
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 532-540.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9055
朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-05-13
修回日期:2019-07-31
出版日期:2019-11-10
发布日期:2019-11-10
通讯作者:
张均华
基金资助:
Chunquan ZHU, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Zhigang BAI, Jie HUANG, Qingduo LIANG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG*( )
)
Received:2019-05-13
Revised:2019-07-31
Online:2019-11-10
Published:2019-11-10
Contact:
Junhua ZHANG
摘要:
目的 低磷胁迫是限制水稻产量的主要因素之一。水稻淹水条件下产生H2S,然而,H2S作为信号分子是否参与调节水稻响应缺磷胁迫还未可知。方法 在正常磷和低磷条件下测定水稻H2S含量,揭示H2S在水稻响应缺磷胁迫中的作用。用2 μmol/L H2S前体物质NaHS预处理水稻1 d,然后在加磷和低磷条件下培养6 d,测定水稻体内总磷含量、酸性磷酸酶活性、抗氧化酶活性、木质部汁液磷含量、磷转运子基因表达以及根系构型变化,从而探究H2S参与调节水稻响应缺磷胁迫的生理和分子机制。结论 低磷胁迫下,水稻根系和地上部H2S含量显著增加。NaHS预处理水稻显著增加低磷条件下水稻体内有效磷和总磷含量,提高根系酸性磷酸酶活性,提高抗氧化酶活性、木质部汁液磷含量和磷转运子基因表达水平,同时还改变水稻根系构型,增加总根长、总根表面积、总根体积和总根尖数,从而促进低磷条件下水稻对外界磷的吸收和转运,最终缓解缺磷胁迫。
中图分类号:
朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华. 硫化氢提高水稻磷吸收转运的生理和分子机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 532-540.
Chunquan ZHU, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Zhigang BAI, Jie HUANG, Qingduo LIANG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Hydrogen Sulfide Enhancing Phosphorus Absorption and Transportation in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 532-540.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward (5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsPT1 | AGCGTTCGGGTTCCTGTA | CGTTCTTGATGCCGATCC |
