
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 357-366.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210711
孙志广1, 代慧敏2, 陈庭木1, 李景芳1, 迟铭1, 周振玲1, 刘艳1, 刘金波1, 徐波1, 邢运高1, 杨波1, 李健1, 卢百关1, 方兆伟1, 王宝祥1,*( ), 徐大勇1,*(
), 徐大勇1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-30
修回日期:2021-08-30
出版日期:2022-07-10
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
王宝祥,徐大勇
基金资助:
SUN Zhiguang1, DAI Huimin2, CHEN Tingmu1, LI Jingfang1, CHI Ming1, ZHOU Zhenling1, LIU Yan1, LIU Jinbo1, XU Bo1, XING Yungao1, YANG Bo1, LI Jian1, LU Baiguan1, FANG Zhaowei1, WANG Baoxiang1,*( ), XU Dayong1,*(
), XU Dayong1,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-30
Revised:2021-08-30
Online:2022-07-10
Published:2022-07-12
Contact:
WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong
摘要:
【目的】对水稻类病斑突变体的研究有助于解析其与植物生长和防御反应的关系。【方法】本研究在粳稻品系FI135胚培养过程中获得了1个类病斑突变体lmm7(lesion mimic mutant 7)。通过对其进行系统的表型鉴定、农艺性状考查、超微结构观察、生理学特性分析,阐明LMM7基因对植物生长的调控。通过病原菌抗性鉴定,明确lmm7对植物防御反应的影响。利用9311B与突变体lmm7杂交所得F2群体对该突变体进行了遗传分析和基因精细定位。【结果】该突变体苗期表型正常,分蘖初期,植株基部叶片从叶尖开始不断出现褐色斑点,并向整株扩散,且斑点数目随植株生长不断增加。与野生型相比,突变体的株高、穗长、有效穗数、每穗粒数、结实率及剑叶长宽都显著降低,但籽粒性状和抽穗期没有显著性差异。遮光处理表明,突变体lmm7的表型受到光照诱导,抽穗期突变体lmm7叶肉细胞严重失绿,光合色素含量显著降低。组织化学分析表明,突变体病斑处的H2O2含量显著升高。透射电镜观察结果表明,突变体lmm7叶肉细胞的叶绿体数目减少,叶绿体类囊体片层结构严重受损,细胞器肿胀解体,并出现大量嗜锇小体,同时病斑内部和周围区域积累了大量的ROS。抗性鉴定结果显示突变体lmm7稻瘟病抗性水平显著高于野生型。遗传分析表明lmm7的突变表型受单个隐性基因控制。利用图位克隆的方法,目的基因被定位于水稻第7染色体短臂两InDel标记7B35和7B43之间,区间范围约260 kb。测序结果表明该区间内候选基因LOC_Os07g0203700第2891位碱基T发生了单碱基缺失,导致后续移码突变及翻译提前终止。【结论】lmm7与spl5互为等位基因,其突变抑制了植株的生长,同时增强了对稻瘟病的抗性。
孙志广, 代慧敏, 陈庭木, 李景芳, 迟铭, 周振玲, 刘艳, 刘金波, 徐波, 邢运高, 杨波, 李健, 卢百关, 方兆伟, 王宝祥, 徐大勇. 水稻类病斑突变体lmm7的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 357-366.
SUN Zhiguang, DAI Huimin, CHEN Tingmu, LI Jingfang, CHI Ming, ZHOU Zhenling, LIU Yan, LIU Jinbo, XU Bo, XING Yungao, YANG Bo, LI Jian, LU Baiguan, FANG Zhaowei, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong. Phenotypic Identification and Gene Mapping of a Lesion Mimic Mutant lmm7 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 357-366.
