
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 247-256.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7103
李玉祥1,2, 何知舟1, 丁艳锋1, 王绍华1, 刘正辉1, 唐设1, 丁承强1, 陈琳1, 李刚华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-08-29
修回日期:2017-11-22
出版日期:2018-05-10
发布日期:2018-05-10
通讯作者:
李刚华
基金资助:
Yuxiang LI1,2, Zhizhou HE1, Yanfeng DING1, Shaohua WANG1, Zhenghui LIU1, She TANG1, Chengqiang DING1, Lin CHEN1, Ganghua LI1,*( )
)
Received:2017-08-29
Revised:2017-11-22
Online:2018-05-10
Published:2018-05-10
Contact:
Ganghua LI
摘要:
【目的】本研究旨在探明水卷苗机插高产适宜的播种量。【方法】以长江中下游地区代表性品种武运粳24号(常规粳稻)和6两优9368(杂交籼稻)为供试材料,研究不同播种量对水卷苗秧苗素质、机插质量、大田生长特性及产量的影响。【结果】移栽前秧苗地上部和根系干物质量、发根力、根系活性、成苗率、苗基宽、重高比及光合速率均随着播种量的降低而显著增强,叶面积指数显著下降。小播量处理秧苗返青活棵快、分蘖发生力强、每穗粒数多,但播量过小导致基本苗和穗数不足,当武运粳24号播种量从180g/盘降低到120g/盘(738.9g/m2)、6两优9368播种量从110g/盘降低到70g/盘(431.0g/m2)时,产量没有显著变化;但播种量继续降低,产量均显著下降。【结论】水卷苗育秧方法适宜播种量,常规粳稻为2.03粒/cm2,杂交籼稻为1.14粒/cm2。
中图分类号:
李玉祥, 何知舟, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强, 陈琳, 李刚华. 播种量对机插水卷苗秧苗素质及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 247-256.
Yuxiang LI, Zhizhou HE, Yanfeng DING, Shaohua WANG, Zhenghui LIU, She TANG, Chengqiang DING, Lin CHEN, Ganghua LI. Effects of Sowing Densities on Quality and YieldFormation of Hydroponically Grown Long-mat Rice Seedlings Under Mechanical Transplanting[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 247-256.
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量(常规秧盘) Sowing density/(g·nursery-1) (0.58 m×0.28 m×0.03 m) | 播种量(水卷苗苗床) Sowing density/(g·nursery-1) (4 m×0.28 m×0.05 m) | 播种量 Sowing density /(g·m-2) | 单位面积种子数 Number of seeds per cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号 Wuyunjing 24 | 90 | 620.7 | 554.2 | 1.52 |
| 120 | 827.6 | 738.9 | 2.03 | |
| 150 | 1034.5 | 923.6 | 2.54 | |
| 180 | 1241.4 | 1108.4 | 3.05 | |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | 50 | 344.8 | 307.9 | 0.82 |
| 70 | 482.8 | 431.0 | 1.14 | |
| 90 | 620.7 | 554.2 | 1.47 | |
| 110 | 758.6 | 677.3 | 1.80 |
表1 播种量设置
Table 1 Design of experimental treatments (sowing density).
