
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 685-694.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240503
毋翔1,2, 张义凯2,*( ), 张鹏2, 马昕伶2, 陈玉林2, 陈惠哲2, 张玉屏2, 向镜2, 王亚梁2, 王志刚2, 李良涛1,*(
), 张鹏2, 马昕伶2, 陈玉林2, 陈惠哲2, 张玉屏2, 向镜2, 王亚梁2, 王志刚2, 李良涛1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-06
修回日期:2024-05-31
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-11-15
通讯作者:
*email: yikaizhang168@163.com;liliangtao@hebeu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Xiang1,2, ZHANG Yikai2,*( ), ZHANG Peng2, MA Xinling2, CHEN Yulin2, CHEN Huizhe2, ZHANG Yuping2, XIANG Jing2, WANG Yaliang2, WANG Zhigang2, LI Liangtao1,*(
), ZHANG Peng2, MA Xinling2, CHEN Yulin2, CHEN Huizhe2, ZHANG Yuping2, XIANG Jing2, WANG Yaliang2, WANG Zhigang2, LI Liangtao1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-06
Revised:2024-05-31
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-11-15
Contact:
*email: yikaizhang168@163.com;liliangtao@hebeu.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】水稻秧苗良好的根系盘结力,利于提高机插效率和质量。探明2,4-表油菜素内酯(2,4-epibrassinolide, EBR)在稻草生物炭育秧基质中对水稻根系生长的影响及作用机制具有重要意义。【方法】采用以300℃下制备的稻草生物炭为主的育秧基质,以甬优538为试验材料,分析了不同浓度EBR(0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 mg/kg)对生物炭基质育秧水稻秧苗根系生长及生理特性的影响。【结果】在生物炭基质中加入EBR后水稻秧苗的根系盘结力增强了4.13%~22.46%,根系活力提高了0.93~1.65倍,根冠比增加了2.20%~14.10%,极大促进根系的生长。基质中添加EBR显著提高水稻秧苗的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)等抗氧化保护酶的活性,降低丙二醛(MDA)、过氧化氢(H2O2)的含量,增加秧苗的可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量。施用EBR后水稻根系和叶片中OsCu/Zn-SOD1和OsCu/Zn-SOD2、OsCAT1和OsCAT2四个基因的表达水平显著高于对照。【结论】生物炭育秧基质中增施EBR能够提高水稻秧苗抗氧化系统酶活性和相关基因表达,降低植株内MDA和H2O2的含量,改善水稻秧苗根系的生长和盘结能力,促进健壮秧苗的形成。基施EBR最适宜的浓度为1.0~1.5 mg/kg。
毋翔, 张义凯, 张鹏, 马昕伶, 陈玉林, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 李良涛. 2,4-表油菜素内酯对生物炭基质育秧水稻秧苗根系生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 685-694.
WU Xiang, ZHANG Yikai, ZHANG Peng, MA Xinling, CHEN Yulin, CHEN Huizhe, ZHANG Yuping, XIANG Jing, WANG Yaliang, WANG Zhigang, LI Liangtao. Effects of 2,4-Epibrassinolide on Root Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Rice Seedlings Raised in Biochar Substrate[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 685-694.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | TTATGGTTGGGATGGGACA | AGCACGGCTTGAATAGCG |
| OsCATB | GGCAAGATCGTTTTCTCCAG | TGGTTTCAGGTTGAGACGTG |
| OsCATC | AGAAGGTGGTGATTGCCAAG | CAGATGCTCCTGATCTCGTG |
| OsAPX1 | CCAAGGGTTCTGACCACCTA | CAAGGTCCCTCAAAACCAGA |
| OsAPX2 | AAGTGACAAAGCCCTCATGG | TCCTCAGCAAATCCCAGTTC |
| OsCu/Zn SOD1 | TGTCCAAGAGGGAGATGGTC | ATCTTCTGGTGCTCCATGCT |
| OsCu/Zn SOD2 | ACAGCCAGATCCCCCTTACT | TACGAGCGAACATGAACAGC |
表1 本研究所用引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences used in the study
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | TTATGGTTGGGATGGGACA | AGCACGGCTTGAATAGCG |
| OsCATB | GGCAAGATCGTTTTCTCCAG | TGGTTTCAGGTTGAGACGTG |
| OsCATC | AGAAGGTGGTGATTGCCAAG | CAGATGCTCCTGATCTCGTG |
| OsAPX1 | CCAAGGGTTCTGACCACCTA | CAAGGTCCCTCAAAACCAGA |
| OsAPX2 | AAGTGACAAAGCCCTCATGG | TCCTCAGCAAATCCCAGTTC |
| OsCu/Zn SOD1 | TGTCCAAGAGGGAGATGGTC | ATCTTCTGGTGCTCCATGCT |
| OsCu/Zn SOD2 | ACAGCCAGATCCCCCTTACT | TACGAGCGAACATGAACAGC |

图1 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻根系生长的影响 CK, EBR0.5, EBR1.0, EBR1.5, EBR2.0分别表示EBR浓度分别为0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mg/kg。下同。
Fig.1. Effects of different concentrations of 2,4-brassinolide on root growth of rice CK, EBR0.5, EBR1.0, EBR1.5, EBR2.0 refer to 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 mg/kg EBR exposure, respectively. The same below.
