
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 50-64.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6072
王海月1, 李玥1, 孙永健1,*( ), 李应洪1, 蒋明金1, 王春雨1, 赵建红1, 孙园园2, 徐徽1, 严奉君1, 马均1,*(
), 李应洪1, 蒋明金1, 王春雨1, 赵建红1, 孙园园2, 徐徽1, 严奉君1, 马均1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-05-02
修回日期:2016-07-28
出版日期:2017-01-20
发布日期:2017-01-10
通讯作者:
孙永健,马均
基金资助:Haiyue WANG1, Yue LI1, Yongjian SUN1,*, Yinghong LI1, Mingjin JIANG1, Chunyu WANG1, Jianhong ZHAO1, Yuanyuan SUN2, Hui XU1, Fengjun YAN1, Jun MA1,*
Received:2016-05-02
Revised:2016-07-28
Online:2017-01-20
Published:2017-01-10
Contact:
Yongjian SUN, Jun MA
摘要:
目的 在高施氮水平和常规施氮水平下,研究缓释氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用和产量的影响及其生理机制,为机插稻的氮肥高效利用提供依据。方法 以中迟熟杂交籼稻川谷优7329为材料,采用二因素裂区设计,设置不同的施氮水平及5种缓释氮肥与常规氮肥(尿素)配施处理,并设置不施氮处理,分析不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用和产量的影响及其生理机制,并探讨氮素利用和产量与生理响应之间的关系。结果 结果表明,施氮水平、缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量均存在显著或极显著的影响,机插稻拔节、抽穗及结实期对氮素的吸收利用以及结实期茎鞘的氮素转运量与干物质量、氮素积累量、氮肥表观利用率、每穗实粒数及最终产量显著或极显著正相关(r=0.38*~0.69**)。与常规氮肥运筹相比,缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施、全缓释氮肥施用处理的机插稻成熟期干物质积累量、氮素积累总量、光合势、叶面积指数、氮肥表观利用率及穗部氮素增加量均显著提高,进而促进增产。结论 据产量及氮素利用效率表现,机插稻产量在180 kg/hm2施氮水平下较高,且在缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施比例为7∶3一次性施用时产量最高,较其他氮肥运筹产量高0.84%~26.59%,氮肥表观利用率高0.28%~47.02%,为最优氮肥运筹模式。但不同施氮水平下,随着缓释氮肥配施比例的降低,群体叶面积指数、光合势及物质积累等指标也降低,且在施氮处理为全常规氮肥时最低,均不利于机插稻氮肥利用效率及最终产量的提高。
中图分类号:
王海月, 李玥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 蒋明金, 王春雨, 赵建红, 孙园园, 徐徽, 严奉君, 马均. 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 50-64.
Haiyue WANG, Yue LI, Yongjian SUN, Yinghong LI, Mingjin JIANG, Chunyu WANG, Jianhong ZHAO, Yuanyuan SUN, Hui XU, Fengjun YAN, Jun MA. Effects of Slow-release Urea on Nitrogen Utilization and Yield in Mechanically-transplanted Rice under Different Nitrogen Application Rates[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 50-64.
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number /(×104hm-2) | 每穗实粒数 Filled spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Actual grain yield /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | |||||
| R0 | 226.3±0.5 d | 116.2±0.6 d | 90.98±0.78 a | 36.13±0.18 a | 9 491.2±168.6 d |
| R1 | 238.6±2.0 b | 133.8±1.6 a | 86.86±0.83 b | 36.64±1.05 a | 11 661.3±110.9 a |
| R2 | 254.5±5.6 a | 130.2±1.4 b | 86.57±0.59 b | 36.45±0.40 a | 11 808.6±66.2 a |
| R3 | 227.8±4.1 cd | 135.9±1.8 a | 84.83±1.14 c | 37.01±1.03 a | 11 424.7±355.2 b |
| R4 | 255.4±1.5 a | 122.8±2.0 c | 85.75±0.96 bc | 36.44±0.83 a | 11 408.2±192.8 b |
| R5 | 230.2±1.9 c | 127.7±0.7 b | 83.07±0.24 d | 36.64±0.80 a | 10 706.9±179.1 c |
| 平均 Average | 238.8±0.2 | 127.8±0.4 | 86.34±0.58 | 36.55±0.23 | 11 083.5±44.3 |
| N2 | |||||
| R0 | 226.3±0.5 d | 116.2±0.6 d | 90.98±0.78 a | 36.13±0.18 a | 9 491.2±168.6 d |
| R1 | 258.4±3.9 a | 136.9±0.7 b | 85.35±1.18 c | 34.03±0.61 c | 11 914.9±99.9 ab |
| R2 | 255.3±1.2 ab | 142.4±1.5 c | 87.39±0.86 b | 34.49±0.26 c | 12 015.4±26.2 a |
| R3 | 236.0±6.0 c | 140.6±6.3 a | 87.64±1.24 b | 35.41±0.43 ab | 11 704.6±22.9 b |
| R4 | 251.9±1.2 b | 129.8±1.1 a | 87.22±1.82 b | 35.84±1.05 ab | 11 696.9±32.8 b |
| R5 | 226.4±1.6 d | 139.9±0.7 a | 83.96±0.48 d | 34.76±0.09 bc | 10 999.2±78.6 c |
| 平均 Average | 242.4±1.7 | 134.3±0.9 | 87.09±0.20 | 35.11±0.16 | 11 303.7±30.3 |
| F值 F value | |||||
| N | 14.43* | 75.51* | 2.95 | 436.12** | 125.34** |
| R | 107.37** | 83.02** | 36.75** | 1.75 | 184.32** |
| N×R | 12.68** | 7.30** | 3.28* | 2.82* | 2.79* |
表 1 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 1 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on yield and its components in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number /(×104hm-2) | 每穗实粒数 Filled spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Actual grain yield /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | |||||
| R0 | 226.3±0.5 d | 116.2±0.6 d | 90.98±0.78 a | 36.13±0.18 a | 9 491.2±168.6 d |
| R1 | 238.6±2.0 b | 133.8±1.6 a | 86.86±0.83 b | 36.64±1.05 a | 11 661.3±110.9 a |
| R2 | 254.5±5.6 a | 130.2±1.4 b | 86.57±0.59 b | 36.45±0.40 a | 11 808.6±66.2 a |
| R3 | 227.8±4.1 cd | 135.9±1.8 a | 84.83±1.14 c | 37.01±1.03 a | 11 424.7±355.2 b |
| R4 | 255.4±1.5 a | 122.8±2.0 c | 85.75±0.96 bc | 36.44±0.83 a | 11 408.2±192.8 b |
| R5 | 230.2±1.9 c | 127.7±0.7 b | 83.07±0.24 d | 36.64±0.80 a | 10 706.9±179.1 c |
| 平均 Average | 238.8±0.2 | 127.8±0.4 | 86.34±0.58 | 36.55±0.23 | 11 083.5±44.3 |
| N2 | |||||
| R0 | 226.3±0.5 d | 116.2±0.6 d | 90.98±0.78 a | 36.13±0.18 a | 9 491.2±168.6 d |
| R1 | 258.4±3.9 a | 136.9±0.7 b | 85.35±1.18 c | 34.03±0.61 c | 11 914.9±99.9 ab |
| R2 | 255.3±1.2 ab | 142.4±1.5 c | 87.39±0.86 b | 34.49±0.26 c | 12 015.4±26.2 a |
| R3 | 236.0±6.0 c | 140.6±6.3 a | 87.64±1.24 b | 35.41±0.43 ab | 11 704.6±22.9 b |
| R4 | 251.9±1.2 b | 129.8±1.1 a | 87.22±1.82 b | 35.84±1.05 ab | 11 696.9±32.8 b |
| R5 | 226.4±1.6 d | 139.9±0.7 a | 83.96±0.48 d | 34.76±0.09 bc | 10 999.2±78.6 c |
| 平均 Average | 242.4±1.7 | 134.3±0.9 | 87.09±0.20 | 35.11±0.16 | 11 303.7±30.3 |
| F值 F value | |||||
| N | 14.43* | 75.51* | 2.95 | 436.12** | 125.34** |
| R | 107.37** | 83.02** | 36.75** | 1.75 | 184.32** |
| N×R | 12.68** | 7.30** | 3.28* | 2.82* | 2.79* |

图1 不同施氮水平下缓释肥与常规氮肥配施比例对机插稻产量的影响
Fig.1. Effects of ratios of slow-release urea to conventional urea on yield in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
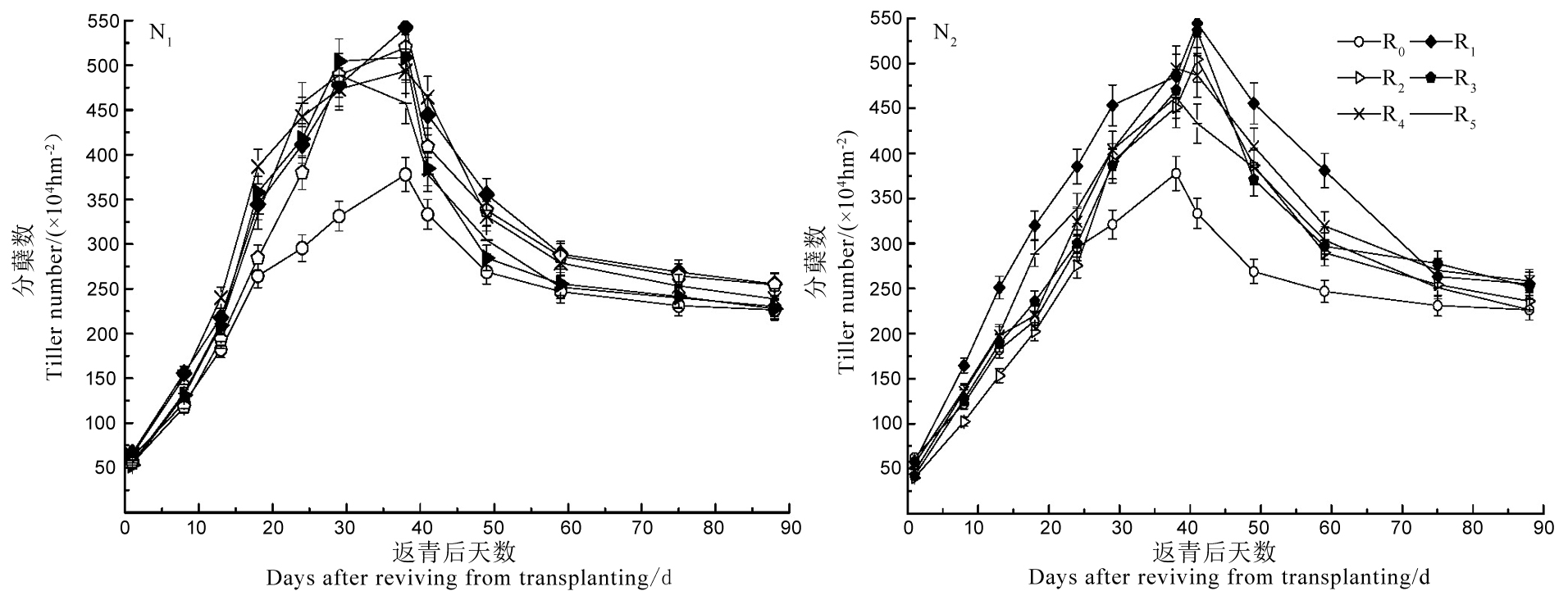
图2 不同施氮量下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻分蘖动态的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on the dynamic changes of stem and tiller numbers in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mol·m-2s-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | ||
| N1 | |||||||
| R0 | 18.31±0.30 e | 15.34±0.25 d | 11.38±0.06 c | 0.73±0.01 e | 0.45±0.00 c | 0.22±0.01 d | |
| R1 | 22.74±0.16 b | 19.43±0.46 a | 15.26±0.24 a | 1.04±0.04 b | 0.84±0.02 a | 0.56±0.04 a | |
| R2 | 23.89±0.39 a | 19.47±0.33 a | 15.28±0.21 a | 1.15±0.01 a | 0.88±0.03 a | 0.49±0.01 b | |
| R3 | 21.21±0.67 c | 18.48±0.42 ab | 15.08±0.17 a | 0.96±0.06 c | 0.67±0.08 b | 0.49±0.02 b | |
| R4 | 21.47±0.35 c | 18.53±0.10 ab | 15.20±0.13 a | 0.98±0.14 bc | 0.68±0.04 b | 0.51±0.01 b | |