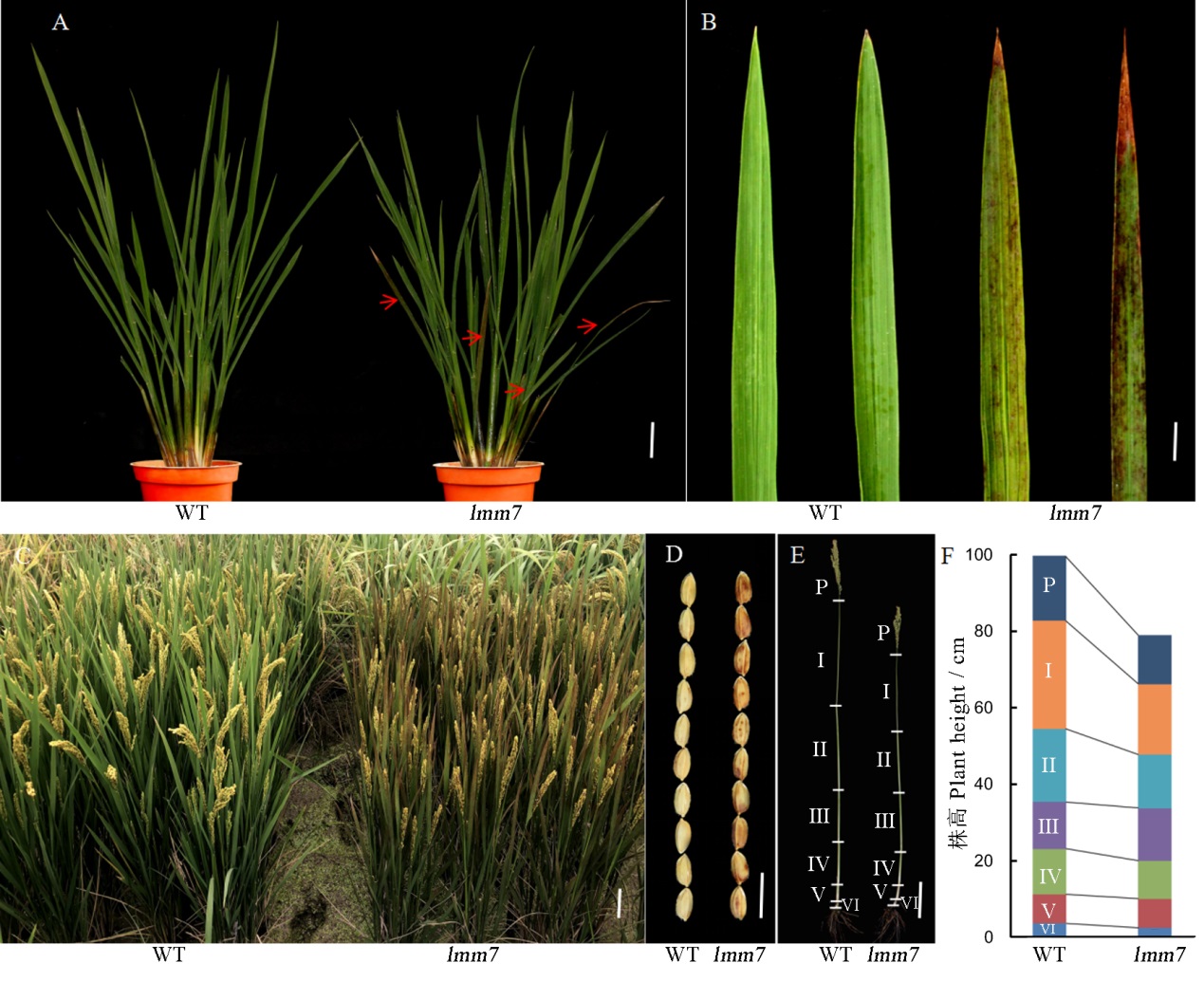
图1 野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的表型鉴定 A―分蘖期野生型(WT)和突变体(lmm7)植株表型,红色箭头指示出现类病斑叶片;B―分蘖期野生型(WT)和突变体(lmm7)基部叶片;C―大田条件下,野生型(WT)和突变体(lmm7)成熟期植株;D―野生型(WT)和突变体(lmm7)成熟种子大小的比较;E~F―植株主茎穗和节间长度的比较。在A中,比例尺为5 cm;在B中比例尺为2 cm;在C和E中,比例尺为10 cm;在D中,比例尺为10 mm。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic identification of WT plants and lmm7. A, Plants of wild type (WT) and lmm7 mutant at the tillering stage, red arrows indicate lesion mimic leaves; B, Basal leaves of wild type (WT) and lmm7 at the tillering stage; C, Plants of wild type (WT) and lmm7 at the mature period in field conditions; D, Comparisons of the size of mature seeds from WT and lmm7 plants; E-F: Panicles and internodes of main culms. P, Panicle; I to VI indicate corresponding internodes from top to bottom. Bars =5 cm in A; 2 cm in B; 10 cm in C, E; 10 mm in D.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型Wild type | 突变体 lmm7 | 性状 Trait | 野生型Wild type | 突变体 lmm7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading date /d | 95.3±0.6 | 95.7±0.6 | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 24.6±0.4 | 23.8±0.5 |
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 102.1±2.6 | 80.8±1.8** | 剑叶长 Flag leaf length/cm | 24.5±1.4 | 18.8±1.2** |
| 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 17.4±0.8 | 13.0±1.2** | 剑叶宽 Flag leaf width/cm | 1.8±0.3 | 1.6±0.2** |
| 有效穗数 Effective panicle | 9.2±1.3 | 6.5±0.7* | 粒长 Grain length/mm | 7.6±0.4 | 7.5±0.6 |
