
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 577-586.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6024
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yan-xiu DU, Xin JI, Hui-jie CHEN, Ting PENG, Jing ZHANG, Jun-zhou LI, Hong-zheng SUN, Quan-zhi ZHAO*( )
)
Received:2016-02-19
Revised:2016-06-03
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-11-10
Contact:
Quan-zhi ZHAO
杜彦修, 季新, 陈会杰, 彭廷, 张静, 李俊周, 孙红正, 赵全志*( )
)
通讯作者:
赵全志
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yan-xiu DU, Xin JI, Hui-jie CHEN, Ting PENG, Jing ZHANG, Jun-zhou LI, Hong-zheng SUN, Quan-zhi ZHAO. CRISPR/Cas9 System-based Editing of OsbHLH116 Gene and Its Off-target Effect Analysis[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 577-586.
杜彦修, 季新, 陈会杰, 彭廷, 张静, 李俊周, 孙红正, 赵全志. 基于CRISPR/Cas9系统的OsbHLH116基因编辑及其脱靶效应分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 577-586.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6024
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列 Sequence | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| sgRNA-F | 5'-GGCGCCTCCATCGGAGGAAGAGA-3' | 靶序列合成Construction of target site |
| sgRNA-R | 5'-AAACTCTCTTCCTCCGATGGAGG-3' | |
| pBUN411-VF | 5'-CCATGAAGCCTTTCAGGACATGTA-3' | 载体构建验证Verification of vector construction |
| pBUN411-VR | 5'-ACGCTGCAAACATGAGACGGAGAA-3' | |
| Basta-F | 5'-AAGCACGGTCAACTTCCGTA-3' | 除草剂基因验证Verification of Bt |
| Basta-R | 5'-GAAGTCCAGCTGCCAGAAAC-3' | |
| OsbHLH116-F | 5'-GTTGATGTGGCAAGGAGGAG-3' | 靶点两侧序列扩增Amplification of target region |
| OsbHLH116-R | 5'-TACGCACCAGACAGTTCACC-3' | |
| LOC_Os01g01380-F | 5'-ACAAGCAATGCAAATGTTGG-3' | 脱靶位点扩增Off-target amplification |
| LOC_Os01g01380-R | 5'-CTCTTCGCCCACACCATC-3' | |
| Chr4:+30193341-F | 5'-AATAGATCACGCCGTCAACC-3' | 脱靶位点扩增Off-target amplification |
| Chr4:+30193341-R | 5'-CGAGACGAATCTTTTGAGCA-3' |
Table 1 Primer sequence used in the study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列 Sequence | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| sgRNA-F | 5'-GGCGCCTCCATCGGAGGAAGAGA-3' | 靶序列合成Construction of target site |
| sgRNA-R | 5'-AAACTCTCTTCCTCCGATGGAGG-3' | |
