
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 285-294.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220810
杨晓龙1, 王彪2, 汪本福1, 张枝盛1, 张作林1, 杨蓝天1, 程建平1,*( ), 李阳1,*(
), 李阳1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-29
修回日期:2023-01-06
出版日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-05-16
通讯作者:
*email: chjp609@163.com;liylcy163.com
基金资助:
YANG Xiaolong1, WANG Biao2, WANG Benfu1, ZHANG Zhisheng1, ZHANG Zuolin1, YANG Lantian1, CHENG Jianping1,*( ), LI Yang1,*(
), LI Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-29
Revised:2023-01-06
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: chjp609@163.com;liylcy163.com
摘要:
【目的】研究旱直播模式下不同水分管理方式对水稻产量、光合生理特性和稻米品质的影响,以期为干旱气候条件下的节水栽培提供理论依据。【方法】采用大田小区试验,以杂交稻旱优73和常规稻黄华占为试验材料,通过设置全生育期内旱管和水管两种水分管理模式,综合考查旱直播模式下不同水分管理方式对水稻叶片光合特性、地上部干物质积累及分配、产量和稻米品质的影响。【结果】水稻旱直播模式下进行旱作栽培显著提高了水分利用效率和水稻产量,降低了稻米的外观品质和食味品质。与淹水灌溉相比,旱作处理显著提高了叶片SPAD值和齐穗期净光合速率,促进了地上部干物质的积累;增加了茎秆和叶片干物质转运量和对籽粒贡献率,进而提高了水稻有效穗和千粒重。其中,黄华占和旱优73 产量分别增加14.0%和11.9%。旱作处理对加工品质没有显著影响,但显著降低了直链淀粉含量,增加了蛋白质含量;同时降低籽粒中重金属砷的含量,增加了重金属镉的含量。【结论】水稻旱直播模式为干旱气候条件下的水稻适应性栽培提供了可能,但稻米品质与产量协同提升因品种而异。因此,旱直播模式下高效优质栽培技术还需进一步研究。
杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294.
YANG Xiaolong, WANG Biao, WANG Benfu, ZHANG Zhisheng, ZHANG Zuolin, YANG Lantian, CHENG Jianping, LI Yang. Effects of Different Water Management on Yield and Rice Quality of Dry-seeded Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 285-294.
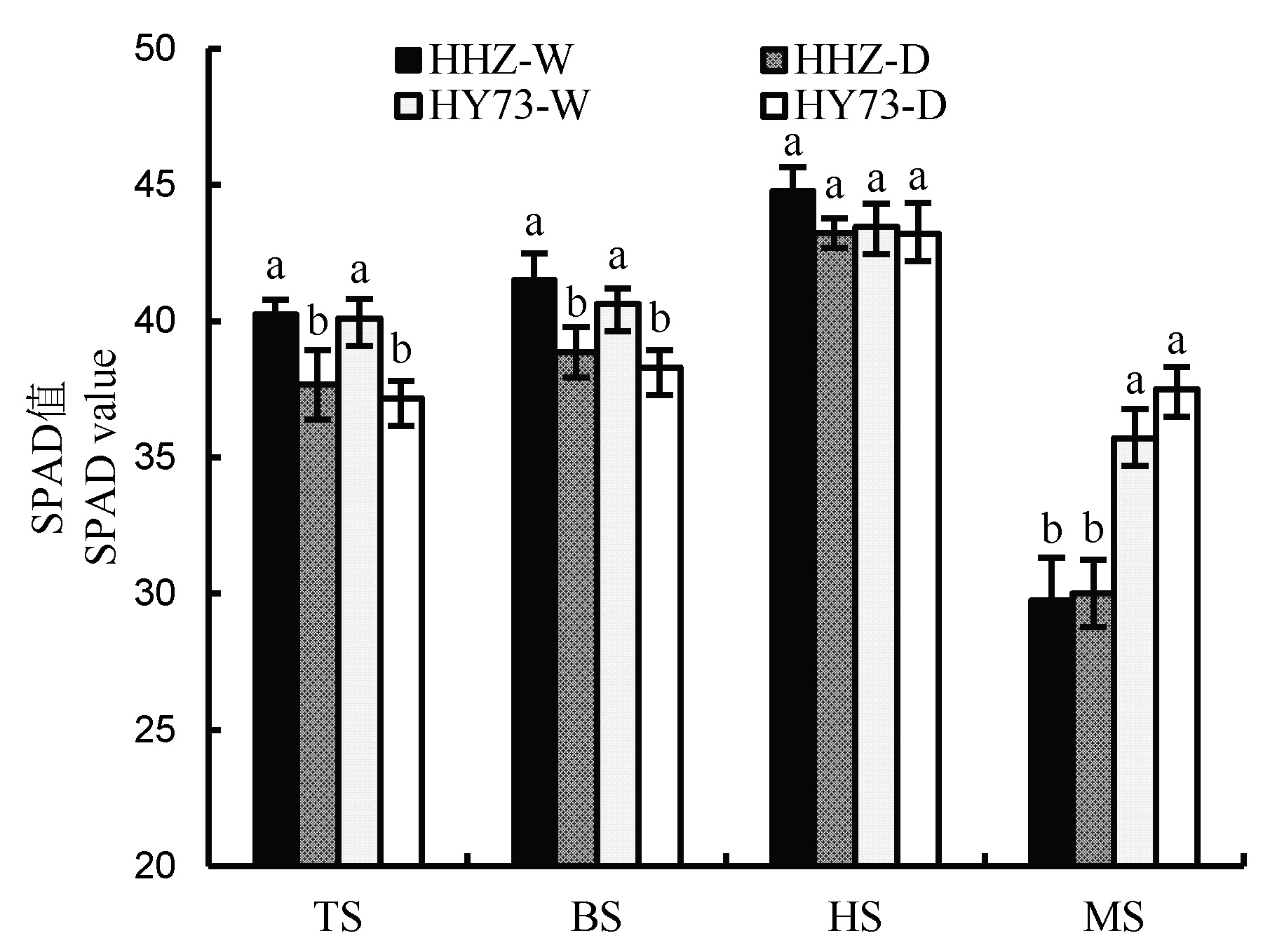
图1 不同水分管理模式下水稻齐穗期剑叶SPAD值 HHZ-黄华占;HY73-旱优73;W-全生育期淹水灌溉;D-全生育期旱作;TS-分蘖盛期;BS-孕穗期;HS-齐穗期;MS-成熟期。柱上不同字母表示在5%水平上差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Fig. 1. SPAD value of flag leaf of rice at heading stage under different water management modes. HHZ, Huanghuazhan; HY73, Hanyou 73; W, Traditional flooding; D, Dry cultivation; TS, Tillering stage; BS, Booting stage; HS, Heading stage; MS, Maturity stage. Different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at P=0.05 level. The same below.
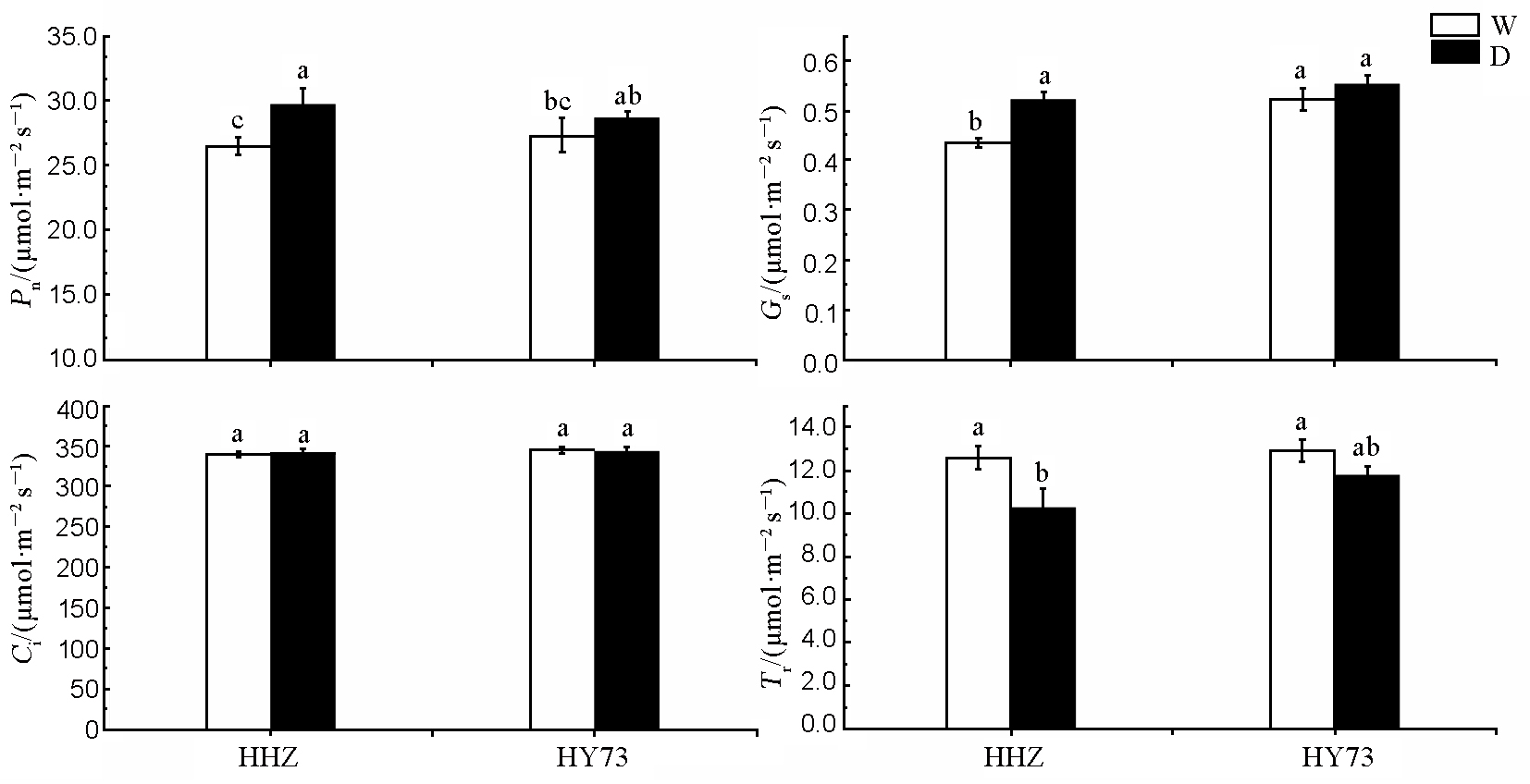
图2 不同水分管理模式下水稻齐穗期剑叶光合参数的变化 HHZ-黄华占;HY73-旱优73;W-全生育期淹水灌溉;D-全生育期旱作。柱形上不同字母表示在5%水平上差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Fig. 2. Photosynthetic parameters of flag leaf of rice at heading stage under different water management modes. HHZ, Huanghuazhan; HY73, Hanyou 73; W, Traditional flooding; D, Dry cultivation. Different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at P=0.05 level. The same as below.
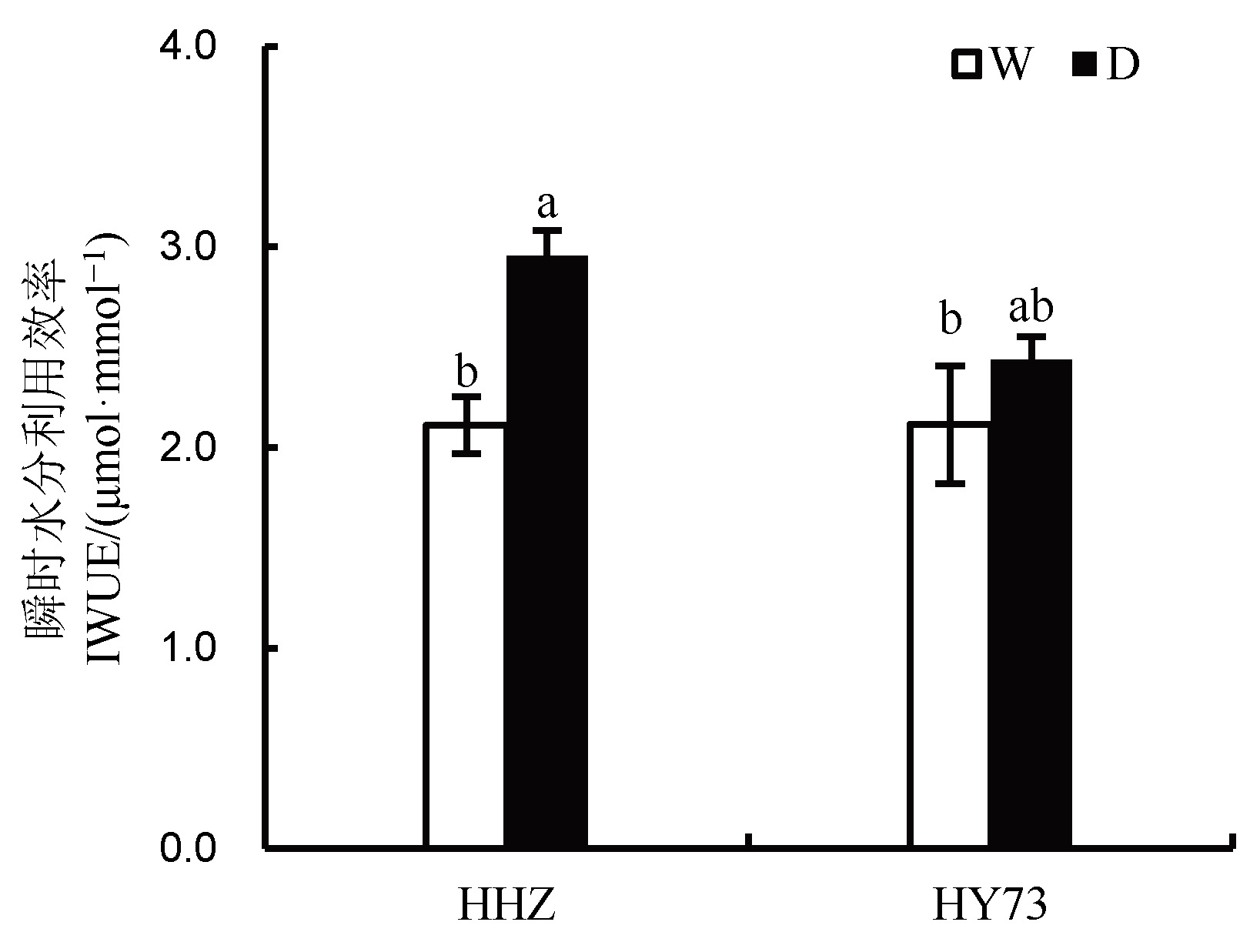
图3 不同水分管理模式下水稻齐穗期剑叶瞬时水分利用效率的变化