| R5 | 20.35±0.32 d | 17.24±0.38 c | 13.64±0.31 b | 0.84±0.02 d | 0.60±0.02 b | 0.35±0.01 c | |
| 平均 Average | 21.33±0.12 | 18.08±0.08 | 14.31±0.08 | 0.95±0.03 | 0.69±0.02 | 0.44±0.01 | |
| N2 | |||||||
| R0 | 18.31±0.30 e | 15.34±0.25 e | 11.38±0.06 d | 0.73±0.01 e | 0.45±0.00 d | 0.22±0.01 e | |
| R1 | 23.77±0.96 ab | 18.43±1.25 ab | 17.15±1.03 a | 0.93±0.03 d | 0.81±0.16 ab | 0.55±0.00 a | |
| R2 | 24.46±0.17 a | 18.73±0.95 a | 17.34±0.72 a | 1.11±0.01 ab | 0.51±0.01 cd | 0.47±0.02 c | |
| R3 | 21.67±0.73 d | 17.48±1.63 bc | 12.37±0.71 c | 1.03±0.01 bc | 0.84±0.15 a | 0.51±0.00 b | |
| R4 | 23.65±0.73 b | 17.16±0.09 c | 14.94±0.36 b | 1.13±0.10 a | 0.71±0.08 b | 0.48±0.02 bc | |
| R5 | 22.77±0.13 c | 16.25±0.08 d | 12.69±1.52 c | 1.00±0.07 cd | 0.59±0.03 c | 0.42±0.00 d | |
| 平均 Average | 22.44±0.15 | 17.23±0.31 | 14.31±0.48 | 0.99±0.00 | 0.65±0.01 | 0.44±0.00 | |
| F值F value | |||||||
| N | 572.79** | 18.17* | 0.00 | 5.89 | 33.33* | 0.79 | |
| R | 86.96** | 22.75** | 65.24** | 28.38** | 16.68** | 225.38** | |
| N×R | 5.08** | 0.61 | 14.30** | 4.58** | 7.38** | 5.43** | |
| 处理 Treatment | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 表观叶肉导度 AMC/(mmol·m-2 s-1) | |||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | ||
| N1 | |||||||
| R0 | 320.3±0.0 a | 336.9±4.9 a | 347.5±9.8 a | 57.17±0.92 e | 45.52±0.09 d | 32.77±0.77 e | |
| R1 | 312.4±1.0 c | 315.7±0.6 c | 313.1±2.1 c | 72.81±0.74 b | 61.53±1.56 a | 46.27±1.48 c | |
| R2 | 310.8±0.4 c | 311.8±2.0 c | 306.8±4.3 c | 76.89±1.36 a | 62.46±1.32 a | 49.81±0.76 a | |
| R3 | 315.5±1.4 b | 324.7±2.1 b | 327.8±2.7 b | 67.22±1.86 c | 56.92±1.58 b | 48.17±0.85 b | |
| R4 | 312.5±1.6 c | 324.2±3.5 b | 330.0±5.5 b | 68.71±1.32 c | 57.15±0.33 b | 46.37±0.13 c | |
| R5 | 315.6±0.6 b | 330.6±1.2 a | 339.7±1.9 a | 64.50±1.12 d | 52.13±1.35 c | 40.15±1.06 d | |
| 平均 Average | 314.5±0.3 | 324.0±0.4 | 327.5±0.4 | 67.88±0.39 | 55.95±0.26 | 43.93±0.27 | |
| N2 | |||||||
| R0 | 320.3±0.0 a | 336.9±4.9 a | 347.5±9.8 a | 57.17±0.92 d | 45.52±0.09 c | 32.77±0.77 c | |
| R1 | 297.1±1.3 d | 293.3±0.5 d | 312.7±3.5 bc | 80.01±2.90 ab | 62.82±4.15 a | 54.82±2.69 a | |
| R2 | 299.2±0.5 d | 296.4±1.4 cd | 304.7±13.0 c | 81.73±0.72 a | 63.20±3.48 a | 57.04±4.79 a | |
| R3 | 306.0±2.9 b | 314.3±2.3 b | 313.3±3.9 bc | 70.82±3.05 c | 55.58±4.79 b | 39.50±2.77 c | |
| R4 | 302.9±0.2 c | 298.5±5.3 c | 310.6±12.2 bc | 78.09±2.38 b | 57.50±0.72 b | 48.16±3.06 b | |
| R5 | 293.4±6.7 e | 292.4±9.0 d | 320.4±5.5 b | 77.61±1.35 b | 55.61±1.94 b | 39.65±5.42 c | |
| 平均 Average | 303.2±1.9 | 305.3±0.8 | 318.2±2.5 | 74.24±0.81 | 56.70±1.10 | 45.32±1.65 | |
| F值 F value | |||||||
| N | 79.99* | 7350.34** | 61.05* | 186.73** | 1.19 | 1.73 | |
| R | 57.47** | 49.79** | 21.53** | 114.34** | 41.82** | 51.76** | |
| N×R | 20.44** | 14.41** | 2.26 | 10.11** | 0.67 | 8.79** | |
表2 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻光合特性的影响
Table 2 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on photosynthetic characteristics in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mol·m-2s-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | ||
| N1 | |||||||
| R0 | 18.31±0.30 e | 15.34±0.25 d | 11.38±0.06 c | 0.73±0.01 e | 0.45±0.00 c | 0.22±0.01 d | |
| R1 | 22.74±0.16 b | 19.43±0.46 a | 15.26±0.24 a | 1.04±0.04 b | 0.84±0.02 a | 0.56±0.04 a | |
| R2 | 23.89±0.39 a | 19.47±0.33 a | 15.28±0.21 a | 1.15±0.01 a | 0.88±0.03 a | 0.49±0.01 b | |
| R3 | 21.21±0.67 c | 18.48±0.42 ab | 15.08±0.17 a | 0.96±0.06 c | 0.67±0.08 b | 0.49±0.02 b | |
| R4 | 21.47±0.35 c | 18.53±0.10 ab | 15.20±0.13 a | 0.98±0.14 bc | 0.68±0.04 b | 0.51±0.01 b | |
| R5 | 20.35±0.32 d | 17.24±0.38 c | 13.64±0.31 b | 0.84±0.02 d | 0.60±0.02 b | 0.35±0.01 c | |
| 平均 Average | 21.33±0.12 | 18.08±0.08 | 14.31±0.08 | 0.95±0.03 | 0.69±0.02 | 0.44±0.01 | |
| N2 | |||||||
| R0 | 18.31±0.30 e | 15.34±0.25 e | 11.38±0.06 d | 0.73±0.01 e | 0.45±0.00 d | 0.22±0.01 e | |
| R1 | 23.77±0.96 ab | 18.43±1.25 ab | 17.15±1.03 a | 0.93±0.03 d | 0.81±0.16 ab | 0.55±0.00 a | |
| R2 | 24.46±0.17 a | 18.73±0.95 a | 17.34±0.72 a | 1.11±0.01 ab | 0.51±0.01 cd | 0.47±0.02 c | |
| R3 | 21.67±0.73 d | 17.48±1.63 bc | 12.37±0.71 c | 1.03±0.01 bc | 0.84±0.15 a | 0.51±0.00 b | |
| R4 | 23.65±0.73 b | 17.16±0.09 c | 14.94±0.36 b | 1.13±0.10 a | 0.71±0.08 b | 0.48±0.02 bc | |
| R5 | 22.77±0.13 c | 16.25±0.08 d | 12.69±1.52 c | 1.00±0.07 cd | 0.59±0.03 c | 0.42±0.00 d | |
| 平均 Average | 22.44±0.15 | 17.23±0.31 | 14.31±0.48 | 0.99±0.00 | 0.65±0.01 | 0.44±0.00 | |
| F值F value | |||||||
| N | 572.79** | 18.17* | 0.00 | 5.89 | 33.33* | 0.79 | |
| R | 86.96** | 22.75** | 65.24** | 28.38** | 16.68** | 225.38** | |
| N×R | 5.08** | 0.61 | 14.30** | 4.58** | 7.38** | 5.43** | |
| 处理 Treatment | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 表观叶肉导度 AMC/(mmol·m-2 s-1) | |||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 齐穗期 FHS | 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | ||
| N1 | |||||||
| R0 | 320.3±0.0 a | 336.9±4.9 a | 347.5±9.8 a | 57.17±0.92 e | 45.52±0.09 d | 32.77±0.77 e | |
| R1 | 312.4±1.0 c | 315.7±0.6 c | 313.1±2.1 c | 72.81±0.74 b | 61.53±1.56 a | 46.27±1.48 c | |
| R2 | 310.8±0.4 c | 311.8±2.0 c | 306.8±4.3 c | 76.89±1.36 a | 62.46±1.32 a | 49.81±0.76 a | |
| R3 | 315.5±1.4 b | 324.7±2.1 b | 327.8±2.7 b | 67.22±1.86 c | 56.92±1.58 b | 48.17±0.85 b | |
| R4 | 312.5±1.6 c | 324.2±3.5 b | 330.0±5.5 b | 68.71±1.32 c | 57.15±0.33 b | 46.37±0.13 c | |
| R5 | 315.6±0.6 b | 330.6±1.2 a | 339.7±1.9 a | 64.50±1.12 d | 52.13±1.35 c | 40.15±1.06 d | |
| 平均 Average | 314.5±0.3 | 324.0±0.4 | 327.5±0.4 | 67.88±0.39 | 55.95±0.26 | 43.93±0.27 | |
| N2 | |||||||
| R0 | 320.3±0.0 a | 336.9±4.9 a | 347.5±9.8 a | 57.17±0.92 d | 45.52±0.09 c | 32.77±0.77 c | |
| R1 | 297.1±1.3 d | 293.3±0.5 d | 312.7±3.5 bc | 80.01±2.90 ab | 62.82±4.15 a | 54.82±2.69 a | |
| R2 | 299.2±0.5 d | 296.4±1.4 cd | 304.7±13.0 c | 81.73±0.72 a | 63.20±3.48 a | 57.04±4.79 a | |
| R3 | 306.0±2.9 b | 314.3±2.3 b | 313.3±3.9 bc | 70.82±3.05 c | 55.58±4.79 b | 39.50±2.77 c | |
| R4 | 302.9±0.2 c | 298.5±5.3 c | 310.6±12.2 bc | 78.09±2.38 b | 57.50±0.72 b | 48.16±3.06 b | |
| R5 | 293.4±6.7 e | 292.4±9.0 d | 320.4±5.5 b | 77.61±1.35 b | 55.61±1.94 b | 39.65±5.42 c | |
