
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 554-564.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.200915
崔欢1, 高巧丽1, 罗立新1, 杨靖1, 陈淳1, 郭涛1, 刘永柱1, 黄永相2, 王慧1, 陈志强1,*( ), 肖武名1,*(
), 肖武名1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-23
修回日期:2021-03-04
出版日期:2021-11-10
发布日期:2021-11-10
通讯作者:
陈志强,肖武名
基金资助:
Huan CUI1, Qiaoli GAO1, Lixin LUO1, Jing YANG1, Chun CHEN1, Tao GUO1, Yongzhu LIU1, Yongxiang HUANG2, Hui WANG1, Zhiqiang CHEN1,*( ), Wuming XIAO1,*(
), Wuming XIAO1,*( )
)
Received:2020-09-23
Revised:2021-03-04
Online:2021-11-10
Published:2021-11-10
Contact:
Zhiqiang CHEN, Wuming XIAO
摘要:
【目的】利用转录组测序技术,探究水稻萌发过程中激素信号转导和细胞内部氧化还原平衡的调控机理,以期增加对萌发过程中复杂调控机制的理解,促进萌发期基因组转录调控网络的构建,并挖掘调控种子萌发的相关基因,为水稻直播稻新品种选育提供理论参考。【方法】利用萌发0、24和48 h的种子进行动态转录组测序分析,以差异倍数≥2、错误发现率≤0.05为阈值筛选差异基因,并利用Gene Ontology(GO)和KEGG Pathway数据库对萌发不同阶段的差异基因进行分析注释;同时利用实时荧光定量PCR对测序结果进行验证;最后运用String蛋白互作数据库以combined_score≥0.9为阈值分析差异基因的蛋白互作网络。【结果】在种子萌发前期鉴定到8719个差异基因,而在萌发后期仅鉴定到3480个。GO和KEGG富集结果均显示与激素信号转导相关的基因主要在萌发前期被诱导,特别是生长素信号转导途径中的GH3家族基因在萌发前期均受到显著诱导;而谷胱甘肽代谢途径中的基因在萌发后期转录更为活跃,其中谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶基因富集最多。此外,两个异柠檬酸脱氢酶基因在萌发过程中被显著诱导,经蛋白互作预测发现两个异柠檬酸脱氢酶基因与GH3家族基因可能存在相互作用。【结论】在种子萌发前期,生长素信号转导途径中的GH3家族基因可能在减弱生长素信号以及降低生长素活性方面发挥着重要作用,其高表达能降低生长素对种子的休眠作用,促进萌发启动;在种子萌发后期,谷胱甘肽代谢途径中的谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶基因可能在细胞抵抗氧化胁迫中发挥主要作用;此外,在整个萌发过程中,GH3和异柠檬酸脱氢酶家族基因的相互作用可能在实现激素转导途径和谷胱甘肽代谢途径的交互串联作用、共同调控种子萌发方面具有重要意义。
崔欢, 高巧丽, 罗立新, 杨靖, 陈淳, 郭涛, 刘永柱, 黄永相, 王慧, 陈志强, 肖武名. 水稻萌发期激素信号转导和谷胱甘肽代谢转录分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 554-564.
Huan CUI, Qiaoli GAO, Lixin LUO, Jing YANG, Chun CHEN, Tao GUO, Yongzhu LIU, Yongxiang HUANG, Hui WANG, Zhiqiang CHEN, Wuming XIAO. Transcriptome Analysis of Hormone Signal Transduction and Glutathione Metabolic Pathway in Rice Seeds at Germination Stage[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 554-564.
