
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 520-530.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.220311
陆丹丹1,2, 雍明玲1,2, 陶钰1,2, 叶苗1,2, 张祖建1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-24
修回日期:2022-06-17
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
张祖建
基金资助:
LU Dandan1,2, YONG Mingling1,2, TAO Yu1,2, YE Miao1,2, ZHANG Zujian1,2( )
)
Received:2022-03-24
Revised:2022-06-17
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
ZHANG Zujian
摘要:
【目的】探讨优良食味水稻品种的籽粒蛋白质积累特征及其对氮素水平的响应。【方法】以食味值不同的常规粳稻和杂交稻为材料,在结实期设置不同氮素施用水平处理,分析不同类型品种在不同氮素水平下的蒸煮食味品质及其与稻米蛋白质及其组分含量的关系。进一步分析各品种在不同氮素水平下稻穗不同部位的氨基酸含量及籽粒蛋白质含量在结实期的动态变化,总结优良食味水稻品种的籽粒蛋白质积累特征及其对氮素水平的响应特征。【结果】优良食味水稻品种籽粒蛋白质含量较低,且随着氮素水平的增加而上升;优良食味水稻崩解值较高,消减值较低;蒸煮食味品质受氮素水平影响较小。优良食味水稻品种蛋白组分含量较低,且稻米蛋白质含量与食味品质呈显著负相关。在常规粳稻中,稻米食味值与清蛋白、球蛋白和醇溶蛋白含量均显著负相关;在杂交稻中,稻米食味值与醇溶蛋白和谷蛋白含量显著负相关。优良食味水稻品种籽粒充实过程中游离氨基酸含量较低,并呈现较低水平的蛋白质积累。而食味较差品种灌浆期籽粒的氨基酸含量较高,成熟籽粒蛋白质含量也较高,且氮素供应水平提升其籽粒蛋白质含量的效应更为显著。【结论】优良食味水稻品种的籽粒蛋白质含量较低,与其充实过程中蛋白质积累水平较低有紧密关系,且受氮素水平影响较小。
陆丹丹, 雍明玲, 陶钰, 叶苗, 张祖建. 优良食味水稻品种籽粒蛋白质积累特征及其对氮素水平的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 520-530.
LU Dandan, YONG Mingling, TAO Yu, YE Miao, ZHANG Zujian. Characteristics of Grain Protein Accumulation and Its Response to Nitrogen Level in Good Taste Rice Varieties[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 520-530.
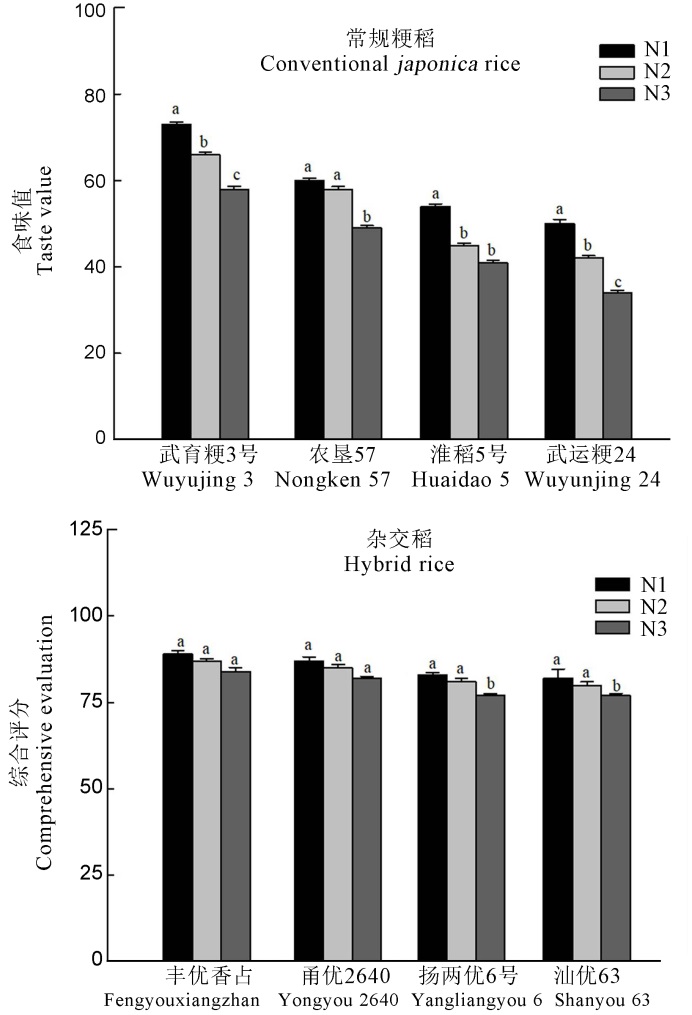
图1 供试品种在不同氮素水平下的食味值 N1、N2和N3为结实期不同氮素施用水平处理,其在结实期的施氮量分别为1、2、3 g/盆。柱上不同字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1. Taste values of the tested varieties under different nitrogen levels. N1, N2 and N3 refer to nitrogen application levels at filling stage, and the nitrogen application rates were 1, 2 and 3 g, respectively. Different letters on the columns indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.