| OsPT2 | GACGAGACCGCCCAAGAAG | TTTTCAGTCACTCACGTCGAGAC |
| OsPT3 | GTGCTCATGGTGGTGTGCT | GAGCCAGAACCGGAAGAAG |
| OsPT4 | GGAGAAGGCTGACGAGGTC | CCCATGGCGTCTCAAAAA |
| OsPT5 | GGCGAGAACGAAATGGAG | GACGGTCTGCCTGTAGGAGT |
| OsPT6 | TATAACTGATCGATCGAGACCAGAG | TGGATAGCCAGGCCAGTTATATATC |
| OsPT7 | GCTTCCTCCTCACCTTCCTT | TTCTCCCGTGACATCTCCTC |
| OsPT8 | AGAAGGCAAAAGAAATGTGTGTTAAAT | AAAATGTATTCGTGCCAAATTGCT |
| OsPT9 | CATAGGCTTGTCATCCTTTGG | CACTGTAAATAAATCCGCGTTTC |
| OsPT10 | GAGCTCGCACCTCAGCAT | GAGTTCACTCACACGGAGACC |
| OsPT12 | AAATCGAGGTGGAGGAGGAG | CGAGAAGAGGCCGTAGTCC |
| OsHistone | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
表1 本研究中使用的引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of primers used in present study.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward (5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsPT1 | AGCGTTCGGGTTCCTGTA | CGTTCTTGATGCCGATCC |
| OsPT2 | GACGAGACCGCCCAAGAAG | TTTTCAGTCACTCACGTCGAGAC |
| OsPT3 | GTGCTCATGGTGGTGTGCT | GAGCCAGAACCGGAAGAAG |
| OsPT4 | GGAGAAGGCTGACGAGGTC | CCCATGGCGTCTCAAAAA |
| OsPT5 | GGCGAGAACGAAATGGAG | GACGGTCTGCCTGTAGGAGT |
| OsPT6 | TATAACTGATCGATCGAGACCAGAG | TGGATAGCCAGGCCAGTTATATATC |
| OsPT7 | GCTTCCTCCTCACCTTCCTT | TTCTCCCGTGACATCTCCTC |
| OsPT8 | AGAAGGCAAAAGAAATGTGTGTTAAAT | AAAATGTATTCGTGCCAAATTGCT |
| OsPT9 | CATAGGCTTGTCATCCTTTGG | CACTGTAAATAAATCCGCGTTTC |
