
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 601-610.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211212
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Yuliang1,#, YANG Yong1,#, LI Xuefei1, LI Qianfeng1, HUANG Lichun1, ZHANG Changquan1, SONG Xuetang2, LIU Qiaoquan1,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-12
Revised:2022-03-30
Online:2022-11-10
Published:2022-11-10
Contact:
LIU Qiaoquan
About author:First author contact:# These authors contributed equally to this work
史玉良1,#, 杨勇1,#, 李雪飞1, 李钱峰1, 黄李春1, 张昌泉1, 宋学堂2, 刘巧泉1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
刘巧泉
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:SHI Yuliang, YANG Yong, LI Xuefei, LI Qianfeng, HUANG Lichun, ZHANG Changquan, SONG Xuetang, LIU Qiaoquan. Comparison of Grain Quality Profiles of japonica Soft Rice Varieties with Different Amylose Contents[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 601-610.
史玉良, 杨勇, 李雪飞, 李钱峰, 黄李春, 张昌泉, 宋学堂, 刘巧泉. 不同直链淀粉含量软米品种品质性状的比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 601-610.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211212
| 品种 Variety | Wx基因型 Wx genotype | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content /% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | Wxb | 15.86±0.47 a | 63.33±4.51 d | 8.08±0.05 a | 62.50±1.29 d |
| 常12 Chang 12 | Wxb | 16.01±0.52 a | 60.25±2.65 d | 7.73±0.16 b | 67.25±0.96 c |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | Wxmp | 10.89±0.21 b | 86.67±3.21 c | 7.88±0.17 b | 80.00±0.82 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | Wxmp | 10.65±0.36 b | 87.53±4.52 c | 7.62±0.16 b | 81.50±1.09 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | Wxb | 8.78±0.21 c | 91.67±5.67 b | 7.73±0.34 b | 83.50±1.29 a |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | Wxb | 8.58±0.14 c | 93.46±6.21 b | 7.61±0.27 b | 83.25±1.31 a |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | wx | 2.34±0.20 d | 112.67±8.25 a | 8.02±0.11 a | |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | wx | 2.41±0.24 d | 108.33±7.26 a | 7.93±0.14 ab |
Table 1. Wx genotype and grain quality profiles of different japonica rice varieties.
| 品种 Variety | Wx基因型 Wx genotype | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content /% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | Wxb | 15.86±0.47 a | 63.33±4.51 d | 8.08±0.05 a | 62.50±1.29 d |