| 序号 No. | 基因号 Gene ID | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物(3′-5′) Reverse primer(3′-5′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Os01g0764800 | TGATCACTCACTACACTACACG | ACACTGACACCGACTGTATAAG |
| 2 | Os07g0592600 | CCTCTTCCTCTCGCTACTACTA | TCTCAACCCCGAACAAGAAAAA |
| 3 | Os05g0143800 | ATACTTCGAGTTCATCCCGTTC | CCGACTTTGTACCGGTACAG |
| 4 | Os11g0528700 | AACATGTGCTACTACGAGTTCA | GTACAACCCTGTGAAGGTGG |
| 5 | Os01g0370200 | CGAGGCCATCTATCAAGAAGAT | CTTTTGTTACGAGGCACAAGAA |
| 6 | Os03g0283100 | AAGATTGTCGCGATTGATCTTG | TGATTGTTGTGCTCAAGTGAAG |
| 7 | Os10g0528300 | CAAGATCTTCGACGAGGAGAAG | CTCATCTTAGCGAACTCGACC |
| 8 | Os10g0529300 | GACCTCCACAACAAGAGTGAG | AACTTGTCATTGATGTAGGCGG |
| 9 | Os03g0718100 | GAATGCTAAGCCAAGAGGAG | AATCACAAGTGAGAACCACAG |
表1 差异表达基因qRT-PCR验证引物
Table 1 Sequences of the primers used in qRT-PCR.
| 序号 No. | 基因号 Gene ID | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物(3′-5′) Reverse primer(3′-5′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Os01g0764800 | TGATCACTCACTACACTACACG | ACACTGACACCGACTGTATAAG |
| 2 | Os07g0592600 | CCTCTTCCTCTCGCTACTACTA | TCTCAACCCCGAACAAGAAAAA |
| 3 | Os05g0143800 | ATACTTCGAGTTCATCCCGTTC | CCGACTTTGTACCGGTACAG |
| 4 | Os11g0528700 | AACATGTGCTACTACGAGTTCA | GTACAACCCTGTGAAGGTGG |
| 5 | Os01g0370200 | CGAGGCCATCTATCAAGAAGAT | CTTTTGTTACGAGGCACAAGAA |
| 6 | Os03g0283100 | AAGATTGTCGCGATTGATCTTG | TGATTGTTGTGCTCAAGTGAAG |
| 7 | Os10g0528300 | CAAGATCTTCGACGAGGAGAAG | CTCATCTTAGCGAACTCGACC |
| 8 | Os10g0529300 | GACCTCCACAACAAGAGTGAG | AACTTGTCATTGATGTAGGCGG |
| 9 | Os03g0718100 | GAATGCTAAGCCAAGAGGAG | AATCACAAGTGAGAACCACAG |
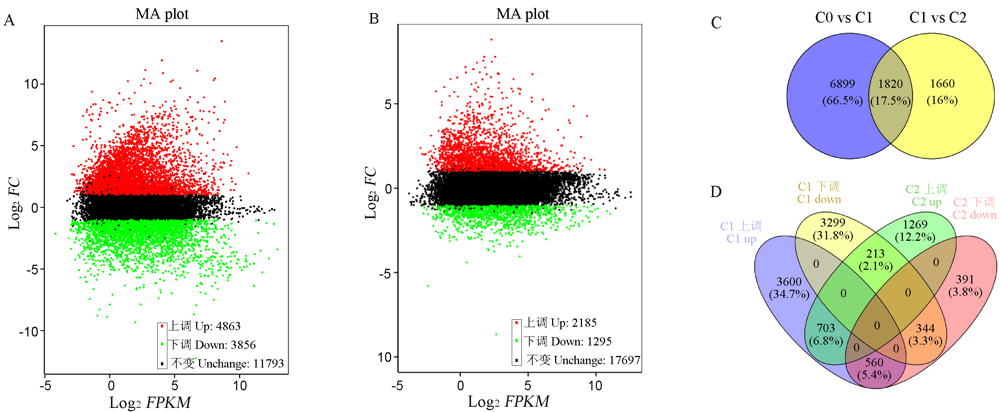
图1 不同萌发阶段差异表达基因分析 A-萌发前期差异基因MA图;B-萌发后期差异基因MA图;C-萌发期差异基因韦恩图;D-萌发期上(下)调差异基因韦恩图。C0-萌发后0 h; C1-萌发后24 h; C2-萌发后48 h。
Fig. 1. Differentially expressed gene analysis during different germination stages. A, MA map of DEG in early germination; B, MA map of DEG in late germination; C, Venn diagram of DEG in germination stage; D, Venn diagram of up-regulation and down-regulation DEG in germination stage. C0, 0 h after germination; C1, 24 h after germination; C2, 48 h after germination.
