
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 587-596.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.230406
冯爱卿, 汪聪颖, 苏菁, 封金奇, 陈凯玲, 林晓鹏, 陈炳, 梁美玲, 杨健源, 朱小源, 陈深*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-20
修回日期:2023-05-22
出版日期:2023-11-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
通讯作者:
*email: 基金资助:
FENG Aiqing, WANG Congying, SU Jing, FENG Jinqi, CHEN Kailing, LIN Xiaopeng, CHEN Bing, LIANG Meiling, YANG Jianyuan, ZHU Xiaoyuan, CHEN Shen*( )
)
Received:2023-04-20
Revised:2023-05-22
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-11-14
Contact:
*email: 摘要:
【目的】 创制水稻细菌性条斑病抗性新品系,为进一步培育抗细菌性条斑病水稻新品种提供核心种质材料。【方法】 通过多代回交、自交,结合分子标辅助选择技术和GSR40K芯片检测,以来自孟加拉国含抗细菌性条斑病Xo2基因的稻种资源BHADOIA 303为供体,以优良籼稻品种五山丝苗为受体,培育抗水稻细菌性条斑病株系,并分别通过田间成株期人工喷雾法和浸入法接种鉴定这些株系的抗病性,评价其农艺性状。【结果】 分子标记和GSR40K芯片检测表明最终获得稳定携带Xo2基因片段的10个新品系(BC4F5);无论是喷雾法接种还是渗入法接种,导入抗病基因的株系和五山丝苗对细菌性条斑病的抗性均差异显著,10个测定株系均表现抗水稻细菌性条斑病,其平均病情指数为5.00~10.37,病斑长度为0.70~0.99 cm,其中以株系1~3抗性表现最好。这3个抗性较好的株系的农艺性状及产量性状指标有些与五山丝苗相似,其中株系1的千粒重、谷粒长、宽与五山丝苗相似,结实率优于五山丝苗;株系2每穗总粒数与五山丝苗相似,谷粒比五山丝苗长些、宽些,千粒重优于五山丝苗;株系3千粒重、结实率与五山丝苗相似,单株穗数优于五山丝苗。【结论】 获得水稻细菌性条斑病抗性显著增强且农艺性状较优良的3个株系,为细菌性条斑病抗病育种提供了抗性新材料,有利于加快水稻细菌性条斑病抗性分子育种进程。
冯爱卿, 汪聪颖, 苏菁, 封金奇, 陈凯玲, 林晓鹏, 陈炳, 梁美玲, 杨健源, 朱小源, 陈深. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性新品系的创制及其农艺性状分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 587-596.
FENG Aiqing, WANG Congying, SU Jing, FENG Jinqi, CHEN Kailing, LIN Xiaopeng, CHEN Bing, LIANG Meiling, YANG Jianyuan, ZHU Xiaoyuan, CHEN Shen. Development and Agronomic Traits Analysis of New Rice Resistance Lines to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 587-596.
| 标记名称Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) | 片段长度 Fragment length/bp |
|---|---|---|
| RM12941 | F:TTATGCCATGTGGTCCAATCAGC R:ATTTGAACCATTTGGGCCTTGG | 187 |
| M6-1 | F:GAATACCCCCATGCGACACCCTA R:CAAGCCGTCCCACGGTGAGAA | 200 |
表1 用于检测Xo2抗性基因的标记名称和序列信息
Table 1. Primers for Xo2 detecting.