Fig. 3. Instantaneous water use efficiency(IWUE) of flag leaves of rice at heading stage under different water management modes.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 茎秆 Culm | 叶片 Leaf | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | |||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 419.1±30.2 b | 12.39±1.61 b | 17.57±2.97 b | 305.3±18.15 c | 22.13±1.18 b | 12.70±0.81 b | |
| D | 696.7±57.7 a | 20.55±1.63 a | 25.00±5.05 a | 496.7±29.05 a | 27.89±2.07 a | 17.76±2.84 a | ||
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 303.3±17.4 c | 9.02±0.19 c | 13.38±2.39 b | 250.6±7.25 d | 19.57±2.65 b | 10.98±1.13 b | |
| D | 791.8±77.3 a | 17.94±1.99 a | 27.39±5.45 a | 426.8±21.97 b | 25.83±2.49 a | 14.72±2.20 a | ||
表1 不同水分管理模式下茎秆、叶片物质转运特性及对籽粒贡献率
Table 1. Dry matter translocation characteristics in stem and leaves and its contribution to grains in various water management modes.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 茎秆 Culm | 叶片 Leaf | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | |||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 419.1±30.2 b | 12.39±1.61 b | 17.57±2.97 b | 305.3±18.15 c | 22.13±1.18 b | 12.70±0.81 b | |
| D | 696.7±57.7 a | 20.55±1.63 a | 25.00±5.05 a | 496.7±29.05 a | 27.89±2.07 a | 17.76±2.84 a | ||
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 303.3±17.4 c | 9.02±0.19 c | 13.38±2.39 b | 250.6±7.25 d | 19.57±2.65 b | 10.98±1.13 b | |
| D | 791.8±77.3 a | 17.94±1.99 a | 27.39±5.45 a | 426.8±21.97 b | 25.83±2.49 a | 14.72±2.20 a | ||
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 源器官 Source organ/% | 籽粒 Grain/% | 源库比 Source/sink | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Culm | 叶 Leaf | 茎鞘+叶 Culm+sheath+leaf | ||||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 44.64±1.64 a | 16.11±0.65 ab | 60.74±1.74 a | 39.25±1.74 b | 1.55±0.11 a |
| D | 37.46±1.78 b | 17.86±0.34 a | 55.32±1.45 b | 44.68±1.45 ab | 1.24±0.07 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 43.14±1.75 a | 14.69±1.80 b | 57.83±3.22 a | 42.17±3.22 b | 1.38±0.17 ab |
| D | 36.70±1.90 b | 14.49±1.08 b | 51.19±0.81 b | 48.81±0.81 a | 1.04±0.04 c | |
表2 不同水分管理模式下成熟期地上部干物质分配比例
Table 2. Dry matter translocation characteristics in stem and leaves in various water management modes.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 源器官 Source organ/% | 籽粒 Grain/% | 源库比 Source/sink | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Culm | 叶 Leaf | 茎鞘+叶 Culm+sheath+leaf | ||||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 44.64±1.64 a | 16.11±0.65 ab | 60.74±1.74 a | 39.25±1.74 b | 1.55±0.11 a |
| D | 37.46±1.78 b | 17.86±0.34 a | 55.32±1.45 b | 44.68±1.45 ab | 1.24±0.07 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 43.14±1.75 a | 14.69±1.80 b | 57.83±3.22 a | 42.17±3.22 b | 1.38±0.17 ab |
