
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 307-320.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220604
Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Dan1, JIANG Min1, MIAO Bo1, GUO Meng1, SHI Chunlin2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-04
Revised:2022-08-05
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: 912050823@qq.com
通讯作者:
*email: 912050823@qq.com
基金资助:LIN Dan, JIANG Min, MIAO Bo, GUO Meng, SHI Chunlin. Research on Simulation Model of High Temperature Stress on Rice and Its Application in Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 307-320.
林聃, 江敏, 苗波, 郭萌, 石春林. 水稻高温热害模型研究及其在福建省的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 307-320.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220604
| 生育期 Growth period | 持续天数DT/d | 高温处理时期(月-日) High temperature treatment duration(Month-Day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | T78优2155 T78 You 2155 | 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | ||
| 减数分裂期Meiosis stage | 3 | / | / | 8-12—8-14 | 8-12—8-14 |
| 7 | / | / | 8-12—8-18 | 8-12—8-18 | |
| 开花期Flowering stage | 3 | 7-13—7-15 | 7-15—7-17 | 8-21—8-23 | 8-24—8-26 |
| 7 | 7-13—7-19 | 7-15—7-21 | 8-21—8-27 | 8-24—8-30 | |
| 灌浆期Grain-filling stage | 3 | 7-23—7-25 | 7-25—7-27 | / | / |
| 7 | 7-23—7-29 | 7-25—7-31 | / | / | |
Table 1. High temperature treatment date of each growth period.
| 生育期 Growth period | 持续天数DT/d | 高温处理时期(月-日) High temperature treatment duration(Month-Day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | T78优2155 T78 You 2155 | 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | ||
| 减数分裂期Meiosis stage | 3 | / | / | 8-12—8-14 | 8-12—8-14 |
| 7 | / | / | 8-12—8-18 | 8-12—8-18 | |
| 开花期Flowering stage | 3 | 7-13—7-15 | 7-15—7-17 | 8-21—8-23 | 8-24—8-26 |
| 7 | 7-13—7-19 | 7-15—7-21 | 8-21—8-27 | 8-24—8-30 | |
| 灌浆期Grain-filling stage | 3 | 7-23—7-25 | 7-25—7-27 | / | / |
| 7 | 7-23—7-29 | 7-25—7-31 | / | / | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 单株穗数 Panicle number per plant | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | CK | 39.0±3.1 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 128.7±4.2 a | 88.9±1.8 a | 29.3±0.9 a |
| T1D1 | 36.3±1.4 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 129.3±8.1 a | 82.8±3.0 b | 29.2±0.3 a | |
| T2D1 | 21.8±2.4 c | 12.3±0.6 a | 130.0±5.0 a | 47.2±1.8 d | 28.7±0.1 a | |
| T1D2 | 30.5±2.8 b | 12.0±1.0 a | 147.0±8.5 a | 59.5±4.1 c | 29.1±0.7 a | |
| T2D2 | 16.9±2.1 d | 13.0±1.0 a | 152.3±25.0 a | 31.6±4.2 e | 27.0±0.8 b | |
