
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 277-286.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240804
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
贾毅帆, 王新峰, 王雅宣, 刘芳, 肖晶, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-06
修回日期:2024-09-12
出版日期:2025-03-10
发布日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
* email:wanpinjun@caas.cn基金资助:
JIA Yifan, WANG Xinfeng, WANG Yaxuan, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun*( )
)
Received:2024-08-06
Revised:2024-09-12
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
* email:wanpinjun@caas.cn摘要:
【目的】SR蛋白(serine/arginine-rich protein)是一类富含丝氨酸/精氨酸的可变剪接因子,在褐飞虱体内对基因的剪接过程起调控作用。本研究通过克隆褐飞虱(Nilaparvata lugens)的5个NlSR基因并鉴定了其分子特性、表达模式和生物学功能,为褐飞虱的防治提供新的思路。【方法】基于褐飞虱基因组数据,利用PCR技术克隆了5个NlSR基因cDNA序列,并利用生物信息学手段分析其序列特征;利用qRT-PCR技术检测它们在不同发育阶段 (卵、1 - 5龄若虫和雌雄成虫)和组织(唾液腺、体壁、脂肪体、卵巢和中肠)中的表达特征;并测定干扰后的基因表达及褐飞虱的存活率、蜜露量和体质量变化。【结果】成功克隆了5个NlSR基因的cDNA序列,分别命名为NlSRSF1、NlSRSF2.1、NlSRSF2.2、NlSRSF7.1和NlSRSF7.2。根据进化树分类,这些基因被分为3个亚家族:SRSF1、SRSF2和SRSF7。NlSRs基因的开放阅读框长度在495 bp到508 bp之间,编码的氨基酸数目介于164 aa到235 aa,预测分子量在19.54 kD到26.76 kD之间,等电点在9.53到11.83之间,均为亲水性碱性蛋白,不稳定指数在63.55到131.97之间。编码的蛋白含有N端的RRM结构域(RNA recognition motif)和C端的RS结构域(Arginine/serine-rich domain),NlSRSF7.1和NlSRSF7.2还含有锌指(ZnF_C2HC)结构域。NlSR基因在褐飞虱的唾液腺、体壁、脂肪体、卵巢和中肠等组织中均有表达,其中NlSRSF1和NlSRSF2.1在唾液腺中的相对表达量较高;NlSRSF1主要在卵和1龄若虫中表达,其他基因主要在成虫中表达。RNAi实验结果表明,与对照组dsGFP相比,干扰NlSRSF1、NlSRSF2.1和NlSRSF7.2显著降低褐飞虱的存活率,干扰NlSRSF2.2和NlSRSF7.1对存活率无显著影响,干扰所有NlSR基因均显著降低了褐飞虱的蜜露量和体质量增加量。【结论】本研究克隆了褐飞虱的5个NlSR基因,分析了其序列和表达特征,并通过干扰确定它们对褐飞虱生命活动的影响,为深入研究褐飞虱NlSRs的生物学功能奠定了基础。
贾毅帆, 王新峰, 王雅宣, 刘芳, 肖晶, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 褐飞虱中富含丝氨酸/精氨酸的可变剪接因子特性和生物学功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 277-286.
JIA Yifan, WANG Xinfeng, WANG Yaxuan, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun. Molecular Characterization and Biological Function of Serine/Arginine-rich Alternative Splicing Factors in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera:Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 277-286.