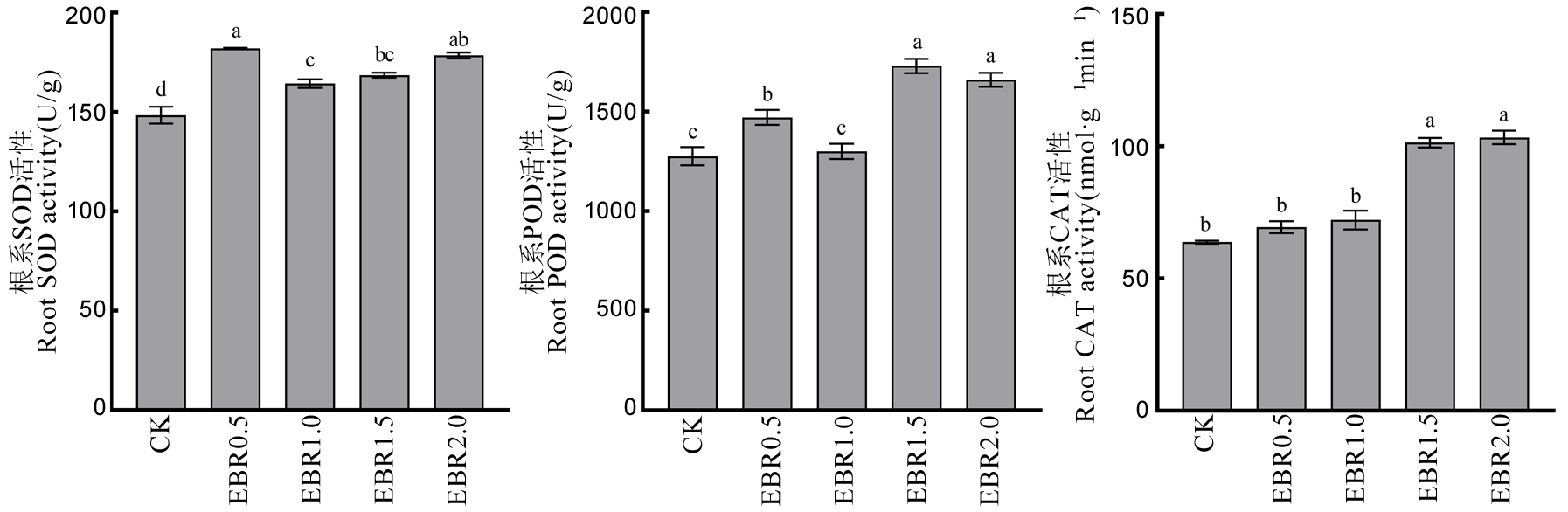
图2 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻秧苗根系抗氧化保护酶活性的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of various concentrations of 2,4-epibrassinolide on activities of antioxidant protective enzymes in the roots of rice seedlings
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 百株地下部干质量 Root dry weigh per 100 plants(g) | 百株地上部干质量 Shoot dry weigh per 100 plants(g) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.4±0.6 b | 0.20±0.01 c | 0.90±0.03 b | 0.23±0.01 b |
| EBR0.5 | 13.7±0.3 a | 0.23±0.01 b | 0.97±0.03 ab | 0.24±0.02 b |
| EBR1.0 | 13.0±0.4 a | 0.23±0.01 b | 0.93±0.07 ab | 0.25±0.01 ab |
| EBR1.5 | 13.8±0.6 a | 0.26±0.01 a | 0.99±0.01 a | 0.26±0.01 a |
| EBR2.0 | 13.0±0.5 ab | 0.21±0.01 c | 0.91±0.04 b | 0.23±0.02 b |
表2 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻秧苗生物量及形态的影响
Table 2. Effects of different concentrations of 2,4-epibrassinolide on biomass and morphology of rice seedlings
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 百株地下部干质量 Root dry weigh per 100 plants(g) | 百株地上部干质量 Shoot dry weigh per 100 plants(g) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.4±0.6 b | 0.20±0.01 c | 0.90±0.03 b | 0.23±0.01 b |
| EBR0.5 | 13.7±0.3 a | 0.23±0.01 b | 0.97±0.03 ab | 0.24±0.02 b |
| EBR1.0 | 13.0±0.4 a | 0.23±0.01 b | 0.93±0.07 ab | 0.25±0.01 ab |
| EBR1.5 | 13.8±0.6 a | 0.26±0.01 a | 0.99±0.01 a | 0.26±0.01 a |
| EBR2.0 | 13.0±0.5 ab | 0.21±0.01 c | 0.91±0.04 b | 0.23±0.02 b |
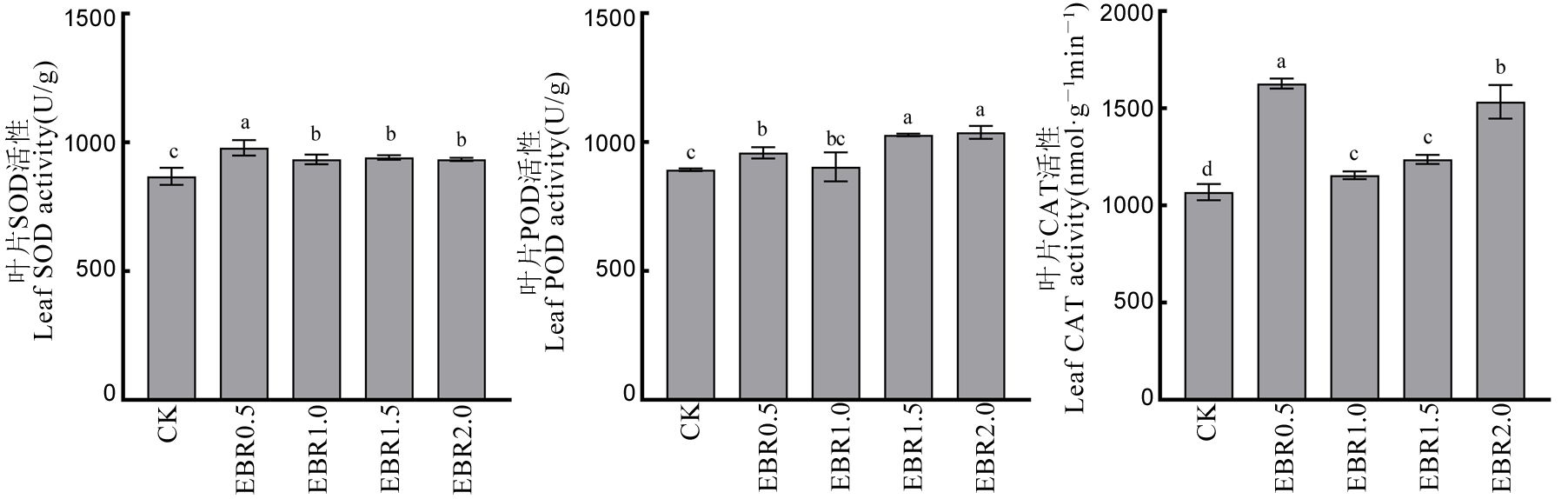
图3 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻秧苗叶片抗氧化保护酶的影响
Fig. 3. Effects of various concentrations of 2,4-ebrassinolide on activities of antioxidant protective enzymes in rice seedling leaves
| 处理 Treatment | 根系丙二醛含量 MDA content(nmol/g) | 根系过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content(μmol/g) | 叶片丙二醛含量 MDA content(nmol/g) | 叶片过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content(μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.31±0.10 a | 8.39±0.16 a | 14.81±0.48 a | 18.94±0.25 a |
| EBR 0.5 | 8.12±0.02 c | 0.91±0.11 d | 14.62±0.18 a | 13.09±0.22 b |
| EBR1.0 | 7.26±0.16 d | 1.29±0.14 c | 13.89±0.58 ab | 13.57±0.43 b |
| EBR1.5 | 9.04±0.25 b | 1.36±0.15 c | 12.22±0.45 c | 11.22±0.55 c |
| EBR2.0 | 9.24±0.11 ab | 1.55±0.11 b | 13.51±0.51 b | 18.54±0.57 a |
表3 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻体内丙二醛和过氧化氢含量的影响
Table 3. Effects of various concentrations of 2,4-brassinolide on the contents of malondialdehyde and hydrogen peroxide in rice
