
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 348-358.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.0103
收稿日期:2020-01-08
修回日期:2020-02-26
出版日期:2020-07-10
发布日期:2020-07-10
通讯作者:
胡铁松
基金资助:
Yun GAO1,2, Tiesong HU2,*( ), Xuebin QI1, Hongwei YUAN3
), Xuebin QI1, Hongwei YUAN3
Received:2020-01-08
Revised:2020-02-26
Online:2020-07-10
Published:2020-07-10
Contact:
Tiesong HU
摘要:
【目的】全球气候变化异常导致旱涝急转事件频发,为保障国家粮食安全,做好农作物的防灾减灾工作,研究了旱涝急转条件下水稻的减产特征。【方法】以淮北平原区水稻为试验对象,在淮委水利科学研究院新马桥农水试验站(117°22′E,33°09′N)开展了为期两年(2017–2018年)的水稻旱涝急转胁迫试验,分析了不同旱涝胁迫程度、不同胁迫持续时间的单一干旱、单一淹涝、旱涝急转胁迫对水稻产量及产量构成的影响,提出先期旱与后期涝的补偿、削减作用量化指标R,揭示了旱涝急转后期淹涝胁迫与前期干旱胁迫对水稻产量影响的交互作用新规律。【结果】拔节期发生旱涝急转产量普遍减少,减产范围12.38%~56.15%。其中,重旱重涝组合对产量最为不利,粒数与粒重减少是旱涝急转胁迫条件下水稻减产主要原因;旱涝急转处理下前期适度干旱可减轻后期淹涝导致的减产,即旱涝急转旱胁迫对涝胁迫具有产量上的补偿效应,主要是提高了每穗粒数、总粒数和结实率;而后期淹涝对前期干旱具有协同作用,表现出产量上的削减效应,主要是每穗粒数、总粒数、千粒质量、结实率的减少。【结论】前期已经发生了轻、中旱胁迫,应尽量避免后期淹涝对水稻的二次损伤;若预测到后期将出现洪涝,并且短时间内田间排水设施无法消除其不利影响,则可提前在水稻拔节中、后期进行旱锻炼以减轻水稻产量损失。
中图分类号:
高芸, 胡铁松, 齐学斌, 袁宏伟. Ⅱ优898产量对旱涝急转的响应规律研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 348-358.
Yun GAO, Tiesong HU, Xuebin QI, Hongwei YUAN. Response of Yield Traits of Rice (Ⅱ-You 898) to Abrupt Drought-flood Alternation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 348-358.
| 处理组 Treatment | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 受旱水平 Drought level | 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 受涝水平 Flood level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADFA1 | 70 | 5 | S-LD | 50 | 5 | S-LF |
| DC1 | 70 | 5 | S-LD | |||
| FC1 | 50 | 5 | S-LF | |||
| ADFA2 | 70 | 10 | M-LD | 75 | 7 | M-MF |
| DC2 | 70 | 10 | M-LD | |||
| FC2 | 75 | 7 | M-MF | |||
| ADFA3 | 70 | 15 | L-LD | 100 | 9 | L-HF |
| DC3 | 70 | 15 | L-LD | |||
| FC3 | 100 | 9 | L-HF | |||
| ADFA4 | 60 | 5 | S-MD | 75 | 9 | L-MF |
| DC4 | 60 | 5 | S-MD | |||
| FC4 | 75 | 9 | L-MF | |||
| ADFA5 | 60 | 10 | M-MD | 100 | 5 | S-HF |
| DC5 | 60 | 10 | M-MD | |||
| FC5 | 100 | 5 | S-HF | |||
| ADFA6 | 60 | 15 | L-MD | 50 | 7 | M-LF |
| DC6 | 60 | 15 | L-MD | |||
| FC6 | 50 | 7 | M-LF | |||
| ADFA7 | 50 | 5 | S-HD | 100 | 7 | M-HF |
| DC7 | 50 | 5 | S-HD | |||
| FC7 | 100 | 7 | M-HF | |||
| ADFA8 | 50 | 10 | M-HD | 50 | 9 | L-LF |
| DC8 | 50 | 10 | M-HD | |||
| FC8 | 50 | 9 | L-LF | |||
| ADFA9 | 50 | 15 | L-HD | 75 | 5 | S-MF |
| DC9 | 50 | 15 | L-HD | |||
| FC9 | 75 | 5 | S-MF |
表2 旱涝因素及水平设置
Table 2 Design of drought and flood factors and levels.
