
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 610-618.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.06.007
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qing ZHANG1, Juan WANG1, Li-quan JING1, Lian-xin YANG1, Yun-xia WANG2,*( )
)
Received:2015-07-25
Revised:2015-09-26
Online:2015-10-25
Published:2015-11-10
Contact:
Yun-xia WANG
About author:*Corresponding author:E-mail:yxwang@yzu.edu.cn
张庆1, 王娟1, 景立权1, 杨连新1, 王云霞2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
王云霞
作者简介:*通讯录作者:E-mail:yxwang@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:Qing ZHANG, Juan WANG, Li-quan JING, Lian-xin YANG, Yun-xia WANG. Effect of Foliar Application of Different Zn Compounds on Zn Concentration and Bioavailability in Brown Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(6): 610-618.
张庆, 王娟, 景立权, 杨连新, 王云霞. 叶面施用不同形态锌化合物对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 610-618.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.06.007
| 参数 Parameters | 锌 Zn | 品种 Cultivar (C) | 部位 Part (P) | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锌浓度Zn concentration | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| 植酸浓度PA concentration | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.602 | <0.001 | 0.385 |
| 植酸与锌摩尔比Molar ratio of PA to Zn | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.049 |
Table 1 Significance test for Zn concentration, phytic acid (PA) concentration and the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) of brown rice among different Zn treatments (P value).
| 参数 Parameters | 锌 Zn | 品种 Cultivar (C) | 部位 Part (P) | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锌浓度Zn concentration | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| 植酸浓度PA concentration | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.602 | <0.001 | 0.385 |
| 植酸与锌摩尔比Molar ratio of PA to Zn | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.049 |
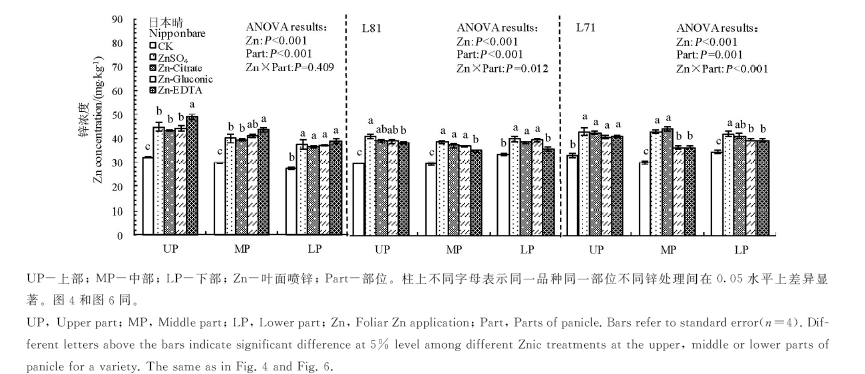
Fig. 2. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on Zn concentrations in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
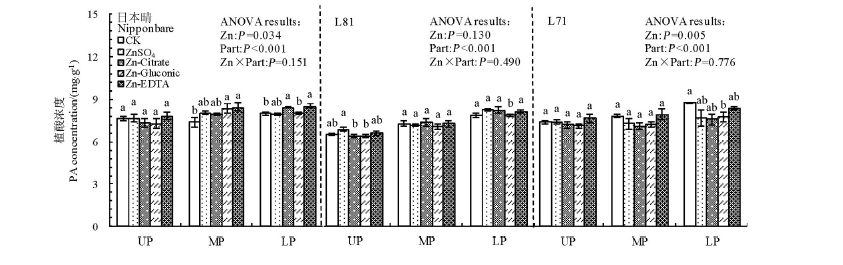
Fig. 4. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on phytic acid (PA) concentrations in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
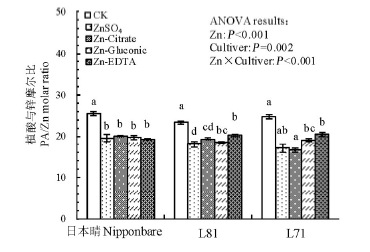
Fig. 5. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn compounds on the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) in brown rice of Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
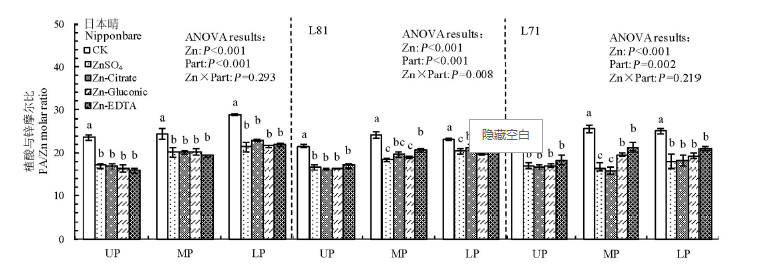
Fig. 6. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
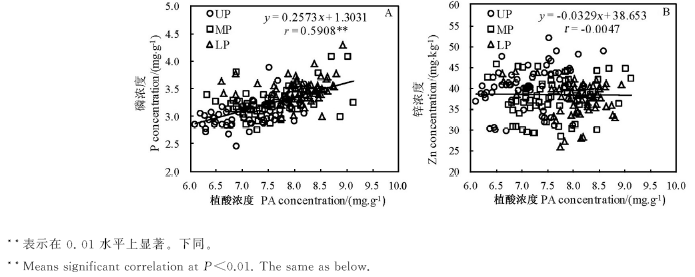
Fig. 7. Relationship between concentrations of phytic acid (PA) and P (A) or Zn (B) in brown rice from different parts of panicles of tested rice cultivars (n=180).
