
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 87-95.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.201208
苏庆旺, 苍柏峰, 白晨阳, 李韫哲, 宋泽, 李俊材, 吴美康, 魏晓双, 崔菁菁, 武志海*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-11
修回日期:2021-07-09
出版日期:2022-01-10
发布日期:2022-01-10
通讯作者:
武志海
基金资助:
SU Qingwang, CANG Baifeng, BAI Chenyang, LI Yunzhe, SONG Ze, LI Juncai, WU Meikang, WEI Xiaoshuang, CUI Jingjing, WU Zhihai*( )
)
Received:2020-12-11
Revised:2021-07-09
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
WU Zhihai
摘要:
【目的】明确直接播种雨养为主的旱作水稻的硅肥最佳施用量并揭示硅肥增加产量的机制。【方法】以绥粳18为材料进行两年大田试验,设计0、15、30、45、60和75 kg/hm 2的有效硅用量(用Si0、Si15、Si30、Si45、Si60和Si75表示),研究不同硅肥用量对旱作水稻生理指标、干物质转运和产量构成因素的影响。【结果】施加硅肥显著增加了旱作水稻的产量,二次回归方程分析表明施用有效硅量47.68 kg/hm 2可获得最大理论产量,当有效硅用量为30~47.68 kg/hm 2时,硅肥显著提高了根系活力、叶片SPAD值和叶面积指数,协调了茎叶干物质向穗部的转移,延缓了后期叶片的衰老,每穗粒数提高了23.62%~24.63%,千粒重提高了8.94%~10.08%,优化了穗粒结构进而增产38.42%~110.20%;有效硅施用量为47.68~75 kg/hm 2时,生育后期加快了茎叶干物质向穗部转移,加速了叶片衰老,不利于籽粒的持续性灌浆,影响了每平方米穗数、每穗粒数和千粒重进而影响产量。【结论】对于绥粳18而言,适宜吉林省中部地区旱作水稻高产高效的最佳有效硅肥施用量为30~47.68 kg/hm 2。
苏庆旺, 苍柏峰, 白晨阳, 李韫哲, 宋泽, 李俊材, 吴美康, 魏晓双, 崔菁菁, 武志海. 施硅量对旱作水稻产量和干物质积累的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 87-95.
SU Qingwang, CANG Baifeng, BAI Chenyang, LI Yunzhe, SONG Ze, LI Juncai, WU Meikang, WEI Xiaoshuang, CUI Jingjing, WU Zhihai. Effect of Silicon Application Rate on Yield and Dry Matter Accumulation of Rice Under Dry Cultivation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 87-95.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Si0 | 360.3±8.4 d | 42.3±2.9 d | 89.47±0.98 b | 24.28±0.08 c | 3470.23±320.66 d |
| Si15 | 418.3±14.3 c | 45.3±0.6 c | 92.66±1.17 a | 26.20±0.62 ab | 4803.48±56.02 c | |
| Si30 | 487.7±13.4 a | 50.7±2.1 a | 93.66±1.19 a | 26.34±0.39 a | 6035.35±392.62 a | |