| 处理组 Treatment | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 受旱水平 Drought level | 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 受涝水平 Flood level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADFA1 | 70 | 5 | S-LD | 50 | 5 | S-LF |
| DC1 | 70 | 5 | S-LD | |||
| FC1 | 50 | 5 | S-LF | |||
| ADFA2 | 70 | 10 | M-LD | 75 | 7 | M-MF |
| DC2 | 70 | 10 | M-LD | |||
| FC2 | 75 | 7 | M-MF | |||
| ADFA3 | 70 | 15 | L-LD | 100 | 9 | L-HF |
| DC3 | 70 | 15 | L-LD | |||
| FC3 | 100 | 9 | L-HF | |||
| ADFA4 | 60 | 5 | S-MD | 75 | 9 | L-MF |
| DC4 | 60 | 5 | S-MD | |||
| FC4 | 75 | 9 | L-MF | |||
| ADFA5 | 60 | 10 | M-MD | 100 | 5 | S-HF |
| DC5 | 60 | 10 | M-MD | |||
| FC5 | 100 | 5 | S-HF | |||
| ADFA6 | 60 | 15 | L-MD | 50 | 7 | M-LF |
| DC6 | 60 | 15 | L-MD | |||
| FC6 | 50 | 7 | M-LF | |||
| ADFA7 | 50 | 5 | S-HD | 100 | 7 | M-HF |
| DC7 | 50 | 5 | S-HD | |||
| FC7 | 100 | 7 | M-HF | |||
| ADFA8 | 50 | 10 | M-HD | 50 | 9 | L-LF |
| DC8 | 50 | 10 | M-HD | |||
| FC8 | 50 | 9 | L-LF | |||
| ADFA9 | 50 | 15 | L-HD | 75 | 5 | S-MF |
| DC9 | 50 | 15 | L-HD | |||
| FC9 | 75 | 5 | S-MF |
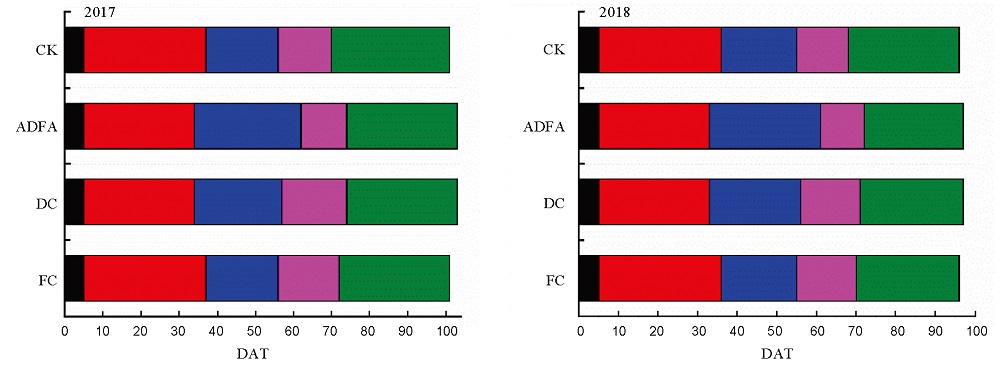
图2 2017–2018年水稻生育期 DAT表示移栽后的时间;CK表示正常组;黑色条形柱表示移栽至分蘖期;红色表示分蘖至拔节期;蓝色表示拔节至抽穗期;品红色表示抽穗至乳熟期;绿色表示乳熟至黄熟期。各生育期表示处理组平均生长时期。
Fig. 2. Duration of growth of rice between 2017 and 2018. DAT, Days after transplanting; CK, Normal control; ADFA, Abrupt drought-flood alternation; DC, Drought control; FC, Flood control; Black bar chart, the duration of tillering stage; Red bar chart, Duration of jointing stage; Blue bar chart, Duration of heading stage; Magenta bar chart, Duration of milky stage; Green bar chart, Duration of maturity. The duration is the average of the treatment groups.