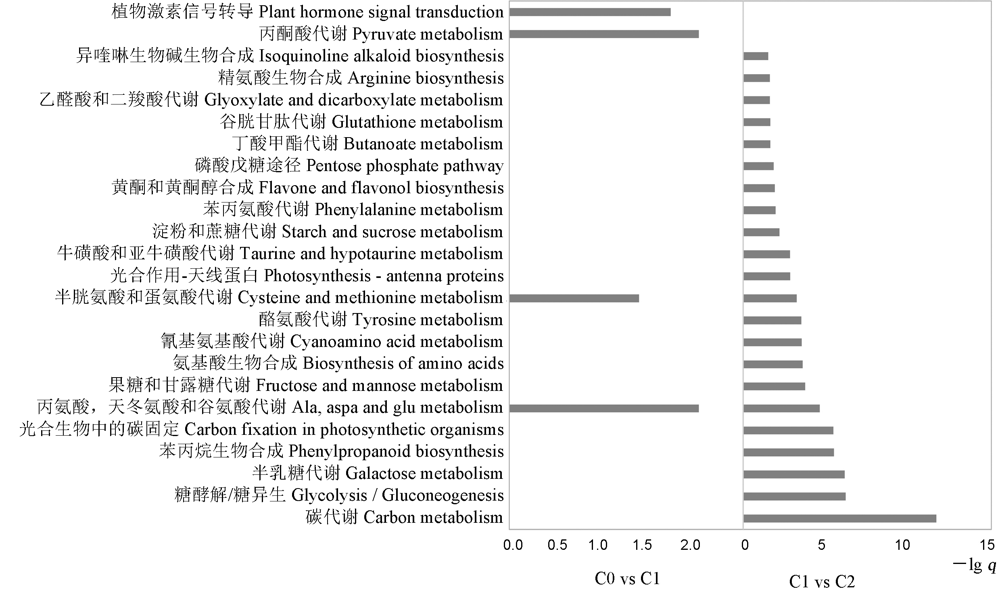
图3 不同萌发阶段差异基因KEGG富集分析 C0-萌发后0 h; C1-萌发后24 h; C2-萌发后48 h。
Fig. 3. KEGG enrichment plots of DEGs at different germination stages. C0, 0 h after germination; C1, 24 h after germination; C2, 48 h after germination.
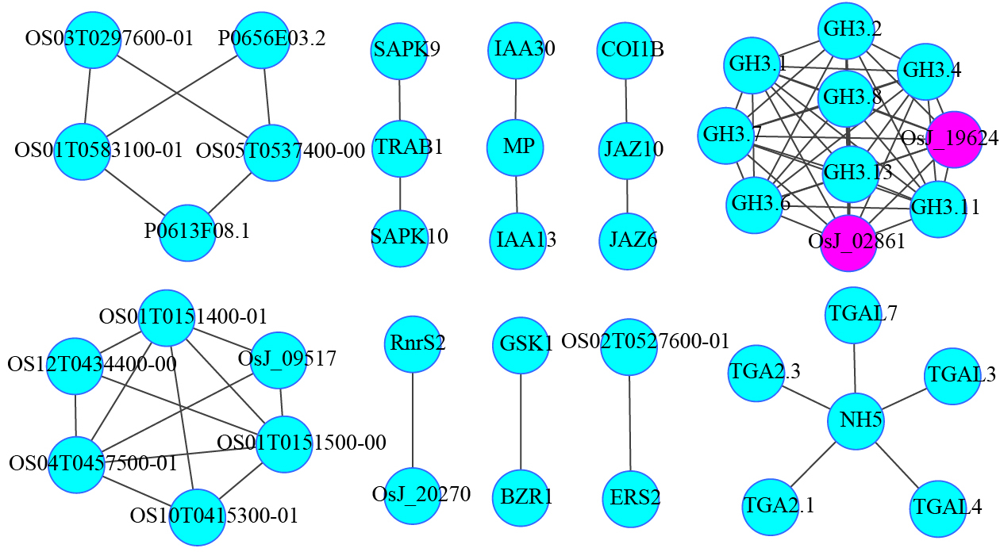
图6 激素信号途径基因与谷胱甘肽代谢途径基因互作预测网络图
Fig. 6. Predicted interaction networks between hormone signaling transduction pathways and glutathione metabolic pathways.