| OsPT10 | GAGCTCGCACCTCAGCAT | GAGTTCACTCACACGGAGACC |
| OsPT12 | AAATCGAGGTGGAGGAGGAG | CGAGAAGAGGCCGTAGTCC |
| OsHistone | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
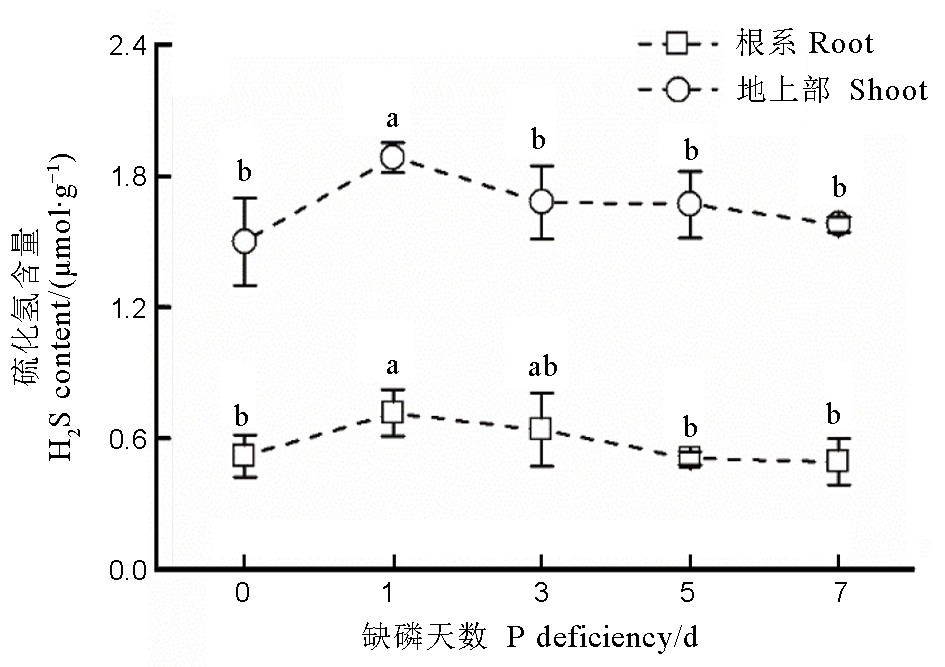
图 1 不同缺磷时间段水稻根系和地上部的硫化氢含量数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在0.05水平上显著。缺磷处理的磷浓度为18 mmol/L。
Fig. 1. Content of H2S in rice root and shoot under different phosphorus deficient durations. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters stand for significant difference at P < 0.05. The P concentration in the nutrient solution is 18 mmol/L under P deficient conditions.
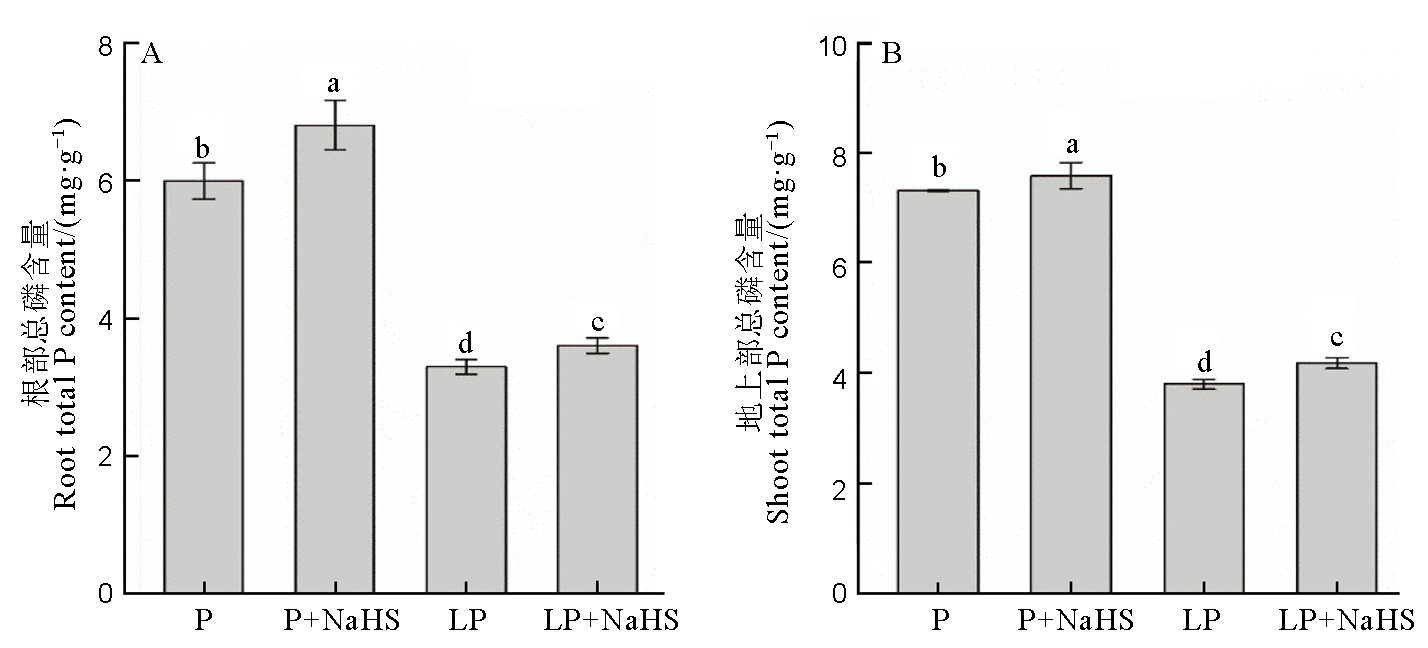
图2 水稻根部和地上部的总磷含量数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在P < 0.05水平上显著。P–营养液中磷浓度为180 mmol/L, LP–18 mmol/L。
Fig. 2. Available P and total P contents in rice roots and shoots. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the columns mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, P concentration of 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
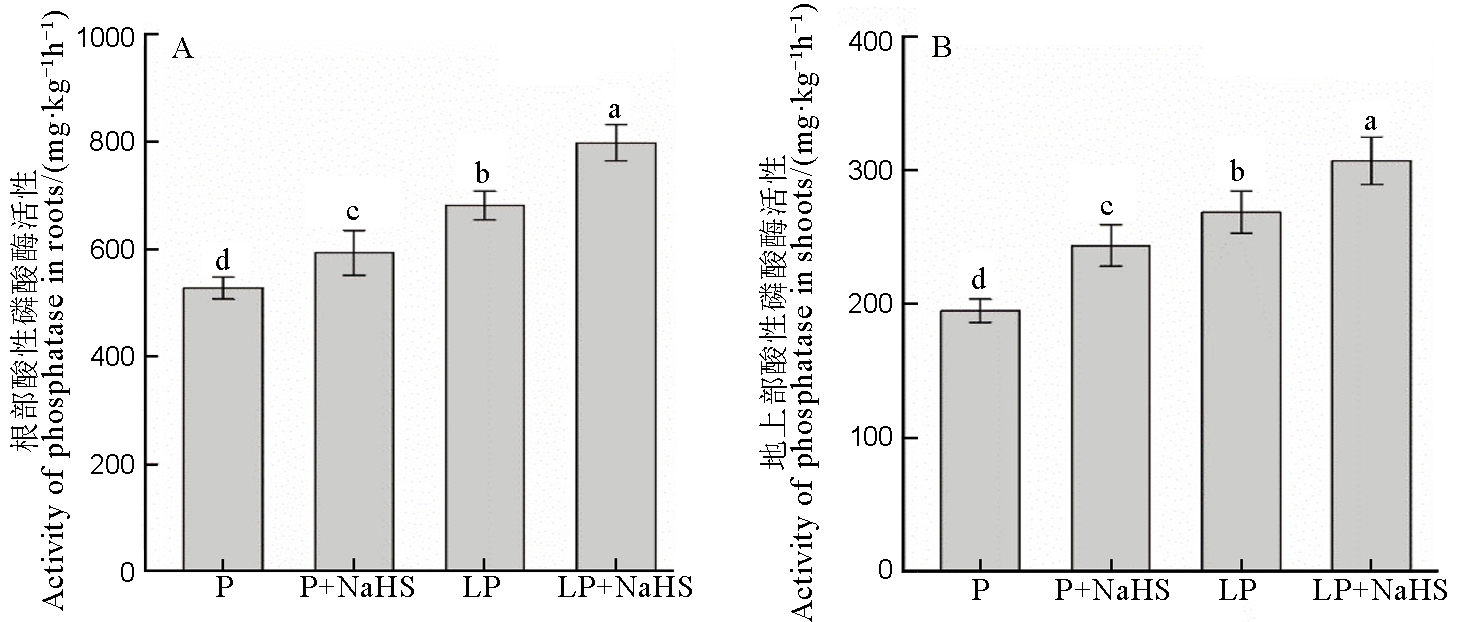
图3 水稻根部和地上部的酸性磷酸酶活性数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在P < 0.05水平上显著。P–180 mmol/L; LP–18 mmol/L。
Fig. 3. Activites of acid phosphatase in rice roots and shoots. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the columns are significantly different at P < 0.05. P, P concentration of 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L.