| D | 36.70±1.90 b | 14.49±1.08 b | 51.19±0.81 b | 48.81±0.81 a | 1.04±0.04 c | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米有效穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 302.7±12.9 b | 152.8±8.2 c | 92.1±2.4 a | 21.7±0.0 d | 6.80±0.20 c |
| D | 410.7±15.0 a | 123.0±0.7 d | 85.8±1.3 b | 22.6±0.1 c | 7.76±0.22 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 257.3±12.9 c | 189.6±4.3 a | 92.1±0.3 a | 28.8±0.1 b | 7.50±0.16 b |
| D | 296.0±8.89 b | 172.7±2.7 b | 86.8±1.6 b | 30.3±0.0 a | 8.39±0.12 a |
表3 不同水分管理方式对水稻产量及其构成的影响
Table 3. Effects of different water management methods on yield and its components of rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米有效穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 302.7±12.9 b | 152.8±8.2 c | 92.1±2.4 a | 21.7±0.0 d | 6.80±0.20 c |
| D | 410.7±15.0 a | 123.0±0.7 d | 85.8±1.3 b | 22.6±0.1 c | 7.76±0.22 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 257.3±12.9 c | 189.6±4.3 a | 92.1±0.3 a | 28.8±0.1 b | 7.50±0.16 b |
| D | 296.0±8.89 b | 172.7±2.7 b | 86.8±1.6 b | 30.3±0.0 a | 8.39±0.12 a |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness/% | 粒长 Grain length/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 78.9±0.7 a | 68.0±0.3 a | 65.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.2 b | 1.2±0.2 b | 6.1±0.01 c |
| D | 76.9±0.4 a | 65.1±1.0 a | 62.3±1.0 a | 7.9±0.2 b | 1.6±0.7 b | 6.0±0.02 c | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 79.4±0.7 a | 66.1±1.0 a | 55.8±1.5 b | 6.4±0.3 b | 1.2±0.3 b | 6.5±0.03 a |
| D | 74.6±2.1 a | 64.5±1.5 a | 51.5±3.2 b | 12.4±1.9 a | 4.6±0.7 a | 6.3±0.08 b |
表4 不同水分管理方式对稻米加工品质和外观品质的影响
Table 4. Effects of different water management methods on rice milling and appearance quality.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness/% | 粒长 Grain length/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 78.9±0.7 a | 68.0±0.3 a | 65.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.2 b | 1.2±0.2 b | 6.1±0.01 c |
| D | 76.9±0.4 a | 65.1±1.0 a | 62.3±1.0 a | 7.9±0.2 b | 1.6±0.7 b | 6.0±0.02 c | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 79.4±0.7 a | 66.1±1.0 a | 55.8±1.5 b | 6.4±0.3 b | 1.2±0.3 b | 6.5±0.03 a |
| D | 74.6±2.1 a | 64.5±1.5 a | 51.5±3.2 b | 12.4±1.9 a | 4.6±0.7 a | 6.3±0.08 b |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 砷含量 As content/(mg·kg−1) | 镉含量 Cd content/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 15.13±0.26 a | 8.41±0.11 c | 0.18±0.01 a | 0.0412±0.00 b |
| D | 14.51±0.21 b | 9.14±0.08 ab | 0.14±0.00 b | 0.0726±0.00 a | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 13.85±0.21 c | 8.33±0.63 c | 0.15±0.00 b | 0.0424±0.00 b |
