
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 505-519.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211104
景文疆1, 顾汉柱1, 张小祥2, 吴昊1, 张伟杨1, 顾骏飞1, 刘立军1, 王志琴1, 杨建昌1, 张耗1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-05
修回日期:2022-03-10
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
张耗
基金资助:
JING Wenjiang1, GU Hanzhu1, ZHANG Xiaoxiang2, WU Hao1, ZHANG Weiyang1, GU Junfei1, LIU Lijun1, WANG Zhiqin1, YANG Jianchang1, ZHANG Hao1( )
)
Received:2021-11-05
Revised:2022-03-10
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
ZHANG Hao
摘要:
【目的】研究不同灌溉方式下中籼水稻品种的稻米品质与根系特征。【方法】以江苏省近80年来各阶段具有代表性的中籼水稻品种为试验材料,全生育期设置干湿交替灌溉(AWD)和常规灌溉(CI)处理。在矮秆、半矮秆常规稻和半矮秆杂交稻中各选择2个水分利用效率(WUE)存在明显差异的品种进行稻米品质和根系特征分析。【结果】无论是在AWD还是CI下,各类型品种的产量和WUE均随品种改良逐渐提高。与CI相比,AWD显著增加了产量和水分利用效率。在AWD下,各类型品种(矮秆品种、半矮秆品种、半矮秆杂交稻)的产量分别为6.96 t/hm2、8.71 t/hm2和10.14 t/hm2,WUE分别为1.30 kg/m3、1.62 kg/m3和1.91 kg/m3。各类型品种的精米率、整精米率、蛋白质含量、淀粉溶解度与膨胀度、根干质量、根冠比、根系氧化力、根系总吸收表面积和活跃吸收表面积、根系伤流液中玉米素和玉米素核苷以及脱落酸含量随品种改良显著提高。与CI相比,AWD改善了稻米的加工和外观品质及根系形态生理特征,提高了稻米淀粉的峰值黏度、热浆黏度、最终黏度和崩解值,降低了淀粉的消减值和相对结晶度。相关分析表明,产量、WUE及稻米品质均与根系生长密切相关。【结论】现代半矮秆品种尤其杂交稻在全生育期干湿交替灌溉条件下可获得较高的产量和水分利用效率以及较优的稻米品质,这与根系形态和生理特征的改善密切相关。
景文疆, 顾汉柱, 张小祥, 吴昊, 张伟杨, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌, 张耗. 中籼水稻品种改良过程中米质和根系特征对灌溉方式的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 505-519.
JING Wenjiang, GU Hanzhu, ZHANG Xiaoxiang, WU Hao, ZHANG Weiyang, GU Junfei, LIU Lijun, WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Hao. Response of Grain Quality and Root Characteristics to Irrigation Methods During Mid-season indica Rice Varieties Improvement[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 505-519.
| 应用年代 Application years | 品种 Variety | 类型 Type | 生育期 Growth duration/d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1940-1950 | 黄瓜籼 Huangguaxian | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 118 |
| 1940-1950 | 银条籼 Yintiaoxian | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 117 |
| 1940-1950 | 南京1号 Nanjing 1 | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 117 |
| 1960-1970 | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 130 |
| 1960-1970 | 南京11 Nanjing 11 | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 122 |
| 1960-1970 | 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 127 |
| 1970-1980 | IR24 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 122 |
| 1980-1990 | 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 145 |
| 1980-1990 | 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 146 |
| 2000-2005 | 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 153 |
| 2000-2005 | 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 152 |
| 2000-2005 | Ⅱ优084 Ⅱyou 084 | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 153 |
表1 江苏省近80年来具有代表性的中籼水稻品种
Table 1. Representative mid-season indica rice varieties in Jiangsu Province in recent 80 years.
| 应用年代 Application years | 品种 Variety | 类型 Type | 生育期 Growth duration/d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1940-1950 | 黄瓜籼 Huangguaxian | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 118 |
| 1940-1950 | 银条籼 Yintiaoxian | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 117 |
| 1940-1950 | 南京1号 Nanjing 1 | 高秆品种 High stalk variety | 117 |
| 1960-1970 | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 130 |
| 1960-1970 | 南京11 Nanjing 11 | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 122 |
| 1960-1970 | 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 矮秆品种 Dwarf variety | 127 |
| 1970-1980 | IR24 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 122 |
| 1980-1990 | 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 145 |
| 1980-1990 | 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 半矮秆品种 Semi-dwarf variety | 146 |
| 2000-2005 | 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 153 |
| 2000-2005 | 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 152 |
| 2000-2005 | Ⅱ优084 Ⅱyou 084 | 半矮秆杂交稻 Semi-dwarf hybrid rice | 153 |
| 月份 Month | 平均气温 Mean air temperature/℃ | 降水量 Precipitation/mm | 日照时数 Sunshine hours / h |
|---|---|---|---|
| 五月 May | 22.7 | 53.0 | 155 |
| 六月 June | 25.8 | 253 | 188 |
| 七月 July | 25.5 | 186 | 139 |
| 八月 August | 30.4 | 246 | 155 |
| 九月 September | 23.8 | 50.2 | 146 |
| 十月 October | 16.7 | 56.9 | 133 |
表2 水稻生长季的平均气温、降水量和日照时数
Table 2. Mean air temperature, precipitation and sunshine hours during rice growing season.
| 月份 Month | 平均气温 Mean air temperature/℃ | 降水量 Precipitation/mm | 日照时数 Sunshine hours / h |
|---|---|---|---|
| 五月 May | 22.7 | 53.0 | 155 |
| 六月 June | 25.8 | 253 | 188 |
| 七月 July | 25.5 | 186 | 139 |
| 八月 August | 30.4 | 246 | 155 |
| 九月 September | 23.8 | 50.2 | 146 |
| 十月 October | 16.7 | 56.9 | 133 |
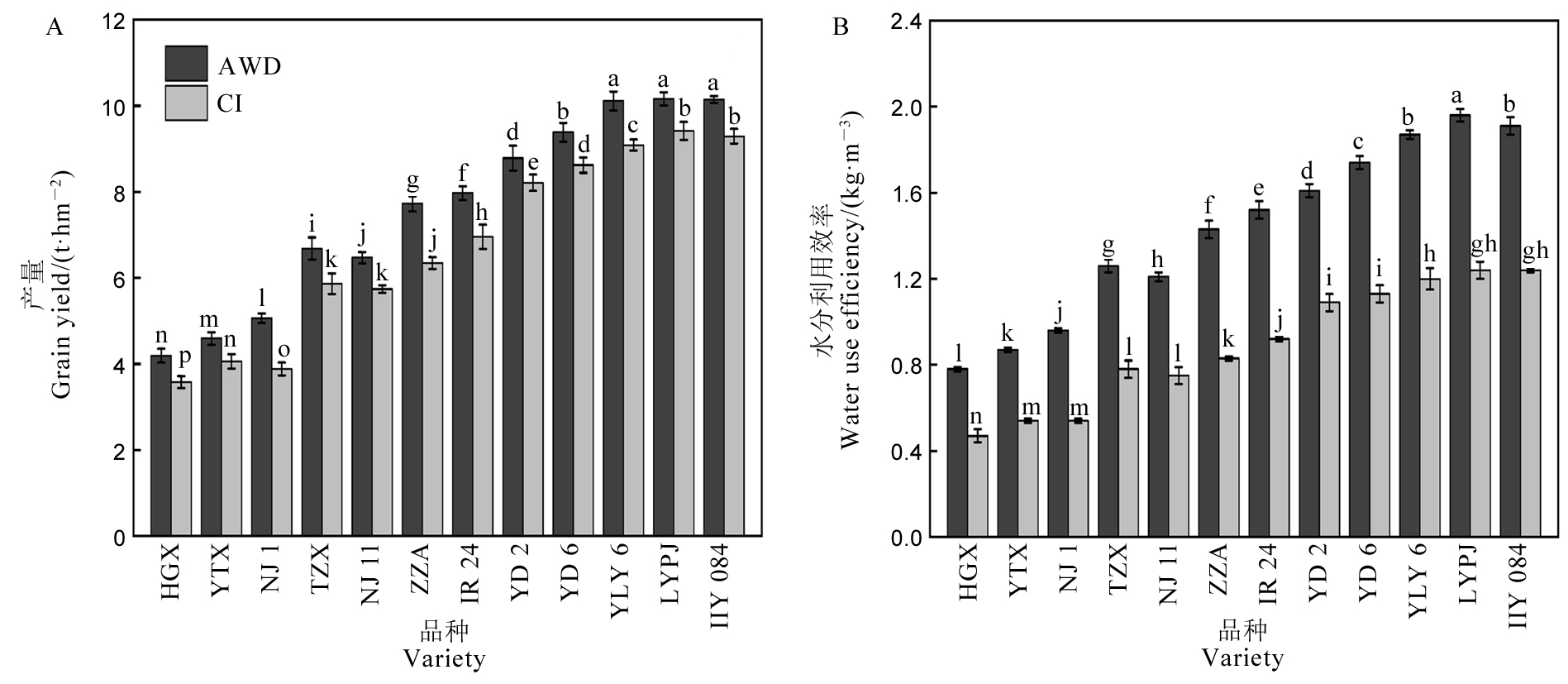
