
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 276-284.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220807
收稿日期:2022-09-06
修回日期:2022-10-30
出版日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-05-16
通讯作者:
*email: lixiaokun@mail.hzau.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2022-09-06
Revised:2022-10-30
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: lixiaokun@mail.hzau.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】科学施肥是提高稻米品质的有效手段之一,整合不同养分与稻米品质的关系,为改善稻米品质提供理论依据。【方法】以氮、磷、钾、钙、镁、硫、锌、铁、硅、水稻和品质为主要关键词,在“中国知网”和“Web of Science”检索2001年至2021年公开发表的文献,共筛选出符合分析标准的文献94篇、共计数据4277组。将文献中的稻米品质分为营养品质、蒸煮食味品质、外观品质和加工品质,以不施某养分肥料处理为对照,应用Meta分析方法整合分析不同养分施用对稻米品质指标的影响。【结果】与不施某养分肥料肥理相比,施用氮、钾、铁肥可以提高水稻的蛋白质含量,平均增幅分别为17.03%、6.10%、5.61%;施用锌肥和铁肥分别提高稻米的锌含量(28.20%)和铁含量(21.81%),均有利于改善稻米的营养品质。施用氮肥降低稻米的胶稠度(3.33%)、直链淀粉含量(6.01%)、峰值黏度(8.05%)和崩解值(9.98%),不利于稻米蒸煮食味品质的提高。施用钾、镁、硫、硅肥均可降低稻米的垩白粒率,平均降幅分别为15.09%、6.50%、24.07%、23.22%,同时,钾、锌、硅肥的施用可以降低稻米的垩白度,有助于改善外观品质。对于加工品质指标,施用氮、钾、锌肥均可以显著提高稻米的整精米率,平均增幅分别为10.29%、2.92%、3.76%,有利于加工品质提高。【结论】不同养分的施用对稻米的营养、蒸煮食味、外观、加工品质均有一定的影响,但其影响的品质指标不同。在实际生产中应根据目标品质需求协调不同养分对稻米品质的影响,以达到稻米品质最优化。
刘嫒桦, 李小坤. 不同肥料施用与稻米品质关系的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 276-284.
LIU Aihua, LI Xiaokun. Meta-analysis of Relationship Between Fertilizer Application and Rice Quality[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 276-284.
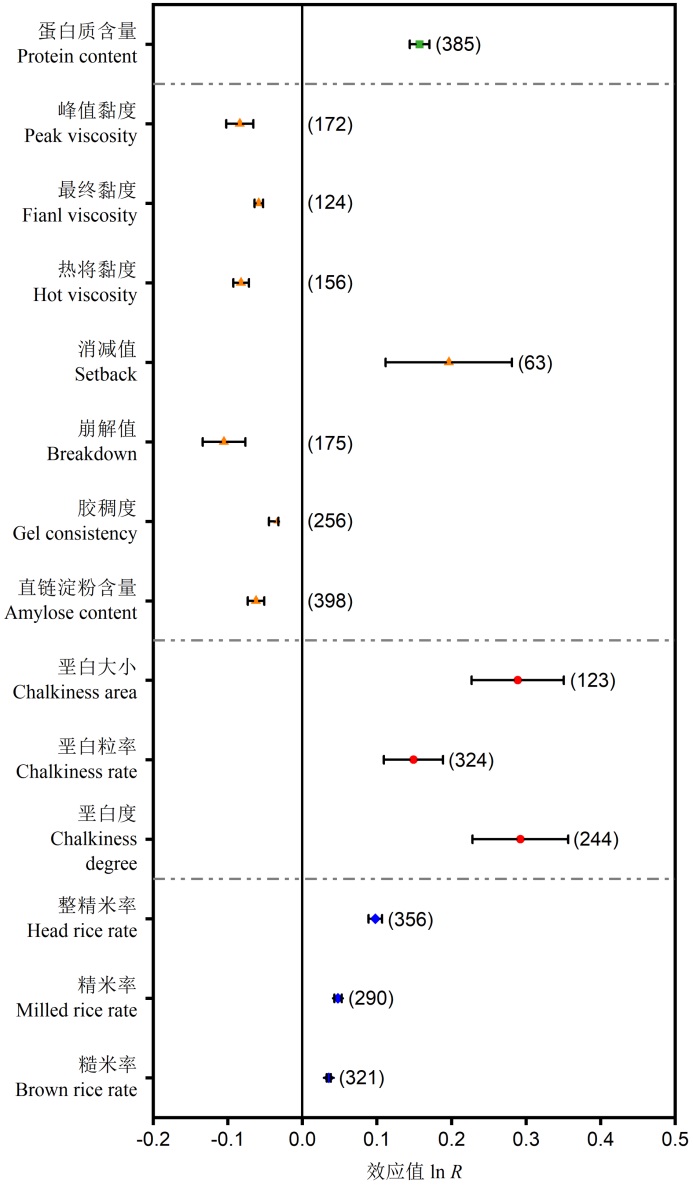
图1 施氮对稻米品质指标的影响 点代表效应值ln R,误差线代表95%置信区间。括号内的值代表样本数。若ln R的95%置信区间不与0重叠,则说明施肥处理对稻米品质指标的影响显著;若ln R的95%置信区间与0重叠,则说明施肥处理对稻米品质指标无显著影响。下同。
Fig. 1. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on the indicators of rice quality. The points represent the effect value ln R and error lines represent 95% confidence interval. The numbers in brackets represent the sample number. The overlap between zero and the 95% confidence interval of ln R mean significant effect of fertilization on rice quality indexes, and vice versa. The same below.