| Si45 | 476.3±13.9 a | 52.3±2.4 a | 94.08±1.74 a | 26.45±0.21 a | 6441.31±234.86 a | |
| Si60 | 470.3±17.1 ab | 51.3±1.2 ab | 93.36±1.12 a | 26.25±0.56 ab | 6264.69±294.27 a | |
| Si75 | 454.7±8.7 b | 48.0±2.7 bc | 93.74±0.35 a | 25.65±0.54 b | 5240.04±392.74 b | |
| 2020 | Si0 | 361.7±38.8 c | 53.6±5.2 b | 74.19±5.89 b | 21.62±0.59 b | 3112.05±396.40 d |
| Si15 | 415.3±68.0 bc | 57.6±11.4 ab | 84.67±7.42 a | 22.78±1.15 ab | 4597.18±373.63 c | |
| Si30 | 484.7±59.2 a | 64.2±6.1 ab | 85.47±3.49 a | 23.38±1.20 a | 6210.59±521.82 a | |
| Si45 | 485.7±9.1 a | 66.8±7.7 a | 85.36±7.97 a | 23.80±0.74 a | 6541.55±320.71 a | |
| Si60 | 480.3±60.0 ab | 62.6±8.7 ab | 85.42±2.16 a | 23.33±1.17 a | 6007.69±369.38 ab | |
| Si75 | 460.3±22.4 ab | 60.6±5.1 ab | 86.22±2.56 a | 23.31±1.55 a | 5600.59±418.30 b |
表1 不同有效硅用量对旱作条件下水稻产量构成的影响
Table 1 Effect of different silicon fertilizer rates on yield components of rice under dry cultivation.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Si0 | 360.3±8.4 d | 42.3±2.9 d | 89.47±0.98 b | 24.28±0.08 c | 3470.23±320.66 d |
| Si15 | 418.3±14.3 c | 45.3±0.6 c | 92.66±1.17 a | 26.20±0.62 ab | 4803.48±56.02 c | |
| Si30 | 487.7±13.4 a | 50.7±2.1 a | 93.66±1.19 a | 26.34±0.39 a | 6035.35±392.62 a | |
| Si45 | 476.3±13.9 a | 52.3±2.4 a | 94.08±1.74 a | 26.45±0.21 a | 6441.31±234.86 a | |
| Si60 | 470.3±17.1 ab | 51.3±1.2 ab | 93.36±1.12 a | 26.25±0.56 ab | 6264.69±294.27 a | |
| Si75 | 454.7±8.7 b | 48.0±2.7 bc | 93.74±0.35 a | 25.65±0.54 b | 5240.04±392.74 b | |
| 2020 | Si0 | 361.7±38.8 c | 53.6±5.2 b | 74.19±5.89 b | 21.62±0.59 b | 3112.05±396.40 d |
| Si15 | 415.3±68.0 bc | 57.6±11.4 ab | 84.67±7.42 a | 22.78±1.15 ab | 4597.18±373.63 c | |
| Si30 | 484.7±59.2 a | 64.2±6.1 ab | 85.47±3.49 a | 23.38±1.20 a | 6210.59±521.82 a | |