| 标记名称Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) | 片段长度 Fragment length/bp |
|---|---|---|
| RM12941 | F:TTATGCCATGTGGTCCAATCAGC R:ATTTGAACCATTTGGGCCTTGG | 187 |
| M6-1 | F:GAATACCCCCATGCGACACCCTA R:CAAGCCGTCCCACGGTGAGAA | 200 |
| 品种名称 Variety | 喷雾法接种Spray inoculation | 浸入法接种Infiltration inoculation | 抗性综合评价Comprehensive evaluation of resistance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数Disease index /% | 病级最高级 The highest grade of disease | 病斑长度 Length of lesion /cm | 病级最高级 The highest grade of disease | ||||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 70.74±2.31 aA | 9 | 3.24±0.09 aA | 9 | HS | ||
| BHADOIA 303 | 1.85±0.32 eD | 1 | 0.54±0.07 fE | 1 | R | ||
| 株系1 Line 1 | 5.37±0.85 cdC | 1 | 0.70±0.08 eD | 1 | R | ||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 5.00±0.00 dC | 1 | 0.72±0.05 eCD | 1 | R | ||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 5.19±0.32 dC | 1 | 0.83±0.09 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系5 Line 5 | 5.74±0.32 cdC | 1 | 0.76±0.08 deCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系8 Line 8 | 10.37±0.85 bB | 3 | 0.99±0.12 bB | 3 | R | ||
| 株系9 Line 9 | 5.37±0.32 cdC | 1 | 0.76±0.10 deCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系10 Line 10 | 6.67±1.11 cdC | 3 | 0.87±0.03 cdBCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系11 Line 11 | 6.30±0.85 cdC | 3 | 0.82±0.08 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系12 Line 12 | 6.11±0.56 cdC | 1 | 0.79±0.07 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系13 Line 13 | 7.04±0.85 cC | 3 | 0.89±0.04 bcBC | 3 | R | ||
表2 携Xo2基因株系的水稻细菌性条斑病抗性鉴定
Table 2. Rice bacterial leaf streak resistance identification of lines with Xo2.
