
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 873-886.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240614
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
罗孳孳1,2, 张德军1,2, 陈东东3,4,*, 毕淼1,2, 朱玉涵1,2, 韩旭5, 武强1,2, 李月臣6
收稿日期:2024-06-24
修回日期:2024-09-29
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:peter19831203@163.com
基金资助:LUO Zizi1,2, ZHANG Dejun1,2, CHEN Dongdong3,4,*, BI Miao1,2, ZHU Yuhan1,2, HAN Xu5, WU Qiang1,2, LI Yuechen6
Received:2024-06-24
Revised:2024-09-29
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:peter19831203@163.com
摘要:
【目的】探究气候变化背景下四川盆地再生稻抽穗灌浆期热量资源的动态变化,为保障区域再生稻安全生产提供科学参考。【方法】采用四川盆地再生稻区1981—2022年气象站日平均气温和农业气象站中稻成熟期观测数据,分析区域再生稻抽穗灌浆期热量资源、安全齐穗期及灌浆终止期的时空演变特征。【结果】1981—2022年,四川盆地再生稻安全齐穗期、灌浆终止期均呈显著推迟趋势,气候倾向率分别为1.58 d·(10a)-1、2.0 d·(10a)-1,区域80%气候保证率日期分别为9月10日−17日、10月15日−28日。安全齐穗期和灌浆终止期的空间分布格局相似,总体自盆地西北方向东南方推迟。区域抽穗灌浆期热量资源增加趋势显著,平均生长度日普遍为100~300℃·d,气候倾向率达9.72℃·d·(10a)-1,呈自盆地西北方向东南方增加的空间分布特征。2010年代至近期,抽穗灌浆期生长度日在200℃·d以上的区域向盆地西北方大幅扩大,面积较1980年代增长超过1万km2。自21世纪以来,全域年代际安全齐穗期和灌浆终止期的整体时间拉长,抽穗灌浆期热量资源波动加剧。【结论】气候变化背景下四川盆地再生稻抽穗灌浆期具备更丰富的热量资源,有利于再生稻蓄留面积的扩大和种植模式的多元化发展,但极端高温、低温天气对热量资源稳定性的影响增大,是再生稻生产的不利气候因素。
