
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 20-27.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8017
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yufei DENG1,2, Minghao LIU2, Dan WANG1, Shimin ZUO3, Houxiang KANG2,*( ), Guoliang WANG2,*(
), Guoliang WANG2,*( )
)
Received:2018-02-08
Revised:2018-06-27
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2019-01-10
Contact:
Houxiang KANG, Guoliang WANG
邓雨飞1,2, 刘明浩2, 王丹1, 左示敏3, 康厚祥2,*( ), 王国梁2,4,*(
), 王国梁2,4,*( )
)
通讯作者:
康厚祥,王国梁
CLC Number:
Yufei DENG, Minghao LIU, Dan WANG, Shimin ZUO, Houxiang KANG, Guoliang WANG. Origin, Distribution and Sequence Diversity of Rice Blast Resistance Locus LABR_64 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(1): 20-27.
邓雨飞, 刘明浩, 王丹, 左示敏, 康厚祥, 王国梁. 抗稻瘟病位点LABR_64的起源及其分布和序列多样性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 20-27.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8017
| 引物名称 Primer name | 目的基因 Target gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物 Backward sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| 引物1 Primer 1 | LABR64-1 | CGGAGAATAACTCCTTCGG | AAGGCTTGTCTTTCCAAAA |
| 引物2 Primer 2 | LABR64-2 | CAAATGTTAGACACGGAAAT | CAACTTGTATGGTGGAACTG |
| 引物3 Primer 3 | LABR_64 | CAGCCATGGCAGCCATATGACTG | CAGAGGAAGATCCTCCTCTCC |
| 测序引物1 Sequencing primer 1 | LABR64-1 | GCCTGTAGGTTTTGGAAAG | GAGGGAGTGCTGTAATAGATAAA |
| 测序引物2 Sequencing primer 2 | LABR64-2 | AGTTGAAGGAAATGTTGAGG | TTGGTAATGAAATCCGGTAA |