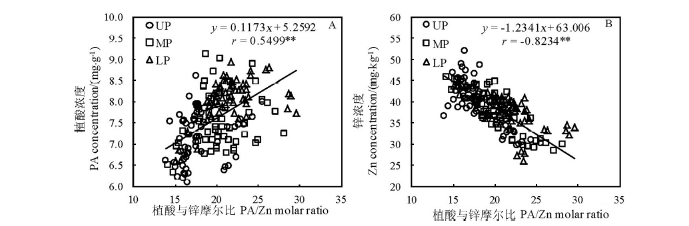
Fig. 8. Relationship between PA/Zn molar ratios and concentrations of Zn or PA in brown rice from different parts of panicles of tested cultivars (n=180)
| 参数 Parameter | 锌 Zn | 品种 C | 部位 P | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 0.337 | 0.056 | 0.256 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.513 | 1.000 |
| 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 0.845 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.096 | 0.279 | <0.001 | 0.993 |
Table 2 Significance test for brown rice rate and grain yield of rice among different treatments (P value).
| 参数 Parameter | 锌 Zn | 品种 C | 部位 P | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 0.337 | 0.056 | 0.256 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.513 | 1.000 |
| 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 0.845 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.096 | 0.279 | <0.001 | 0.993 |
| [1] | 黄秋蝉, 韦友欢, 石景芳. 微量元素锌对人体健康的生理效应及其防治途径. 微量元素与健康研究, 2009, 26(1): 68-70. |
| [2] | WHO. Reducing risks, promoting healthy life//World Health Organization. The World Health Report. Geneva, Switzerland:WHO, 2002. |
| [3] | Cakmak I.Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification.Plant Soil, 2008, 302: 1-17. |
| [4] | 邹春琴, 张福锁. 籽粒铁、锌营养与人体健康研究进展. 广东微量元素科学, 2006, 13(7): 1-8. |
| [5] | 郭九信, 廖文强, 孙玉明, 等. 锌肥施用方法对水稻产量及籽粒氮锌含量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 185-192. |
| [6] | Cakmak I, Pfeiffer W H, McClafferty B, et al. Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron.Cereal Chem, 2010, 87: 10-20. |
| [7] | Cakmak I.Enrichment of fertilizers with zinc: An excellent investment for humanity and crop production in India.J Trace Elem Med Bio, 2009, 23: 281-289. |
| [8] | Wang Y X, Specht A, Horst W J.Stable isotope labelling and zinc distribution in grains studied by laser ablation ICP-MS in an ear culture system reveals zinc transport barriers during grain filling in wheat.New Phytol, 2011, 189: 428-437. |
| [9] | 曹玉贤, 田霄鸿, 李秀丽, 等.土施和喷施锌肥对冬小麦子粒锌含量及生物有效性的影响.植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(6): 1394-1401. |
| [10] | 李辛, 李志洪, 孙建华, 等.土壤施锌和叶面喷锌对风沙土玉米Zn吸收与积累的影响.西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 42(1):144-150. |
| [11] | ZhangY Q, Sun Y X, Ye Y L,et al. Zinc biofortification of wheat through fertilizer applications in different locations of China.Field Crops Res, 2012, 125: 1-7. |
| [12] | Wei Y Y,Shohag M J I,Yang X E. Biofortification and bioavailability of rice grain zinc asaffected by different forms of foliar zinc fertilization.PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(9): 1-10. |
| [13] | Haslett B S, Reid R J, Rengel Z.Zinc mobility in wheat: Uptake and distribution of zinc applied to leaves or roots.AnnBot, 2001, 87: 379-386. |
| [14] | Wu C, Lu L, Yang X, et al.Uptake, translocation, and remobilization of zinc absorbed at different growth stages by rice genotypes of different Zn densities.J Agric Food Chem, 58: 6767-6773. |
| [15] | Harris N S, Taylor G J.Remobilization of cadmium in maturing shoots of near isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium accumulation.J Exp Bot, 2001, 52: 1473-1481. |
| [16] | 王云霞, 杨连新, Horst W J.重金属复合处理对小麦铜锌镍镉积累和分布的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(11):2145-2151. |
| [17] | 王云霞, 杨连新, Horst W J.用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱研究小麦籽粒元素的共分布. 作物学报, 2012, 38(3): 514-521. |