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量(常规秧盘) Sowing density/(g·nursery-1) (0.58 m×0.28 m×0.03 m) | 播种量(水卷苗苗床) Sowing density/(g·nursery-1) (4 m×0.28 m×0.05 m) | 播种量 Sowing density /(g·m-2) | 单位面积种子数 Number of seeds per cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号 Wuyunjing 24 | 90 | 620.7 | 554.2 | 1.52 |
| 120 | 827.6 | 738.9 | 2.03 | |
| 150 | 1034.5 | 923.6 | 2.54 | |
| 180 | 1241.4 | 1108.4 | 3.05 | |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | 50 | 344.8 | 307.9 | 0.82 |
| 70 | 482.8 | 431.0 | 1.14 | |
| 90 | 620.7 | 554.2 | 1.47 | |
| 110 | 758.6 | 677.3 | 1.80 |
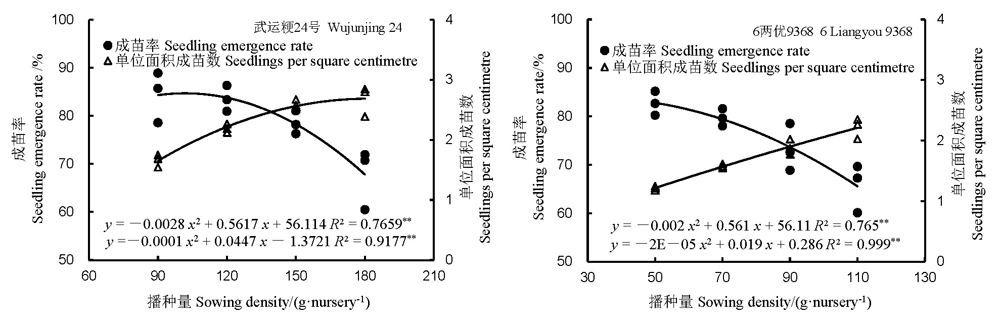
图1 播种量对机插水卷苗成苗率及单位面积成苗数的影响
Fig. 1. Seedling emergence rate and seedling numberper cm2 of two cultivars under different sowing densities before transplanting for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
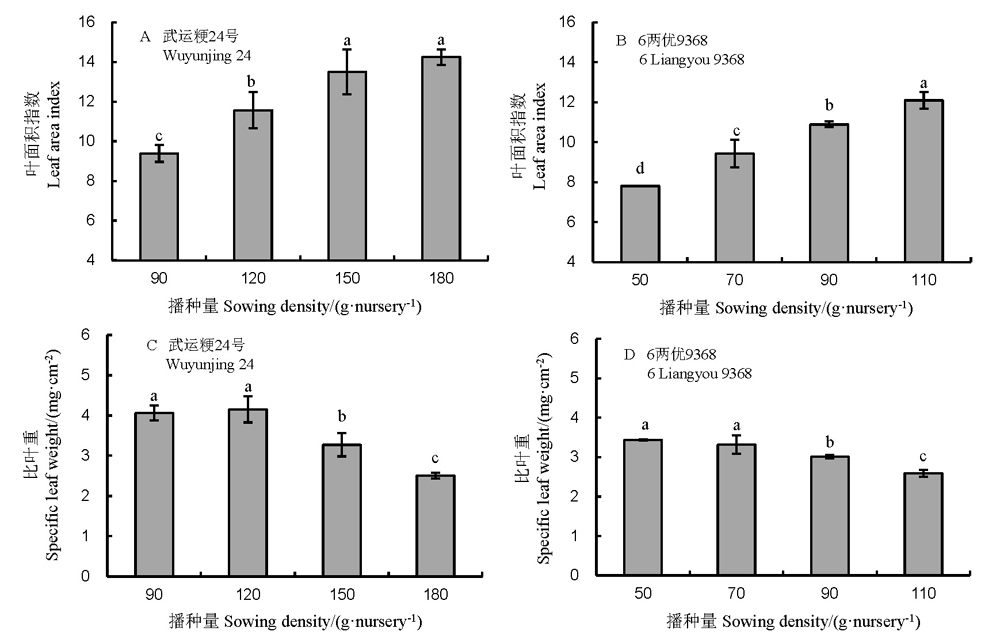
图2 播种量对机插水卷苗秧苗形态指标的影响柱上不同小写字母表示同一品种下在5%水平上差异显著(n=3,最小显著差数法)。下同。
Fig. 2. Leaf area index and specific leaf weight of two rice cultivars under different sowing densities before transplanted for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS). Different letters above the bars are significantly different at P<0.05 (n =3, LSD). The same as below.
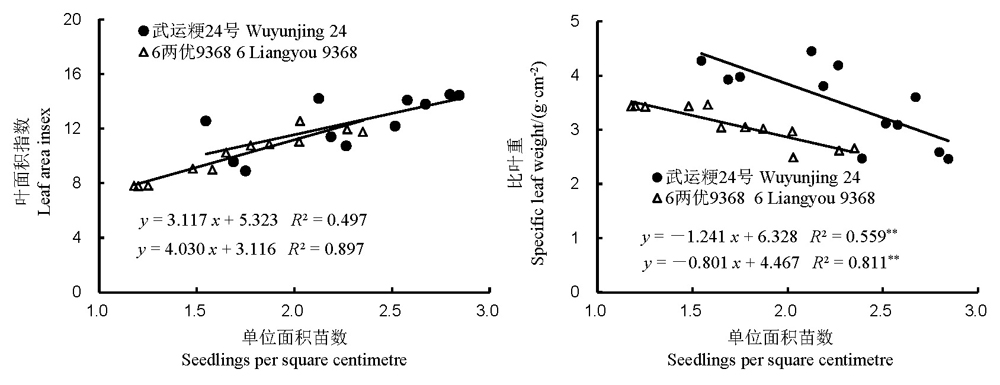
图3 苗床单位面积成苗数和叶面积及比叶重相关性分析
Fig. 3. Relationship among seedlings per square centimetre and leaf area index and specific leaf weight of both cultivars before transplanting for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 叶龄 NAL | 株高 SH/cm | 根数 NR | 根长 LR/cm | 地上部干质量 DWS/g | 根质量 DWR/g | 质量高度比 DW/H/(mg·cm-1) | 根冠比 R/S | 苗基宽 SD/mm | 根系活性 RA/(ug-1·g-1) | 发根力 RDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | |||||||||||
| 90 | 3.9±0.2 a | 10.8±0.2 a | 10.7±0.6 a | 8.2±1.4 a | 4.51±0.49 a | 2.29±0.10 a | 4.16±0.36 a | 0.51±0.08 a | 2.9±0.131 a | 105.1±7.0 a | 8.4±0.7 a |
| 120 | 3.8±0.1 a | 10.0±0.9 a | 10.1±1.5 a | 7.3±0.8 a | 4.34±0.37 a | 2.22±0.05 a | 4.32±0.69 a | 0.51±0.03 a | 2.6±0.06 b | 98.6±9.1 ab | 7.6±0.2 a |
| 150 | 3.9±0.6 a | 11.2±0.3 a | 10.3±2.1 a | 8.6±0.6 a | 3.14±0.71 b | 2.00±0.14 ab | 2.81±0.62 b | 0.66±0.14 a | 2.6±0.09 b | 93.3±6.3 ab | 6.3±0.4 b |
