
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2026, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 37-50.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2026.250202
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUE Xuanyu1,2, XIE Wenya1,2,3,*( ), FENG Zhiming1,2,3, CHEN Zongxiang1,2,3, HU Keming1,2, ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*(
), FENG Zhiming1,2,3, CHEN Zongxiang1,2,3, HU Keming1,2, ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-11
Revised:2025-05-23
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-21
Contact:
XIE Wenya, ZUO Shimin
岳轩宇1,2, 谢文亚1,2,3,*( ), 冯志明1,2,3, 陈宗祥1,2,3, 胡珂鸣1,2, 左示敏1,2,3,*(
), 冯志明1,2,3, 陈宗祥1,2,3, 胡珂鸣1,2, 左示敏1,2,3,*( )
)
通讯作者:
谢文亚,左示敏
基金资助:YUE Xuanyu, XIE Wenya, FENG Zhiming, CHEN Zongxiang, HU Keming, ZUO Shimin. Function of OsERF93 in Regulating Resistance to Sheath Blight in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 37-50.
岳轩宇, 谢文亚, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. OsERF93参与调控水稻纹枯病抗性的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 37-50.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2026.250202
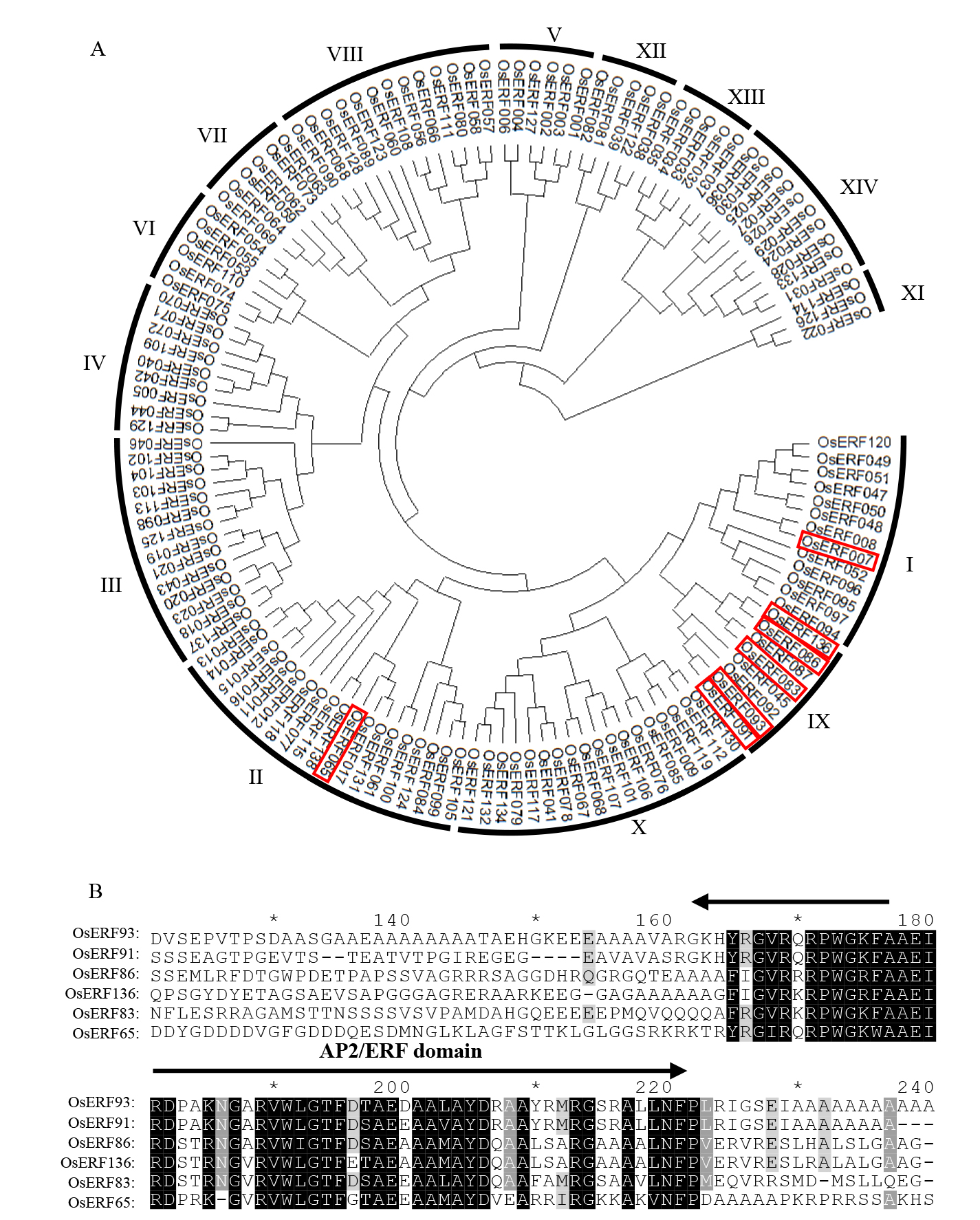
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analysis of rice OsERFs gene family and protein sequence alignment of subfamily containing OsERF93 A, Phylogenetic tree analysis of the ERFs gene family, with the genes highlighted in red boxes showing differential expression in resistant and susceptible materials after inoculation with R. Solani; B, Alignment of protein sequence of ERF family genes involved in sheath blight response.
