
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 97-105.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2015.01.012
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guo-juan XU1,2, Zheng-jie YUAN2, Shi-min ZUO3, Xue-biao PAN3, Zhi-long WANG4, Shao-hong QU2,*( )
)
Received:2014-03-02
Revised:2014-04-13
Online:2015-01-10
Published:2015-01-10
Contact:
Shao-hong QU
徐国娟1,2, 袁正杰2, 左示敏3, 潘学彪3, 王志龙4, 瞿绍洪2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
瞿绍洪
基金资助:CLC Number:
Guo-juan XU, Zheng-jie YUAN, Shi-min ZUO, Xue-biao PAN, Zhi-long WANG, Shao-hong QU. Improvement of the Micro-chamber Inoculation Method for Determination of Rice Seedling Resistance to Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(1): 97-105.
徐国娟, 袁正杰, 左示敏, 潘学彪, 王志龙, 瞿绍洪. 水稻苗期纹枯病抗性鉴定微室接种技术的改良[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(1): 97-105.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2015.01.012
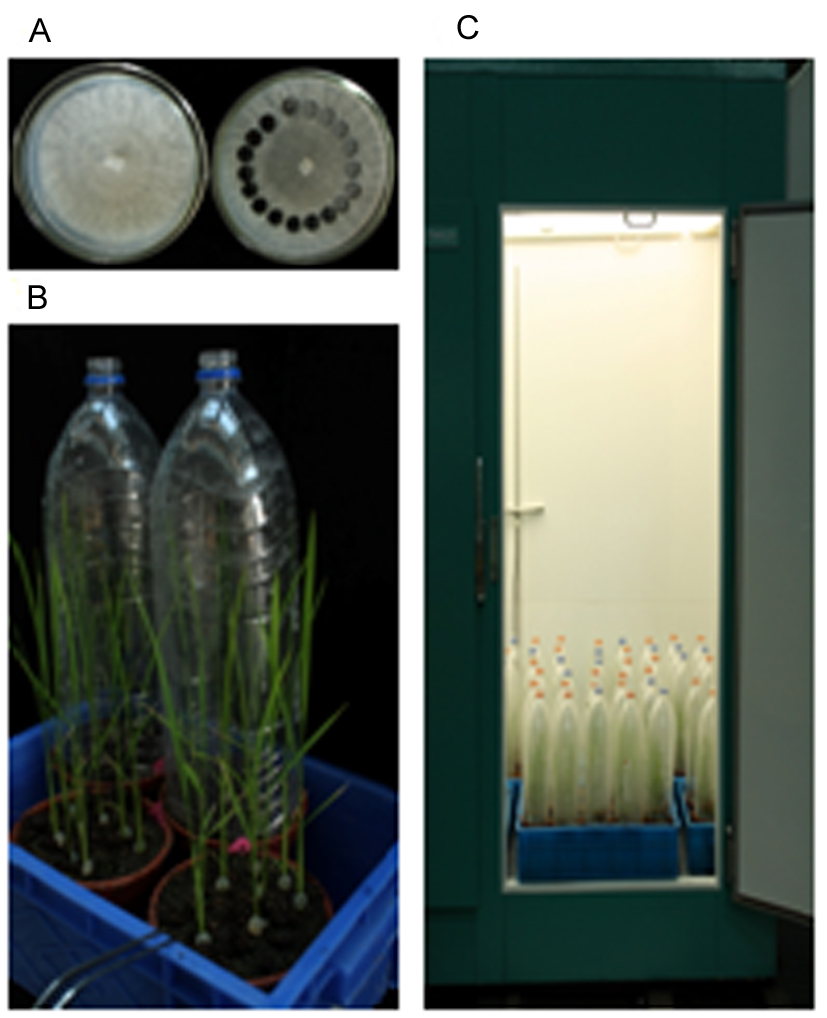

Fig. 1. Inoculation of the sheath blight pathogen (R. solani) to rice seedlings in a plant growth chamber using a micro-chamber method. A, R. solani on PDA after three days of culture. B, Rice plants inoculated with R. solani; C, Rice plants inoculated with R. solani grown in a plant growth chamber.
| 接种时间 Time after inoculation/h | 取样长度 Length of sampled tissue/cm | 取样植株数 Number of sampled plants |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 10 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 10 |
| 12 | 1 | 9 |
| 24 | 1 | 9 |
| 48 | 2 | 6 |
| 72 | 2 | 6 |
| 108 | 2 | 6 |
Table 1 Sampling method from Taijing 394 plants infected with R. solani.