| 引物名称 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Upstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Downstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | Use 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cNlSRSF1 | AAGACGACGCCTTGCCT | AGCTGTGTGTTGCTCCTTAATT | 克隆 Clone |
| cNlSRSF2.1 | TCCACAACTTCACATAAGTTCG | TTAGGCTTGGTAGCCAGCA | |
| cNlSRSF2.2 | GCATCTGTTTCTTGGCGG | TGAGCAGTATTGGTCGCCT | |
| cNlSRSF7.1 | TCGGTAGTAGCCTAAGCAGTCA | ACGTGGGTATCAAATAATTAACAAA | |
| cNlSRSF7.2 | CATGTAATTTCTGCTGGTGTTG | GACTTTGTTGTGTGATGTGAGG | |
| qNlSRSF1 | GATATCGCGACAGCGAGGAC | CACCGGAGAGTAAACCGGAC | qPCR |
| qNlSRSF2.1 | GCGGTCAGACAGCAAGAGTT | GAGTGCGACCTTGACTTGGA | |
| qNlSRSF2.2 | GAGCTGAAAGTTCAGATGGC | TGATGCGAGTGATGGCGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.1 | CGCGGTCACTACGCAAGGAAC | GGACGACCTTGACCGTGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.2 | AGGTCACGCGATAGACGTTC | CGTTGCCATTTCTCTCGGGT | |
| qNlRPS15 | TAAAAATGGCAGACGAAGAGCCCAA | TTCCACGGTTGAAACGTCTGCG | |
| dsNlSRSF1 | T7-TTGAAGAACCGAAGAGGCCC | T7-TAAATCCTGCCAGCTTCCCG | RNAi |
| dsNlSRSF2.1 | T7-GTCCGTCTAAAAGGCGTCCA | T7-ATGAGTTACGGACGCCCACC | |
| dsNlSRSF2.2 | T7-GTTTTGGAAGACCACCCCCT | T7-TCGGCATCACGCTTGTCATA | |
| dsNlSRSF7.1 | T7-TGCGTAGTGACCGCGTTTAT | T7-AATCAGGAACGTGTGGGTGG | |