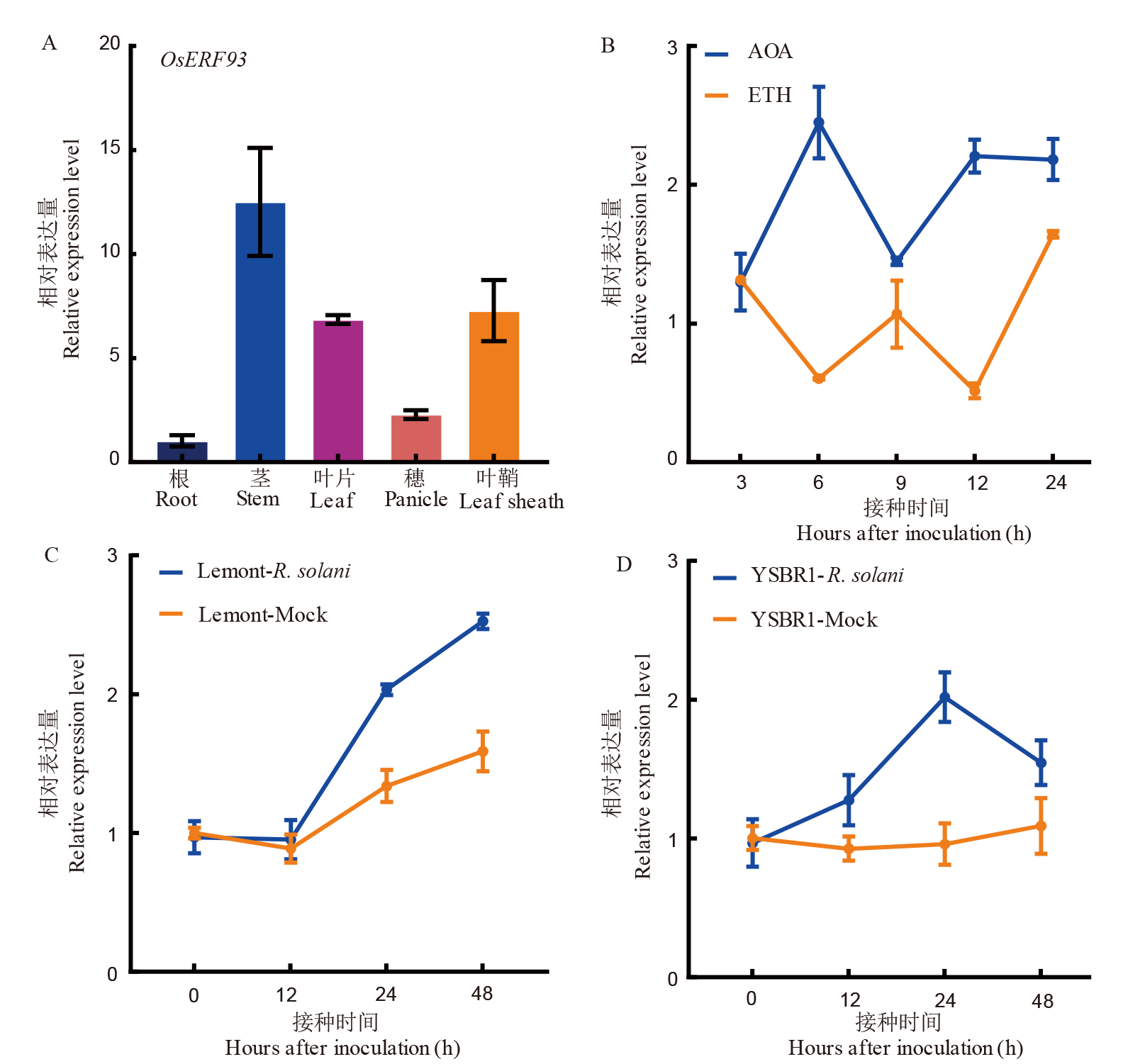
Fig. 2. Analysis of OsERF93 expression pattern A, Tissue-specific expression of OsERF93; B, Differential response of OsERF93 to ETH (Ethylene) and AOA (Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid); C, Relative expression levels of the susceptible variety Lemont after inoculation with sheath blight pathogen; D, Relative expression levels of the resistant variety YSBR1 after inoculation with sheath blight pathogen. In the figures, R. solani represents the treatment group, and Mock represents the control group.
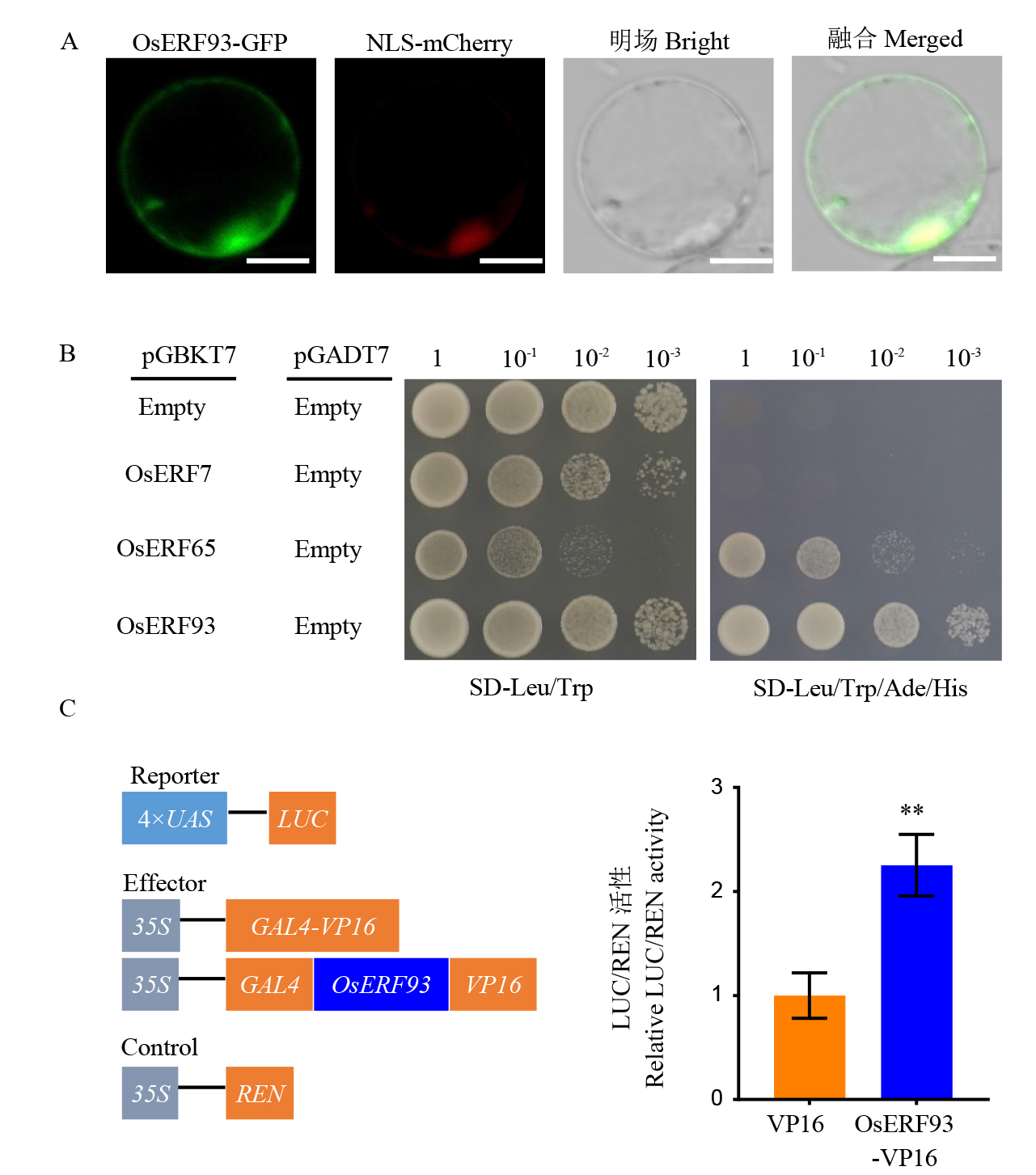
Fig. 3. Analysis of transcriptional activation activity and subcellular localization of OsERF93 A, Subcellular localization of OsERF93 in rice cells(bar=10 μm), and NLS denoting the nuclear localization signal; B, Transcriptional activation activity verified by yeast two-hybrid