| 处理 Treatment | 根系丙二醛含量 MDA content(nmol/g) | 根系过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content(μmol/g) | 叶片丙二醛含量 MDA content(nmol/g) | 叶片过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content(μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.31±0.10 a | 8.39±0.16 a | 14.81±0.48 a | 18.94±0.25 a |
| EBR 0.5 | 8.12±0.02 c | 0.91±0.11 d | 14.62±0.18 a | 13.09±0.22 b |
| EBR1.0 | 7.26±0.16 d | 1.29±0.14 c | 13.89±0.58 ab | 13.57±0.43 b |
| EBR1.5 | 9.04±0.25 b | 1.36±0.15 c | 12.22±0.45 c | 11.22±0.55 c |
| EBR2.0 | 9.24±0.11 ab | 1.55±0.11 b | 13.51±0.51 b | 18.54±0.57 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 根系可溶性糖含量 Root soluble sugar content (mg/g) | 根系可溶性蛋白含量 Root soluble protein content (mg/g) | 叶片可溶性糖含量 Soluble sugar content in leaves (mg/g) | 叶片可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein content in leaves (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.77±0.08 c | 2.09±0.01 d | 12.47±0.44 c | 18.04±1.26 d |
| EBR 0.5 | 3.32±0.19 ab | 2.61±0.12 c | 15.32±0.12 a | 20.20±0.49 bc |
| EBR1.0 | 2.78±0.06 c | 2.35±0.06 cd | 13.24±0.70 b | 18.64±0.28 cd |
| EBR1.5 | 3.10±0.03 bc | 3.03±0.19 b | 13.47±0.50 b | 21.63±0.72 b |
| EBR2.0 | 3.37±0.31 a | 3.32±0.16 a | 15.14±0.61 a | 24.83±0.45 a |
表4 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对水稻体内可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量的影响
Table 4. Effects of different concentrations of 2,4-ebrassinolide on the contents of soluble sugars and soluble proteins in rice
| 处理 Treatment | 根系可溶性糖含量 Root soluble sugar content (mg/g) | 根系可溶性蛋白含量 Root soluble protein content (mg/g) | 叶片可溶性糖含量 Soluble sugar content in leaves (mg/g) | 叶片可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein content in leaves (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.77±0.08 c | 2.09±0.01 d | 12.47±0.44 c | 18.04±1.26 d |
| EBR 0.5 | 3.32±0.19 ab | 2.61±0.12 c | 15.32±0.12 a | 20.20±0.49 bc |
| EBR1.0 | 2.78±0.06 c | 2.35±0.06 cd | 13.24±0.70 b | 18.64±0.28 cd |
| EBR1.5 | 3.10±0.03 bc | 3.03±0.19 b | 13.47±0.50 b | 21.63±0.72 b |
| EBR2.0 | 3.37±0.31 a | 3.32±0.16 a | 15.14±0.61 a | 24.83±0.45 a |
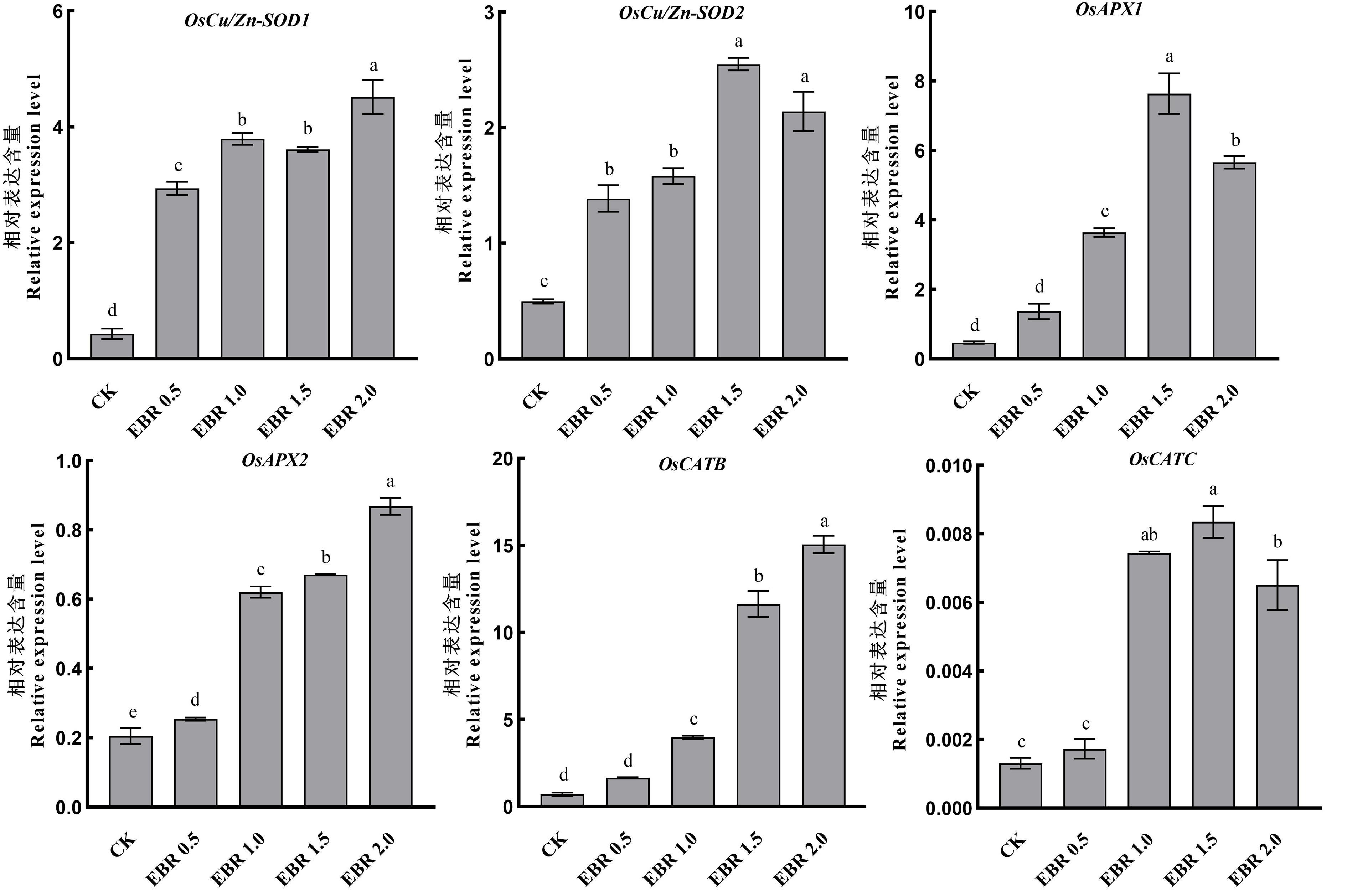
图4 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对秧苗根系抗氧化酶基因表达的影响
Fig. 4. Effects of various concentrations of 2,4-ebrassinolide on the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes in rice seedling roots
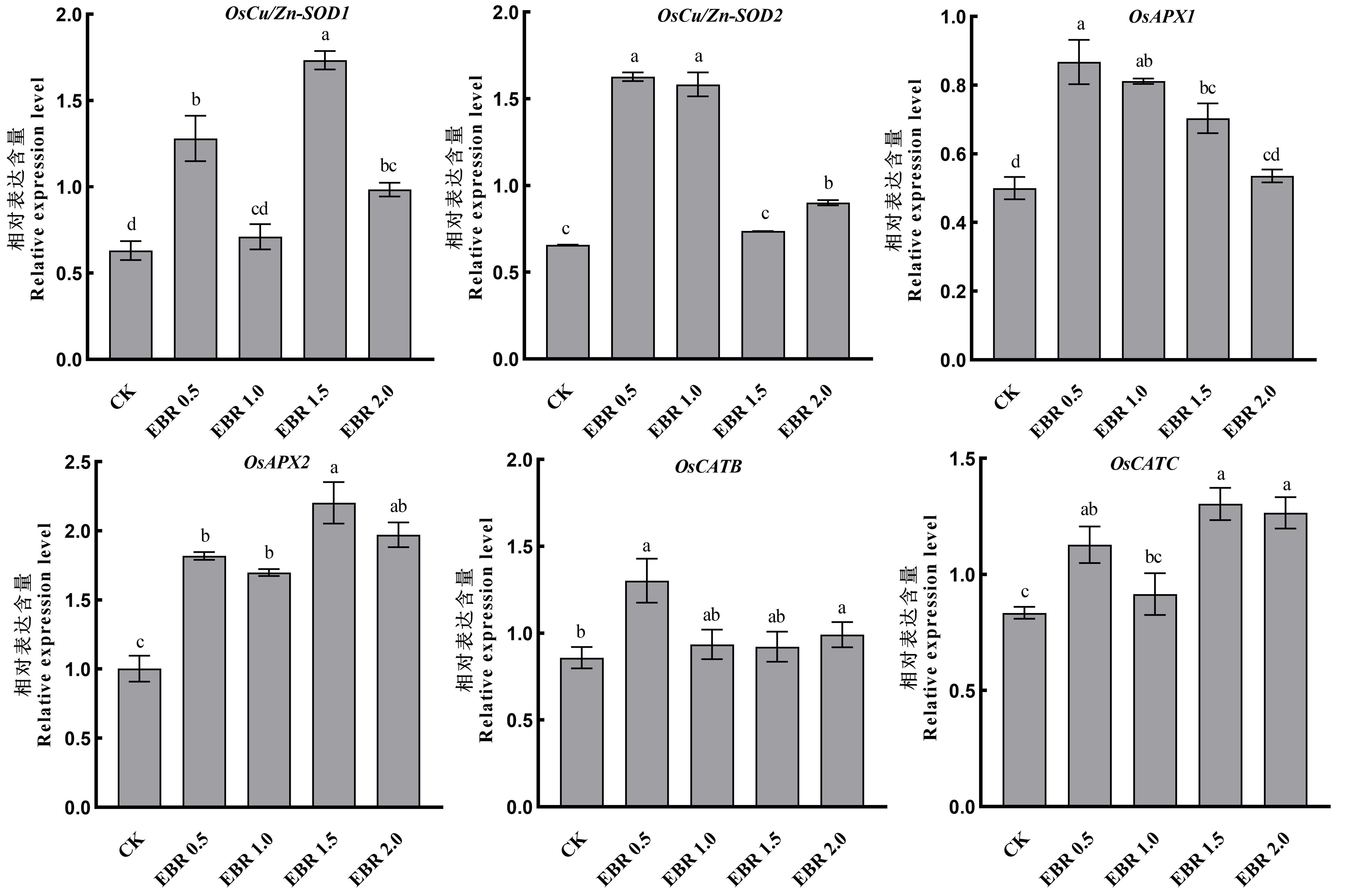
图5 不同浓度2,4-表油菜素内酯对秧苗叶片抗氧化酶基因表达的影响
Fig. 5. Effects of concentrations of 2,4-ebrassinolide on the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes in rice seedling leaves
| [1] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 徐一成, 张义凯. 杂交稻低播量精量播种育秧及机插取秧特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. |