| 品种名称 Variety | 喷雾法接种Spray inoculation | 浸入法接种Infiltration inoculation | 抗性综合评价Comprehensive evaluation of resistance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数Disease index /% | 病级最高级 The highest grade of disease | 病斑长度 Length of lesion /cm | 病级最高级 The highest grade of disease | ||||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 70.74±2.31 aA | 9 | 3.24±0.09 aA | 9 | HS | ||
| BHADOIA 303 | 1.85±0.32 eD | 1 | 0.54±0.07 fE | 1 | R | ||
| 株系1 Line 1 | 5.37±0.85 cdC | 1 | 0.70±0.08 eD | 1 | R | ||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 5.00±0.00 dC | 1 | 0.72±0.05 eCD | 1 | R | ||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 5.19±0.32 dC | 1 | 0.83±0.09 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系5 Line 5 | 5.74±0.32 cdC | 1 | 0.76±0.08 deCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系8 Line 8 | 10.37±0.85 bB | 3 | 0.99±0.12 bB | 3 | R | ||
| 株系9 Line 9 | 5.37±0.32 cdC | 1 | 0.76±0.10 deCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系10 Line 10 | 6.67±1.11 cdC | 3 | 0.87±0.03 cdBCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系11 Line 11 | 6.30±0.85 cdC | 3 | 0.82±0.08 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系12 Line 12 | 6.11±0.56 cdC | 1 | 0.79±0.07 cdeCD | 3 | R | ||
| 株系13 Line 13 | 7.04±0.85 cC | 3 | 0.89±0.04 bcBC | 3 | R | ||
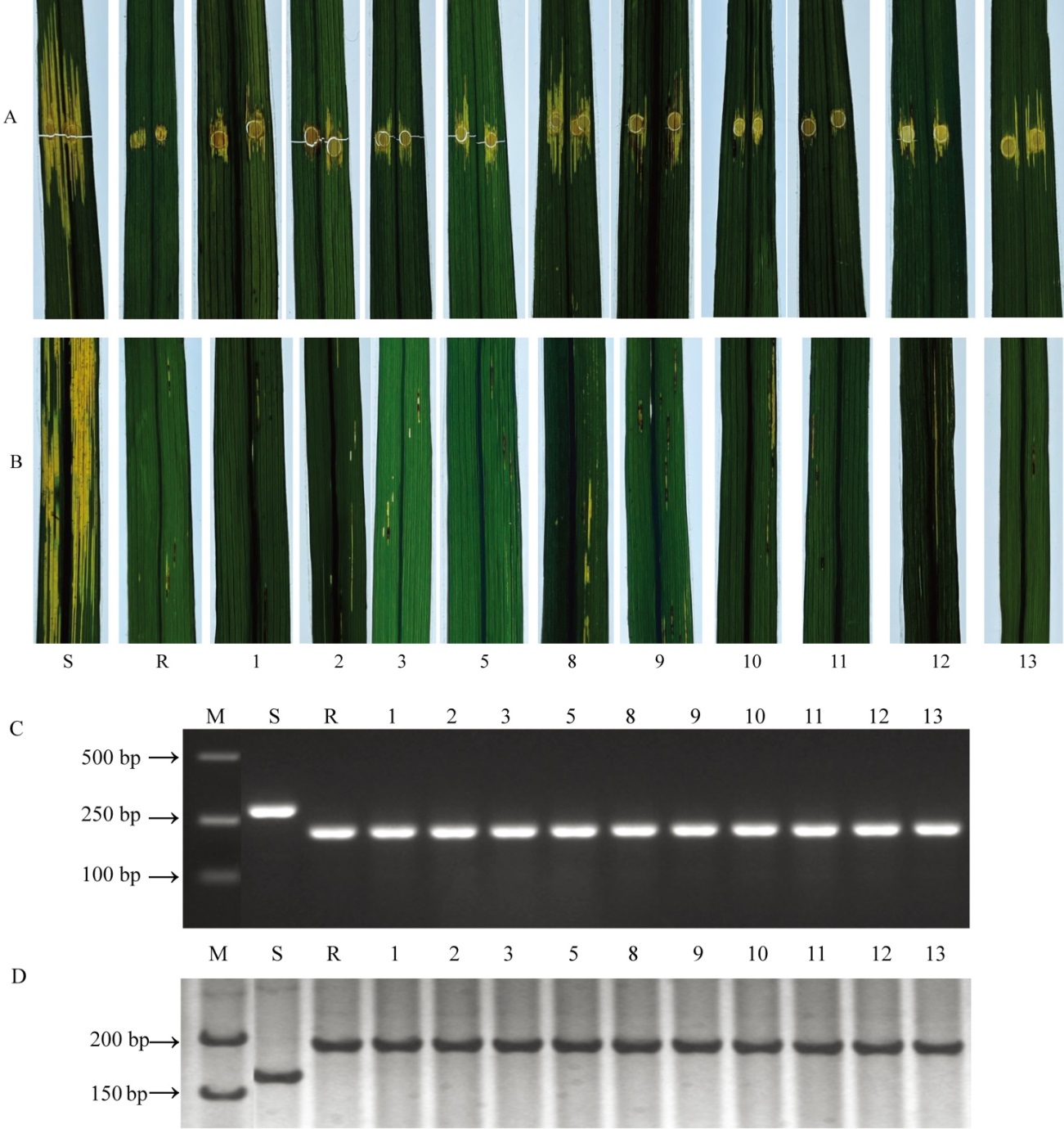
图2 亲本和测定株系的接种表型及Xo2基因的分子检测 A―亲本及测定株系(浸入法接种);B―亲本及测定株系(喷雾法接种);C―亲本及测定株系分子标记M6-1的检测结果;D―亲本及测定株系分子标记RM12941的检测结果。M―Marker;S―五山丝苗;R―BHADOIA 303;1~13代表株系编号。
Fig. 2. Inoculation symptom and molecular detection of Xo2 gene of parents and tested lines. A, Syringe infiltration inoculation of parents and tested lines;B, Spray inoculation of parents and tested lines;C, Detection result of the molecular marker M6-1 of the parents and tested lines; D, Detection result of the molecular marker RM12941 of the parents and tested lines. M, Marker; S, Wushansimiao; R, BHADOIA303; 1-13, Line number.