assay; C, Transient transformation of rice protoplasts, with VP16 serving as the transcriptional activation control. ** indicates a highly significant difference as determined by a t-test with P< 0.01.
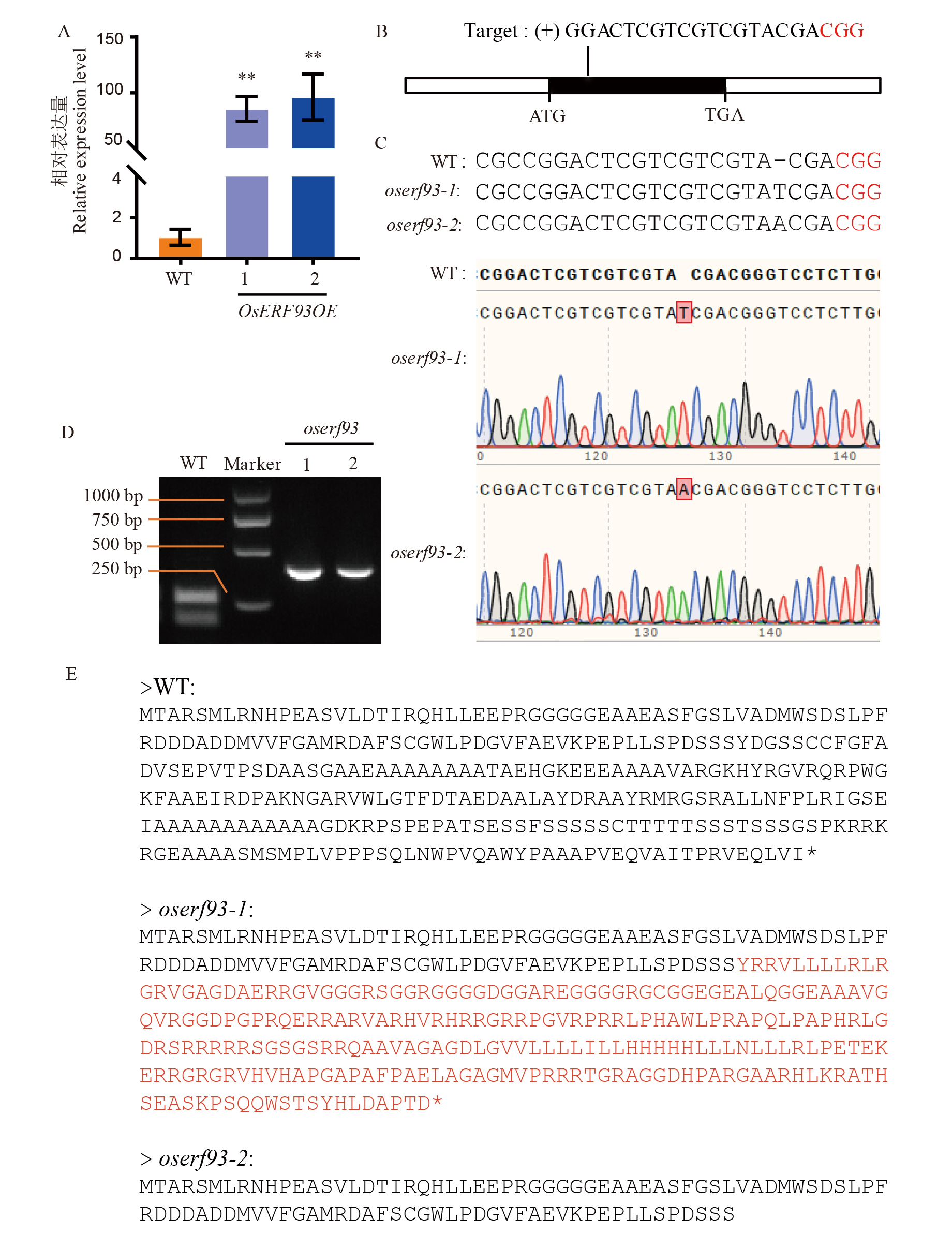
Fig. 4. Relative expression levels of the OsERF93 overexpression lines A, Transcript levels of OsERF93 in two OsERF93 overexpression lines; B, Schematic diagram of OsERF93 gene structure and CRISPR/Cas9 target sites; C, DNA sequence alignment of the identified homozygous oserf93 mutants with the wild-type control; D, CAPS marker validation of oserf93 mutants and wild-type, with primer sequences listed in Table S1, showing fragment lengths of 417 bp for oserf93-1 and oserf93-2, and the wild-type fragments being 248 bp and 169 bp after enzyme digestion; E, Amino acid sequence analysis of the OsERF93 gene encoded in the wild-type and two knockout lines.