| Si45 | 485.7±9.1 a | 66.8±7.7 a | 85.36±7.97 a | 23.80±0.74 a | 6541.55±320.71 a | |
| Si60 | 480.3±60.0 ab | 62.6±8.7 ab | 85.42±2.16 a | 23.33±1.17 a | 6007.69±369.38 ab | |
| Si75 | 460.3±22.4 ab | 60.6±5.1 ab | 86.22±2.56 a | 23.31±1.55 a | 5600.59±418.30 b |
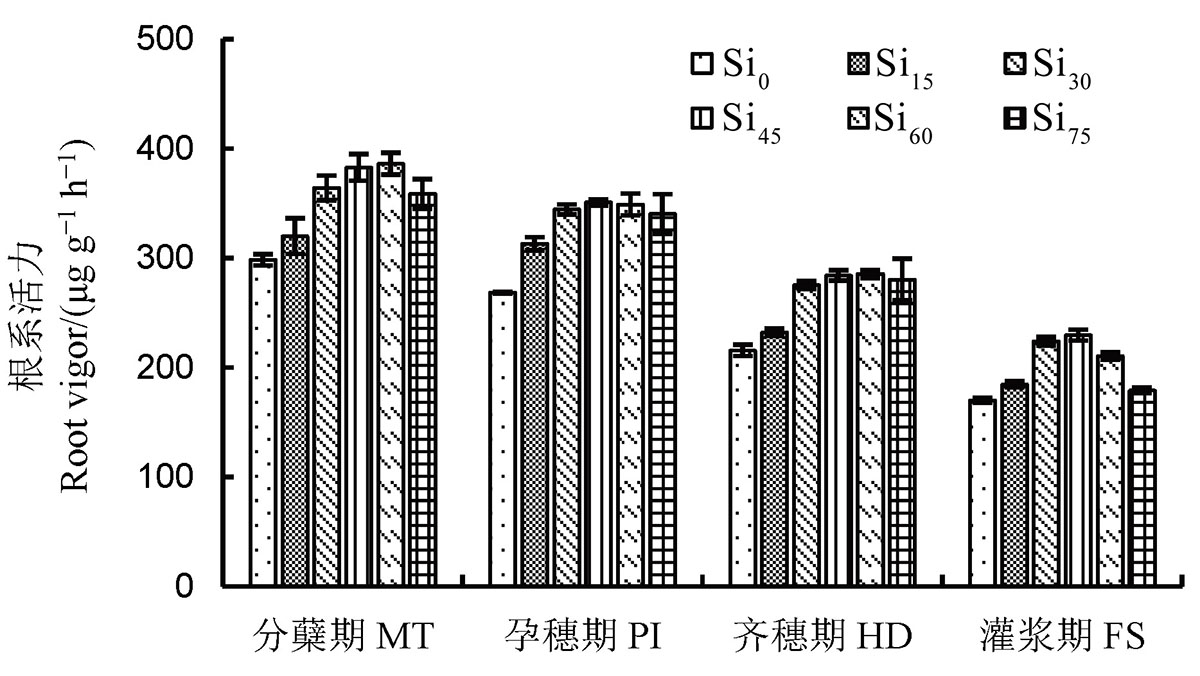
图2 不同生育阶段不同有效硅用量下旱作水稻根系活力的比较 MT–分蘖期;PI–孕穗期;HD–齐穗期;FS–灌浆期。柱上不同小写字母表示在 5%水平上差异显著(n=3,最小显著差数法)。下同。
Fig. 2. Comparison of root vigor of dry farming rice under different silicon fertilizer rates at different growth stages. MT, Mid-tilling stage; PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Full heading stage; FS, Filling stage. Values (mean± SD) under the same treatments followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 (n =3, LSD). The same below.
| 处理 Treatment | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | 干物质转运 对穗的贡献率 CRDM/% | 干物质积累总量 TDMA /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质转运量 TVDM/(kg·hm-2) | 干物质转运率 TRDM/% | 干物质转运量 TVDM/(kg·hm-2) | 干物质转运率 TRDM/% | 干物质增加量 IDM/(kg·hm-2) | |||
| Si0 | 711.54 a | 14.65 a | 515.00 c | 35.40 ab | 2880.10 d | 43.21 a | 8555.71 c |
| Si15 | 447.71 c | 7.32 bc | 412.90 c | 23.63 b | 4574.48 c | 18.73 c | 12183.96 b |
| Si30 | 460.90 c | 6.38 c | 526.84 c | 22.56 b | 5641.22 a | 17.48 c | 14867.06 a |
| Si45 | 505.55 bc | 7.08 c | 715.24 b | 29.80 ab | 5509.06 a | 22.10 c | 14535.05 a |
| Si60 | 591.58 b | 8.32 bc | 825.19 b | 36.37 ab | 5235.20 ab | 27.05 bc | 14105.63 a |
| Si75 | 727.12 a | 10.32 b | 1052.10 a | 47.26 a | 4685.91 bc | 38.44 ab | 13146.33 b |
表2 不同有效硅量对旱作水稻干物质转运及植株硅积累总量的影响
Table 2 Effects of different silicon fertilizer levels on dry matter transport and silicon accumulation of rice under dry cultivation.
