
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 580-589.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6152
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuqiong WANG1, Yaolong YANG1, Yujia LENG1, Lichao HUANG1, Long CHEN1, Liping DAI1, Zhengjun TU1, Yihong GAO1, Jiang HU1, Li ZHU1, Guangheng ZHANG1, Deyong REN1, Zhenyu GAO1, Guojun DONG1, Guang CHEN1, Longbiao GUO1, Guoyou YE2, Qian QIAN1,*( ), Dali ZENG1,*(
), Dali ZENG1,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-05
Revised:2017-04-03
Online:2017-11-25
Published:2017-11-10
Contact:
Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG
汪玉琼1, 杨窑龙1, 冷语佳1, 黄李超1, 陈龙1, 代丽萍1, 涂政军1, 高易宏1, 胡江1, 朱丽1, 张光恒1, 任德勇1, 高振宇1, 董国军1, 陈光1, 郭龙彪1, 叶国友2, 钱前1,*( ), 曾大力1,*(
), 曾大力1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
钱前,曾大力
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuqiong WANG, Yaolong YANG, Yujia LENG, Lichao HUANG, Long CHEN, Liping DAI, Zhengjun TU, Yihong GAO, Jiang HU, Li ZHU, Guangheng ZHANG, Deyong REN, Zhenyu GAO, Guojun DONG, Guang CHEN, Longbiao GUO, Guoyou YE, Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG. Identification and Fine Mapping of Small Grain Gene SG101 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 580-589.
汪玉琼, 杨窑龙, 冷语佳, 黄李超, 陈龙, 代丽萍, 涂政军, 高易宏, 胡江, 朱丽, 张光恒, 任德勇, 高振宇, 董国军, 陈光, 郭龙彪, 叶国友, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻小粒基因SG101的鉴定和精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 580-589.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6152
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| UBQ5 | CTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | TCTTGGGCTTCCTCTACGTCTT |
| E2F2 | TGTTGGTGGCTGCCGATAT | CGCCAGGTGCACCCTTT |
| CYCT1;2 | GCATTTGTTGCAGCTCAAG | TCACCACTTCGCTGACTTATTG |
| CYCD4;1 | GCCATGGAGTTGATACATCCAA | CCAGTAGGGCTCCGTGGAAT |
| CYCD7;1 | CCTTCCACACTGACGGTACAGTT | TGCCGCTGCCAAATAGACA |
| CYCB2;2 | CTCAAGGCTGCACAATCTGACA | GCATTGACGGCTGGAATTTG |
| D2 | TTCAACCCATGGAGGTGGAA | GCACGGTGGGGAAGTTGACGA |
| OsCPOD | TTCTTCTCCATCCCCTTTCCTCTCGCCA | CACCCTCCGCCTCAAGAAGCTCCTCAA |
| DWARF4Q | GAGATGGTTTTCACGCAATGTG | ACCCTTGTAGTGCACGTCCTTG |
| BU1 | GTAGCCAGCTTGATCTCATCTC | GGGACGACTCTACTGCATCA |
| BZRF | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| D61 | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC-3' | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| PAVL1 | GCACTCCTCGTTGGATCTCGAT | GCAGCAGACGGAAGATGGATT |
| OsLIC | GGAGTTTCGAGCGTATCTGGAA | TGGACAGAGGAAGCAGGAGACT |
| OsMDP1 | TTATTGACCGGTACAACTCGCA | TCCAGTCCATCGATCTCATCC |
Table 1 Primers used for real-time RT-PCR in the study.