Table 1 Sequences of the primers used in this study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 目的基因 Target gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物 Backward sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| 引物1 Primer 1 | LABR64-1 | CGGAGAATAACTCCTTCGG | AAGGCTTGTCTTTCCAAAA |
| 引物2 Primer 2 | LABR64-2 | CAAATGTTAGACACGGAAAT | CAACTTGTATGGTGGAACTG |
| 引物3 Primer 3 | LABR_64 | CAGCCATGGCAGCCATATGACTG | CAGAGGAAGATCCTCCTCTCC |
| 测序引物1 Sequencing primer 1 | LABR64-1 | GCCTGTAGGTTTTGGAAAG | GAGGGAGTGCTGTAATAGATAAA |
| 测序引物2 Sequencing primer 2 | LABR64-2 | AGTTGAAGGAAATGTTGAGG | TTGGTAATGAAATCCGGTAA |
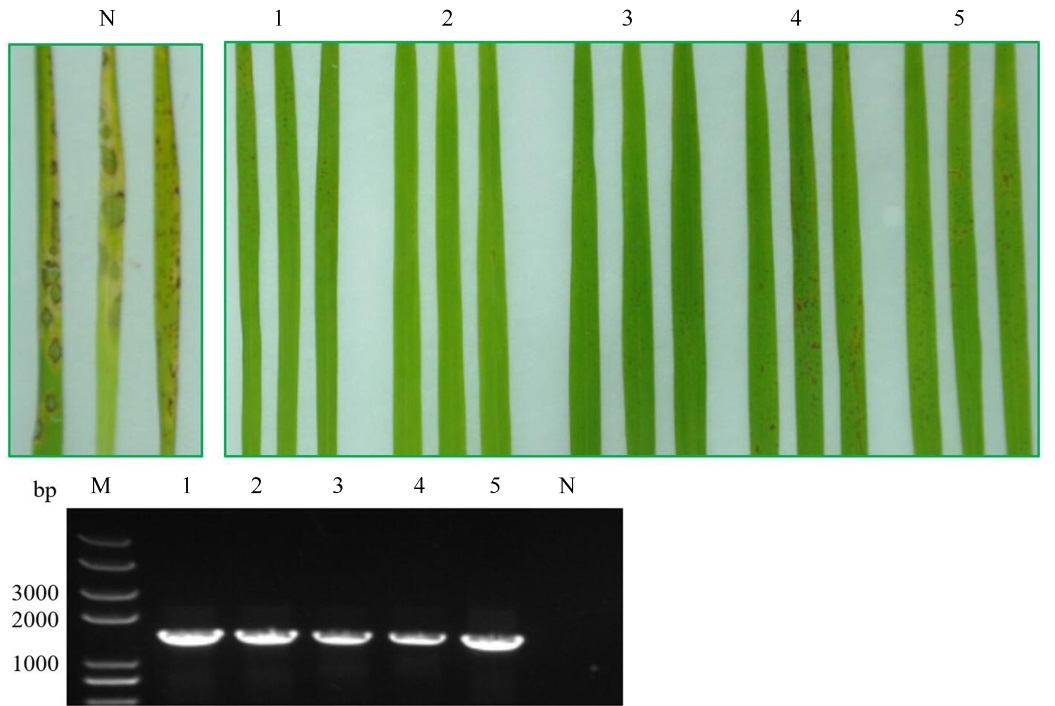
Fig. 1. Blast resistance evaluation of the rice varieties which contain LABR_64 locus. M, 5000 bp marker; 1, Binulawan(indica, resistance level is 0); 2, IR36(indica, 0); 3, IR8(indica, 0); 4, Carolina Gold(japonica, 1); 5, Iguape Cateto(japonica, 1); N, Nipponbare.
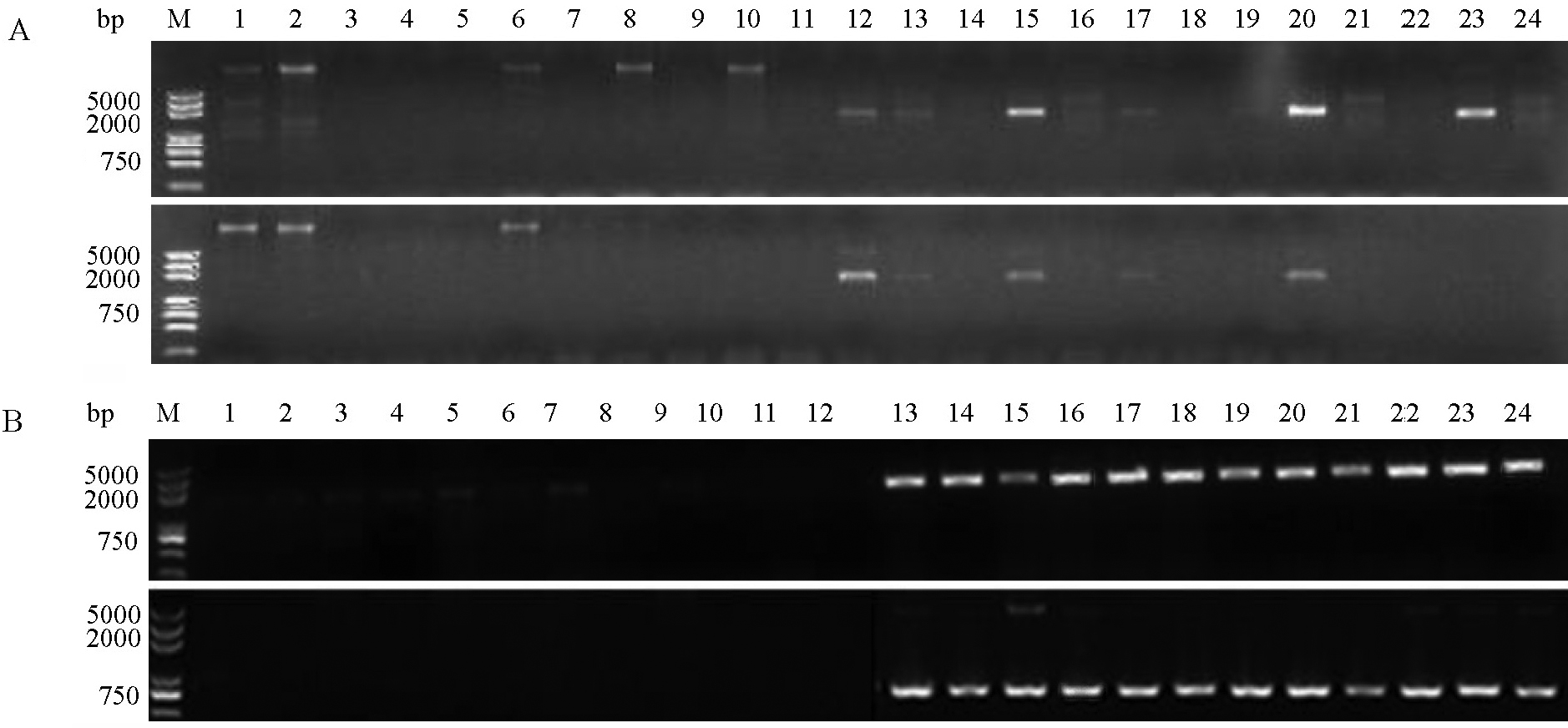
Fig. 2. Distribution of LABR_64 in indica and japonica rice. A, Distribution of LABR_64-1(above), LABR_64-2(below) in resistant and susceptible indica rice. M, 5000 bp marker;Lanes 1-12, Susceptible cultivars; Lanes 13-24, Resistant cultivars. B, Distribution of LABR_64-1(above), LABR_64-2(below) in resistant and susceptible japonica rice. M, 5000 bp Marker;Lanes 1-12, Susceptible cultivars; Lanes 13-24, Resistant cultivars.