| 处理 Treatment | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | 干物质转运 对穗的贡献率 CRDM/% | 干物质积累总量 TDMA /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质转运量 TVDM/(kg·hm-2) | 干物质转运率 TRDM/% | 干物质转运量 TVDM/(kg·hm-2) | 干物质转运率 TRDM/% | 干物质增加量 IDM/(kg·hm-2) | |||
| Si0 | 711.54 a | 14.65 a | 515.00 c | 35.40 ab | 2880.10 d | 43.21 a | 8555.71 c |
| Si15 | 447.71 c | 7.32 bc | 412.90 c | 23.63 b | 4574.48 c | 18.73 c | 12183.96 b |
| Si30 | 460.90 c | 6.38 c | 526.84 c | 22.56 b | 5641.22 a | 17.48 c | 14867.06 a |
| Si45 | 505.55 bc | 7.08 c | 715.24 b | 29.80 ab | 5509.06 a | 22.10 c | 14535.05 a |
| Si60 | 591.58 b | 8.32 bc | 825.19 b | 36.37 ab | 5235.20 ab | 27.05 bc | 14105.63 a |
| Si75 | 727.12 a | 10.32 b | 1052.10 a | 47.26 a | 4685.91 bc | 38.44 ab | 13146.33 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 硅素农学利用率 Si agronomic efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 硅素生理利用率 Si physiological efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 硅肥偏生产力 Partial factor productivity of applied Si/(kg·kg-1) | 硅素稻谷生产效率 Si use efficiency for grain production /(kg·kg-1) | 硅投入 Si input /(kg·hm-2) | 籽粒硅携出 Si output /(kg·hm-2) | 硅平衡 Si balance /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | 7.13 ab | 0 | 179.70 c | -179.70 a | |||
| Si15 | 88.88 a | 5.73 b | 320.23 a | 6.71 b | 15 | 288.18 b | -273.18 e |
| Si30 | 85.50 a | 6.98 ab | 201.18 b | 7.04 ab | 30 | 307.79 a | -277.79 e |
| Si45 | 66.02 b | 8.21 a | 143.14 c | 7.53 ab | 45 | 308.34 a | -263.34 d |
| Si60 | 46.57 c | 8.32 a | 104.41 d | 7.62 a | 60 | 311.79 a | -251.79 c |
| Si75 | 23.60 d | 6.01 b | 69.87 e | 6.72 b | 75 | 308.41 a | -233.41 b |
表3 不同有效硅量对旱作水稻硅肥利用效率的影响
Table 3 Effects of different amounts of silicon fertilizer on silicon utilization efficiency of rice under dry cultivation.
| 处理 Treatment | 硅素农学利用率 Si agronomic efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 硅素生理利用率 Si physiological efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 硅肥偏生产力 Partial factor productivity of applied Si/(kg·kg-1) | 硅素稻谷生产效率 Si use efficiency for grain production /(kg·kg-1) | 硅投入 Si input /(kg·hm-2) | 籽粒硅携出 Si output /(kg·hm-2) | 硅平衡 Si balance /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | 7.13 ab | 0 | 179.70 c | -179.70 a | |||
| Si15 | 88.88 a | 5.73 b | 320.23 a | 6.71 b | 15 | 288.18 b | -273.18 e |
| Si30 | 85.50 a | 6.98 ab | 201.18 b | 7.04 ab | 30 | 307.79 a | -277.79 e |
| Si45 | 66.02 b | 8.21 a | 143.14 c | 7.53 ab | 45 | 308.34 a | -263.34 d |
| Si60 | 46.57 c | 8.32 a | 104.41 d | 7.62 a | 60 | 311.79 a | -251.79 c |
| Si75 | 23.60 d | 6.01 b | 69.87 e | 6.72 b | 75 | 308.41 a | -233.41 b |
| 指标 Index | 产量 Grain yield | 根系活力 Root vigor | SPAD值 SPAD value | 光合势 LAD | 干物质积累总量 TDMA | 茎干物质转运量 STVDM | 叶干物质转运量 LTVDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根系活力 RV | 0.868** | ||||||
| SPAD值 SPAD value | 0.791** | 0.836** | |||||
| 光合势 LAD | 0.924** | 0.741** | 0.724** | ||||
| 干物质积累总量 TDMA | 0.943** | 0.820** | 0.846** | 0.916** | |||
| 茎干物质转运量 STVDM | -0.437 | -0.580* | -0.796** | -0.300 | -0.495* | ||
| 叶干物质转运量 LTVDM | 0.336 | 0.005 | -0.052 | 0.509* | 0.292 | 0.542* | |
| 干物质转运对穗的贡献率CRDM | -0.521* | -0.578* | -0.723** | -0.414 | -0.589* | 0.775** | 0.411 |
表4 灌浆期生理指标及干物质转运与产量相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between yield, dry matter transport and physiological indicators during filling stage.