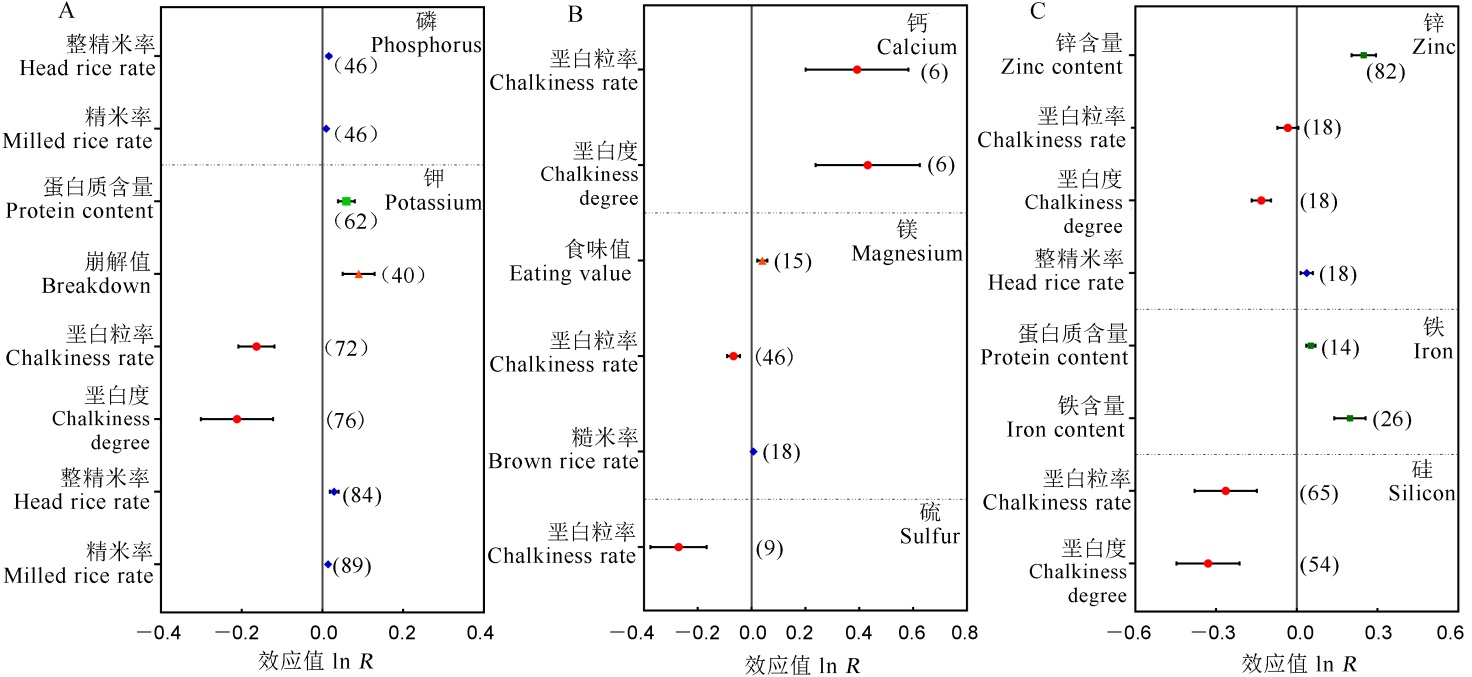
图2 磷、钾、钙、镁、硫、锌、铁、硅肥施用对稻米品质的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, zinc, iron and silicon fertilizer on rice quality.