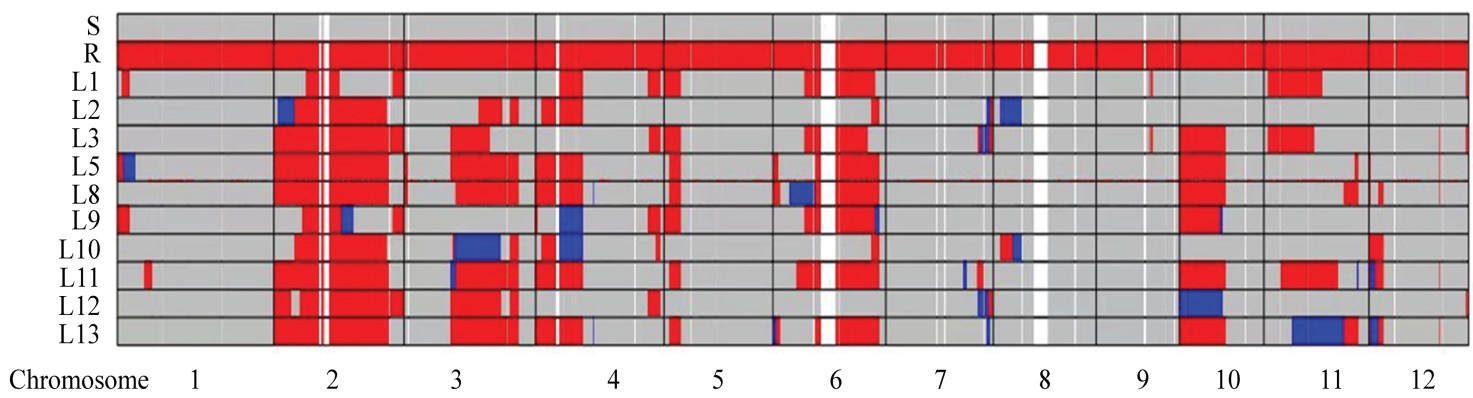
图3 亲本及测定株系的GSR40K芯片检测结果 S―五山丝苗;R―BHADOIA 303;L1~L13代表株系编号。
Fig. 3. Detection results of GSR40K chip of parents and tested strain. S, Wushansimiao; R, BHADOIA303; L1-L13, Line number.
| 材料名称 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 单株穗数 Number of panicles per plant | 粒长 Grain length / mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系1 Line 1 | 115.81±0.87 aA | 23.71±0.33 cB | 15.42±0.88 cC | 9.39±0.17 bB | 2.61±0.02 bBC | |||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 113.55±0.72 bA | 25.29±0.27 aA | 14.67±0.61 cC | 10.14±0.13 aA | 2.82±0.08 aA | |||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 109.28±1.69 cB | 22.85±0.27 dC | 21.58±1.00 aA | 9.07±0.05 cB | 2.73±0.05 aAB | |||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 107.41±0.72 dB | 24.77±0.34 bA | 18.50±1.37 bB | 9.33±0.06 bB | 2.56±0.05 bC | |||
| 材料名称 Material | 每穗总粒数 Total grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 小区产量 Plot yield/kg | ||||
| 株系1 Line 1 | 164.93±5.74 bB | 89.28±1.40 aA | 21.75±0.85 bB | 2.48±0.05 bB | ||||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 210.18±12.78 aA | 58.54±1.41 dC | 24.82±0.98 aA | 2.51±0.10 bB | ||||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 156.81±23.87 bB | 72.84±5.45 bB | 21.41±0.32 bB | 2.60±0.16 bB | ||||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 207.82±13.20 aA | 65.50±1.46 cBC | 21.35±0.83 bB | 3.01±0.12 aA | ||||
表3 部分测定株系的农艺性状及产量分析
Table 3. Analysis of agronomic traits and yield of some tested lines.
