
中国水稻科学 ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 239-246.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5176
张宏根, 王茂宇, 张丽佳, 胡雅, 马佳琦, 张翼帆, 汤述翥*( ), 梁国华, 顾铭洪
), 梁国华, 顾铭洪
收稿日期:2015-11-30
修回日期:2015-12-24
出版日期:2016-05-10
发布日期:2016-05-10
通讯作者:
汤述翥
作者简介:# 共同第一作者;
基金资助:
Hong-Gen ZHANG, Mao-yu WANG, Li-jia ZHANG, Ya HU, Jia-qi MA, Yi-fan ZHANG, Shu-zhu TANG*( ), Guo-hua LIANG, Ming-hong GU
), Guo-hua LIANG, Ming-hong GU
Received:2015-11-30
Revised:2015-12-24
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-05-10
Contact:
Shu-zhu TANG
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work;
摘要:
在粳稻品种武育粳3号栽培群体中获得一个类病斑突变体wy3。该突变体类病斑出现于苗期,分蘖期扩散至整张叶片,属于扩散型类病斑突变体。相比野生型,突变体wy3的株高明显降低,有效分蘖数减少,穗长、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低。遮光处理表明,突变体wy3类病斑的产生受自然光诱导。台盼蓝染色结果表明,类病斑部位有大量的死亡细胞。突变体wy3的光合色素含量和净光合速率较野生型显著降低,SOD、POD、CAT活性和MDA含量均显著高于野生型。遗传分析表明突变体表型受单隐性核基因控制,采用BSA将该基因初步定位在第2染色体短臂端粒附近。采用F2群体中1099株类病斑单株将基因定位在标记W2-17和W2-18之间28kb的物理距离内。测序结果表明,突变体wy3中的LOC_Os02g02000编码区(CDS)第375位碱基C缺失,导致翻译提前终止,突变体中该候选基因为OsHPL3的一个新等位基因。
中图分类号:
张宏根, 王茂宇, 张丽佳, 胡雅, 马佳琦, 张翼帆, 汤述翥, 梁国华, 顾铭洪. 水稻类病斑突变体wy3的鉴定和基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 239-246.
Hong-Gen ZHANG, Mao-yu WANG, Li-jia ZHANG, Ya HU, Jia-qi MA, Yi-fan ZHANG, Shu-zhu TANG, Guo-hua LIANG, Ming-hong GU. Characterization and Gene Mapping of Lesion Mimic Mutant wy3 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 239-246.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 分蘖数 No. of tillers | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 56.9±0.6** | 3.5±0.6** | 14.8±1.2** | 79.0±0.1** | 89.6±6.8** | 7.5±2.2 | 3.4±1.4 | 26.54±0.56 |
| WT | 87.5±0.5 | 10.0±1.7 | 16.6±0.8 | 98.3±0.1 | 123.6±11.0 | 7.3±2.8 | 3.3±0.9 | 26.85±0.62 |
表1 突变体和野生型的农艺与产量性状
Table 1 Performance of agronomic and yield traits of the mutant wy3 and the wild type(WT).
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 分蘖数 No. of tillers | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 56.9±0.6** | 3.5±0.6** | 14.8±1.2** | 79.0±0.1** | 89.6±6.8** | 7.5±2.2 | 3.4±1.4 | 26.54±0.56 |
| WT | 87.5±0.5 | 10.0±1.7 | 16.6±0.8 | 98.3±0.1 | 123.6±11.0 | 7.3±2.8 | 3.3±0.9 | 26.85±0.62 |

图1 突变体wy3及其野生型表型 A-苗期植株表型; B-分蘖初期野生型(左)和突变体wy3(右)植株表型; C-成熟期野生型(左)和突变体wy3(右)植株表型; D-野生型(左)和突变体wy3 (右) 穗部表型; E-分蘖期野生型(左)和突变体wy3(右)叶片表型。
Fig.1. Phenotypes of wy3 and wild type(WT). A, Phenotypes of wy3 during seedling stage; B, Phenotypes of WT (left) and wy3(right) during the early tillering stage; C, Phenotypes of WT (left) and wy3(right) during the mature stage; D, Panicle traits of WT (left) and wy3(right); E, Leaves of WT (left) and wy3 (right) during the early tillering stage.