| Wang Y L, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Xu Y C, Zhang Y K. Characteristics of low-sowing precision seeding and mechanical transplanting of hybrid rice[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 司绍诚, 吴宇澄, 李远, 涂晨, 付传城, 骆永明. 耕地和草地土壤健康研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(3): 625-642. |
| Si S C, Wu Y C, Li Y, Tu C, Fu C C, Luo Y M. Research progress and prospect of soil health in cultivated land and grassland[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(3): 625-642. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 林育炯, 张均华, 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 禹盛苗, 金千瑜. 不同类型基质对机插水稻秧苗生理特征及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(8): 18-26. |
| Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Hu J J, Zhu L F, Cao X C, Yu S M, Jin Q Y. Effects of different types of substrates on physiological characteristics and yield of mechanically transplanted rice seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(8): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 李亦昊. 沼渣和生物炭育秧基质对水稻秧苗生长影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2023. |
| Li Y H. Effects of biogas residue and biochar substrate on the growth of rice seedlings[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 丁伟. 水稻育苗基质制备及成型工艺参数研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2023. |
| Ding W. Study on preparation and molding process parameters of rice seedling substrate[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 邓亮, 卢碧林, 王浩宇, 李鹏辉, 张志敏. 水稻育秧基质肥力特征、育秧效果及环境生态风险评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(2): 312-317. |
| Deng L, Lu B L, Wang H Y, Li Peng H, Zhang Z M. Fertility characteristics, seedling raising effect and environmental ecological risk assessment of rice seedling raising substrate[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(2): 312-317. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 沈巧梅, 赵泽松, 萧长亮, 孙桂芳, 王贺. 水稻育秧基质的理化性质及生产中存在的问题与对策[J]. 现代农业科技, 2012(19): 46-47. |
| Shen Q M, Zhao Z S, Xiao C L, Sun G F, Wang H. Physicochemical properties of rice seedling substrate and problems and countermeasures in production[J]. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2012(19): 46-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Zhang C, Zeng G M, Huang D L, Lai C, Chen M, Cheng M, Tang H H, Tang L, Dong H R, Huang B B. Biochar for environmental management: Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, contaminant treatment, and potential negative impacts[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 23(373): 902-922. |