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | CK | 43.5±0.4 a | 12.0±1.0 a | 154.0±13.5 a | 92.4±1.2 a | 25.6±0.2 a |
| T1D1 | 39.9±1.5 b | 11.7±1.2 a | 152.7±13.7 a | 88.3±4.2 a | 25.5±0.1 a | |
| T2D1 | 25.5±0.9 d | 12.0±2.0 a | 160.3±20.5 a | 55.0±1.5 c | 25.1±0.1 a | |
| T1D2 | 33.3±0.6 c | 11.3±1.5 a | 157.3±12.2 a | 74.0±4.6 b | 25.4±0.1 a | |
| T2D2 | 17.1±1.4 e | 12.3±0.6 a | 156.7±5.5 a | 38.2±1.5 d | 23.1±0.7 b |
Table 2. Effects of high temperature on grain yield and its components of early rice at flowering stage.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 单株穗数 Panicle number per plant | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | CK | 39.0±3.1 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 128.7±4.2 a | 88.9±1.8 a | 29.3±0.9 a |
| T1D1 | 36.3±1.4 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 129.3±8.1 a | 82.8±3.0 b | 29.2±0.3 a | |
| T2D1 | 21.8±2.4 c | 12.3±0.6 a | 130.0±5.0 a | 47.2±1.8 d | 28.7±0.1 a | |
| T1D2 | 30.5±2.8 b | 12.0±1.0 a | 147.0±8.5 a | 59.5±4.1 c | 29.1±0.7 a | |
| T2D2 | 16.9±2.1 d | 13.0±1.0 a | 152.3±25.0 a | 31.6±4.2 e | 27.0±0.8 b | |
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | CK | 43.5±0.4 a | 12.0±1.0 a | 154.0±13.5 a | 92.4±1.2 a | 25.6±0.2 a |
| T1D1 | 39.9±1.5 b | 11.7±1.2 a | 152.7±13.7 a | 88.3±4.2 a | 25.5±0.1 a | |
| T2D1 | 25.5±0.9 d | 12.0±2.0 a | 160.3±20.5 a | 55.0±1.5 c | 25.1±0.1 a | |
| T1D2 | 33.3±0.6 c | 11.3±1.5 a | 157.3±12.2 a | 74.0±4.6 b | 25.4±0.1 a | |
| T2D2 | 17.1±1.4 e | 12.3±0.6 a | 156.7±5.5 a | 38.2±1.5 d | 23.1±0.7 b |
| 品种 Variety | 产量构成因素 Yield component | 系数及R2值 Coefficients and R2 | 生育期Growth period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 开花期Flowering stage | 灌浆期Grain-filling stage | |||
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | 相对结实率 RSSR | A1 | 0.309 19 | 0.884 49 |
| x0 | 124.152 53 | 141.462 46 | ||
| p | 3.120 29 | 80.687 67 | ||
| R2 | 0.987 93 | 0.9753 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.923 08 | 0.909 66 | |
| x0 | 157.457 88 | 119.082 35 | ||
| p | 23.755 46 | 3.007 38 | ||
| R2 | 0.991 17 | 0.962 87 | ||
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | 相对结实率 RSSR | A1 | 0.1723 | 143.553 09 |
| x0 | 231.633 21 | 32.650 81 | ||
| p | 2.158 66 | 0.983 81 | ||
| R2 | 0.997 88 | 0.989 53 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.903 09 | 0.738 54 | |
| x0 | 160.394 05 | 532.208 03 | ||
| p | 20.170 34 | 1.558 12 | ||
| R2 | 0.938 31 | 0.983 97 | ||