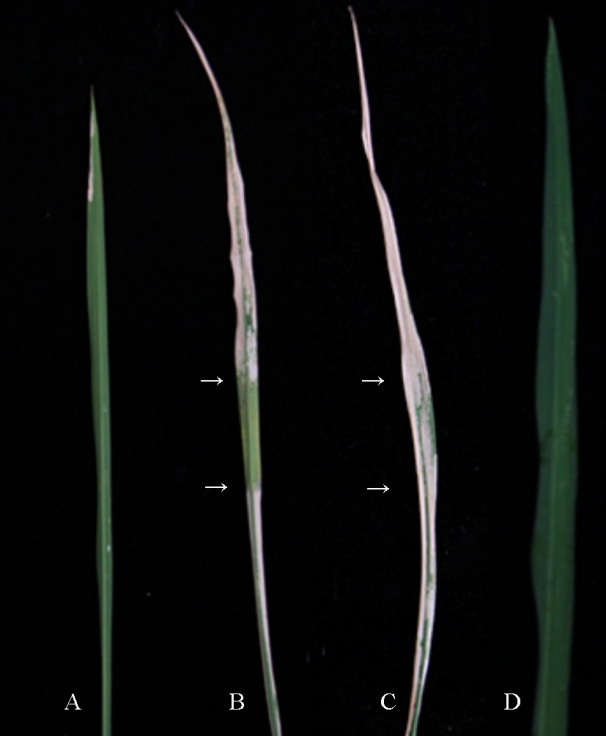

图2 遮光对突变体wy3叶片的影响 A-遮光前 wy3; B-未发生斑点部位遮光15 d后; C-遮光部位恢复光照7 d后; D-野生型。
Fig. 2. Effects of shading on wy3 leaves. A, Leaf of wy3 before shading; B, Leaf without lesion after shading for 15 days; C, Leaf shaded for 7 days then under normal light for 7 days; D, Wild type.
| 材料 Material | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content /(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content /(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素a/b Chlorophyll a/b | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content /(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 1.28±0.09** | 0.27±0.11** | 4.68±0.13** | 0.15±0.11** |
| WT | 2.28±0.03 | 0.99±0.08 | 2.31±0.07 | 0.59±0.04 |
表2 突变体wy3和野生型叶片光合色素含量
Table 2 Pigment contents in leaves of wy3 and wild type(WT).
| 材料 Material | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content /(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content /(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素a/b Chlorophyll a/b | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content /(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 1.28±0.09** | 0.27±0.11** | 4.68±0.13** | 0.15±0.11** |
| WT | 2.28±0.03 | 0.99±0.08 | 2.31±0.07 | 0.59±0.04 |
| 材料 Material | 净光合速率 Pn /(mmol·m-2 s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr /(mmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs /(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci /(mmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 14.16±0.27** | 193.27±10.10** | 0.13±0.02** | 2.76±0.23** |
| WT | 22.46±0.29 | 276.96±6.30 | 0.66±0.08 | 8.93±0.43 |
表3 突变体wy3和野生型武育粳3号分蘖期叶片光合特性
Table 3 Photosynthetic parameters of wy3 and wild type(WT) at the initial tillering stage.
| 材料 Material | 净光合速率 Pn /(mmol·m-2 s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr /(mmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs /(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci /(mmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wy3 | 14.16±0.27** | 193.27±10.10** | 0.13±0.02** | 2.76±0.23** |
| WT | 22.46±0.29 | 276.96±6.30 | 0.66±0.08 | 8.93±0.43 |
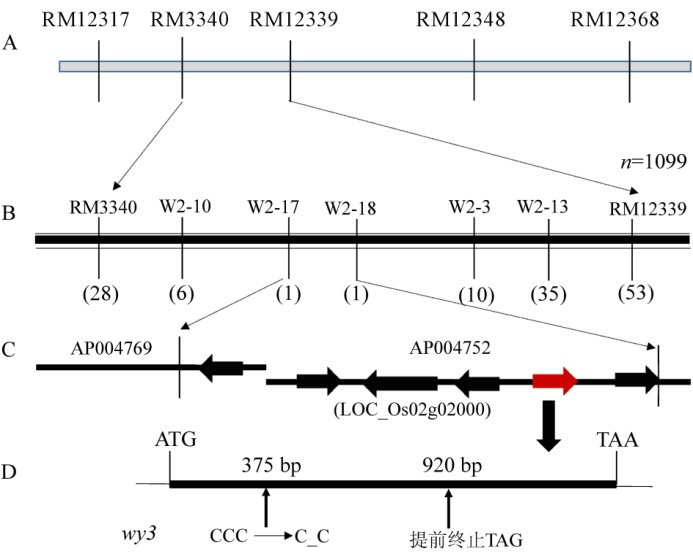
图5 水稻类病斑突变体基因定位 A-基因的初步定位; B-基因的精细定位; C-覆盖基因物理图谱; D-基因内变异位点。
Fig. 5. Mapping of the target gene in wy3. A, Primarily mapping of target gene; B, Fine mapping of target gene; C, Physical map of genes; D, The mutation locus of target gene.