| 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 142.3±6.5 | 115.4±7.6** | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 4.4±0.2 | 4.3±0.1 |
| 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 90.6±2.5 | 82.7±4.3* | 粒厚 Grain thickness /mm | 2.1±0.2 | 2.1±0.2 |
表1 野生型(WT)和lmm7突变体的农艺性状比较
Table 1. Agronomic traits comparison between WT plants and lmm7.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型Wild type | 突变体 lmm7 | 性状 Trait | 野生型Wild type | 突变体 lmm7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading date /d | 95.3±0.6 | 95.7±0.6 | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 24.6±0.4 | 23.8±0.5 |
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 102.1±2.6 | 80.8±1.8** | 剑叶长 Flag leaf length/cm | 24.5±1.4 | 18.8±1.2** |
| 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 17.4±0.8 | 13.0±1.2** | 剑叶宽 Flag leaf width/cm | 1.8±0.3 | 1.6±0.2** |
| 有效穗数 Effective panicle | 9.2±1.3 | 6.5±0.7* | 粒长 Grain length/mm | 7.6±0.4 | 7.5±0.6 |
| 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 142.3±6.5 | 115.4±7.6** | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 4.4±0.2 | 4.3±0.1 |
| 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 90.6±2.5 | 82.7±4.3* | 粒厚 Grain thickness /mm | 2.1±0.2 | 2.1±0.2 |
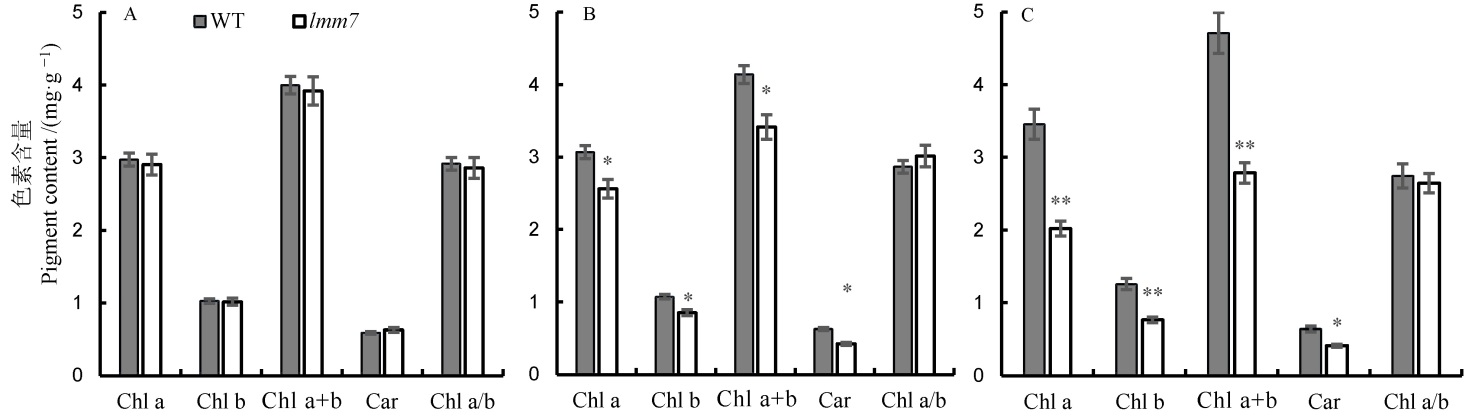
图2 野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7抽穗期光合色素含量 A―抽穗期野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的剑叶光合色素含量;B―倒2叶光合色素含量;C―倒3叶光合色素含量。