Table 3. Fitting coefficients and R2 values of relative seed setting rate(RSSR) and relative 1000-grain weight(RTGW) of early rice as a function of the cumulative degree of high temperature-period hour.
| 品种 Variety | 产量构成因素 Yield component | 系数及R2值 Coefficients and R2 | 生育期Growth period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 开花期Flowering stage | 灌浆期Grain-filling stage | |||
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | 相对结实率 RSSR | A1 | 0.309 19 | 0.884 49 |
| x0 | 124.152 53 | 141.462 46 | ||
| p | 3.120 29 | 80.687 67 | ||
| R2 | 0.987 93 | 0.9753 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.923 08 | 0.909 66 | |
| x0 | 157.457 88 | 119.082 35 | ||
| p | 23.755 46 | 3.007 38 | ||
| R2 | 0.991 17 | 0.962 87 | ||
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | 相对结实率 RSSR | A1 | 0.1723 | 143.553 09 |
| x0 | 231.633 21 | 32.650 81 | ||
| p | 2.158 66 | 0.983 81 | ||
| R2 | 0.997 88 | 0.989 53 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.903 09 | 0.738 54 | |
| x0 | 160.394 05 | 532.208 03 | ||
| p | 20.170 34 | 1.558 12 | ||
| R2 | 0.938 31 | 0.983 97 | ||
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | CK | 39.1±3.1 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 128.7±4.2 a | 88.9±1.8 a | 29.3±0.9 a |
| T1D1 | 38.2±0.8 a | 12.0±2.0 a | 127.7±18.0 a | 87.6±3.1 ab | 28.9±0.1 ab | |
| T2D1 | 34.8±0.6b | 13.0±1.0 a | 125.3±17.0 a | 78.7±3.5 b | 27.3±0.2 c | |
| T1D2 | 37.7±0.9 a | 11.7±1.5 a | 134.0±16.1 a | 85.8±0.6 ab | 28.4±0.4 b | |
| T2D2 | 33.7±1.0 b | 12.0±1.0 a | 135.0±19.1 a | 78.6±7.8 b | 26.7±0.2 c | |
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | CK | 43.5±0.4 a | 12.0±1.0 a | 154.0±13.5 a | 92.4±1.2 a | 25.6±0.2 a |
| T1D1 | 41.0±1.9 b | 12.0±0.0 a | 146.3±3.1 a | 92.0±2.4 a | 25.4±0.2 a | |
| T2D1 | 37.4±0.9 cd | 12.3±1.5 a | 141.7±11.8 a | 89.6±1.7 a | 24.1±0.6 b | |
| T1D2 | 38.6±0.9 c | 11.7±1.2 a | 144.7±9.0 a | 91.4±1.6 a | 25.1±0.4 a | |
| T2D2 | 35.7±0.8 d | 12.0±0.9 a | 144.7±9.0 a | 89.0±9.2 a | 23.3±0.1c |
Table 4. Effects of high temperature at grain-filling stage on yield and its components of early rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | CK | 39.1±3.1 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 128.7±4.2 a | 88.9±1.8 a | 29.3±0.9 a |
| T1D1 | 38.2±0.8 a | 12.0±2.0 a | 127.7±18.0 a | 87.6±3.1 ab | 28.9±0.1 ab | |
| T2D1 | 34.8±0.6b | 13.0±1.0 a | 125.3±17.0 a | 78.7±3.5 b | 27.3±0.2 c | |
| T1D2 | 37.7±0.9 a | 11.7±1.5 a | 134.0±16.1 a | 85.8±0.6 ab | 28.4±0.4 b | |
| T2D2 | 33.7±1.0 b | 12.0±1.0 a | 135.0±19.1 a | 78.6±7.8 b | 26.7±0.2 c | |