| 类型 Type | 处理Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 胶稠度 Gel consistency / mm | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content / % | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 74.0±0.5 b | 19.15±0.83 a | 6.07±0.04 c | |
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 75.0±1.0 b | 17.90±0.93 b | 6.31±0.01 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 78.0±1.5 a | 17.90±0.44 b | 6.30±0.10 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 79.0±1.0 a | 18.10±0.05 b | 6.93±0.21 a | |||
| N2 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 77.0±2.0 b | 19.10±0.33 a | 7.12±0.02 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 76.0±1.0 b | 17.83±0.27 b | 7.27±0.02 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 79.0±1.0 a | 17.70±1.09 b | 7.29±0.04 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 82.0±0.5 a | 17.70±0.49 b | 7.70±0.21 a | |||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 73.0±1.0 c | 19.04±0.34 a | 7.98±0.02 b | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 74.0±1.0 c | 17.79±1.07 b | 8.01±0.02 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 77.0±0.0 b | 17.50±1.16 b | 8.15±0.04 a | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 80.0±1.0 a | 17.43±0.62 b | 8.00±0.20 b | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 87.0±0.0 a | 14.64±0.27 c | 6.49±0.09 b | |
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 77.0±1.0 b | 18.46±0.03 b | 6.38±0.08 b | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 73.0±0.0 b | 17.25±0.55 b | 7.32±0.20 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 44.0±3.0 c | 25.93±0.61 a | 6.43±0.10 b | |||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 89.0±0.5 a | 14.33±0.30 c | 7.11±0.10 b | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 81.0±2.0 b | 18.12±0.50 b | 6.85±0.08 c | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 76.0±1.0 b | 17.03±0.09 b | 7.72±0.01 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 47.0±0.5 c | 25.33±0.58 a | 7.26±0.09 b | |||
| N3 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 85.0±0.5 a | 14.11±0.41 c | 7.74±0.11 c | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 75.0±1.0 b | 17.92±0.61 b | 8.63±0.07 b | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 72.0±0.5 b | 16.96±0.80 b | 9.09±0.09 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 44.0±0.5 c | 24.75±0.50 a | 8.25±0.10 b | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ns | ** | ||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ns | |||
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | |||
表1 不同氮素水平下供试水稻品种的蒸煮食味品质性状
Table 1. Characteristics of cooking and eating quality of the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 类型 Type | 处理Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 胶稠度 Gel consistency / mm | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content / % | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 74.0±0.5 b | 19.15±0.83 a | 6.07±0.04 c | |
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 75.0±1.0 b | 17.90±0.93 b | 6.31±0.01 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 78.0±1.5 a | 17.90±0.44 b | 6.30±0.10 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 79.0±1.0 a | 18.10±0.05 b | 6.93±0.21 a | |||
| N2 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 77.0±2.0 b | 19.10±0.33 a | 7.12±0.02 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 76.0±1.0 b | 17.83±0.27 b | 7.27±0.02 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 79.0±1.0 a | 17.70±1.09 b | 7.29±0.04 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 82.0±0.5 a | 17.70±0.49 b | 7.70±0.21 a | |||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 73.0±1.0 c | 19.04±0.34 a | 7.98±0.02 b | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 74.0±1.0 c | 17.79±1.07 b | 8.01±0.02 b | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 77.0±0.0 b | 17.50±1.16 b | 8.15±0.04 a | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 80.0±1.0 a | 17.43±0.62 b | 8.00±0.20 b | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 87.0±0.0 a | 14.64±0.27 c | 6.49±0.09 b | |
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 77.0±1.0 b | 18.46±0.03 b | 6.38±0.08 b | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 73.0±0.0 b | 17.25±0.55 b | 7.32±0.20 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 44.0±3.0 c | 25.93±0.61 a | 6.43±0.10 b | |||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 89.0±0.5 a | 14.33±0.30 c | 7.11±0.10 b | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 81.0±2.0 b | 18.12±0.50 b | 6.85±0.08 c | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 76.0±1.0 b | 17.03±0.09 b | 7.72±0.01 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 47.0±0.5 c | 25.33±0.58 a | 7.26±0.09 b | |||
| N3 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 85.0±0.5 a | 14.11±0.41 c | 7.74±0.11 c | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 75.0±1.0 b | 17.92±0.61 b | 8.63±0.07 b | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 72.0±0.5 b | 16.96±0.80 b | 9.09±0.09 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 44.0±0.5 c | 24.75±0.50 a | 8.25±0.10 b | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ns | ** | ||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ns | |||