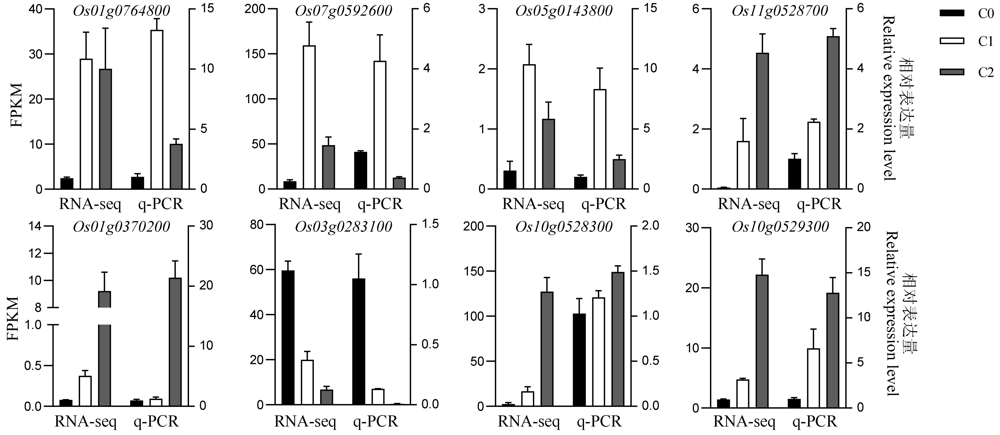
图7 部分DEG表达模式的qRT-PCR验证 C0-萌发后0 h; C1-萌发后24 h; C2-萌发后48 h。
Fig. 7. Expression patterns of selected DEG were verified by qRT-PCR. C0, 0 h after germination; C1, 24 h after germination; C2, 48 h after germination. FPKM, Fragments per kilobase per million.
| [1] | Wei F, Droc G, Guiderdoni E, Hsing Y C.International consortium of rice mutagenesis: Resources and beyond[J]. Rice, 2013, 6: 39. |
| [2] | Mahender A, Anandan A, Pradhan S K.Early seedling vigour, an imperative trait for direct-seeded rice: An overview on physio-morphological parameters and molecular markers[J]. Planta, 2015, 241(5): 1027-1050. |
| [3] | Miura K, Lin S Y, Araki H, Nagamine T, Kuroki M, Shimizu H, Ando I, Yano M.Genetical studies on germination of seed and seedling establishment for breeding of improved rice varieties suitable for direct seeding culture[J]. Jarq-Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly, 2004, 38(1): 1-5. |
| [4] | Hsu S, Tung C.Genetic mapping of anaerobic Germination-associated QTLs controlling coleoptile elongation in rice[J]. Rice, 2015, 8: 38. |
| [5] | Wang Z, Wang J, Bao Y, Wu Y, Zhang H.Quantitative trait loci controlling rice seed germination under salt stress[J]. Euphytica, 2011, 178(3): 297-307. |
| [6] | Dametto A, Sperotto R A, Adamski J M, Blasi E A R, Cargnelutti D, de Oliveira L F V, Ricachenevsky F K, Fregonezi J N, Mariath J E A, Da Cruz R P, Margis R, Fett J P. Cold tolerance in rice germinating seeds revealed by deep RNAseq analysis of contrasting indica genotypes[J]. Plant Science, 2015, 238: 1-12. |
| [7] | Mccormac A C, Keefe P D.Cauliflower(Brassica oleracea L.) seed vigour: imbibition effects[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1990(7): 893-899. |
| [8] | Weitbrecht K, Mueller K, Leubner-Metzger G.First off the mark: Early seed germination[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(10): 3289-3309. |
| [9] | Yang P, Li X, Wang X, Chen H, Chen F, Shen S.Proteomic analysis of rice (Oryza sativa) seeds during germination[J]. Proteomics, 2007, 7(18): 3358-3368. |
| [10] | He D, Han C, Yang P.Gene expression profile changes in germinating rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2011, 53(10): 835-844. |
| [11] | He D, Han C, Yao J, Shen S, Yang P.Constructing the metabolic and regulatory pathways in germinating rice seeds through proteomic approach[J]. Proteomics, 2011, 11(13): 2693-2713. |
| [12] | He D, Yang P.Proteomics of rice seed germination[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4: 246. Doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00246. |
| [13] | Sano N, Ono H, Murata K, Yamada T, Hirasawa T, Kanekatsu M.Accumulation of long-lived mRNAs associated with germination in embryos during seed development of rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(13): 4035-4046. |
| [14] | Wei T, He Z, Tan X, Liu X, Yuan X, Luo Y, Hu S.An integrated RNA-Seq and network study reveals a complex regulation process of rice embryo during seed germination[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 464(1): 176-181. |
| [15] | Chen C, Letnik I, Hacham Y, Dobrev P, Ben-Daniel B, Vankova R, Amir R, Miller G.ASCORBATE PEROXIDASE6 protects arabidopsis desiccating and germinating seeds from stress and mediates cross talk between reactive oxygen species, abscisic acid, and auxin[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 166(1): 370-383. |