| 材料名称 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 单株穗数 Number of panicles per plant | 粒长 Grain length / mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系1 Line 1 | 115.81±0.87 aA | 23.71±0.33 cB | 15.42±0.88 cC | 9.39±0.17 bB | 2.61±0.02 bBC | |||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 113.55±0.72 bA | 25.29±0.27 aA | 14.67±0.61 cC | 10.14±0.13 aA | 2.82±0.08 aA | |||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 109.28±1.69 cB | 22.85±0.27 dC | 21.58±1.00 aA | 9.07±0.05 cB | 2.73±0.05 aAB | |||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 107.41±0.72 dB | 24.77±0.34 bA | 18.50±1.37 bB | 9.33±0.06 bB | 2.56±0.05 bC | |||
| 材料名称 Material | 每穗总粒数 Total grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 小区产量 Plot yield/kg | ||||
| 株系1 Line 1 | 164.93±5.74 bB | 89.28±1.40 aA | 21.75±0.85 bB | 2.48±0.05 bB | ||||
| 株系2 Line 2 | 210.18±12.78 aA | 58.54±1.41 dC | 24.82±0.98 aA | 2.51±0.10 bB | ||||
| 株系3 Line 3 | 156.81±23.87 bB | 72.84±5.45 bB | 21.41±0.32 bB | 2.60±0.16 bB | ||||
| 五山丝苗Wushansimiao | 207.82±13.20 aA | 65.50±1.46 cBC | 21.35±0.83 bB | 3.01±0.12 aA | ||||
| [1] | 黄大辉, 岑贞陆, 刘驰, 贺文爱, 陈英之, 马增凤, 杨朗, 韦绍丽, 刘亚利, 黄思良, 杨新庆, 李容柏. 野生稻细菌性条斑病抗性资源筛选及遗传分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(1): 11-14. |
| Huang D H, Cen Z L, Liu C, He W A, Chen Y Z, Ma Z F, Yang L, Wei S L, Liu Y L, Huang S L, Yang X Q, Li R P. Identification and genetic analysis of resistance to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2008, 9(1): 11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 张荣胜, 戴秀华, 王晓宇, 罗楚平, 刘永锋, 陈志谊. 江苏省水稻品种对水稻细菌性条斑病抗性鉴定及评价[J]. 植物保护学报, 2014, 41(4): 385-389. |
| Zhang R S, Dai X H, Wang X Y, Luo C P, Liu Y F, Chen Z Y. Evaluation of rice varieties resistant to bacterial leaf streak in Jiangsu[J]. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2014, 41(4): 385-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 冯爱卿, 陈深, 杨健源, 汪聪颖, 汪文娟, 苏菁, 曾列先, 朱小源. 水稻品种资源对细菌性条斑病菌的抗性评价[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(6): 1045-1054. |
| Feng A Q, Chen S, Yang J Y, Wang C Y, Wang W J, Su J, Zeng L X, Zhu X Y. Evaluation of the resistance of rice germplasm against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2018, 19(6): 1045-1054. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 肖友伦, 肖放华, 刘勇, 李小娟, 张德咏, 梁建文, 胡立冬. 湖南水稻主栽品种对水稻细菌性条斑病的抗性鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2011, 37(1): 45-49. |
| Xiao Y L, Xiao F H, Liu Y, Li X J, Zhang D Y, Liang J W, Hu L D. Resistance identification of leading rice varieties to bacterial leaf streak in Hunan[J]. Plant Protection, 2011, 37(1): 45-49. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 温绵福, 黄明, 钟林生, 曾国华. 不同药剂防治水稻细菌性条斑病药效探析[J]. 基层农技推广, 2017, 5(8): 20-22. |
| Wen M F, Huang M, Zhong L S, Zeng G H. Control effect of different fungicides on rice bacterial leaf streak[J]. Basic Level Agricultural Technology Extension, 2017, 5(8): 20-22. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 全国龙, 孙淑玲, 陈观浩. 防治水稻白叶枯病、水稻细菌性条斑病药效试验[J]. 南方农业, 2018, 12(35): 62-63. |
| Quan G L, Sun S L, Chen G H. Efficacy of fungicides against rice bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak[J]. South China Agriculture, 2018, 12(35): 62-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 冯爱卿, 陈深, 汪聪颖, 杨健源, 封金奇, 陈凯玲, 陈炳, 朱小源. 8种杀菌剂对水稻细菌性条斑病的防效评价[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(1): 55-62. |