| 接种时间 Time after inoculation/h | 取样长度 Length of sampled tissue/cm | 取样植株数 Number of sampled plants |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 10 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 10 |
| 12 | 1 | 9 |
| 24 | 1 | 9 |
| 48 | 2 | 6 |
| 72 | 2 | 6 |
| 108 | 2 | 6 |
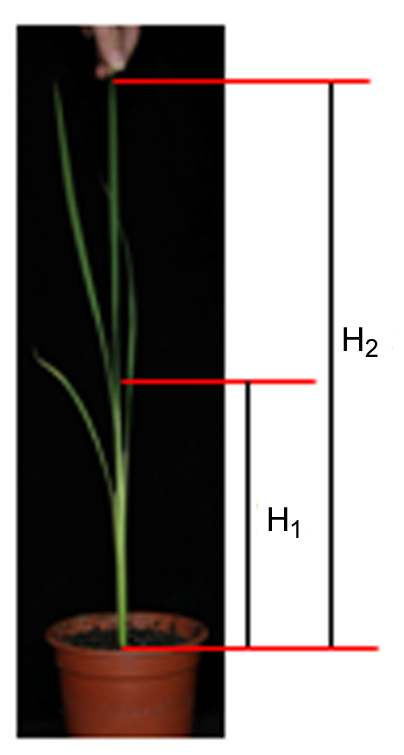
Fig. 2. Illustration of the height of the pulvinus of the second leaf from the top and the straightened seedling height. H1, The height of the pulvinus of the second leaf from the top; H2, The straightened seedling height.
| 基因缩写 Gene symbol | 参考文献 Reference | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | Jain et al.(2006)[ | Os03g50885 | F:CCCTCCTGAAAGGAAGTACAGTGT |
| R:GTCCGAAGAATTAGAAGCATTTCC | |||
| E2F-related protein | Os03g13050 | F:ACGTCACGCACGTTCATTAGCA | |
| R:GACCGAATAAATGGCTGCTGGT | |||
| OsPR1b | Agrawal et al.(2000)[ | Os01g28450 | F:GCGTCTTCATCACATGCAACTA |
| R:ACCTGAAACAGAAAGAAACAGAGG | |||
| PBZ1 | Kim et al.(2011)[ | Os12g36880 | F:CAAATTCTCGTGGCGTTTGAGTC |
| R:CGGCAGCATTCACAATGATTTTC | |||
| PDR (pleiotropic drug | Crouzet et al.(2003)[ | Os01g42370 | F:TGGTGGAGATGGTACTGCTGGA |
| resistance protein) | R:ATGATGGCAAAGCCAAAGAGGA |
Table 2 Primers for RT-PCR analysis of rice sheath blight resistance genes.
| 基因缩写 Gene symbol | 参考文献 Reference | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | Jain et al.(2006)[ | Os03g50885 | F:CCCTCCTGAAAGGAAGTACAGTGT |
| R:GTCCGAAGAATTAGAAGCATTTCC | |||
| E2F-related protein | Os03g13050 | F:ACGTCACGCACGTTCATTAGCA | |
| R:GACCGAATAAATGGCTGCTGGT | |||
| OsPR1b | Agrawal et al.(2000)[ | Os01g28450 | F:GCGTCTTCATCACATGCAACTA |
| R:ACCTGAAACAGAAAGAAACAGAGG | |||
| PBZ1 | Kim et al.(2011)[ | Os12g36880 | F:CAAATTCTCGTGGCGTTTGAGTC |
| R:CGGCAGCATTCACAATGATTTTC | |||
| PDR (pleiotropic drug | Crouzet et al.(2003)[ | Os01g42370 | F:TGGTGGAGATGGTACTGCTGGA |
| resistance protein) | R:ATGATGGCAAAGCCAAAGAGGA |
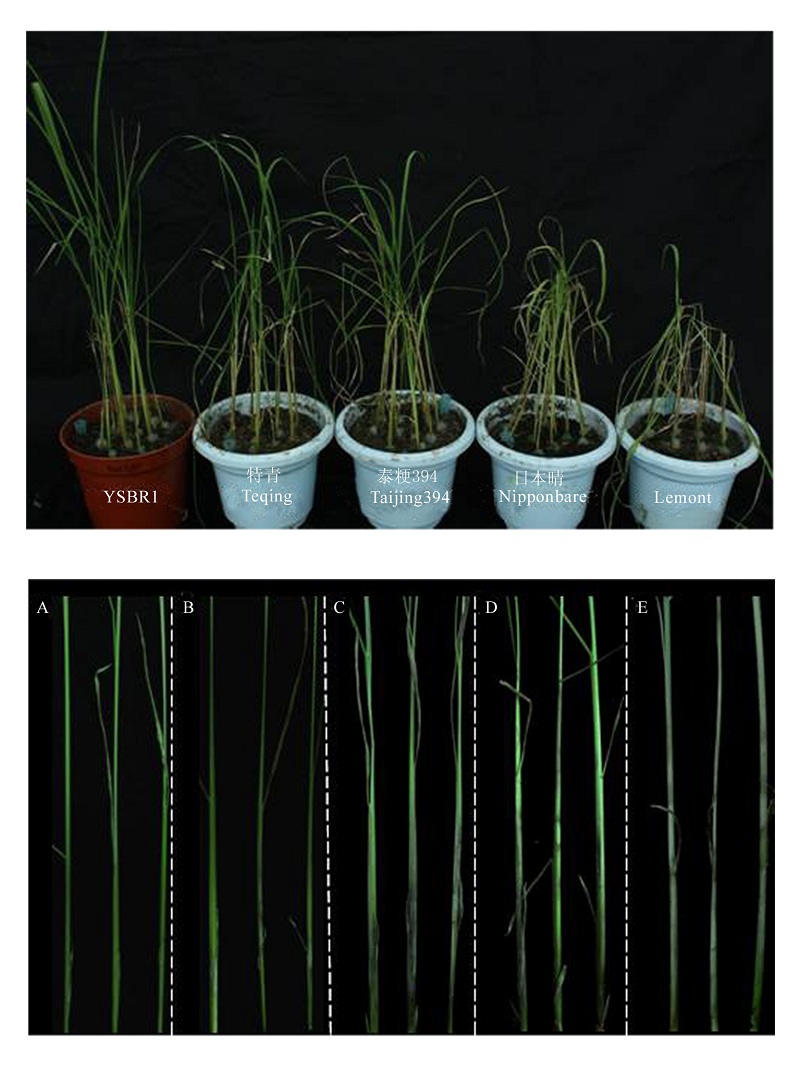