罗孳孳, 张德军, 陈东东, 毕淼, 朱玉涵, 韩旭, 武强, 李月臣. 1981−2022年四川盆地再生稻抽穗灌浆期热量资源时空演变特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 873-886.
LUO Zizi, ZHANG Dejun, CHEN Dongdong, BI Miao, ZHU Yuhan, HAN Xu, WU Qiang, LI Yuechen. Characteristics of Spatiotemporal Evolution of Thermal Resources in Ratoon Rice at Heading and Grain-filling Stages in Sichuan Basin in 1981−2022[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 873-886.
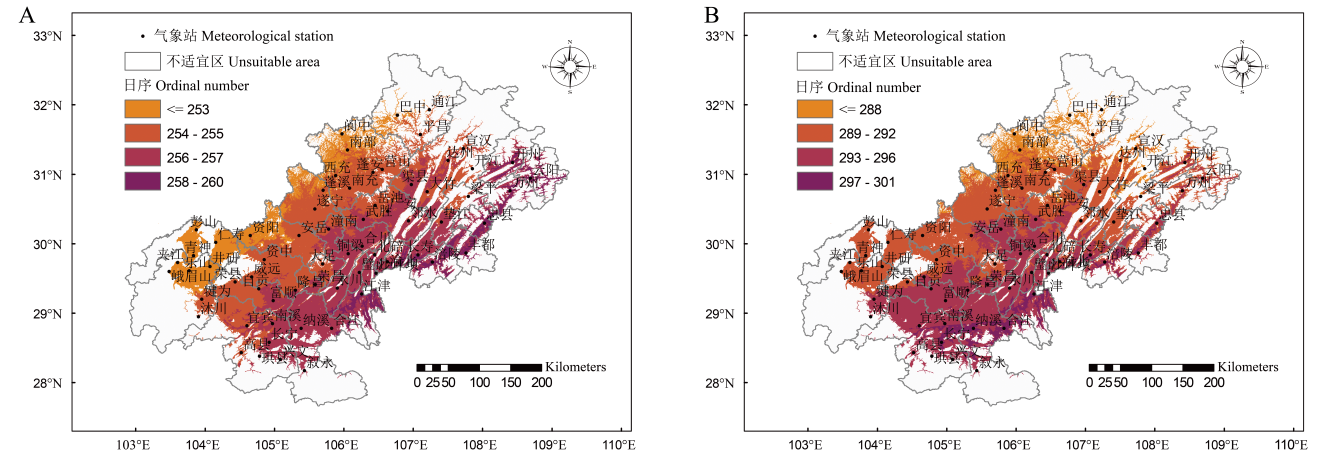
图3 80%气候保证率再生稻安全齐穗期与灌浆终止期日序空间分布
Fig. 3. Spatial distribution of safe full heading dates and safe grain-filling dates of ratoon rice with 80% climate guarantee rate
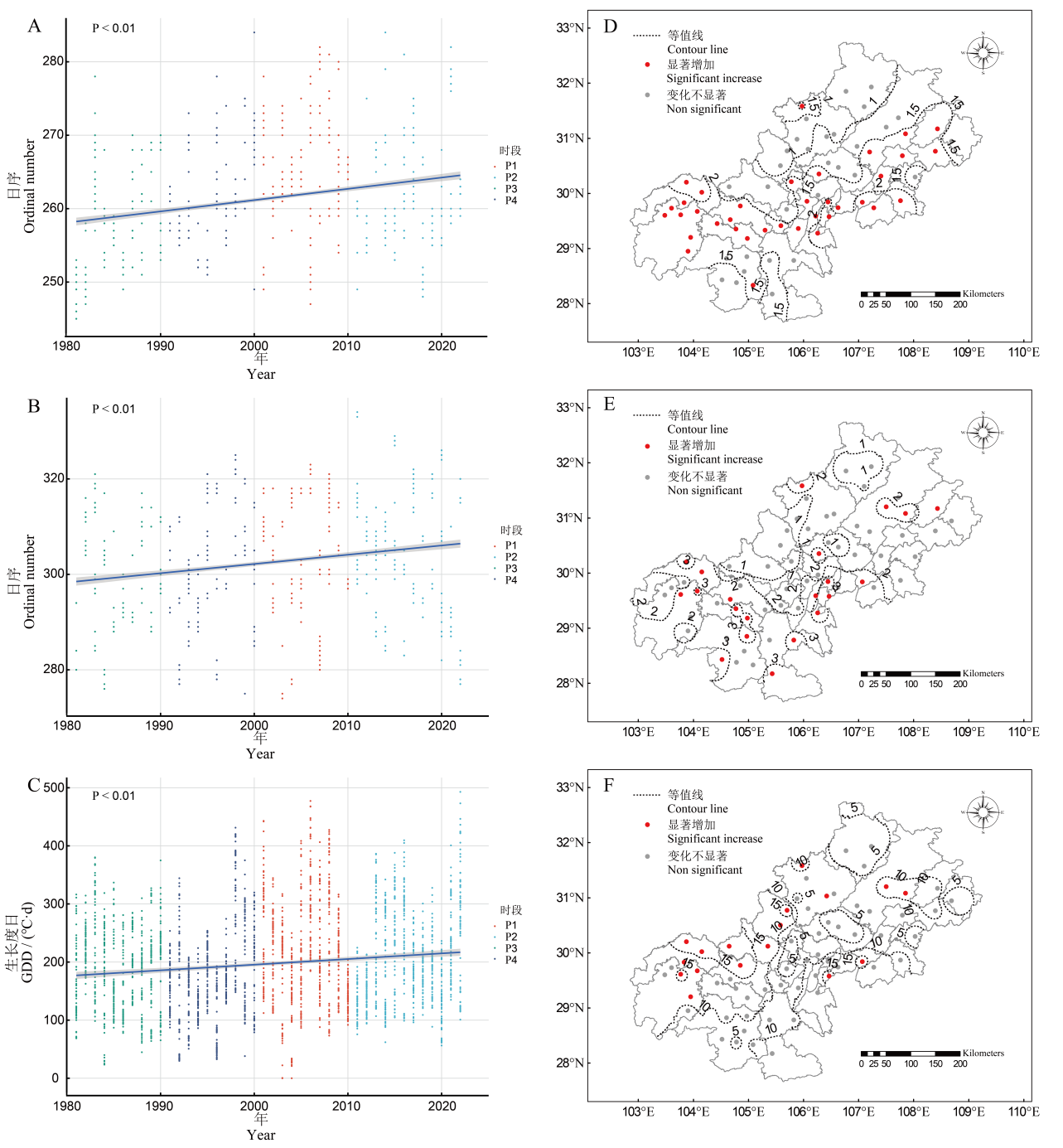
图5 安全齐穗期、灌浆终止期和抽穗灌浆期GDD年际变化及其气候倾向率空间分布 A—C中圆点代表1981—2022年66个站点再生稻安全齐穗期日序、灌浆终止期日序和抽穗灌浆期GDD的数值,蓝色线条为年际变化趋势线。
Fig. 5. Interannual variability of safe full heading dates, safe grain-filling dates, GDD at heading and grain-filling stages, and spatial distribution of their climatic propensities The dots in panel 5 A-C represent the values of safe full heading dates, safe grain-filling dates, or GDD at heading and grain-filling stages for 66 stations of ratoon rice from 1981 to 2022. The blue line represent is the trend line of interannual the interannual variation.