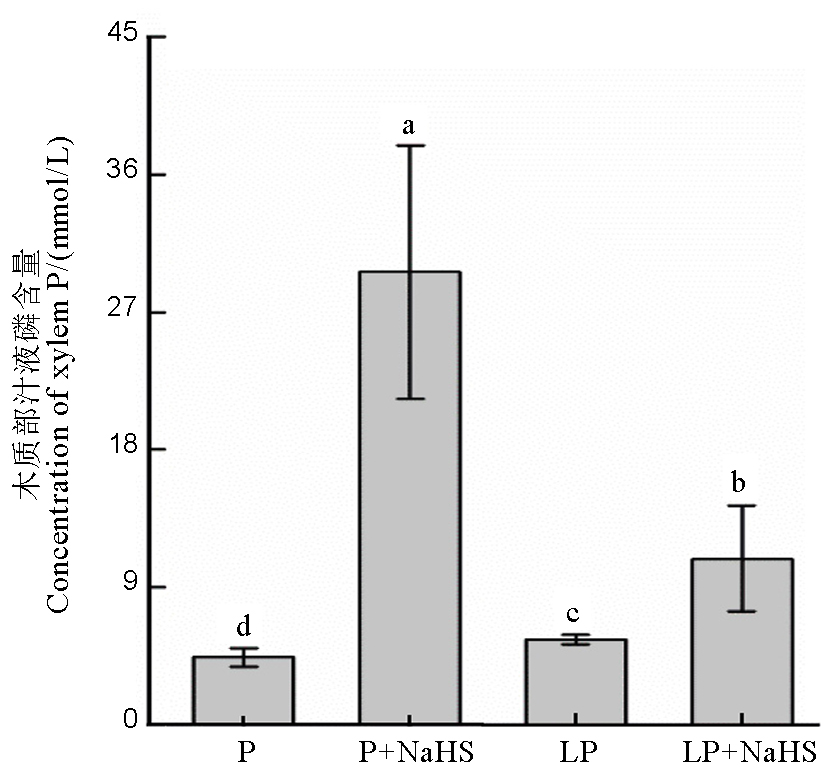
图4 水稻木质部汁液磷含量 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在P < 0.05水平上显著。P–180 mmol/L, LP–18 mmol/L。
Fig. 4. Xylem P concentration in rice. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
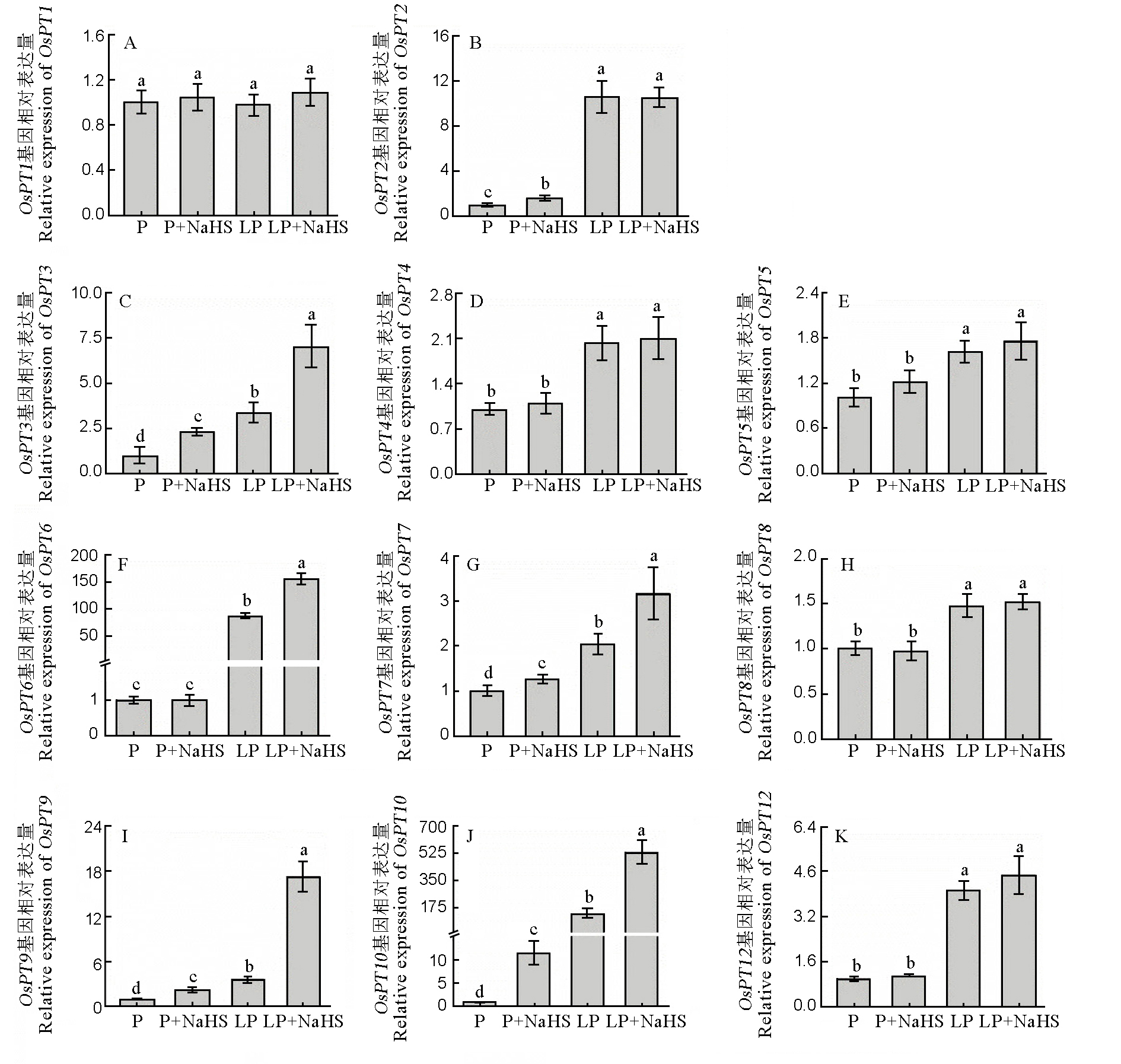
图5 磷转运子基因相对表达量数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在P < 0.05水平上显著。P–180 mmol/L, LP–18 mmol/L。
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of P transporter genes. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L.
| 酶的名称 Enzyme name | 部位 Position | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 3.39±0.08 d | 3.89±0.39 c | 6.21±0.88 b | 10.74±1.24 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 35.82±2.61 d | 49.44±5.17 c | 63.32±5.00 b | 73.20±2.62 a | |
| 过氧化物酶 Peroxidase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 837.56±35.96 d | 1300.92±74.56 c | 1852.22±160.51 b | 2601.40±94.97 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 1745.27±346.02 d | 2649.98±178.02 c | 5070.26±639.59 b | 7627.11±688.69 a | |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 Ascorbate peroxidase/(μmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 0.17±0.04 c | 0.47±0.10 b | 0.45±0.08 b | 0.62±0.07 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 0.26±0.06 d | 0.45±0.04 c | 0.65±0.09 b | 0.92±0.22 a | |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(nmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 10.56±0.16 d | 12.90±0.14 c | 17.51±0.28 b | 22.79±1.83 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 7.08±2.44 d | 23.23±3.88 c | 36.30±4.57 b | 63.21±16.26 a | |
表2 水稻根系和地上抗氧化酶活性
Table 2 Activities of antioxidant enzymes in rice roots and shoots.