图1 中籼水稻品种的产量(A)和水分利用效率(B) AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。HGX-黄瓜籼;YTX-银条籼;NJ 1-南京1号;TZX-台中籼;NJ 11-南京11;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九;ⅡY 084-Ⅱ优084。水分利用效率(kg·m−3)=籽粒产量/灌溉水用量。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 1. Grain yield(A) and water use efficiency(B) of the mid-season indica rice varieties. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation; HGX, Huangguaxian; YTX, Yintiaoxian; NJ 1, Nanjing 1; TZX, Taichung Sen; NJ 11, Nanjing 11; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu; ⅡY 084, II you 084. Water use efficiency(kg·m−3)=Grain yield/Irrigation water consumption. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 穗数 Number of panicles /(×104 hm−2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 总颖花量 Total spikelets /(×106 hm−2) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 结实率 Filled grain rate /% | 产量 Grain yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 239 ± 1.70 c | 138 ± 4.39 e | 332 ± 3.95 f | 25.16 ± 0.22 c | 80.25 ± 1.63 c | 6.68 ± 0.48 e |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 253 ± 2.13 a | 148 ± 4.52 d | 376 ± 4.37 e | 26.18 ± 0.29 b | 78.30 ± 1.27 d | 7.72 ± 0.54 d | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 239 ± 1.21 c | 166 ± 3.83 b | 397 ± 3.68 c | 25.95 ± 0.26 b | 85.02 ± 1.29 a | 8.78 ± 0.54 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 242 ± 1.47 b | 157 ± 2.32 c | 379 ± 2.73 d | 29.16 ± 0.30 a | 84.87 ± 1.17 a | 9.38 ± 0.46 b | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 221 ± 2.63 d | 196 ± 4.91 a | 432 ± 4.76 b | 28.87 ± 0.55 a | 81.11 ± 0.64 bc | 10.11 ± 0.65 a | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 242 ± 1.27 b | 196 ± 2.16 a | 476 ± 4.31 a | 26.03 ± 0.43 b | 82.28 ± 1.31 b | 10.16 ± 0.57 a | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taizhongxian | 247 ± 1.11 cd | 125 ± 3.17 f | 309 ± 1.21 f | 24.95 ± 0.52 c | 75.91 ± 1.48 d | 5.86 ± 0.46 f |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 257 ± 2.56 b | 130 ± 5.14 e | 360 ± 4.88 d | 25.08 ± 0.38 bc | 70.37 ± 1.81 e | 6.34 ± 0.53 e | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 246 ± 1.32 d | 154 ± 4.18 c | 376 ± 2.79 c | 25.59 ± 0.32 b | 85.08 ± 1.67 a | 8.21 ± 0.57 d | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 263 ± 2.17 a | 135 ± 3.96 d | 352 ± 1.77 e | 29.11 ± 0.13 a | 84.08 ± 1.43 b | 8.62 ± 0.51 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 235 ± 2.88 e | 168 ± 2.65 b | 391 ± 1.46 b | 28.75 ± 0.39 a | 80.66 ± 1.29 c | 9.08 ± 0.53 b | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 249 ± 1.64 c | 186 ± 4.38 a | 464 ± 3.44 a | 24.90 ± 0.50 c | 81.33 ± 1.11 c | 9.41 ± 0.64 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | * | * | * | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | ** | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | |
表3 不同灌溉方式对稻米产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 3. Effects of different irrigation methods on grain yield and its components.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 穗数 Number of panicles /(×104 hm−2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 总颖花量 Total spikelets /(×106 hm−2) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 结实率 Filled grain rate /% | 产量 Grain yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 239 ± 1.70 c | 138 ± 4.39 e | 332 ± 3.95 f | 25.16 ± 0.22 c | 80.25 ± 1.63 c | 6.68 ± 0.48 e |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 253 ± 2.13 a | 148 ± 4.52 d | 376 ± 4.37 e | 26.18 ± 0.29 b | 78.30 ± 1.27 d | 7.72 ± 0.54 d | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 239 ± 1.21 c | 166 ± 3.83 b | 397 ± 3.68 c | 25.95 ± 0.26 b | 85.02 ± 1.29 a | 8.78 ± 0.54 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 242 ± 1.47 b | 157 ± 2.32 c | 379 ± 2.73 d | 29.16 ± 0.30 a | 84.87 ± 1.17 a | 9.38 ± 0.46 b | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 221 ± 2.63 d | 196 ± 4.91 a | 432 ± 4.76 b | 28.87 ± 0.55 a | 81.11 ± 0.64 bc | 10.11 ± 0.65 a | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 242 ± 1.27 b | 196 ± 2.16 a | 476 ± 4.31 a | 26.03 ± 0.43 b | 82.28 ± 1.31 b | 10.16 ± 0.57 a | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taizhongxian | 247 ± 1.11 cd | 125 ± 3.17 f | 309 ± 1.21 f | 24.95 ± 0.52 c | 75.91 ± 1.48 d | 5.86 ± 0.46 f |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 257 ± 2.56 b | 130 ± 5.14 e | 360 ± 4.88 d | 25.08 ± 0.38 bc | 70.37 ± 1.81 e | 6.34 ± 0.53 e | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 246 ± 1.32 d | 154 ± 4.18 c | 376 ± 2.79 c | 25.59 ± 0.32 b | 85.08 ± 1.67 a | 8.21 ± 0.57 d | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 263 ± 2.17 a | 135 ± 3.96 d | 352 ± 1.77 e | 29.11 ± 0.13 a | 84.08 ± 1.43 b | 8.62 ± 0.51 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 235 ± 2.88 e | 168 ± 2.65 b | 391 ± 1.46 b | 28.75 ± 0.39 a | 80.66 ± 1.29 c | 9.08 ± 0.53 b | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 249 ± 1.64 c | 186 ± 4.38 a | 464 ± 3.44 a | 24.90 ± 0.50 c | 81.33 ± 1.11 c | 9.41 ± 0.64 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | * | * | * | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | ** | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 82.58 ± 2.57 a | 67.07 ± 1.28 c | 47.08 ± 2.62 d | 59.25 ± 3.12 a | 15.50 ± 1.28 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 81.18 ± 1.90 ab | 69.33 ± 1.03 bc | 49.30 ± 1.28 cd | 43.95 ± 4.01 b | 12.20 ± 1.09 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 81.09 ± 3.10 ab | 70.73 ± 3.32 ab | 50.60 ± 1.03 bc | 32.35 ± 4.11 c | 9.25 ± 0.38 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 79.49 ± 2.15 b | 72.07 ± 2.31 ab | 51.53 ± 0.97 bc | 13.70 ± 2.58 d | 4.40 ± 0.97 d | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 79.29 ± 3.61 b | 73.32 ± 2.02 a | 52.70 ± 0.86 b | 6.00 ± 2.73 e | 3.20 ± 1.35 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 78.99 ± 2.40 b | 73.51 ± 1.34 a | 58.58 ± 2.69 a | 2.30 ± 2.16 f | 3.05 ± 1.88 d | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 