| 常12 Chang 12 | Wxb | 16.01±0.52 a | 60.25±2.65 d | 7.73±0.16 b | 67.25±0.96 c |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | Wxmp | 10.89±0.21 b | 86.67±3.21 c | 7.88±0.17 b | 80.00±0.82 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | Wxmp | 10.65±0.36 b | 87.53±4.52 c | 7.62±0.16 b | 81.50±1.09 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | Wxb | 8.78±0.21 c | 91.67±5.67 b | 7.73±0.34 b | 83.50±1.29 a |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | Wxb | 8.58±0.14 c | 93.46±6.21 b | 7.61±0.27 b | 83.25±1.31 a |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | wx | 2.34±0.20 d | 112.67±8.25 a | 8.02±0.11 a | |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | wx | 2.41±0.24 d | 108.33±7.26 a | 7.93±0.14 ab |
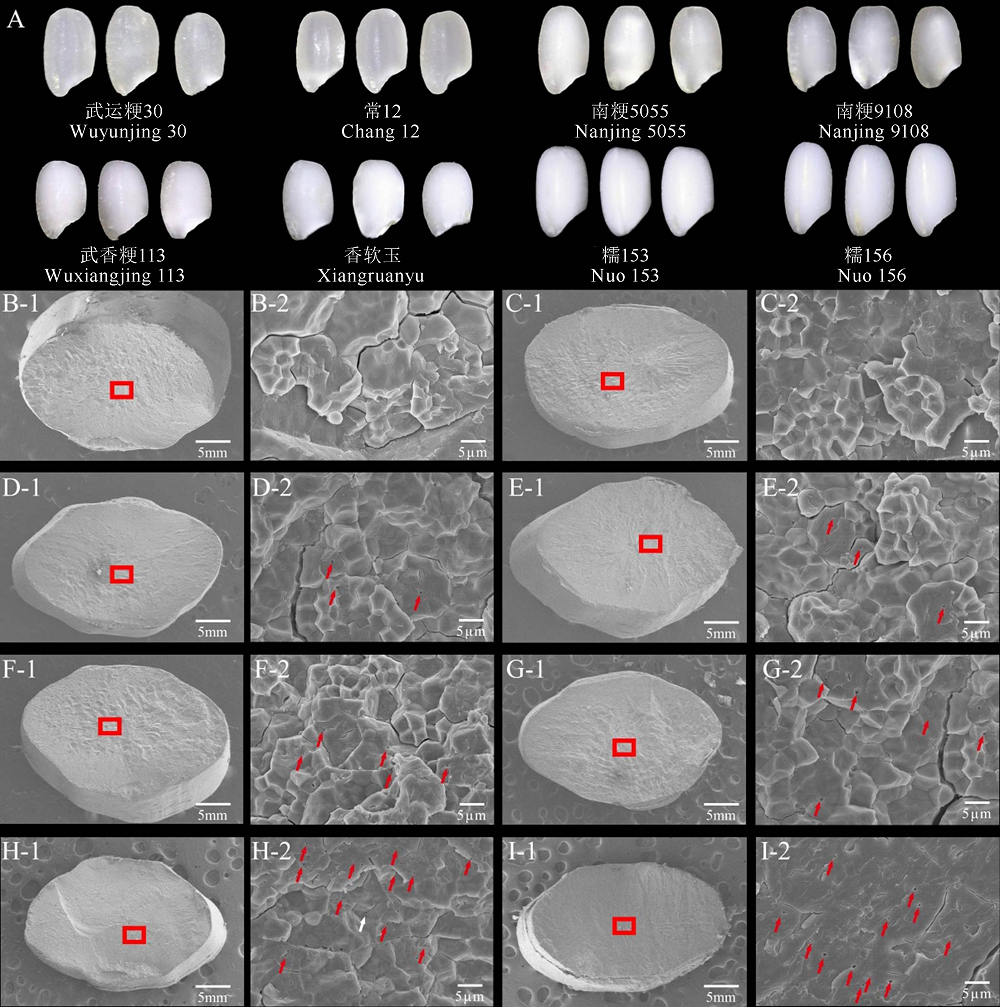
Fig. 1. Grain appearance (A) and SEM observation of rice grain cross-section (B-I) from different rice varieties. B-I indicate rice varieties Wuyunjing 30, Chang 12, Nanjing 5055, Nanjing 9108, Wuxiangjing 113, Xiangruanyu, Nuo 153, and Nuo 156.
| 品种 Variety | 峰值黏度 | 热浆黏度 | 崩解值 | 冷胶黏度 | 消减值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKV / cP | HPV / cP | BDV / cP | CPV / cP | SBV / cP | |
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing30 | 3659±62 b | 2410±64 a | 1249±38 d | 3387±121 b | −272.5±58 a |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 3839±36 a | 2400±38 a | 1439±35 c | 3625±74 a | −213.5±37 a |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 3347±39 c | 2134±42 b | 1262±25 d | 2960±44 c | −435.5±14 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 3381±16 c | 2126±64 b | 1155±48 f | 3005±50 c | −376.5±34 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 3212±60 d | 1176±35 d | 2036±24 b | 1579±39 e | −1633.5±20 f |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 3919±34 a | 1394±57 c | 2525±22 a | 1908±69 d | −2011.0±34 g |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 2344±43 e | 941±22 f | 1403±20 c | 1176±28 g | −1168.0±14 e |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 2352±19 e | 1096±12 e | 1255±31 d | 1348±26 f | −1003.0±45 d |
Table 2. RVA characteristics of rice flours from different varieties.