| [18] | Frossard E, Bucher M, Mächler F, et al.Potential for increasing the content and bioavailability of Fe, Zn and Ca in plants for human nutrition.JSci Food Agr, 2000, 80: 861-879. |
| [19] | Palmgren M G, Clemens S, Williams L E, et al.Zinc biofortification of cereals: Problems and solutions.Trends Plant Sci,2008,13: 464-473. |
| [20] | Fang Y, Wang L, Xin Z, et al.Effect of foliar application of zinc, selenium, and iron fertilizers on nutrients concentration and yield of rice grain in China.J Agric Food Chem,2008,56: 2079-2084. |
| [21] | Wissuwa M, Ismail A M, Graham R D.Rice grain zinc concentrations as affected by genotype, native soil-zinc availability, and zinc fertilization.Plant Soil,2008,306: 37-48. |
| [22] | Phattarakul N, Rerkasem B, Li L, et al.Biofortification of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries.Plant Soil,2012, 361: 131-141. |
| [23] | 周三妮, 赖上坤, 吴艳珍, 等. 大气CO2浓度升高和叶面施锌对武运粳23稻米不同部位锌浓度和有效性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(9):1689-1692. |
| [24] | 周三妮, 王云霞, 赖上坤, 等. FACE下二氧化碳、施氮量、密度和锌肥对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响.中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3):289-296. |
| [25] | Colle C, Madoz-Escande C, Leclerc E.Foliar transfer into the biosphere: Review of translocation factors to cereal grains.J Environ Radioactiv,2009, 100: 683-689. |
| [26] | Amrani M, Westfall D, Peterson G.Influence of water solubility of granular zinc fertilizers on plant uptake and growth.J Nutr, 1999, 22(12): 1815-1827. |
| [27] | Karak T, Singh U, Das S, et al.Comparative efficacy of ZnSO4 and Zn-EDTA application for fertilization of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Arch Agron Soil Sci, 2005,51(3): 253-264. |
| [28] | Wang Y X, Yang L X, Höller M, et al.Pyramiding of ozone tolerance QTLs OzT8 and OzT9 confers improved tolerance to season-long ozone exposure in rice.Environ Exp Bot, 2014,104: 26-33. |
| [29] | 周三妮. 不同条件下结实期叶面施锌对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响. 扬州:扬州大学, 2015:1-91. |
| [30] | Lapteva N A.Colorimetric determination of phytate in unpurified extracts of seeds and the products of their processing.Anal Biochem, 1988, 175: 227-230. |
| [31] | 付力成, 王人民, 孟杰, 等. 叶面锌、铁配施对水稻产量、品质及铁锌分布的影响及其品种差异.中国农业科学, 2010, 43(24): 5009-5018. |
| [32] | 李宏云, 王少霞, 李萌, 等. 不同水氮管理下锌与氮磷肥配合喷施对冬小麦锌营养品质的影响.中国农业科学, 2014, 47(20): 4016-4026. |
| [33] | 李燕婷, 李秀英, 肖艳, 等. 叶面肥的营养机理及应用研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(1):162-172. |
| [34] | 杨芸, 周坤, 徐卫红, 等. 外源铁对不同品种番茄光合特性、品质及镉积累的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(4):1006-1015. |
| [35] | 付景, 徐云姬, 陈露, 等. 超级稻花后强弱势粒淀粉合成相关酶活性和激素含量变化及其与籽粒灌浆的关系. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3):302-310. |
| [36] | Cheryan M, Rackis J.Phytic acid interactions in food systems.Int J Food SciNutr, 1980,13(4): 297-335. |
| [37] | Lonnerdal B.Dietary factors influencing zinc absorption.J Nutr,2000,130: 1378S-1383S. |
| [38] | Ockenden I,Dorsch J A, Reid M M, et al.Characterization of the storage of phosphorus, inositol phosphate and cations in grain tissues of four barley low phytic acid genotypes.Plant Sci, 2004, 167(5):1131-1142. |
| [39] | Persson D P, Hansen T H, Laursen K H, et al.Simultaneous iron, zinc, sulfur and phosphorus speciation analysis of barley grain tissues using SEC-ICP-MS and IP-ICP-MS.Metallomics, 2009, 5: 418-426. |
| [40] | Morris E R, Ellis R.Usefulness of the dietary phyticacid/zinc molar ratio as an index of zinc bioavailabi1ity to rats and humans.Biol Trace Elem Res,1989,19:107-117. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||