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 类型 Type | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 最高黏度 Peak viscosity | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity | 崩解值 Breakdown | 最终黏度 Final viscosity | 消减值 Setback | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3587±58 a | 2627±82 b | 960±140 a | 3437±36 b | −150±94 c | |||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3363±17 b | 2422±82 c | 941±99 a | 3310±52 c | −53±69 c | |||||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3333±13 b | 2625±21 b | 708±9 b | 3441±12 b | 108±1 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3378±10 b | 3039±60 a | 339±40 c | 3671±10 a | 293±10 a | |||||
| N2 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3618±20 a | 2732±78 b | 886±90 a | 3580±30 a | −38±10 c | ||||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3414±71 b | 2568±40 b | 846±31 a | 3477±75 b | 63±4 bc | |||||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3326±30 b | 2636±40 b | 690±0 b | 3473±0 b | 147±30 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3253±11 b | 2953±55 a | 300±44 c | 3562±18 a | 309±7 a | |||||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3616±14 a | 2765±75 a | 851±61 a | 3602±40 a | −14±26 c | ||||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3235±38 b | 2724±72 a | 511±110 b | 3485±3 b | 250±36 b | |||||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 3194±67 b | 2514±70 b | 680±3 b | 3448±9 b | 254±58 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3124±19 b | 2837±24 a | 287±43 c | 3526±25 b | 402±6 a | |||||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3387±10 b | 2267±30 c | 1120±20 a | 3185±22 c | −202±6 c | |||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3774±66 a | 2503±29 b | 1271±37 a | 3365±39 b | −409±27 d | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3052±12 c | 2197±40 c | 855±13 b | 3133±21 c | 81±30 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3449±54 b | 2801±49 a | 648±5 c | 3686±53 a | 237±2 a | |||||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3736±2 a | 2699±2 b | 1037±1 a | 3641±12 b | −95±14 c | ||||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3502±40 b | 2501±30 c | 1001±40 a | 3439±30 c | −63±16 c | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3228±6 c | 2394±14 c | 834±20 b | 3358±14 c | 130±20 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3499±22 b | 2926±122 a | 573±144 c | 3780±13 a | 281±35 a | |||||
| N3 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3725±47 a | 2723±100 a | 1002±53 a | 3653±48 a | −72±1 c | ||||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3354±24 b | 2566±35 b | 788±59 b | 3452±25 b | 98±49 b | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3281±27 b | 2509±97 b | 772±124 b | 3473±45 b | 192±72 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3337±14 b | 2888±29 a | 449±15 c | 3694±3 a | 357±11 a | |||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level(N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||
| 氮素水平×品种N×C | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||
表2 不同氮素水平下供试品种稻米淀粉的糊化特征(RVA谱)的差异
Table 2. Differences of starch gelatinization characteristics (RVA spectrum) of tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels. cP
| 类型 Type | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 最高黏度 Peak viscosity | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity | 崩解值 Breakdown | 最终黏度 Final viscosity | 消减值 Setback | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3587±58 a | 2627±82 b | 960±140 a | 3437±36 b | −150±94 c | |||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3363±17 b | 2422±82 c | 941±99 a | 3310±52 c | −53±69 c | |||||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3333±13 b | 2625±21 b | 708±9 b | 3441±12 b | 108±1 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3378±10 b | 3039±60 a | 339±40 c | 3671±10 a | 293±10 a | |||||
| N2 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3618±20 a | 2732±78 b | 886±90 a | 3580±30 a | −38±10 c | ||||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3414±71 b | 2568±40 b | 846±31 a | 3477±75 b | 63±4 bc | |||||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3326±30 b | 2636±40 b | 690±0 b | 3473±0 b | 147±30 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3253±11 b | 2953±55 a | 300±44 c | 3562±18 a | 309±7 a | |||||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3616±14 a | 2765±75 a | 851±61 a | 3602±40 a | −14±26 c | ||||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 3235±38 b | 2724±72 a | 511±110 b | 3485±3 b | 250±36 b | |||||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 3194±67 b | 2514±70 b | 680±3 b | 3448±9 b | 254±58 b | |||||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 3124±19 b | 2837±24 a | 287±43 c | 3526±25 b | 402±6 a | |||||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3387±10 b | 2267±30 c | 1120±20 a | 3185±22 c | −202±6 c | |||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3774±66 a | 2503±29 b | 1271±37 a | 3365±39 b | −409±27 d | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3052±12 c | 2197±40 c | 855±13 b | 3133±21 c | 81±30 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3449±54 b | 2801±49 a | 648±5 c | 3686±53 a | 237±2 a | |||||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3736±2 a | 2699±2 b | 1037±1 a | 3641±12 b | −95±14 c | ||||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3502±40 b | 2501±30 c | 1001±40 a | 3439±30 c | −63±16 c | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3228±6 c | 2394±14 c | 834±20 b | 3358±14 c | 130±20 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3499±22 b | 2926±122 a | 573±144 c | 3780±13 a | 281±35 a | |||||