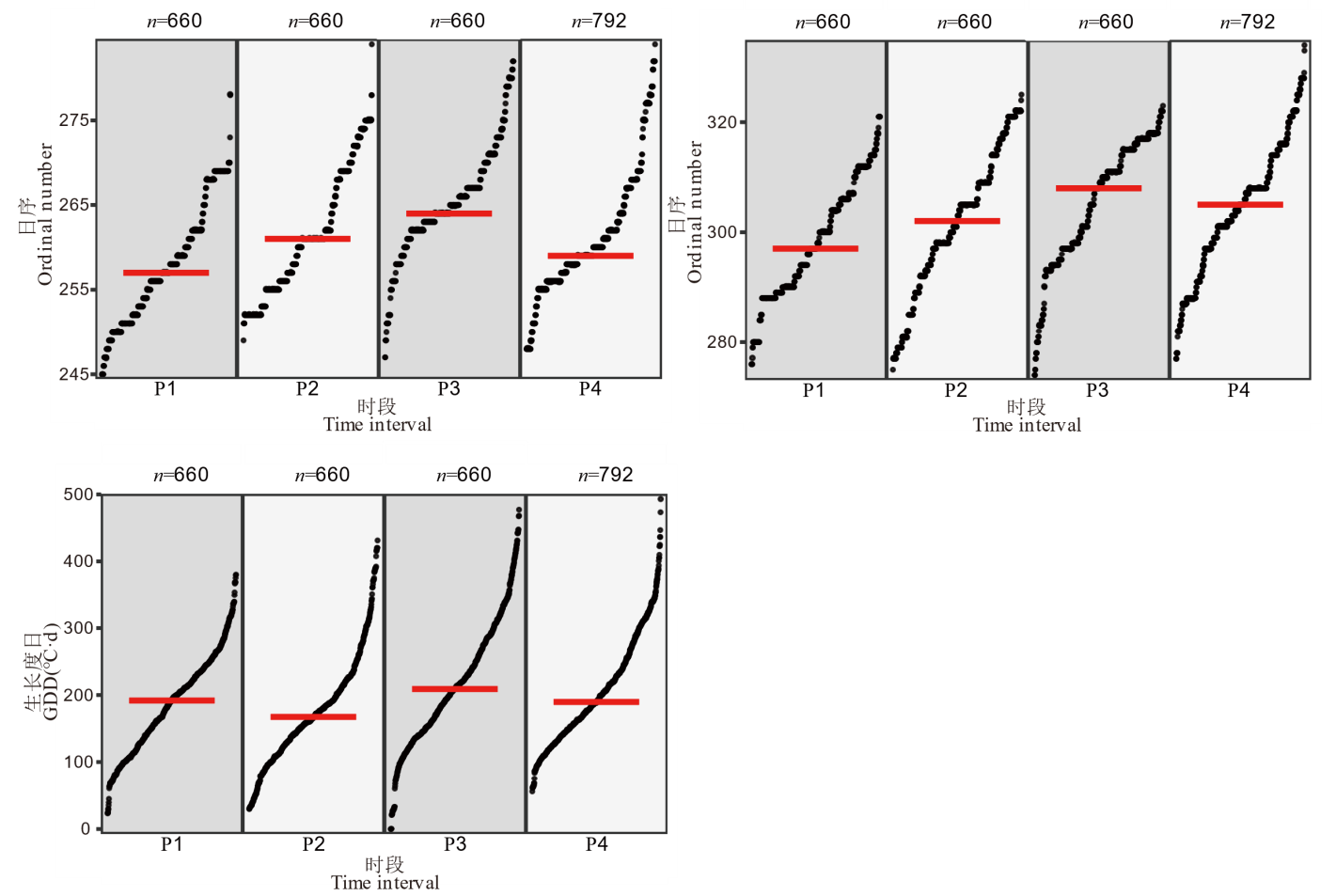
图6 安全齐穗期、灌浆终止期日序及抽穗灌浆期GDD年代际变化 黑色圆点为时段内各年66个站点再生稻安全齐穗期日序、灌浆终止期日序和抽穗灌浆期GDD的数值。数值按由小到大的顺序从左下至右上排列。红色横线为该时段内数值的中位数,n为样本数。
Fig. 6. Interdecadal variability of safe full heading dates, safe grain-filling dates, GDD at heading and grain-filling stages The black dots represent the values of safe full heading dates, safe grain-filling dates, or GDD at heading to grain-filling stage for 66 stations of ratoon rice in each year during the time interval. The values are arranged in ascending order from bottom left to top right. The red horizontal line represents the median value of the values during the time interval. n is the number of samples.