| Feng A Q, Chen S, Wang C Y, Yang J Y, Feng J Q, Chen K L, Chen B, Zhu X Y. Evaluation on the disease control efficacy of eight fungicides against rice bacterial leaf streak[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(1): 55-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢. 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| Wei M Y, Ma Z F, Huang D H, Qin Y Y, Liu C, Lu Y P, Luo T P, Li Z J, Zhang Y X, Qin G. QTL-seq analysis for identification of resistance locus to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Bossa-Castro A M, Tekete C, Raghavan C, Delorean E E, Dereeper A, Dagno K, Koita O, Mosquera G, Leung H, Verdier V, Leach J E. Allelic variation for broad- spectrum resistance and susceptibility to bacterial pathogens identified in a rice MAGIC population[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018(1): 1-10. |
| [10] | 韩庆典, 陈志伟, 段远霖, 兰涛, 官华忠, 周元昌, 吴为人. 利用基因芯片检测水稻细菌性条斑病抗性相关基因[J]. 分子植物育种, 2008, 6(2): 239-244. |
| Han Q D, Chen Z W, Duan Y L, Lan T, Guan H Z, Zhou Y C, Wu W R. Detection of genes related to resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice using microarray[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2008, 6(2): 239-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Jiang N, Yan J, Liang Y, Shi Y L, He Z Z, Wu Y T, Zeng Q, Liu X L, Peng J H. Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.): An updated review[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 3. |
| [12] | Zhao B Y, Ardales E, Brasset E, Claflin L E, Leach J E, Hulbert S H. The Rxo1/Rba1 locus of maize controls resistance reactions to pathogenic and non-host bacteria[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2004, 109: 71-79. |
| [13] | Zhao B Y, Ardales E Y, Raymundo A, Bai J, Trick H N, Leach J E, Hulbert S H. The avrRxo1gene from the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola confers a nonhost defense reaction on maize with resistance gene Rxo1[J]. The American Phytopathological Society, 2004, 17(7): 771-779. |
| [14] | Zhao B, Lin X, Poland J, Trick H, Leach J, Hulbert S. A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 2005, 102(43): 15383-15388. |
| [15] | Triplett L R, Cohen S P, Heffelfinger C, Schmidt C L, Huerta A I, Tekete C, Verdier V, Bogdanove A J, Leach J E. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(5): 472-483. |
| [16] | Read A C, Hutin M, Moscou M J, Rinaldi F C, Bogdanove A J. Cloning of the rice Xo1 resistance gene and interaction of the Xo1 protein with the defense- suppressing Xanthomonas effector Tal2h[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2020, 33(10): 1189-1195. |
| [17] | He W A, Huang D H, Li R B, Qiu Y F, Song J D, Yang H N, Zheng J X, Huang Y Y, Li X Q, Liu C, Zhang Y X, Ma Z F, Yang Y. Identification of a resistance gene bls1 to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2012, 11: 962-969. |
| [18] | Ma Z F, Qin G, Zhang Y X, Liu C, Wei M Y, Cen Z L, Yan Y, Luo T P, Li Z J, Liang H F, Huang D H, Deng G F. Bacterial leaf streak 1 encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase confers the rice resistance to bacterial leaf streak[J]. The Plant Journal, 2021, 107(4): 1084-1101. |
| [19] | Tang D Z, Wu W R, Li W M, Lu H R, Worland A J. Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2000, 101: 286-291. |