| N3 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 3725±47 a | 2723±100 a | 1002±53 a | 3653±48 a | −72±1 c | ||||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 3354±24 b | 2566±35 b | 788±59 b | 3452±25 b | 98±49 b | |||||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 3281±27 b | 2509±97 b | 772±124 b | 3473±45 b | 192±72 b | |||||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 3337±14 b | 2888±29 a | 449±15 c | 3694±3 a | 357±11 a | |||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level(N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||
| 氮素水平×品种N×C | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||
| 类型 Type | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 清蛋白 Albumin | 球蛋白 Globulin | 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 谷蛋白 Glutenin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 0.26±0.19 c | 0.52±0.08 b | 0.63±0.01 a | 3.04±0.08 b | |
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.36±0.00 b | 0.57±0.01 a | 0.56±0.03 b | 3.47±0.19 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.42±0.02 a | 0.51±0.01 b | 0.61±0.01 a | 3.03±0.07 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.41±0.01 a | 0.62±0.08 a | 0.69±0.02 a | 3.42±0.23 a | |||
| N2 | 武育粳3号Wuyujing 3 | 0.29±0.05 b | 0.53±0.00 b | 0.66±0.01 c | 3.31±0.10 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.37±0.01 b | 0.60±0.01 ab | 0.65±0.04 c | 4.32±0.05 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.47±0.01 a | 0.68±0.04 a | 0.72±0.03 b | 3.64±0.17 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.50±0.03 a | 0.68±0.03 a | 0.82±0.01 a | 3.85±0.05 b | |||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 0.30±0.02 b | 0.64±0.02 b | 0.78±0.05 b | 3.89±0.12 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.38±0.01 b | 0.73±0.05 a | 0.67±0.01 c | 4.83±0.08 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.51±0.02 a | 0.71±0.05 a | 1.07±0.21 a | 4.17±0.10 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.59±0.03 a | 0.69±0.01 ab | 1.06±0.03 a | 4.31±0.17 b | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.33±0.00 b | 0.33±0.02 b | 0.46±0.01 b | 2.78±0.02 b | |
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.46±0.02 a | 0.42±0.04 a | 0.62±0.03 a | 3.02±0.08 ab | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 0.24±0.04 c | 0.40±0.00 a | 0.61±0.03 a | 3.23±0.09 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.26±0.01 c | 0.36±0.45 b | 0.55±0.03 a | 3.16±0.12 a | |||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.35±0.01 b | 0.43±0.03 b | 0.55±0.03 b | 3.21±0.24 c | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.47±0.02 a | 0.49±0.04 a | 0.64±0.02 a | 4.03±0.12 a | |||
| 扬两优6号Yangliangyou 6 | 0.26±0.03 c | 0.45±0.01 ab | 0.67±0.11 a | 3.33±0.08 c | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.29±0.05 c | 0.37±0.01 c | 0.64±0.05 a | 3.73±0.09 b | |||
| N3 | 丰优香占Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.36±0.02 b | 0.53±0.03 b | 0.64±0.03 c | 3.85±0.18 b | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.68±0.02 a | 0.98±0.06 a | 4.40±0.14 a | |||
| 扬两优6号Yangliangyou 6 | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.52±0.01 b | 0.81±0.06 b | 4.62±0.04 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.41±0.01 b | 0.47±0.02 c | 0.81±0.02 b | 4.38±0.02 a | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 氮素水平×品种N×C | ns | ** | ** | ** | |||
表3 不同氮素水平下供试水稻品种的籽粒蛋白组分含量的差异
Table 3. Differences in protein component contents in grains of the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels. %
| 类型 Type | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 清蛋白 Albumin | 球蛋白 Globulin | 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 谷蛋白 Glutenin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | N1 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 0.26±0.19 c | 0.52±0.08 b | 0.63±0.01 a | 3.04±0.08 b | |
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.36±0.00 b | 0.57±0.01 a | 0.56±0.03 b | 3.47±0.19 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.42±0.02 a | 0.51±0.01 b | 0.61±0.01 a | 3.03±0.07 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.41±0.01 a | 0.62±0.08 a | 0.69±0.02 a | 3.42±0.23 a | |||
| N2 | 武育粳3号Wuyujing 3 | 0.29±0.05 b | 0.53±0.00 b | 0.66±0.01 c | 3.31±0.10 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.37±0.01 b | 0.60±0.01 ab | 0.65±0.04 c | 4.32±0.05 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.47±0.01 a | 0.68±0.04 a | 0.72±0.03 b | 3.64±0.17 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.50±0.03 a | 0.68±0.03 a | 0.82±0.01 a | 3.85±0.05 b | |||
| N3 | 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 0.30±0.02 b | 0.64±0.02 b | 0.78±0.05 b | 3.89±0.12 c | ||
| 农垦57 Nongken 57 | 0.38±0.01 b | 0.73±0.05 a | 0.67±0.01 c | 4.83±0.08 a | |||
| 淮稻5号Huaidao 5 | 0.51±0.02 a | 0.71±0.05 a | 1.07±0.21 a | 4.17±0.10 b | |||
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | 0.59±0.03 a | 0.69±0.01 ab | 1.06±0.03 a | 4.31±0.17 b | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | N1 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.33±0.00 b | 0.33±0.02 b | 0.46±0.01 b | 2.78±0.02 b | |
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.46±0.02 a | 0.42±0.04 a | 0.62±0.03 a | 3.02±0.08 ab | |||