82.18 ± 3.22 a | 65.67 ± 1.41 d | 45.55 ± 2.03 b | 65.00 ± 3.88 a | 23.35 ± 1.62 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 80.90 ± 1.08 ab | 67.65 ± 1.65 cd | 47.76 ± 1.55 b | 63.05 ± 2.19 a | 13.45 ± 1.77 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 80.66 ± 1.85 ab | 70.05 ± 3.01 bc | 50.55 ± 2.67 a | 32.95 ± 3.62 b | 11.90 ± 0.88 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 79.41 ± 2.76 ab | 71.00 ± 2.52 ab | 51.12 ± 1.47 a | 26.75 ± 3.15 c | 7.75 ± 1.55 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 79.05 ± 3.55 ab | 71.59 ± 1.40 ab | 51.82 ± 1.09 a | 8.50 ± 2.18 d | 5.45 ± 1.30 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 78.54 ± 3.07 b | 72.98 ± 2.71 a | 53.03 ± 2.64 a | 8.05 ± 1.47 d | 4.00 ± 0.54 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | NS | NS | NS | ** | ** | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | NS | NS | ** | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
表4 不同灌溉方式对稻米加工品质和外观品质的影响
Table 4. Effects of different irrigation methods on milling and appearance quality of rice.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 82.58 ± 2.57 a | 67.07 ± 1.28 c | 47.08 ± 2.62 d | 59.25 ± 3.12 a | 15.50 ± 1.28 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 81.18 ± 1.90 ab | 69.33 ± 1.03 bc | 49.30 ± 1.28 cd | 43.95 ± 4.01 b | 12.20 ± 1.09 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 81.09 ± 3.10 ab | 70.73 ± 3.32 ab | 50.60 ± 1.03 bc | 32.35 ± 4.11 c | 9.25 ± 0.38 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 79.49 ± 2.15 b | 72.07 ± 2.31 ab | 51.53 ± 0.97 bc | 13.70 ± 2.58 d | 4.40 ± 0.97 d | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 79.29 ± 3.61 b | 73.32 ± 2.02 a | 52.70 ± 0.86 b | 6.00 ± 2.73 e | 3.20 ± 1.35 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 78.99 ± 2.40 b | 73.51 ± 1.34 a | 58.58 ± 2.69 a | 2.30 ± 2.16 f | 3.05 ± 1.88 d | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 82.18 ± 3.22 a | 65.67 ± 1.41 d | 45.55 ± 2.03 b | 65.00 ± 3.88 a | 23.35 ± 1.62 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 80.90 ± 1.08 ab | 67.65 ± 1.65 cd | 47.76 ± 1.55 b | 63.05 ± 2.19 a | 13.45 ± 1.77 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 80.66 ± 1.85 ab | 70.05 ± 3.01 bc | 50.55 ± 2.67 a | 32.95 ± 3.62 b | 11.90 ± 0.88 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 79.41 ± 2.76 ab | 71.00 ± 2.52 ab | 51.12 ± 1.47 a | 26.75 ± 3.15 c | 7.75 ± 1.55 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 79.05 ± 3.55 ab | 71.59 ± 1.40 ab | 51.82 ± 1.09 a | 8.50 ± 2.18 d | 5.45 ± 1.30 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 78.54 ± 3.07 b | 72.98 ± 2.71 a | 53.03 ± 2.64 a | 8.05 ± 1.47 d | 4.00 ± 0.54 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | NS | NS | NS | ** | ** | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | NS | NS | ** | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 8.42 ± 0.82 a | 25.53 ± 1.65 a | 76.45 ± 2.03 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 8.58 ± 1.87 a | 23.75 ± 1.74 b | 74.20 ± 1.34 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 8.90 ± 1.65 a | 21.76 ± 1.83 c | 73.55 ± 1.62 bc | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 9.14 ± 1.74 a | 20.39 ± 2.03 d | 72.38 ± 2.42 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 9.36 ± 1.95 a | 19.64 ± 1.12 d | 61.45 ± 1.40 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 9.73 ± 1.24 a | 21.86 ± 1.49 c | 60.33 ± 1.53 d | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 8.20 ± 1.06 b | 24.86 ± 1.23 a | 72.40 ± 1.98 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 8.55 ± 1.37 ab | 23.27 ± 1.57 b | 65.38 ± 2.58 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 8.61 ± 0.79 ab | 21.06 ± 1.82 c | 62.60 ± 1.32 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 9.02 ± 1.48 ab | 19.93 ± 1.39 d | 58.20 ± 0.98 d | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 9.26 ± 1.53 ab | 18.71 ± 1.32 e | 54.90 ± 1.00 e | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 9.39 ± 1.26 a | 20.10 ± 1.19 d | 51.23 ± 2.43 f | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | NS | * | ** | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | NS | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | NS | NS | NS | |
表5 不同灌溉方式对稻米蒸煮食味与营养品质的影响
Table 5. Effects of different irrigation methods on cooking, eating and nutrition quality of rice.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 8.42 ± 0.82 a | 25.53 ± 1.65 a | 76.45 ± 2.03 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 8.58 ± 1.87 a | 23.75 ± 1.74 b | 74.20 ± 1.34 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 8.90 ± 1.65 a | 21.76 ± 1.83 c | 73.55 ± 1.62 bc | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 9.14 ± 1.74 a | 20.39 ± 2.03 d | 72.38 ± 2.42 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 9.36 ± 1.95 a | 19.64 ± 1.12 d | 61.45 ± 1.40 d | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 9.73 ± 1.24 a | 21.86 ± 1.49 c | 60.33 ± 1.53 d | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 8.20 ± 1.06 b | 24.86 ± 1.23 a | 72.40 ± 1.98 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 8.55 ± 1.37 ab | 23.27 ± 1.57 b | 65.38 ± 2.58 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 8.61 ± 0.79 ab | 21.06 ± 1.82 c | 62.60 ± 1.32 c | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 9.02 ± 1.48 ab | 19.93 ± 1.39 d | 58.20 ± 0.98 d | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 9.26 ± 1.53 ab | 18.71 ± 1.32 e | 54.90 ± 1.00 e | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 9.39 ± 1.26 a | 20.10 ± 1.19 d | 51.23 ± 2.43 f | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | NS | * | ** | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | NS | ** | ** | |