| pBUN411-VF | 5'-CCATGAAGCCTTTCAGGACATGTA-3' | 载体构建验证Verification of vector construction |
| pBUN411-VR | 5'-ACGCTGCAAACATGAGACGGAGAA-3' | |
| Basta-F | 5'-AAGCACGGTCAACTTCCGTA-3' | 除草剂基因验证Verification of Bt |
| Basta-R | 5'-GAAGTCCAGCTGCCAGAAAC-3' | |
| OsbHLH116-F | 5'-GTTGATGTGGCAAGGAGGAG-3' | 靶点两侧序列扩增Amplification of target region |
| OsbHLH116-R | 5'-TACGCACCAGACAGTTCACC-3' | |
| LOC_Os01g01380-F | 5'-ACAAGCAATGCAAATGTTGG-3' | 脱靶位点扩增Off-target amplification |
| LOC_Os01g01380-R | 5'-CTCTTCGCCCACACCATC-3' | |
| Chr4:+30193341-F | 5'-AATAGATCACGCCGTCAACC-3' | 脱靶位点扩增Off-target amplification |
| Chr4:+30193341-R | 5'-CGAGACGAATCTTTTGAGCA-3' |
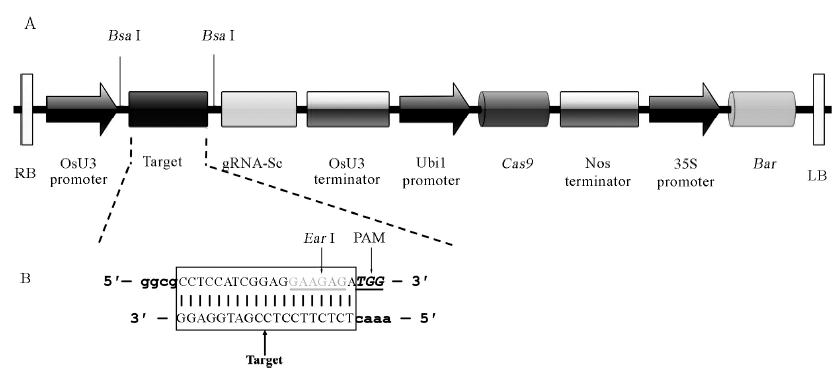
Fig. 1. Linear structure of pBUN411-gRNA expression vectors between LB and RB and the construction of target site. A, Physical map between RB and LB of pBUN411-gRNA expression vectors. Vertical lines stand for BsaⅠ restriction sites; RB, Right border of T-DNA; OsU3 promoter, Rice U3 promoters; gRNA-Sc, Guide RNA scaffold; OsU3 terminator, Rice U3 terminators; Ubi1 promoter, Maize ubiquitin gene promoter; Cas9, Cas9 gene; Nos Terminator, Agrobacterium tumefaciens nopaline synthase gene (Nos) terminator; 35S Promoter, Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter; Bar, Herbicide resistance Bar gene; LB, Left border of T-DNA. B, The target sites of gRNA complementary with double-stranded DNA. The target sequences are in the box; Gray letters stand for EarⅠ restriction sites; Letters with italics stand for PAM (not in the expression vectors); The lowercase stand for sticky ends of BsaⅠ.
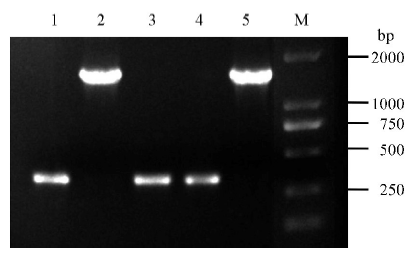
Fig. 2. Verification of pBUN411-gRNA expression vectors via colony PCR. 1-4, Four independent colonies to detect expression vectors; 5, pBUN411 empty vectors (negative contrast); M, DM2000 marker.
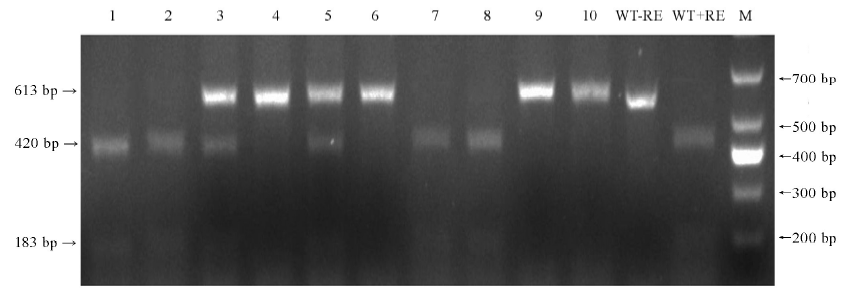
Fig. 3. Mutation analysis of 10 T0 transgenic lines by EarⅠ digestion of PCR product. 1-10, 10 transgenic lines; WT, Wild type; M, DM1000 marker; -RE, PCR product without restriction enzyme digestion; +RE, EarⅠ digested PCR product; Arrowheads, PCR fragments after EarI digested.