Fig. 3. Symptoms of sheath blight disease on five rice cultivars inoculated by micro-chamber method (9 days after inoculation). A, YSBR1, resistant; B, Teqing, moderately resistant; C, Taijing 394, moderately susceptible; D, Nipponbare, susceptible; E, Lemont, highly susceptible.
| 品种 Cultivar | 平均病级 Average disease score | 显著水平 Significance level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 1% | ||
| Lemont | 8.54 | a | A |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 6.12 | b | B |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 4.52 | c | C |
| 特青Teqing | 3.48 | d | D |
| YSBR1 | 2.82 | d | D |
Table 3 Multiple comparisons of sheath blight scores among five rice cultivars by the disease rating method based on the height of the pulvinus of the second leaf from the top.
| 品种 Cultivar | 平均病级 Average disease score | 显著水平 Significance level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 1% | ||
| Lemont | 8.54 | a | A |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 6.12 | b | B |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 4.52 | c | C |
| 特青Teqing | 3.48 | d | D |
| YSBR1 | 2.82 | d | D |
| 品种 Cultivar | 平均病级 Average disease score | 显著水平 Significance level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 1% | ||
| Lemont | 3.39 | a | A |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 2.82 | b | B |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 2.04 | c | C |
| 特青Teqing | 1.52 | d | D |
| YSBR1 | 1.20 | d | D |
Table 4 Multiple comparisons of sheath blight scores among rice cultivars by the disease rating method based on the height of straightened seedling.
| 品种 Cultivar | 平均病级 Average disease score | 显著水平 Significance level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 1% | ||
| Lemont | 3.39 | a | A |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 2.82 | b | B |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 2.04 | c | C |
| 特青Teqing | 1.52 | d | D |
| YSBR1 | 1.20 | d | D |
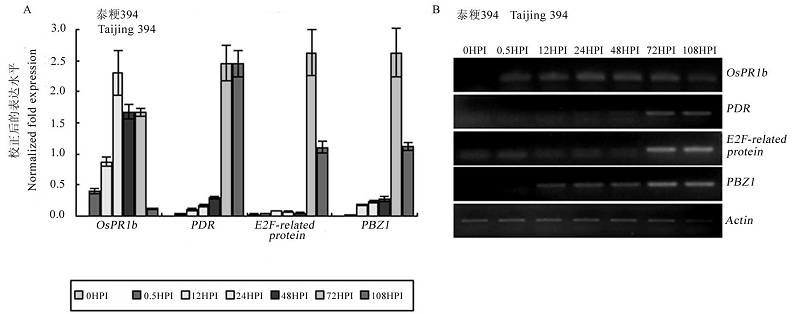
Fig. 4. Expression levels of resistance-related genes in the seedlings of rice cultivar Taijing 394 induced by R.solani inoculation. HPI,Hours post-inoculation.