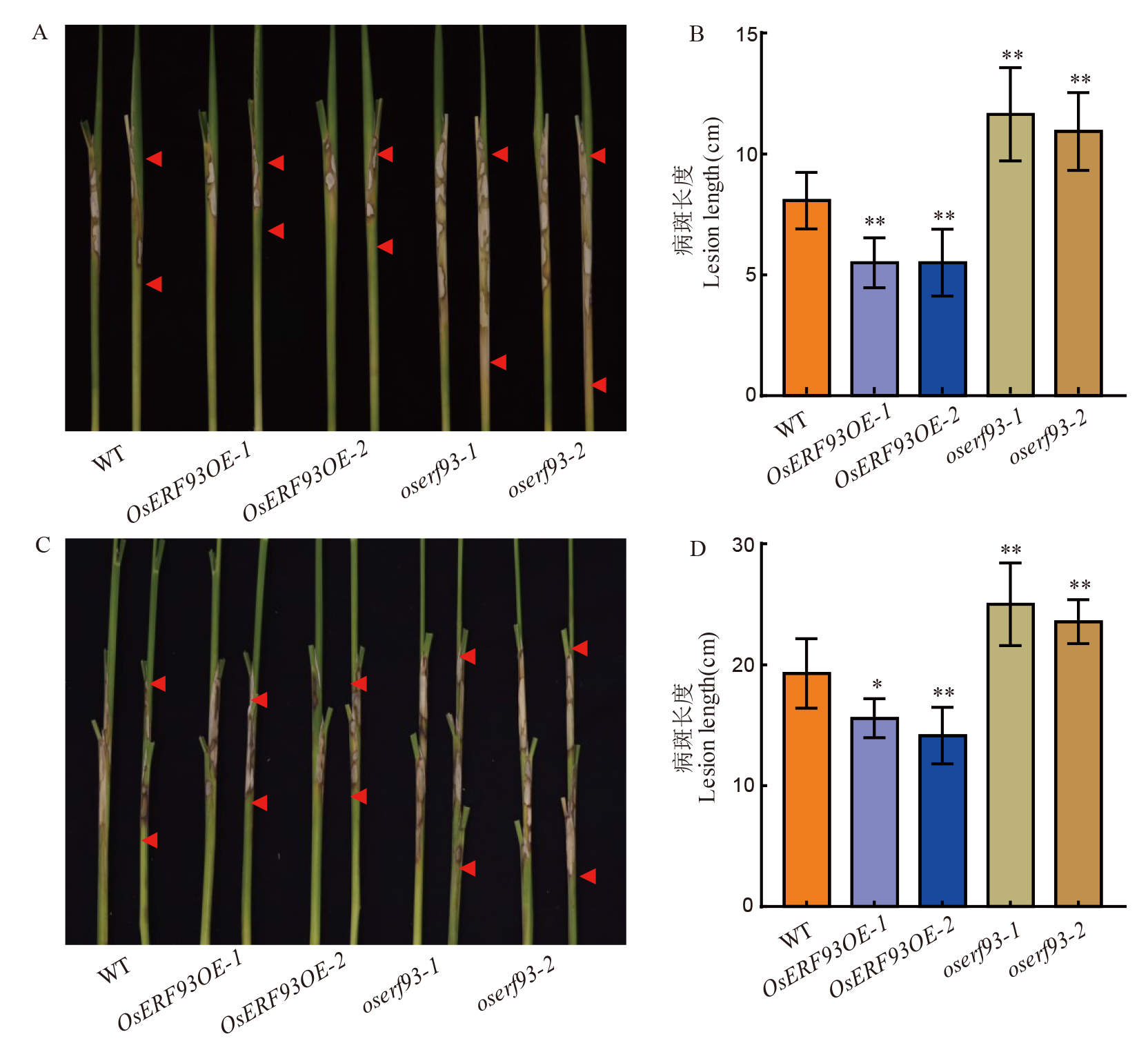
Fig. 5. Resistance evaluation of OsERF93 overexpression and knock-out lines to sheath blight disease A and B respectively present the phenotypic photographs and statistical comparisons of lesion lengths at 5 days post-inoculation in the control and OsERF93-related transgenic lines during the in vitro stem inoculation assay; C and D respectively display the phenotypic photographs and statistical comparisons of lesion heights at 14 days post-inoculation in the OsERF93-related transgenic lines during the greenhouse adult plant inoculation assay. ** and * indicate statistical significance levels of P< 0.01 and P< 0.05, respectively.