*在0.05水平上差异显著;**在0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 2. Photosynthetic pigments contents of the wild type and the lmm7 mutant at heading stage. A, Photosynthetic pigment contents of flag leaf of the wild type and lmm7 mutant at the heading stage; B, Photosynthetic pigment contents of the second leaf from top; C, Photosynthetic pigment contents of the third leaf from top; *,** significantly different at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
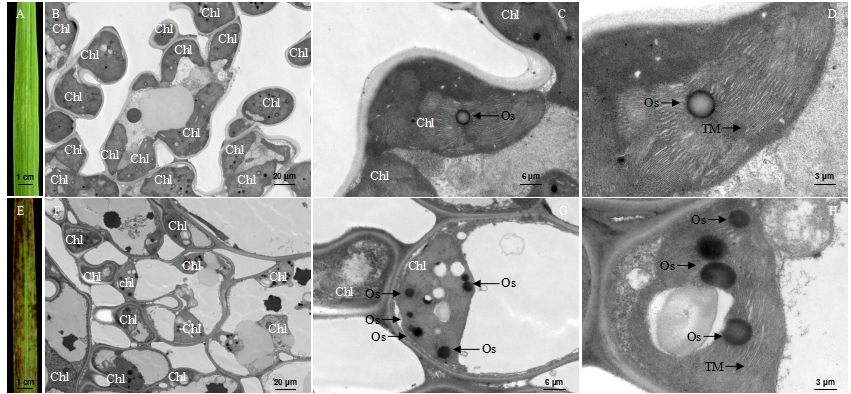
图3 成熟期野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的叶肉细胞超微结构 A―成熟期WT剑叶叶片;B~D―WT剑叶细胞超微结构;E―成熟期突变体lmm7剑叶叶片;F~H―突变体lmm7剑叶细胞超微结构;Chl―叶绿体;Os―嗜锇小体;TM―类囊体膜。标尺为20 μm (B, F), 6 μm (C, G), 3 μm (D, H)。
Fig. 3. Ultrastructure of mesophyll cells in the wild type (WT) and the lmm7 mutant at mature period. A, Flag leaf of WT at mature period; B-D, Ultrastructure of the blade of WT; E, Flag leaf of lmm7 mutant at mature period; F-G, Ultrastructure of the blade of lmm7 mutant; Chl, Chloroplast; Os, Osmiophilic granule; TM, Thylakoid membranes. Bars: 20 μm (B, F), 6 μm (C, G), 3 μm (D, H).
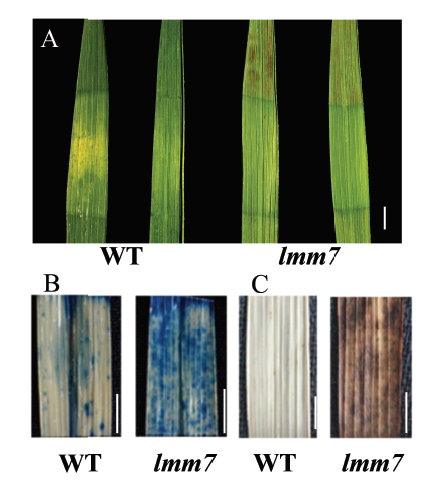

图4 野生型和突变体lmm7的遮光处理及组织化学分析 A―遮光处理7 d后野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的叶片;B―野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7叶片的台盼蓝染色观察;C―野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7叶片的DAB染色观察。在A、B、C中,比例尺均为1 cm。
Fig. 4. Shading treatment and histochemical analysis of the wild type and lmm7 mutant. A, Effects of shading on the wild type(WT) and the lmm7 mutant leaves 7 days after shading; Leaves of WT and the lmm7 mutant stained by trypan blue(B) and DAB(C). Bars =1 cm in A, B and C.