| [9] | Yang Z, Sun T, Subdiaga E, Obst M, Haderlein SB, Maisch M, Kretzschmar R, Angenent LT, Kappler A. Aggregation-dependent electron transfer via redox-active biochar particles stimulate microbial ferrihydrite reduction[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 48(703): 135515. |
| [10] | 高继平, 隋阳辉, 霍轶琼, 唐亮, 孟军, 张文忠, 陈温福. 生物炭用作水稻育苗基质的研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2014(2): 16-21. |
| Gao J P, Duo Y H, Huo Y Q, Tang L, Meng J, Zhang W Z, Chen W F. Research progress of biochar as rice seedling substrate[J]. Crops, 2014(2): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 李志刚, 刘晓刚, 李健. 硫酸铵与鸡粪配比在含生物质炭育苗基质中的应用效果[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2012, 48(1): 83-87. |
| Li Z G, Liu X G, Li J. The application effect of the ratio of ammonium sulfate to chicken manure in the substrate containing biochar[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2012(1): 83-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 文中华, 刘喜雨, 孟军, 刘遵奇, 史国宏. 生物炭和腐熟秸秆组配基质对水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020, 51(1): 10-17. |
| Wen Z H, Liu X Y, Meng J, Liu Z Q, Shi G H. Effects of combined substrates of biochar and decomposed straw on the growth of rice seedlings[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020, 51(1): 10-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Asadi H, Ghorbani M, Rezaei-Rashti M, Abrishamkesh S, Amirahmadi E, Chen C R, Gorji M. Application of rice husk biochar for achieving sustainable agriculture and environment[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(4): 325-343. |
| [14] | Li Z Y, Zheng Z W, Li H C, Xu D, Li X, Xiang L J, Tu S X. Review on rice husk biochar as an adsorbent for soil and water remediation[J]. Plants, 2023, 12(7): 1524. |
| [15] | 林肖庆, 吕豪豪, 刘玉学, 汪玉瑛, 杨生茂. 生物质原料及炭化温度对生物炭产率与性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(7): 1216-1223. |
| Lin X Q, L H H, Liu Y X, et al. Effects of biomass raw materials and carbonization temperature on the yield and properties of biochar[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(7): 1216-1223. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 赵雪松, 王倩, 闫青地, 赵亚林, 王凤茹, 董金皋. 油菜素内酯对水稻根系发育的调控作用[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2016, 38(10): 1191-1198. |
| Zhao X S, Wang Q, Yan Q D, Zhao Y L, Wang F R, Dong J G. Regulation of brassinolide on rice root development[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2016, 38(10): 1191-1198. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 王黎明, 杨瑞珍, 孙加强. 油菜素内酯调控作物农艺性状和非生物胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(1): 34-49. |