| [20] | Xie X F, Chen Z W, Cao J L, Guan H Z, Lin D G, Li C L, Lan T, Duan Y L, Mao D M, Wu W R. Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping sub- CSSLs in rice[J]. PloS One, 2014, 9(4): e95751. |
| [21] | 罗登杰, 万瑶, 覃雪梅, 施力军, 张慧, 李容柏, 刘芳. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性基因bls2 SSR分子标记开发[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(5): 1167-1173. |
| Luo D J, Wan Y, Qin X M, Shi L J, Zhang H, Li R B, Liu F. Development of SSR molecular markers for bacterial leaf streak resistance gene bls2 in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(5): 1167-1173. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 施力军, 罗登杰, 赵严, 岑贞陆, 刘芳, 李容柏. 普通野生稻抗细菌性条斑病基因的遗传分析与定位[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(2): 1-5. |
| Shi L J, Luo D J, Zhao Y, Cen Z L, Liu F, Li R B. Genetic analysis and mapping of bacterial leaf streak resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(2): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Chen S, Feng A Q, Wang C Y, Zhao J L, Feng J Q, Chen B, Yang J Y, Wang W J, Zhang M Y, Chen K L, Chen W Q, Su J, Liu B, Zhu X Y. Identification and fine-mapping of Xo2, a novel rice bacterial leaf streak resistance gene[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2022, 135: 3195-3209. |
| [24] | Wang C Y, Chen S, Feng A Q, Su J, Wang W J, Feng J Q, Chen B, Zhang M Y, Yang J Y, Zeng L X, Zhu X Y. Xa7, a small orphan gene harboring promoter trap for AvrXa7, leads to the durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae[J]. Rice, 2021, 14(1): 48. |
| [25] | Chen X F, Liu P C, Mei L, He X L, Chen L, Liu H, Shen S R, Ji Z D, Zheng X X, Gao Z Y, Zeng D L, Qian Q, Ma B J. Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(3): 100143. |
| [26] | Luo D, Huguet-Tapia J C, Raborn R T, White F F, Yang B. The Xa7 resistance gene guards the susceptibility gene SWEET14 of rice against exploitation by bacterial blight pathogen[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(3): 100164. |
| [27] | 黄道强, 周少川, 李宏, 卢德城, 赖穗春, 王志东, 周德贵. 优质稻新品种五山丝苗的选育及利用[J]. 广东农业科学, 2011(9): 15-16. |
| Huang D Q, Zhou S C, Li H, Lu D C, Lai S C, Wang Z D, Zhou D G. Breeding and utilization of new high quality rice variety Wushansimiao[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 2011(9): 15-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 冯爱卿, 汪聪颖, 汪文娟, 陈尉芹, 苏菁, 杨健源, 陈深, 朱小源. 广东水稻细菌性条斑病菌致病性分化研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2018, 45(9): 84-89. |
| Feng A Q, Wang C Y, Wang W J, Chen W Q, Su J, Yang J Y, Chen S, Zhu X Y. Study on the pathogenicity diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola from Guangdong Province[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 2018, 45(9): 84-89. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | Yang B, Bogdanove A. A. Inoculation and virulence assay for bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak of rice//Rice Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology[M]. Totowa N J: Humana Press, 2013, 956: 249-255. |
| [30] | International Rice Research Institute. Standard Evaluation System for Rice[M]. 4th ed. Manila: IRRI, 1996: 20 |
| [31] | 文艳华, 何月秋, 黄瑞荣, 曾小萍. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性鉴定方法研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 1994, 6(2): 112-117. |