| 处理 × 品种 (T × V) | NS | NS | NS | |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 最终黏度 Final viscosity /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature /℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 3052.5 ± 44.6 a | 2478.5 ± 47.9 a | 549.5 ± 35.8 e | 3269.0 ± 52.7 a | 330.5 ± 12.5 b | 80.27 ± 2.4 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 2996.0 ± 47.9 b | 2469.5 ± 43.2 a | 586.0 ± 29.4 d | 3233.5 ± 50.8 b | 364.0 ± 17.9 a | 79.93 ± 2.2 a | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 2843.0 ± 50.2 c | 2172.5 ± 35.7 b | 620.5 ± 33.6 bc | 2967.0 ± 51.8 c | 233.5 ± 14.0 de | 78.48 ± 2.4 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 2780.5 ± 40.7 d | 2087.0 ± 46.6 c | 682.5 ± 37.6 a | 2913.5 ± 45.7 d | 250.0 ± 11.3 c | 78.13 ± 1.9 b | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 2691.0 ± 34.9 e | 1832.5 ± 50.3 d | 609.0 ± 42.8 c | 2756.0 ± 37.7 e | 238.5 ± 17.9 d | 77.68 ± 1.4 b | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 2618.5 ± 42.0 f | 1798.5 ± 52.4 e | 629.0 ± 37.9 b | 2709.5 ± 35.3 f | 226.5 ± 12.6 e | 77.43 ± 2.1 b | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 2969.5 ± 45.8 a | 2388.5 ± 36.6 a | 506.0 ± 48.6 d | 3246.0 ± 43.3 a | 357.5 ± 10.3 b | 81.93 ± 1.5 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 2855.5 ± 53.7 b | 2330.0 ± 42.5 b | 566.0 ± 30.3 c | 3221.5 ± 41.5 b | 371.5 ± 16.9 a | 80.20 ± 1.4 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 2793.0 ± 52.4 c | 2064.5 ± 41.8 c | 614.5 ± 37.1 b | 2942.0 ± 46.6 c | 257.0 ± 14.3 d | 79.73 ± 1.3 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 2740.5 ± 40.8 d | 1982.0 ± 47.1 d | 678.5 ± 42.6 a | 2895.0 ± 50.2 d | 268.5 ± 11.4 c | 78.52 ± 1.7 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 2481.5 ± 38.3 e | 1765.0 ± 39.8 e | 596.0 ± 49.1 b | 2722.0 ± 42.0 e | 251.5 ± 15.9 de | 77.98 ± 1.5 cd | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 2427.5 ± 33.6 f | 1640.5 ± 46.9 f | 618.0 ± 38.9 b | 2689.0 ± 42.8 f | 243.0 ± 11.1 e | 77.74 ± 1.7 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | NS | NS | * | NS | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | NS | |
| 处理 × 品种 T × V | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
表6 不同灌溉方式对稻米淀粉黏滞性的影响
Table 6. Effects of different irrigation methods on viscosity of rice starch.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 最终黏度 Final viscosity /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature /℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWD | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 3052.5 ± 44.6 a | 2478.5 ± 47.9 a | 549.5 ± 35.8 e | 3269.0 ± 52.7 a | 330.5 ± 12.5 b | 80.27 ± 2.4 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 2996.0 ± 47.9 b | 2469.5 ± 43.2 a | 586.0 ± 29.4 d | 3233.5 ± 50.8 b | 364.0 ± 17.9 a | 79.93 ± 2.2 a | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 2843.0 ± 50.2 c | 2172.5 ± 35.7 b | 620.5 ± 33.6 bc | 2967.0 ± 51.8 c | 233.5 ± 14.0 de | 78.48 ± 2.4 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 2780.5 ± 40.7 d | 2087.0 ± 46.6 c | 682.5 ± 37.6 a | 2913.5 ± 45.7 d | 250.0 ± 11.3 c | 78.13 ± 1.9 b | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 2691.0 ± 34.9 e | 1832.5 ± 50.3 d | 609.0 ± 42.8 c | 2756.0 ± 37.7 e | 238.5 ± 17.9 d | 77.68 ± 1.4 b | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 2618.5 ± 42.0 f | 1798.5 ± 52.4 e | 629.0 ± 37.9 b | 2709.5 ± 35.3 f | 226.5 ± 12.6 e | 77.43 ± 2.1 b | |
| CI | 台中籼 Taichung Sen | 2969.5 ± 45.8 a | 2388.5 ± 36.6 a | 506.0 ± 48.6 d | 3246.0 ± 43.3 a | 357.5 ± 10.3 b | 81.93 ± 1.5 a |
| 珍珠矮 Zhenzhuai | 2855.5 ± 53.7 b | 2330.0 ± 42.5 b | 566.0 ± 30.3 c | 3221.5 ± 41.5 b | 371.5 ± 16.9 a | 80.20 ± 1.4 b | |
| 扬稻2号 Yangdao 2 | 2793.0 ± 52.4 c | 2064.5 ± 41.8 c | 614.5 ± 37.1 b | 2942.0 ± 46.6 c | 257.0 ± 14.3 d | 79.73 ± 1.3 b | |
| 扬稻6号 Yangdao 6 | 2740.5 ± 40.8 d | 1982.0 ± 47.1 d | 678.5 ± 42.6 a | 2895.0 ± 50.2 d | 268.5 ± 11.4 c | 78.52 ± 1.7 c | |
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 2481.5 ± 38.3 e | 1765.0 ± 39.8 e | 596.0 ± 49.1 b | 2722.0 ± 42.0 e | 251.5 ± 15.9 de | 77.98 ± 1.5 cd | |
| 两优培九 Liangyoupeijiu | 2427.5 ± 33.6 f | 1640.5 ± 46.9 f | 618.0 ± 38.9 b | 2689.0 ± 42.8 f | 243.0 ± 11.1 e | 77.74 ± 1.7 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | NS | NS | * | NS | |
| 品种 Variety (V) | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | NS | |
| 处理 × 品种 T × V | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
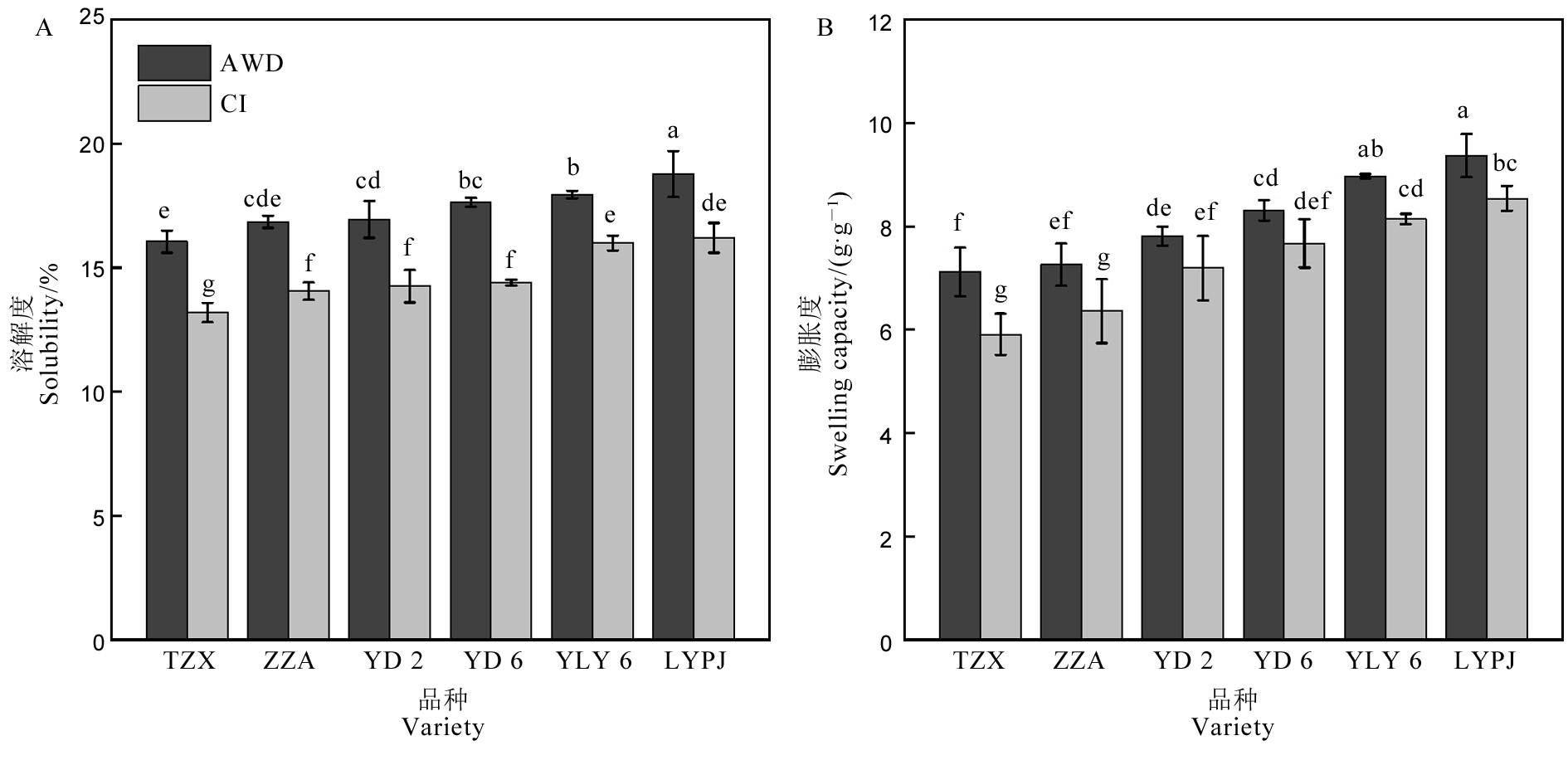
图2 不同灌溉方式对稻米淀粉溶解度(A)和膨胀度(B)的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 2. Effects of different irrigation methods on solubility(A) and swelling capacity(B) of rice starch. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
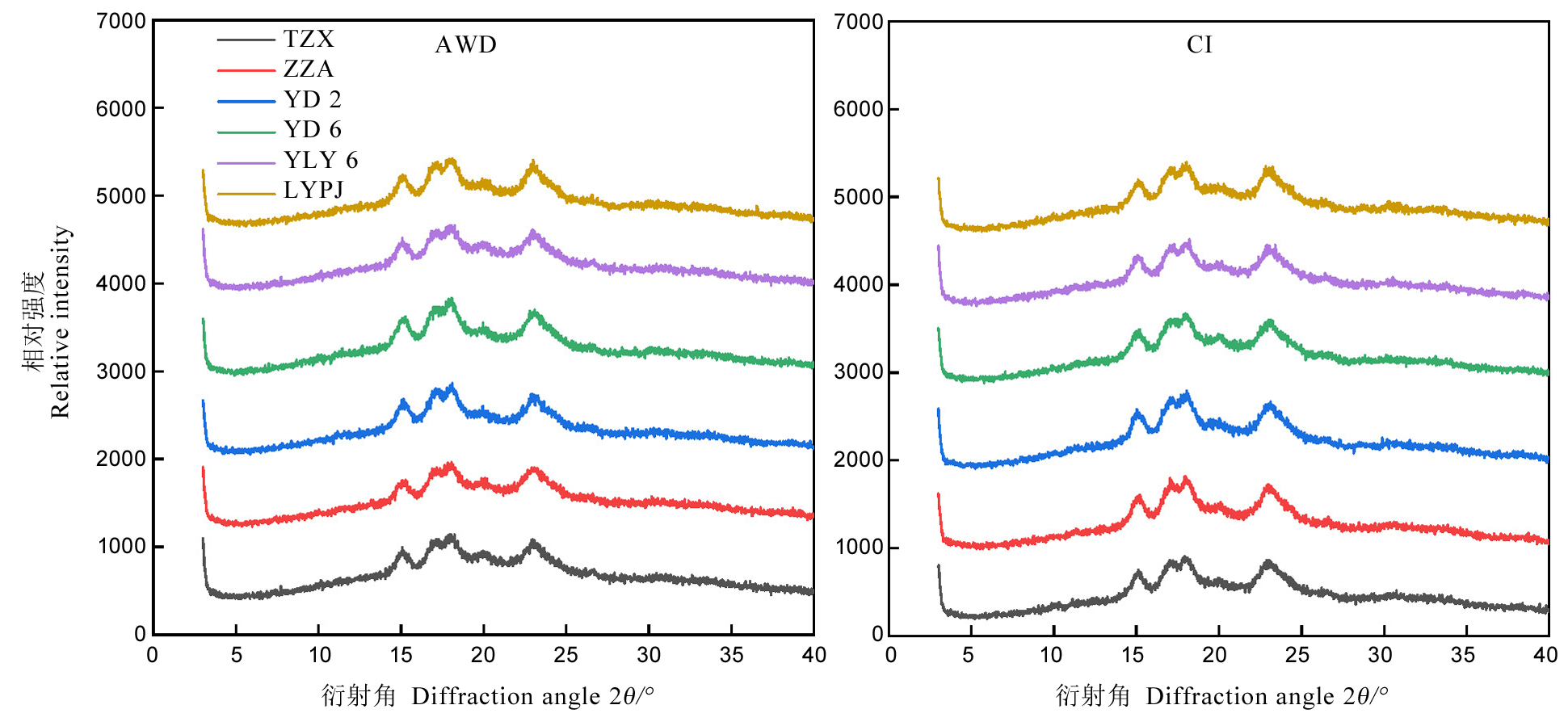
图3 不同灌溉方式对稻米淀粉XRD衍射图谱的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。
Fig. 3. Effects of different irrigation methods on XRD patterns of rice starch. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu.