| 180 | 3.9±0.1 a | 10.8±0.2 a | 10.8±1.2 a | 8.8±0.5 a | 2.38±0.55 c | 1.50±0.11 c | 2.21±0.54 c | 0.65±0.16 a | 2.7±0.14 b | 79.4±6.5 b | 4.5±0.1 c |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | |||||||||||
| 50 | 2.9±0.2 a | 10.3±0.4 c | 6.8±0.9 a | 9.7±2.7 a | 4.40±0.53 a | 2.47±0.30 a | 4.26±0.41 a | 0.57±0.14 a | 2.9±0.12 a | 34.2±1.8 a | 7.9±0.7 a |
| 70 | 3.0±0.2 a | 12.0±0.8 ab | 6.5±0.2 a | 9.4±0.9 a | 3.95±0.27 ab | 2.29±0.10 a | 3.31±0.37 b | 0.58±0.04 a | 2.8±0.10 a | 35.7±2.0 a | 7.2±1.0 a |
| 90 | 2.9±0.1 a | 10.3±0.5 c | 7.2±0.8 a | 7.9±0.7 a | 3.47±0.15 c | 2.06±0.17 ab | 3.35±0.06 b | 0.59±0.07 a | 2.5±0.11 b | 33.9±1.7 a | 6.7±0.6 ab |
| 110 | 3.1±0.2 a | 11.2±0.9 a | 6.8±0.7 a | 9.3±1.2 a | 2.82±0.17 d | 1.85±0.28 c | 2.52±0.25 c | 0.65±0.07 a | 2.5±0.11 b | 29.4±0.5 b | 5.1±1.2 b |
表2 播种量对机插水卷苗秧苗物质积累的影响
Table 2 Seedling biomass accumulation of two cultivars under different sowing densities before transplanting for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 叶龄 NAL | 株高 SH/cm | 根数 NR | 根长 LR/cm | 地上部干质量 DWS/g | 根质量 DWR/g | 质量高度比 DW/H/(mg·cm-1) | 根冠比 R/S | 苗基宽 SD/mm | 根系活性 RA/(ug-1·g-1) | 发根力 RDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | |||||||||||
| 90 | 3.9±0.2 a | 10.8±0.2 a | 10.7±0.6 a | 8.2±1.4 a | 4.51±0.49 a | 2.29±0.10 a | 4.16±0.36 a | 0.51±0.08 a | 2.9±0.131 a | 105.1±7.0 a | 8.4±0.7 a |
| 120 | 3.8±0.1 a | 10.0±0.9 a | 10.1±1.5 a | 7.3±0.8 a | 4.34±0.37 a | 2.22±0.05 a | 4.32±0.69 a | 0.51±0.03 a | 2.6±0.06 b | 98.6±9.1 ab | 7.6±0.2 a |
| 150 | 3.9±0.6 a | 11.2±0.3 a | 10.3±2.1 a | 8.6±0.6 a | 3.14±0.71 b | 2.00±0.14 ab | 2.81±0.62 b | 0.66±0.14 a | 2.6±0.09 b | 93.3±6.3 ab | 6.3±0.4 b |
| 180 | 3.9±0.1 a | 10.8±0.2 a | 10.8±1.2 a | 8.8±0.5 a | 2.38±0.55 c | 1.50±0.11 c | 2.21±0.54 c | 0.65±0.16 a | 2.7±0.14 b | 79.4±6.5 b | 4.5±0.1 c |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | |||||||||||
| 50 | 2.9±0.2 a | 10.3±0.4 c | 6.8±0.9 a | 9.7±2.7 a | 4.40±0.53 a | 2.47±0.30 a | 4.26±0.41 a | 0.57±0.14 a | 2.9±0.12 a | 34.2±1.8 a | 7.9±0.7 a |