| 时段 Time interval | GDD(℃·d) | 面积Area(×104km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Average value | 最大值 Maximum value | 最小值 Minimum value | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | ||
| P1 | 185.4 | 302.4 | 70.8 | 1.62 | 3.16 | 2.60 | 0.55 | |
| P2 | 173.8 | 282.8 | 62.4 | 2.08 | 3.46 | 2.20 | 0.07 | |
| P3 | 213.9 | 340.2 | 87.7 | 0.72 | 2.42 | 2.90 | 2.01 | |
| P4 | 203.1 | 317.6 | 82.8 | 0.85 | 2.89 | 3.00 | 1.31 | |
表1 研究区P1—P4时段GDD值与不同热量等级的区域面积
Table 1. GDD values and area of different thermal levels in the study area during P1-P4 interval
| 时段 Time interval | GDD(℃·d) | 面积Area(×104km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Average value | 最大值 Maximum value | 最小值 Minimum value | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | ||
| P1 | 185.4 | 302.4 | 70.8 | 1.62 | 3.16 | 2.60 | 0.55 | |
| P2 | 173.8 | 282.8 | 62.4 | 2.08 | 3.46 | 2.20 | 0.07 | |
| P3 | 213.9 | 340.2 | 87.7 | 0.72 | 2.42 | 2.90 | 2.01 | |
| P4 | 203.1 | 317.6 | 82.8 | 0.85 | 2.89 | 3.00 | 1.31 | |
| [1] | Yuan S, Cassman K G, Huang J L, Peng S B, Grassini P. Can ratoon cropping improve resource use efficiencies and profitability of rice in central China?[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 234: 66-72. |
| [2] | 李一诺, 李跃清. 近20年华西秋雨演变特征及其异常机理的进展[J]. 高原气象, 2024, 43(1): 1-15. |
| Li Y N, Li Y Q. Progress of the evolutionary characteristics of autumn rain in Western China and its anomalous mechanism for the past 20 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2024, 43(1): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 徐富贤, 袁驰, 王学春, 韩冬, 廖爽, 张志勇, 陈琨, 曾世清, 孔晓谦, 曾正明, 张林, 杨波, 蒋鹏, 周兴兵. 四川盆地东南部再生稻开花期受低温冷害的风险预测[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(1): 92-97, 102. |
| Xu F X, Yuan C, Wang X C, Han D, Liao S, Zhang Z Y, Chen K, Zeng S Q, Kong X Q, Zeng Z M, Zhang L, Yang B, Jiang P, Zhou X B. Risk prediction of the damage of low temperature injury flowering period of ratooning rice in southeastern of Sichuan basin[J]. China Rice, 2023, 29(1): 92-97, 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 赵正洪, 戴力, 黄见良, 潘晓华, 游艾青, 赵全志, 陈光辉, 周政, 胡文彬, 纪龙. 长江中游稻区水稻产业发展现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. |
| Zhao Z H, Dai L, Huang J L, Pan X H, You A Q, Zhao Q Z, Chen G H, Zhou Z, Hu W B, Ji L. Status, problems and solutions in rice industry development in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Satake T, Koike S. Sterility caused by cooling treatment at the flowering stage in rice plants: I. The stage and organ susceptible to cool temperature[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 1983, 52(2): 207-214. |
| [6] | Jacobs B C, Pearson C J. Growth, development and yield of rice in response to cold temperature[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 1999, 182(2): 79-88. |
| [7] | Zheng H B, Li B, Chen Y W, Tang Q Y. Elastic sowing dates with low seeding rate for grain yield maintenance in mechanized large-scale double-cropped rice production[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 9185. |
| [8] | 龚金龙, 张洪程, 胡雅杰, 龙厚元, 常勇, 王艳, 邢志鹏, 霍中洋. 灌浆结实期温度对水稻产量和品质形成的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(2): 482-491. |
| Gong J L, Zhang H C, Hu Y J, Long H Y, Chang Y, Wang Y, Xing Z P, Huo Z Y. Effects of air temperature during rice grain-filling period on the formation of rice grain yield and its quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(2): 482-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 高文波, 何鹏, 林正雨, 张媛. 气候变化背景下四川省热量资源时空变化特征研究[J]. 农业大数据学报, 2020, 2(1): 60-69. |
| Gao W B, He P, Lin Z Y, Zhang Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics of thermal resources in Sichuan Province against the background of climate change[J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2020, 2(1): 60-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 邓彪, 王顺久, 王春学, 孙蕊. 1991-2020年四川省气候平均值的变化及业务应用评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2023, 43(2): 90-95. |