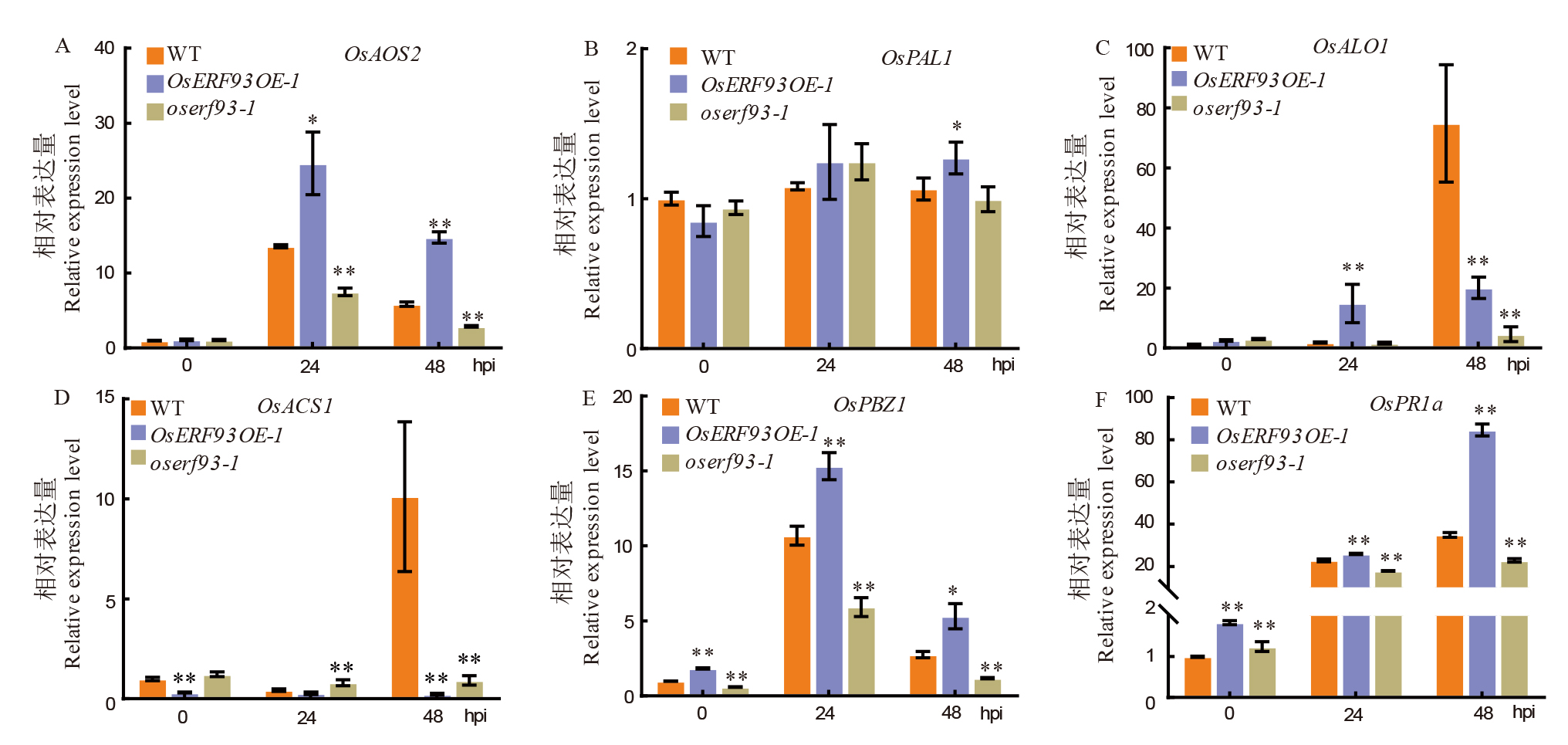
Fig. 6. Expression changes of pathogenesis-related genes in OsERF93 overexpression and knock-out lines after inoculation with sheath blight fungus A and B respectively depict the expression level changes of the jasmonic acid signal related gene OsAOS2 and the salicylic acid pathway marker gene OsPAL1 in the wild-type control and OsERF93-related transgenic lines after inoculation with the sheath blight pathogen; C and D represent the expression changes of ethylene signal related genes OsACO1 and OsACS1 in wild-type and OsERF93-related transgenic lines after inoculation with the sheath blight pathogen; E and F respectively show the expression level changes of the pathogenesis-related protein genes OsPBZ1 and OsPR1a in the wild-type and OsERF93-related transgenic lines after inoculation with the sheath blight pathogen. ** and * denote statistical significance levels of P< 0.01 and P< 0.05, respectively.
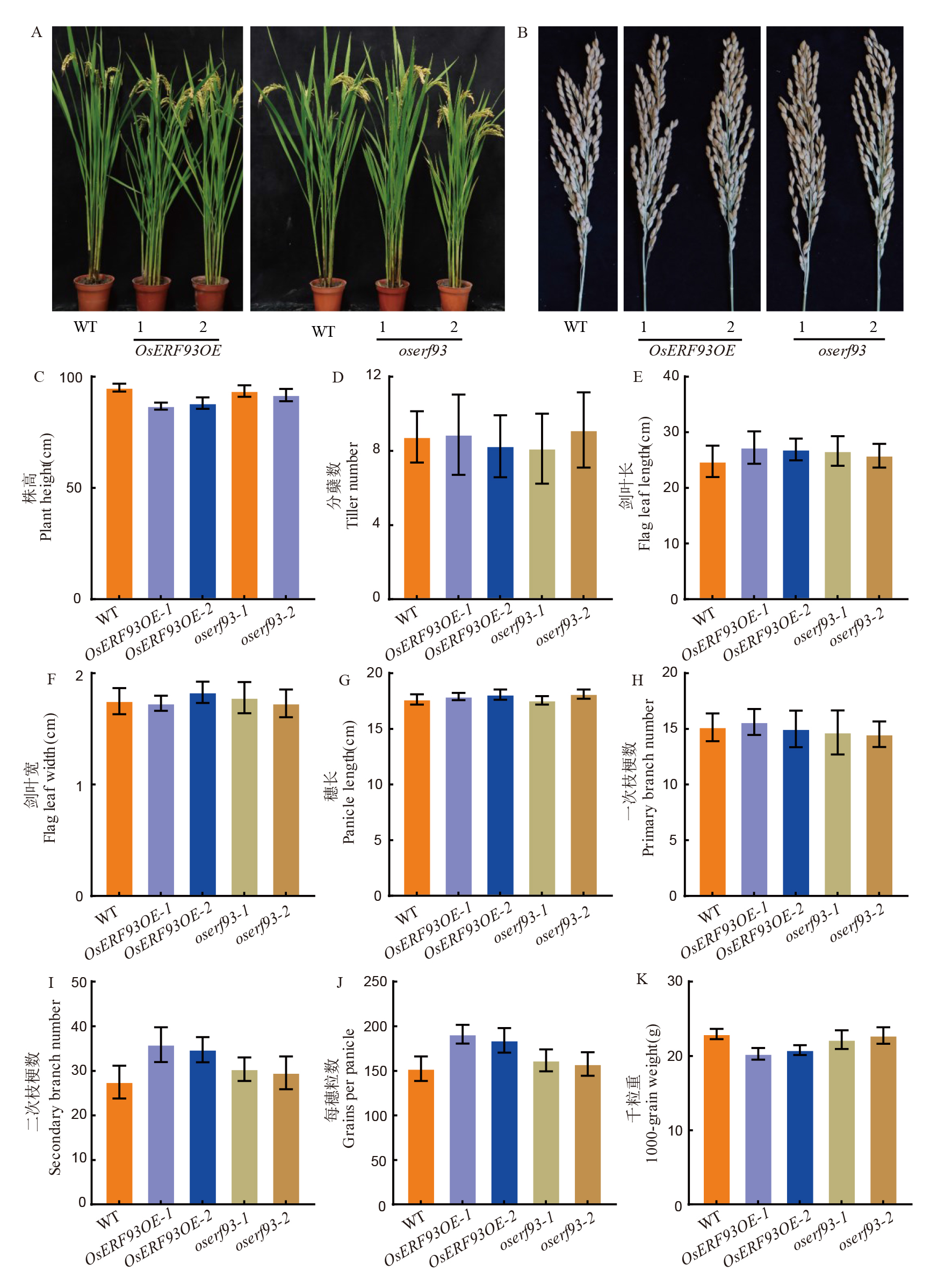
Fig. 7. Comparison of some agronomic traits among WT, OsERF93 overexpression and knock-out transgenic lines A and B show comparisons of plant architecture and panicle morphology between the wild-type (WT), OsERF93 overexpression lines (OsERF93OE-1, OsERF93OE-2), and knockout lines (oserf93-1, oserf93-2). C-K present statistical comparisons of differences between the wild-type(WT), OsERF93 overexpression lines, and knockout lines for traits including plant height (C), tiller number (D), flag leaf length (E), flag leaf width (F), panicle length (G), primary branch number (H), secondary branch number (I), grain number per panicle (J), and 1000-grain weight (K). ** and * indicate statistically significant differences at P< 0.01 and P< 0.05, respectively.
| [1] | Kumar K V K, Reddy M S, Kloepper J W, Lawrence K S, Groth D E, Miller M E. Sheath blight disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.): An overview[J]. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia, 2016, 6(2): 465-480. |
| [2] | Nasimi Z, Barriuso J, Keshavarz T, Zheng A. Molecular, physiological, and biochemical properties of Sclerotia metamorphosis in Rhizoctonia solani[J]. Fungal Biology Reviews, 2024, 48: 100351. |
| [3] | 王爱军, 王娜, 顾思思, 赵文娟, 李平, 郑爱萍. 我国水稻纹枯病菌的融合类群及致病性差异[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27 (7): 55-63. |
| Wang A J, Wang N, Gu S S, Zhao W J, Li P, Zheng A P. The fusion groups and pathogenicity differences of rice sheath blight pathogen in China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 55-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Wu W, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L, Wang Q, Yang F, Shah F, Yao F, Peng S. Sheath blight reduces stem breaking resistance and increases lodging susceptibility of rice plants[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 128: 101-108. |
| [5] | 姜伟. 水稻纹枯病对产量和抗倒性的影响研究与抗病分子改良[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015. |
| Jiang W. Study on the effects of rice sheath blight on yield and lodging resistance, and molecular breeding for disease resistance[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 陈海霞, 朱明芬, 常晓丽. 4种杀菌剂防治水稻纹枯病效果研究[J]. 上海农业学报, 2019, 35(2): 52-55. |
| Chen H X, Zhu M F, Chang X L. Study on the effect of four fungicides on sheath blight of rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2019, 35(2): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 袁筱萍, 魏兴华, 余汉勇, 王一平, 汤圣祥. 不同品种及有关外因对水稻纹枯病抗性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2004, 30(8): 768-773. |
| Yuan X P, Wei X H, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Tang S X. Influence of different varieties and related external factors on the resistance of rice to sheath blight[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2004, 30(8): 768-773. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 桑海旭, 王井士, 刘郁, 李运动, 马晓慧, 刘志恒. 水稻纹枯病对水稻产量及米质的影响[J]. 北方水稻, 2013(1): 10-13. |
| Sang H X, Wang J S, Liu Y, Li Y D, Ma X H, Liu Z H. The impact of rice sheath blight on rice yield and rice quality[J]. Northern Rice, 2013(1): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 秦息林. 水稻纹枯病对水稻产量的影响[J]. 南方农业, 2015, 9(3): 27-28. |
| Qin X L. The impact of rice sheath blight on rice yield[J]. Southern Agriculture, 2015, 9(3): 27-28. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(2): 411-432. |