| 平均 Average | 303.2±1.9 | 305.3±0.8 | 318.2±2.5 | 74.24±0.81 | 56.70±1.10 | 45.32±1.65 | |
| F值 F value | |||||||
| N | 79.99* | 7350.34** | 61.05* | 186.73** | 1.19 | 1.73 | |
| R | 57.47** | 49.79** | 21.53** | 114.34** | 41.82** | 51.76** | |
| N×R | 20.44** | 14.41** | 2.26 | 10.11** | 0.67 | 8.79** | |
| 处理 Treatment | 叶面积指数 LAI | 齐穗期高效 叶面积指数 High effective LAI at full heading stage | 齐穗期高效 叶面积率 High effective leaf area rate at full heading stage /% | 拔节-齐穗 光合势 Photosynthetic potential at jointing-full heading /(×104m2 d·hm-2) | 拔节-齐穗 群体生长率 Crop growth rate at jointing-full heading /(g·m-2 d-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 Jointing stage | 齐穗期 Full heading stage | |||||
| N1 | ||||||
| R0 | 2.37±0.45 b | 3.21±0.13 d | 2.04±0.08 e | 63.52±0.14 f | 94.76±8.01 c | 20.89±0.38 b |
| R1 | 3.83±0.63 a | 4.49±0.45 bc | 3.38±0.34 bc | 75.30±0.06 b | 141.51±10.89 b | 24.64±0.91 a |
| R2 | 4.10±0.59 a | 6.13±0.64 a | 4.64±0.48 a | 75.83±0.04 a | 173.89±20.91 a | 25.64±0.44 a |
| R3 | 4.40±0.37 a | 4.98±0.87 b | 3.67±0.64 b | 73.60±0.06 c | 159.53±20.63 a | 22.09±0.49 b |
| R4 | 4.06±0.34 a | 4.22±0.43 bc | 2.90±0.29 cd | 68.71±0.07 d | 140.74±12.93 b | 22.37±0.18 b |
| R5 | 3.90±0.53 a | 4.14±0.29 c | 2.82±0.20 d | 68.09±0.14 e | 136.71±12.77 b | 20.84±0.62 b |
| 平均 Average | 3.78±0.18 | 4.53±0.28 | 3.24±0.20 | 70.84±0.03 | 141.19±7.63 | 22.75±0.34 |
| N2 | ||||||
| R0 | 2.37±0.45 c | 3.21±0.13 c | 2.04±0.08 c | 63.52±0.14 d | 94.76±8.01 c | 20.89±0.38 bc |
| R1 | 4.25±0.56 ab | 7.69±1.31 a | 4.90±0.84 a | 63.72±0.04 c | 203.03±16.94 a | 23.43±6.68 ab |
| R2 | 4.32±0.49 ab | 7.87±0.69 a | 5.02±0.44 a | 63.79±0.03 c | 207.16±18.34 a | 24.26±2.75 a |
| R3 | 4.68±0.49 a | 5.11±0.71 b | 3.63±0.51 b | 70.92±0.02 a | 166.46±7.39 b | 21.28±4.12 bc |
| R4 | 4.19±0.40 ab | 5.09±0.09 b | 3.61±0.06 b | 70.83±0.09 a | 157.91±5.58 b | 20.08±4.39 c |
| R5 | 4.06±0.27 b | 5.13±0.67 b | 3.48±0.45 b | 67.71±0.12 b | 156.25±15.52 b | 19.68±2.35 c |
| 平均 Average | 3.98±0.38 | 5.68±0.17 | 3.78±0.12 | 66.75±0.06 | 164.26±3.52 | 21.60±3.25 |
| F值 F value | ||||||
| N | 2.99 | 21.73* | 9.15 | 9683.17** | 57.24* | 0.32 |
| R | 21.53** | 24.62** | 28.45** | 7356.86** | 32.51** | 3.56* |
| N×R | 0.19 | 5.04** | 2.60 | 8108.31** | 3.70* | 3.37* |
表 3 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻光合物质生产的影响
Table 3 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on photosynthetic production in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 叶面积指数 LAI | 齐穗期高效 叶面积指数 High effective LAI at full heading stage | 齐穗期高效 叶面积率 High effective leaf area rate at full heading stage /% | 拔节-齐穗 光合势 Photosynthetic potential at jointing-full heading /(×104m2 d·hm-2) | 拔节-齐穗 群体生长率 Crop growth rate at jointing-full heading /(g·m-2 d-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 Jointing stage | 齐穗期 Full heading stage | |||||
| N1 | ||||||
| R0 | 2.37±0.45 b | 3.21±0.13 d | 2.04±0.08 e | 63.52±0.14 f | 94.76±8.01 c | 20.89±0.38 b |
| R1 | 3.83±0.63 a | 4.49±0.45 bc | 3.38±0.34 bc | 75.30±0.06 b | 141.51±10.89 b | 24.64±0.91 a |
| R2 | 4.10±0.59 a | 6.13±0.64 a | 4.64±0.48 a | 75.83±0.04 a | 173.89±20.91 a | 25.64±0.44 a |
| R3 | 4.40±0.37 a | 4.98±0.87 b | 3.67±0.64 b | 73.60±0.06 c | 159.53±20.63 a | 22.09±0.49 b |
| R4 | 4.06±0.34 a | 4.22±0.43 bc | 2.90±0.29 cd | 68.71±0.07 d | 140.74±12.93 b | 22.37±0.18 b |
| R5 | 3.90±0.53 a | 4.14±0.29 c | 2.82±0.20 d | 68.09±0.14 e | 136.71±12.77 b | 20.84±0.62 b |
| 平均 Average | 3.78±0.18 | 4.53±0.28 | 3.24±0.20 | 70.84±0.03 | 141.19±7.63 | 22.75±0.34 |
| N2 | ||||||
| R0 | 2.37±0.45 c | 3.21±0.13 c | 2.04±0.08 c | 63.52±0.14 d | 94.76±8.01 c | 20.89±0.38 bc |
| R1 | 4.25±0.56 ab | 7.69±1.31 a | 4.90±0.84 a | 63.72±0.04 c | 203.03±16.94 a | 23.43±6.68 ab |
| R2 | 4.32±0.49 ab | 7.87±0.69 a | 5.02±0.44 a | 63.79±0.03 c | 207.16±18.34 a | 24.26±2.75 a |
| R3 | 4.68±0.49 a | 5.11±0.71 b | 3.63±0.51 b | 70.92±0.02 a | 166.46±7.39 b | 21.28±4.12 bc |
| R4 | 4.19±0.40 ab | 5.09±0.09 b | 3.61±0.06 b | 70.83±0.09 a | 157.91±5.58 b | 20.08±4.39 c |
| R5 | 4.06±0.27 b | 5.13±0.67 b | 3.48±0.45 b | 67.71±0.12 b | 156.25±15.52 b | 19.68±2.35 c |
| 平均 Average | 3.98±0.38 | 5.68±0.17 | 3.78±0.12 | 66.75±0.06 | 164.26±3.52 | 21.60±3.25 |
| F值 F value | ||||||
| N | 2.99 | 21.73* | 9.15 | 9683.17** | 57.24* | 0.32 |
| R | 21.53** | 24.62** | 28.45** | 7356.86** | 32.51** | 3.56* |
| N×R | 0.19 | 5.04** | 2.60 | 8108.31** | 3.70* | 3.37* |
| 处理 Treatment | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.61±0.04 b | 6.59±0.14 d | 4.60±0.21 b | 1.12±0.05 c | 1.85±0.04 b | 1.46±0.08 b | ||
| R1 | 2.21±0.09 a | 8.07±0.06 ab | 5.20±0.03 a | 1.89±0.05 a | 2.53±0.04 a | 2.48±0.04 a | ||
| R2 | 2.21±0.01 a | 8.49±0.03 a | 5.23±0.03 a | 1.89±0.09 a | 2.66±0.15 a | 2.47±0.03 a | ||
| R3 | 2.23±0.02 a | 7.54±0.17 c | 5.09±0.02 a | 1.91±0.01 a | 2.46±0.01 a | 2.33±0.12 a | ||
| R4 | 2.28±0.08 a | 7.57±0.11 bc | 5.17±0.03 a | 1.97±0.07 a | 2.48±0.03 a | 2.37±0.16 a | ||
| R5 | 1.76±0.03 b | 6.75±0.23 d | 4.88±0.04 ab | 1.51±0.04 b | 2.05±0.05 b | 2.45±0.07 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.05±0.01 | 7.50±0.36 | 5.03±0.03 | 1.71±0.03 | 2.34±0.03 | 2.26±0.03 | ||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.61±0.04 d | 6.59±0.14 d | 4.60±0.21 b | 1.12±0.05 c | 1.85±0.04 c | 1.46±0.08 c | ||
| R1 | 2.55±0.54 ab | 8.05±1.30 ab | 5.37±0.31 a | 2.34±0.58 a | 3.12±1.18 a | 3.28±0.08 a | ||
| R2 | 2.35±0.30 bc | 7.75±0.68 ab | 5.43±0.55 a | 2.17±0.35 ab | 2.66±0.64 ab | 3.46±1.09 a | ||
| R3 | 2.73±0.29 a | 7.56±0.21 bc | 5.43±0.18 a | 2.17±0.32 ab | 2.66±0.73 ab | 2.99±0.46 ab | ||
| R4 | 2.55±0.35 ab | 7.14±0.07 c | 5.75±0.19 a | 2.07±0.36 ab | 2.47±0.84 b | 2.98±0.34 ab | ||
| R5 | 2.12±0.18 c | 8.33±0.48 a | 5.21±1.04 a | 1.94±0.15 b | 2.37±1.21 b | 2.65±0.62 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.32±0.08 | 7.57±0.04 | 5.30±0.13 | 1.97±0.11 | 2.52±0.76 | 2.80±0.29 | ||
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 24.84* | 0.11 | 16.06 | 20.28* | 0.17 | 9.16 | ||
| R | 11.59** | 10.32** | 3.74* | 13.44** | 6.86** | 12.31** | ||