| 70 | 3.0±0.2 a | 12.0±0.8 ab | 6.5±0.2 a | 9.4±0.9 a | 3.95±0.27 ab | 2.29±0.10 a | 3.31±0.37 b | 0.58±0.04 a | 2.8±0.10 a | 35.7±2.0 a | 7.2±1.0 a |
| 90 | 2.9±0.1 a | 10.3±0.5 c | 7.2±0.8 a | 7.9±0.7 a | 3.47±0.15 c | 2.06±0.17 ab | 3.35±0.06 b | 0.59±0.07 a | 2.5±0.11 b | 33.9±1.7 a | 6.7±0.6 ab |
| 110 | 3.1±0.2 a | 11.2±0.9 a | 6.8±0.7 a | 9.3±1.2 a | 2.82±0.17 d | 1.85±0.28 c | 2.52±0.25 c | 0.65±0.07 a | 2.5±0.11 b | 29.4±0.5 b | 5.1±1.2 b |
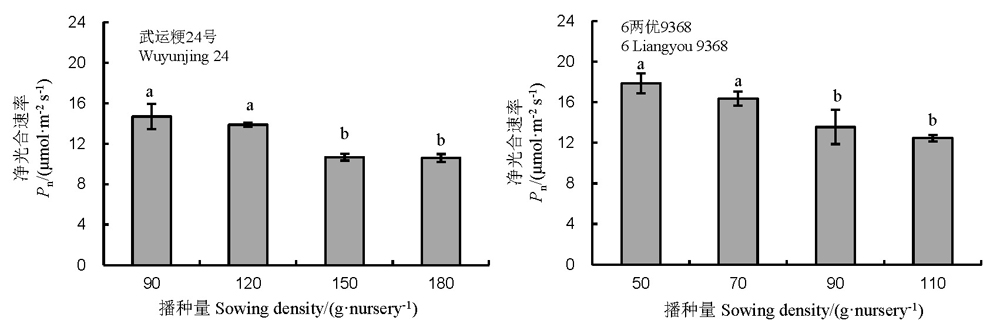
图4 播种量对机插水卷苗移栽前净光合速率(Pn)的影响
Fig. 4. Photosynthetic rate (Pn) of two rice cultivars under different sowing densities before transplanted for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 空穴率 Missing hill rate/% | 漂秧率 Floating seedling rate/% | 伤秧率 Damaged seedling rate/% | 勾秧率 Folded seedling rate/% | 翻倒率 Overturned seedling rate/% | 每穴苗数 Seedlings per hill |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | ||||||
| 90 | 12.1±8.3 a | 2.11±1.35 b | 0.44±0.51 a | 0.44±0.39 a | 0.89±0.38 a | 3.2±0.6 b |
| 120 | 8.6±1.5 b | 3.04±2.31 ab | 1.00±0.33 a | 0.44±0.77 a | 0.66±0.34 a | 3.5±0.7 b |
| 150 | 5.5±3.9 b | 6.44±0.39 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 0.77±0.50 a | 0.44±0.51 a | 4.1±0.3 b |
| 180 | 4.6±2.5 c | 4.89±1.68 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 1.22±0.51 a | 0.33±0.01 a | 5.5±0.8 a |
| 6两优9368 6 Liangyou 9368 | ||||||
| 50 | 18.8±4.7 a | 3.33±1.76 b | 0.44±1.96 a | 0.66±0.34 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 3.0±0.5 b |
| 70 | 11.9±2.7 b | 2.66±1.20 b | 0.66±0.34 a | 0.56±0.39 a | 0.44±0.20 a | 3.3±0.1 b |
| 90 | 8.5±1.3 bc | 4.18±2.14 ab | 0.89±0.38 a | 0.23±0.19 a | 0.22±0.19 a | 3.4±0.2 b |
| 110 | 5.1±3.7 d | 5.33±2.01 a | 1.55±0.96 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 0.11±0.19 a | 4.3±0.4 a |
表3 播种量对水卷苗机插质量的影响
Table 3 Mechanical transplanting quality in paddy field of two cultivars under different sowing densities for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 空穴率 Missing hill rate/% | 漂秧率 Floating seedling rate/% | 伤秧率 Damaged seedling rate/% | 勾秧率 Folded seedling rate/% | 翻倒率 Overturned seedling rate/% | 每穴苗数 Seedlings per hill |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | ||||||