| [11] | Xie W, Ding C, Hu H, Dong G, Zhang G, Qian Q, Ren D. Molecular events of rice AP2/ERF transcription factors[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(19): 12013. |
| [12] | Shigyo M, Ito M. Analysis of gymnosperm two-AP2-domain-containing genes[J]. Development Genes and Evolution, 2004, 214(3): 105-114. |
| [13] | Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress[J]. The Plant Cell, 1994, 6(2): 251-264. |
| [14] | Agarwal P K, Agarwal P, Reddy M K, Sopory S K. Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2006, 25(12): 1263-1274. |
| [15] | Tezuka D, Kawamata A, Kato H, Saburi W, Mori H, Imai R. The rice ethylene response factor OsERF83 positively regulates disease resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 135: 263-271. |
| [16] | Feng K, Hou X L, Xing G M, Liu J X, Duan A Q, Xu Z S, Li M Y, Zhuang J, Xiong A S. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2020, 40(6): 750-776. |
| [17] | Kitomi Y, Hidemi K, Inukai Y. Molecular mechanism of crown root initiation and the different mechanisms between crown root and radicle in rice[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2011, 6(9): 1276-1278. |
| [18] | Lee D Y, An G. Two ap2 family genes, supernumerary bract (snb) and OsINDETERMINATE spikelet 1 (OsIDS1), synergistically control inflorescence architecture and floral meristem establishment in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2012, 69(3): 445-461. |
| [19] | Jung H, Chung P J, Park S H, Redillas M C F R, Kim Y S, Suh J W, Kim J K. Overexpression of OsERF48 causes regulation of OsCML16, a calmodulin-like protein gene that enhances root growth and drought tolerance[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(10): 1295-1308. |
| [20] | Zhao Y, Cheng S, Song Y, Huang Y, Zhou S, Liu X, Zhou D X. The interaction between rice ERF3 and WOX11 promotes crown root development by regulating gene expression involved in cytokinin signaling[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(9): 2469-2483. |
| [21] | Lee D Y, Lee J, Moon S, Park S Y, An G. The rice heterochronic gene SUPERNUMERARY BRACT regulates the transition from spikelet meristem to floral meristem[J]. The Plant Journal, 2007, 49(1): 64-78. |
| [22] | Guo H, Ecker J R. The ethylene signaling pathway: New insights[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2004, 7(1): 40-49. |
| [23] | Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2006, 57: 781-803. |
| [24] | Tran T T, Pérez-Quintero A L, Wonni I, Carpenter S C D, Yu Y, Wang L, Leach J E, Verdier V, Cunnac S, Bogdanove A J, Koebnik R, Hutin M, Szurek B. Functional analysis of African Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae TALomes reveals a new susceptibility gene in bacterial leaf blight of rice[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2018, 14(6): e1007092. |
| [25] | Takeuchi K, Gyohda A, Tominaga M, Kawakatsu M, Hatakeyama A, Ishii N, Shimaya K, Nishimura T, Riemann M, Nick P, Hashimoto M, Komano T, Endo A, Okamoto T, Jikumaru Y, Kamiya Y, Terakawa T, Koshiba T. RSOsPR10 expression in response to environmental stresses is regulated antagonistically by jasmonate/ethylene and salicylic acid signaling pathways in rice roots[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(9): 1686-1696. |
| [26] | Xie W, Cao W, Lu S, Zhao J, Shi X, Yue X, Wang G, Feng Z, Hu K, Chen Z, Zuo S. Knockout of transcription factor OsERF65 enhances ROS scavenging ability and confers resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2023, 24(12): 1535-1551. |
| [27] | Zarbafi S S, Ham J H. An overview of rice QTLs associated with disease resistance to three major rice diseases: Blast, sheath blight, and bacterial panicle blight[J]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(4): 177. |
| [28] | Channamallikarjuna V, Sonah H, Prasad M, Rao G J N, Chand S, Upreti H C, Singh N K, Sharma T R. Identification of major quantitative trait loci qSBR11-1 for sheath blight resistance in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2010, 25(1): 155-166. |
| [29] | Helliwell E E, Wang Q, Yang Y. Transgenic rice with inducible ethylene production exhibits broad-spectrum disease resistance to the fungal pathogens Magnaporthe oryzae and Rhizoctonia Solani[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 11(1): 33-42. |