| Wang L M, Yang R Z, Sun J Q. Research progress on the regulation of crop agronomic traits and abiotic stress responses by brassinolide[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(1): 34-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 廖莎, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡凯, 潘晓华, 石庆华. 稻草基质育秧不同芸薹素内酯处理对水稻秧苗生长的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2017, 39(5): 851-858. |
| Liao S, Tang X M, Li M Y, Hu K, Pan X H, Shi Q H. Effects of different treatments of brassinolide on seedling growth of rice in straw substrates[J]. Acta Agricultural Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2017, 39(5): 851-858. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 傅友强, 杨旭健, 吴道铭, 沈宏. 磷素对水稻根表红棕色铁膜的影响及营养效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(6): 1072-1085. |
| Fu Y Q, Yang X J, Wu D M, Shen H. Effects of phosphorus on reddish-brown iron plaque on rice root surface and its nutritional effects[J]. China Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 47(6): 1072-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003. |
| Zhang Z L, Qu W J. Plant Physiology Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2003. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 167-169. |
| Li H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 167-169. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 陈建勋, 王晓峰. 植物生理学模块实验指导[M]. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2002: 120-123. |
| Chen J X, Wang X F. Plant Physiology Module Experiment Guide[M]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press, 2002: 120-123. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 李玲. 植物生理学模块实验指导[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 95-97. |
| Li L. Plant Physiology Module Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 95-97. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 朱春权, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 张均华. 不同属性特征基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 503-512. |
| Zhu C Q, Xu Q S, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Effects of different attribute characteristic substrates on low temperature tolerance of early rice seedlings[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 503-512. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 赵世杰. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2004: 26-34. |
| Zhao S J. Plant Physiology Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2004: 26-34. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | Shouichi Y, Douglas A F, James H C. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice[M]. Philippines: International Rice Research Institution, 1976. |