| dsNlSRSF7.2 | T7-ATACAGGGACTCAGGCAACC | T7-GCTACGCCCATCTAGACCAC | |
| dsGFP | T7-CCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCAC | T7-TGATGCCGTTCTTCTGCTTGT |
表1 本研究所用的扩增引物、表达引物和双链合成引物
Table 1. Primers for amplification, mRNA expression and dsRNA synthesis in this study
| 引物名称 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Upstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Downstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | Use 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cNlSRSF1 | AAGACGACGCCTTGCCT | AGCTGTGTGTTGCTCCTTAATT | 克隆 Clone |
| cNlSRSF2.1 | TCCACAACTTCACATAAGTTCG | TTAGGCTTGGTAGCCAGCA | |
| cNlSRSF2.2 | GCATCTGTTTCTTGGCGG | TGAGCAGTATTGGTCGCCT | |
| cNlSRSF7.1 | TCGGTAGTAGCCTAAGCAGTCA | ACGTGGGTATCAAATAATTAACAAA | |
| cNlSRSF7.2 | CATGTAATTTCTGCTGGTGTTG | GACTTTGTTGTGTGATGTGAGG | |
| qNlSRSF1 | GATATCGCGACAGCGAGGAC | CACCGGAGAGTAAACCGGAC | qPCR |
| qNlSRSF2.1 | GCGGTCAGACAGCAAGAGTT | GAGTGCGACCTTGACTTGGA | |
| qNlSRSF2.2 | GAGCTGAAAGTTCAGATGGC | TGATGCGAGTGATGGCGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.1 | CGCGGTCACTACGCAAGGAAC | GGACGACCTTGACCGTGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.2 | AGGTCACGCGATAGACGTTC | CGTTGCCATTTCTCTCGGGT | |
| qNlRPS15 | TAAAAATGGCAGACGAAGAGCCCAA | TTCCACGGTTGAAACGTCTGCG | |