| 酶的名称 Enzyme name | 部位 Position | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 3.39±0.08 d | 3.89±0.39 c | 6.21±0.88 b | 10.74±1.24 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 35.82±2.61 d | 49.44±5.17 c | 63.32±5.00 b | 73.20±2.62 a | |
| 过氧化物酶 Peroxidase/(U·g-1) | 根部 Roots | 837.56±35.96 d | 1300.92±74.56 c | 1852.22±160.51 b | 2601.40±94.97 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 1745.27±346.02 d | 2649.98±178.02 c | 5070.26±639.59 b | 7627.11±688.69 a | |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 Ascorbate peroxidase/(μmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 0.17±0.04 c | 0.47±0.10 b | 0.45±0.08 b | 0.62±0.07 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 0.26±0.06 d | 0.45±0.04 c | 0.65±0.09 b | 0.92±0.22 a | |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(nmol·min-1 g-1) | 根部 Roots | 10.56±0.16 d | 12.90±0.14 c | 17.51±0.28 b | 22.79±1.83 a |
| 地上部 Shoots | 7.08±2.44 d | 23.23±3.88 c | 36.30±4.57 b | 63.21±16.26 a | |
| 参数 Parameter | 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total length/cm | 234.77±6.63 c | 262.77±2.27 b | 269.38±5.49 b | 309.72±8.28 a |
| 总表面积Total surface area/cm2 | 31.18±1.00 c | 35.60±1.12 b | 35.76±0.69 b | 45.37±3.63 a |
| 平均直径Average diagram/cm | 0.42±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a |
| 根系总体积Root volume/cm3 | 0.35±0.01 c | 0.39±0.01 b | 0.39±0.00 b | 0.45±0.03 a |
| 根尖数Root tip number | 448.0±15.0 d | 392.0±20.0 c | 549.0±5.3 b | 639.7±23.2 a |
表3 水稻根系发育相关指标
Table 3 Root development parameters in rice.
| 参数 Parameter | 正常磷 P | 磷+硫氢化钠 P+NaHS | 低磷 LP | 低磷+硫氢化钠 LP+NaHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total length/cm | 234.77±6.63 c | 262.77±2.27 b | 269.38±5.49 b | 309.72±8.28 a |
| 总表面积Total surface area/cm2 | 31.18±1.00 c | 35.60±1.12 b | 35.76±0.69 b | 45.37±3.63 a |
| 平均直径Average diagram/cm | 0.42±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a |
| 根系总体积Root volume/cm3 | 0.35±0.01 c | 0.39±0.01 b | 0.39±0.00 b | 0.45±0.03 a |
| 根尖数Root tip number | 448.0±15.0 d | 392.0±20.0 c | 549.0±5.3 b | 639.7±23.2 a |
| [1] | Marschner H.Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 2nd edn. Boston, MA, USA: Academic Press, 1995. |
| [2] | Vance C P, Uhde-Stone C, Allan D L.Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource.New Phytol, 2003, 157: 423-447. |
| [3] | Shen J B, Yuan L X, Zhang J L, Li H G, Bai Z H, Chen X P, Zhang W F, Zhang F S.Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156: 997-1005. |
| [4] | Holford I.Soil phosphorus: its measurement, and its uptake by plants.Soil Res, 1997, 35: 227-240. |
| [5] | Lynch J P, Brown K M.Topsoil foraging-an architectural adaptation of plants to low phosphorus availability.Plant Soil, 2001, 237: 225-237. |
| [6] | Steingrobe B, Schmid H, Claassen N.Root production and root mortality of winter barley and its implication with regard to phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil, 2001, 237: 239-248. |
| [7] | Clarkson D T, Nutrient interception and transport by root systems. Physiological processes limiting plant productivity, London: Butterworths, 1981: 307-330. |
| [8] | Bolan N, Elliott J, Gregg P, Weil S.Enhanced dissolution of phosphate rocks in the rhizosphere.Biol Fert Soils, 1997, 24: 169-174. |
| [9] | Otani T, Ae N, Tanaka H.Phosphorus (P) uptake mechanisms of crops grown in soils with low P status: Ⅱ. Significance of organic acids in root exudates of pigeonpea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 1996, 42: 553-560. |
| [10] | Theodorou M E, Plaxton W C.Metabotic adaptations of plant respiration to nutrional phosphate deprivation.Plant physiol, 1993, 101: 339-344. |
| [11] | Miller S S, Liu J Q, Allan D L, Menzhuber C J, Fedorova M, Vance C P.Molecular control of acid phosphatase secretion into the rhizosphere of proteoid roots from phosphorus-stressed white lupin. Plant Physiol, 2001, 127: 594-606. |
| [12] | Zhu C Q, Zhu X F, Hu A Y,., Wang C, Wang B, Shen R F.Differential effects of nitrogen forms on cell wall phosphorus remobilization are mediated by nitric oxide, pectin content, and phosphate transporter expression. Plant Physiol, 2016. 171: 1407-1417. |