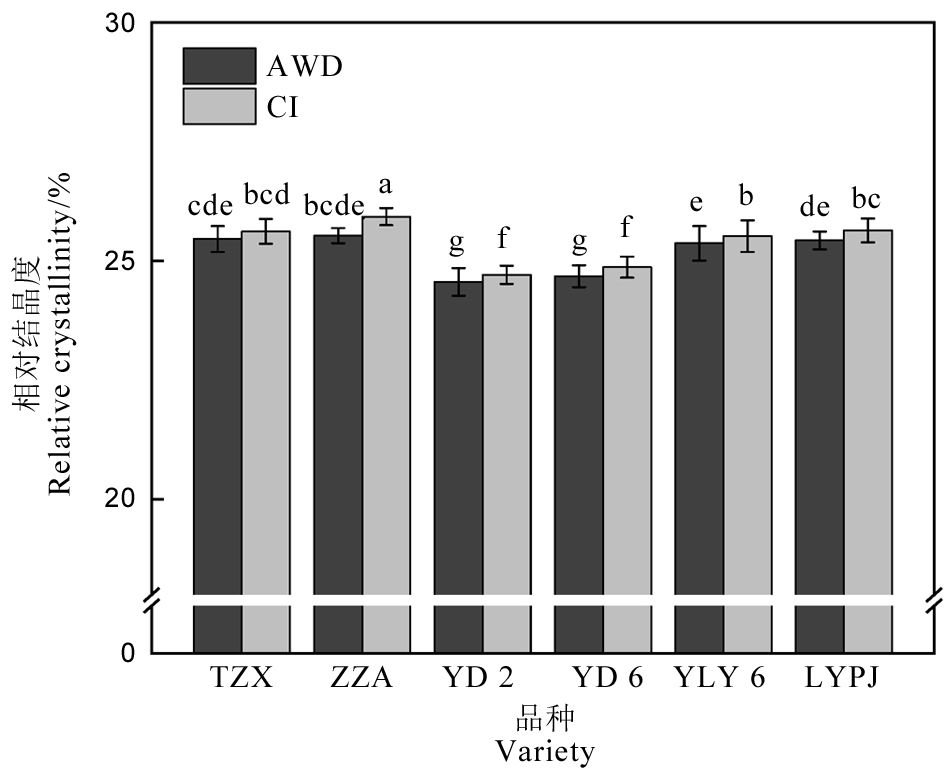
图4 不同灌溉方式对稻米淀粉相对结晶度的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 4. Effects of different irrigation methods on relative crystallinity of rice starch. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
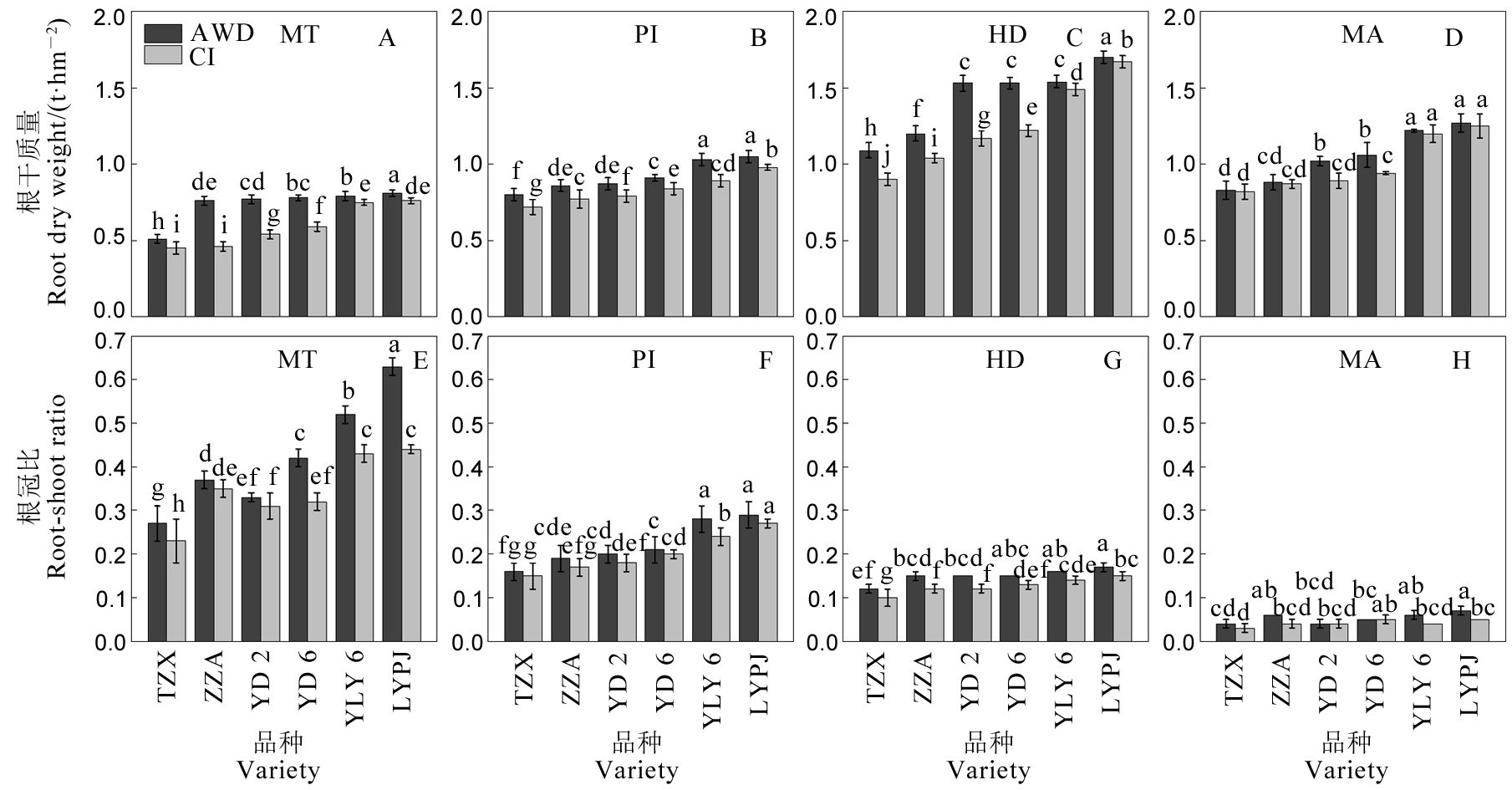
图5 不同灌溉方式对水稻根干质量和根冠比的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。MT-分蘖中期;PI-穗分化始期;HD-抽穗期;MA-成熟期。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 5. Effects of different irrigation methods on root dry weight and root-shoot ratio of rice. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. MT, Mid-tillering stage; PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Heading stage; MA, Maturity stage. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
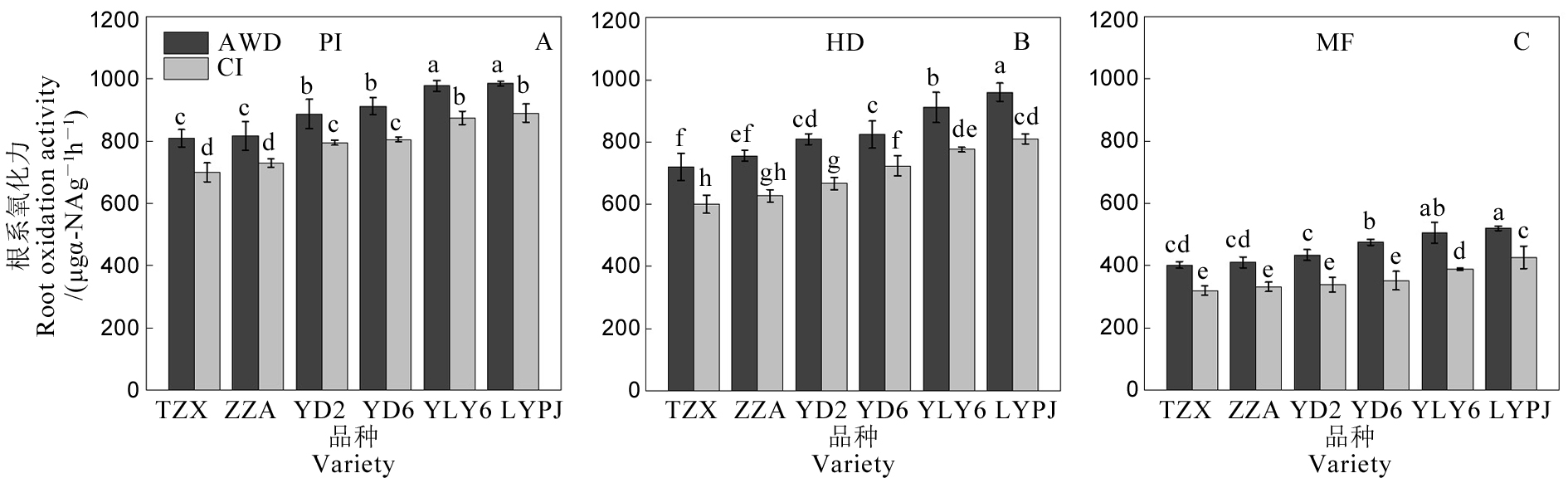
图6 不同灌溉方式对水稻根系氧化力的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。PI-穗分化始期;HD-抽穗期;MF-灌浆中期。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD2-扬稻2号;YD6-扬稻6号;YLY6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 6. Effects of different irrigation methods on root oxidation activity of rice. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Heading stage; MF, Mid-filling stage. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD2, Yangdao 2; YD6, Yangdao 6; YLY6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