| Deng B, Wang S J, Wang C X, Sun R. Changes of average climate value in Sichuan Province from 1991 to 2020 and assessment of operational applications[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 2023, 43(2): 90-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 彭国照, 邢开瑜. 四川盆区近50年的水稻气候资源变化特征[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2017, 45(4): 128-133. |
| Peng G Z, Xing K Y. Change characteristics of rice climate resources of past 50 years in Sichuan Basin area[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(4): 128-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 赵艺, 秦宁生, 卢杰. 近53年四川省水稻生育期热量条件变化规律研究[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 38(11): 8-15. |
| Zhao Y, Qin N S, Lu J. The research into the change law of heat conditions during the growing period of rice in Sichuan Province in the recent 53 years[J]. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 38(11): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 庞艳梅, 陈超, 马振峰. 未来气候变化对四川省水稻生育期气候资源及生产潜力的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(1): 58-67. |
| Pang Y M, Chen C, Ma Z F. Impacts of future climate change on climatic resources and production potential during growth period of rice in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 43(1): 58-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 张蕾, 李森, 郭安红, 王纯枝. RCP情景下中国一季稻热量资源变化动态[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(10): 1533-1542. |
| Zhang L, Li S, Guo A H, Wang C Z. Thermal resource change dynamics for single-season rice in China under RCP scenarios[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(10): 1533-1542. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李实蕡, 杨明均, 崔明新. 四川省再生稻种植区划初探[J]. 西南农业学报, 1989, 2(2): 1-6. |
| Li S F, Yang M J, Cui M X. Primary research on regional planning of ratoon rice plantation in Sichuan[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1989, 2(2): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 四川省气象局农气中心再生稻课题组. 四川盆地再生稻气候生态条件分析及适宜种植区研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 1990, 10(4): 25-32. |
| The Research Group of Ratoon Rice at the Agrometeorological Center of Sichuan Provincial Meteorological Bureau. Analysis of climatic and ecological conditions of ratoon rice and study on suitable planting areas in sichuan basin[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 1990, 10(4): 25-32. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 段里成, 郭瑞鸽, 蔡哲, 林志坚, 吴自明, 方圣, 张崇华, 刘丹. 南方九省再生稻安全生长期及高温热害时空变化[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(12): 2061-2073. |
| Duan L C, Guo R G, Cai Z, Lin Z J, Wu Z M, Fang S, Zhang C H, Liu D. Spatiotemporal changes in the characteristics of the safe growth period and high temperature damage of ratoon rice in nine southern provinces of South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(12): 2061-2073. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 罗孳孳, 方立魁, 武强, 韩旭, 李月臣, 朱玉涵, 陈欢, 张悦, 阳园燕. 四川盆地东部再生稻高温伏旱区腋芽萌发期气象适宜度[J]. 气象, 2024, 50(4): 461-474. |
| Luo Z Z, Fang L K, Wu Q, Han X, Li Y C, Zhu Y H, Chen H, Zhang Y, Yang Y Y. Meteorological suitability of axillary bud germination stage in the high temperature and summer drought areas of ratoon rice in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2024, 50(4): 461-474. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 任天举, 李经勇, 王培华, 邹亚兰, 龚见非, 李超平, 唐永群. 年际间气候差异对杂交中稻、再生稻的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2001, 22(4): 1-5. |
| Ren T J, LI J Y, Wang P H, Zou Y L, Gong J F, Li C P, Tang Y Q. The effect of interannual climate difference on ratooning rice of hybrid midseason rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2001, 22(4): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 肖人鹏, 刘强明, 张现伟, 文明, 姚雄, 张巫军, 段秀建, 唐永群, 李经勇. 适宜重庆地区直播中稻蓄留再生稻品种筛选及其丰产性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(1): 104-114. |