| 指标 Index | 产量 Grain yield | 根系活力 Root vigor | SPAD值 SPAD value | 光合势 LAD | 干物质积累总量 TDMA | 茎干物质转运量 STVDM | 叶干物质转运量 LTVDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根系活力 RV | 0.868** | ||||||
| SPAD值 SPAD value | 0.791** | 0.836** | |||||
| 光合势 LAD | 0.924** | 0.741** | 0.724** | ||||
| 干物质积累总量 TDMA | 0.943** | 0.820** | 0.846** | 0.916** | |||
| 茎干物质转运量 STVDM | -0.437 | -0.580* | -0.796** | -0.300 | -0.495* | ||
| 叶干物质转运量 LTVDM | 0.336 | 0.005 | -0.052 | 0.509* | 0.292 | 0.542* | |
| 干物质转运对穗的贡献率CRDM | -0.521* | -0.578* | -0.723** | -0.414 | -0.589* | 0.775** | 0.411 |
| [1] | Liu X, Wang H, Zhou J, Hu F Q, Zhu D J, Chen Z M, Liu Y Z. Effect of N fertilization pattern on rice yield, N use efficiency and fertilizer-N fate in the Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. PloS ONE, 2016,11(11):e0166002. |
| [2] | Luo L J. Breeding for water-saving and drought- resistance rice (WDR) in China[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011: 3509-3517. |
| [3] | Cai H F, Chen Q G. Rice production in China in the early 21st Century[J]. Chinese Rice Research Newsletter, 2000(2):14-16. |
| [4] | Jia L, Hu C, Li Z, Zhou J, Fu J F, Jia X Y. Development prospect and strategies of water-saving and drought- resistance rice[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2016,17(5):1125-1128. |
| [5] | 王瑗, 盛连喜, 李科, 孙弘颜. 中国水资源现状分析与可持续发展对策研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2008(3):10-14. |
| Wang Y, Sheng LX, Li K, Sun H Y. Analysis of present situation of water resources and countermeasures for sustainable development in China[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2008(3):10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Cao B L, Ma Q, Xu K. Silicon restrains drought-induced ROS accumulation by promoting energy dissipation in leaves of tomato[J]. Protoplasma, 2020,257(2):537-547. |
| [7] | Hosseini S A, Maillard A, Hajirezaei M R, Ali N, Schwarzenberg A, Jamois F, Yvin J. Induction of barley silicon transporter HvLsi1 and HvLsi2, increased silicon concentration in the shoot and regulated Starch and ABA homeostasis under osmotic stress and concomitant potassium deficiency[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017,8:1359. |
| [8] | Ye Y S, Liang X Q, Chen Y X, Liu J, Gu J T, Guo R, Li L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013,144(2013):212-224. |
| [9] | Ramasamy S, Berge H, Purushothaman S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application[J]. Field Crops Research, 1997,51(1-2):65-82. |
| [10] | Zhang Z C, Zhang S F, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Yield, grain quality and water use efficiency of rice under non-flooded mulching cultivation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2008,108(1):71-81. |
| [11] | 黄晨. 冀中南地区旱稻生产现状及发展对策[J]. 河北农业, 2018,281(8):55-57. |
| Huang C. Status and development strategies of dry rice production in central and southern Hebei[J]. Hebei Agriculture, 2018,281(8):55-57.(in Chinese) | |
| [12] | Sandhu N, Yadaw R B, Chaudhary B, Prasai H, Iftekharuddaula K, Venkateshwarlu C, Annamalai A, Xangsayasane P, Battan K R, Ram M, Cruz M S, Pablico P, Maturan P C, Raman K, Catolos M, Kumar A. Evaluating the performance of rice genotypes for improving yield and adaptability under direct seeded aerobic cultivation conditions[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019,10:159. |
| [13] | Ma J F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses[J]. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 2004,50(1):11-18. |
| [14] | Etesami H. Can interaction between silicon and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria benefit in alleviating abiotic and biotic stresses in crop plants?[J] Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2018,253:98-112. |
| [15] | Luyckx M, Hausman J, Lutts S, Guerriero G. Silicon and plants: Current knowledge and technological perspectives[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017,8:411. |
| [16] | Gong H J, Chen K M, Chen G C, Wang S M, Zhang C L. Effects of silicon on growth of wheat under drought[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2003,26(5):1055-1063. |