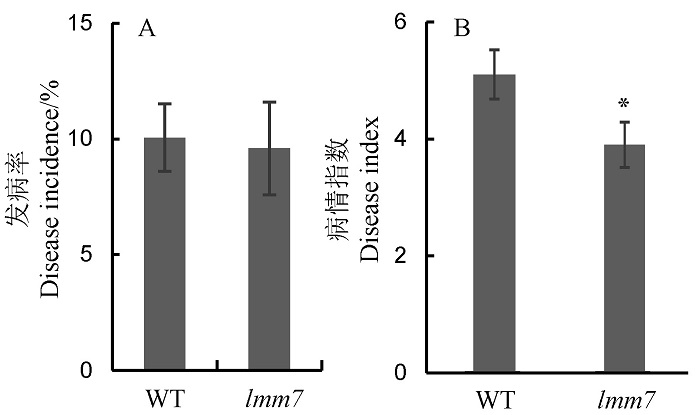
图5 野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7人工接种鉴定条件下水稻黑条矮缩病和稻瘟病抗性评价 A―人工接种鉴定条件下,野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的水稻黑条矮缩病平均发病率;B―人工接种鉴定条件下,野生型(WT)和突变体lmm7的稻瘟病病情指数。*P < 0.05(t检验)。
Fig. 5. Resistance evaluation of wild type (WT) and lmm7 mutant to rice black-streaked dwarf virus disease (RBSDVD) and rice blast under artificial inoculation condition. A, Disease incidence of wild type (WT) and lmm7 mutant to rice black-streaked dwarf virus disease (RBSDVD) by the artificial inoculation. B, Disease index of wild type (WT) and lmm7 to rice blast by the artificial inoculation. *P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test.
| [1] | 王晨, 王备芳, 张迎信, 曹永润, 张越, 江敏, 边康吉, 张小惠, 刘群恩. 水稻类病斑突变体lm8015-2的鉴定与基因的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 352-358. |
| Wang C, Wang B F, Zhang Y X, Cao Y R, Zhang Y, Jiang M, Bian K J, Zhang X H, Liu Q E. Identification and gene mapping of a lesion mimic mutant lm8015-2 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 352-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Hu G, Richter T E, Hulbert S H, Pryor T. Disease lesion mimicry caused mutations in the rust resistance gene rp1[J]. Plant Cell, 1996, 8(8): 1367-1376. |
| [3] | Wu C J, Bordeos A, Madamba M R S, Baraoidan M, Ramos M, Wang G L, Leach J E, Leung H. Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2008, 279: 605-619. |
| [4] | Shirsekar G S, Vega-Sanchez M E, Bordeos A, Baraoidan M, Swisshelm A, Fan J, Park C H, Leung H, Wang G L. Identification and characterization of suppressor mutants of spl11-mediated cell death in rice[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2014, 27: 528-536. |
| [5] | Wang S, Lei C L, Wang J L, Ma J, Tang S, Wang C L, Zhao K J, Tian P, Zhang H, Qi C Y, Cheng Z J, Zhang X, Guo X P, Liu L L, Wu C Y, Wan J M. SPL33, encoding an eEF1A-like protein, negatively regulates cell death and defense responses in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68: 899-913. |
| [6] | Hofius D, Tsitsigiannis D I, Jones J D, Mundy J. Inducible cell death in plant immunity[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 2007, 17: 166-187. |
| [7] | Dietrich R A, Richberg M H, Schmidt R, Dean C, Dangl J L. A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death[J]. Cell, 1997, 88: 685-694. |
| [8] | Hoisington D A, Neuffer M G, Walbot V. Disease lesion mimics in maize: I. Effect of genetic background, temperature, developmental age, and wounding on necrotic spot formation with Les1[J]. Developmental Biology, 1982, 93(2): 381-388. |
| [9] | Yao Q, Zhou R H, Fu T H, Wu W R, Zhu Z D, Li A L, Jia J Z. Characterization and mapping of complementary lesion-mimic genes lm1 and lm2 in common wheat[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2009, 119: 1005-1012. |
| [10] | Spassieva S, Hille J. A lesion mimic phenotype in tomato obtained by isolating and silencing an Lls1, homologue[J]. Plant Science, 2002, 162: 543-549. |
| [11] | Wolter M, Hollricher K, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P. The mlo resistance alleles to powdery mildew infection in barley trigger a developmentally controlled defence mimic phenotype[J]. Molecular and General Genetics, 1993, 239: 122-128. |
| [12] | 张宏根, 王茂宇, 张丽佳, 胡雅, 马佳琦, 张翼帆, 汤述翥, 梁国华, 顾铭洪. 水稻类病斑突变体wy3的鉴定和基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 239-246. |
| Zhang H G, Wang M Y, Zhang L J, Hu Y, Ma J Q, Zhang Y F, Tang S Z, Liang G H, Gu M H. Characterization and gene mapping of lesion mimic mutant wy3 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 239-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Buschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M, Frijters A, Daelen R, Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J, Topsch S, Vos P, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P. The barley mlo gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance[J]. Cell, 1997, 88: 695-705. |