| [16] | He Y, Zhao J, Feng D, Huang Z, Liang J, Zheng Y, Cheng J, Ying J, Wang Z.RNA-Seq study reveals AP2-Domain-Containing signalling regulators involved in initial imbibition of seed germination in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 302-314. |
| [17] | Penfield S.Seed dormancy and germination[J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(17): R874-R878. |
| [18] | Gimeno-Gilles C, Lelievre E, Viau L, Malik-Ghulam M, Ricoult C, Niebel A, Leduc N, Limami A M.ABA-Mediated inhibition of germination is related to the inhibition of genes encoding Cell-Wall biosynthetic and architecture: Modifying enzymes and structural proteins in medicago truncatula embryo axis[J]. Molecular Plant, 2009, 2(1): 108-119. |
| [19] | Wang Y, Hou Y, Qiu J, Wang H, Wang S, Tang L, Tong X, Zhang J.Abscisic acid promotes jasmonic acid biosynthesis via a 'SAPK10-bZIP72-AOC' pathway to synergistically inhibit seed germination in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. New Phytologist, 2020, 228(4): 1336-1353. |
| [20] | Shu K, Liu X, Xie Q, He Z.Two faces of one seed: Hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(1): 34-45. |
| [21] | Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Miyakawa T, Kuromori T, Tanokura M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K.Molecular basis of the core regulatory network in ABA responses: Sensing, signaling and transport[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(11): 1821-1839. |
| [22] | Nee G, Kramer K, Nakabayashi K, Yuan B, Xiang Y, Miatton E, Finkemeier I, Soppe W J J. DELAY of GERMINATION1 requires PP2C phosphatases of the ABA signalling pathway to control seed dormancy[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 72. |
| [23] | Song S, Wang G, Wu H, Fan X, Liang L, Zhao H, Li S, Hu Y, Liu H, Ayaad M, Xing Y.OsMFT2 is involved in the regulation of ABA signaling-mediated seed germination through interacting with OsbZIP23/66/72 in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2020, 103(2): 532-546. |
| [24] | Liu X, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Feng Z, Li Q, Yang H, Luan S, Li J, He Z.Auxin controls seed dormancy through stimulation of abscisic acid signaling by inducing ARF-mediated ABI3 activation in Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(38): 15485-15490. |
| [25] | He Y, Zhao J, Yang B, Sun S, Peng L, Wang Z.Indole-3-acetate beta-glucosyltransferase OsIAGLU regulates seed vigour through mediating crosstalk between auxin and abscisic acid in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(9): 1933-1945. |
| [26] | Corbineau F, Xia Q, Bailly C, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H. Ethylene, a key factor in the regulation of seed dormancy[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5: 539. |
| [27] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real-Time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [28] | Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M.The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor[J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7041): 441-445. |
| [29] | Soon F, Ng L, Zhou X E, West G M, Kovach A, Tan M H E, Suino-Powell K M, He Y, Xu Y, Chalmers M J, Brunzelle J S, Zhang H, Yang H, Jiang H, Li J, Yong E, Cutler S, Zhu J, Griffin P R, Melcher K, Xu H E. Molecular mimicry regulates ABA signaling by SnRK2 kinases and PP2C phosphatases[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6064): 85-88. |