| 品种 Variety | 峰值黏度 | 热浆黏度 | 崩解值 | 冷胶黏度 | 消减值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKV / cP | HPV / cP | BDV / cP | CPV / cP | SBV / cP | |
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing30 | 3659±62 b | 2410±64 a | 1249±38 d | 3387±121 b | −272.5±58 a |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 3839±36 a | 2400±38 a | 1439±35 c | 3625±74 a | −213.5±37 a |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 3347±39 c | 2134±42 b | 1262±25 d | 2960±44 c | −435.5±14 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 3381±16 c | 2126±64 b | 1155±48 f | 3005±50 c | −376.5±34 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 3212±60 d | 1176±35 d | 2036±24 b | 1579±39 e | −1633.5±20 f |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 3919±34 a | 1394±57 c | 2525±22 a | 1908±69 d | −2011.0±34 g |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 2344±43 e | 941±22 f | 1403±20 c | 1176±28 g | −1168.0±14 e |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 2352±19 e | 1096±12 e | 1255±31 d | 1348±26 f | −1003.0±45 d |
| 品种 Variety | 起始温度 T0 / ℃ | 峰值温度 TP / ℃ | 终止温度 TC / ℃ | 热焓值 △H /(J·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | 62.52±0.14 b | 67.80±0.14 c | 75.20±0.14 c | 9.48±0.04 d |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 60.70±0.14 d | 66.55±0.35 d | 73.40±0.28 e | 9.37±0.04 d |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 62.15±0.07 c | 67.45±0.21 c | 74.40±0.14 d | 10.25±0.01 c |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 63.15±0.07 a | 69.05±0.07 a | 77.30±0.14 a | 10.03±0.02 c |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 62.65±0.21 b | 69.30±0.14 a | 77.20±0.14 a | 11.60±0.02 b |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 62.70±0.28 b | 68.40±0.14 b | 76.30±0.14 b | 11.46±0.00 b |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 59.55±0.07 e | 66.65±0.07 d | 75.55±0.07 c | 12.70±0.02 a |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 60.40±0.00 d | 66.60±0.14 d | 76.25±0.49 b | 12.80±0.14 a |
Table 3. Thermal profiles of rice starch from different rice varieties.
| 品种 Variety | 起始温度 T0 / ℃ | 峰值温度 TP / ℃ | 终止温度 TC / ℃ | 热焓值 △H /(J·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | 62.52±0.14 b | 67.80±0.14 c | 75.20±0.14 c | 9.48±0.04 d |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 60.70±0.14 d | 66.55±0.35 d | 73.40±0.28 e | 9.37±0.04 d |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 62.15±0.07 c | 67.45±0.21 c | 74.40±0.14 d | 10.25±0.01 c |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 63.15±0.07 a | 69.05±0.07 a | 77.30±0.14 a | 10.03±0.02 c |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 62.65±0.21 b | 69.30±0.14 a | 77.20±0.14 a | 11.60±0.02 b |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 62.70±0.28 b | 68.40±0.14 b | 76.30±0.14 b | 11.46±0.00 b |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 59.55±0.07 e | 66.65±0.07 d | 75.55±0.07 c | 12.70±0.02 a |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 60.40±0.00 d | 66.60±0.14 d | 76.25±0.49 b | 12.80±0.14 a |
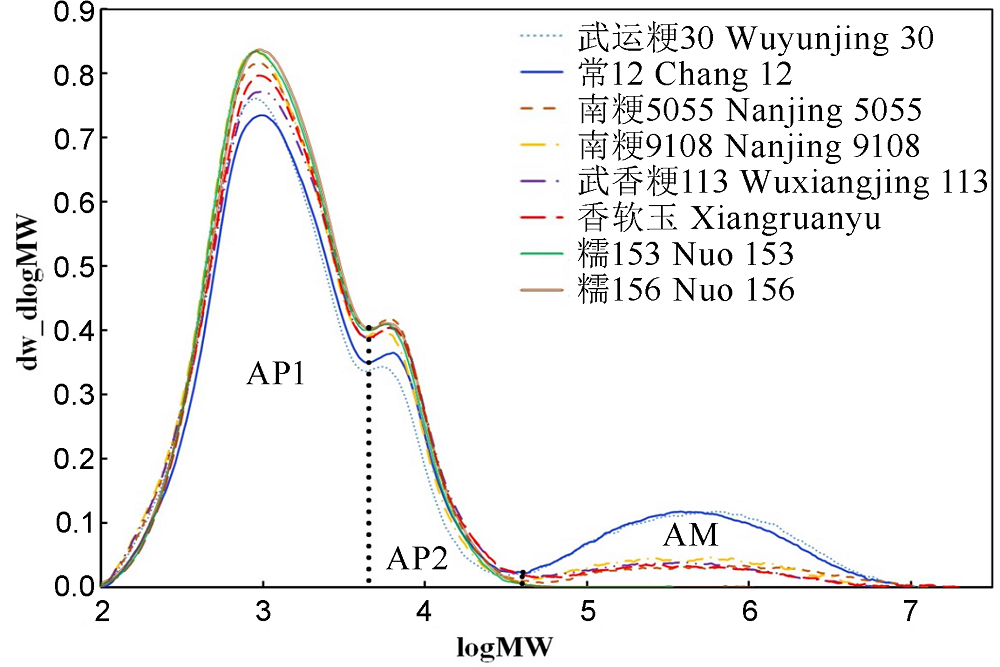
Fig. 3. Relative molecular weight distribution of rice starch from different varieties. AP1, AP2, and AM correspond to the short-branch chains of amylopectin, long-branch chains of amylopectin and amylose fraction, respectively.