| T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | CK | 43.5±0.4 a | 12.0±1.0 a | 154.0±13.5 a | 92.4±1.2 a | 25.6±0.2 a |
| T1D1 | 41.0±1.9 b | 12.0±0.0 a | 146.3±3.1 a | 92.0±2.4 a | 25.4±0.2 a | |
| T2D1 | 37.4±0.9 cd | 12.3±1.5 a | 141.7±11.8 a | 89.6±1.7 a | 24.1±0.6 b | |
| T1D2 | 38.6±0.9 c | 11.7±1.2 a | 144.7±9.0 a | 91.4±1.6 a | 25.1±0.4 a | |
| T2D2 | 35.7±0.8 d | 12.0±0.9 a | 144.7±9.0 a | 89.0±9.2 a | 23.3±0.1c |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou3301 | CK | 39.6±0.8 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.0±4.4 a | 79.4±3.6 a | 27.4±0.7 a |
| T1D1 | 37.3±1.0 b | 10.3±0.6 a | 172.7±4.5 a | 77.4±2.9 a | 27.1±0.7 ab | |
| T2D1 | 26.4±0.8 d | 10.3±1.2 a | 153.3±11.4 b | 64.9±4.1 b | 25.9±1.0 ab | |
| T1D2 | 30.0±1.6 c | 10.0±1.0 a | 168.3±7.6 a | 67.7±3.2 b | 26.4±1.4 ab | |
| T2D2 | 23.3±1.0 e | 10.7±0.6 a | 151.0±7.9 b | 58.1±3.6 c | 24.9±1.4 b | |
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou676 | CK | 41.9±2.5 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.7±3.8 a | 80.9±2.4 a | 28.1±0.5 a |
| T1D1 | 38.5±2.4 a | 10.7±0.6 a | 174.0±5.3 ab | 74.3±2.6 b | 27.9±0.5 ab | |
| T2D1 | 28.0±1.9 c | 11.3±0.6 a | 149.4±5.5 c | 62.9±1.8 c | 26.2±0.9 cd | |
| T1D2 | 32.2±1.4 b | 11.0±0.0 a | 166.0±10.0 b | 65.6±1.2 c | 26.9±0.5 bc | |
| T2D2 | 23.6±1.4 d | 11.3±0.6 a | 147.7±3.2 c | 56.0±5.6 d | 25.3±0.6 d |
Table 5. Effects of high temperature during meiosis on yield and its components of middle rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou3301 | CK | 39.6±0.8 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.0±4.4 a | 79.4±3.6 a | 27.4±0.7 a |
| T1D1 | 37.3±1.0 b | 10.3±0.6 a | 172.7±4.5 a | 77.4±2.9 a | 27.1±0.7 ab | |
| T2D1 | 26.4±0.8 d | 10.3±1.2 a | 153.3±11.4 b | 64.9±4.1 b | 25.9±1.0 ab | |
| T1D2 | 30.0±1.6 c | 10.0±1.0 a | 168.3±7.6 a | 67.7±3.2 b | 26.4±1.4 ab | |
| T2D2 | 23.3±1.0 e | 10.7±0.6 a | 151.0±7.9 b | 58.1±3.6 c | 24.9±1.4 b | |
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou676 | CK | 41.9±2.5 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.7±3.8 a | 80.9±2.4 a | 28.1±0.5 a |
| T1D1 | 38.5±2.4 a | 10.7±0.6 a | 174.0±5.3 ab | 74.3±2.6 b | 27.9±0.5 ab | |
| T2D1 | 28.0±1.9 c | 11.3±0.6 a | 149.4±5.5 c | 62.9±1.8 c | 26.2±0.9 cd | |
| T1D2 | 32.2±1.4 b | 11.0±0.0 a | 166.0±10.0 b | 65.6±1.2 c | 26.9±0.5 bc | |
| T2D2 | 23.6±1.4 d | 11.3±0.6 a | 147.7±3.2 c | 56.0±5.6 d | 25.3±0.6 d |
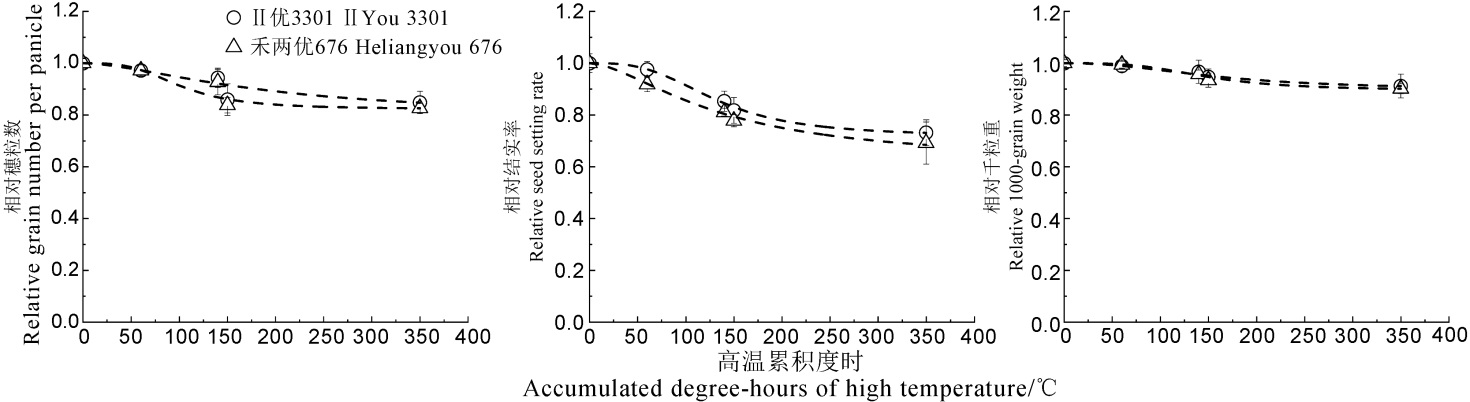
Fig. 4. Changes of grain number per panicle, seed setting rate and 1000-grain weight of medium rice with accumulated degree-hours of high temperature.