| 标记 Marker | 反向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 正向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| W2-10 | GAGATGCCAGGAGAATGA | TGTAGCTGAGGGTTTGATA |
| W2-17 | AAATCTGGACCTGAAAGT | TTAGGGAAGATTCTCAAA |
| W2-18 | GCCAGCGAGAAGAAGAAG | GAGGATGTGGTCGGGTGT |
| W2-3 | GCAGCACGGACTACAAGA | CAATTCTGCCATGACCAA |
| W2-13 | TAGTGTCGCCCCTTTTAA | CATCACAGCAAACAAGCA |
表4 本研究开发的多态性STS标记
Table 4 Polymorphic STS markers developed in this study.
| 标记 Marker | 反向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 正向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| W2-10 | GAGATGCCAGGAGAATGA | TGTAGCTGAGGGTTTGATA |
| W2-17 | AAATCTGGACCTGAAAGT | TTAGGGAAGATTCTCAAA |
| W2-18 | GCCAGCGAGAAGAAGAAG | GAGGATGTGGTCGGGTGT |
| W2-3 | GCAGCACGGACTACAAGA | CAATTCTGCCATGACCAA |
| W2-13 | TAGTGTCGCCCCTTTTAA | CATCACAGCAAACAAGCA |
| [1] | 王忠华. 植物类病变突变体的诱发与突变机制. 细胞生物学杂志, 2006, 27(5): 530-534. |
| Wang Z H.Induction and mutation mechanism of plant lesion mimic mutants.Chin J Cell Biol, 2005, 27: 530-534 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Dietrich R A, Delaney T P, Uknes S J, et al.Arabidopsis mutants simulating disease resistance response.Cell, 1994, 77(4): 565-577. |
| [3] | Büschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, et al.The barley Mlo gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance.Cell, 1997, 88(5): 695-705. |
| [4] | Gray J, Close P S, Briggs S P, et al.A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the Lls1 gene of maize.Cell, 1997, 89(1): 25-31. |
| [5] | Badigannavar A M, Kale D M, Eapen S, et al.Inheritance of disease lesion mimic leaf trait in groundnut.J Hered, 2002, 93(1): 50-52. |
| [6] | Malamy J, Carr J P, Klessig D F, et al.Salicylic acid: A likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection.Science, 1990, 250(4983): 1002-1004. |
| [7] | Takahashi A, Kawasaki T, Henmi K, et al.Lesion mimic mutants of rice with alterations in early signaling events of defense.Plant J, 1999, 17(5): 535-545. |
| [8] | Dangl J L, Dietrich R A, Richberg M H.Death don’t have no mercy: Cell death programs in plant-microbe interactions.Plant Cell, 1996, 8(10): 1793. |
| [9] | Neuffer M G, Calvert O H.Dominant disease lesion mimics in maize.J Hered, 1975, 66(5): 265-270. |
| [10] | Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P.Regulators of cell death in disease resistance.Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44(3): 371-385. |
| [11] | Dietrich R A, Richberg M H, Schmidt R, et al.A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death.Cell, 1997, 88(5): 685-694. |
| [12] | Ryerson D E, Heath M C.Cleavage of nuclear DNA into oligonucleosomal fragments during cell death induced by fungal infection or by abiotic treatments.Plant Cell, 1996, 8(3): 393-402. |
| [13] | Lamb C, Dixon R A.The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 1997, 48(1): 251-275. |
| [14] | 王建军, 朱旭东, 王林友, 等. 水稻类病变突变体 lrd40 的抗病性与细胞学分析. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(2): 111-116. |
| Wang J J, Zhu X D, Wang L Y, et al.Disease resistance and cytological analyses on lesion resembling disease mutant lrd40 inOryza sativa. Chin J Rice Sci, 2005, 19: 111-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 陈析丰, 金杨, 马伯军. 水稻类病变突变体及抗病性的研究进展. 植物病理学报, 2011, 41(1): 1-9. |
| Chen X F, Jin Y, Ma B J.Progress on the studies of rice lesion mimics and their resistant mechanism to the pathogens.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2011, 41: 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Qiao Y, Jiang W, Lee J H, et al.SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit μ1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa).New Phytol, 2010, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [17] | Wu C, Bordeos A, Madamba M R S, et al. Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases.Mol Genet Genom, 2008, 279(6): 605-619. |
| [18] | Yin Z, Chen J, Zeng L, et al.Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight.Mol Plant-Microbe Interac, 2000, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [19] | 李小红, 施勇烽, 张晓波, 等. 水稻斑点叶突变体 hm197 的鉴定及其基因定位. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 447-456. |