| [14] | Jambunathan N, Siani J M, Mcnellis T W. A humidity sensitive Arabidopsis copine mutant exhibits precocious cell death and increased disease resistance[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13: 2225-2240. |
| [15] | Lorrain S, Lin B, Auriac M C, Kroj T, Saindrenan P, Nicole M, Balague C, Roby D. Vascular associated death1, a novel GRAM domain-containing protein, is a regulator of cell death and defense responses in vascular tissues[J]. Plant Cell, 2004, 16: 2217-2232. |
| [16] | Noutoshi Y, Kuromori T, Wada T, Hirayama T, Kamiya A, Imura Y, Yasuda M, Nakashita H, Shirasu K, Shinozaki K. Loss of Necrotic Spotted Lesions 1 associates with cell death and defense responses in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2006, 62: 29-42. |
| [17] | Balague C, Lin B, Alcon C, Flottes G, Malmstrom S, Kohler C, Neuhaus G, Pelletier G, Gaymard F, Roby D. HLM1, an essential signaling component in the hypersensitive response, is a member of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel ion channel family[J]. Plant Cell, 2003, 15: 365-379. |
| [18] | Rostoks N, Schmierer D, Mudie S, Drader T, Brueggeman R, Caldwell D G, Waugh R, Kleinhofs A. Barley necrotic locus nec1 encodes the cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 4 homologous to the Arabidopsis HLM1[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2006, 275: 159-168. |
| [19] | Mosher S, Moeder W, Nishimura N, Jikumaru Y, Joo S H, Urquhart W, Klessig D F, Kim S K, Nambara E, Yoshioka K. The lesion-mimic mutant cpr22 shows alterations in abscisic acid signaling and abscisic acid insensitivity in a salicylic acid-dependent manner[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152: 1901-1913. |
| [20] | Wang L, Pei Z, Tian Y, He C. OsLSD1, a rice zinc finger protein, regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation[J]. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions, 2005, 18: 375-384. |
| [21] | Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, Ashikari M, Yamada K. A rice spotted leaf gene, Spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein[J]. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2002, 99: 7530-7535. |
| [22] | Zeng L, Qu S, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm B H, Leung H, Wang G. Spotted leaf 11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-box/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity[J]. Plant Cell, 2004, 16: 2795-2808. |
| [23] | Qiao Y, Jiang W, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J. SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit micro 1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 185: 258-274. |
| [24] | Kachroo P, Shanklin J, Shah J, Whittle E J, Klessig D F. A fatty acid desaturase modulates the activation of defense signaling pathways in plants[J]. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2001, 98: 9448-9453. |
| [25] | Brodersen P, Petersen M, Pike H M, Olszak B, Skov S, Odum N, Jorgensen L B, Brown R E, Mundy J. Knockout of Arabidopsis accelerated-cell-death11 encoding a sphingosine transfer protein causes activation of programmed cell death and defense[J]. Genes & Development, 2002, 16: 490-502. |
| [26] | Hu G, Yalpani N, Briggs S P, Johal G S. A porphyrin pathway impairment is responsible for the phenotype of a dominant disease lesion mimic mutant of maize[J]. Plant Cell, 1998, 10: 1095-1105. |
| [27] | Ishikawa A, Okamoto H, Iwasaki Y, Asahi T. A deficiency of coproporphyrinogen III oxidase causes lesion formation in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Journal, 2001, 27: 89-99. |