| 品种 Variety | AP1 | AP2 | AM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | 66.99±0.27 c | 16.16±0.26 b | 16.84±1.44 a |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 67.24±0.27 c | 16.38±0.41 b | 16.37±0.24 a |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 76.09±0.22 b | 17.74±0.32 a | 6.06±0.35 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 75.80±0.57 b | 18.77±0.23 a | 5.92±0.40 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 76.66±0.61 b | 18.61±0.59 a | 4.71±0.21 c |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 76.26±0.60 b | 18.99±0.46 a | 4.73±0.05 c |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 82.16±0.36 a | 17.83±0.36 a | 0.0 |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 81.96±0.17 a | 18.03±0.17 a | 0.0 |
Table 4. GPC parameters of rice starch from different rice varieties. %
| 品种 Variety | AP1 | AP2 | AM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30 Wuyunjing 30 | 66.99±0.27 c | 16.16±0.26 b | 16.84±1.44 a |
| 常12 Chang 12 | 67.24±0.27 c | 16.38±0.41 b | 16.37±0.24 a |
| 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 | 76.09±0.22 b | 17.74±0.32 a | 6.06±0.35 b |
| 南粳9108 Nanjing 9108 | 75.80±0.57 b | 18.77±0.23 a | 5.92±0.40 b |
| 武香粳113 Wuxiangjing 113 | 76.66±0.61 b | 18.61±0.59 a | 4.71±0.21 c |
| 香软玉 Xiangruanyu | 76.26±0.60 b | 18.99±0.46 a | 4.73±0.05 c |
| 糯153 Nuo 153 | 82.16±0.36 a | 17.83±0.36 a | 0.0 |
| 糯156 Nuo 156 | 81.96±0.17 a | 18.03±0.17 a | 0.0 |
| [1] | Zhou H, Xia D, He Y Q. Rice grain quality traditional traits for high quality rice and health-plus substances[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2020, 40(1): 1-17. |
| [2] | Li H Y, Prakash S, Nicholson T M, Fitzgerald M A, Gilbert R G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 196: 702-711. |
| [3] | Tian Z X, Qian Q, Liu Q Q, Yan M X, Liu X F, Yan C J, Liu G F, Gao Z Y, Tang S Z, Zeng D L, Wang Y H, Yu J M, Gu M H, Li J Y. Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(51): 21760-21765. |
| [4] | 张昌泉, 冯琳皓, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 江苏省水稻品质性状遗传和重要基因克隆研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(5): 425-441. |
| Zhang C Q, Feng L H, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progress on inheritance and gene cloning for rice grain quality in Jiangsu Province[J]. Hereditas, 2021, 43(5): 425-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Shao Y, Peng Y, Mao B G, Lü Q M, Yuan D Y, Liu X L, Zhao B R. Allelic variations of the Wx locus in cultivated rice and their use in the development of hybrid rice in China[J]. Plos ONE, 2020, 15(5): 0232279. |
| [6] | 王才林, 张亚东, 赵春芳, 魏晓东, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 路凯, 梁文化. 江苏省优良食味粳稻的遗传与育种研究[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(5): 442-458. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhao C F, Wei X D, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Lu K, Liang W H. Inheritance and breeding of japonica rice with good eating quality in Jiangsu Province[J]. Hereditas, 2021, 43(5): 442-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 陈智慧, 王芳权, 许扬, 王军, 李文奇, 范方军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 软米基因Wx-mp在部分粳稻品种资源中的分布[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. |