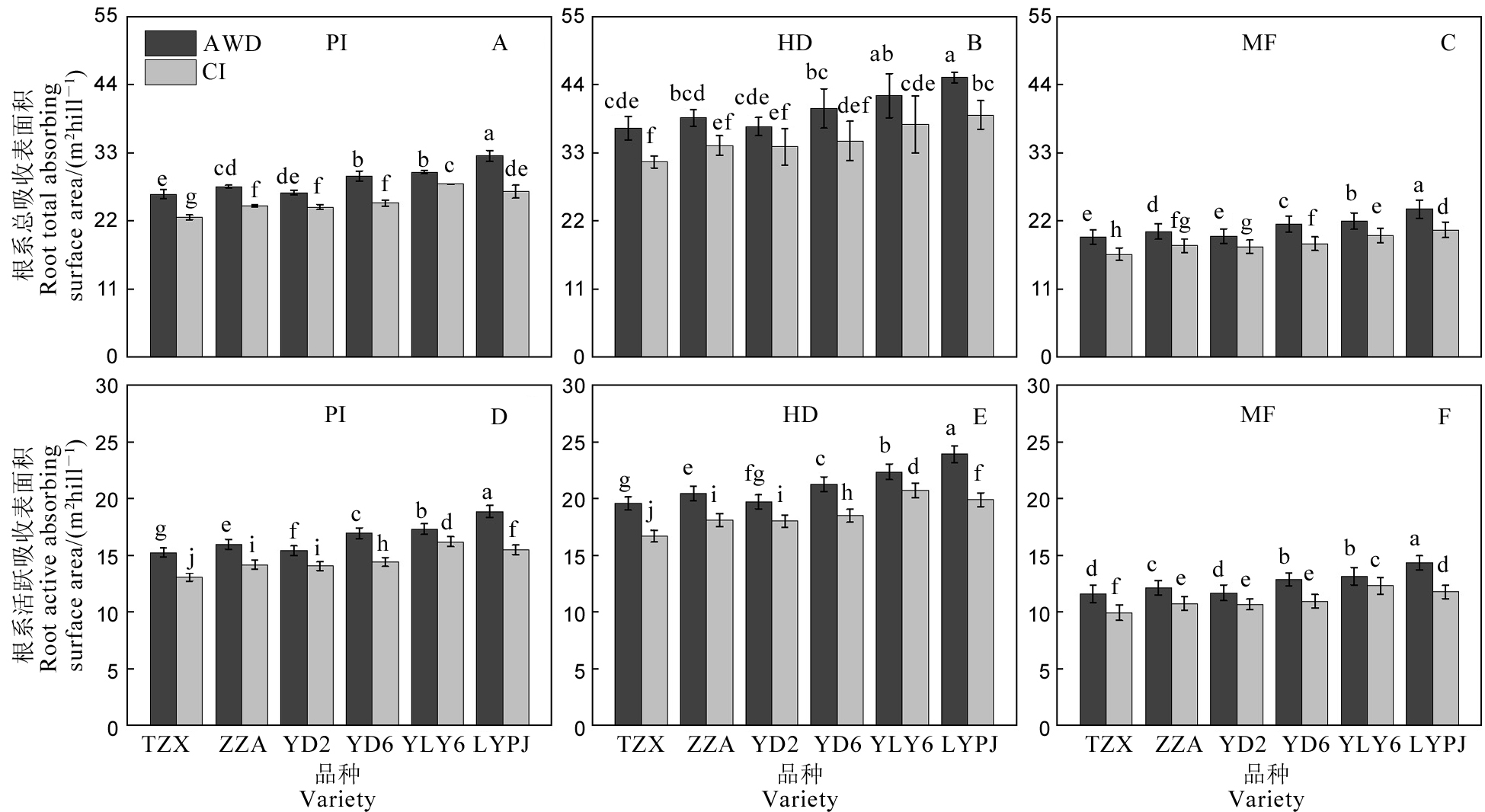
图7 不同灌溉方式对水稻根系总吸收表面积和活跃吸收表面积的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。PI-穗分化始期;HD-抽穗期;MF-灌浆中期。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 7. Effects of different irrigation methods on root total absorbing surface area and active absorbing surface area of rice. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Heading stage; MF, Mid-filling stage. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6: Yangdao 6; YLY 6: Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
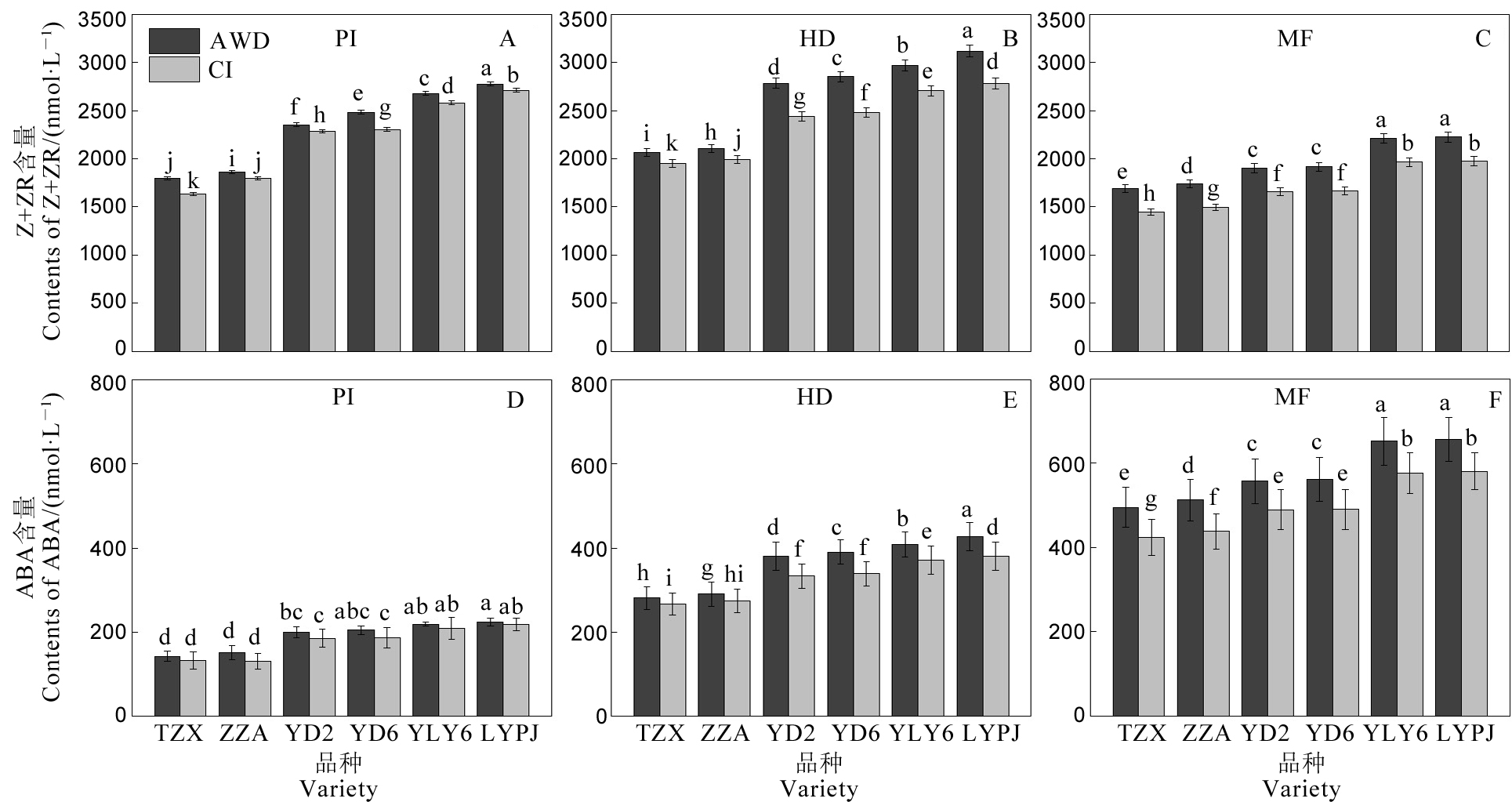
图8 不同灌溉方式对水稻根系伤流液中Z+ZR和ABA含量的影响 AWD-干湿交替灌溉;CI-常规灌溉。PI-穗分化始期;HD-抽穗期;MF-灌浆中期。TZX-台中籼;ZZA-珍珠矮;YD 2-扬稻2号;YD 6-扬稻6号;YLY 6-扬两优6号;LYPJ-两优培九。不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。
Fig. 8. Effects of different irrigation methods on Z+ZR and ABA contents in rice root bleeding sap of rice. AWD, Alternate wetting and drying irrigation; CI, Conventional irrigation. PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Heading stage; MF, Mid-filling stage. TZX, Taichung Sen; ZZA, Zhenzhuai; YD 2, Yangdao 2; YD 6, Yangdao 6; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; LYPJ, Liangyoupeijiu. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.