| [17] | Parveen N, Ashraf M. Role of silicon in mitigating the adverse effects of salt stress on growth and photosynthetic attributes of two maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars grown hydroponically[J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2010,42(3):1675-1684. |
| [18] | Zhang W J, Yu X X, Li M, Lang D Y, Zhang X H, Xie Z C. Silicon promotes growth and root yield of Glycyrrhiza uralensis under salt and drought stresses through enhancing osmotic adjustment and regulating antioxidant metabolism[J]. Crop Protection, 2018,107:1-11. |
| [19] | Zhu Y X, Gong H J. Beneficial effects of silicon on salt and drought tolerance in plants[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2013,34(2):455-472. |
| [20] | 陈健晓, 屠乃美, 易镇邪, 朱红林. 硅肥对超级早稻产量形成和部分生理特性的影响[J]. 作物研究, 2011,25(6):544-549. |
| Chen J X, Tu N M, Yi Z X, Zhu H L. Effects of silicon fertilizer on yield formation and some physiological characteristics of super early rice[J]. Crop Research, 2011,25(6):544-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 韦还和, 孟天瑶, 李超, 张洪程, 史天宇, 马荣荣, 王晓燕, 杨筠文, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 郭保卫. 施硅量对甬优系列籼粳交超级稻产量及相关形态生理性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016,42(3):437-445. |
| Wei H H, Meng T Y, Li C, Zhang H C, Shi T Y, Ma R R, Wang X Y, Yang J W, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Guo B W. Effects of silicon application rate on the yield and related morphological and physiological characteristics of Yongyou series indica-japonica super rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016,42(3):437-445. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 商全玉, 张文忠, 韩亚东, 荣蓉, 徐海, 徐正进, 陈温福. 硅肥对北方粳稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009,23(6):661-664. |
| Shang Q Y, Zhang W Z, Han Y D, Rong R, Xu H, Xu Z J, Chen W F. The effect of silicon fertilizer on the yield and quality of northern japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009,23(6):661-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 龚金龙, 胡雅杰, 龙厚元, 常勇, 葛梦婕, 高辉, 刘艳阳, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 李德剑, 沙安勤, 周有炎, 罗学超. 不同时期施硅对超级稻产量和硅素吸收、利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012,45(8):1475-1488. |
| Gong J L, Hu Y J, Long H Y, Chang Y, Ge M J, Gao H, Liu Y Y, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Li D J, Sha A Q, Zhou Y Y, Luo X C. The effects of silicon application in different periods on the yield and silicon absorption and utilization efficiency of super rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012,45(8):1475-1488. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 赵雁. 硅肥在水稻上的应用研究[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2016,57(12):52-54. |
| Zhao Y. Research on the application of silicon fertilizer on rice[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2016,57(12):52-54. | |
| [25] | Cuong T X, Ullah H, Datta A, Hanh T C. Effects of silicon-based fertilizer on growth, yield and nutrient uptake of rice in tropical zone of Vietnam[J]. Rice Science, 2017,24(5):283-290. |
| [26] | 张国良, 戴其根, 王建武, 张洪程, 霍中洋, 凌励, 王显, 张军. 施硅量对粳稻品种武育粳3号产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007,21(3):299-303. |
| Zhang G L, Dai Q G, Wang J W, Zhang H C, Huo Z Y, Ling L, Wang X, Zhang J. Effects of silicon fertilizer rate on yield and quality of japonica rice Wuyujing 3[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007,21(3):299-303. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 黄益宗, 张文强, 招礼军, 曹慧明. Si对盐胁迫下水稻根系活力、丙二醛和营养元素含量的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2009,4(6):860-866. |
| Huang Y Z, Zhang W Q, Zhao L J, Cao H M. Effects of Si on rice root vigor, malondialdehyde and nutrient element contents under salt stress[J]. Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2009,4(6):860-866. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 贾雨薇, 杨瑞林, 张洋, 房娟娟, 陈惠. 一种优化的测定水稻硅含量的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2016,51(5):679-683. |