| 90 | 12.1±8.3 a | 2.11±1.35 b | 0.44±0.51 a | 0.44±0.39 a | 0.89±0.38 a | 3.2±0.6 b |
| 120 | 8.6±1.5 b | 3.04±2.31 ab | 1.00±0.33 a | 0.44±0.77 a | 0.66±0.34 a | 3.5±0.7 b |
| 150 | 5.5±3.9 b | 6.44±0.39 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 0.77±0.50 a | 0.44±0.51 a | 4.1±0.3 b |
| 180 | 4.6±2.5 c | 4.89±1.68 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 1.22±0.51 a | 0.33±0.01 a | 5.5±0.8 a |
| 6两优9368 6 Liangyou 9368 | ||||||
| 50 | 18.8±4.7 a | 3.33±1.76 b | 0.44±1.96 a | 0.66±0.34 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 3.0±0.5 b |
| 70 | 11.9±2.7 b | 2.66±1.20 b | 0.66±0.34 a | 0.56±0.39 a | 0.44±0.20 a | 3.3±0.1 b |
| 90 | 8.5±1.3 bc | 4.18±2.14 ab | 0.89±0.38 a | 0.23±0.19 a | 0.22±0.19 a | 3.4±0.2 b |
| 110 | 5.1±3.7 d | 5.33±2.01 a | 1.55±0.96 a | 0.33±0.34 a | 0.11±0.19 a | 4.3±0.4 a |

图5 播种量和机插空穴率及基本苗数相关性分析
Fig. 5. Regression analysis of sowing density on missing hill rate and basic seedlings of two cultivars for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
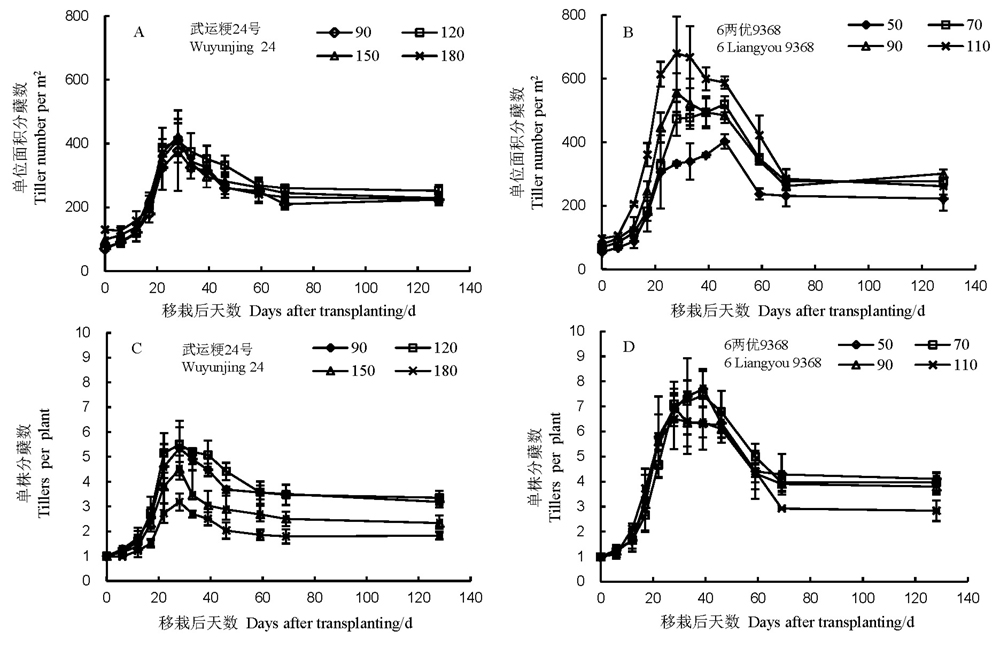
图6 播种量对机插水卷苗群体茎蘖动态(A, B)及单株分蘖发生动态(C, D)的影响
Fig. 6. Tiller dynamics of population (A, B) and tiller number per plant (C, D) of two cultivars under different sowing densities in paddy field for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
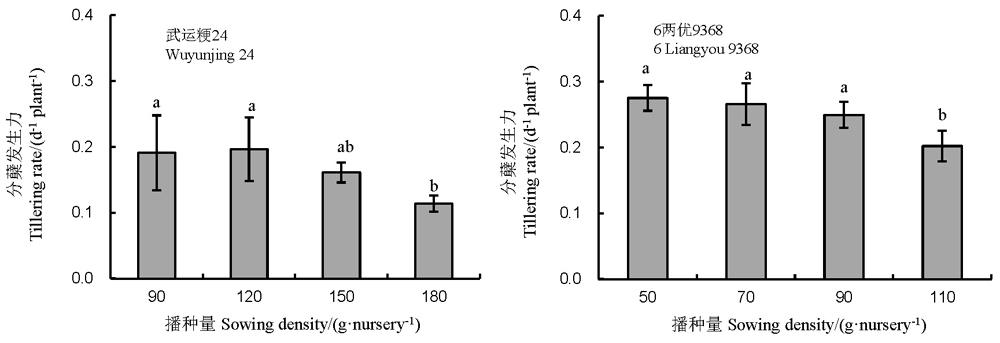
图7 播种量对机插水卷苗分蘖发生力的影响
Fig. 7. Tillering rate per plant of two cultivars under different sowing densities from sowing to max-tilleringfor hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
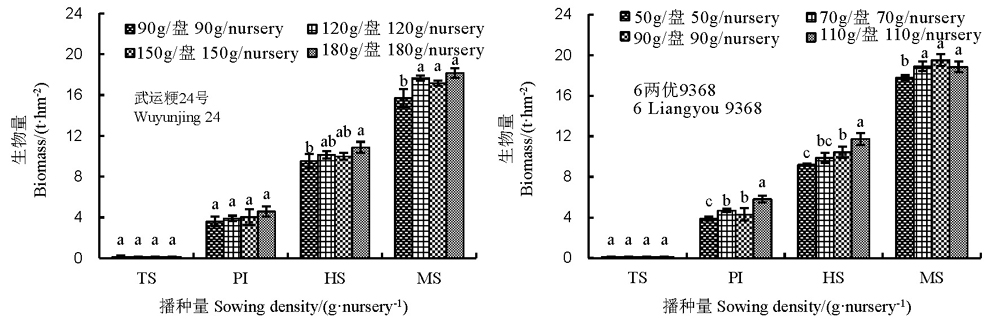
图8 播种量对机插水卷苗关键生育期干物质积累的影响 TS–移栽期; PI–穗分化期; HS–抽穗期; MS–成熟期。
Fig. 8. Biomass accumulation of two cultivars at different growth stages under different sowing densities for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS). TS, Transplanting stage; PI, Panicle initiation stage; HS, Heading stage; MS, Maturity stage.