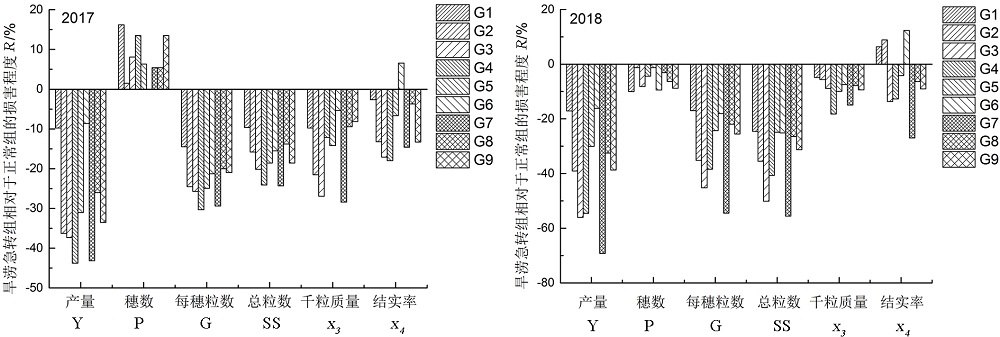
图4 旱涝急转组相对于正常组的损害程度 Y代表产量指标; P代表穗数; G代表每穗粒数; SS代表总粒数; x3代表千粒质量; x4代表结实率; R表示旱涝急转组相对于正常组的损害程度;G1表示ADFA1与CK;G2表示ADFA2与CK;以此类推。
Fig. 4. Damage degree of the ADFA groups relative to the normal control group. Y, Yield; P, Panicle number per barrel; G, Grain number per panicle; SS, Total grain number; x3, Thousand-grain weight; x4, Seed setting rate; R, Damage degree of the ADFA groups relative to normal control group; G1, ADFA1 and CK; G2, ADFA2 and CK, and so on.
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight | 结实率 Seed setting rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | * | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | ** | NS | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | ** | ** | * | NS | NS | NS | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | ** | NS | * | ** | NS | ** |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** |
表3 旱涝胁迫对产量及产量构成影响的差异性分析
Table 3 Significant influence of test factors on yield and yield components.
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight | 结实率 Seed setting rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | * | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | ** | NS | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | ** | ** | * | NS | NS | NS | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | ** | NS | * | ** | NS | ** |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | ** |
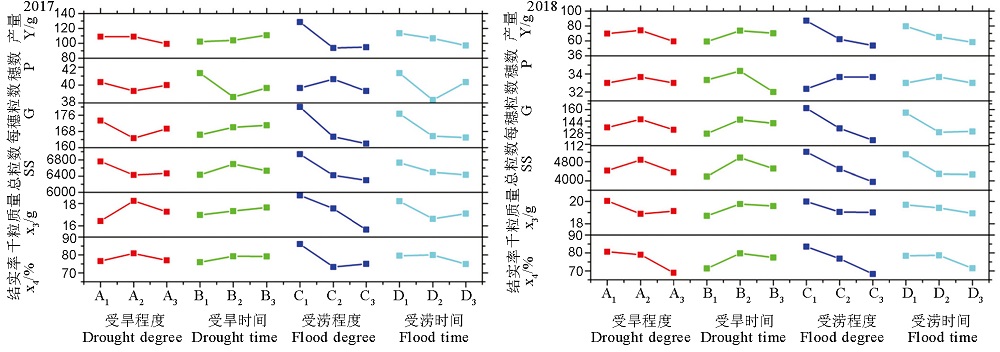
图5 旱涝程度和持续时间对产量及产量构成因素的影响 A1、A2、A3分别表示70%,60%,50%田间持水量;B1、B2、B3分别表示受旱5,10,15 d;C1、C2、C3分别表示50%、75%、100%株高淹水深度;D1、D2、D3分别表示受涝5、7、9 d。
Fig. 5. Influence of drought and flood degree and time on yield and yield components. Y, Yield; P, Panicle number per barrel; G, Grain number per panicle; SS, Total grain number; x3, Thousand-grain weight; x4, Seed setting rate; A1, A2 and A3, 70%, 60%, 50% field water-holding rates; B1, B2 and B3, Duration of drought for 5, 10, 15 d; C1, C2 and C3, Submergence depth of 50%, 75%, 100% plant height; D1, D2 and D3, Duration of flood for 5, 7, 9 d.