| [1] | Fairhurst T H, Dobermann D. Rice in the global food supply[J]. Better Crops, 2002, 16(S): 3-6. |
| [2] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 中国水稻生产、市场与进出口贸易的回顾与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(4): 17-21. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Historical review and prospect of China’s rice production, market and import and export trade[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(4): 17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 付亭亭, 贾健斌, 尹岩, 王宇, 魏少芳, 李启平. 可追溯大米的消费行为研究[J]. 食品科技, 2015, 40(2): 360-367. |
| Fu T T, Jia J B, Yin Y, Wang Y, Wei S Y, Li Q P. The traceability of rice consumption behavior research[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2015, 40(2): 360-367. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 吕爱清, 罗天相, 刘沐生. 隐性饥饿的研究现状与应对策略[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. |
| Lü A Q, Luo T S, Liu M S. Research advancements and coping strategies on hidden hunger[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | Shaw B P, Sekhar S, Panda B B, Sahu G, Chandra T, Parida A K. Biochemical and molecular processes contributing to grain filling and yield in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 179: 120-133. |
| [6] | Zahra N, Hafeez M B, Nawaz A, Farooq M. Rice production systems and grain quality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2022, 105: 103463. |
| [7] | 黄海祥, 钱前. 水稻粒形遗传与长粒型优质粳稻育种进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 665-672. |
| Huang H X, Qian Q. Progress in genetic research of rice grain shape and breeding achievements of long-grain shape and good quality japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 665-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 王云霞, 杨连新. 水稻品质对主要气候变化因子的响应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 822-833. |
| Wang Y X, Yang L X. Response of rice quality to major climate change factors[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 822-833. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Ishfaq M, Akbar N, Zulfiqar U, Ali N, Ahmad M, Anjum S A, Farooq M. Influence of water management techniques on milling recovery, grain quality and mercury uptake in different rice production systems[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 243: 106500. |
| [10] | 马兆惠, 张维本, 程海涛, 路连吉, 宋文雯, 吕文彦, 莫倩. 通过养分管理调控水稻胚乳成分提高稻米食味品质[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(1): 45-57. |
| Ma Z H, Zhang W B, Cheng H T, Lu L J, Song W W, Lü W Y. Regulating endosperm composition of rice through nutrient management for improved taste[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2022, 28(1): 45-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 李亚辉, 高庆超, 潘超, 孙晨晨, 张志勇, 梁颖. 矿质元素对稻米品质影响研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(2): 24-31. |
| Li Y F, Gao Q C, Pan C, Sun C C, Zhang Z Y, Liang Y. Research progress on the effects of mineral elements on quality of rice[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(2): 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Mae T. Physiological nitrogen efficiency in rice: Nitrogen utilization, photosynthesis, and yield potential[J]. Plant and Soil, 1997, 196(2): 201-210. |
| [13] | 金正勋, 朱方旭, 郭雪冬, 张忠臣. 不同施氮方法对粳稻灌浆成熟期蔗糖代谢相关酶活性及品质性状影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2016, 47(6): 1-7. |
| Jin Z X, Zhu F X, Guo X D, Zhang Z C. Effect of different nitrogen application methods on activity of sucrose metabolism correlation enzymes and quality in rice at filling stage[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2016, 47(6): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Zhang J, Zhang Y Y, Song N Y, Chen Q L, Sun H Z, Peng T, Huang S, Zhao Q Z. Response of grain-filling rate and grain quality of mid-season indica rice to nitrogen application[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(6): 1465-1473. |
| [15] | Zhu D W, Zhang H C, Guo B W, Xu K, Dai Q G, Wei H Y, Gao H, Hu Y J, Cui P Y, Huo Z Y. Effects of nitrogen level on yield and quality of japonica soft super rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(5): 1018-1027. |
| [16] | Peng L, Chen G, Tu Y, Wang J, Lan Y, Hu M, Li C, He X, Li T. Effects of phosphorus application rate on lipid synthesis and eating quality of two rice grains[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(5): 667. |
| [17] | 邱园园, 刘昆, 卓鑫鑫, 余锋, 李思宇, 黄建, 朱安, 汪浩, 刘立军. 铁的生理功能及其对水稻产量和品质影响的研究综述[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(1): 43-47. |