| Wen Y H, He Y Q, Huang R R, Zeng X P. Study on the method to identify the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf streak[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 1994, 6(2): 112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 周明华, 许志刚, 沈秀萍. 水稻品种对水稻细菌性条斑病的抗性鉴定[J]. 植物检疫, 2001, 15(2): 65-67. |
| Zhou M H, Xu Z G, Shen X P. Resistance identification of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. Plant Quarantine, 2001, 15(2): 65-67. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 陈志伟, 吴为人, 周元昌, 景艳军. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性微卫星(SSR)标记的筛选及其在标记辅助选择中的应用[J]. 福建农业大学学报, 2004(2): 202-205. |
| Chen Z W, Wu W R, Zhou Y C, Jing Y J. Screening of microsatellite markers for resistance to bacterial leaf streak and their application to marker-assisted selection in rice[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2004(2): 202-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 李齐向, 周元昌, 陈由禹. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性QTL微卫星标记的筛选及其在基因聚合育种研究中的应用[J]. 福建农业学报, 2012, 27(5): 470-474. |
| Li Q X, Zhou Y C, Chen Y Y. Screening of microsatellite markers for resistance to bacterial leaf blight and their application to gene pyramiding breeding in rice[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Science, 2012, 27(5): 470-474. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [35] | 罗同平, 黄春东, 张月雄, 秦媛媛, 岑贞陆, 刘驰, 韦敏益, 秦钢, 马增凤, 黄大辉. 兼抗白叶枯病和细条病水稻材料的创新及育种利用[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(9): 2038-2045. |
| Luo T P, Huang C D, Zhang Y X, Qin Y Y, Cen Z L, Liu C, Wei M Y, Qin G, Ma Z F, Huang D H. Innovation and application of breeding utilization for resistance to bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(9): 2038-2045. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [2] | 王炫栋, 余俊杰, 高润杰, 兰赫婷, 江樱姿, 齐文杰, 宋振, 蒋冬花. 一株兼具防病促生功能的沙阿霉素链霉菌Sz-11[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 200-212. |
| [3] | 王石光, 陆展华, 刘维, 卢东柏, 王晓飞, 方志强, 巫浩翔, 何秀英. 应用CRISPR/Cas9技术与分子标记辅助选择创制广东丝苗米新种质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 29-36. |
| [4] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [5] | 李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. |
| [6] | 梁程, 向珣朝, 张欧玲, 游慧, 许亮, 陈永军. 两份新株型水稻品系的农艺性状与遗传特性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 171-180. |
| [7] | 董铮, 王雅美, 黎用朝, 熊海波, 薛灿辉, 潘孝武, 刘文强, 魏秀彩, 李小湘. 基于MAGIC群体的水稻镉含量全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 35-42. |
| [8] | 乔胜锋, 邓亚萍, 瞿寒冰, 张伟杨, 顾骏飞, 张耗, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同籼稻品种对低磷响应的差异及其农艺生理性状[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 396-406. |
| [9] | 杨晓龙, 程建平, 汪本福, 李阳, 张枝盛, 李进兰, 李萍. 灌浆期干旱胁迫对水稻生理性状和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| [10] | 彭永彬, 谢先芝. 表型组学在水稻研究中的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 300-306. |
| [11] | 李可, 禹晴, 徐云姬, 杨建昌. 水稻叶片早衰突变体的农艺与生理性状研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 104-114. |
| [12] | 吕川根, 李霞, 宗寿余, 邹江石. 超级杂交稻两优培九的广适性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 191-205. |
| [13] | 张宏根, 仲崇元, 司华, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪, 汤述翥. 分子标记辅助选择改良C418对红莲型粳稻不育系的恢复力[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 445-452. |
| [14] | 井文, 章文华. 水稻耐盐基因定位与克隆及品种耐盐性分子标记辅助选择改良研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(2): 111-123. |
| [15] | 李威, 圣忠华, 朱子亮, 魏祥进, 石磊, 邬亚文, 唐绍清, 王建龙, 胡培松. 粳稻柱头外露率QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 23-30. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||