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield/g | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | 9.713 | 1 | 8.666 | 335 | 1.81 | 4.274 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | 8.636 | 2.666 | 4.667 | 263 | 0.666 | 3.334 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | 34.773 | 1.334 | 18 | 641 | 3.056 | 12.82 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | 16.514 | 3 | 11.667 | 298.666 | 1.577 | 5.03 | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | 14.737 | 0.667 | 9.333 | 525.334 | 0.773 | 7.83 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | 14.596 | 2.333 | 12.333 | 797 | 0.7 | 5.644 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | 33.31 | 1.334 | 29.667 | 1268.666 | 0.647 | 10.19 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | 21.294 | 0.667 | 18.334 | 849.333 | 0.514 | 4.793 |
表4 旱涝胁迫对产量及产量构成影响的极差分析
Table 4 Extreme differences of test factors on yield and yield components.
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield/g | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | 9.713 | 1 | 8.666 | 335 | 1.81 | 4.274 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | 8.636 | 2.666 | 4.667 | 263 | 0.666 | 3.334 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | 34.773 | 1.334 | 18 | 641 | 3.056 | 12.82 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | 16.514 | 3 | 11.667 | 298.666 | 1.577 | 5.03 | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree | 14.737 | 0.667 | 9.333 | 525.334 | 0.773 | 7.83 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time | 14.596 | 2.333 | 12.333 | 797 | 0.7 | 5.644 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree | 33.31 | 1.334 | 29.667 | 1268.666 | 0.647 | 10.19 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time | 21.294 | 0.667 | 18.334 | 849.333 | 0.514 | 4.793 |
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight | 结实率 Seed setting rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 60 | 60 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 15 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 10 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 50 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 70 | 70 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 50 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 |
表5 水稻产量及产量构成影响最小的旱涝组合
Table 5 Optimal combination of drought and flood with the lowest impact on yield and yield components.
| 年份 Year | 旱涝程度和时间 Drought/Flood degree and time | 产量 Yield | 穗数 Panicle number per barrel | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 总粒数 Total grain number | 千粒质量 Thousand-grain weight | 结实率 Seed setting rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 60 | 60 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 15 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 10 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 50 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | |
| 2018 | 受旱程度 Drought degree/% | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 70 | 70 |
| 受旱时间 Drought time/d | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 受涝程度 Flood degree/% | 50 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| 受涝时间 Flood time/d | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 |

图6 旱涝急转组相对于单旱组的损害程度 G1表示ADFA1与DC1;G2表示ADFA2与DC2;以此类推;产量及产量构成采用3个重复组的平均值。
Fig. 6. Damage degree of the ADFA groups relative to drought groups. G1, DC1 and ADFA1; G2, DC2 and ADFA2; and so on. n=3.
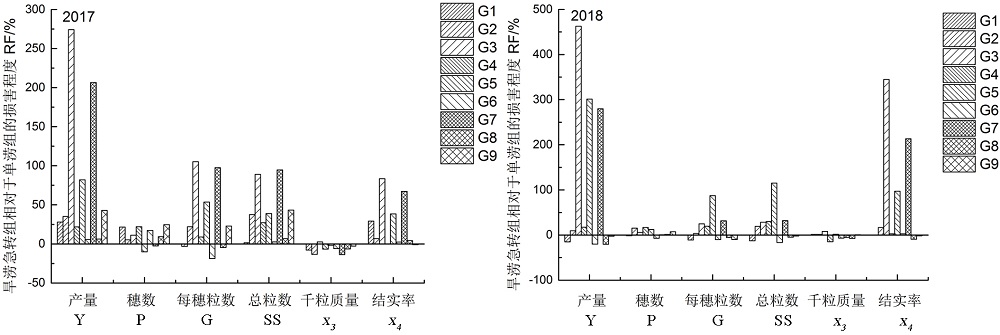
图7 旱涝急转组相对于单涝组的损害程度 G1表示ADFA1与FC1;G2表示ADFA2与FC2;以此类推;产量及产量构成采用3个重复组的平均值。
Fig. 7. Damage degree of the ADFA groups relative to flood groups. G1, FC1 and ADFA1; G2, FC2 and ADFA2; and so on. n=3.