| D | 12.80±0.18 d | 9.61±0.42 a | 0.12±0.00 c | 0.0653±0.00 a |
表5 不同水分管理方式对稻米营养品质和重金属含量的影响
Table 5. Effects of different water management methods on nutritional quality and As/Cd concentrations in milled rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 砷含量 As content/(mg·kg−1) | 镉含量 Cd content/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 15.13±0.26 a | 8.41±0.11 c | 0.18±0.01 a | 0.0412±0.00 b |
| D | 14.51±0.21 b | 9.14±0.08 ab | 0.14±0.00 b | 0.0726±0.00 a | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 13.85±0.21 c | 8.33±0.63 c | 0.15±0.00 b | 0.0424±0.00 b |
| D | 12.80±0.18 d | 9.61±0.42 a | 0.12±0.00 c | 0.0653±0.00 a |
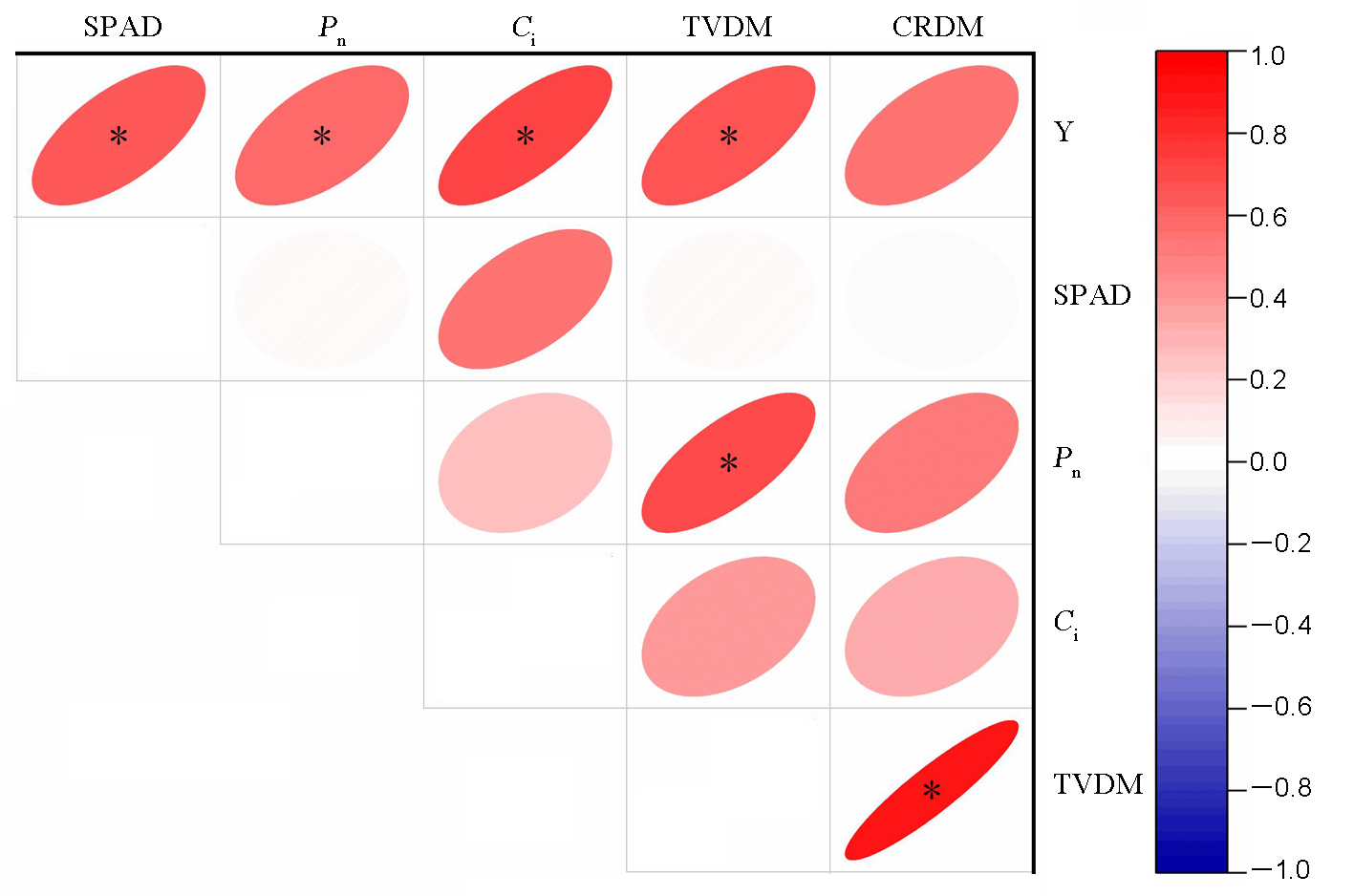
图4 生理指标与干物质转运的相关关系 Y-产量; Pn-净光合速率;Ci-胞间二氧化碳浓度;TVDM-干物质转运量;CRDM-干物质转运贡献率;*表示在0.05水平上显著相关。
Fig. 4. Correlation analysis between yield, dry matter transport and physiological indicators. Y, Yield; Pn, Net photosynthetic rate; Ci, Intercellular CO2 concentration; TVDM, Transport volume of dry matter; CRDM, Contribution rate of dry matter transport to panicle. *Significantly correlated at the 0.05 probability level.
| [1] | Li Y Y, Shao X H, Sheng Z P, Guan W L, Xiao M H. Water conservation and nitrogen loading reduction effects with controlled and mid-gathering irrigation in a paddy field[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2016, 25(3): 1085-1091. |
| [2] | Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B. Current status and challenges of rice production in China[J]. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [3] | 马世浩, 杨丞, 王贵兵, 张赓, 李小坤. 水稻节水灌溉技术模式研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2021, 8: 19-24. |
| Ma S H, Yang C, Wang G B, Zhang G, Li X K. Research progress of rice water-saving irrigation technology mode[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2021, 8: 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Bouman B A M, Peng S B, Castaneda A R, Visperas A R. Yield and water use of irrigated tropical aerobic rice systems[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2005, 74: 87-105. |
| [5] | Singh S, Ladha J K, Gupta R K, Bhushan L, Rao A N, Sivaprasad B, Singh P P. Evaluation of mulching, intercropping with Sesbania and herbicide use for weed management in dry-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Crop Protection, 2007, 26(4): 518-524. |
| [6] | 杜云峰, 江颂颂, 陈宗奎, 毛紫琳, 张志娟, 曹凑贵, 李萍. 播期与补灌对节水抗旱稻旱优73产量、品质与资源利用效率的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 123-132. |