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 穗数 Effective panicles /(×104·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 颖花量 Spikelets per square meter/(×103m-2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | ||||||
| 90 | 201.6±13.5 c | 150.8±13.1 a | 31.4±1.5 b | 92.7±0.7 a | 27.27±0.05 a | 7.96±0.33 b |
| 120 | 248.7±10.4 ab | 152.1±10.8 a | 37.8±2.8 a | 93.2±1.3 a | 27.83±0.20 a | 9.82±0.63 a |
| 150 | 241.2±7.6 b | 151.2±5.5 a | 36.4±1.6 a | 92.2±2.4 a | 27.31±0.39 a | 9.20±0.33 ab |
| 180 | 258.3±7.9 a | 145.9±9.7 a | 36.8±3.3 a | 91.7±3.1 a | 27.06±0.96 a | 9.36±1.08 a |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | ||||||
| 50 | 192.2±6.6 b | 207.5±13.5 a | 39.9±2.0 b | 85.9±1.4 b | 28.17±1.09 a | 10.04±0.90 b |
| 70 | 249.3±5.6 a | 196.8±25.2 ab | 49.1±5.6 a | 87.5±1.7 ab | 28.32±0.35 a | 11.93±1.19 a |
| 90 | 260.9±3.3 a | 190.7±15.5 b | 49.7±3.9 a | 88.6±1.0 ab | 28.74±0.81 a | 12.67±0.79 a |
| 110 | 271.3±20.1 a | 184.9±3.6 b | 50.1±4.0 a | 89.6±2.5 a | 28.31±0.27 a | 12.71±1.13 a |
表4 播种量对机插水卷苗育秧方法产量及产量构成的影响
Table 4 Grain yield and its components under different sowing densities for hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings(HLMS).
| 播种量 Sowing density /(g·nursery-1) | 穗数 Effective panicles /(×104·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 颖花量 Spikelets per square meter/(×103m-2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24号Wuyunjing 24 | ||||||
| 90 | 201.6±13.5 c | 150.8±13.1 a | 31.4±1.5 b | 92.7±0.7 a | 27.27±0.05 a | 7.96±0.33 b |
| 120 | 248.7±10.4 ab | 152.1±10.8 a | 37.8±2.8 a | 93.2±1.3 a | 27.83±0.20 a | 9.82±0.63 a |
| 150 | 241.2±7.6 b | 151.2±5.5 a | 36.4±1.6 a | 92.2±2.4 a | 27.31±0.39 a | 9.20±0.33 ab |
| 180 | 258.3±7.9 a | 145.9±9.7 a | 36.8±3.3 a | 91.7±3.1 a | 27.06±0.96 a | 9.36±1.08 a |
| 6两优9368 6 liangyou 9368 | ||||||
| 50 | 192.2±6.6 b | 207.5±13.5 a | 39.9±2.0 b | 85.9±1.4 b | 28.17±1.09 a | 10.04±0.90 b |
| 70 | 249.3±5.6 a | 196.8±25.2 ab | 49.1±5.6 a | 87.5±1.7 ab | 28.32±0.35 a | 11.93±1.19 a |
| 90 | 260.9±3.3 a | 190.7±15.5 b | 49.7±3.9 a | 88.6±1.0 ab | 28.74±0.81 a | 12.67±0.79 a |
| 110 | 271.3±20.1 a | 184.9±3.6 b | 50.1±4.0 a | 89.6±2.5 a | 28.31±0.27 a | 12.71±1.13 a |
| [1] | Tasaka K, Ogura A,Karahashi M.Development of hydroponic raising and transplanting technology for mat type rice seedlings Ⅰ: Raising test of seedlings.J Japan SocAgric Mach, 1996, 58: 89-99. |
| [2] | Tasaka K, Ogura A,Karahashi M,.Development of hydroponic raising and transplanting technology for mat type rice seedlings:Ⅱ. Development and field test of rice transplanters for long mat type hydroponic rice seedlings.J Japan SociAgric Mach, 1997, 59: 87-98. |
| [3] | Tasaka K.Raising and transplanting technology for long mat with hydroponically grown rice seedlings.JpnAgricRrsQuar, 1999, 33: 31-37. |
| [4] | Wang Y D, Tasaka K, Ogura A, Maruyama S.Growth and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings raised with long mat by hydroponics: Comparison with young seedlings raised in soil.Plant Prod Sci, 1999, 2: 115-120. |
| [5] | 李刚华, 李玉祥, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 雷武生. 水稻水培育秧营养液及其制备方法:ZL 2011104579679.2014-04-04. |
| Li G H, Li Y X, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Lei W S. Nutrient solution for the hydroponic cultivation and preparation of rice seedlings method: 2011104579679.2014-04-04. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 李刚华, 李玉祥, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强.一种水稻无土育秧方法及应用: ZL 201410211815.4.2015-09-09. |