| dsNlSRSF1 | T7-TTGAAGAACCGAAGAGGCCC | T7-TAAATCCTGCCAGCTTCCCG | RNAi |
| dsNlSRSF2.1 | T7-GTCCGTCTAAAAGGCGTCCA | T7-ATGAGTTACGGACGCCCACC | |
| dsNlSRSF2.2 | T7-GTTTTGGAAGACCACCCCCT | T7-TCGGCATCACGCTTGTCATA | |
| dsNlSRSF7.1 | T7-TGCGTAGTGACCGCGTTTAT | T7-AATCAGGAACGTGTGGGTGG | |
| dsNlSRSF7.2 | T7-ATACAGGGACTCAGGCAACC | T7-GCTACGCCCATCTAGACCAC | |
| dsGFP | T7-CCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCAC | T7-TGATGCCGTTCTTCTGCTTGT |
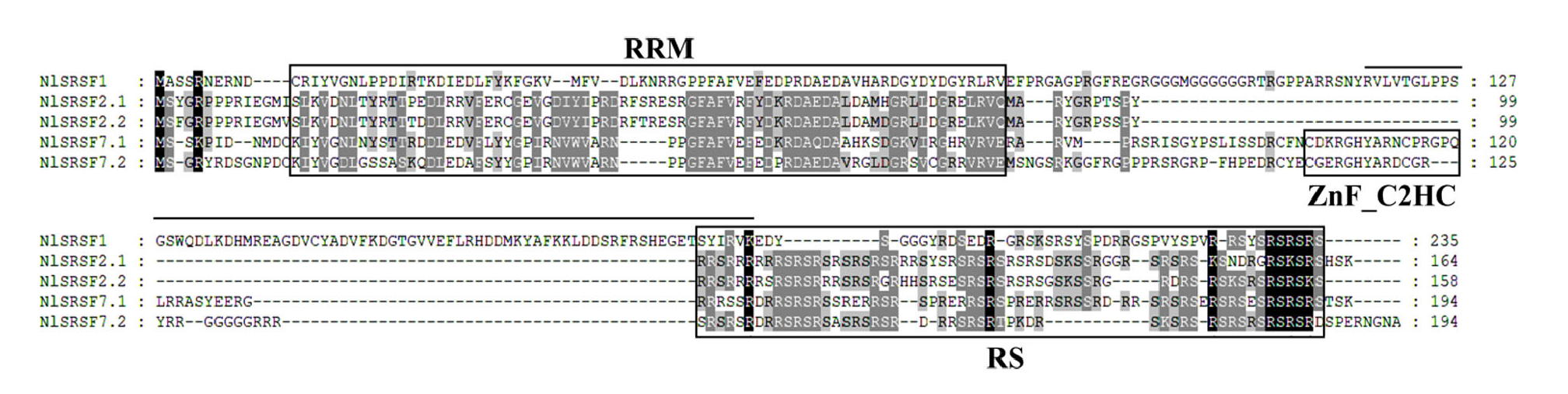
图1 五个NlSR的多序列比对和功能结构域 氨基酸位置显示在右边,预测的RRM结构域、RS结构域和ZnF_C2HC结构域分别用框线标记。
Fig. 1. Alignment of amino acid residues of SRs in Nilaparavata lugens Amino acid positions are indicated on the right. The predicted RRM domain, RS domain, and ZnF_C2HC domain are highlighted with boxes, respectively.
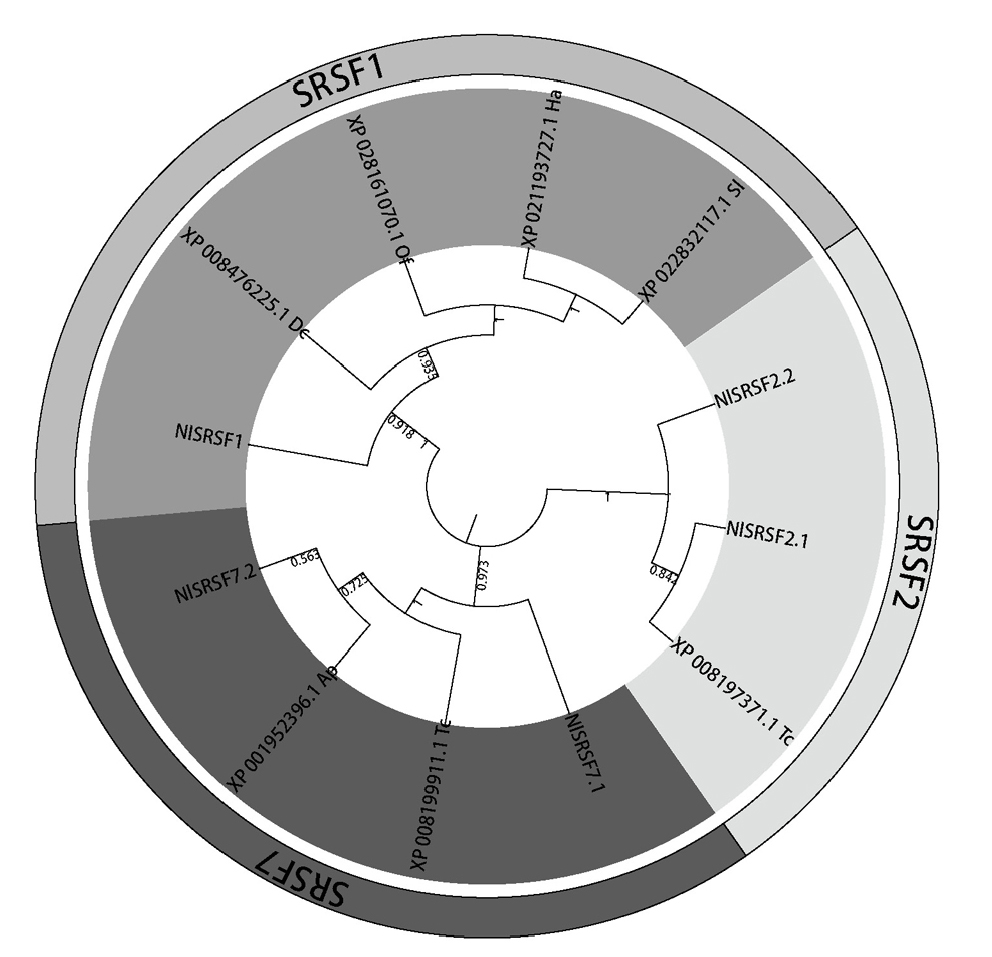
图2 褐飞虱SR与其他昆虫同源序列的系统进化树 Tc: 赤拟谷盗; Ap: 豌豆蚜; Dc: 柑橘木虱; Ha: 棉铃虫; Sl: 斜纹夜蛾; Of: 亚洲玉米螟。系统发育构建使用邻接法;不同阴影代表不同分组。
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic tree of NlSRs in Nilaparvata lugens and homologs from other insects Tc, Tribolium castaneum;Ap, Acyrthosiphon pisum;Dc, Diaphorina citri;Ha, Helicoverpa armigera;Sl, Spodoptera litura;Of, Ostrinia furnacalis. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method, and different groups are represented by shaded areas.
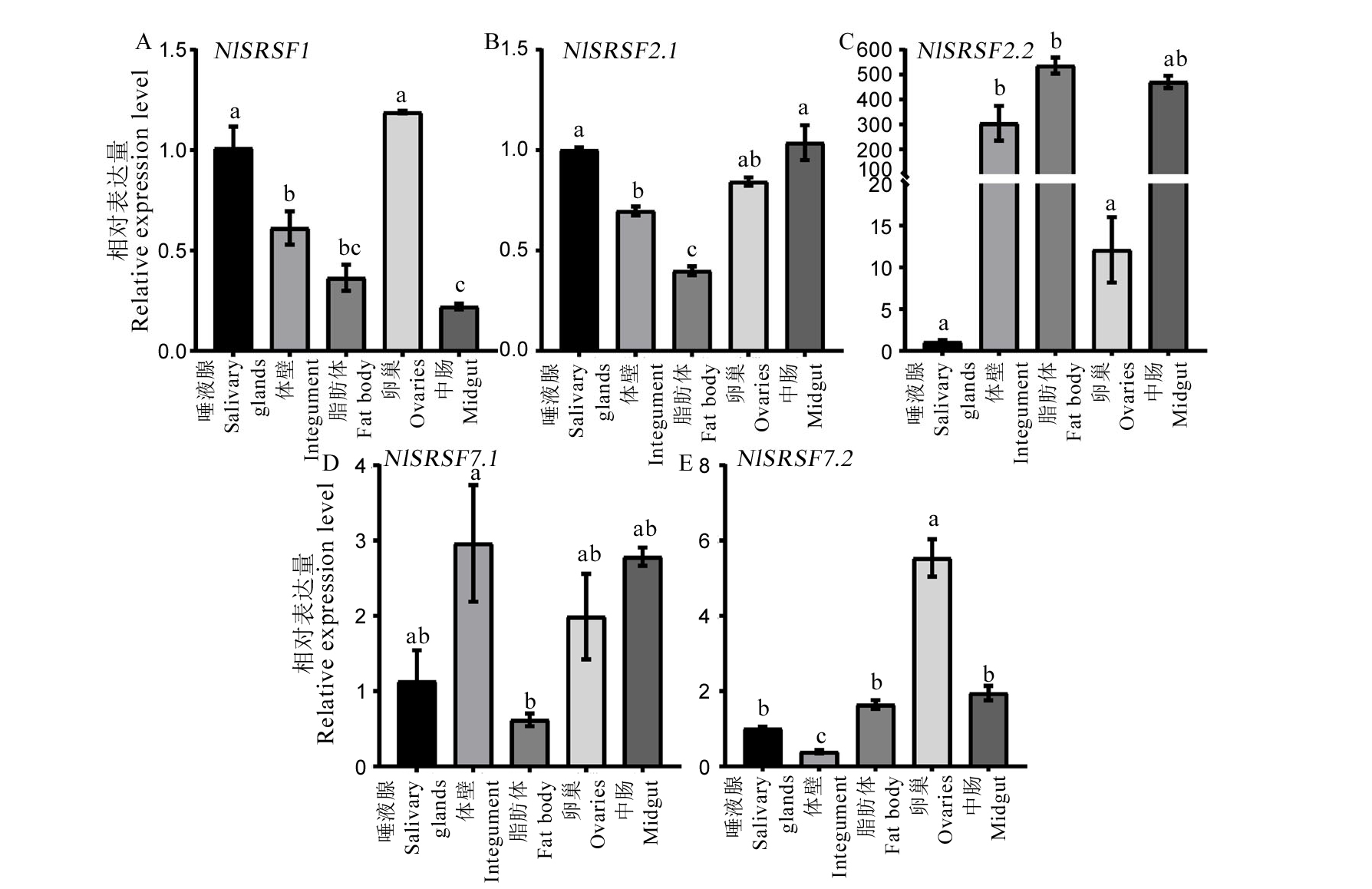