| N×R | 0.77 | 5.28** | 0.39 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 1.43 | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | ||||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.39±0.05 d | 8.91±0.05 c | 2.73±0.08 b | 9.83±0.14 c | 14.96±0.34 b | |||
| R1 | 1.89±0.21 a | 9.69±0.06 a | 4.10±0.14 a | 12.48±0.17 ab | 17.37±0.08 a | |||
| R2 | 1.82±0.03 ab | 9.74±0.05 a | 4.10±0.08 a | 12.97±0.21 a | 17.44±0.06 a | |||
| R3 | 1.65±0.04 c | 9.64±0.04 a | 4.14±0.02 a | 11.65±0.16 b | 17.06±0.06 a | |||
| R4 | 1.66±0.04 bc | 9.62±0.03 a | 4.26±0.07 a | 11.71±0.14 b | 17.16±0.19 a | |||
| R5 | 1.55±0.04 cd | 9.30±0.02 b | 3.27±0.06 b | 10.36±0.25 c | 16.62±0.10 a | |||
| 平均 Average | 1.66±0.04 | 9.48±0.02 | 3.77±0.03 | 11.50±0.10 | 16.77±0.04 | |||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.39±0.05 b | 8.91±0.05 c | 2.73±0.08 c | 9.83±0.14 d | 14.96±0.34 d | |||
| R1 | 1.69±0.40 a | 9.77±0.31 b | 4.90±1.11 a | 12.86±2.83 a | 18.41±0.69 bc | |||
| R2 | 1.54±0.12 ab | 10.93±0.44 a | 4.53±0.65 ab | 11.96±1.38 abc | 19.82±1.81 a | |||
| R3 | 1.50±0.07 ab | 10.72±0.21 a | 4.89±0.60 a | 11.72±0.89 bc | 19.14±0.61 ab | |||
| R4 | 1.50±0.06 ab | 10.90±0.09 a | 4.62±0.71 ab | 11.12±0.79 c | 19.63±0.52 a | |||
| R5 | 1.62±0.05 a | 9.97±0.60 b | 4.07±0.30 b | 12.32±1.15 ab | 17.83±1.35 c | |||
| 平均 Average | 1.54±0.08 | 10.20±0.14 | 4.29±0.19 | 11.63±1.13 | 18.30±0.41 | |||
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 3.89 | 62.49* | 22.67* | 0.04 | 49.32* | |||
| R | 5.24** | 30.02** | 12.53** | 12.08** | 19.75** | |||
| N×R | 1.27 | 8.15** | 0.63 | 3.10* | 2.49 | |||
表 4 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻干物质积累的影响
Table 4 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on biomass accumulation in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.t/hm2
| 处理 Treatment | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.61±0.04 b | 6.59±0.14 d | 4.60±0.21 b | 1.12±0.05 c | 1.85±0.04 b | 1.46±0.08 b | ||
| R1 | 2.21±0.09 a | 8.07±0.06 ab | 5.20±0.03 a | 1.89±0.05 a | 2.53±0.04 a | 2.48±0.04 a | ||
| R2 | 2.21±0.01 a | 8.49±0.03 a | 5.23±0.03 a | 1.89±0.09 a | 2.66±0.15 a | 2.47±0.03 a | ||
| R3 | 2.23±0.02 a | 7.54±0.17 c | 5.09±0.02 a | 1.91±0.01 a | 2.46±0.01 a | 2.33±0.12 a | ||
| R4 | 2.28±0.08 a | 7.57±0.11 bc | 5.17±0.03 a | 1.97±0.07 a | 2.48±0.03 a | 2.37±0.16 a | ||
| R5 | 1.76±0.03 b | 6.75±0.23 d | 4.88±0.04 ab | 1.51±0.04 b | 2.05±0.05 b | 2.45±0.07 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.05±0.01 | 7.50±0.36 | 5.03±0.03 | 1.71±0.03 | 2.34±0.03 | 2.26±0.03 | ||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.61±0.04 d | 6.59±0.14 d | 4.60±0.21 b | 1.12±0.05 c | 1.85±0.04 c | 1.46±0.08 c | ||
| R1 | 2.55±0.54 ab | 8.05±1.30 ab | 5.37±0.31 a | 2.34±0.58 a | 3.12±1.18 a | 3.28±0.08 a | ||
| R2 | 2.35±0.30 bc | 7.75±0.68 ab | 5.43±0.55 a | 2.17±0.35 ab | 2.66±0.64 ab | 3.46±1.09 a | ||
| R3 | 2.73±0.29 a | 7.56±0.21 bc | 5.43±0.18 a | 2.17±0.32 ab | 2.66±0.73 ab | 2.99±0.46 ab | ||
| R4 | 2.55±0.35 ab | 7.14±0.07 c | 5.75±0.19 a | 2.07±0.36 ab | 2.47±0.84 b | 2.98±0.34 ab | ||
| R5 | 2.12±0.18 c | 8.33±0.48 a | 5.21±1.04 a | 1.94±0.15 b | 2.37±1.21 b | 2.65±0.62 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.32±0.08 | 7.57±0.04 | 5.30±0.13 | 1.97±0.11 | 2.52±0.76 | 2.80±0.29 | ||
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 24.84* | 0.11 | 16.06 | 20.28* | 0.17 | 9.16 | ||
| R | 11.59** | 10.32** | 3.74* | 13.44** | 6.86** | 12.31** | ||
| N×R | 0.77 | 5.28** | 0.39 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 1.43 | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | ||||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.39±0.05 d | 8.91±0.05 c | 2.73±0.08 b | 9.83±0.14 c | 14.96±0.34 b | |||
| R1 | 1.89±0.21 a | 9.69±0.06 a | 4.10±0.14 a | 12.48±0.17 ab | 17.37±0.08 a | |||
| R2 | 1.82±0.03 ab | 9.74±0.05 a | 4.10±0.08 a | 12.97±0.21 a | 17.44±0.06 a | |||
| R3 | 1.65±0.04 c | 9.64±0.04 a | 4.14±0.02 a | 11.65±0.16 b | 17.06±0.06 a | |||
| R4 | 1.66±0.04 bc | 9.62±0.03 a | 4.26±0.07 a | 11.71±0.14 b | 17.16±0.19 a | |||
| R5 | 1.55±0.04 cd | 9.30±0.02 b | 3.27±0.06 b | 10.36±0.25 c | 16.62±0.10 a | |||
| 平均 Average | 1.66±0.04 | 9.48±0.02 | 3.77±0.03 | 11.50±0.10 | 16.77±0.04 | |||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 1.39±0.05 b | 8.91±0.05 c | 2.73±0.08 c | 9.83±0.14 d | 14.96±0.34 d | |||
| R1 | 1.69±0.40 a | 9.77±0.31 b | 4.90±1.11 a | 12.86±2.83 a | 18.41±0.69 bc | |||
| R2 | 1.54±0.12 ab | 10.93±0.44 a | 4.53±0.65 ab | 11.96±1.38 abc | 19.82±1.81 a | |||
| R3 | 1.50±0.07 ab | 10.72±0.21 a | 4.89±0.60 a | 11.72±0.89 bc | 19.14±0.61 ab | |||
| R4 | 1.50±0.06 ab | 10.90±0.09 a | 4.62±0.71 ab | 11.12±0.79 c | 19.63±0.52 a | |||
| R5 | 1.62±0.05 a | 9.97±0.60 b | 4.07±0.30 b | 12.32±1.15 ab | 17.83±1.35 c | |||
| 平均 Average | 1.54±0.08 | 10.20±0.14 | 4.29±0.19 | 11.63±1.13 | 18.30±0.41 | |||
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 3.89 | 62.49* | 22.67* | 0.04 | 49.32* | |||
| R | 5.24** | 30.02** | 12.53** | 12.08** | 19.75** | |||
| N×R | 1.27 | 8.15** | 0.63 | 3.10* | 2.49 | |||
| 处理 Treatment | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 14.82±0.62 d | 30.69±0.63 d | 18.94±0.85 d | 31.68±1.36 c | 31.88±0.59 c | 9.91±0.57 c | ||
| R1 | 27.62±1.14 a | 49.42±0.35 a | 28.10±0.14 ab | 58.29±1.43 a | 51.26±0.72 ab | 23.17±0.38 ab | ||
| R2 | 24.78±0.19 ab | 53.76±0.22 a | 29.22±0.16 a | 57.17±2.81 a | 58.80±3.27 a | 24.51±0.30 a | ||
| R3 | 22.30±0.21 bc | 40.51±0.88 b | 25.17±0.10 c | 53.99±0.04 ab | 47.30±0.24 b | 20.90±1.06 ab | ||
| R4 | 25.05±0.91 ab | 40.68±0.59 b | 26.23±0.14 c | 58.24±1.99 a | 49.25±0.67 ab | 21.43±1.47 ab | ||
| R5 | 20.08±0.46 c | 35.19±1.19 c | 21.19±0.18 d | 47.03±1.27 ab | 37.14±0.91 c | 19.43±0.50 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 22.44±0.14 | 41.71±0.21 | 24.81±0.12 | 51.07±0.70 | 45.94±0.53 | 19.89±0.29 | ||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 14.82±0.62 d | 30.69±0.63 d | 18.94±0.85 d | 31.68±1.36 c | 31.88±0.59 c | 9.91±0.57 d | ||
| R1 | 37.27±7.84 a | 70.68±11.42 a | 29.19±1.66 ab | 78.59±19.35 a | 71.96±27.13 a | 34.73±0.85 a | ||
| R2 | 28.44±3.66 b | 52.99±4.66 b | 29.76±3.02 a | 68.09±11.20 ab | 54.42±13.12 b | 31.94±10.08 b | ||