| 扬两优6号 Yangliangyou 6 | 0.24±0.04 c | 0.40±0.00 a | 0.61±0.03 a | 3.23±0.09 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.26±0.01 c | 0.36±0.45 b | 0.55±0.03 a | 3.16±0.12 a | |||
| N2 | 丰优香占 Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.35±0.01 b | 0.43±0.03 b | 0.55±0.03 b | 3.21±0.24 c | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.47±0.02 a | 0.49±0.04 a | 0.64±0.02 a | 4.03±0.12 a | |||
| 扬两优6号Yangliangyou 6 | 0.26±0.03 c | 0.45±0.01 ab | 0.67±0.11 a | 3.33±0.08 c | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.29±0.05 c | 0.37±0.01 c | 0.64±0.05 a | 3.73±0.09 b | |||
| N3 | 丰优香占Fengyouxiangzhan | 0.36±0.02 b | 0.53±0.03 b | 0.64±0.03 c | 3.85±0.18 b | ||
| 甬优2640 Yongyou 2640 | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.68±0.02 a | 0.98±0.06 a | 4.40±0.14 a | |||
| 扬两优6号Yangliangyou 6 | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.52±0.01 b | 0.81±0.06 b | 4.62±0.04 a | |||
| 汕优63 Shanyou 63 | 0.41±0.01 b | 0.47±0.02 c | 0.81±0.02 b | 4.38±0.02 a | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 氮素水平×品种N×C | ns | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 类型 Type | 蛋白组分 Protein component | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content | 崩解值 Breakdown | 消减值 Setback | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | 清蛋白 Albumin | 0.753** | −0.865** | −0.752** | 0.874** | −0.954** |
| 球蛋白 Globulin | 0.228 | −0.601* | −0.613* | 0.737** | −0.798** | |
| 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 0.385 | −0.423 | −0.510 | 0.652* | −0.743** | |
| 谷蛋白 Glutenin | −0.066 | −0.509 | −0.384 | 0.545 | −0.555 | |
| 蛋白质总量 Total protein | 0.144 | −0.349 | −0.485 | 0.624* | −0.675* | |
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | 清蛋白 Albumin | 0.234 | −0.102 | 0.305 | −0.409 | 0.259 |
| 球蛋白Globulin | 0.219 | −0.248 | −0.076 | 0.101 | −0.300 | |
| 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | −0.201 | 0.142 | −0.444 | 0.430 | −0.649* | |
| 谷蛋白 Glutenin | −0.234 | 0.167 | −0.521 | 0.534 | −0.728** | |
| 蛋白质总量 Total protein | −0.075 | −0.077 | −0.474 | 0.531 | −0.735** |
表4 不同类型水稻品种的籽粒蛋白质及其组分含量与稻米蒸煮食味品质性状的关系
Table 4. Relationship between the contents of grain protein and its components in different rice varieties and the quality traits of cooking and eating rice.
| 类型 Type | 蛋白组分 Protein component | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content | 崩解值 Breakdown | 消减值 Setback | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | 清蛋白 Albumin | 0.753** | −0.865** | −0.752** | 0.874** | −0.954** |
| 球蛋白 Globulin | 0.228 | −0.601* | −0.613* | 0.737** | −0.798** | |
| 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 0.385 | −0.423 | −0.510 | 0.652* | −0.743** | |
| 谷蛋白 Glutenin | −0.066 | −0.509 | −0.384 | 0.545 | −0.555 | |
| 蛋白质总量 Total protein | 0.144 | −0.349 | −0.485 | 0.624* | −0.675* | |
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | 清蛋白 Albumin | 0.234 | −0.102 | 0.305 | −0.409 | 0.259 |
| 球蛋白Globulin | 0.219 | −0.248 | −0.076 | 0.101 | −0.300 | |
| 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | −0.201 | 0.142 | −0.444 | 0.430 | −0.649* | |
| 谷蛋白 Glutenin | −0.234 | 0.167 | −0.521 | 0.534 | −0.728** | |
| 蛋白质总量 Total protein | −0.075 | −0.077 | −0.474 | 0.531 | −0.735** |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 抽穗后天数 Days after heading | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 d | 20 d | 30 d | 40 d | |||||||
| 上部 | 下部 | 上部 | 下部 | 上部 | 下部 | 下部 | ||||
| Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Lower | ||||
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | ||||||||||
| N1 | WYJ 3 | 258.39±5.58 b | 246.32±5.32 c | 90.87±1.96 b | 92.67±2.00 c | 65.12±1.41 c | 65.17±1.41 b | 56.38±1.22 c | ||
| NK 57 | 270.61±5.85 b | 246.50±5.33 c | 96.30±2.08 b | 88.45±1.91 c | 66.72±1.44 c | 59.91±1.29 b | 57.52±1.24 c | |||
| HD 5 | 343.29±7.42 a | 304.14±6.57 b | 118.26±2.55 a | 167.08±3.61 b | 73.17±1.58 b | 104.33±2.25 a | 69.55±1.50 b | |||
| WYJ 24 | 370.77±8.01 a | 368.92±7.97 a | 121.71±2.63 a | 216.83±4.68 a | 86.77±1.87 a | 128.65±2.78 a | 79.94±1.73 a | |||
| N2 | WYJ 3 | 265.76±5.74 c | 252.62±5.46 c | 92.03±1.99 c | 96.72±2.09 c | 67.81±1.46 c | 71.66±1.55 c | 56.80±1.23 c | ||
| NK 57 | 300.32±6.49 bc | 251.13±5.43 c | 98.18±2.12 c | 94.77±2.05 c | 70.15±1.52 c | 62.57±1.35 c | 57.69±1.25 c | |||
| HD 5 | 348.92±7.54 b | 348.10±7.52 b | 140.26±3.03 b | 176.16±3.81 b | 79.36±1.71 b | 110.90±2.40 b | 76.77±1.66 b | |||
| WYJ 24 | 447.00±9.66 a | 397.37±8.58 a | 185.74±4.01 a | 226.68±4.90 a | 98.21±2.12 a | 135.91±2.94 a | 87.14±1.88 a | |||
| N3 | WYJ 3 | 276.76±5.98 c | 253.61±5.48 c | 93.61±2.02 c | 103.49±2.24 c | 68.33±1.48 c | 77.14±1.67 c | 58.36±1.26 b | ||
| NK 57 | 322.91±6.98 bc | 262.91±5.68 c | 100.55±2.17 c | 98.01±2.12 c | 77.04±1.66 c | 70.35±1.52 c | 60.58±1.31 b | |||
| HD 5 | 373.84±8.08 b | 370.33±8.00 b | 147.25±3.18 b | 181.1±3.91 b | 87.64±1.89 b | 111.44±2.41 b | 85.16±1.84 a | |||
| WYJ 24 | 495.97±10.71 a | 458.07±9.90 a | 190.46±4.11 a | 238.46±5.15 a | 109.74±2.37 a | 149.30±3.23 a | 93.94±2.03 a | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | ||||||||||
| N1 | FYXZ | 116.45±2.52 c | 155.05±3.35 c | 114.13±2.47 c | 113.02±2.44 b | 69.02±1.49 c | 93.19±2.01 c | 73.67±1.59 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 170.16±3.68 a | 204.61±4.42 b | 144.73±3.13 a | 117.84±2.55 a | 101.12±2.18 a | 101.30±2.19 b | 75.33±1.63 b | |||
| YLY 6 | 147.60±3.19 b | 203.94±4.41 b | 123.74±2.67 b | 119.12±2.57 a | 70.97±1.53 c | 110.50±2.39 a | 74.15±1.60 b | |||