| 品种 Cultivar | 成株期平均病级 Average disease score of adult plants | 5%显著水平 5% significance level | 1%显著水平 1% significance level | 苗期平均病级 Average disease score of seedlings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemont | 8.09 | a | A | 8.54 |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 7.55 | a | A | 6.12 |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 4.68 | b | B | 4.52 |
| YSBR1 | 2.65 | c | C | 2.82 |
Table 5 Multiple comparisons of sheath blight scores among four rice cultivars inoculated with R.solani at the adult plant stage in field.
| 品种 Cultivar | 成株期平均病级 Average disease score of adult plants | 5%显著水平 5% significance level | 1%显著水平 1% significance level | 苗期平均病级 Average disease score of seedlings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemont | 8.09 | a | A | 8.54 |
| 日本晴Nipponbare | 7.55 | a | A | 6.12 |
| 泰粳394Taijing 394 | 4.68 | b | B | 4.52 |
| YSBR1 | 2.65 | c | C | 2.82 |
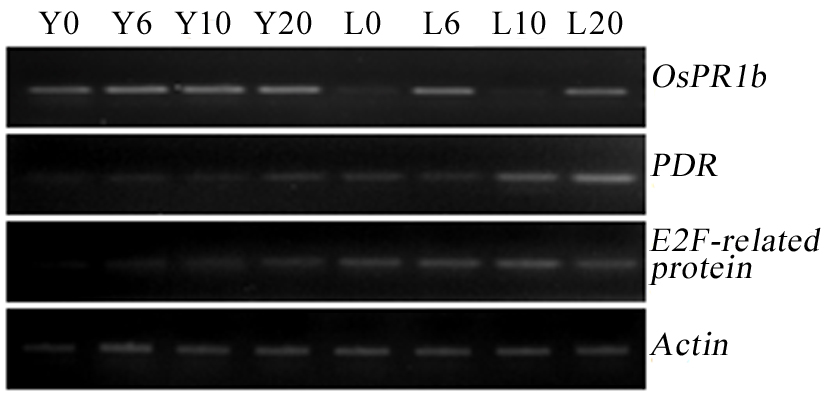
Fig. 5. RT-PCR analysis of expression of resistance-related genes in the adult plants of rice cultivars YSBR1 and Lemont inoculated with R.solani in field. Y0, Y6, Y10 and Y20, YSBR1 plants 0 h, 6 h, 10 h and 20 h post-inoculation, respectively; L0, L6, L10 and L20, Lemont plants 0 h, 6 h, 10 h and 20 h post-inoculation, respectively.
| [1] | Lee F N, Rush M C.Rice sheath blight: A major rice disease.Plant Dis, 1983, 67(7): 829-832. |
| [2] | Pan X B, Rush M C, Sha X Y, et al.Major gene, nonallelic sheath blight resistance from the rice cultivars Jasmine 85 and Teqing.Crop Sci, 1999, 39(2): 338-346. |
| [3] | Zou J H, Pan X B, Chen Z X, et al.Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling sheath blight resistance in two rice cultivars(Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 101(4): 569-573. |
| [4] | Jia Y L, Correa-Victoria F, McClung A, et al. Rapid determination of rice cultivar responses to the sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani using a micro-chamber screening method.Plant Dis, 2007, 91(5): 485-489. |
| [5] | Savary S, Castilla N P, Elazegui F A, et al.Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen supply and disease source structure on rice sheath blight spread.Phytopathol, 1995, 85(9): 959-965. |
| [6] | Lee F N, Moldenhauer K A K, Gibbons J W, et al. Rice blast and sheath blight evaluation results for the 2002 uniform regional rice nursery//Norman R J, Meullenet J F, Molden hayer K A K. Rice Research Studies. Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Agriculture Experiment Station Research, 2002: 73-84. |
| [7] | Sha X Y, Zhu L H.Resistance of some rice varieties to sheath blight (ShB).Int Rice Res Newsl, 1990, 15(6): 7-8. |
| [8] | Li Z K, Pinson S R M, Marchetti M A, et al. Characterization of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in cultivated rice contributing to field resistance to sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani).Theor Appl Genet, 1995, 91(2): 382-388. |
| [9] | Pinson S R M, Capdevielle F M, Oard J H. Confirming QTLs and finding additional loci conditioning sheath blight resistance in rice using recombinant inbred lines.Crop Sci, 2005, 45(2): 503-510. |
| [10] | 左示敏,张亚芳,殷跃军,等. 田间水稻纹枯病抗性鉴定体系的确立与完善. 扬州大学学报:农业与生命科学版,2006,27(4):57-61. |
| [11] | 左示敏,王子斌,陈夕军,等. 水稻纹枯病改良新抗源 YSBR1 的抗性评价. 作物学报,2009,35(4):608-614. |