| Xiao R P, Liu Q M, Zhang X W, Wen M, Yao X, Zhang W J, Duan X J, Tang Y Q, Li J Y. Screening for ratooning rice of direct seeding medium rice varieties suitable in Chongqing area and their high-yield abilities[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(1): 104-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 陈东东, 栗晓玮, 张玉芳. 四川省水稻关键生育期不同等级干旱评估研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 42(10): 69-77. |
| Chen D D, Li X W, Zhang Y F. Assessment of different grade drought on critical growing period of rice in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 42(10): 69-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Zhang Y F, Qu H H, Yang X G, Wang M T, Qin N S, Zou Y J. Cropping system optimization for drought prevention and disaster reduction with a risk assessment model in Sichuan Province[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2020, 23: e01095. |
| [23] | 方文, 熊洪, 姚文力. 提高再生稻产量的气象条件探讨[J]. 中国农业气象, 1990, 11(1): 35-38. |
| Fang W, Xiong H, Yao W L. Exploration of meteorological conditions for increasing the yield of ratoon rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 1990, 11(1): 35-38. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 张景国. 杂交再生稻开花期耐寒性及安全抽穗期研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2014, 4(3): 115-117. |
| Zhang J G. The cold tolerance at flowering time and optimum heading stage for hybrid ratooning rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 4(3): 115-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Datta S K D. Principles and practices of rice production[M]. Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 1981. |
| [26] | 李勇, 杨晓光, 叶清, 陈阜. 全球气候变暖对中国种植制度可能影响: Ⅸ. 长江中下游地区单双季稻高低温灾害风险及其产量影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(19): 3997-4006. |
| Li Y, Yang X G, Ye Q, Chen F. The possible effects of global warming on cropping systems in China Ⅸ. The risk of high and low temperature disasters for single and double rice and its impacts on rice yield in the middle-lower Yangtze Plain[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(19): 3997-4006. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 和骅芸, 胡琦, 唐书玥, 赵金媛, 潘学标, 潘志华, 王靖. 基于站点数据分析中国大陆区域喜凉/温作物界限温度的时空演变[J]. 中国农业气象, 2023, 44(2): 85-95. |
| He H Y, Hu Q, Tang S Y, Zhao J Y, Pan X B, Pan Z H, Wang J. Analysis of spatio-temporal evolution of the boundary temperature of chimonophilous/thermophilic crops in Chinese mainland based on site data[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2023, 44(2): 85-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 章起明, 易艳红, 廖满庭, 郭水连. 气候变暖背景下江西不同育秧方式双季早稻安全播期分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2022, 43(11): 893-901. |
| Zhang Q M, Yi Y H, Liao M T, Guo S L. Analysis on safe sowing date of double-cropping early rice with different deedling raising methods in Jiangxi under climate warming[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2022, 43(11): 893-901. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Shaykewich C F. An appraisal of cereal crop phenology modelling[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 1995, 75(2): 329-341. |
| [30] | 沈国权. 考虑宏观地形的小网格温度场分析方法及应用[J]. 气象, 1984, 10(6): 22-27. |
| Shen G Q. Microgrid temperature field analysis method considering macroscopic terrain and its application[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 1984, 10(6): 22-27. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 梁轶, 屈振江, 鲁成, 张黎, 刘璐, 王景红. 陕西北扩区苹果种植的气候适宜性及潜力分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2023, 44(5): 347-360. |
| Liang Y, Qu Z J, LU C, Zhang L, Liu L, Wang J H. Climatic suitability and potential analysis of apple planting in northern expansion area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2023, 44(5): 347-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 石延英, 郭尔静, 张镇涛, 朱茜, 杨晓光. 东北三省水稻生长季农业气候资源及障碍型冷害的时空特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(5): 1625-1635. |