| Qiu Y Y, Liu K, Zhuo X X, Yu D, Li S Y, Huang J, Zhu A, Wang H, Liu L J. Physiological function of iron and its effect on rice yield and quality[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(1): 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Xia J, Wan S. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition[J]. The New Phytologist, 2008, 179: 428-439. |
| [19] | Feng Z, Wang S, Szantoi Z, Chen S, Wang X. Protection of plants from ambient ozone by applications of ethylenediurea (EDU): A meta-analytic review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(10): 3236-3242. |
| [20] | Hedges L, Gurevitch J, Curtis P. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80: 1150-1156. |
| [21] | Rosenthal R. The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results[J]. Psychological Bulletin, 1979, 86: 638-641. |
| [22] | 王伟妮, 鲁剑巍, 何予卿, 李小坤, 李慧. 氮、磷、钾肥对水稻产量、品质及养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. |
| Wang W N, Lu J W, He Y Q, Li X K, Li H. Effects of N, P, K fertilizer application on grain yield, quality, nutrient uptake and utilization of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘建祥, 杨肖娥, 吴良欢, 杨玉爱. 水稻籽粒钾和蛋白质含量的基因型差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002(1): 84-86. |
| Liu J X, Yang X E, Wu L H, Yang Y A. Genotypic difference in potassium and protein content in rice grain[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2002(1): 84-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Fu P, Wang J, Zhang T, Huang J. High nitrogen input causes poor grain filling of spikelets at the panicle base of super hybrid rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 244: 107635. |
| [25] | 习敏, 许有尊, 孙雪原, 吴文革, 周永进. 氮素穗肥对水稻垩白籽粒灌浆影响及与加工品质的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 144-151. |
| Xi M, Xu Y Z, Sun X Y, Wu W G, Zhou Y J. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer topdressing on grain filling and milling quality of rice with high grain chalkiness[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23 (9): 144, 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Lv X, Han J, Liao Y, Liu Y. Effect of phosphorus and potassium foliage application post-anthesis on grain filling and hormonal changes of wheat[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 214: 83-93. |
| [27] | 韩金香, 胡培松, 焦桂爱, 罗炬, 邵高能, 唐绍清. 稻米蒸煮食味品质及其仪器分析的研究现状[J]. 中国稻米, 2009(2): 1-4. |
| Han J X, Hu P S, Jiao G A, Luo J, Shao G N, Tang S Q. Current status of research on flavor quality of steamed rice and its instrumental analysis[J]. China Rice, 2009(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 石吕, 张新月, 孙惠艳, 曹先梅, 刘建, 张祖建. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. |
| Shi L, Zhang X Y, Sun H Y, Cao X M, Liu J, Zhang Z J. Relationship of grain protein content with cooking and eating quality as affected by nitrogen fertilizer at late growth stage for different types of rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Furukawa S, Tanaka K, Masumura T, Ogihara Y, Kiyokawa Y, Wakai Y. Influence of rice proteins on eating quality of cooked rice and on aroma and flavor of sake[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2006, 83(4): 439-446. |
| [30] | Likitwattanasade T, Hongsprabhas P. Effect of storage proteins on pasting properties and microstructure of Thai rice[J]. Food Research International, 2010, 43(5): 1402-1409. |
| [31] | 刘立军, 常二华, 范苗苗, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 结实期钾、钙对水稻根系分泌物与稻米品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(4): 661-669. |
| Liu L J, Chang E H, Fan M M, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effects of potassium and calcium on root exudates and grain quality during grain filling[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(4): 661-669. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 周立军, 江玲, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 水稻垩白的研究现状与改良策略[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(6): 563-572. |
| Zhou L J, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Wan J M. Current status and strategies for improvement of rice grain chalkiness[J]. Hereditas, 2009, 31(6): 563-572. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wu M, Liu G, Zhang Z, Yang J. Effects of irrigation schedules and phosphorus fertilizer rates on grain yield and quality of upland rice and paddy rice[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2021, 186: 104465. |
| [34] | 王娇, 王洁, 强爱玲, 官景得, 孙国才, 孙建昌, 齐国锋, 王兴盛, 韩龙植. 北方不同气候条件对稻米品质性状的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(6): 13-18. |