| R3 | 31.51±3.44 b | 49.92±1.42 b | 24.37±0.78 c | 65.21±9.47 b | 57.41±15.70 b | 29.50±4.58 b | ||
| R4 | 27.76±3.75 b | 43.96±0.44 c | 26.91±0.91 ab | 58.31±10.08 b | 50.98±17.41 b | 30.77±3.50 b | ||
| R5 | 19.26±1.95 c | 44.91±2.57 c | 26.45±5.27 bc | 60.12±4.68 b | 49.75±25.35 b | 18.28±4.27 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 26.51±1.26 | 48.86±2.83 | 25.94±0.60 | 60.33±3.88 | 52.73±16.31 | 25.85±2.78 | ||
| F值F value | ||||||||
| N | 28.15* | 18.93* | 13.49 | 23.78* | 0.49 | 11.97 | ||
| R | 23.70** | 54.94** | 21.75** | 15.29** | 12.83** | 28.62** | ||
| N×R | 3.06* | 8.76** | 1.67 | 1.47 | 2.52 | 3.71* | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | ||||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 21.89±0.79 d | 73.96±0.44 e | 46.50±1.76 c | 84.46±1.24 c | 102.81±1.85 d | |||
| R1 | 31.89±3.42 a | 115.27±0.68 b | 85.91±2.55 a | 132.56±3.24 a | 166.55±0.84 a | |||
| R2 | 28.78±0.51 ab | 119.80±0.63 a | 81.95±2.68 a | 141.34±3.99 a | 173.53±0.57 a | |||
| R3 | 25.88±0.71 bc | 100.27±0.37 c | 76.29±0.17 ab | 113.70±0.95 b | 146.34±0.60 b | |||
| R4 | 26.34±0.58 bc | 100.07±0.31 c | 83.29±1.55 a | 116.27±1.30 b | 147.74±1.58 b | |||
| R5 | 24.02±0.55 cd | 85.53±0.15 d | 67.11±1.45 b | 96.35±1.65 c | 126.14±0.60 c | |||
| 平均 Average | 26.47±0.58 | 99.15±0.22 | 73.51±0.73 | 114.11±1.26 | 143.85±0.13 | |||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 21.89±0.79 c | 73.96±0.44 e | 46.50±1.76 d | 84.46±1.24 c | 102.81±1.85 e | |||
| R1 | 29.89±7.20 a | 134.08±2.29 ab | 115.86±27.19 a | 172.53±45.07 a | 198.01±4.78 a | |||
| R2 | 25.60±2.08 b | 136.58±5.48 a | 96.53±14.78 b | 133.01±18.98 b | 198.28±16.39 a | |||
| R3 | 25.49±1.08 b | 130.80±2.54 b | 96.72±12.86 b | 132.82±16.81 b | 184.66±5.60 b | |||
| R4 | 25.09±0.95 b | 119.88±0.98 c | 86.08±13.82 bc | 120.03±17.07 b | 177.56±4.48 c | |||
| R5 | 26.36±0.75 ab | 108.66±6.56 d | 79.39±6.27c | 121.03±24.13 b | 153.39±7.47 d | |||
| 平均 Average | 25.72±1.34 | 117.33±1.36 | 86.84±5.13 | 127.31±19.95 | 169.12±3.46 | |||
| F值F value | ||||||||
| N | 0.49 | 430.47** | 25.09* | 1.17 | 139.47** | |||
| R | 8.57** | 320.26** | 17.30** | 27.93** | 146.04** | |||
| N×R | 0.89 | 20.27** | 1.53 | 4.08* | 6.57** | |||
表5 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻氮素积累的影响
Table 5 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on N accumulation in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.kg/hm2
| 处理 Treatment | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 14.82±0.62 d | 30.69±0.63 d | 18.94±0.85 d | 31.68±1.36 c | 31.88±0.59 c | 9.91±0.57 c | ||
| R1 | 27.62±1.14 a | 49.42±0.35 a | 28.10±0.14 ab | 58.29±1.43 a | 51.26±0.72 ab | 23.17±0.38 ab | ||
| R2 | 24.78±0.19 ab | 53.76±0.22 a | 29.22±0.16 a | 57.17±2.81 a | 58.80±3.27 a | 24.51±0.30 a | ||
| R3 | 22.30±0.21 bc | 40.51±0.88 b | 25.17±0.10 c | 53.99±0.04 ab | 47.30±0.24 b | 20.90±1.06 ab | ||
| R4 | 25.05±0.91 ab | 40.68±0.59 b | 26.23±0.14 c | 58.24±1.99 a | 49.25±0.67 ab | 21.43±1.47 ab | ||
| R5 | 20.08±0.46 c | 35.19±1.19 c | 21.19±0.18 d | 47.03±1.27 ab | 37.14±0.91 c | 19.43±0.50 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 22.44±0.14 | 41.71±0.21 | 24.81±0.12 | 51.07±0.70 | 45.94±0.53 | 19.89±0.29 | ||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 14.82±0.62 d | 30.69±0.63 d | 18.94±0.85 d | 31.68±1.36 c | 31.88±0.59 c | 9.91±0.57 d | ||
| R1 | 37.27±7.84 a | 70.68±11.42 a | 29.19±1.66 ab | 78.59±19.35 a | 71.96±27.13 a | 34.73±0.85 a | ||
| R2 | 28.44±3.66 b | 52.99±4.66 b | 29.76±3.02 a | 68.09±11.20 ab | 54.42±13.12 b | 31.94±10.08 b | ||
| R3 | 31.51±3.44 b | 49.92±1.42 b | 24.37±0.78 c | 65.21±9.47 b | 57.41±15.70 b | 29.50±4.58 b | ||
| R4 | 27.76±3.75 b | 43.96±0.44 c | 26.91±0.91 ab | 58.31±10.08 b | 50.98±17.41 b | 30.77±3.50 b | ||
| R5 | 19.26±1.95 c | 44.91±2.57 c | 26.45±5.27 bc | 60.12±4.68 b | 49.75±25.35 b | 18.28±4.27 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 26.51±1.26 | 48.86±2.83 | 25.94±0.60 | 60.33±3.88 | 52.73±16.31 | 25.85±2.78 | ||
| F值F value | ||||||||
| N | 28.15* | 18.93* | 13.49 | 23.78* | 0.49 | 11.97 | ||
| R | 23.70** | 54.94** | 21.75** | 15.29** | 12.83** | 28.62** | ||
| N×R | 3.06* | 8.76** | 1.67 | 1.47 | 2.52 | 3.71* | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | 拔节期 JS | 齐穗期 FHS | 成熟期 MS | ||||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 21.89±0.79 d | 73.96±0.44 e | 46.50±1.76 c | 84.46±1.24 c | 102.81±1.85 d | |||
| R1 | 31.89±3.42 a | 115.27±0.68 b | 85.91±2.55 a | 132.56±3.24 a | 166.55±0.84 a | |||
| R2 | 28.78±0.51 ab | 119.80±0.63 a | 81.95±2.68 a | 141.34±3.99 a | 173.53±0.57 a | |||
| R3 | 25.88±0.71 bc | 100.27±0.37 c | 76.29±0.17 ab | 113.70±0.95 b | 146.34±0.60 b | |||
| R4 | 26.34±0.58 bc | 100.07±0.31 c | 83.29±1.55 a | 116.27±1.30 b | 147.74±1.58 b | |||
| R5 | 24.02±0.55 cd | 85.53±0.15 d | 67.11±1.45 b | 96.35±1.65 c | 126.14±0.60 c | |||
| 平均 Average | 26.47±0.58 | 99.15±0.22 | 73.51±0.73 | 114.11±1.26 | 143.85±0.13 | |||
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 21.89±0.79 c | 73.96±0.44 e | 46.50±1.76 d | 84.46±1.24 c | 102.81±1.85 e | |||
| R1 | 29.89±7.20 a | 134.08±2.29 ab | 115.86±27.19 a | 172.53±45.07 a | 198.01±4.78 a | |||
| R2 | 25.60±2.08 b | 136.58±5.48 a | 96.53±14.78 b | 133.01±18.98 b | 198.28±16.39 a | |||
| R3 | 25.49±1.08 b | 130.80±2.54 b | 96.72±12.86 b | 132.82±16.81 b | 184.66±5.60 b | |||
| R4 | 25.09±0.95 b | 119.88±0.98 c | 86.08±13.82 bc | 120.03±17.07 b | 177.56±4.48 c | |||
| R5 | 26.36±0.75 ab | 108.66±6.56 d | 79.39±6.27c | 121.03±24.13 b | 153.39±7.47 d | |||
| 平均 Average | 25.72±1.34 | 117.33±1.36 | 86.84±5.13 | 127.31±19.95 | 169.12±3.46 | |||
| F值F value | ||||||||
| N | 0.49 | 430.47** | 25.09* | 1.17 | 139.47** | |||
| R | 8.57** | 320.26** | 17.30** | 27.93** | 146.04** | |||
| N×R | 0.89 | 20.27** | 1.53 | 4.08* | 6.57** | |||
| 处理 Treatment | 氮素转运量 N translation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮素转运率 N translation efficiency/% | 氮素贡献率 N contribution rate/% | 穗部氮素增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 11.75±0.98 b | 21.97±0.61 b | 38.27±2.85 bc | 68.93±1.61 a | 15.89±1.40 bc | 29.71±0.90 a | 52.07±0.36 e | |