| Shi Y Y, Guo E J, Zhang Z T, Zhu X, Yang X G. Spatial-temporal characteristics of agricultural climate resources and sterile-type chilling injury in rice growing season in three provinces of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(5): 1625-1635. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 庞艳梅. 气候变化对四川水稻产量的影响及农业气象灾害发生趋势研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2016. |
| Pang Y M. Impact of climate change on rice yield and trend of agricultural meteorological disasters during rice growth period in Sichuan Province[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 谢远玉, 黄淑娥, 田俊, 王钰, 叶清. 长江中下游热量资源时空演变特征及其对双季稻种植的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(9): 2950-2958. |
| Xie Y Y, Huang S E, Tian J, Wang Y, Ye Q. Spatial-temporal characteristics of thermal resources and its influence on the growth of double cropping rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(9): 2950-2958. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 邹丹, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 陈元伟, 唐启源, 张相, 刘功义. 播期对再生稻生长影响的研究进展[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(4): 6-10. |
| Zou D, Wang W Q, Zheng H B, Chen Y W, Tang Q Y, Zhang X, Liu G Y. Research progress of the influence of seeding time on growth of ratooning rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(4): 6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 闫茜, 黄晓军, 张玉星, 赵凯旭, 李琳钰. 长江经济带高温热浪演化特征及人口暴露风险研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2024, 33(5): 1041-1054. |
| Yan Q, Huang X J, Zhang Y X, Zhao K X, Li L Y. Research on evolution characteristics and population exposure risk of heat waves in Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2024, 33(5): 1041-1054. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 宋开付, 张广斌, 徐华, 马静. 中国再生稻种植的影响因素及可持续性研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(6): 1365-1377. |
| Song K F, Zhang G B, Xu H, Ma J. A review of research on influencing factors and sustainability of ratoon rice cultivation in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(6): 1365-1377. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 张洪, 陈国惠, 刘仕琳, 王贵学, 任昌福, 黄友钦. 四川省再生稻气候生态区划研究[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 1993, 15(6): 483-488. |
| Zhang H, Chen G H, Liu S L, Wang G X, Ren C F, Huang Y Q. Studies on eco-climatical regional assignment for ratooning rice cultivation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 1993, 15(6): 483-488. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 高阳华, 陈志军, 杨世琦, 唐云辉, 袁德胜. 基于GIS的重庆市再生稻光热资源适宜性区划[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2011, 20(6): 672-676. |
| Gao Y H, Chen Z J, Yang S Q, Tang Y H, Yuan D S. Gis-based sunshine and heat resources adaptive regionalization of ratoon rice in Chongqing area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2011, 20(6): 672-676. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 朱永川, 蒋鹏, 郭晓艺, 刘茂. 再生稻产量形成特点与关键调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9): 1702-1717. |
| Xu F X, Xiong H, Zhang L, Zhu Y C, Jiang P, Guo X Y, Liu M. Progress in research of yield formation of ratooning rice and its high-yielding key regulation technologies[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(9): 1702-1717. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 何伟民, 章道周, 缪叶旻子. 籼粳交杂交水稻甬优4901再生栽培示范及高产高效栽培技术[J]. 杂交水稻, 2023, 38(1): 133-135. |
| He W M, Zhang D Z, Miao Y M Z. Demonstration and high-yield efficient techniques of ratooning cultivation of Indica-japonica hybrid rice Yongyou 4901[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2023, 38(1): 133-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 张现伟, 李超明, 肖人鹏, 唐永群, 刘强明, 潘晓雪, 甘兴友, 李经勇. 丰产稳产型三系杂交水稻新组合渝优8421[J]. 杂交水稻, 2022, 37(3): 72-74. |
| Zhang X W, Li C M, Xiao R P, Tang Y Q, Liu Q M, Pan X X, Gan X Y, Li J Y. Yuyou 8421, a new three-line hybrid rice combination with high and stable yield[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2022, 37(3): 72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 熊洪, 冉茂林, 徐富贤, 洪松. 南方稻区再生稻研究进展及发展[J]. 作物学报, 2000, 26(3): 297-304. |