| [28] | Gray J, Close P S, Briggs S P, Johal G S. A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the Lls1 gene of maize[J]. Cell, 1997, 89: 25-31. |
| [29] | Undan J R, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Takagi H, Yoshida K, Kanzaki H, Saitoh H, Fekih R. Mutation in OsLMS, a gene encoding a protein with two double-stranded RNA binding motifs causes lesion mimic phenotype and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 2012, 87(3): 169-179. |
| [30] | Wang Z, Wang Y, Hong X, Hu D, Liu C, Yang J, Li Y, Huang Q, Feng Y, Gong H, Li Y, Fang G, Tang H, Li Y,. Functional inactivation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1 (UAP1) induces early leaf senescence and defence responses in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66: 973-987. |
| [31] | Lichtenthaler H K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 1987, 148: 350-382. |
| [32] | Fang L K, Li Y F, Gong X P, Sang X C, Ling Y H, Wang X W, Cong Y F, He G H. Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a dominant presenescing leaf gene PSL3 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55: 2517-2521. |
| [33] | 刘永锋, 陆凡, 陈志谊, 吉建安, 陈毓苓, 高渊. 江苏省水稻新品种(系)对稻瘟病的抗性评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002, 16(1): 96-98. |
| Liu Y F, Lu G, Chen Z Y, Ji J A, Chen Y L, Gao Y. Resistance evaluation of new rice varieties (lines) to rice blast in Jiangsu Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 2002, 16(1): 96-98. | |
| [34] | International Rice Research Institute. Standard Evaluation System for Rice (SES). Los Baños, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 2002: 14-18. |
| [35] | Zhou T, Du L, Wang L J, Wang Y, Gao C Y, Lan Y, Sun F, Fan Y J, Wang G L, Zhou Y J. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of QTLs for resistance to rice black-streaked dwarf disease in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 10509. |
| [36] | Zhu X B, Ze M, Chen M S, Chen X W, Wang J. Deciphering rice lesion mimic mutants to understand molecular network governing plant immunity and growth[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 278-288. |
| [37] | 奉保华, 杨杨, 施勇烽, 林璐, 陈洁, 黄奇娜, 魏彦林, LEUNG H, 吴建利. 水稻淡褐斑叶突变体lbsl1的遗传分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3): 297-301. |
| Feng B H, Yang Y, Shi Y F, Lin L, Chen J, Huang Q N, Wei Y L, Leung H, Wu J L. Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a light brown spotted leaf mutant in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 2012, 26(3): 297-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 王建军, 朱旭东, 王林友, 张利华, 薛庆中, 何祖华. 水稻类病斑突变体的生理与遗传分析[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2004, 30(3): 331-338. |
| Wang J J, Zhu X D, Wang L Y, Zhang L H, Xue Q Z, He Z H. Physiological and genetic analysis of lesion resembling disease mutants (lrd) of Oryza sativa L[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2004, 30(3): 331-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Yoshimura A, Ideta O, Iwata N. Linkage map of phenotype and RFLP markers in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1997, 35: 49-60. |
| [40] | Chern M, Xu Q F, Bart R S, Bai W, Ruan D L, Sze-To W H, Canlas P E, Jain R, Chen X W, Ronald P C. A genetic screen identifies a requirement for cysteine-rich- receptor-like kinases in rice NH1 (OsNPR1)-mediated immunity[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2016, 12(5): e1006049. |
| [41] | Tang J Y, Zhu X D, Wang Y Q, Liu L C, Xu B, Li F, Fang J, Chu C C. Semi-dominant mutations in the CC-NB-LRR-type R gene, NLS1, lead to constitutive activation of defense responses in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2011, 66: 996-1007. |
| [42] | Li Z Q, Ding B, Zhou X P, Wang G L. The rice dynamin related protein OsDRP1E negatively regulates programmed cell death by controlling the release of cytochrome c from Mitochondria[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2017, 13(1): e1006157. |