| [30] | Cutler S R, Rodriguez P L, Finkelstein R R, Abrams S R.Abscisic acid: Emergence of a core signaling network[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010: 651-679. |
| [31] | Chapman E J, Estelle M.Mechanism of Auxin-Regulated gene expression in plants[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2009, 43(1): 265-285. |
| [32] | Jain M, Kaur N, Tyagi A K, Khurana J P.The auxin-responsive GH3 gene family in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2006, 6(1): 36-46. |
| [33] | Zagorchev L, Seal C E, Kranner I, Odjakova M.A central role for thiols in plant tolerance to abiotic stress[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2013, 14(4): 7405-7432. |
| [34] | Chi Y, Cheng Y, Vanitha J, Kumar N, Ramamoorthy R, Ramachandran S, Jiang S.Expansion mechanisms and functional divergence of the glutathione S-Transferase family in sorghum and other higher plants[J]. DNA Research, 2011, 18(1): 1-16. |
| [35] | Jo S H, Lee S H, Chun H S, Lee S M, Koh H J, Lee S E, Chun J S, Park J W, Huh T L.Cellular defense against UVB-induced phototoxicity by cytosolic NADP(+)- dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2002, 292(2): 542-549. |
| [36] | Jo S, Son M, Koh H, Lee S, Song I, Kim Y, Lee Y, Jeong K, Kim W B, Park J, Song B J, Huhe T.Control of mitochondrial redox balance and cellular defense against oxidative damage by mitochondrial NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(19): 16168-16176. |
| [37] | Noctor G, Mhamdi A, Chaouch S, Han Y, Neukermans J, Marquez-Garcia B, Queval G, Foyer C H.Glutathione in plants: An integrated overview[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2012, 35(2SI): 454-484. |
| [38] | Moons A.Regulatory and functional interactions of plant growth regulators and plant glutathione S-transferases (GSTS)[J]// Vitamins and Hormones, 2005,72: 155-202. |
| [39] | Miller G.Reactive oxygen signaling and abiotic stress[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 133(3): 481-489. |
| [40] | Murata Y, Pei Z M, Mori I C, Schroeder J.Abscisic acid activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ channels in guard cells requires cytosolic NAD(P)H and is differentially disrupted upstream and downstream of reactive oxygen species production in abi1-1 and abi2-1 protein phosphatase 2C mutants[J]. Plant Cell, 2002, 14(1): 287. |
| [41] | Kusumi K, Yaeno T, Kojo K, Hirayama M, Hirokawa D, Yara A, Iba K.The role of salicylic acid in the glutathione-mediated protection against photooxidative stress in rice[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2006, 128(4): 651-661. |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [7] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [8] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [9] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [10] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [11] | 伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 转录组和代谢组联合分析揭示稻曲病菌的致病因子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [12] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [13] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [14] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [15] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||