| [27] | 朱春权, 魏倩倩, 项兴佳, 胡文君, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 刘佳, 金千瑜, 张均华. 褪黑素和茉莉酸甲酯基质育秧对水稻耐低温胁迫的调控作用[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(8): 2016-2027. |
| Zhu C Q, Wei Q Q, Xiang X J, Hu W J, Xu Q S, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Liu J, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. The regulatory effect of melatonin and methyl jasmonate substrate on the tolerance of rice to low temperature stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2016-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 李睿, 董立强, 商文奇, 马亮, 王先俱, 王铮, 李跃东. 育秧基质和喷水间隔处理对机插秧苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 59-68. |
| Li R, Dong L Q, Shang W Q, Ma L, Wang X J, Wang Z, Li Y D. Effects of seedling substrate and spraying interval on seedling quality and yield of mechanical transplanting[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35 (1): 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 周劲松, 闫平, 张伟明, 郑福余, 程效义, 陈温福. 生物炭对东北冷凉区水稻秧苗根系形态建成与解剖结构的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(1): 72-81. |
| Zhou J S, Yan P, Zhang W M, Zheng F Y, Chen X Y, Chen W F. Effects of biochar on root morphogenesis and anatomical structure of rice seedlings in cold region of Northeast China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43 (1): 72-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Fridman Y, Elkouby L, Holland N, Vragovic K, Elbaum R, Savaldi-Goldstein S. Root growth is modulated by differential hormonal sensitivity in neighboring cells[J]. Genes & Development, 2014, 28(8): 912-920. |
| [31] | 胡泽友, 邓小波, 彭喜旭, 何艳, 刘文海, 戴光宇, 王海华. 外源钙对镍胁迫下水稻幼苗抗氧化酶活性及膜脂过氧化的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, (4): 367-371. |
| Hu Z Y, Deng X B, Peng X X, He Y, Liu W H, Dai G Y, Wang H H. Effects of exogenous calcium on antioxidant enzyme activities and membrane lipid peroxidation in rice seedlings under nickel stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007, (4): 367-371. | |
| [32] | Talaat N B, Shawky B T. 24-Epibrassinolide alleviates salt-induced inhibition of productivity by increasing nutrients and compatible solutes accumulation and enhancing antioxidant system in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2013, 35: 729-740. |
| [33] | 廖莎, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡凯, 潘晓华, 石庆华. 芸薹素内酯对稻草基质育秧水稻秧苗生理特性及栽后生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 181-190. |