| 品种 Variety | 产量构成因素 Yield component | 拟合系数及R2值 Fitting coefficients and R2 | 生育期Growth period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 减数分裂期Meiosis stage | 开花期Flowering stage | |||
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | 相对穗粒数 RGN | A1 | 0.791 63 | / |
| x0 | 190.109 58 | / | ||
| p | 1.6427 | / | ||
| R2 | 0.911 88 | / | ||
| 相对结实率 RGN | A1 | 0.717 58 | 0.633 19 | |
| x0 | 131.3975 | 86.169 17 | ||
| p | 3.068 56 | 2.030 04 | ||
| R2 | 0.996 26 | 0.997 49 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.896 71 | 0.9426 | |
| x0 | 159.3183 | 147.443 26 | ||
| p | 2.270 27 | 24.822 37 | ||
| R2 | 0.981 53 | 0.992 88 | ||
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | 相对穗粒数 RGN | A1 | 0.823 09 | / |
| x0 | 101.515 02 | / | ||
| p | 3.3079 | / | ||
| R2 | 0.966 49 | / | ||
| 相对结实率 RGN | A1 | 0.617 84 | 0.493 48 | |
| x0 | 135.960 37 | 174.413 57 | ||
| p | 1.643 85 | 1.441 28 | ||
| R2 | 0.989 55 | 0.987 03 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.896 25 | 0.948 31 | |
| x0 | 148.222 61 | 147.529 44 | ||
| p | 3.453 69 | 44.2462 | ||
| R2 | 0.987 73 | 1 | ||
Table 6. Fitting coefficients and R2 values of relative grain number per panicle, relative seed setting rate and relative 1000-grain weight of middle rice with accumulated degree-hours of high temperature.
| 品种 Variety | 产量构成因素 Yield component | 拟合系数及R2值 Fitting coefficients and R2 | 生育期Growth period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 减数分裂期Meiosis stage | 开花期Flowering stage | |||
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | 相对穗粒数 RGN | A1 | 0.791 63 | / |
| x0 | 190.109 58 | / | ||
| p | 1.6427 | / | ||
| R2 | 0.911 88 | / | ||
| 相对结实率 RGN | A1 | 0.717 58 | 0.633 19 | |
| x0 | 131.3975 | 86.169 17 | ||
| p | 3.068 56 | 2.030 04 | ||
| R2 | 0.996 26 | 0.997 49 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.896 71 | 0.9426 | |
| x0 | 159.3183 | 147.443 26 | ||
| p | 2.270 27 | 24.822 37 | ||
| R2 | 0.981 53 | 0.992 88 | ||
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | 相对穗粒数 RGN | A1 | 0.823 09 | / |
| x0 | 101.515 02 | / | ||
| p | 3.3079 | / | ||
| R2 | 0.966 49 | / | ||
| 相对结实率 RGN | A1 | 0.617 84 | 0.493 48 | |
| x0 | 135.960 37 | 174.413 57 | ||
| p | 1.643 85 | 1.441 28 | ||
| R2 | 0.989 55 | 0.987 03 | ||
| 相对千粒重 RTGW | A1 | 0.896 25 | 0.948 31 | |
| x0 | 148.222 61 | 147.529 44 | ||
| p | 3.453 69 | 44.2462 | ||
| R2 | 0.987 73 | 1 | ||
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | CK | 39.9±0.8 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.0±4.4 a | 79.4±3.6 a | 27.4±0.7 a |
| T1D1 | 33.8±4.0 b | 10.7±1.2 a | 168.0±19.1 a | 69.7±5.1 b | 27.2±0.4 a | |
| T2D1 | 27.3±0.6 c | 10.0±0.0 a | 181.3±2.5 a | 57.0±1.3 c | 26.4±0.2 ab | |
| T1D2 | 26.6±1.3 c | 9.7±0.6 a | 174.3±3.2 a | 58.5±1.1 c | 27.0±0.5 a | |