| R1 | 21.31±0.26 a | 28.09±0.67 ab | 43.13±0.26 ab | 54.79±0.77 bc | 18.49±0.17 ab | 24.36±0.44 ab | 83.39±3.29 b | |
| R2 | 24.54±0.07 a | 34.29±3.05 a | 45.64±0.07 a | 58.25±2.02 ab | 20.48±0.10 a | 28.63±2.56 a | 91.02±0.85 a | |
| R3 | 15.34±0.95 b | 26.40±0.97 ab | 37.85±1.52 bc | 55.82±2.14 bc | 15.30±1.01 bc | 26.33±0.88 ab | 74.39±0.41 c | |
| R4 | 14.45±0.45 b | 27.82±1.78 ab | 35.51±0.60 c | 56.47±3.19 bc | 14.44±0.46 c | 27.80±1.80 a | 73.73±0.80 c | |
| R5 | 14.00±1.06 b | 17.72±0.82 c | 39.74±1.65 abc | 47.69±1.38 c | 16.36±1.22 bc | 20.72±0.93 b | 61.50±0.67 d | |
| 平均 Average | 16.90±0.09 | 26.05±0.81 | 40.03±0.07 | 56.99±0.96 | 16.83±0.05 | 26.26±0.65 | 72.68±0.38 | |
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 11.75±0.98 d | 21.97±0.61 bc | 38.27±2.85 b | 68.93±1.61 a | 15.89±1.40 bc | 29.71±0.90 a | 52.07±0.36 e | |
| R1 | 41.49±9.87 a | 37.23±26.43 a | 58.24±4.24 a | 47.74±16.13 bc | 30.86±6.80 a | 27.58±19.13 ab | 104.19±5.09 b | |
| R2 | 23.23±2.80 b | 22.48±19.47 bc | 43.83±3.24 b | 38.19±27.55 de | 17.08±2.76 bc | 16.86±15.03 c | 110.98±6.69 a | |
| R3 | 25.55±2.13 b | 27.91±19.06 abc | 51.13±2.85 a | 45.45±18.55 cd | 19.53±1.56 b | 21.23±14.18 bc | 105.30±1.93 a | |
| R4 | 17.05±0.70 c | 20.21±20.76 c | 38.78±1.73 b | 33.85±26.09 e | 14.22±0.50 c | 16.85±17.25 c | 94.79±1.92 c | |
| R5 | 18.47±7.45 c | 31.47±26.51 ab | 40.62±15.04 b | 56.51±20.24 ab | 16.89±6.53 bc | 28.09±22.03 c | 82.30±7.30 d | |
| 平均 Average | 22.92±3.31 | 26.88±18.67 | 45.15±3.47 | 48.44±17.93 | 19.08±2.38 | 23.39±14.68 | 91.61±0.64 | |
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 9.79 | 0.00 | 6.44 | 1.19 | 2.21 | 0.11 | 1096.16** | |
| R | 28.31** | 1.75 | 7.14** | 8.56** | 10.01** | 1.51 | 133.08** | |
| N×R | 9.28** | 2.84 | 3.66* | 1.94 | 6.31** | 3.05* | 10.94** | |
表6 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻氮素转运的影响
Table 6 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on N translocation in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 氮素转运量 N translation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮素转运率 N translation efficiency/% | 氮素贡献率 N contribution rate/% | 穗部氮素增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | |||
| N1 | ||||||||
| R0 | 11.75±0.98 b | 21.97±0.61 b | 38.27±2.85 bc | 68.93±1.61 a | 15.89±1.40 bc | 29.71±0.90 a | 52.07±0.36 e | |
| R1 | 21.31±0.26 a | 28.09±0.67 ab | 43.13±0.26 ab | 54.79±0.77 bc | 18.49±0.17 ab | 24.36±0.44 ab | 83.39±3.29 b | |
| R2 | 24.54±0.07 a | 34.29±3.05 a | 45.64±0.07 a | 58.25±2.02 ab | 20.48±0.10 a | 28.63±2.56 a | 91.02±0.85 a | |
| R3 | 15.34±0.95 b | 26.40±0.97 ab | 37.85±1.52 bc | 55.82±2.14 bc | 15.30±1.01 bc | 26.33±0.88 ab | 74.39±0.41 c | |
| R4 | 14.45±0.45 b | 27.82±1.78 ab | 35.51±0.60 c | 56.47±3.19 bc | 14.44±0.46 c | 27.80±1.80 a | 73.73±0.80 c | |
| R5 | 14.00±1.06 b | 17.72±0.82 c | 39.74±1.65 abc | 47.69±1.38 c | 16.36±1.22 bc | 20.72±0.93 b | 61.50±0.67 d | |
| 平均 Average | 16.90±0.09 | 26.05±0.81 | 40.03±0.07 | 56.99±0.96 | 16.83±0.05 | 26.26±0.65 | 72.68±0.38 | |
| N2 | ||||||||
| R0 | 11.75±0.98 d | 21.97±0.61 bc | 38.27±2.85 b | 68.93±1.61 a | 15.89±1.40 bc | 29.71±0.90 a | 52.07±0.36 e | |
| R1 | 41.49±9.87 a | 37.23±26.43 a | 58.24±4.24 a | 47.74±16.13 bc | 30.86±6.80 a | 27.58±19.13 ab | 104.19±5.09 b | |
| R2 | 23.23±2.80 b | 22.48±19.47 bc | 43.83±3.24 b | 38.19±27.55 de | 17.08±2.76 bc | 16.86±15.03 c | 110.98±6.69 a | |
| R3 | 25.55±2.13 b | 27.91±19.06 abc | 51.13±2.85 a | 45.45±18.55 cd | 19.53±1.56 b | 21.23±14.18 bc | 105.30±1.93 a | |
| R4 | 17.05±0.70 c | 20.21±20.76 c | 38.78±1.73 b | 33.85±26.09 e | 14.22±0.50 c | 16.85±17.25 c | 94.79±1.92 c | |
| R5 | 18.47±7.45 c | 31.47±26.51 ab | 40.62±15.04 b | 56.51±20.24 ab | 16.89±6.53 bc | 28.09±22.03 c | 82.30±7.30 d | |
| 平均 Average | 22.92±3.31 | 26.88±18.67 | 45.15±3.47 | 48.44±17.93 | 19.08±2.38 | 23.39±14.68 | 91.61±0.64 | |
| F值 F value | ||||||||
| N | 9.79 | 0.00 | 6.44 | 1.19 | 2.21 | 0.11 | 1096.16** | |
| R | 28.31** | 1.75 | 7.14** | 8.56** | 10.01** | 1.51 | 133.08** | |
| N×R | 9.28** | 2.84 | 3.66* | 1.94 | 6.31** | 3.05* | 10.94** | |
| 处理 Treatment | 氮素收获指数 NHI/% | 氮素干物质 生产效率NBPE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷 生产效率NGPE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥偏生产力 NPP /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥农学利用率 NAE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥表观利用率 NAUE /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | ||||||
| R0 | 71.95±0.87 a | 145.60±0.66 a | 92.33±1.23 a | - | - | - |
| R1 | 69.21±0.25 ab | 104.27±0.14 d | 70.02±0.65 d | 77.74±0.74 a | 14.47±1.51 a | 42.49±1.69 a |
| R2 | 69.04±0.23 ab | 100.52±0.08 d | 68.05±0.57 d | 78.72±0.44 a | 15.45±1.55 a | 47.15±0.88 a |
| R3 | 68.52±0.52 b | 116.62±0.04 c | 78.07±2.60 c | 76.17±2.37 b | 12.89±3.37 b | 29.02±1.17 b |
| R4 | 67.74±0.75 b | 116.13±0.06 c | 77.23±1.91 c | 76.05±1.29 b | 12.78±0.26 b | 29.95±2.29 b |
| R5 | 67.80±0.39 b | 125.44±1.55 b | 84.88±1.30 b | 71.38±1.20 c | 8.11±0.71 c | 15.56±1.18 c |
| 平均 Average | 69.05±0.17 | 118.10±0.36 | 78.43±0.31 | 76.01±0.33 | 12.74±1.25 | 32.83±1.41 |
| N2 | ||||||
| R0 | 71.95±0.87 a | 145.60±0.66 a | 92.33±1.23 a | - | - | - |
| R1 | 67.72±0.50 b | 92.97±1.37 c | 60.20±1.57 e | 66.20±0.56 ab | 13.47±1.44 ab | 52.89±2.98 a |
| R2 | 69.07±3.76 ab | 104.45±8.84 b | 60.87±4.86 de | 66.75±0.14 a | 14.02±0.92 a | 53.04±8.08 a |
| R3 | 70.86±2.07 a | 103.61±0.70 b | 63.42±1.99 cd | 65.03±0.13 b | 12.29±0.99 b | 45.48±2.11 b |
| R4 | 67.54±1.64 b | 110.59±0.44 b | 65.90±1.59 c | 64.98±0.18 b | 12.25±0.76 b | 41.53±1.57 b |
| R5 | 70.94±5.10 a | 107.03±16.90 b | 71.84±4.01 b | 61.11±0.44 c | 8.38±0.65c | 28.10±5.07 c |
| 平均 Average | 69.68±1.36 | 110.71±1.15 | 69.09±0.93 | 64.81±0.05 | 12.08±0.93 | 44.21±1.09 |
| F值 F value | ||||||
| N | 0.43 | 63.85* | 377.60** | 4528.56** | 8.80 | 53.69* |
| R | 3.09* | 49.29** | 103.00** | 32.23** | 32.12** | 51.05** |
| N×R | 1.12 | 3.00* | 6.47** | 0.51 | 0.51 | 1.26 |
表7 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥与常规氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用的影响
Table 7 Effects of slow-release urea combined with conventional urea on N use efficiency in mechanically-transplanted rice under different N application rates.