| Du Y F, Jiang S S, Chen Z K, Mao Z L, Zhang Z J, Cao C G, Li P. Effects of sowing dates and periods of supplementary irrigation on yield, quality and resource utilization efficiency of water-saving and drought-resistant rice[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 123-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Fqrooq M, Siddique K H M, Rehman H, Aziz T, Lee D J, Wahid A. Rice direct seeding: experiences, challenges and opportunities[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2011, 111(2): 87-98. |
| [8] | 余灿, 王直华, 张家亮, 曹金华, 刘东华, 黄峰, 靳德明. 水稻半期旱作的节水效果及其对产量和品质的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2009, 28(2): 136-140. |
| Yu C, Wang Z H, Zhang J L, Cao J H, Liu D H, Huang F, Jin D M. The water saving effect of half period dry management of paddy field and its impacts on the yield and grain quality of rice[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2009, 28(2): 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Liu H Y, Hussain S, Zheng M M, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in Central China[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 15:285-294. |
| [10] | 刘宏岩. 旱直播水稻在不同水分管理下高产高效的生理基础研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| Liu H Y. Physiological mechanism of high yield and high resources use efficiency of dry seeded rice under different water managements[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 魏永霞, 季俊超, 刘慧, 郭彦君, 郑衍波, 石蕴. 水分管理对旱直播稻温室气体排放与土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(11): 305-314. |
| Wei Y X, Ji J C, Liu H, Guo Y J, Zheng Y B, Shi Y. Effects of water management on greenhouse gas emission and soil inorganic nitrogen of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(11): 305-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Nagarjun P, Nanjappa D G, Sanjay M T, Boregowda Y S, Ramaiah M. Reduction of soil weedseedbank with increased yield in dry direct-seeded rice through weed management[J]. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 2021, 53(4): 363-366. |
| [13] | Joshi E, Kumar D, Lal B, Nepalia V, Gautam P, Vyas A K. Management of direct seeded rice for enhanced resource - use efficiency[J]. Plant Knowledge Journal, 2013, 2(3): 119-134. |
| [14] | Wang W Q, Peng S B, Liu H Y, Tao Y, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: A review[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 214: 310-320. |
| [15] | Zahra N, Hafeez M B, Nawaz A, Farooq M. Rice production systems and grain quality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2022, 105: 103463. |
| [16] | Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Adrees M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Qayyum M F, Nawaz R. Residual effects of biochar on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cd stress with different water conditions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 206: 676-683. |