| T2D2 | 26.5±1.5 c | 10.7±0.6 a | 185.7±5.5 a | 52.0±2.7 c | 25.8±0.1 b | |
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | CK | 41.9±2.5 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.7±3.8 a | 80.9±2.4 a | 28.1±0.5 a |
| T1D1 | 35.5±0.4 b | 10.7±0.6 a | 162.7±15.7 a | 73.4±4.8 b | 28.1±0.1 a | |
| T2D1 | 27.4±1.3 d | 10.7±1.5 a | 174.3±10.8 a | 55.4±6.4 d | 27.1±0.9 ab | |
| T1D2 | 30.2±0.6 c | 10.3±2.1 a | 166.3±24.3 a | 63.9±1.3 c | 27.9±0.5 ab | |
| T2D2 | 24.2±0.7 e | 11.0±1.7 a | 164.7±15.5 a | 51.0±3.3 d | 26.6±1.2 b |
Table 7. Effects of high temperature during meiosis on yield and its components of middle rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株产量 Yield per plant / g | 穗数 Panicle number | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | CK | 39.9±0.8 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.0±4.4 a | 79.4±3.6 a | 27.4±0.7 a |
| T1D1 | 33.8±4.0 b | 10.7±1.2 a | 168.0±19.1 a | 69.7±5.1 b | 27.2±0.4 a | |
| T2D1 | 27.3±0.6 c | 10.0±0.0 a | 181.3±2.5 a | 57.0±1.3 c | 26.4±0.2 ab | |
| T1D2 | 26.6±1.3 c | 9.7±0.6 a | 174.3±3.2 a | 58.5±1.1 c | 27.0±0.5 a | |
| T2D2 | 26.5±1.5 c | 10.7±0.6 a | 185.7±5.5 a | 52.0±2.7 c | 25.8±0.1 b | |
| 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | CK | 41.9±2.5 a | 10.3±0.6 a | 178.7±3.8 a | 80.9±2.4 a | 28.1±0.5 a |
| T1D1 | 35.5±0.4 b | 10.7±0.6 a | 162.7±15.7 a | 73.4±4.8 b | 28.1±0.1 a | |
| T2D1 | 27.4±1.3 d | 10.7±1.5 a | 174.3±10.8 a | 55.4±6.4 d | 27.1±0.9 ab | |
| T1D2 | 30.2±0.6 c | 10.3±2.1 a | 166.3±24.3 a | 63.9±1.3 c | 27.9±0.5 ab | |
| T2D2 | 24.2±0.7 e | 11.0±1.7 a | 164.7±15.5 a | 51.0±3.3 d | 26.6±1.2 b |
| 品种 Variety | 生育期 Growth period | 损失率 Loss rate |
|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 开花期 Flowering stage | ={1―{0.240745+0.759255/[1+( |
| 灌浆期 Grain-filling stage | ={1―{0.92368+0.07632/[1+( | |
| 中稻 Middle rice | 减数分裂期 Meiosis stage | ={1―{0.80736+0.19264/[1+( |
| 开花期 Flowering stage | ={1―{0.563335+0.436665/[1+( |
Table 8. Heat-induced yield loss rate of early rice and middle rice at different developmental phases.
| 品种 Variety | 生育期 Growth period | 损失率 Loss rate |
|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 开花期 Flowering stage | ={1―{0.240745+0.759255/[1+( |
| 灌浆期 Grain-filling stage | ={1―{0.92368+0.07632/[1+( | |
| 中稻 Middle rice | 减数分裂期 Meiosis stage | ={1―{0.80736+0.19264/[1+( |
| 开花期 Flowering stage | ={1―{0.563335+0.436665/[1+( |
| 品种参数 Varieties of parameter | 品种Variety | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | |
| P1 | 92.04 | 92.04 | 81.98 | 81.98 |
| P2 | 1392.35 | 1392.35 | 1387.47 | 1387.47 |
| P3 | 904.12 | 925.56 | 1208.82 | 1184.76 |
| P4 | 709.08 | 732.45 | 976.79 | 948.42 |
Table 9. Variety parameters of four rice varieties during developmental phase in Fujian Province.