图3 褐飞虱不同组织间NlSR基因的相对表达量 qPCR均以NlRPS15基因为内参,所有数据为各个组织褐飞虱NlSR基因的相对表达量±标准误。图中数据采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和Tukey法进行多重比较检验,数据柱上标的不同字母表示组间存在显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3. Relative expression levels of NlSRs in various tissues of Nilaparavata lugens The expression levels of NlSR genes in various tissues of Nilaparvata lugens were determined by qPCR, using the NlRPS15 gene as an internal reference. The bars represent 2−△△CT values (± SE), normalized to the geometric mean of housekeeping gene expression. Different letters indicate significant differences at P value < 0.05, as analyzed by ANOVA and Turkey’s test.

图4 NlSRs基因在褐飞虱不同发育时期的表达 qPCR均以NlRPS15基因为内参,所有数据为各个龄期褐飞虱NlSR基因的相对表达量±标准误。图中数据采用ANOVA和Turkey法分析检验,数据柱上标的不同字母代表数字之间的显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4. Relative expression levels of NlSRs in different developmental stages of Nilaparavata lugens The expression levels of NlSR genes in different development stages of Nilaparavata lugens were determined by qPCR, using the NlRPS15 gene as an internal reference. The bars represent 2-△△CT values ( ± SE) normalized to the geometric mean of housekeeping gene expression. Different letters indicate a significant difference at P value < 0.05, as analyzed by ANOVA and Turkey’s test.