| [17] | 郭咏梅, 穆平, 刘家富, 卢义宣, 李自超. 水、旱栽培条件下稻米品质主要品质性状的比较研究[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(11): 59-64. |
| Guo Y M, Mu P, Liu J F, Lu Y X, Li Z C. Comparative studies on quality characters of rice under water-and-dry cultivation conditions[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2005, 31(11): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Wang G J, Zeng F L, Song P, Sun B, Wang Q, Wang J Y. Effects of reduced chlorophyII content on photosystem functions and photosynthetic electron transport rate in rice leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2022, 272: 153669. |
| [19] | Nan S, Xi L, Zhang Q, Li N F, Xu D L, Cao B S. Better revisiting chlorophyll content retrieval with varying senescent material and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence simulation on paddy rice during the entire growth stages[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 130: 108057. |
| [20] | Song Q F, Chu C C, Parry M A J, Zhu X G. Genetics-based dynamic systems model of canopy photosynthesis: The key to improve light and resource use efficiencies for crops[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2016, 5(1): 18-25. |
| [21] | 刘宇峰, 李伏生. 灌溉方式与施肥水平对超级稻光合生理的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 21(4): 416-425. |
| Liu Y F, Li F S. Effect of irrigation method and fertilization dose on photosynthetic physiology of super rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 21(4): 416-425. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 蔡昆争, 吴学祝, 骆世明. 不同生育时期土壤干旱后复水对水稻生长发育的补偿效应[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2008, 27(5): 34-36. |
| Cai K Z, Wu X Z, Luo S M. Compensatory effects of re-watering after soil drying on rice growth and development[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2008, 27(5): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 易子豪, 朱德峰, 王亚梁, 胡国辉, 张玉屏, 向镜, 张义凯, 陈惠哲. 水稻生长对干旱的响应及其补偿效应研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(4): 1-6. |
| Yi Z H, Zhu D F, Wang Y L, Hu G H, Zhang Y P, Xiang J, Zhang Y K, Chen H Z. Advances of rice growth response to drought and its compensatory effects[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 朱海平, 李贵勇, 夏琼梅, 龙瑞平, 邓安凤, 黄军, 相罕章, 杨从党. 不同时期干旱胁迫对水稻产量和生长特性的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2017, 23(4): 135-138. |