| 品种参数 Varieties of parameter | 品种Variety | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 榕盛优1131 Rongshengyou 1131 | T78优2155 T78 you 2155 | Ⅱ优3301 ⅡYou 3301 | 禾两优676 Heliangyou 676 | |
| P1 | 92.04 | 92.04 | 81.98 | 81.98 |
| P2 | 1392.35 | 1392.35 | 1387.47 | 1387.47 |
| P3 | 904.12 | 925.56 | 1208.82 | 1184.76 |
| P4 | 709.08 | 732.45 | 976.79 | 948.42 |
| [1] | 福建省统计局. 福建统计年鉴2021[M]. 福建: 福建省统计局, 2022. |
| Fujian Bureau of Statistics. Fujian Statistical Yearbook 2021[M]. Fujian: Fujian Bureau of Statistics, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 张婷, 程昌秀. 顾及空间集聚程度的中国高温灾害危险性评价[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(6): 865-874. |
| Zhang T, Cheng C X. Assessment of China's high-temperature hazards: Accounting for spatial agglomeration[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2019, 21(6): 865-874. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 卢淑云. 高温对水稻后期生长发育的影响及防御技术措施[J]. 现代经济信息, 2009(2): 145. |
| Lu S Y. Effects of high temperature on late growth and development of rice and preventive measures[J]. Modern Economic Information, 2009(2): 145. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 段骅, 佟卉, 刘燕清, 许庆芬, 马骏, 王春敏. 高温和干旱对水稻的影响及其机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 206-218. |
| Duan H, Tong H, Liu Y Q, Xu Q F, Ma J, Wang C M. Research advances in the effect of heat and drought on rice and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 206-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 杨军, 章毅之, 贺浩华, 李迎春, 陈小荣, 边建民, 金国花, 李翔翔, 黄淑娥. 水稻高温热害的研究现状与进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2817-2830. |
| Yang J, Zhang Y Z, He H H, Li Y C, Chen X R, Bian J M, Jin G H, Li X X, Huang S E. Current status and research advances of high-temperature hazards in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2817-2830. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 骆宗强, 石春林, 江敏, 刘杨, 宣守丽, 金之庆. 孕穗期高温对水稻物质分配及产量结构的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2016, 37(3): 326-334. |
| Luo Z Q, Shi C L, Jiang M, Liu Y, Xuan S L, Jin Z Q. Effect of high temperature on rice dry matter partition and yield component during booting stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2016, 37(3): 326-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Bouman B A M, Kropff M J, Tuong T P, Wopereis M C S, Berge H F M T, Laar H H V. ORYZA2000: Modeling Lowland Rice[M]. Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 2001: 235. |
| [8] | Sun Q, Zhao Y X, Zhang Y, Chen S N, Ying Q, Lü Z F, Chen X H, Wang D L. Heat stress may cause a significant reduction of rice yield in China under future climate scenarios[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 818: 151746. |
| [9] | 石春林, 金之庆, 汤日圣, 郑建初. 水稻高温败育模拟模型[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007(2): 220-222. |
| Shi C L, Jin Z Q, Tang R S, Zheng J C. Model to Simulate high temperature-induced sterility of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007(2): 220-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | van Dort O P A J, Saito K, Zwart S J, Shrestha, S. A simple model for simulating heat induced sterility in rice as a function of flowering time and transportational cooling[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 156: 303-312. |
| [11] | Irfan R N, Fahd R, Ashfaq A, Hafiz N A, Gerrit H. Climate change impacts and adaptations for fine, coarse, and hybrid rice using CERES-Rice[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(9): 9454-9464. |
| [12] | Muhammad K A, Tayyaba H, Shahzad H, Muhammad H N. Modeling adaptation strategies against climate change impacts in integrated rice-wheat agricultural production system of Pakistan[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2020, 17(7): 2522. |
| [13] | Sudharsan D, Adinarayana J, Reddy D R, Sreenivas G, Ninomiya S, Hirafuji M, Kiura T, Tanaka K, Desai U B, Merchant S N. Evaluation of weather-based rice yield models in India[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2013, 57(1): 107-123. |
| [14] | 高亮之, 金之庆, 黄耀, 陈华, 李秉柏. 水稻栽培计算机模拟优化决策系统[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1992. |
| Gao L Z, Jin Z Q, Huang Y, Chen H, Li B B. Computer Simulation and Optimization Decision System for Rice Cultivation[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1992. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | Zhang T, Li T, Yang X G, Elisabeth S. Model biases in rice phenology under warmer climates[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27355. |
| [16] | 郭建茂, 王星宇, 刘慎彬, 钱娅, 李羚. 基于稻田实测温度的水稻模型ORYZA2000应用[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(4): 211-221. |
| Guo J M, Wang X Y, Liu S B, Qian Y, Li L. Application of rice model ORYZA2000 based on measured temperature in rice fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(4): 211-221. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Tang L, Zhu Y, Hannaway D, Meng Y, Liu L, Chen L, Cao W. RiceGrow: A rice growth and productivity model[J]. Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences, 2009, 57(1): 83-92. |