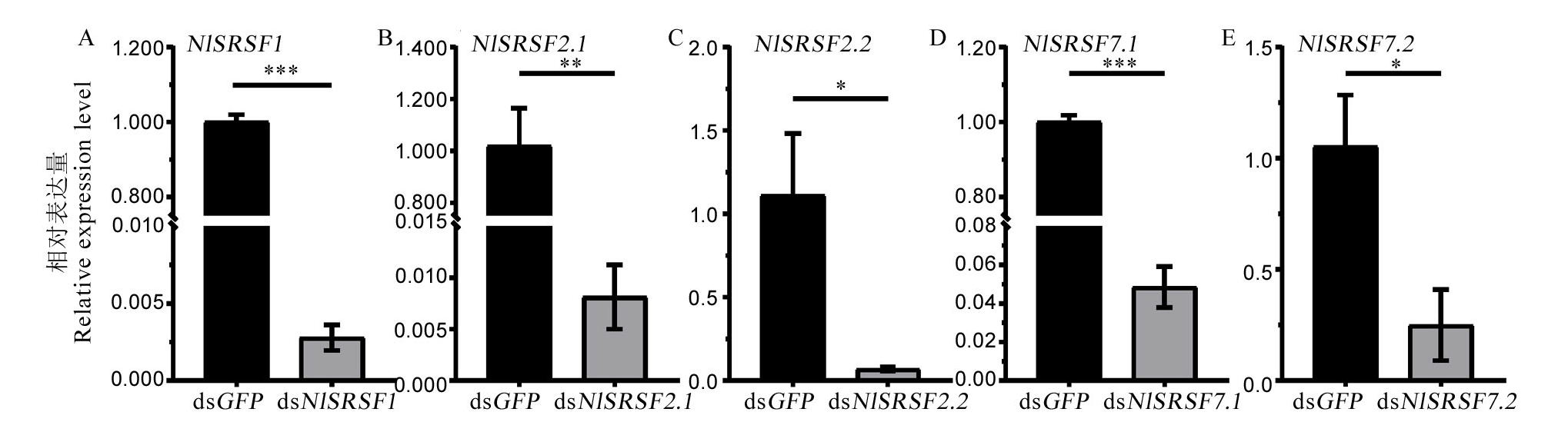
图5 dsRNA注射后第3天NlSR相对表达量变化 qPCR均以NlRPS15基因为内参,所有数据为各处理组NlSRs基因的相对表达量 ± 标准误。图中数据采用非配对t检验法分析,*代表P < 0.05,**代表P < 0.01,***代表P < 0.001。
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of NlSRs on the 3rd day after injection with dsRNA in Nilaparavata lugens Utilizing the brown planthopper RPS15 gene as an internal reference for normalization, the relative expression levels of NlSR were determined in each treatment. Different symbols indicate significant differences, as analyzed by the Student’s t test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001.

图6 注射dsNlSRSF后褐飞虱4龄若虫的存活率(A)、雌成虫的蜜露量(B)和体质量增量(C) 以dsGFP为对照组,B和C图中的数据为平均值 ± 标准误,柱上不同字母表示基因表达量经Tukey HSD检验存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。A图中数据采用Kaplan-Meier法计算,并采用Log-rank检验进行比较。
Fig. 6. Survival rate (A) of the 4th instar nymphs and the honeydew amount (B) and body weight gain (C) of Nilaparvata lugens after dsRNA injection The brown planthopper injected with dsGFP were used as controls. Data in Figs. B and C are mean ± SE. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) in the gene expression levels, as analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test. Data in Fig. A were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test.