| Jia Y W, Yang R L, Zhang Y, Fang J J, Chen H. An optimized method for measuring silicon content in rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016,51(5):679-683. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Bouman B, Humphreys E, Tuong T, Barker R. Rice and water[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 2007,92(4):187-237. |
| [30] | Prakash N B, Chandrashekar N, Mahendra C, Patil S U, Thippeshappa G N, Laane H M. Effect of foliar spray of soluble silicic acid on growth and yield parameters of wetland rice in hilly and coastal zone soils of Karnataka, south India[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2011,34(12), 1883-1893. |
| [31] | Pati S, Pal B, Badole S, Mandal B. Effect of silicon fertilization on growth, yield, and nutrient uptake of rice[J]. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 2016,47(3):284-290. |
| [32] | Crooks R, Prentice P. Extensive investigation into field based responses to a silica fertilizer[J]. Silicon-neth, 2017,9(2):301-304. |
| [33] | Detmann K C, Araújo W L, Martins S C V, Sanglard L M V P, Reis J V, Detmann E, Rodrigues F A, Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie A R, DaMatta F M. Silicon nutrition increases grain yield, which, in turn, exerts a feed-forward stimulation of photosynthetic rates via enhanced mesophyll conductance and alters primary metabolism in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 196(3):752-762. |
| [34] | Chen W, Yao X Q, Cai K Z, Chen J N. Silicon alleviates drought stress of rice plants by improving plant water status, photosynjournal and mineral nutrient absorption[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2011,142(1):67-76. |
| [35] | Ambavaram M M R, Basu S, Krishnan A, Ramegowda V, Batlang U, Rahman L, Baisakh N, Pereira A. Coordinated regulation of photosynjournal in rice increases yield and tolerance to environmental stress[J]. Nature Communications, 2014,5(1):20-29. |
| [36] | 武志海, 赵国臣, 徐克章, 邸玉婷, 姜楠, 凌凤楼. 吉林省水稻品种遗传改良过程中地上干物质积累特性[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2012,34(5):483-490. |
| Wu Z H, Zhao G C, Xu K Z, Di Y T, Jiang N, Ling F L. Characteristics of above ground dry matter accumulation during genetic improvement of rice varieties in Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2012,34(5):483-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 张娟, 张智, 张广鑫, 刘传玉, 宋继富. 关于土壤中施用固体硅肥有效利用率的探讨[J]. 黑龙江科学, 2016,7(19):8-10. |
| Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang G X, Liu C Y, Song J F. Discussion on the effective utilization rate of solid silicon fertilizer in soil[J]. Heilongjiang Science, 2016,7(19):8-10. (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | 于广武, 李晓冰, 何长兴, 郑连举, 林永德. 硅肥对水稻生育性状及产量的影响[J]. 肥料与健康, 2020(3):19-23. |
| Yu G W, Li X B, He C X, Zheng L J, Lin Y D. Effects of silicon fertilizer on rice growth traits and yield[J]. Fertilizers and Health, 2020(3):19-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 谢凡. 不同硅肥用量对水稻生长发育及养分吸收的影响[D]. 南昌:江西农业大学, 2016. |
| Xie F. The effect of different amounts of silicon fertilizer on rice growth and nutrient absorption[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2016. ( in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 葛玮健, 常艳丽, 刘俊梅, 张树兰, 孙本华, 杨学云. 土区长期施肥对小麦-玉米轮作体系钾素平衡与钾库容量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012,18(3):629-636. |
| Ge W J, Chang Y L, Liu J M, Zhang S L, Sun B H, Yang X Y. Effects of long-term fertilization in soil area on potassium balance and potassium storage capacity of wheat-corn rotation system[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2012,18(3):629-636. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [9] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [10] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [11] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [12] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [13] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [14] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [15] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||