桃, 王剑, 陈诚, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 水稻幼穗响应稻曲病菌毒素胁迫早期的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 447-458. |
| [4] | 孙志广, 代慧敏, 陈庭木, 李景芳, 迟铭, 周振玲, 刘艳, 刘金波, 徐波, 邢运高, 杨波, 李健, 卢百关, 方兆伟, 王宝祥, 徐大勇. 水稻类病斑突变体lmm7的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 357-366. |
| [5] | 刘鑫, 张恒, 阚虎飞, 周立帅, 黄昊, 宋林林, 翟焕趁, 张君, 鲁国东. 水稻泛素结合酶基因家族的生物信息学与表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 223-231. |
| [6] | 徐丽慧,邱文,张唯一,李斌,谢关林. 水稻细菌性褐条病病原的鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(3): 302-306 . |
| [7] | 罗金燕, 徐福寿,王平,徐丽慧,谢关林, . 水稻细菌性谷枯病病原菌的分离鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(1): 82-86 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||