| [1] | Sahebi M, Hanafi M M, van Wijnen A J, Azizi P, Abiri R, Ashkani S, Taheri S. Towards understanding pre-mRNA splicing mechanisms and the role of SR proteins[J]. Gene, 2016, 587(2): 107-119. |
| [2] | Wahl M C, Will C L, Lührmann R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine[J]. Cell, 2009, 136(4): 701-718. |
| [3] | Fu X D, Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus[J]. Nature, 1990, 343(6257): 437-441. |
| [4] | Chen S, Li J, Liu Y, Li H. Genome-wide analysis of serine/arginine-rich protein family in wheat and Brachypodium distachyon[J]. Plants, 2019, 8(7): 188. |
| [5] | Shepard P J, Hertel K J. The SR protein family[J]. Genome Biology, 2009, 10(10): 242. |
| [6] | Bennick R A, Nagengast A A, DiAngelo J R. The SR proteins SF2 and RBP1 regulate triglyceride storage in the fat body of Drosophila[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2019, 516(3): 928-933. |
| [7] | Heinrichs V, Baker B S. The Drosophila SR protein RBP1 contributes to the regulation of doublesex alternative splicing by recognizing RBP1 RNA target sequences[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1995, 14(16): 3987-4000. |
| [8] | Wan P J, Zhou R N, Nanda S, He J C, Yuan S Y, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Phenotypic and transcriptomic responses of two Nilaparvata lugens populations to the Mudgo rice containing Bph1[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 14049. |
| [9] | 娄永根, 程家安. 稻飞虱灾变机理及可持续治理的基础研究[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(2): 231-238. |
| Lou Y G, Cheng J A. Basic research on the outbreak mechanism and sustainable management of rice planthoppers[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2011, 48(2): 231-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 芮明方, 谭宏, 沈卫新, 马善林. 稻褐飞虱发生规律及防治研究进展[J]. 上海农业科技, 2011(3): 115-117. |
| Rui M F, Tan H, Shen W X, Ma S L. Research progress on the occurrence pattern and control of rice brown planthopper[J] Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011(3): 115-117. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 程家安, 祝增荣. 中国水稻病虫草害治理60年: 问题与对策[J]. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(6): 885-895. |
| Cheng J A, Zhu Z R. Development of rice pest management in the past 60 years in China: Problems and strategies[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2017, 44(6): 885-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Wan P J, Tang Y H, Yuan S Y, He J C, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in symbiont Entomomyces delphacidicola of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42206. |
| [13] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods, 2001, 9(3): 299-308. |
| [14] | Wang W X, Li K L, Chen Y, Lai F X, Fu Q. Identification and function analysis of enolase gene NlEno1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Journal of Insect Science, 2015, 15(1): 66. |
| [15] | Li K L, Wan P J, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Ran involved in the development and reproduction is a potential target for RNA-interference-based pest management in Nilaparvata lugens[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0142142. |
| [16] | Manley J L, Krainer A R. A rational nomenclature for serine/arginine-rich protein splicing factors (SR proteins)[J]. Genes & Development, 2010, 24(11): 1073-1074. |
| [17] | Brown R S. Zinc finger proteins: Getting a grip on RNA[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2005, 15(1): 94-98. |
| [18] | Gamsjaeger R, Liew C K, Loughlin F E, Crossley M, MacKay J P. Sticky fingers: Zinc-fingers as protein-recognition motifs[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2007, 32(2): 63-70. |
| [19] | Hall T M T. Multiple modes of RNA recognition by zinc finger proteins[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2005, 15(3): 367-373. |
| [20] | Klug A. Zinc finger peptides for the regulation of gene expression[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1999, 293(2): 215-218. |
| [21] | Matthews J M, Sunde M. Zinc fingers: Folds for many occasions[J]. IUBMB Life, 2002, 54(6): 351-355. |