| Wang J, Wang J, Qiang A L, Guan J D, Sun G C, Sun J C, Qi G F, Wang X S, Han L Z. The influence of different climatic ecological conditions on rice quality traits in northern China[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(6): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 闫浩亮, 王松, 王雪艳, 党程成, 周梦, 郝蓉蓉, 田小海. 不同水稻品种在高温逼熟下的表现及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 617-628. |
| Yan H L, Wang S, Wang X Y, Dang C C, Zhou M, Hao R R, Tian X H. Performance of different rice varieties under high temperature and its relationship with field meteorological factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 617-628. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 王文玉, 郑桂萍, 万思宇, 陈立强, 赵海成, 赫臣, 康楷, 李红宇, 吕艳东. 15%调环酸钙对水稻产量与品质的影响[J]. 大麦与谷类科学, 2019, 36(3): 11-17. |
| Wang W Y, Zheng G P, Wan S Y, Chen L Q, Zhao H C, Hao C, Kai K, Li H Y, Lv Y D. Effects of 15% prohexadione calcium on rice yield and quality[J]. Barley and Cereal Sciences, 2019, 36(3): 11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 文炯, 李祖胜, 许望龙, 陈鸽, 白玲玉, 曾希柏, 吴家梅. 生石灰和钙镁磷肥对晚稻生长及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(11): 2496-2502. |
| Wen J, Li Z S, Xu W L, Chen G, Bai L Y, Zeng X B, Wu J M. Effects of quicklime and calcium magnesium phosphate application on late-season rice growth and grain cadmium uptake[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(11): 2496-2502. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 刘璐璐. 硫对粳稻稻米品质的影响及其机理[D]. 南京农业大学, 2009. |
| Liu L L. Effects of sulfur on rice quality of japonica rice and its mechanism[D]. Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 金正勋, 曲悦, 何沈雨, 朱琳, 杨玲, 王思宇, 王珊, 王剑, 张忠臣. 根外喷施硫酸镁对水稻淀粉品质的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2019, 50(9): 1-9. |
| Jin Z X, Qu Y, He S Y, Zhu L, Yang L, Wang S Y, Wang S, Wang J, Zhang Z C. Effect of applying magnesium sulfate on rice starch quality[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2019, 50(9): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 郭九信, 隋标, 商庆银, 胡香玉, 廖文强, 郭世伟. 氮锌互作对水稻产量及籽粒氮、锌含量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6): 1336-1342. |
| Guo J X, Sui B, Shang Q Y, Hu X Y, Liao W Q, Guo S W. Effects of N and Zn interaction on yield and contents of N and Zn in grains of rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(6): 1336-1342. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 付力成, 王人民, 孟杰, 万吉丽. 叶面锌、铁配施对水稻产量、品质及锌铁分布的影响及其品种差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(24): 5009-5018. |
| Fu L C, Wang R M, Meng J, Wan J L. Effect of foliar application of zinc and iron fertilizers on distribution of zinc and iron, quality and yield of rice grain[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(24): 5009-5018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 叶廷红, 张赓, 李小坤. 水稻锌营养及锌肥高效施用研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(6): 1-6. |
| Ye T H, Zhang G, Li X K. Research advance of zinc nutrition and efficient application of zinc fertilizer in rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(6): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 吕倩, 吴良欢, 徐建龙, 寿惠霞, 杨肖娥. 叶面喷施氨基酸铁肥对稻米铁含量和营养品质的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2010, 36(5): 528-534. |
| Lü Q, Wu L H, Xu J L, Shou H X, Yang X E. Effects of foliar iron amino acids fertilizer on iron content and nutrition quality of rice grain[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Agriculture & Life Science, 2010, 36(5): 528-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 韩金玲, 李雁鸣, 马春英. 锌对冬小麦叶片碳酸酐酶活性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2003(2): 21-25. |
| Han J L, Li Y M, Ma C Y. Effect of zinc on activity of carbonic anhydrase in winter wheat leaves[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2003(2): 21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 张国良, 戴其根, 王建武, 张洪程, 霍中洋, 凌励, 王显, 张军. 施硅量对粳稻品种武育粳3号产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007(3): 299-303. |
| Zhang G L, Dai Q G, Wang J W, Zhang H C, Huo Z Y, Ling L, Wang X, Zhang J. Effects of silicon fertilizer rate on yield and quality of japonica rice Wuyujing 3[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007(3): 299-303. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 赵灿, 刘光明, 戴其根, 许轲, 高辉, 霍中洋. 氮肥对水稻产量、品质和氮利用效率的影响研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(1): 48-52. |
| Zhao C, Liu G M, Dai Q G, Xu K, Gao H, Huo Z Y. Research progress on the effects of nitrogen fertilizer on rice yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(1): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [14] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [15] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