| SY 63 | 147.12±3.18 b | 256.24±5.54 a | 129.27±2.79 b | 118.16±2.55 a | 81.41±1.76 b | 102.01±2.20 b | 88.01±1.90 a | |||
| N2 | FYXZ | 133.08±2.87 c | 159.31±3.44 c | 132.04±2.85 c | 126.53±2.73 c | 78.60±1.70 c | 103.91±2.24 b | 84.27±1.82 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 186.24±4.02 a | 210.46±4.55 b | 147.42±3.18 a | 126.90±2.74 c | 103.44±2.23 a | 103.94±2.25 b | 82.00±1.77 c | |||
| YLY 6 | 151.12±3.26 c | 223.20±4.82 b | 138.63±2.99 b | 133.62±2.89 a | 84.85±1.83 c | 116.95±2.53 a | 85.19±1.84 b | |||
| SY 63 | 174.24±3.76 b | 289.99±6.26 a | 142.04±3.07 a | 129.20±2.79 b | 95.71±2.07 b | 104.60±2.26 b | 89.19±1.93 a | |||
| N3 | FYXZ | 145.05±3.13 c | 161.31±3.48 c | 143.25±3.09 c | 130.31±2.82 b | 87.12±1.88 c | 106.26±2.30 b | 85.34±1.84 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 203.53±4.40 a | 217.61±4.70 b | 161.94±3.50 a | 133.89±2.89 b | 116.85±2.52 a | 111.58±2.41 b | 84.69±1.83 b | |||
| YLY 6 | 178.20±3.85 b | 229.69±4.96 b | 146.63±3.17 c | 136.04±2.94 a | 101.76±2.20 b | 123.22±2.66 a | 88.34±1.91 b | |||
| SY 63 | 191.05±4.13 a | 306.14±6.61 a | 151.07±3.26 b | 132.50±2.86 b | 107.71±2.33 b | 110.92±2.40 b | 99.71±2.15 a | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| 氮素水平 Nitrogen (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 氮素水×品种N×C | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
表5 不同氮素水平对供试水稻品种上下部籽粒氨基酸含量的影响
Table 5. Effects of different nitrogen levels on amino acid content in upper and lower grains of the tested rice varieties.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 抽穗后天数 Days after heading | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 d | 20 d | 30 d | 40 d | |||||||
| 上部 | 下部 | 上部 | 下部 | 上部 | 下部 | 下部 | ||||
| Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Lower | ||||
| 常规粳稻 Conventional japonica rice | ||||||||||
| N1 | WYJ 3 | 258.39±5.58 b | 246.32±5.32 c | 90.87±1.96 b | 92.67±2.00 c | 65.12±1.41 c | 65.17±1.41 b | 56.38±1.22 c | ||
| NK 57 | 270.61±5.85 b | 246.50±5.33 c | 96.30±2.08 b | 88.45±1.91 c | 66.72±1.44 c | 59.91±1.29 b | 57.52±1.24 c | |||
| HD 5 | 343.29±7.42 a | 304.14±6.57 b | 118.26±2.55 a | 167.08±3.61 b | 73.17±1.58 b | 104.33±2.25 a | 69.55±1.50 b | |||
| WYJ 24 | 370.77±8.01 a | 368.92±7.97 a | 121.71±2.63 a | 216.83±4.68 a | 86.77±1.87 a | 128.65±2.78 a | 79.94±1.73 a | |||
| N2 | WYJ 3 | 265.76±5.74 c | 252.62±5.46 c | 92.03±1.99 c | 96.72±2.09 c | 67.81±1.46 c | 71.66±1.55 c | 56.80±1.23 c | ||
| NK 57 | 300.32±6.49 bc | 251.13±5.43 c | 98.18±2.12 c | 94.77±2.05 c | 70.15±1.52 c | 62.57±1.35 c | 57.69±1.25 c | |||
| HD 5 | 348.92±7.54 b | 348.10±7.52 b | 140.26±3.03 b | 176.16±3.81 b | 79.36±1.71 b | 110.90±2.40 b | 76.77±1.66 b | |||
| WYJ 24 | 447.00±9.66 a | 397.37±8.58 a | 185.74±4.01 a | 226.68±4.90 a | 98.21±2.12 a | 135.91±2.94 a | 87.14±1.88 a | |||
| N3 | WYJ 3 | 276.76±5.98 c | 253.61±5.48 c | 93.61±2.02 c | 103.49±2.24 c | 68.33±1.48 c | 77.14±1.67 c | 58.36±1.26 b | ||
| NK 57 | 322.91±6.98 bc | 262.91±5.68 c | 100.55±2.17 c | 98.01±2.12 c | 77.04±1.66 c | 70.35±1.52 c | 60.58±1.31 b | |||
| HD 5 | 373.84±8.08 b | 370.33±8.00 b | 147.25±3.18 b | 181.1±3.91 b | 87.64±1.89 b | 111.44±2.41 b | 85.16±1.84 a | |||
| WYJ 24 | 495.97±10.71 a | 458.07±9.90 a | 190.46±4.11 a | 238.46±5.15 a | 109.74±2.37 a | 149.30±3.23 a | 93.94±2.03 a | |||
| 杂交稻 Hybrid rice | ||||||||||
| N1 | FYXZ | 116.45±2.52 c | 155.05±3.35 c | 114.13±2.47 c | 113.02±2.44 b | 69.02±1.49 c | 93.19±2.01 c | 73.67±1.59 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 170.16±3.68 a | 204.61±4.42 b | 144.73±3.13 a | 117.84±2.55 a | 101.12±2.18 a | 101.30±2.19 b | 75.33±1.63 b | |||
| YLY 6 | 147.60±3.19 b | 203.94±4.41 b | 123.74±2.67 b | 119.12±2.57 a | 70.97±1.53 c | 110.50±2.39 a | 74.15±1.60 b | |||
| SY 63 | 147.12±3.18 b | 256.24±5.54 a | 129.27±2.79 b | 118.16±2.55 a | 81.41±1.76 b | 102.01±2.20 b | 88.01±1.90 a | |||
| N2 | FYXZ | 133.08±2.87 c | 159.31±3.44 c | 132.04±2.85 c | 126.53±2.73 c | 78.60±1.70 c | 103.91±2.24 b | 84.27±1.82 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 186.24±4.02 a | 210.46±4.55 b | 147.42±3.18 a | 126.90±2.74 c | 103.44±2.23 a | 103.94±2.25 b | 82.00±1.77 c | |||
| YLY 6 | 151.12±3.26 c | 223.20±4.82 b | 138.63±2.99 b | 133.62±2.89 a | 84.85±1.83 c | 116.95±2.53 a | 85.19±1.84 b | |||
| SY 63 | 174.24±3.76 b | 289.99±6.26 a | 142.04±3.07 a | 129.20±2.79 b | 95.71±2.07 b | 104.60±2.26 b | 89.19±1.93 a | |||
| N3 | FYXZ | 145.05±3.13 c | 161.31±3.48 c | 143.25±3.09 c | 130.31±2.82 b | 87.12±1.88 c | 106.26±2.30 b | 85.34±1.84 b | ||
| YY 2640 | 203.53±4.40 a | 217.61±4.70 b | 161.94±3.50 a | 133.89±2.89 b | 116.85±2.52 a | 111.58±2.41 b | 84.69±1.83 b | |||
| YLY 6 | 178.20±3.85 b | 229.69±4.96 b | 146.63±3.17 c | 136.04±2.94 a | 101.76±2.20 b | 123.22±2.66 a | 88.34±1.91 b | |||
| SY 63 | 191.05±4.13 a | 306.14±6.61 a | 151.07±3.26 b | 132.50±2.86 b | 107.71±2.33 b | 110.92±2.40 b | 99.71±2.15 a | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| 氮素水平 Nitrogen (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 氮素水×品种N×C | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
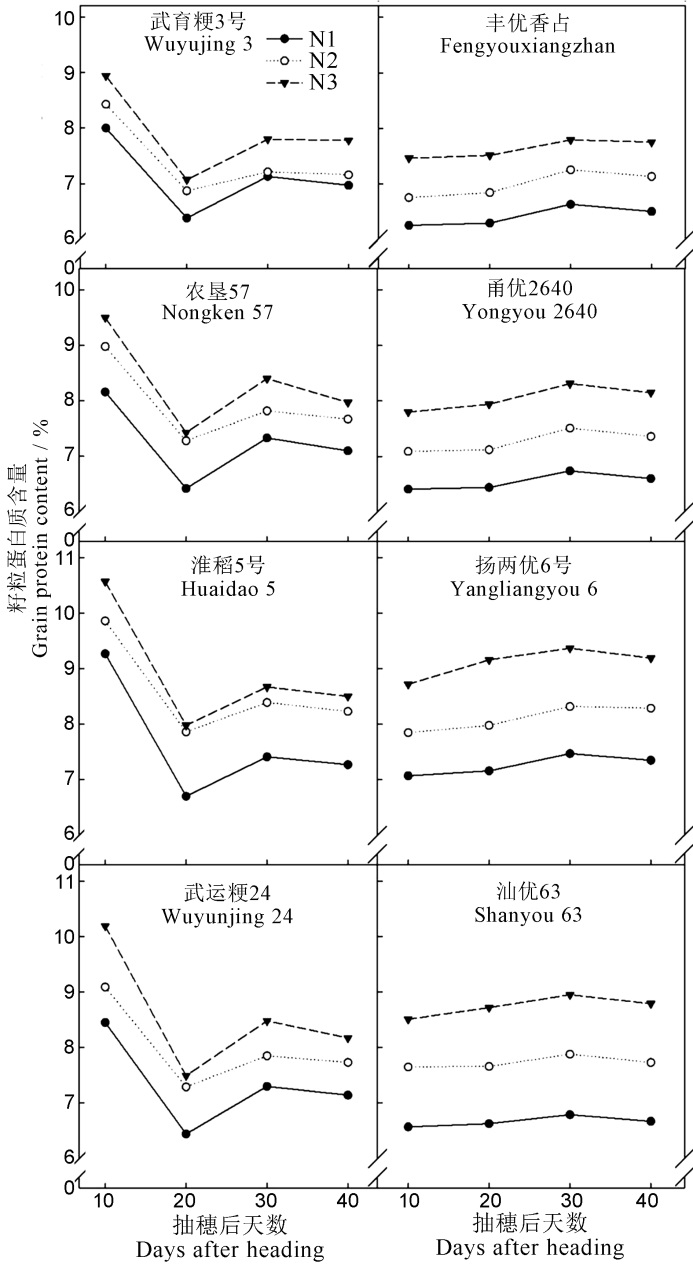
图2 不同氮素水平下供试品种的籽粒蛋白质积累动态 数据为3个重复的平均值。N1、N2和N3为结实期不同氮素施用水平处理,在结实期的施氮量分别为1、2、3 g/盆。
Fig. 2. Dynamics of protein accumulation in grains of tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels. Data are means of 3 replicates. N1, N2 and N3 refer to nitrogen application levels of 1, 2, 3 g/pot at the filling stage, respectively.