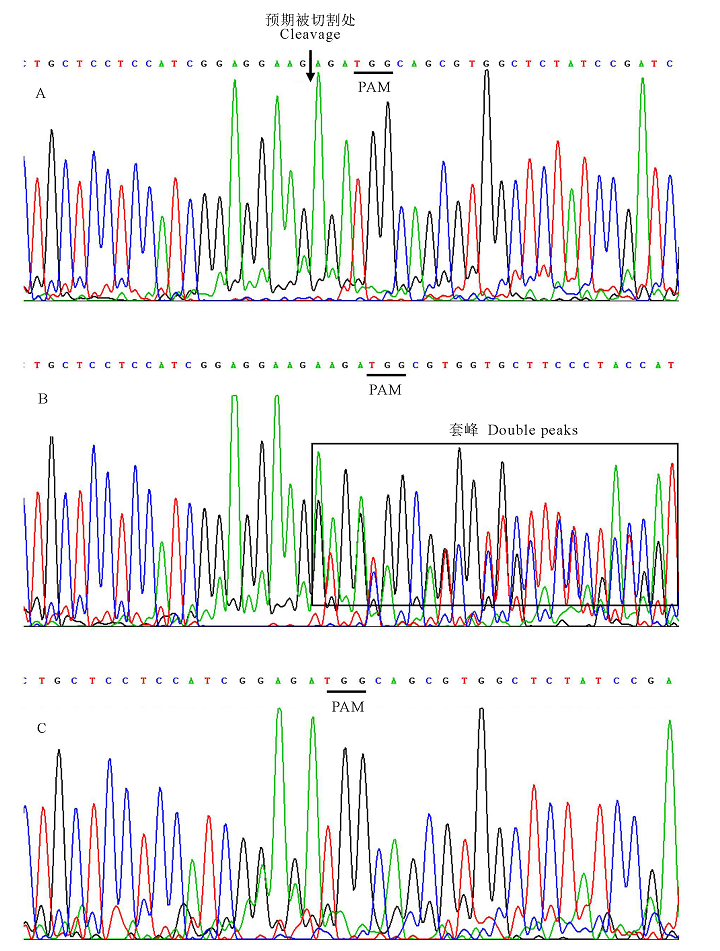
Fig.4. Sanger sequencing results for PCR products of number 4, 7 and 10. Underlines stand for PAM (TGG); The arrows stand for the intended cleavage site; The double peak phenomenon is in the box. A, Sanger sequencing results for PCR products of non-mutation number 7 ; B, Sanger sequencing results for PCR products of biallelic mutation number 10; C, Sanger sequencing results for PCR products of homozygous mutation number 4.

Fig. 5. DNA sequence alignment of wild type with six mutant versions. The gRNA target site is shown in blue; The yellow highlighting denote PAM; Red dashes deleted bases; Insertion nucleotides are shown in red lowercases; -, Deletion; +, Insertion; (0/0)-Sequencing by using PCR product.
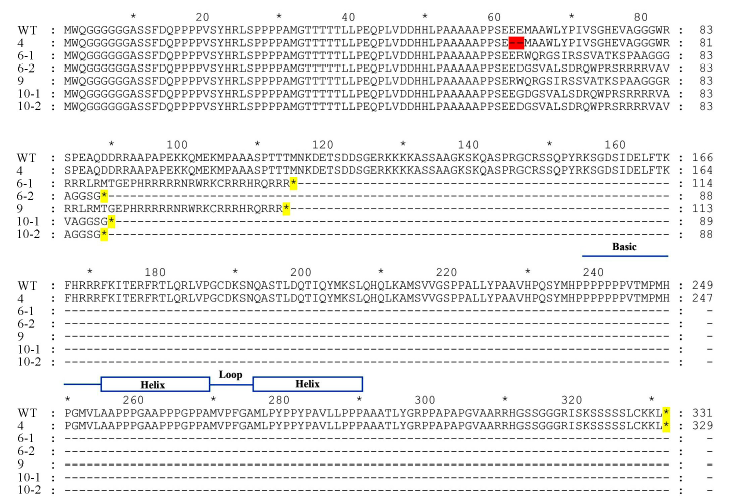
Fig.6. Comparison of the amino acid sequences between wild type and OsbHLH116 mutants. Blue lines and boxes denote basic-helix-loop-helix domain; The red highlighting denote amino acid deletion; The yellow highlighting denote translation termination.
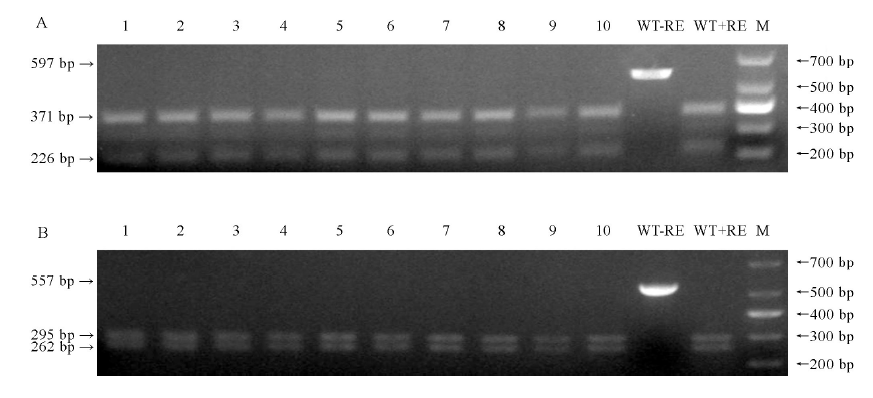
Fig. 8. PCR/ restriction enzyme (PCR/RE) assay to detect off-target of 10 plants of T0 transgenic lines. 1-10, 10 transgenic lines; WT, Wild type; M, DM1000 Marker; -RE, PCR product without restriction enzyme digestion; +RE, EarI digested PCR product; Arrowheads, PCR fragments after EarI digestion. A, PCR/RE assay to detect off-target of LOC_Os01g01380; B, PCR/RE assay to detect off-target of Chr4: +30 193 341.