| Li G H, Li Y X, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q.One kind of soilless medium for rice seedling culture: 2014202617618.2015-09-09. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 李刚华, 李玉祥, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强.一种水稻育秧无土板及其在水稻无土机插领域应用:ZL 201410215744.5.2016-04-13. |
| Li G H, Li Y X, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q.A method of rice seedling soilless-raising and its application: 2014102118154 .2016-04-13. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 李玉祥, 李刚华, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 雷武生.水稻水培育秧装置: ZL 2011205558872.2012-10-03. |
| Li Y X, Li G H, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, and Lei W S. Nursery bed for hydroponic cultivation: 2011205558872.2012-10-03. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 李玉祥, 邢晓鸣, 李刚华, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强, 丁艳锋.机插水卷苗秧苗素质及本田生长特性研究.全国青年作物栽培与生理学术研讨会论文集.扬州: 中国作物学会. 2014. |
| Li Y X, Xing X M, Li G H, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q,Ding Y F.Studies on seedling quality and field growth characteristics of long mat seedlings cultivated with hydroponics of mechanical transplanting rice. Proceedings of the National Symposium on Crop Cultivation and Physiology in Young People. Yangzhou: The Crop ScienceSociety of China. 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 李玉祥, 李刚华, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 李小春, 邢晓鸣.一种机插水稻无土育秧板: ZL 201520302874.2.2015-09-09. |
| Li Y X, Li G H, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Li X C, Xing X M. One kind of seedling soilless-raising raising board for mechanical transplanting rice: ZL201520302874.2, 2015-09-09. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Li Y X, He Z Z, Li X C, Ding Y F, Li G H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Wang S H.Quality and Field Growth Characteristics of Hydroponically Grown Long-Mat Seedlings.Agron J, 2016, 108: 1581-1591. |
| [12] | Lei W S, Ding Y F, Li G H, Tang S, Wang S H.Effects of soilless substrates on seedling quality and the growth of transplanted super japonica rice.J IntegAgric, 2017, 16(5): 1053-1063. |
| [13] | 李玉祥. 水稻机插水卷苗育秧方法及配套技术研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. |
| Li Y X.Research on new method and matching technology for long mat seedlings cultivated with hydroponics of mechanical transplanting rice. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Sarangi S K, Maji B, Singh S, Burman D, Mandal S, Sharma D K, Ismail A M,Haefele S M.Improved nursery management further enhances the productivity of stress-tolerant rice varieties in coastal rainfed lowlands.Field Crops Res, 2015, 174: 61-70. |
| [15] | Fageria N K, Baligar V C,Clark R B.Physiology of crop production:plant canopy architecture. New York: Food Products Press, 2005: 8-12. |
| [16] | Liu Q H, Wu X, Ma J Q, Chen B, Xin C Y.Effects of delaying transplanting on agronomic traits and grain yield of rice under mechanical transplantation pattern.PLoS ONE, 2015, 10: 1-18. |
| [17] | Li J W, Yang J P, Li D S, Fei P P, Guo T T, Ge C S, Chen W Y.Chlorophyll meter’s estimate of weight-based nitrogen concentration in rice leaf is influenced by leaf thickness.Plant ProdSci, 2011, 14: 177-183. |
| [18] | Makino A, Mae T,Ohira K.Relation between nitrogen and ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphatecarboxylase in riceleaves from emergence through senescence.Plant Cell Physiol, 1984, 25: 429-437. |
| [19] | Makino A, Harada M, Sato T, Shimada T, Yamamoto N.Plant growth and nitrogen allocation in rice under CO2 enrichment.Plant Physiol, 1997, 115: 199-203. |
| [20] | Huang M, Yang C, Ji Q, Jiang L G, Tan J L, Li Y Q.Tillering responses of rice to plant density and nitrogen rate in a subtropical environment of southern China.Field Crops Res, 2013, 149: 187-192. |