| 处理 Treatment | 氮素收获指数 NHI/% | 氮素干物质 生产效率NBPE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷 生产效率NGPE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥偏生产力 NPP /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥农学利用率 NAE /( kg·kg-1) | 氮肥表观利用率 NAUE /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | ||||||
| R0 | 71.95±0.87 a | 145.60±0.66 a | 92.33±1.23 a | - | - | - |
| R1 | 69.21±0.25 ab | 104.27±0.14 d | 70.02±0.65 d | 77.74±0.74 a | 14.47±1.51 a | 42.49±1.69 a |
| R2 | 69.04±0.23 ab | 100.52±0.08 d | 68.05±0.57 d | 78.72±0.44 a | 15.45±1.55 a | 47.15±0.88 a |
| R3 | 68.52±0.52 b | 116.62±0.04 c | 78.07±2.60 c | 76.17±2.37 b | 12.89±3.37 b | 29.02±1.17 b |
| R4 | 67.74±0.75 b | 116.13±0.06 c | 77.23±1.91 c | 76.05±1.29 b | 12.78±0.26 b | 29.95±2.29 b |
| R5 | 67.80±0.39 b | 125.44±1.55 b | 84.88±1.30 b | 71.38±1.20 c | 8.11±0.71 c | 15.56±1.18 c |
| 平均 Average | 69.05±0.17 | 118.10±0.36 | 78.43±0.31 | 76.01±0.33 | 12.74±1.25 | 32.83±1.41 |
| N2 | ||||||
| R0 | 71.95±0.87 a | 145.60±0.66 a | 92.33±1.23 a | - | - | - |
| R1 | 67.72±0.50 b | 92.97±1.37 c | 60.20±1.57 e | 66.20±0.56 ab | 13.47±1.44 ab | 52.89±2.98 a |
| R2 | 69.07±3.76 ab | 104.45±8.84 b | 60.87±4.86 de | 66.75±0.14 a | 14.02±0.92 a | 53.04±8.08 a |
| R3 | 70.86±2.07 a | 103.61±0.70 b | 63.42±1.99 cd | 65.03±0.13 b | 12.29±0.99 b | 45.48±2.11 b |
| R4 | 67.54±1.64 b | 110.59±0.44 b | 65.90±1.59 c | 64.98±0.18 b | 12.25±0.76 b | 41.53±1.57 b |
| R5 | 70.94±5.10 a | 107.03±16.90 b | 71.84±4.01 b | 61.11±0.44 c | 8.38±0.65c | 28.10±5.07 c |
| 平均 Average | 69.68±1.36 | 110.71±1.15 | 69.09±0.93 | 64.81±0.05 | 12.08±0.93 | 44.21±1.09 |
| F值 F value | ||||||
| N | 0.43 | 63.85* | 377.60** | 4528.56** | 8.80 | 53.69* |
| R | 3.09* | 49.29** | 103.00** | 32.23** | 32.12** | 51.05** |
| N×R | 1.12 | 3.00* | 6.47** | 0.51 | 0.51 | 1.26 |
| 指标 Index | 总干物质量 Dry matter amount | 总氮素 积累量 N accumulation | 氮肥农学 利用率 NAE | 氮肥表观 利用率 NAUE | 每穗实粒数 Spikelet number panicle | 产量 Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮素积累量 N accumulation amount | ||||||
| 拔节期 JS | 0.70** | 0.85** | 0.39* | 0.64** | 0.70** | 0.83** |
| 齐穗期 FHS | 0.56** | 0.77** | 0.40* | 0.65** | 0.60** | 0.73** |
| 成熟期 MS | 0.90** | 1.00** | 0.50** | 0.97** | 0.78** | 0.91** |
| 结实期氮素转运量 N translocation amount | ||||||
| 茎鞘 Stem-sheath | 0.42* | 0.69** | 0.38* | 0.61** | 0.54** | 0.59** |
| 叶片 Leaf | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
| 结实期净光合速率 Pn | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 0.77** | 0.89** | 0.48** | 0.75** | 0.72** | 0.89** |
| 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 0.42** | 0.62** | 0.72** | 0.38* | 0.49** | 0.78** |
| 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 0.58** | 0.72** | 0.56** | 0.52** | 0.50** | 0.78** |
| 拔节-齐穗光合势 Photosynthetic potential | 0.71** | 0.86** | 0.36* | 0.65** | 0.78** | 0.82** |
| 拔节-齐穗群体生长率 Crop growth rate | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.19 |
表8 氮素积累转运、光合生产与干物质量、氮素利用特征及产量的相关性
Table 8 Correlation coefficients between N accumulation translocation, photosynthetic production and N use efficiency, dry matter, and yield.
| 指标 Index | 总干物质量 Dry matter amount | 总氮素 积累量 N accumulation | 氮肥农学 利用率 NAE | 氮肥表观 利用率 NAUE | 每穗实粒数 Spikelet number panicle | 产量 Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮素积累量 N accumulation amount | ||||||
| 拔节期 JS | 0.70** | 0.85** | 0.39* | 0.64** | 0.70** | 0.83** |
| 齐穗期 FHS | 0.56** | 0.77** | 0.40* | 0.65** | 0.60** | 0.73** |
| 成熟期 MS | 0.90** | 1.00** | 0.50** | 0.97** | 0.78** | 0.91** |
| 结实期氮素转运量 N translocation amount | ||||||
| 茎鞘 Stem-sheath | 0.42* | 0.69** | 0.38* | 0.61** | 0.54** | 0.59** |
| 叶片 Leaf | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
| 结实期净光合速率 Pn | ||||||
| 齐穗期 FHS | 0.77** | 0.89** | 0.48** | 0.75** | 0.72** | 0.89** |
| 齐穗后15 d 15 d after FHS | 0.42** | 0.62** | 0.72** | 0.38* | 0.49** | 0.78** |
| 齐穗后30 d 30 d after FHS | 0.58** | 0.72** | 0.56** | 0.52** | 0.50** | 0.78** |
| 拔节-齐穗光合势 Photosynthetic potential | 0.71** | 0.86** | 0.36* | 0.65** | 0.78** | 0.82** |
| 拔节-齐穗群体生长率 Crop growth rate | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.19 |
| [1] | Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B.Current status and challenges of rice production in China.Plant Prod Sci, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [2] | 朱德峰, 陈惠哲. 水稻机插秧发展与粮食安全.中国稻米, 2009(6): 4-7. |
| Zhu D F, Chen H Z.The development and food security of mechanical-transplanted rice.China Rice, 2009(6): 4-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 刘利, 雷小龙, 黄光忠, 刘代银, 任万军. 机械化播栽对杂交稻氮素积累分配及碳氮比的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4): 831-844. |
| Liu L, Lei X L, Huang G Z, Liu D Y, Ren W J.Influences of mechanical sowing and transplanting on nitrogen accumulation, distribution and C/N of hybrid rice cultivars.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2014, 20(4): 831-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 雷小龙, 刘利, 刘波, 黄光忠, 郭翔, 马荣朝,任万军. 机械化种植对杂交籼稻F优498产量构成与株型特征的影响. 作物学报, 2014, 40(4): 719-730. |
| Lei X L, Liu L, Liu B, Huang G Z, Guo X, Ma R Z, Ren W J.Effects of mechanized planting methods on yield components and plant type characteristics of indica hybrid rice F you 498.Acta Agron Sin, 2014, 40(4): 719-730. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 孙永健, 马均, 孙园园, 杨志远, 徐徽, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 施氮量和株距对机插杂交稻结实期养分转运和产量的影响. 核农学报, 2014, 28(8): 1510-1520. |
| Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun Y Y, Yang Z Y, Xu H, Xiong H, Xu F X.Effects of nitrogen application rates and plant spacing on nutrient translocation during filling stage and yield of mechanical-transplanted hybrid rice.J Nucl Agric Sci, 2014, 28(8): 1510-1520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 霍晓玲, 周虹, 袁勇, 胡剑锋, 任万军. 秧板处理及育秧方式对机插杂交稻秧苗生长、产量及育秧成本的影响. 杂交水稻, 2014, 29(2): 51-56. |
| Huo X L, Zhou H, Yuan Y, Hu J F, Ren W J.Effects of Seedbed-preparing and seedling-raising methods on seedling growth, grain yield and seedling-raising cost in machine-transpianted hybrid rice.Hybrid Rice, 2014, 29(2): 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 邢晓鸣, 李小春, 丁艳锋, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强, 李刚华, 魏广彬. 缓控释肥组配对机插常规粳稻群体物质生产和产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(24): 4892-4902. |
| Xing X M, Li X C, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q, Li G H, Wei G B.Effects of types of controlled released nitrogen and fertilization modes on yield and dry mass production.Sci Agric Sin, 2015, 48(24): 4892-4902. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 刘树金, 杨志远, 程洪彪, 贾现文, 马均. 水分管理和氮肥运筹对水稻养分吸收、转运及分配的影响. 作物学报, 2011, 37(12): 2221-2232. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Liu S J, Yang Z Y, Cheng H B, Jia X W, Ma J.Effects of water management and nitrogen application strategies on nutrient absorption, transfer, and distribution in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(12): 2221-2232. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 黎远文, 冯兴, 成美琴. 测土配方施肥对水稻产量及化肥利用率的影响. 南方农业, 2014, 8(19): 25-27. |
| Li Y W, Feng X, Cheng M Q.Effects of testing soil for formulated fertilization on rice grain yield and chemical fertilizer use efficiency.South China Agric, 2014, 8(19): 25-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Wang L J, Sun M Q, Niu D.Physiology and biochemistry changes ofEuphorbia pulcherrima during leaf color transformation. J Northeast Agric Univ: English Ed, 2010, 17(2): 48-54. |
| [11] | 欧立军. 水稻叶色突变体的高光合特性. 作物学报, 2011, 37(10): 1860-1867. |
| Ou L J.High Photosynthetic efficiency of leaf colour mutant of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(10): 1860-1867. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 郑圣先, 聂军, 熊金英, 肖剑, 罗尊长, 易国英. 控释肥料提高氮素利用率的作用及对水稻效应的研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2001, 7(1): 11-16. |
| Zheng S X, Nie J, Xiong J Y, Xiao J, Luo Z C, Yi G Y.Study on role of controlled release fertilizer in increasing the efficiency of nitrogen utilization and rice yield.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2001, 7(1): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 谢春生, 唐拴虎, 徐培智, 张发宝, 陈建生. 一次性施用控释肥对水稻植株生长及产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006, 12(2): 2177-2182. |