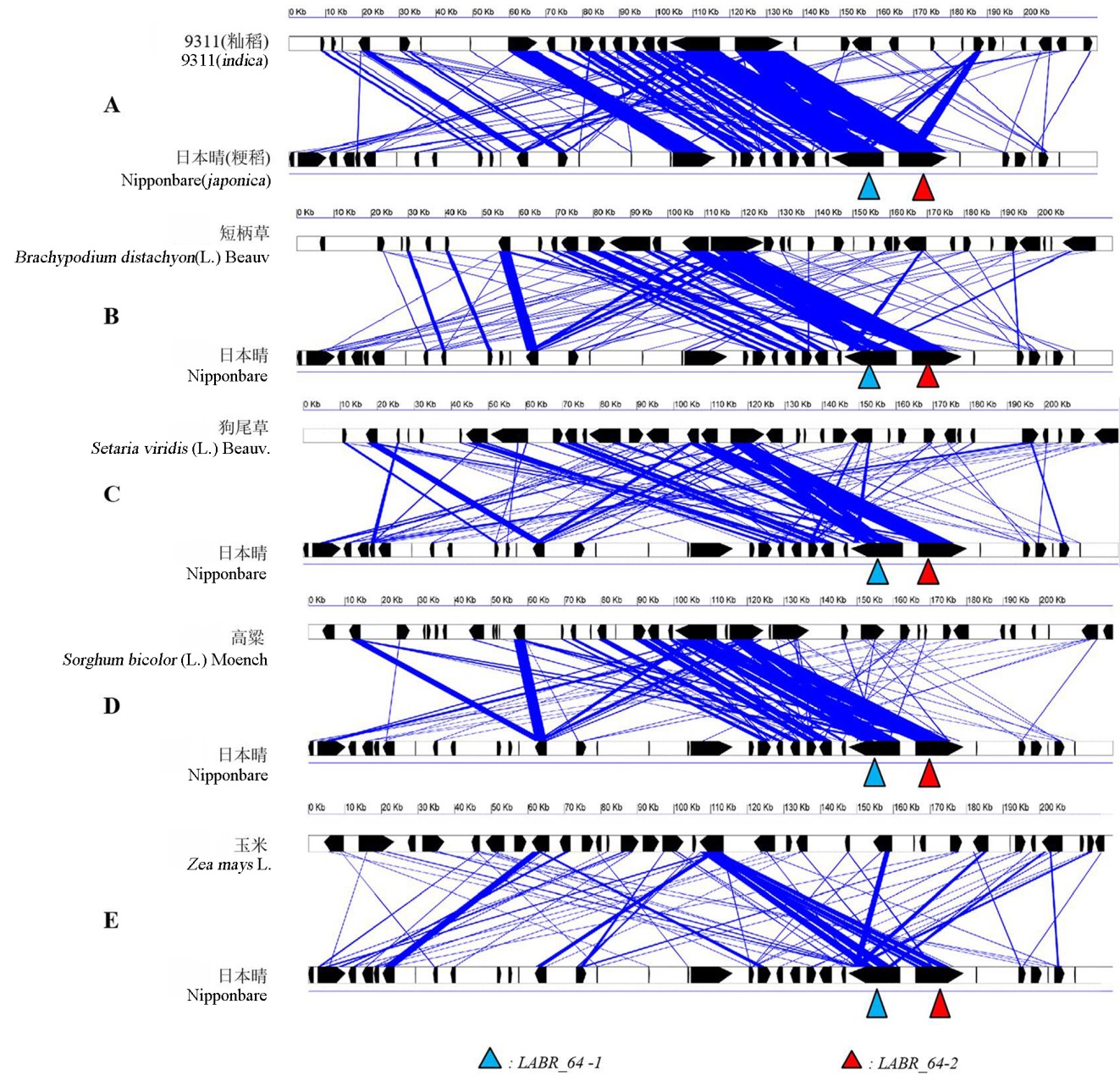
Fig. 5. Microsynteny of the LABR_64 orthologous regions in different monocotyledons. A, Nipponbare and 9311 (Nipponbare does not contain LABR_64, the triangles represent the LABR64-1 and LABR64-2 genes from the resistant japonica varieties). B, Nipponbare and Brachypodium distachyon; C, Nipponbare and Setaria viridis; D, Nipponbare and Sorghum bicolor; E, Nipponbare and Zea mays.