图9 根系特征和产量、水分利用效率及稻米品质的相关性分析 RDW-根干质量;RSR-根冠比;ROA-根系氧化力;RTASA-根系总吸收表面积;RAASA-根系活跃吸收表面积;Zr-根系伤流液中玉米素+玉米素核苷含量;Ar-根系伤流液中脱落酸含量。MT-分蘖中期;PI-穗分化始期;HD-抽穗期;MF-灌浆中期;MA-成熟期。红色和蓝色圆圈分别表示参数之间的负相关或正相关关系。颜色越深,相关性越高。*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平上有显著性差异。
Fig. 9. Correlation of root characteristics with yield, water use efficiency and grain quality. RDW, Root dry weight; RSR, Root-shoot ratio; ROA, Root oxidation activity; RTASA, Root total absorbing surface area; RAASA, Root active absorbing surface area; Zr, Z+ZR content in root bleeding sap; Ar, ABA content in root bleeding sap; MT, Mid-tillering stage; PI, Panicle initiation stage; HD, Heading stage; MF, Middle grain filling stage; MA, Maturity stage. The red and blue circles indicate negative or positive correlations between parameters, respectively. The darker the color is, the closer the correlation is. *, ** and *** indicate significant differences at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
| [1] | Suleiman S O, Habila D G, Mamadou F, Abolanle B M, Olatunbosun A N. Grain yield and leaf gas exchange in upland NERICA rice under repeated cycles of water deficit at reproductive growth stage[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2022, 264: 107507. |
| [2] | Muthayy S, Sugimoto J D, Montgomery S, Marberly G F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade and consumption[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2014, 1324(1): 7-14. |
| [3] | Foley J A, Ramankutty N, Brauman K A, Cassidy E S, Gerber J S, Johnston M, Mueller N D, O’Connell C, Ray D K, West P C, Balzer C, Bennett E M, Carpenter S R, Hill J, Monfreda C, Polasky S, Rockstrom J, Sheehan J, Siebert S, Tilman D, Zaks D P M. Solutions for a cultivated planet[J]. Nature, 2011, 478(7369): 337-342. |
| [4] | Zhang W Y, Yu J X, Xu Y J, Wang Z Q, Liu L J, Zhang H, Gu J F, Zhang J H, Yang J C. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation combined with the proportion of polymer-coated urea and conventional urea rates increases grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 268: 108165. |
| [5] | 杨建昌, 王朋, 刘立军, 王志琴, 朱庆森. 中籼水稻品种产量与株型演进特征研究[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(7): 949-955. |
| Yang J C, Wang P, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S. Evolution characteristics of grain yield and plant type for mid-season indica rice varieties[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(7): 949-955. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Zhang J H. China's success in increasing per capita food production[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(11): 3707-3711. |
| [7] | Zhang Q F. Strategies for developing green super rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104(42): 16402-16409. |
| [8] | Fu Y Y, Gu Q Q, Dong Q, Zhang Z H, Lin C, Hu W M, Pan R H, Guan Y J, Hu J. Spermidine enhances heat tolerance of rice seeds by modulating endogenous starch and polyamine metabolism[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(3): 13-95. |
| [9] | Bouman B A M, Tuong T P. Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2001, 49(1): 11-30. |
| [10] | Bouman B A M. A conceptual framework for the improvement of crop water productivity at different spatial scales[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2006, 93(1): 43-60. |
| [11] | Wang Z Q, Xu Y J, Chen T T, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Abscisic acid and the key enzymes and genes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in rice spikelets in response to soil drying during grain filling[J]. Planta, 2015, 241(5): 1091-1107. |
| [12] | Yang J C, Zhou Q, Zhang J H. Moderate wetting and drying increases rice yield and reduces water use, grain arsenic level, and methane emission[J]. The Crop Journal, 2017, 5(2): 151-158. |
| [13] | Ye Y S, Liang X Q, Chen Y X, Liu J, Gu J T, Guo R, Li L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 144: 212-224. |
| [14] | Shao G C, Deng S, Liu N, Yu S E, Wang M H, She D L. Effects of controlled irrigation and drainage on growth, grain yield and water use in paddy rice[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2014, 53: 1-9. |
| [15] | Li S, Zuo Q, Jin X X, Ma W W, Shi J C, Ben-Gal A. The physiological processes and mechanisms for superior water productivity of a popular ground cover rice production system[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 201: 11-20. |
| [16] | Kadiyala M D M, Mylavarapu R S, Li Y C, Reddy G B, Reddy M D. Impact of aerobic rice cultivation on growth, yield, and water productivity of rice-maize rotation in semiarid topics[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2012, 104(6): 1757-1765. |
| [17] | 李婷婷, 冯钰枫, 朱安, 黄健, 汪浩, 李思宇, 刘昆, 彭如梦, 张宏路, 刘立军. 主要节水灌溉方式对水稻根系形态生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. |
| Li T T, Feng Y F, Zhu A, Huang J, Wang H, Li S Y, Liu K, Peng R M, Zhang H L, Liu L J. Effects of main water-saving irrigation methods on morphological and physiological traits of rice roots[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Lampayan R, Rejesus R, Singleton G, Bouman B. Adoption and economics of alternate wetting and drying water management for irrigated lowland rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 170: 95-108. |
| [19] | Ye Y, Liang X, Chen Y, Liu J, Gu J, Guo R, Li L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 144: 212-224. |
| [20] | Arjun P, Van T, Duong Q, Thi P, Thi L, Lars S, Andreas N. Organic matter and water management strategies to reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddies in Vietnam[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2014, 196: 137-146. |
| [21] | Liu L J, Chen T T, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Combination of site-specific nitrogen management and alternate wetting and drying irrigation increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in super rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 154: 226-235. |
| [22] | Yang J C, Zhang J H. Crop management techniques to enhance harvest index in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(12): 3177-3189. |
| [23] | 杨建昌. 水稻根系形态生理与产量、品质形成及养分吸收利用的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(1): 36-46. |
| Yang J C. Relationships of rice root morphology and physiology with the formation of grain yield and quality and the nutrient absorption and utilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(1): 36-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 陈达刚, 周新桥, 李丽君, 刘传光, 张旭, 陈友订. 华南主栽高产籼稻根系形态特征及其与产量构成的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(10): 1899-1908. |
| Chen D G, Zhou X Q, Li L J, Liu C G, Zhang X, Chen Y D. Relationship between root morphological characteristics and yield components of major commercial indica rice in south China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 39(10): 1899-1908. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 褚光, 刘洁, 张耗, 杨建昌. 超级稻根系形态生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(5): 850-858. |
| Chu G, Liu J, Zhang H, Yang J C. Morphology and physiology of roots and their relationships with yield formation in super rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 850-858. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 刘红江, 蒋银涛, 陈留根, 郑建初. 不同播栽方式对水稻根系生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2015, 31(2): 310-316. |
| Liu H J, Jiang Y T, Chen L G, Zheng J C. Influence of planting modes on root growth and yield of Oryza sativa L.[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 31(2): 310-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Yan F J, Sun Y J, Xu H, Yin Y Z, Wang H Y, Wang C Y, Guo C C, Yang Z Y, Sun Y Y, Ma J. Effects of wheat straw mulch application and nitrogen management on rice root growth, dry matter accumulation and rice quality in soils of different fertility[J]. Paddy and Water Environment, 2018, 16(3): 507-518. |
| [28] | 罗德强, 江学海, 周维佳, 王学鸿, 涂丹, 李敏, 姬广梅. 不同籼稻品种的籽粒灌浆特性及根系活力[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2013, 41(6): 49-51. |
| Luo D Q, Jiang X H, Zhou W J, Wang X H, Tu D, Li M, Ji G M. Grain-filling properties and root activity of different indica rice varieties[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(6): 49-51. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 陈婷婷, 许更文, 钱希旸, 王志琴, 张耗, 杨建昌. 花后轻干湿交替灌溉提高水稻籽粒淀粉合成相关基因的表达[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(7): 1288-1299. |
| Chen T T, Xu G W, Qian X Y, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C. Post-anthesis alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation enhance gene expressions of enzymes involved in starch synthesis in rice grains[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(7): 1288-1299. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Zhang H, Li H W, Yuan L M, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Post-anthesis alternate wetting and moderate soil drying enhances activities of key enzymes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in inferior spikelets of rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(1): 215-227. |
| [31] | 高君恺, 叶红霞, 舒小丽, 吴殿星. 水稻低淀粉粘滞突变体的理化特性和淀粉结构[J]. 核农学报, 2009, 23(1): 23-27. |