| [1] | 周正平, 占小登, 沈希宏, 曹立勇. 我国水稻育种发展现状、展望及对策[J]. 中国稻米, 2019, 25(5): 1-4. |
| Zhou Z P, Zhan X D, Shen X H, Cao L Y. Current situation, prospect and countermeasures of rice breeding in China[J]. China Rice, 2019, 25(5): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 何秀英, 廖耀平, 程永盛, 陈钊明, 陈粤汉. 水稻品质研究进展与展望[J]. 广东农业科学, 2009(1): 11-16. |
| He X Y, Liao Y P, Cheng Y S, Chen Z M, Chen Y H. Progress and prospect of rice quality research[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2009(1): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张昌泉, 赵冬生, 李钱峰, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 稻米品质性状基因的克隆与功能研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283. |
| Zhang C Q, Zhao D S, Li Q F, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Advances in cloning and functional studies of rice quality trait genes[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 张玉荣, 周显青, 杨兰兰. 大米食味品质评价方法的研究现状与展望[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2009, 24(8): 155-160. |
| Zhang Y R, Zhou X Q, Yang L L. Research status and prospect of rice taste Quality evaluation methods[J]. Journal of The Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2009, 24(8): 155-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 胡桂仙, 王建军, 王小骊, 董秀金, 朱加虹. 稻米食味品质检测评价技术的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(19): 62-65. |
| Hu G X, Wang J J, Wang X L, Dong X J, Zhu J H. Research status and prospect of rice taste quality detection and evaluation technology[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(19): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 蔡一霞, 刘春香, 王维, 张洪熙, 张祖建, 杨静, 唐汉忠. 灌浆期直链淀粉含量相似品种稻米胶稠度和RVA谱的动态差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(12): 2439-2445. |
| Cai Y X, Liu C X, Wang W, Zhang H X, Zhang Z J, Yang J, Tang H Z. Dynamic difference of gel consistency and RVA spectrum of rice varieties with similar apparent amylose content at filling stage[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(12): 2439-2445. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 李宏, 周少川, 黄道强, 赖穗春, 王志东, 周德贵, 王重荣. 水稻优质食味的认知及育种实践[J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(4): 15-18, 31. |
| Li H, Zhou S C, Huang D Q, Lai S C, Wang Z D, Zhou D G, Wang C R. Cognition and breeding practice of high quality food taste in rice[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 41(4): 15-18, 31. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 董明辉, 惠锋, 顾俊荣, 陈培峰, 杨代凤, 乔中英. 灌浆期不同光强对水稻不同粒位籽粒品质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(2): 164-170. |
| Dong M H, Hui F, Gu J R, Chen P F, Yang D F, Qiao Z Y. Effects of different light intensity at filling stage on grain quality of rice at different grain positions[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(2): 164-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 王丽. 穗后弱光胁迫对杂交稻稻米淀粉品质与产量的影响及其生理响应机制[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2016. |
| Wang L. Effects of post-panicle low light stress on starch quality and yield formation of hybrid rice and its physiological response mechanism[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 盛婧, 陶红娟, 陈留根. 灌浆结实期不同时段温度对水稻结实与稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007(4): 396-402. |
| Sheng J, Tao H J, Chen L G. Effects of temperature on rice setting and rice quality in Different filling stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007(4): 396-402. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王秋菊. 黑龙江地区土壤肥力和积温对水稻产量、品质影响研究[D]. 沈阳农业大学, 2012. |
| Wang Q J. Effects of soil fertility and accumulated temperature on rice yield and quality in Heilongjiang Province[D]. Shenyang Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 朱大伟. 三种关键栽培措施对软米粳稻产量与品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. |
| Zhu D W. Effects of three key cultivation measures on yield and quality of soft rice japonica[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 谢戎, 张林, 朱永川, 郭晓艺, 杨大金, 周兴兵, 刘茂. 水稻氮素利用效率的研究进展及其动向[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(5): 1215-1225. |
| Xu F X, Xiong H, Xie R, Zhang L, Zhu Y C, Guo X Y, Yang D J, Zhou X B, Liu M. Advances and trends in nitrogen use efficiency of rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2009, 15(5): 1215-1225. | |
| [14] | 宁慧峰. 氮素对稻米品质的影响及其理化基础研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. |
| Ning H F. Effects of nitrogen on rice quality and its Physicochemical basis[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李敏, 张洪程, 李国业, 马群, 杨雄, 魏海燕. 生育类型与施氮水平对粳稻淀粉RVA谱特性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(2): 293-300. |
| Li M, Zhang H C, Li G Y, Ma Q, Yang X, Wei H Y. Effects of growth type and nitrogen application level on starch RVA spectrum characteristics of japonica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(2): 293-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 从夕汉, 施伏芝, 阮新民, 罗玉祥, 马廷臣, 罗志祥. 氮肥水平对不同基因型水稻氮素利用率、产量和品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(4): 1219-1226. |
| Cong X H, Shi F Z, Ruan X M, Luo Y X, Ma T C, Luo Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level on nitrogen use efficiency, yield and quality of rice genotypes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(4): 1219-1226. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Kashiwagi T. Effects of rice grain protein QTL, TGP12, on grain composition, yield components, and eating quality with different nitrogen applications[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 263: 108051. |
| [18] | Graeme B, Christopher B, Zhao J. Effects of glutelin and globulin on the physicochemical properties of starch and flour[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2014, 60(2): 414-420. |
| [19] | 张欣, 施利利, 刘晓宇, 丁得亮, 王松文, 崔晶. 不同施肥处理对水稻产量、食味品质及蛋白质组分的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(4): 104-108. |
| Zhang X, Shi L L, Liu X Y, Ding D L, Wang S W, Cui J. Effects of different fertilization treatments on rice yield, eating quality and protein components[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(4): 104-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Wakamatsu K I, Sasaki O, Uezono I, Tanaka A. Effect of the amount of nitrogen application on occurrence of white-back kernels during ripening of rice (Oryza sativa) under high-temperature conditions[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 2008, 77(4): 424-433. |
| [21] | 陈莹莹. 江苏早熟晚粳品种稻米品质对氮肥的响应及其类型[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2012. |