| [22] | 邵伟, 樊玉杰, 徐永镇. SR蛋白家族在RNA剪接中的调控作用[J]. 生命科学, 2010, 22(7): 710-716. |
| Shao W, Fan Y J, Xu Y Z. Function of SR protein family in pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2010, 22(7): 710-716. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Arrese E L, Soulages J L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2010, 55: 207-225. |
| [24] | Barta A, Kalyna M, Reddy A S N. Implementing a rational and consistent nomenclature for serine/arginine-rich protein splicing factors (SR proteins) in plants[J]. The Plant Cell, 2010, 22(9): 2926-2929. |
| [25] | Duque P. A role for SR proteins in plant stress responses[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2011, 6(1): 49-54. |
| [26] | Christiaens O, Smagghe G. The challenge of RNAi-mediated control of hemipterans[J]. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 2014, 6: 15-21. |
| [27] | Ma X, Yin Z, Li H, Guo J. Roles of herbivorous insects salivary proteins[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(7): e29201. |
| [28] | Huang H J, Wang Y Z, Li L L, Lu H B, Lu J B, Wang X, Ye Z X, Zhang Z L, He Y J, Lu G, Zhuo J C, Mao Q Z, Sun Z T, Chen J P, Li J M, Zhang C X. Planthopper salivary sheath protein LsSP1 contributes to manipulation of rice plant defenses[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 737. |
| [29] | Tang C, Xu Q, Zhao J, Yue M, Wang J, Wang X, Kang Z, Wang X. A rust fungus effector directly binds plant pre-mRNA splice site to reprogram alternative splicing and suppress host immunity[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(6): 1167-1181. |
| [30] | Gao X, Yin C, Liu X, Peng J, Chen D, He D, Wei S, Zhao W S, Yang Jun, Peng Y L. A glycine-rich protein MoGrp1 functions as a novel splicing factor to regulate fungal virulence and growth in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Phytopathology Research, 2019, 1(1): 2. |
| [31] | Rao W, Zheng X, Liu B, Guo Q, Guo J, Wu Y, Shangguan X, Wang H, Wu D, Wang Z, Hu L, Xu C, Jiang W, Huang J, Shi S, He G. Secretome analysis and in planta expression of salivary proteins identify candidate effectors from the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2019, 32(2): 227-239. |
| [1] | 杨奇欣, 赖凤香, 何佳春, 魏琪, 王渭霞, 万品俊, 傅强. 不同抗感水稻品种对褐飞虱胁迫的高光谱响应特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 81-90. |
| [2] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [3] | 罗举, 杨素文, 贝文勇, 余军伟, 唐健, 刘淑华. 直接多重TaqMan qPCR方法快速鉴定褐飞虱属3种飞虱[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [4] | 何佳春, 何雨婷, 万品俊, 魏琪, 赖凤香, 陈祥盛, 傅强. 温度对褐飞虱天敌黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 318-326. |
| [5] | 罗举, 唐健, 王爱英, 杨保军, 刘淑华. 基于重组酶介导扩增-侧流层析试纸条的褐飞虱快速鉴定方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [6] | 马银花, 李萍芳, 董文静, 易松望, 杨芳, 杜波, 金晨钟. 水稻抗性蛋白OsRRK1抗褐飞虱机理分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 512-519. |
| [7] | 潘磊, 王利华, 朱凤, 韩阳春, 王培, 方继朝. 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因表达特性和功能[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 37-45. |
| [8] | 朱永生, 白建林, 谢鸿光, 吴方喜, 罗曦, 姜身飞, 何炜, 陈丽萍, 蔡秋华, 谢华安, 张建福. 聚合白背飞虱和褐飞虱抗性基因创制杂交水稻恢复系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 421-428. |
| [9] | 何佳春, 李波, 谢茂成, 赖凤香, 胡国文, 傅强. 新烟碱类及其他稻田杀虫剂对褐飞虱的室内药效评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 467-478. |
| [10] | 降好宇, 曾盖, 郝明, 黄湘桂, 肖应辉. 广谱抗稻瘟病种质75-1-127的褐飞虱抗性基因鉴定及分子标记辅助选择育种[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 227-234. |
| [11] | 张珏锋, 李芳, 钟海英, 陈建明. 制霉菌素对褐飞虱若虫解毒酶、尿酸酶含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [12] | 朱欢欢, 陈洋, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 赖凤香, 傅强. 共生菌Arsenophonus、水稻品种和温度对褐飞虱黄绿绿僵菌发病率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 643-651. |
| [13] | 单丹, 王利华, 张月亮, 韩阳春, 牛洪涛, 潘磊, 方继朝. 褐飞虱热激蛋白70在不同温度胁迫下的差异表达特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. |
| [14] | 赵晨星, 俞叶微, 许益鹏, 俞晓平. 褐飞虱两个dynamin-1-like基因的克隆、多克隆抗体制备及 表达定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [15] | 陈龙飞, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 傅强, 朱廷恒. 褐飞虱NlTgo基因的克隆及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 653-660. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||