| [13] | Chapin L J, Jones M L.Ethylene regulates phosphorus remobilization and expression of a phosphate transporter (PhPT1) during petunia corolla senescence. J Exp Bot, 2009, 60: 2179-2190. |
| [14] | Wang B, Tang X, Cheng L, Zhang A Z, Zhang W H, Zhang F S, Liu J Q, Cao Y, Allan D L, Vance C P, Shen J B.Nitric oxide is involved in phosphorus deficiency -induced cluster-root development and citrate exudation in white lupin. New Phytol, 2010, 187: 1112-1123. |
| [15] | Li L, Rose P, Moore P.K. Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling.Ann Rev Pharmaco Toxicol, 2011, 51: 169-187. |
| [16] | Zhang H, Tan Z Q, Hu L Y, Wang S H, Luo J P, Jones R L.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in germinating wheat seedlings.J Integ Plant Biol, 2010, 52: 556-567. |
| [17] | Zhang H, Tang J, Liu X P, Wang Y, Yu W, Peng W Y, Fang F, Ma D F, Wei Z J, Hu L Y.Hydrogen sulfide promotes root organogenesis in Ipomoea batatas, Salix matsudana and Glycine max. J Integ Plant Biol, 2009, 51: 1086-1094. |
| [18] | García-Mata C, Lamattina L.Hydrogen sulphide, a novel gasotransmitter involved in guard cell signalling. New Phytol, 2010, 188: 977-984. |
| [19] | Wang B L, Shi L, Li Y X, Zhang W H.Boron toxicity is alleviated by hydrogen sulfide in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings. Planta, 2010, 231: 1301-1309. |
| [20] | Li Z G, Ding X J,. Du P F.Hydrogen sulfide donor sodium hydrosulfide-improved heat tolerance in maize and involvement of proline. J Plant Physiol, 2013, 170: 741-747. |
| [21] | 朱春权, 朱晓芳, 沈仁芳. 硫化氢促进缺磷条件下水稻根系细胞壁磷的再利用. 土壤, 2018, 50: 51-58. |
| Zhu C Q, Zhu X F, Shen R F.Hydrogen sulfide promote rice (Oryza sativa) cell wall P remobilization under P starvation condition. Soils, 2018 50: 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Zhang H, Ye Y K, Wang S H, Luo J P, Tang J, Ma D F.Hydrogen sulfide counteracts chlorophyll loss in sweetpotato seedling leaves and alleviates oxidative damage against osmotic stress. Plant Growth Reg, 2009, 58: 243-250. |
| [23] | Chang C, Hu Y S, Zhu Y, Ma G, Xu G H.Proton pump OsA8 is linked to phosphorus uptake and translocation in rice.J Exp Bot, 2009, 60: 557-565. |
| [24] | Toshiaki T, Hiroshi S.Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of several crop species under phosphorus -deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 1991, 37: 129-140. |
| [25] | Beauchamp C, Fridovich I.Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels.Anal Biochem, 1971, 44: 276-287. |
| [26] | Dhindsa R S, Plumbdhindsa P, Thorpe T A. leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exper Bot, 1981, 32: 93-101. |
| [27] | Nakano Y, Asada K.Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts.Plant Cell Physiol, 1981, 22: 867-880. |
| [28] | Chen J, Wang W H, Wu F H, You C Y, Liu T W, Dong X J, He J X, Zheng H L.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Soil, 2013, 362: 301-318. |
| [29] | Che J, Yamaji N, Shao J F, Ma J F.Silicon decreases both uptake and root-to-shoot translocation of manganese in rice.J Exp Bot, 2016, 67: 1535-1544. |
| [30] | Zhang H, Xue Y H, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H.Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with shoot growth in “super”rice. Field Crops Res, 2009, 113: 31-40. |
| [31] | Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J, Fan X R, Xin W J, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q R, Wu P, Miller A J.Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1; 2 and OsPht1; 6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation.Plant J, 2009, 57: 798-809. |
| [32] | Jia H, Ren H, Gu M, Zhao J N, Sun S B, Zhang X, Chen J Y, Wu P, Xu G H.The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1; 8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156: 1164-1175. |
| [33] | Liu F, Wang Z, Ren H, Shen C, Li Y, Ling H Q, Wu C, Lian X, Wu P.OsSPX1 suppresses the function of OsPHR2 in the regulation of expression of OsPT2 and phosphate homeostasis in shoots of rice.Plant J, 2010, 62: 508-517. |
| [34] | Wang X, Wang Y, Piñeros M A, Wang Z, Wang W, Li C, Wu Z, Kochian LV, Wu P.Phosphate transporters OsPHT1;9 and OsPHT1;10 are involved in phosphate uptake in rice.Plant Cell Environ, 2014, 37: 1159-1170. |