| Gao J K, Ye H X, Shu X L, Wu D X. Physicochemical properties and starch structure of a rice mutant with reduction of starch paste viscosity[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 23(1): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 章骏德, 刘国屏, 施永宁. 植物生理实验法[M]. 南昌: 江西人民出版社, 1982. |
| Zhang J D, Liu G P, Shi Y N. Experimental Method of Plant Physiology[M]. Nanchang: Jiangxi People's Publishing House, 1982. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 萧浪涛, 王三根. 植物生理学实验技术. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005: 61-62. |
| Xiao L T, Wang S G. Experimental Techniques of Plant Physiology. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005: 61-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 常二华, 王朋, 唐成, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻根和籽粒细胞分裂素和脱落酸浓度与籽粒灌浆及蒸煮品质的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(4): 540-547. |
| Chang E H, Wang P, Tang C, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Concentrations of cytokinin and abscisic acid in roots and grains and its relationship with grain filling and cooking quality of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(4): 540-547. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 魏海燕, 凌启鸿, 张洪程, 郭文善, 杨建昌, 陈德华, 冷锁虎, 陆卫平, 邢志鹏. 作物群体质量及其关键调控技术[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2018, 39(2): 1-9. |
| Wei H Y, Ling Q H, Zhang H C, Guo W S, Yang J C, Chen D H, Leng S H, Lu W P, Xing Z P. The quality of crop population and its key regulation technology[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2018, 39(2): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Belder P, Bouman B A M, Cabangon R, Lu G A, Quilang E J P, Li Y H, Spiertz J H J, Tuong T P. Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2003, 65(3): 193-210. |
| [37] | Belder P, Spiertz J H J, Bouman B A M, Lu G, Tuong T P. Nitrogen economy and water productivity of lowland rice under water-saving irrigation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2004, 93(2): 169-185. |
| [38] | Carrijo D R, Lundy M E, Linquist B A. Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: A meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203: 173-180. |
| [39] | 张耗, 马丙菊, 张春梅, 赵步洪, 许京菊, 邵士梅, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 全生育期干湿交替灌溉对稻米品质及淀粉特性的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2020, 41(6):1-8. |
| Zhang H, Ma B J, Zhang C M, Zhao B H, Xu J J, Shao S M, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation during whole growing season on quality and starch properties of rice[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2020, 41(6): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 张耗, 谈桂露, 孙小淋, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 江苏省中籼水稻品种演进过程中稻米品质的变化[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(11): 2037-2044. |
| Zhang H, Tan G L, Sun X L, Liu L J, Yang J C. Changes in grain quality during the evolution of mid-Season indica rice varieties in Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(11): 2037-2044. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 朱安, 高捷, 黄健, 汪浩, 陈云, 刘立军. 水稻根系形态生理及其与稻米品质关系的研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2020(2): 1-8. |
| Zhu A, Gao J, Huang J, Wang H, Chen Y, Liu L J. Advances in morphology and physiology of root and their relationships with grain quality in rice[J]. Crops, 2020(2): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | Zhang H, Jing W J, Zhao B H, Wang W L, Xu Y J, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Alternative fertilizer and irrigation practices improve rice yield and resource use efficiency by regulating source-sink relationships[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 265: 108124. |
| [43] | 蔡昆争, 骆世明, 段舜山. 水稻群体根系特征与地上部生长发育和产量的关系[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2005(2): 1-4. |
| Cai K Z, Luo S M, Duan S S. The relationship between root system of rice and aboveground characteristics and yield[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2005(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 蒋玉兰. 干湿交替灌溉对水稻产量、根系形态生理和土壤性状的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. |
| Jiang Y L. Effect of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on yield, root morphological physiology and soil properties of rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Taghipour M, Jalali M. Influence of organic acids on kinetic release of chromium in soil contaminated with leather factory waste in the presence of some adsorbents[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 155: 395-404. |
| [46] | 孙静文, 陈温福, 臧春明, 王彦荣, 吴淑琴. 水稻根系研究进展[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2002(6): 466-470. |
| Sun J W, Chen W F, Zang C M, Wang Y R, Wu S Q. Advances of research on rice root systems[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2002(6): 466-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 肖金川, 武志海, 徐克章, 凌凤楼, 崔菁菁, 李鑫. 吉林省47年育成的水稻品种根系伤流液重量变化及其与剑叶光合速率的关系[J]. 植物生理学报, 2012, 48(5): 499-504. |
| Xiao J C, Wu Z H, Xu K Z, Ling F L, Cui J J, Li X. Changes of root bleeding sap weight and its correlation with flag leaf net photosynthetic rate in rice varieties released 47 Years in Jilin Province of China[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2012, 48(5): 499-504. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 李敏, 张洪程, 杨雄, 葛梦婕, 马群, 魏海燕, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 曹利强, 吴浩. 水稻高产氮高效型品种的根系形态生理特征[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(4): 648-656. |
| Li M, Zhang H C, Yang X, Ge M J, Ma Q, Wei H Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Cao L Q, Wu H. Root morphological and physiological characteristics of rice varieties with high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(4): 648-656. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 张耗. 水稻根系形态生理与产量形成的关系及其栽培调控技术[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2011. |
| Zhang H. Morphology and physiology of rice roots in relation to yield formation and cultivation regulation techniques[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | 郑华斌, 姚林, 刘建霞, 贺慧, 陈阳, 黄璜. 种植方式对水稻产量及根系性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(4): 667-677. |
| Zheng H B, Yao L, Liu J X, He H, Chen Y, Huang H. Effect of ridge and terraced cultivation on rice yield and root trait[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(4): 667-677. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | 戢林, 李廷轩, 张锡洲, 余海英. 氮高效利用基因型水稻根系形态和活力特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(23): 4770-4781. |
| Ji L, Li T X, Zhang X Z, Yu H Y. Root morphological and activity characteristics of rice genotype with high nitrogen utilization efficiency[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(23): 4770-4781. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | 褚光, 展明飞, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 干湿交替灌溉对水稻产量与水分利用效率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(7): 1026-1036. |
| Chu G, Zhan M F, Zhu K Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1026-1036. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | 熊溢伟. 氮肥对不同的水稻品种根系形态生理与产量的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015. |
| Xiong Y W. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on grain yield and root morphology physiology in different rice varieties[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | 魏海燕, 张洪程, 张胜飞, 杭杰, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 马群, 张庆, 刘艳阳. 不同氮利用效率水稻基因型的根系形态与生理指标的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2008(3): 429-436. |
| Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Zhang S F, Hang J, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Ma Q, Zhang Q, Liu Y Y. Root morphological and physiological characteristics in rice genotypes with different N use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008(3): 429-436. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [55] | 钟旭华, 黄农荣. 水稻结实期根系活性与稻米垩白形成的相关性初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(5): 471-474. |
| Zhong X H, Huang N R. Preliminary study on the relationship between rice grain chalkiness and root activity at grain-filling stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(5): 471-474. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [56] | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Huang Z L, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S, Liu L J. Correlation of cytokinin levels in the endosperms and roots with cell number and cell division activity during endosperm development in rice[J]. Annals of Botany, 2002, 90(3): 369-377. |
| [57] | Schussler J R, Brenner M L, Brun W A. Relationship of endogenous abscisic acid to sucrose level and seed growth rate of soybeans[J]. Plant Physiology, 1991, 96(4): 1308-1313. |
| [58] | Zhang H, Jing W J, Xu J J, Ma B J, Wang W L, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Changes in starch quality of mid-season indica rice varieties in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River in last 80 years[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19(12): 2983-2996. |
| [59] | Zhang H, Hou D P, Peng X L, Ma B J, Shao S M, Jing W J, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Liu Y Y, Yang J C. Optimizing integrative cultivation management improves grain quality while increasing yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18(12): 2716-2731. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||