| Zhu H P, Li G Y, Xia Q M, Long R P, Deng A F, Huang J, Xiang H Z, Yang C D. Effects of drought stress on yield and growth characteristics of rice in different periods[J]. China Rice, 2017, 23(4): 135-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 杨晓龙, 程建平, 汪本福, 李阳, 张枝盛, 李进兰, 李萍. 灌浆期干旱胁迫对水稻生理性状和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| Yang X L, Cheng J P, Wang B F, Li Y, Zhang Z S, Li J L, Li P. Effects of drought stress at grain filling stage on rice physiological characteristics and yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Yang X L, Wang B F, Chen L, Li P, Cao C G. The different influences of drought stress at the flowering stage on rice physiological traits, grain yield, and quality[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 3742. |
| [27] | 何海兵, 武立权, 杨茹, 马富裕, 黄义德. 干旱区控制灌溉下水稻光合特性与蒸腾效率研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(9):186-193. |
| He H B, Wu L Q, Yang R, Ma F Y, Huang Y D. Photosynthesis characteristics and transpiration efficiency of rice plants under controlled irrigation technology in arid region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 王熹, 陶龙兴, 黄效林, 闵绍楷, 程式华. 滴灌稻田水稻旱作法研究-水稻的生育与生理特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(9): 1274-1281. |
| Wang X, Tao L X, Huang X L, Min S K, Cheng S H. Study on no-flooding farming technique in irrigated paddy field-physiological and developmental characteristics of rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(9): 1274-1281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王志军, 叶春秀, 董永梅, 李有忠, 田又升, 陈林, 孙国清, 谢宗铭. 滴灌和淹灌栽培模式下水稻光合生理、荧光参数及产量构成因素分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(5): 723-735. |
| Wang Z J, Ye C X, Dong Y M, Li Y Z, Tian Y S, Chen L, Sun G Q, Xie Z M. Photosynthetic physiology, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and yield components of rice under drip irrigation with plastic film mulching and continuous flooding[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(5): 723-735. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Chen Z K, Yang X L, Song W Z, Khan A, Najeeb U, Li P, Cao C G. Water-saving cultivation plus super rice hybrid genotype improves water productivity and yield[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 112(3): 1764-1777. |
| [31] | 殷春渊, 王书玉, 刘贺梅, 孙建权, 胡秀明, 王和乐, 田芳慧, 马朝阳, 张栩, 张瑞平, 马晓红. 节水灌溉与常规灌溉对旱直播水稻叶片生理特性、产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(18): 1-9. |
| Yin C Y, Wang S Y, Liu H M, Sun J Q, Hu X M, Wang H L, Tian F H, Ma C Y, Zhang X, Zhang R P, Ma X H. Effects on leaf physiological characteristics, yield and quality of dry seeding rice: water-saving irrigation and conventional irrigation[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(18): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Mahajan G, Chauhan B S, Timsina J, Singh P P, Singh K. Crop performance and water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies in dry-seeded rice in response to irrigation and fertilizer amounts in northwest India[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 134: 59-70. |