| [30] | Tonnessen B W, Manosalva P, Lang J M, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Mauleon R, Oard J, Hulbert S, Leung H, Leach J E. Rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene OsPAL4 is associated with broad spectrum disease resistance[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2015, 87(3): 273-286. |
| [31] | Liu Y, Liu W W, Li L, Frederic F, Wang X F. Transcriptome analysis reveals different response of resistant and susceptible rice varieties to rice stripe virus infection[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2023, 22(6): 1750-1762. |
| [32] | Yang X, Yan S, Li Y, Li G, Sun S, Li J, Cui Z, Huo J, Sun Y, Wang X, Liu F. Comparison of transcriptome between tolerant and susceptible rice cultivar reveals positive and negative regulators of response to Rhizoctonia Solani in rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(18): 14310. |
| [33] | Xue X, Cao Z X, Zhang X T, Wang Y, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Pan X B, Zuo S M. Overexpression of OsOSM1 enhances resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Plant Disease, 2016, 100(8): 1634-1642. |
| [34] | Cao W, Cao X, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Feng Z, Ouyang S, Zuo S. Comprehensive characteristics of microRNA expression profile conferring to sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 101-112. |
| [35] | Xie Y, Xie W, Zhao J, Xue X, Cao W, Shi X, Wang Z, Wang Y, Wang G, Feng Z, Hu K, Chen X, Chen Z, Zuo S. OsERF7 negatively regulates resistance to sheath blight disease by inhibiting phytoalexin biosynthesis[J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 367-379. |
| [36] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| He M, Yin J J, Feng Z M, Zhu X B, Zhao J H, Zuo S M, Chen X W. Identification methods for resistance to rice blast and sheath blight in rice[J]. Journal of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 王志鹏. 水稻纹枯病的发生与防控技术[J]. 种子科技, 2022, 40 (6): 118-120. |
| Wang Z P. Occurrence and control techniques of rice sheath blight[J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2022, 40(6): 118-120. (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | 吴婕, 席亚东, 李洪浩, 王晓黎, 彭化贤. 四川省水稻纹枯病菌对井冈霉素抗药性监测[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28 (6): 2501-2504. |
| Wu J, Xi Y D, Li H H, Wang X L, Peng H X. Monitoring of resistance to Jinggangmycin in Rhizoctonia solani causing rice sheath blight in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Southwest Agriculture, 2015, 28(6): 2501-2504. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 吴志明, 李昆太. 水稻纹枯病的危害及其微生物防治概述[J]. 生物灾害科学, 2018, 41 (2): 81-88. |
| Wu Z M, Li K T. Overview of the harm of rice sheath blight and its microbiological control[J]. Journal of Biological Disaster Science, 2018, 41(2): 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Huang Y, Li W, Liu T, Lin X, Xia Y, Zhu W, Cai Q. Rice extracellular vesicles send defense proteins into fungus Rhizoctonia solani to reduce disease[J]. Developmental Cell, 2025, 60(8): 1168-1181. |
| [41] | Cao B, Wang J, Ma J, Hai Y, Wang X, Fu Z, Xiang Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Wang J, Li S. Large-scale screening and function analysis of Rhizoctonia Solani effectors targeting rice chloroplasts[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(44): 24336-24346. |
| [42] | Gutterson N, Reuber T L. Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2004, 7(4): 465-471. |
| [43] | 许世达, 耿兴敏, 王露露. 植物乙烯响应因子(ERF)的结构、功能及表达调控研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(3): 624-633. |
| Xu S D, Geng X M, Wang L L. Research progress on the structure, function, and expression regulation of plant ethylene response factors (ERF)[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2021, 38(3): 624-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | Wang L, Liu W, Wang Y. Heterologous expression of Chinese wild grapevine VqERFs in Arabidopsis thaliana enhance resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 and to Botrytis cinerea[J]. Plant Science, 2020, 293: 110421. |
| [45] | Hughes P W. OsGSK2 integrates jasmonic acid and brassinosteroid signaling in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(9): 2669-2670. |