| [1] | Yan D H, Wu D, Huang R, Wang L N.Drought evolution characteristics and precipitation intensity changes during alternating dry-wet changes in the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 2013, 17: 2859-2871. |
| [2] | Li X H, Ye X C.Spatiotemporal characteristics of dry-wet abrupt transition based on precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China[J]. Water, 2015, 7(5): 1943-1958. |
| [3] | Shi W Y.Study on the flood and drought disasters of Chaohu Lake Basin in the past 600 years[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2011. |
| [4] | Wang S, Tian H, Ding X J.Climate characteristics of precipitation and phenomenon of drought-flood abrupt alternation during main flood season in Huaihe River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2009, 30(1): 31-34. |
| [5] | Wu W B, Verburg P H, Tang H J.Climate change and the food production system: impacts and adaptation in China[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2014, 14(1): 1-5. |
| [6] | Darzi-Naftchali A, Ritzema H, Karandish F, Mokhtassi B, Ghasemi N.Alternate wetting and drying for different subsurface drainage systems to improve paddy yield and water productivity in Iran[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2017, 193: 221-231. |
| [7] | Yao F X, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X, Xiang J, Liu X J, Wu W, Chen M X, Peng S B.Agronomic performance of high-yielding rice variety grown under alternate wetting and drying irrigation[J]. Field Crop Research, 2012, 126: 16-22. |
| [8] | Shao G C, Deng S, Liu N, Yu S E, Wang M H, She D L.Effects of controlled irrigation and drainage on growth, grain yield and water use in paddy rice[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2014, 53: 1-9. |
| [9] | Gao Y, Hu T S, Wang Q, Yuan H W, Yang J W.Effect of drought-flood abrupt alternation on rice yield and yield components[J]. Crop Science, 2019, 58: 1-13. |
| [10] | 高芸, 胡铁松, 袁宏伟, 杨继伟. 淮北平原旱涝急转条件下水稻减产规律分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(21): 128-136. |
| Gao Y, Hu T S, Yuan H W, Yang J W.Analysis on yield reduced law of rice in Huaibei plain under drought-flood abrupt alternation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(21): 128-136. | |
| [11] | 刘凯, 张耗, 张慎凤, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 结实期土壤水分和灌溉方式对水稻产量和品质的影响及其生理原因[J]. 作物学报. 2008, 34(2): 268-276. |
| Liu K, Zhang H, Zhang S F, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Effect of soil moisture and irrigation patterns during grain filling on grain yield and quality of rice and their physiological mechanism[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(2): 268-276. | |
| [12] | 郭相平,杨骕,王振昌, 杨静晗, 李小朴. 旱涝交替胁迫对水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2015,34(1):13-16. |
| Guo X P, Yang S, Wang Z C, Yang J H, Li X P.Effects of alternative stress of drought and waterlogging on rice yield and quality[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2015, 34(1): 13-16.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 熊强强, 沈天花, 钟蕾, 陈小荣, 朱昌兰, 彭小松, 贺浩华. 分蘖期和幼穗分化期旱涝急转对超级杂交早稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2017, 36(10): 40-45. |
| Xiong Q Q, Shen T H, Zhong L, Chen X R, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He H H.Effect of a sudden change from drought to waterlogging at the tillering or young spiking stage on yield and grain of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2017, 36(10): 40-45. | |
| [14] | 熊强强, 钟蕾, 沈天花, 陈小荣, 朱昌兰, 彭小松, 傅军如, 贺浩华. 穗分化期旱涝急转对双季超级杂交稻物质积累和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2017, 38(9): 597-608. |
| Xiong Q Q, Zhong L, Shen T H, Chen X R, Zhu C L, Peng X S, Fu J R, He H H.Effects of drought-floods abrupt alternation during panicle differentiation stage on matter accumulation and yield formation in double-season super hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2017, 38(9): 597-608. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 邓艳, 钟蕾, 陈小荣, 朱昌兰, 彭小松, 贺晓鹏, 傅军如, 边建民, 胡丽芳, 欧阳林娟, 贺浩华. 穗分化期旱涝急转对超级杂交早稻产量和生理特性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(4): 768-776. |