| [35] | Xia J, Yamaji N, Ma J F.A plasma membrane-localized small peptide is involved in rice aluminum tolerance.Plant J, 2013, 76: 345-55. |
| [36] | Zhou J, Jiao F C, Wu Z C, Li Y Y, Wang X M, He X W, Zhong W Q, Wu P.OsPHR2 is involved in phosphate- starvation signaling and excessive phosphate accumulation in shoots of plants. Plant Physiol, 2008, 146: 1673-1686. |
| [37] | Li H, Guo L, Tao C, Yang L M, Wang X Z.Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 gene family. Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 4236-4251. |
| [38] | Paszkowski U, Kroken S, Roux C, Briggs SP.Rice phosphate transporters include an evolutionarily divergent gene specifically activated in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis.PNAS, 2002, 99: 13324-13329. |
| [39] | Zhu C Q, Zhang J H, Sun L M, Zhu L F, Abliz B, Hu W J, Zhong C, Bai Z G, Sajid H, Cao X C, Jin Q Y.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity via decreasing apoplast and symplast Al contents in rice. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9. |
| [40] | Dracup M N H, Barrett-Lennard E G, Greenway H, Robson, A D. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on phosphatase activity of cell walls from roots of subterranean clover. J Exp Bot, 1984, 35: 466-480. |
| [41] | 庞欣, 张福锁, 李春俭. 部分根系供磷对黄瓜根系和幼苗生长及根系酸性磷酸酶活性影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2000, 26: 153-158. |
| Pang X, Zhang F S, Li C J.Effect of the part of P-supply roots on cucumber seedling growth, P concentration in shoot and root and secreted acid phosphatase activity by root.Acta Phytophysiol Sin, 2000, 26: 153-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 樊明寿, 徐冰, 王艳. 缺磷条件下玉米根系酸性磷酸酶活性的变化. 中国农业科技导报, 2001, 3: 33-36. |
| Fan M S, Xu B, Wang Y.Acid phosphatase activities of intact roots and ground root tissues of maize grown in high P or low P nutrient solution.Rev China Agric Sci Technol, 2001, 3: 33-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 张丽梅, 郭再华, 张琳, 贺立源. 缺磷对不同耐低磷玉米基因型酸性磷酸酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21: 898-910. |
| Zhang L M, Guo Z H, Zhang L, He L Y.Effect of phosphate deficiency on acid phosphatase activities of different maize genotypes tolerant to low-P stress.J Plant Nutr Fert, 2015, 21: 898-910. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 黄宇, 张海伟, 徐芳森. 植物酸性磷酸酶的研究进展. 华中农业大学学报, 2008, 27: 148-154. |
| Huang Y, Zhang H W, Xu F S.Research progress on plant acid phosphatase.J Huazhong Agric Univ, 2008, 27: 148-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Seo H M, Jung Y, Song S, Kim Y, Kwon T, Kim D H, Jeung S J, Yi Y B, Yi G, Nam M H.Increased expression of OsPT1, a high-affinity phosphate transporter, enhances phosphate acquisition in rice. Biotechnol Let, 2008, 30: 1833-1838. |
| [46] | Zhang F, Sun Y, Pei W, Jain A, Sun R, Cao Y, Wu X, Jiang T, Zhang L, Fan X.Involvement of OsPht1;4 in phosphate acquisition and mobilization facilitates embryo development in rice. Plant J, 2015, 82: 556-569. |
| [47] | Sun S, Gu M, Cao Y, Huang X P, Zhang X, Ai P H, Zhao J N, Fan X R, Xu G H.A constitutive expressed phosphate transporter, OsPht1;1, modulates phosphate uptake and translocation in phosphate-replete rice. Plant Physiol, 2012, 159: 1571-1581. |
| [48] | Suzuki N. Suzuki N, Miller G, Morales J, Shulaev V, Torres M A, Mittler R.Respiratory burst oxidases: The engines of ROS signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2011, 14: 691-699. |
| [49] | Marques A T, Santos S P, Rosa M G, Rodrigues M A, Abreu I A, Frazão C, Romão C V.Expression, purification and crystallization of MnSOD from Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Crystall, 2014, 70: 669-672. |
| [50] | Ward J T, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Salt D E, Raghothama K G.The effect of iron on the primary root elongation of Arabidopsis during phosphate deficiency. Plant Physiol, 2008, 147: 1181-1191. |
| [51] | Bates T R, Lynch J P.Root hairs confer a competitive advantage under low phosphorus availability. Plant Soil, 2001, 236: 243-250. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||