| Chen Y Y. Responses of rice quality to nitrogen fertilizer and its types in Jiangsu early maturity and late japonica varieties[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 张春红, 李金州, 田孟祥, 王才林. 不同食味粳稻品种稻米蛋白质相关性状与食味的关系[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2010, 26(6): 1126-1132. |
| Zhang C H, Li J Z, Tian M X, Wang C L. Relationship between protein-related traits and eating taste in japonica rice varieties with different taste value[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 26(6): 1126-1132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 钱春荣, 冯延江, 杨静, 刘海英, 金正勋. 水稻籽粒蛋白质含量选择对杂种早代蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007(3): 323-326. |
| Qian C R, Feng Y J, Yang J, Liu H Y, Jin Z X. Effects of grain protein content selection on eating quality of early hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007(3): 323-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 杨静, 罗秋香, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金正勋. 氮素对稻米蛋白质组分含量及蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2006, 37(2): 145-150. |
| Yang J, Luo Q X, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin Z X. Effects of nitrogen on protein content and cooking and eating quality of rice[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2006, 37(2): 145-150. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 张欣, 施利利, 丁得亮, 王松文, 崔晶. 稻米蛋白质相关性状与RVA特征谱及食味品质的关系[J]. 食品科技, 2014, 39(10): 188-191. |
| Zhang X, Shi L L, Ding D L, Wang S W, Cui J. Relationship between protein-related traits and RVA characteristics and eating quality in rice[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2014, 39(10): 188-191. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 曲红岩, 张欣, 施利利. 水稻食味品质主要影响因子分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(6): 172-175. |
| Qu H Y, Zhang X, Shi L L. Analysis on main influencing factors of rice eating quality[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(6): 172-175. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 王继馨, 张云江, 程爱华, 吕彬, 李霞辉, 赵镛洛, 廖辉, 李大林, 李辉, 马文东, 黄晓群. 水稻蛋白亚基含量对米饭食味的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008(1): 89-92. |
| Wang J X, Zhang Y J, Cheng A H, Lv B, Li X H, Zhao Y L, Liao H, Li D L, LI H, Ma W D, Huang X Q. Effects of protein subunits contents on eating quality in rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008(1): 89-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 张军, 周冬冬, 许轲. 淮北麦茬机插优质食味粳稻氮肥减量的精确运筹[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(2): 410-422. |
| Zhang J, Zhou D D, Xu K. Precise management of nitrogen reduction in mechanized wheat stubble good taste japonica rice in Huaibei region[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 410-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 兰艳, 黄曌, 隋晓东, 龚静, 涂云彪, 孙影影, 伍鑫, 丁春邦, 李天. 施氮量对低谷蛋白水稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(4): 8-15. |
| Lan Y, Huang Z, Sui X D, Gong J, Tu Y B, Sun Y Y, Wu X, Ding C B, Li T. Effects of nitrogen application rate on yield and quality of low-glutenin rice[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(4): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 朱永波, 韩展誉, 程方民. 氮肥对水稻营养、外观和加工品质的影响[J]. 基层农技推广, 2019, 7(12): 26-29. |
| Zhu Y B, Han Z Y, Cheng F M. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on rice nutritional quality, appearance quality and processing quality[J]. Primary Agricultural Technology Extension, 2019, 7(12): 26-29. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 耿春苗. 氮肥及播期对低谷蛋白水稻产量和品质形成的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. |
| Geng C M. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and sowing date on yield and quality formation of low-glutenin rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 石吕. 水稻精米蛋白质含量与稻米品质变化的关系[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2017. |
| Shi L. Relationship between protein content and rice quality changes in milled rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 石吕, 张新月, 孙惠艳, 曹先梅, 刘建, 张祖建. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. |
| Shi L, Zhang X Y, Sun H Y, Cao X M, Liu J, Zhang Z J. Relationship between protein content and cooking and eating quality of different varieties and effect of nitrogen fertilizer in late stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 钟明. 水稻精米蛋白质和氨基酸含量QTL定位及遗传基础研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2007. |
| Zhong M. QTL mapping and genetic basis of protein and amino acid in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 隆艳喜, 罗雁茹, 竺正航. 四倍体水稻蛋白质含量和谷蛋白基因表达研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(6): 78-87. |
| Long Y X, Luo Y R, Zhu Z H. Protein content and glutenin gene expression in tetraploid rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(6): 78-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Ishimaru T, Parween S, Saito Y, Shigemitsu T, Yamakawa H, Nakazono M. Regular paper laser microdissection-based tissue specific transcriptome analysis reveals novel regulatory network of genes involved in heat-induced grain chalk in rice endosperm[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2019, 60(3): 626-642 |
| [37] | Kawakatsu T, Takaiwa F. Differences in transcriptional regulatory mechanisms functioning for free lysine content and seed storage protein accumulation in rice grain[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(12): 1964-1974. |
| [38] | 揭厚胜. 不同直链淀粉含量的水稻品种籽粒淀粉和蛋白质积累特性的研究[D]. 四川农业大学, 2004. |
| Jie H S. Study on starch and protein accumulation characteristics of rice varieties with different amylose contents[D]. Sichuan Agricultural University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 刘保国, 任昌福. 水稻籽粒蛋白质积累特性的研究[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 1992(1): 70-74. |
| Liu B G, Ren C F. Study on characteristics of protein accumulation in rice grains[J]. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 1992(1): 70-74. (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 陈婷婷, 谈桂露, 褚光, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 超级稻花后强、弱势粒灌浆相关蛋白质表达的差异[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(8): 1471-1482. |
| Chen T T, Tan G L, Chu G, Liu L J, Yang J C. Differences in grain filling related proteins expression between strong and weak grains in super rice after anthesis[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(8): 1471-1482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 董明辉. 水稻穗上不同粒位籽粒品质的差异及其影响因素的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2006. |
| Dong M H. Study on the difference of grain quality and its influencing factors in different grain positions on rice panicle[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2006. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||