| Deng Y, Zhong L, Chen X R, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He X P, Fu J R, Bian J M, Hu L F, Ouyang L J, He H H.Effects of drought-floods abrupt alternation on physiological and yield characteristics in super hybrid early rice during panicle differentiation stage[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(4): 768-776. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Cannell R Q, Belford R K, Gales K, Thomson R J, Webster C P.Effects of waterlogging and drought on winter wheat and winter barley grown on a clay and a sandy loam soil: I. Crop growth and yield[J]. Plant and Soil, 1984, 80: 53-66. |
| [17] | Shao G C, Cheng X, Liu N, Zhang Z.Effect of drought pretreatment before anthesis and post-anthesis waterlogging on water relation, photosynthesis, and growth of tomatoes[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2016, 62(7): 935-946. |
| [18] | Cannell R Q, Belford R K, Gales K, Dennis C W, Prew R D.Effects of waterlogging at different stages of development on the growth and yield of winter wheat[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1980, 31: 117-132. |
| [19] | Dickin E, Wright D.The effects of winter waterlogging and summer drought on the growth and yield of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2008, 28: 234-244. |
| [20] | 郭相平, 袁静, 郭枫, 陈治平. 旱涝快速转换对分蘖后期水稻生理特性的影响. 河海大学学报:自然科学版[J]. 2008, 36(4): 516-519. |
| Guo X P, Yuan J, Guo F, Chen Z P.Effects of rapid shift from drought to waterlogging stress on physiological characteristics of rice in late tillering stage[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2008, 36(4): 516-519. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Kawano N, Ito O, Sakagami J I.Morphological and physiological responses of rice seedlings to complete submergence (flash flooding)[J]. Annals of Botany, 2008, 103(2): 161-169. |
| [22] | Wang C, Yang A, Yin H, Zhang J.Influence of water stress on endogenous hormone contents and cell damage of maize seedlings[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2008, 50(4): 427-434. |
| [23] | 郝树荣, 郭相平, 张展羽.作物干旱胁迫及复水的补偿效应研究进展. 水利水电科技进展. 2009, 29(1): 81-84. |
| Hao S R, Guo X P, Zhang Z Y.Research progress on compensatory effects at crops in drought stress and rehydration[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2009, 29(1): 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 崔远来, 茆智, 李远华. 水稻水分生产函数时空变异规律研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2002, 13(4): 484-491. |
| Cui Y L, Mao Z, Li Y H.Study on temporal and spatial variation of rice water production function[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2002, 13(4): 484-491. | |
| [25] | 李阳生, 彭凤英, 李达模, 李振声. 杂交水稻苗期耐淹特性及其与亲本的关系[J]. 杂交水稻, 2001, 16(2): 50-53. |
| Li Y S, Peng F Y, Li D M, Li Z S.Relationship between hybrids and their parents on submergence tolerance at seedling stage[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2001, 16(2): 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Gravois K A, Helms R S.Path analysis of rice yield and yield components as mected by seeding rate[J]. Agronomy Journal, 1992, 84: 1-4. |
| [27] | Gravois K A, McNew R W. Genetic relationships among and selection for rice yield and yield components[J]. Crop Science, 1993, 33(2): 249-252. |
| [28] | Bhatia D, Joshi S, Das A.Introgression of yield component traits in rice (Oryza sativa ssp. indica) through interspecific hybridization[J]. Crop Science, 2017, 57(3): 1557-1573. |
| [29] | Singh S, Mackill D J, Ismail A M.Responses of SUB1 rice introgression lines to submergence in the field: Yield and grain quality[J]. Field Crops Research, 2009, 113(1): 12-23. |
| [30] | Dar N H, Janvry A D, Emerick K, Raitzer D, Sadoulet E.Flood-tolerant rice reduces yield variability and raises expected yield, differentially benefitting socially disadvantaged groups[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 3315. |
| [31] | Subere J O Q, Bolatete D, Bergantin R, Pardales A, Belmonte J J. Genotypic variation in responses of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) to drought and rewatering: Root system development[J]. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(4): 462-474. |
| [32] | Zhang H, Tan G L, Yang L N, Yang J C, Zhang J H.Hormones in the grains and roots in relation to post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in japonica/indica hybrid rice[J]. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 2009, 47(3): 195-204. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||