| Liao S, Tan X M, Li M Y, Hu K, Pan X H, Shi Q H. Effects of brassinolide on physiological characteristics and post-planting growth of rice seedlings in rice straw substrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34 (2): 181-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Zhou G Z, Liu C C, Cheng Y, Ruan M Y, Ye Q J, Wang R Q, Yao Z P, Wang H J. Molecular evolution and functional divergence of stress-responsive Cu/Zn superoxide dismutases in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(13): 7082. |
| [35] | Zhang Z G, Zhang Q, Wu J X, Zheng X, Zheng S, Sun X H, Qiu Q S, Lu T G. Gene knockout study reveals that cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 2 (OsAPX2) plays a critical role in growth and reproduction in rice under drought, salt and cold stresses[J]. PloS ONE, 2013, 8(2): e57472. |
| [36] | Jiang W X, Ye Q, Wu Z, Zhang Q Y, Wang L H, Liu J L, Hu X F, Guo D D, Wang X Q, Zhang Z L. Analysis of CAT gene family and functional identification of OsCAT3 in rice[J]. Genes, 2023, 14(1): 138. |
| [1] | 随晶晶, 赵桂龙, 金欣, 卜庆云, 唐佳琦. 水稻孕穗期耐冷调控的分子及生理机制研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 1-10. |
| [2] | 任宁宁, 孙永建, 申聪聪, 朱双兵, 李慧菊, 张志远, 陈凯. 水稻中胚轴研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 11-23. |
| [3] | 张丰勇, 应晓平, 张健, 杨隆维, 应杰政. 半矮秆基因sd1调控水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 24-32. |
| [4] | 陈智慧, 陶亚军, 范方军, 许扬, 王芳权, 李文奇, 古丽娜尔·巴合提别克, 蒋彦婕, 朱建平, 李霞, 杨杰. 水稻抽穗期调控基因Hd6功能标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 47-54. |
| [5] | 胡风越, 王健, 王春, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 水稻DMP1、DMP2、DMP3基因突变体的创制及其单倍体诱导能力鉴定 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 55-66. |
| [6] | 陈书融, 朱练峰, 秦碧蓉, 王婕, 朱旭华, 田文昊, 朱春权, 曹小闯, 孔亚丽, 张均华, 金千瑜. 增氧灌溉下配施硝化抑制剂对水稻生长、产量和氮肥利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 92-100. |
| [7] | 吴猛, 倪川, 康钰莹, 毛雨欣, 叶苗, 张祖建. 水稻分蘖早发特性的品种间差异及其氮素响应 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 101-114. |
| [8] | 王晓茜, 蔡创, 宋练, 周伟, 杨雄, 顾歆悦, 朱春梧. 开放式大气CO2浓度升高和温度升高对扬稻6号稻米品质的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 115-127. |
| [9] | 江敏, 王广伦, 李明璐, 苗波, 李明煊, 石春林. 基于模型的水稻高温热害风险评估与动态预警 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 128-142. |
| [10] | 冯向前, 王爱冬, 洪卫源, 李子秋, 覃金华, 詹丽钏, 陈里鹏, 张运波, 王丹英, 陈松. 基于低空无人机遥感的水稻产量估测方法研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 604-616. |
| [11] | 叶苗, 毛雨欣, 张德海, 康钰莹, 袁榕, 张祖建. 高光效水稻品种的叶片和冠层生理生态特征及其氮素调控机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 617-626. |
| [12] | 汪晴, 王艳茹, 张秀丽, 吕启明. 水稻孤雌生殖诱导基因BBM1序列变异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 627-637. |
| [13] | 钟智慧, 秦璐, 黎志力, 杨珍, 贺晓鹏, 蔡怡聪. 水稻IDD基因家族的全基因组鉴定及综合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 638-652. |
| [14] | 杜彦修, 孙文玉, 袁泽科, 张倩倩, 李富豪, 李俊周, 孙红正. 利用QTL-Seq结合分子标记定位粳稻垩白粒率控制位点qChalk8[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 665-671. |
| [15] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||