| [1] | Jiang N, Liu X L, Dai L Y, Wang G L.Advances on the mapping and cloning of blast resistance gene in rice.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2010, 26(10): 270-275. |
| [2] | He X Y, Wang L, Wu W H, Chen Z M, Lin F, Chen Y S, Liu W, Chen Y H, Liao Y P.The progress of mapping, isolation of the genes resistance to blast and their breeding application in rice.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2014, 30(6): 1-12. |
| [3] | Dangl J L, Jones J D G. Plant pathogens and integrated defense responses to infection.Nature, 2001, 411(6839): 826-333. |
| [4] | Iyer A S, Mccouch S R.The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance. Mol Plant-Microbe Int, 2004, 17(12): 1348-1354. |
| [5] | Kobe B, Deisenhofer J.A structural basis of the interactions between leucine-rich repeats and protein ligands.Nature, 1995, 374(6518): 183-186. |
| [6] | Tameling W I, Elzinga S D, Darmin P S, Vossen J H, Takken F L, Haring M A, Cornelissen B J.The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity.Plant Cell, 2002, 14(11): 2929. |
| [7] | Zhang X, Yang S, Wang J, Jia Y, Huang J, Tan S, Zhong Y, Wang L, Gu L, Chen J Q, Pan Q, Bergrelson J, Tian D.A genome-wide survey reveals abundant rice blast R genes in resistant cultivars. Plant J, 2015, 84(1): 20-28. |
| [8] | Wang Z X, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T.The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J, 1999, 19(1): 55-64. |
| [9] | Bryan G T, Wu K S, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey H P, McAdams S A, Faulk K N, Donaldson G K, Tarchini R, Valent B. A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell, 2000, 12(11): 2033-2046. |
| [10] | Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G, Bellizzi M, Wang G L.The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant-Microbe Int, 2006, 19(11): 1216-1228. |
| [11] | Qu S H, Liu G F, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L R, Dai L Y, Han B, Wang G L.The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics, 2006, 172(3): 1901-1914. |
| [12] | Lee S K, Song M Y, Seo Y S, Kim H K, Ko S, Cao P J, Suh J P, Yi G, Roh J H, Lee S, An G, Hahn T R, Wang G L, Ronald P, Jeon J S.Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two coiled-coil-nucleotide-binding-leucine-rich repeat genes. Genetics, 2009, 181(4): 1627-1638. |
| [13] | Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Masahiro Yano.Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice.Science, 2009, 325(5943): 998-1001. |
| [14] | Lin F, Chen S, Que Z Q, Wang L, Liu X Q, Pan Q H.The blast resistance gene Pi37 encodes a nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a resistance gene cluster on rice chromosome 1. Genetics, 2007, 177(3): 1871-1880. |
| [15] | Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu J Z, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M.Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance. Genetics, 2008, 180(4): 2267-2276. |
| [16] | Takahashi A, Hayashi N, Miyao A, Hirochika H.Unique features of the rice blast resistance Pish locus revealed by large scale retrotransposon-tagging. Bmc Plant Biol, 2010, 10(1): 175-186. |
| [17] | Zhai C, Lin F, Dong Z Q, He X Y, Yuan B, Zeng X S, Wang L, Pan Q H.The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication. New Phytol, 2011, 189(1): 321-334. |
| [18] | Deng Y, Zhai K, Xie Z, Yang D, Zhu X, Liu J, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y, Zhang G, Li Q, Zhang J, Wu S, Millazzo J, Mao B, Wang E, Xie H, Tharreau D, He Z.Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance.Science, 2017, 355(6328): 962-966. |