| [46] | Liu D, Chen X, Liu J, Ye J, Guo Z. The rice ERF transcription factor OsERF922 negatively regulates resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae and salt tolerance[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(10): 3899-3911. |
| [47] | Hong Y, Wang H, Gao Y, Bi Y, Xiong X, Yan Y, Wang J, Li D, Song F. ERF transcription factor OsBIERF3 positively contributes to immunity against fungal and bacterial diseases but negatively regulates cold tolerance in rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(2): 606. |
| [1] | LI Xingyi, CHEN Ling, SHAO Jiantao, XIAO Suqin, LI Jinlu, FU Huixian, YIN Fuyou, ZHANG Jianhong, CHENG Zaiquan, LIU Li. Progress in Molecular Genetic Research on Co-regulation of Grain Yield and Starch Quality in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 1-17. |
| [2] | MIAO Zhening, CHEN Jijin, LI Ziming, LIU Yi, LUO Lijun. Advances and Prospects in Breeding Bacterial Blight-resistant Rice in South China [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 18-26. |
| [3] | WANG Yixin, LIN Shen, MA Liuyang, CHEN Long, FENG Baohua, NI Shen, WEI Xiangjin, HE Jiwai, CHEN Tianxiao. Regulation of Nitrogen Uptake and Yield in Rice by the Alanine Aminotransferase Gene OsAlaAT4 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 51-60. |
| [4] | HUANG Qina, JIANG Hongrui, YANG Jie, YU Kunyu, YANG Changdeng, LIANG Yan. Bioinformatics Analysis, Development and Application of Molecular Markers for Seed Dormancy Gene Sdr4 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 61-71. |
| [5] | CHENG Zhaoping, HE Niqing, BAI Kangcheng, LIN Shaojun, HUANG Fenghuang, LIU Junhua, CHENG Zuxin, HUANG Chengzhi, YANG Dewei. Breeding and Utilization of the Three-Line Male Sterile Line Fumeng A with Pyramided Rice Blast Resistance Genes Pigm-1 and Pid2 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 72-84. |
| [6] | LIU Yaping, DONG Yici, ZHENG Junyan, QIU Xuan, LIU Pengcheng, YE Yafeng, LIU Binmei, CHEN Xifeng, MA Bojun. Phenotypic Identification and Gene Fine Mapping of the Lesion Mimic and Early Senescence Mutant lmes7 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 85-94. |
| [7] | LIAO Zhengming, GUO Liang, PAN Xiaowu, LI Yongchao, DONG Zheng, LI Xiaoxiang. Identification of Genes for Rice Seed Storability and Transcriptome Analysis Under Different Aging Conditions [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 95-105. |
| [8] | ZHANG Cheng, SHAO Guojun, ZHANG Xue, TIAN Shujun, SUN Chi, GUO Yanying, ZHOU Ran, HAN Yong, ZHENG Wenjing, SUN Lianping. QTL Mapping and Pyramiding Effect Analysis of Diurnal Floret Opening Time Traits in japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 106-117. |
| [9] | XIAO Wuwei, ZHANG Yuqing, ZHU Chenguang, TIAN Guisheng, CAI Yuehong, WANG Fei, XIONG Dongliang, HUANG Jianliang, PENG Shaobing, CUI Kehui. Effects of Application Time and Rate of Bud-promoting Fertilizer on Main Crop Quality and Annual Yield of Ratoon Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 118-130. |
| [10] | XIE Shimin, ZHOU Yuzhu, XUE Xiaodi, ZHU Guangfei, SUN Liang, CHEN Jianneng. Design and Experiment of an Integrated Picking and Planting Mechanism for Rice Pot Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 131-144. |
| [11] | CHEN Ling, LIN Wenying, LIANG Limei, OUYANG Younan, YE Shenghai, JI Zhijuan. Flowering Habits of Rice and Its Application in Breeding japonica Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Lines [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 731-743. |
| [12] | WANG Juan, WU Lijuan, HONG Haibo, YAO Zhiwen, WANG Lei, E Zhiguo. Research Progress on Biological Functions of Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzymes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [13] | TAO Shibo, XU Na, XU Zhengjin, LIU Chang, XU Quan. Cloning of Cold6 Conferring Cold Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [14] | CHEN Wei, YE Yuanmei, ZHAO Jianhua, FENG Zhiming, CHEN Zongxiang, HU Keming, ZUO Shimin. Modifying Heading Date of Nanjing 46 via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Editing [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [15] | HOU Guihua, ZHOU Liguo, LEI Jianguo, CHEN Hong, NIE Yuanyuan. Preliminary Analysis of Function and Mechanism of OsRDR5 Gene in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||