| [33] | Pan S G, Wen X C, Wang Z M, Ashraf U, Tian H, Duan M Y, Mo Z W, Fan P S, Tang X R. Benefits of mechanized deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer in direct-seeded rice in South China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203:139-149. |
| [34] | 夏朵, 周浩, 何予卿. 稻米品质的遗传研究及分子育种进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. |
| Xia D, Zhou H, He Y Q. Progress on genetic study and molecular breeding of rice quality[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Li X K, Wu L, Geng X, Xia X H, Wang X H, Xu Z J, Xu Q. Deciphering the environmental impacts on rice quality for different rice cultivated areas[J]. Rice, 2018, 11(1): 1-10 |
| [36] | 杨丞, 汪洋, 张万洋, 叶廷红, 鲁剑巍, 张赓, 李小坤. 灌溉模式与施氮量互作对水稻茎蘖产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. |
| Yang C, Wang Y, Zhang W Y, Ye T H, Lu J W, Zhang G, Li X K. Effects of interaction between irrigation mode and nitrogen application rate on the yield formation of main stem and tillers of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Yun P, Luo L J, Yan B, Peng B, Xie W B, Wang G W, Li X H, Xiao J H, Xu C G, He Y Q. Chalk5 encodes a vacuolar H +-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(4): 398-404. |
| [38] | 刘东华. 干旱胁迫对稻谷品质性状及WX基因表达的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. |
| Liu H D. The impacts of drought stress on grain quality and Wx gene expression in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 金正勋, 杨静, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金学泳, 秋太权. 灌浆成熟期温度对水稻籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. |
| Jin Z X, Yang J, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin X Y, Qiu T Q. Effects of temperature during grain filling period on activities of key enzymes for starch synthesis and rice grain quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 陈璐, 杨斗龙, 米艳华, 李倩, 王丹, 王文治, 杜丽娟, 尹本林. 水分管理对复合污染稻田Pb、Cd和As迁移特性及稻米质量安全的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 2022, 11(1): 96-103. |
| Chen L, Yang D L, Mi Y H, Li Q, Wang D, Wang W Z, Du L J, Yin B L. Effects of water management on soil heavy metal transport and rice quality safety[J]. Soils and Crops, 11(1): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Zhang Q, Chen H F, Huang D Y, Xu C, Zhu H H, Zhu Q H. Water managements limit heavy metal accumulation in rice: Dual effects of iron-plaque formation and microbial communities[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 618: 790-799. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||