| Xiong H, Ran M L, Xu F X, Hong S. Achievements and developments of ratooning rice in South of China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2000, 26(3): 297-304. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 黄振标, 胡香玉, 钟旭华, 梁开明, 潘俊峰, 叶群欢, 尹媛红. 粤北地区不同留桩高度下适宜再生稻品种筛选及产量构成分析[J]. 广东农业科学, 2023, 50(12): 160-171. |
| Huang Z B, Hu X Y, Zhong X H, Liang K M, Pan J F, Ye Q H, Yin Y H. Analysis on screening of suitable varieties for rice ratooning and yield components under different cutting heights in North Guangdong[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 50(12): 160-171. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 张玉烛, 张桂和, 朱国奇, 邓启云, 詹庆才. 阴雨对早稻开花及受精结实的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1995, 9(3): 173-178. |
| Zhang Y Z, Zhang G H, Zhu G Q, Deng Q Y, Zhan Q C. Effects of overcast and raining on flowering, fertilizing and seed setting of early rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1995, 9(3): 173-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 艾治勇, 郭夏宇, 刘文祥, 马国辉, 青先国. 农业气候资源变化对双季稻生产的可能影响分析[J]. 自然资源学报2014, 29(12): 14. |
| Ai Z Y, Guo X Y, Liu W X, Ma G H, Qing X G. Analysis on possible influences of agricultural climate resources change on double-season rice production[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(12): 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 徐曼琳, 周波涛, 程志刚. 2010年以来华西秋季降水年代际增多原因初探[J]. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(3): 568-576. |
| Xu M L, Zhou B T, Cheng Z G. Preliminary analysis on the interdecadal increase of autumn rainfall in western China since 2010[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 43(3): 568-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 陈剀, 钟霖浩, 华丽娟, 陈文. 华西秋雨趋势变化的年代际转折及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2020, 25(1): 90-102. |
| Chen K, Zhong L H, Hua L J, Chen W. Analysis on the interdecadal transition and its causes of the autumn precipitation trend in west China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2020, 25(1): 90-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张海维, 顾欣怡, 陈明帅, 李福康, 施玥丞, 杨挺, 姜硕琛. 基肥氮素类型对再生稻生长、产量和氮素利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 387-398. |
| [2] | 肖无为, 朱辰光, 王飞, 熊栋梁, 黄见良, 彭少兵, 崔克辉. 再生稻稻米品质研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 33-46. |
| [3] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [4] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [5] | 王敏羽, 戴志刚, 余德芳, 王向平, 关绍华, 邵远刚, 张家学, 李小坤. “水稻-再生稻”种植模式专用肥轻简施用对产量、肥料利用率及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 531-542. |
| [6] | 杨晨, 郑常, 袁珅, 徐乐, 彭少兵. 再生稻肥料管理对不同品种产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 65-76. |
| [7] | 蒋艳方, 陈基旺, 崔璨, 王晓玉, 陈平平, 周文新, 易镇邪. 杂交稻头季与再生季镉积累分配特性差异研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 55-64. |
| [8] | 黄锦文, 吴珈谊, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 方长旬, 邵彩虹, 林伟伟, 翁佩莹, 林文雄. 头季稻氮肥运筹对再生稻根际机能及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 383-395. |
| [9] | 汪浩, 刘祥臣, 张强, 余贵龙, 张文地, 黄健, 朱安, 刘立军. 豫南地区头季和再生季水稻产量与品质差异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 425-434. |
| [10] | 汪浩, 张强, 张文地, 李思宇, 黄健, 朱安, 刘立军. 腋芽萌发能力对再生稻产量影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 205-216. |
| [11] | 解振兴, 张居念, 林祁, 刘锋, 张初长, 卓芳梅, 姜照伟, 卓传营. 植物生长调节剂对再生稻头季抗倒伏能力和两季产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 158-166. |
| [12] | 何爱斌, 于朋超, 陈乾, 姜广磊, 王慰亲, 聂立孝. 甬优4949和超优1000在华中地区再生稻种植的氮肥运筹研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 47-56. |
| [13] | 段门俊, 田玉聪, 吴芸紫, 金涛, 陈阜, 刘章勇. 叶面喷施亚硒酸钠对再生稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 96-102. |
| [14] | 王森, 莫菁华, 汪洋, 游秋香, 任涛, 丛日环, 李小坤. 水稻-再生稻体系干物质积累及氮磷钾养分的吸收利用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 67-77. |
| [15] | 张建福, 朱永生,蔡秋华,卓传营,张上守,郑荣和,谢华安,. 再生稻净光合速率与产量及其构成因素的相关性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 103-106 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||