| Xie C S, Tang S H, Xu P Z, Zhang F B, Chen J S.Effects of single basal application of controlled-release fertilizers on growth and yield of rice.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2006, 12(2): 2177-2182. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 李贵勇, 高森, 栾鸭红, 资月娥, 常小详, 杨翠玲, 何兴林, 相罕章, 黄军, 夏琼梅, 龙瑞平, 朱海平, 杨从党. 控释肥用量对水稻干物质积累和产量的影响. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(4): 88-90. |
| Li G Y, Gao S, Luan Y H, Zi Y E, Chang X X, Yang C L, He X L, Xiang H Z, Huang J, Xia Q M, Long R P, Zhu H P, Yang C D.Effects of different controlled-release fertilizer amount on dry matter production and grain yield of rice.China Rice, 2015, 21(4): 88-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 彭玉, 孙永健, 蒋明金, 徐徽, 秦俭, 杨志远, 马均. 不同水分条件下缓/控释氮肥对水稻干物质量和氮素吸收、运转及分配的影响. 作物学报, 2014, 40(5): 859-870. |
| Peng Y, Sun Y J, Jiang M J, Xu H, Qin J, Yang Z Y, Ma J.Effects of water management and slow/controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on biomass and nitrogen accumulation, translocation, and distribution in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2014, 40(5): 859-870. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 田小海,马国辉,杨令芝,肖宇, 王晓玲, 徐凤英, 吴晨阳.缓释氮肥对超级杂交稻后期生长与生理功能的影响.杂交水稻. 2010,25(5): 64-69. |
| Tian X H, Ma G H, Yang L Z,Xiao Y, Wang X L, Xu F Y, Wu C Y.Effects of slow release nitrogen fertilizer on growth and physiological functions in the late stage of super hybrid rice.Hybrid Rice, 2010,25(5): 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李玥, 李应洪, 赵建红, 孙永健, 徐徽, 严奉君, 谢华英, 马均. 缓控释氮肥对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响. 浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2015, 41(6): 673-684. |
| Li Y, Li Y H, Zhao J H, Sun Y J, Xu H, Yan F J, Xie H Y, Ma J.Effects of slow-and controlled-release fertilizer on nitrogen utilization characteristics and yield of machine-transplanted rice.J Zhejiang Univ, 2015, 41(6): 673-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 李杰, 张洪程, 常勇, 龚金龙, 郭振华, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉. 不同种植方式水稻高产栽培条件下的光合物质生产特征研究. 作物学报, 2011, 37(7): 1235-1248. |
| Li J, Zhang H C, Chang Y, Gong J L, Guo Z H, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H.Characteristics of photosynthesis and matter production of rice with different planting methods under high-yielding cultivation condition.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(7): 1235-1248. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | R A Fisher, D Rees, K D Sayre, Z M Lu, A G Condon, A Larque Saavedra.Wheat yield progress associated with higher stomatal conductance and photosynthetic rate, and cooler canopies.Crop Sci, 1998, 38(6): 1467-1475. |
| [20] | 杨建昌, 杜永, 吴长付, 刘立军, 王志琴, 朱庆森. 超高产粳型水稻生长发育特性的研究. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(7): 1336-1345. |
| Yang J C, Du Y, Wu Z F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S.Growth and development characteristics of super-high-yielding mid-season japonica rice.Sci Agric Sin, 2006, 39(7): 1336-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 李刚华, 张国发, 陈功磊, 王绍华, 凌启鸿, 丁艳锋. 超高产常规粳稻宁粳1号和宁粳3号群体特征及对氮的响应. 作物学报, 2009, 35(6): 1106-1114. |
| Li G H, Zhang G F, Chen G L, Wang S H, Ling Q H, Ding Y F.Population characteristics of super japonica rice Ningjing 1 and Ningjing 3 and its responses to nitrogen.Acta Agron Sin, 2009, 35(6): 1106-1114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 敖和军, 王淑红, 邹应斌, 彭少兵, 唐启源, 方远祥, 肖安民, 陈玉梅, 熊昌明. 超级杂交稻干物质生产特点与产量稳定性研究. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(7): 1927-1936. |
| Ao H J, Wang S H, Zou Y B, Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Fang Y X, Xiao A M, Chen Y M, Xiong C M.Study on yield stability and dry matter characteristics of super hybrid rice.Sci Agric Sin, 2008, 41(7): 1927-1936. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Huang M, Zou Y, Jiang P, Xia B, Md I, Ao H J.Relationship between grain yield and yield components in super hybrid rice.Agric Sci China, 2011, 10(10): 1537-1544. |
| [24] | Zhang H, Chen T T, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H.Performance in grain yield and physiological traits of rice in the Yangtze River Basin of China during the last 60 yr.J Integr Agric, 2013, 12(1): 57-66. |
| [25] | 韦还和, 姜元华, 赵珂, 许俊伟, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. 甬优系列杂交稻品种的超高产群体特征. 作物学报, 2013, 39(12): 2201-2210. |
| Wei H H, Jiang Y H, Zhao K, Xu J W, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y.Characteristics of super-high yield population in Yongyou series of hybrid rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2013, 39(12): 2201-2210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张洪程, 赵品恒, 孙菊英, 吴桂成, 徐军, 端木银熙, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. 机插杂交粳稻超高产形成群体特征. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(2): 39-44. |
| Zhang H C, Zhao P H, Sun J Y, Wu G C, Xu J, Duan Mu Y X, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y. Population characteristics of super high yield formation of mechanical transplanted japonica hybrid rice.Trans CSAE, 2012, 28(2): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 胡春花, 罗革彬, 曾建华, 潘孝忠. 不同类型缓释氮肥对水稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(15): 174-177. |
| Hu C H, Luo G B, Ceng J H, Pan X Z.Influence of different types of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer on rice yield and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2011, 27(15): 174-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 李华, 徐长青, 李世峰, 钱宗华. 不同氮肥管理对机插水稻产量及氮肥利用的影响. 贵州农业科学, 2008, 36(5): 39-41. |
| Li H, Xu Z Q, Li S F, Qian Z H.Effects of different nitrogen management on yield and nitrogen utilization of machine-transplanted rice.Guizhou Agric Sci, 2008, 36(5): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 马均, 朱庆森, 马文波, 田彦华, 杨建昌, 周开达. 重穗型水稻光合作用、物质积累与运转的研究. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36(4): 375-381. |
| Ma J, Zhu Q S, Ma W B, Tian Y H, Yang J C, Zhou K D.Studies on the photosynthetic characteristics and accumulation and transformation of assimilation product in heavy panicle type of rice.Sci Agric Sin, 2003, 36(4): 375-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 吴文革, 张洪程, 钱银飞, 陈烨, 徐军, 吴桂成, 翟超群, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 超级杂交中籼水稻物质生产特性分析. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(3): 287-293. |
| Wu W G, Zhang H C, Qian Y F, Chen Y, Xu J, Wu G C, Zhai C Q, Huo Z Y, Dai Q G.Analysis on dry matter production characteristics of middle-season indica super hybrid rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(3): 287-293. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 李敏, 张洪程, 杨雄, 葛梦婕, 马群, 魏海燕, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲. 水稻高产氮高效型品种的物质积累与转运特性. 作物学报, 2013, 39(1): 101-109. |
| Li M, Zhang H C, Yang X, Ge M J, Ma Q, Wei H Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K.Characteristics of dry matter accumulation and translocation in rice cultivars with high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency.Acta Agron Sin, 2013, 39(1): 101-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 霍中洋,杨雄,张洪程,葛梦婕, 马群, 李敏, 戴其根, 许轲, 魏海燕, 李国业, 朱聪聪, 王亚江, 颜希亭. 不同氮肥群体最高生产力水稻品种各器官的干物质和氮素的积累与转运. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012,18(5): 1035-1045. |
| Huo Z Y, Yang X, Zhang H C, Ge M J, Ma Q, Li M, Dai Q G, Xu K, Wei H Y, Li G Y, Zhu C C, Wang Y J, Yan X T.Accumulation and translocation of dry matter and nitrogen nutrition in organs of rice cultivars with different productivity levels.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2012, 18(5): 1035-1045. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [9] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [10] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [11] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [12] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [13] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [14] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [15] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||