| [43] | Chen X F, Pan J W, Cheng J, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J. Fine genetic mapping and physical delimitation of the lesion mimic gene spotted leaf 5 (spl5) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2009, 24(4): 387. |
| [44] | Chen X F, Hao L, Pan J W, Zheng X X, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J. SPL5, a cell death and defense related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2012, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [45] | Babu R, Jiang C J, Xu X, Kottapalli K R, Takatsuji H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Kawasaki S. Isolation, fine mapping and expression profiling of a lesion mimic genotype, spl(NF4050-8) that confers blast resistance in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 122: 831-854. |
| [46] | Li Z, Zhang Y, Liu L, Liu Q, Bi Z, Yu N, Cheng S, Cao L. Fine mapping of the lesion mimic and early senescence 1 (lmes1) in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 80: 300-307. |
| [47] | 夏赛赛, 崔玉, 李凤菲, 谭佳, 谢园华, 桑贤春, 凌英华. 水稻类病斑早衰突变体lmps1的表型鉴定与基因定位[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 46-54. |
| Xia S S, Cui Y, Li F F, Tan J, Xie Y H, Sang X C, Ling Y H. Phenotypic characterizing and gene mapping of a lesion mimic and premature senescence 1 (lmps1) mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 46-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 郭丹, 施勇烽, 王惠梅, 张晓波, 宋莉欣, 徐霞, 贺彦, 郭梁, 吴建利. 一个水稻显性斑点叶突变体的鉴定和基因精细定位[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(7): 966-975. |
| Guo D, Shi Y F, Wang H M, Zhang X B, Song L X, Xu X, Guo L, Wu J L. Characterization and gene fine mapping of a rice dominant spotted-leaf mutant[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 966-975. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | Sun L T, Wang Y H, Liu L L, Wang C M, Gan T, Zhang Z Y, Wang Y L, Wang D, Niu M, Long W H, Li X H, Zheng M, Jiang L, Wan J M. Isolation and characterization of a spotted leaf 32 mutant with early leaf senescence and enhanced defense response in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 41846. |
| [1] | 任志奇, 薛可欣, 董铮, 李小湘, 黎用朝, 郭玉静, 刘文强, 郭梁, 盛新年, 刘之熙, 潘孝武. 水稻外卷叶突变体ocl1的鉴定及基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 337-346. |
| [2] | 肖乐铨, 李雷, 戴伟民, 强胜, 宋小玲. 转cry2A*/bar基因水稻与杂草稻杂交后代的苗期生长特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 347-358. |
| [3] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [4] | 汪胜勇, 陈宇航, 陈会丽, 黄钰杰, 张啸天, 丁双成, 王宏伟. 水稻减数分裂期高温对苯丙烷类代谢及下游分支代谢途径的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 368-378. |
| [5] | 董立强, 杨铁鑫, 李睿, 商文奇, 马亮, 李跃东, 隋国民. 株行距配置对超高产田水稻产量及根系形态生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| [6] | 韩聪, 何禹畅, 吴丽娟, 郏丽丽, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻碱性亮氨酸拉链(bZIP)蛋白家族功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 436-448. |
| [7] | 沈雨民, 陈明亮, 熊焕金, 熊文涛, 吴小燕, 肖叶青. 水稻内外稃异常发育突变体blg1 (beak like grain 1)的表型分析与精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 225-232. |
| [8] | 段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243. |
| [9] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [10] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [11] | 刘嫒桦, 李小坤. 不同肥料施用与稻米品质关系的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 276-284. |
| [12] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [13] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| [14] | 林聃, 江敏, 苗波, 郭萌, 石春林. 水稻高温热害模型研究及其在福建省的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 307-320. |
| [15] | 郑承梅, 孙金秋, 刘梦杰, 杨永杰, 陆永良, 郭怡卿, 唐伟. 水稻田糠稷种子萌发和出苗特性及化学防除药剂筛选[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 321-328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||