| [12] | Cartwright R D, Parsons P E, Sutton E A, et al.Disease monitoring and evaluation of rice cultivars on Arkansas farms//Norman R J, Meullenet J F, Molden hayer K A K. Rice Research Studies. Fayetteville, AR:University of Arkansas Agriculture Experiment Station Research, 2002: 219-228. |
| [13] | 王子斌,左示敏,李刚,等. 水稻抗纹枯病苗期快速鉴定技术研究. 植物病理学报,2009,39(2):174-182. |
| [14] | Jia Y L, Singh P, Eizenga G C, et al.In vitro identification of cultivar responses to rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani//Norman R J, Meullenet J F, Molden hayer K A K. Rice Research Studies. Fayetteville, AR:University of Arkansas Agriculture Experiment Station Research, 2002: 229-236. |
| [15] | Prasad B, Eizenga G C.Rice sheath blight disease resistance identified in Oryza spp. accessions.Plant Dis, 2008, 92(11): 1503-1509. |
| [16] | Jia L M, Yan W G, Zhu C S, et al.Allelic analysis of sheath blight resistance with association mapping in rice. PloS One, 2012, 7(3): e32703. ( |
| [17] | Liu G, Jia Y L, Correa-Victoria F J, et al. Mapping quantitative trait loci responsible for resistance to sheath blight in rice.Phytopathol, 2009, 99(9): 1078-1084. |
| [18] | Yoshida S, Forno D A, Cock J H, et al.2nd edn.Laboratory Manual for physiological studies of rice. Los Bafios, Philippines:International Rice Research Institute, 1972: 57-63. |
| [19] | 潘学彪,陈宗祥. 不同接种调查方法对抗水稻纹枯病遗传研究的影响. 江苏农学院学报,1997,18(3):27-32. |
| [20] | 王子斌,左示敏,李刚,等. 水稻成株期对纹枯病的抗性表现研究. 吉林农业大学学报,2011,33(2):144-150. |
| [21] | Singh G, Kumar S, Singh P.A quick method to isolate RNA from wheat and other carbohydrate-rich seeds.Plant Mol Biol Rep, 2003, 21(1): 93. |
| [22] | Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi A K, et al.Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR.Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 345(2): 646-651. |
| [23] | Magyar Z.Keeping the balance between proliferation and differentiation by the E2F transcriptional regulatory network is central to plant growth and development//Bögre L, Beemster G T S. Plant Growth Signaling. Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co. K, 2008, 10: 89-105. |
| [24] | Agrawal G K, Rakwal R, Jwa N S.Rice (Oryza sativa L.) OsPR1b gene is phytohormonally regulated in close interaction with light signals.Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2000, 278(2): 290-298. |
| [25] | Kim S G, Kim S T, Wang Y M, et al.The RNase activity of rice probenazole-induced protein1 (PBZ1) plays a key role in cell death in plants.Mol Cells, 2011, 31(1): 25-31. |
| [26] | Crouzet J, Trombik T, Fraysse Å S, et al.Organization and function of the plant pleiotropic drug resistance ABC transporter family.FEBS lett, 2006, 580(4): 1123-1130. |
| [27] | Rush M C, Hoff B J, Mellrath W O.A uniform disease rating system for rice disease in the United States. Proc 16th Rice Tech Working Group, Lake Charles, Louisana, USA, 1976: 64. |
| [28] | Eizenga G C, Lee F N, Rutger J N.Screening Oryza species plants for rice sheath blight resistance.Plant Dis, 2002, 86(7): 808-812. |
| [29] | Wasano K, Oro S, Kido Y.The syringe inoculation method for selecting rice plants resistant to sheath blight, Rhizoctonia solani Kühn.Japan J Trop Agric, 1983, 27(3): 131-134. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||