| [21] | Hiroyuki S, Hisashi K, Kensuke O, Kazuyasu N, Mitsmunori S, Akio O Morio M,Staoko Y. Development of rice “seed-mats”consisting of hardendened seeds with a cover of soil for the rice transplantor.Plant Prod. Sci, 2008, 1: 108-115. |
| [22] | Datta D S K. Principles and practices of rice production.New York John Wiley & Sons, 1981. |
| [23] | Miller B C, Hill J E,Roberts S R.Plant population effects on growth and yield in water-seeded rice. Agron.J, 1991, 83: 291-297. |
| [24] | Pinson S R M,Jia Y. QTLs for early tiller production and relationships with rapid seedling growth and increased panicle number in rice. Crop Sci, 2016, 56: 505-519. |
| [25] | Sun L M, Hussain S, Liu H Y, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H,Nie L X.Implications of low sowing rate for hybrid rice varieties under dry direct-seeded rice system in Central China.Field Crops Res, 2015, 175: 87-95. |
| [26] | Kato Y, Collard B C Y, Septiningsih EM, Ismail A M. Physiological analyses of traits associated with tolerance of long-term partial submergence in rice.AoB Plants, 2014, 6: 1-11. |
| [27] | 凌启鸿, 张洪程, 苏祖芳, 郭文善, 陈德华, 陆卫平, 冷锁虎, 凌励, 杨建昌, 丁艳锋, 吴云康, 曹显祖, 朱庆森, 朱耕如. 作物群体质量. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2000. |
| Ling Q H, Zhang H C, Su Z F, Guo W S, Chen D H, Lu W P,Leng S H, Ling L,Yang J C, Ding Y F, Wu Y K, Cao X Z, Zhu Q S, Zhu G R. Crop Population Quality.Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2000. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 凌启鸿,张洪程, 丁艳锋.水稻精确定量栽培理论与技术.北京:中国农业出版社, 2007. |
| Ling Q H, Zhang H C,Ding YF.Theory and Technology of Precise and Quantitative Cultivation in Rice. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 沈建辉, 邵文娟, 张祖建, 杨建昌, 曹卫星, 朱庆森. 水稻机插中苗双膜育秧落谷密度对苗质和产量影响的研究. 作物学报, 2004, 30(9): 906-911. |
| Shen J H, Shao W J, Zhang Z J, Yang J C, Cao W X, Zhu Q S.Effects of sowing density on quality of medium-seedling nursed with two-layer plastic film and grain yield in mechanical transplanting Rice.ActaAgron Sin, 2004, 30(9): 906-911. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 李泽华, 马旭, 谢俊峰, 陈国锐, 郑志雄, 谭永炘, 黄益强. 双季稻区杂交稻机插秧低播量精密育秧试验.农业工程学报, 2014, 30(6): 17-27. |
| LiZH,MaX,XieJF,ChenGR,ZhengZX,TanYX, Hang Y Q.Experiment on precision seedling raising and mechanizedtransplantingofhybridriceunderlowsowingratein double cropping area.Trans CSAE, 2014, 30(6): 17-27.(inChinesewithEnglishabstract) | |
| [31] | 胡剑锋, 杨波, 周伟,. 张培培, 张强, 李培程, 任万军, 杨文钰. 播种方式和播种密度对杂交籼稻机插秧节本增效的研究. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 81-90. |
| Hu J F, Yang B, Zhou W, Zhang P P, Zhang Q, Li P C, Ren W J, Yang W Y.Effect of Seeding Method and Density on the benefit of mechanical transplantinginindicahybridrice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2017, 31(1): 81-90.(inChinesewithEnglishabstract) | |
| [32] | Gravois K A,Helms R S.Path analysis of rice yield components as affected by seeding rate.Agron J, 1992, 84:1-4. |
| [33] | Jones D B,Synder G H.Seeding rate and row spacing effects on yield and yield components of ratoon rice.Agron J, 1987, 79: 627-629. |
| [34] | Bond J A, Walker T W, Bollich P K, Koger C H, Gerard P.Seeding rates for stale seedbed rice production in the mid southern United States.Agron J, 2005, 97: 1560-1563. |
| [35] | Bond J A, Walker T W, Ottis B V,Harrel D L.Rice seeding and nitrogen rate effects on yield and yield components of two rice cultivars. Agron J,2008, 100: 393-397. |
| [36] | HarrellD L,Blanche S B. Tillage, seeding, and nitrogen rate effects on rice density, yield, and yield components of two rice cultivars.Agron J, 2010, 102: 592-597. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||