| Chen Z H, Wang F Q, Xu Y, Wang J, Li W Q, Fan F J, Zhong W G, Yang J. The distribution of low amylose content allele Wx-mp in Japonica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Zhang C Q, Yang Y, Chen S J, Liu X Y, Zhu J H, Zhou L H, Lu Y, Li Q F, Fan X L, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. A rare Waxy allele coordinately improves rice eating and cooking quality and grain transparency[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(5): 889-901. |
| [9] | Zhang C Q, Zhu J H, Chen S J, Fan X L, Li Q F, Lu Y, Wang M, Yu H X, Yi C D, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Wxlv, the ancestral allele of rice Waxy gene[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1157-1166. |
| [10] | Zhang C Q, Chen S J, Ren X Y, Lu Y, Liu D R, Cai X L, Li Q F, Gao J P, Liu Q Q. Molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from rice with different amylose contents resulting from modification of OsGBSSⅠ activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(10): 2222-2232. |
| [11] | 陆彦, 张晓敏, 祁琰, 张昌泉, 凌裕平, 刘巧泉. 不同透明度水稻籽粒横断面扫描电镜分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(2): 189-199. |
| Lu Y, Zhang X M, Qi Y, Zhang C Q, Ling Y P, Liu Q Q. Scanning electron microscopic analysis of grain cross-section from rice with different transparency[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(2): 189-199. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Zhang L, Zhao L L, Zhang J, Cai X L, Liu Q Q, Wei C X. Relationships between transparency, amylose content, starch cavity, and moisture of brown rice kernels[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2019, 90: 102854. |
| [13] | 吴殿星, 舒庆尧, 夏英武. 利用RVA谱快速鉴别不同表观直链淀粉含量早籼稻的淀粉粘滞特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2001, 15(1): 57-59. |
| Wu D X, Shu Q Y, Xia Y W. Rapid identification of starch viscosity property of early indica rice varieties with different apparent amylose content by RVA profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2001, 15(1): 57-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Li C, Luo J X, Zhang C Q, Yu W W. Causal relations among starch chain-length distributions, short-term retrogradation and cooked rice texture[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020, 108(6): 106064 |
| [15] | Song Y, Jane J. Characterization of barley starches of waxy, normal, and high amylose varieties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2000, 41(4): 365-377 |
| [16] | Zeng D L, Yan M X, Wang Y H, Liu X F, Qian Q, Li J Y. Du1, encoding a novel Prp1 protein, regulates starch biosynthesis through affecting the splicing of Wxb pre-mRNAs in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(4): 501-509. |
| [17] | Kimiko I, Hiroko O, Kyoko O, Hidetaka H, Yasuhito T, Toshiaki M. Introduction of Wx transgene into rice wx mutants leads to both high- and low-amylose rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2003(5): 473-480 |
| [18] | Huang L C, Sreenivasulu N, Liu Q Q. Waxy editing: Old meets new[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(10): 963-966. |
| [19] | Xu Y, Lin Q P, Li X F, Wang F Q, Chen Z H, Wang J, Li W Q, Fan F J, Tao Y J, Jiang Y J, Wei X D, Zhang R, Zhu Q H, Bu Q Y, Yang J, Gao C X. Fine-tuning the amylose content of rice by precise base editing of the Wx gene[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(1): 11-13. |
| [20] | Takemoto-Kuno Y, Mitsueda H, Suzuki K, Hirabayashi H, Ideta O, Aoki N Umemoto T, Ishii T, Ando I, Kato H, Nemoto H, Imbe T, Takeuchi Y. qAC2, a novel QTL that interacts with Wx and controls the low amylose content in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128(4): 563-573. |