| [18] | Horie T. Global warming and rice production in Asia: Modeling, impact prediction and adaptation[J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B: Physical and Biological Sciences, 2019, 95(6): 211-245. |
| [19] | 吕厚荃, 张艳红, 冯明, 李秉柏, 刘安国, 毛飞, 庄立伟, 李祎君, 吴门新. 水稻热害气象等级: GB/T 37744―2019[S]. 北京: 国家市场监督管理总局/国家标准化管理委员会. 2019. |
| Lu H Q, Zhang Y H, Feng M, Li B B, Liu A G, Mao F, Zhuang L W, Li Y J, Wu M X. Meteorological Grades of Hot Damage to Rice: GB/T37744―2019[S]. Beijing: State Administration for Market Regulation/State Standardization Administration, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | Shi P H, Tang L, Lin C B, Liu L L, Wang H H, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Modeling the effects of post-anthesis heat stress on rice phenology[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 177: 26-36. |
| [21] | 石春林, 金之庆, 郑建初, 汤日圣. 减数分裂期高温对水稻颖花结实率影响的定量分析[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(4): 627-631. |
| Shi C L, Jin Z Q, Zheng J C, Tang R S. Quantitative analysis on the effects of high temperature at meiosis stage on seed-setting rate of rice florets[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(4): 627-631. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Tao F L, Zhang S, Zhang Z. Changes in rice disasters across China in recent decades and the meteorological and agronomic causes[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2013, 13(4): 743-759. |
| [23] | 陈升孛, 吴坤悌, 陈明, 赵蕾, 张亚杰. 海南早稻灌浆成熟期高温热害对千粒重的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(27): 8-11. |
| Chen S B, Wu K T, Chen M, Chen M, Zhang Y J. High temperature damage at grain filling stage of early rice in Hainan: Effects on 1000-grain weight[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(27): 8-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Muhammad S A, Muhammad F, Folkard A, Jagadish S V K, Prasad P V, Kadambot H M S. Thermal stress impacts reproductive development and grain yield in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 115: 57-72. |
| [25] | 曹云英, 段骅, 杨立年, 王志琴, 周少川, 杨建昌. 减数分裂期高温胁迫对耐热性不同水稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. |
| Cao Y Y, Duan Y, Yang L N, Wang Z Q, Zhou S C, Yang J C. Effect of heat-stress during meiosis on grain yield of rice cultivars differing in heat-tolerance and its physiological mechanism[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 石春林, 金之庆, 汤日圣, 郑建初. 水稻颖花结实率对减数分裂期和开花期高温的响应差异[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2010, 26(6): 1139-1142. |
| Shi C L, Jin Z Q, Tang R S, Zheng J C. Response difference of seed setting rate of rice florets at the meiosis and anthesis stages to high temperature[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 26(6): 1139-1142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Hu Q, Wang W, Lu Q, Huang J L, Peng S B, Cui K H. Abnormal anther development leads to lower spikelet fertility in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under high temperature during the panicle initiation stage[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 428. |
| [28] | 宋有金, 吴超. 高温影响水稻颖花育性的生理机制综述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(16): 41-48. |
| Song Y J, Wu C. Physiological mechanism of high temperature affecting fertility of rice spikelets: A review[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(16): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 陈建珍, 闫浩亮, 刘科, 穆麒麟, 朱开典, 张运波, 田小海. 大穗型水稻品种抽穗开花期遭遇高温后的结实表现[J]. 中国农业气象, 2018, 39(2): 84-91. |
| Chen J Z, Yan H L, Liu K, Mu Q L, Zhu K D, Zhang Y B, Tian X H. Seed-set of large-panicle rice cultivars suffered from high temperature at anthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2018, 39(2): 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Mahmood A, Wang W, Ali I, Zhen F X, Raheel O, Liu B, Liu L L, Zhu Y, Cao W X, Tang L. Individual and combined effects of booting and flowering high- temperature stress on rice biomass accumulation[J]. Plants (Basel), 2021, 10(5): 1021. |
| [31] | 褚丽敏, 赵洪利, 韩万海. 灌浆结实期高温胁迫对水稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 现代化农业, 2015(5): 1-2. |
| Chu L M, Zhao H L, Han W H. Effects of high temperature stress on yield and quality of rice during filling stage[J]. Modernizing Agriculture, 2015(5): 1-2. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | Shi P H, Zhu Y, Tang L, Chen J L, Sun T, Cao W X, Tian Y C. Differential effects of temperature and duration of heat stress during anthesis and grain filling stages in rice[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 132: 28-41. |
| [33] | Park J R, Kim E G, Jang Y H, Kim K M. Screening and identification of genes affecting grain quality and spikelet fertility during high-temperature treatment in grain filling stage of rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 263. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||