| Li X H, Shi Y F, Zhang X B,et al.Identification and gene mapping of a spotted-leaf mutant hm197 in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2015, 29(5): 447-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Chen X, Hao L, Pan J, et al.spl5, a cell death and defense-related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) in rice.Mol Breeding, 2012, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [21] | Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, et al.A rice spotted leaf gene, spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein.PNAS, 2002, 99(11): 7530-7535. |
| [22] | Zeng L R, Qu S, Bordeos A, et al.Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-box/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.Plant Cell, 2004, 16(10): 2795-2808. |
| [23] | Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, et al.Isolation and molecular characterization of a spotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2007, 63(6): 847-860. |
| [24] | Takahashi A, Agrawal G K, Yamazaki M, et al.Rice Pti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses.Plant Cell, 2007, 19(9): 2940-2951. |
| [25] | Yin Z, Chen J, Zeng L, et al.Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight.Mol Plant-Microbe Interac, 2000, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [26] | Lichtenthaler H K.Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic bio membranes.Methods Enzymol, 1987 (148C): 350-382. |
| [27] | 张志良,瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990. |
| Zhang Z L, Qu W J.Plant Physiology Experimental Guidance. 3rd edn. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2003. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 王丹. 水稻分蘖调控基因TE的功能分析和类病变突变体lms1的图位克隆. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2012. |
| Wang D.Functional analysis of a key tillering regulator TE and map-based cloning of gene lms1 in rice (Orzya sativa L.). Beijing: CAAS, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 邱结华, 马宁, 蒋汉伟, 等. 水稻类病斑突变体 lmm4 的鉴定及其基因定位. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(4): 367-376. |
| Qiu J H, Ma N, Jiang H W, et al.Identification and gene mapping of a lesion mimic mutant lmm4 in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2014, 28(4):367-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 钟振泉, 罗文龙, 刘永柱, 等. 一份新的水稻斑点叶突变体 spl32 的鉴定和基因定位. 作物学报, 2015, 41(6): 861-871. |
| Zhong Z Q, Luo W L, Liu Y Z, et al.Characterization of a novel spotted leaf mutant spl32 and mapping of spl32(t) gene in rice (Oryza sativa).Acta Agron Sin, 2015, 41(6): 861-871. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 刘林. 水稻类病变突变体g340的鉴定和基因定位.北京:中国农业科学院, 2014. |
| Liu L.Identification and gene mapping of a rice lesion mimic mutant g340. Beijing: CAAS, 2014 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 代高猛, 朱小燕, 李云峰, 等. 水稻类病斑突变体spl31的遗传分析与基因定位. 作物学报, 2013, 39(7): 1223-1230. |
| Dai G M, Zhu X Y, Li Y F, et al.Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a lesion mimic mutant spl31 in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2013, 39(7): 1223-1230. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Samuilov V D, Kiselevsky D B, Sinitsyn S V, et al.H2O2 intensifies CN--induced apoptosis in pea leaves.Biochem (Moscow), 2006, 71(4): 384-394. |
| [34] | Wang L, Pei Z Y, He C.OsLSD1, a rice zinc finger protein, regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation.Mol Plant-Microbe Interac, 2005, 18(5):375-384. |
| [35] | Kojo K, Yaeno T, Kusumi K, et al.Regulatory mechanisms of ROI generation are affected by rice spl mutations.Plant Cell Physiol, 2006, 47(8): 1035-1044. |
| [36] | Liu X, Li F, Tang J, et al.Activation of the jasmonic acid pathway by depletion of the hydro peroxide lyase OsHPL3 reveals crosstalk between the HPL and AOS branches of the oxylipin pathway in rice.PLoS ONE,2012,7(11):1-14. |
| [37] | Tong X, Qi J, Zhu X, et al.The rice hydro peroxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway.Plant J, 2012, 71(5): 763-775. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||