| [21] | Igarashi H, Ito H, Shimada T, Kang D J, Hamada S. A novel rice dull gene, LowAC1, encodes an RNA recognition motif protein affecting Waxy pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 162: 100-109. |
| [22] | Zhang H, Xu H, Feng M J, Zhu Y. Suppression of OsMADS7 in rice endosperm stabilizes amylose content under high temperature stress[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(1): 18-26. |
| [23] | Huang L C, Tan H Y, Zhang C Q, Li Q F, Liu Q Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(5): 100237. |
| [24] | Butardo V M, Sreenivasulu N, Juliano B O. Improving rice grain quality: State-of-the-Art and future prospects//Clifton N J. Methods in Molecular Biology[M]. Springer, 2019: 19-55. |
| [25] | Zhou H, Xia D, Zhao D, Li Y H, Li P B, Wu B, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, Wang G W, Xiao J H, Li S B, Lian X M, He Y Q. The origin of Wxla provides new insights into the improvement of grain quality in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2020, 63(5): 878-888. |
| [26] | Zhang H, Zhou L H, Xu H, Wang LC, Liu H J, Zhang C Q, Li Q F, Gu M H, Wang C L, Liu Q Q, Zhu Y. The qSAC3 locus from indica rice effectively increases amylose content under a variety of conditions[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 275. |
| [27] | Li Q F, Huang L C, Chu R, Li J, Jiang M Y, Zhang C Q, Fan X L, Yu H X, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Down-regulation of SSSII-2 gene expression results in novel low-amylose rice with soft, transparent grains[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(37): 9750-9760. |
| [28] | Zhang L X, Zhang C Q, Yan Y, Hu Z J, Wang K, Zhou J H, Zhou Y, Cao L M, Wu S J. Influence of starch fine structure and storage proteins on the eating quality of rice varieties with similar amylose contents[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 101(9): 3811-3818. |
| [29] | Chen Z Z, Lu Y, Feng L H, Hao W Z, Yang Y, Fan X L, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Liu Q Q. Genetic dissection and functional differentiation of ALKa and ALKb, two natural alleles of the ALK/SSIIa gene, responding to low gelatinization temperature in rice. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 39. |
| [30] | Nakata M, Miyashita T, Kimura R, Nakata Y, Takagi H, Kuroda M, Yamaguchi T, Umemoto T, Yamakawa H. MutMapPlus identified novel mutant alleles of a rice starch branching enzyme IIb gene for fine-tuning of cooked rice texture[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 16(1): 111-123. |
| [31] | Wang L L, Gong Y, Li Y X, Tian Y Q. Structure and properties of soft rice starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 157: 10-16. |
| [32] | Wang S Y, Yang Y H, Guo M, Zhong C Y, Yan C J, Sun S Y. Targeted mutagenesis of amino acid transporter genes for rice quality improvement using the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. The Crop Journal, 2020, 8(3): 457-464. |
| [33] | Sreenivasulu N, Zhang C Q, Tiozon R N, Liu Q Q. Post-genomics revolution in the design of premium quality rice in a high-yielding background to meet consumer demands in the 21st century[J]. Plant Communications, 2022, 3(3): 100271. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||