| [1] | Wiedenheft B, Sternberg S H, Doudna J A.RNA-guided genetic silencing systems in bacteria and archaea.Nature, 2012, 482(7385): 331-338. |
| [2] | Cong L, Ran F A, Cox D, et al.Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems.Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| [3] | Miao J, Guo D, Zhang J, et al.Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system.Cell Res, 2013, 23(10): 1233. |
| [4] | Shan Q, Wang Y, Li J, et al.Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system.Nat Biotechnol, 2013, 31(8): 686-688. |
| [5] | Atchley W R, Terhalle W, Dress A.Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain.J Mol Evol, 1999, 48(5): 501-516. |
| [6] | Nesi N, Debeaujon I, Jond C, et al.The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell, 2000, 12(10): 1863-1878. |
| [7] | Martı'nez-Garcı'A J F, Huq E, Quail P H. Direct targeting of light signals to a promoter element-bound transcription factor.Science, 2000, 288(5467): 859-863. |
| [8] | Massari M E, Murre C.Helix-loop-helix proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms.Mol Cell Biol, 2000, 20(2): 429-440. |
| [9] | Pires N, Dolan L.Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants.Mol Biol Evol, 2010, 27(4):862-874. |
| [10] | Komatsu K, Maekawa M, Ujiie S, et al.LAX and SPA: Major regulators of shoot branching in rice.PNAS, 2003, 100(20): 11765-11770. |
| [11] | Sakamoto W, Ohmori T, Kageyama K, et al.The Purple leaf (Pl) locus of rice: The Plw allele has a complex organization and includes two genes encoding basic helix-loop-helix proteins involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis.Plant Cell Physiol, 2001, 42(9): 982-991. |
| [12] | Seo J S, Joo J, Kim M J, et al.OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice.Plant J, 2011, 65(6): 907-921. |
| [13] | Xing H, Dong L, Wang Z, et al.A CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for multiplex genome editing in plants.BMC Plant Biol, 2014, 14(1): 327. |
| [14] | Nishimura A, Aichi I, Matsuoka M.A protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in rice. Nat Protoc, 2006, 1(6): 2796-2802. |
| [15] | Hall T A.BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT.Nucl Acids Sympos Ser, 1999, 41: 95-98. |
| [16] | Nicholas K B, Nicholas H, Deerfield D W.GeneDoc: Analysis and visualization of genetic variation.Embnew News, 1997, 4: 1-4. |
| [17] | Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, et al.Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2006, 141(4): 1167-1184. |
| [18] | Carroll D, Morton J J, Beumer K J, et al.Design, construction and in vitro testing of zinc finger nucleases.Nat Protoc, 2006, 1(3): 1329-1341. |
| [19] | Li T, Liu B, Spalding M H, et al.High-efficiency TALEN-based gene editing produces disease-resistant rice.Nat Biotechnol, 2012, 30(5): 390-392. |
| [20] | Mussolino C, Cathomen T.RNA guides genome engineering.Nat Biotechnol, 2013, 31(3): 208-209. |
| [21] | Mao Y, Zhang H, Xu N, et al.Application of the CRISPR-Cas system for efficient genome engineering in plants.Mol Plant, 2013, 6(6): 2008. |
| [22] | Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, et al.A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity.Science, 2012, 337(6096): 816-821. |
| [23] | Ran F A, Hsu P D, Lin C, et al.Double nicking by RNA-guided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity.Cell, 2013, 154(6): 1380-1389. |
| [24] | Zhou H, Liu B, Weeks D P, et al.Large chromosomal deletions and heritable small genetic changes induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in rice.Nucl Acids Res, 2014, 42(17): 10903-10914. |
| [25] | Feng Z, Mao Y, Xu N, et al.Multigeneration analysis reveals the inheritance, specificity, and patterns of CRISPR/Cas-induced gene modifications inArabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2014, 111(12): 4632-4637. |
| [26] | Zhang H, Zhang J, Wei P, et al.The CRISPR/Cas9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation.Plant Biotechnol J, 2014, 12(6): 797-807. |
| [27] | Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, et al.Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2006, 141(4): 1167-1184. |
| [28] | Gu X, Liu T, Feng J, et al.The qSD12 underlying gene promotes abscisic acid accumulation in early developing seeds to induce primary dormancy in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2010, 73(1-2): 97-104. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||