| [19] | Yi G, Lee S K, Hong Y K, Cho Y C, Nam M H, Kim S C, Han S S, Wang G L, Hahn T R, Ronald P C, Jeon J S.Use of Pi5(t) markers in marker-assisted selection to screen for cultivars with resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Theor Appl Genet, 2004, 109(5): 978-985. |
| [20] | Jeon J S, Chen D, Yi G H, Wang G L, Ronald P C.Genetic and physical mapping of Pi5(t), a locus associated with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast. Mol Genet Genom, 2003, 269(2): 280-289. |
| [21] | Inukai T, Zeigler R S, Sarkarung S, Bronson M, Dung L V, Kinoshita T, Nelson R J.Development of pre-isogenic lines for rice blast-resistance by marker-aided selection from a recombinant inbred population.Theor Appl Genet, 1996, 93(4): 560-567. |
| [22] | Kang H X, Wang Y, Peng S S, Zhang Y L, Xiao Y H, Wang D, Qu S H, Li Z Q, Yan S Y, Wang Z L, Liu W D, Ning Y S, Korniliev P, Leung H, Mezey J, McCouch S R, Wang G L. Dissection of the genetic architecture of rice resistance to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Pathol, 2015, 17(6): 959-972. |
| [23] | ParK C H, Wang G L. The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AvrPiz-t Targets the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase APIP6 to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in rice. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(11): 4748-4762. |
| [24] | Wang B H, Zhen W, Lu G D, Zhang X B, Wang Z H.Screening on the spore-producing media ofPyricularia oryzae. Fujian Agric Sci Technol, 2000(2): 1-2. |
| [25] | Huang X H, Yang S H, Gong J Y, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhan Q L, Zhao Y, Li W J, Cheng B Y, Xia J H, Chen N, Huang T, Zhang L, Fan D L, Chen J Y, Zhou C C, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Han B.Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice.Nature, 2016, 537(7622): 629-633. |
| [26] | Vogel J P, Garvin D F, Mockler T C.Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon. Nature, 2010, 463(7282):763-768. |
| [27] | Zhang L, Yu H, Ma B, Liu G F, Wang J J, Wang J M, Gao R C, Li J J, Liu J Y, Xu J, Zhang Y Y, Li Q, Huang X H, Xu J L, Li J M, Qian Q, Han B, He Z H, Li J Y.A natural tandem array alleviates epigenetic repression of IPA1 and leads to superior yielding rice.Nat Commun, 2017, 8(14789): 1-14. |
| [28] | Marschalek R, Silva M C, Santos S B D, Manke J R, Bieging C, Porto G, Wickert E, Andrade A D. Image-Rice Grain Scanner: A three-dimensional fully automated assessment of grain size and quality traits.Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol, 2017, 17: 89-97. |
| [29] | Luo C P, Ni L, Chen Z Y, Liu Y F, Liu Y Z, Nie Y F. Inoculation technology of rice blast and rice resistance to it in Jiangsu regional tests in 2009. Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2009(6): 178-179. |
| [30] | Zhu Y Y, Chen H, Wang Y Y, Li Z S, Li Y, Fan J H, Chen J B, Yang S S, Ma G L, Hu L P, Zou J Y, Mundt C C, Borromeo E, Leung H, Mew T W.Diversifying variety for the control of rice blast in China.Biodiversity, 2001, 2(1): 10-14. |
| [31] | Lei C L, Wang J L, Jiang W R, Ling Z Z, George M L.Population structure and genetic variation of rice blast fungus in some rice-growing regions in northern China.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2002, 32(3): 219-226. |
| [32] | Wang G L, Mackill D J, Bonman J M, McCouch S, Champoux M C, Nelson R J. RFLP Mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance to blast in a durably resistant rice cultivar.Genetics, 1994, 136(4): 1421-1434. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||