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| UBQ5 | CTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | TCTTGGGCTTCCTCTACGTCTT |
| E2F2 | TGTTGGTGGCTGCCGATAT | CGCCAGGTGCACCCTTT |
| CYCT1;2 | GCATTTGTTGCAGCTCAAG | TCACCACTTCGCTGACTTATTG |
| CYCD4;1 | GCCATGGAGTTGATACATCCAA | CCAGTAGGGCTCCGTGGAAT |
| CYCD7;1 | CCTTCCACACTGACGGTACAGTT | TGCCGCTGCCAAATAGACA |
| CYCB2;2 | CTCAAGGCTGCACAATCTGACA | GCATTGACGGCTGGAATTTG |
| D2 | TTCAACCCATGGAGGTGGAA | GCACGGTGGGGAAGTTGACGA |
| OsCPOD | TTCTTCTCCATCCCCTTTCCTCTCGCCA | CACCCTCCGCCTCAAGAAGCTCCTCAA |
| DWARF4Q | GAGATGGTTTTCACGCAATGTG | ACCCTTGTAGTGCACGTCCTTG |
| BU1 | GTAGCCAGCTTGATCTCATCTC | GGGACGACTCTACTGCATCA |
| BZRF | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| D61 | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC-3' | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| PAVL1 | GCACTCCTCGTTGGATCTCGAT | GCAGCAGACGGAAGATGGATT |
| OsLIC | GGAGTTTCGAGCGTATCTGGAA | TGGACAGAGGAAGCAGGAGACT |
| OsMDP1 | TTATTGACCGGTACAACTCGCA | TCCAGTCCATCGATCTCATCC |
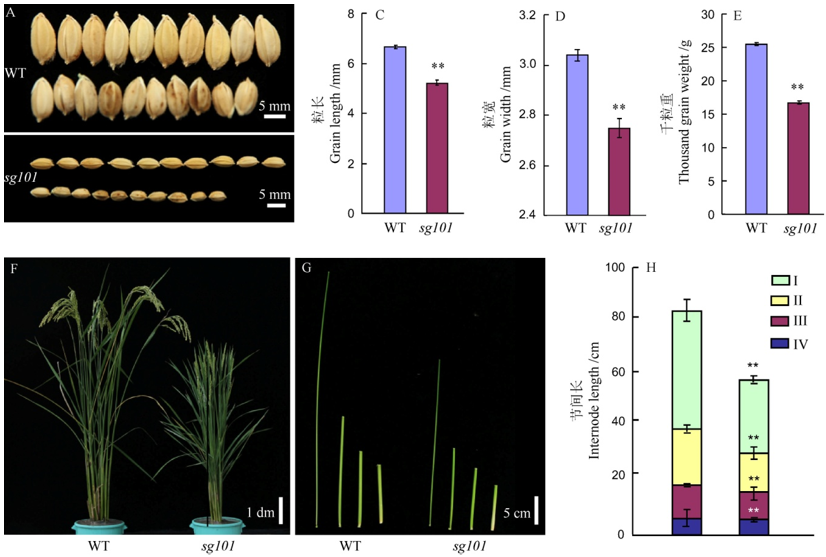
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. **Significant difference at 0.01 level between wild type and mutant sg101. The same as that in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 sg101 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 88.8±2.4 | 67.6±6.1 |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.7±1.1 | 17.1±1.2 |
| 着粒密度Spikelet density | 11.8±1.3 | 9.9±1.4 |
| 一次枝梗数Primary rachis branch number per panicle | 15.0±1.0 | 13.0±3.0 |
| 二次枝梗数Secondary rachis branch number per panicle | 51.3±11.1 | 33.6±7.1 |
| 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 270.0±40.0 | 170.0±29.3 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 70.0±4.3 | 5.0±3.2 |
Table 2 Comparison of panicle-related traits between Zhonghua 11 and sg101.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 sg101 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 88.8±2.4 | 67.6±6.1 |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.7±1.1 | 17.1±1.2 |
| 着粒密度Spikelet density | 11.8±1.3 | 9.9±1.4 |
| 一次枝梗数Primary rachis branch number per panicle | 15.0±1.0 | 13.0±3.0 |
| 二次枝梗数Secondary rachis branch number per panicle | 51.3±11.1 | 33.6±7.1 |
| 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 270.0±40.0 | 170.0±29.3 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 70.0±4.3 | 5.0±3.2 |
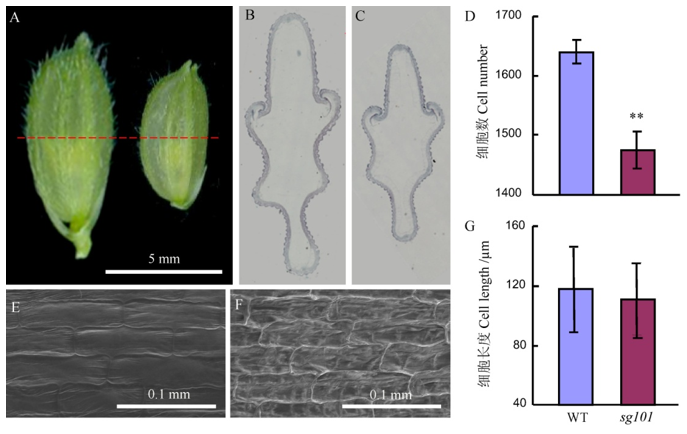
Fig. 2. The comparison of grain between Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. A, Developed lemma; B and C, Paraffin section of the lemmas of wild-type and sg101, respectively. D, Cell number of the lemma; E and F, SEM analysis of the lemma outer surface of wild-type and sg101, respectively. G, Cell length of the outer epidermal lemma.
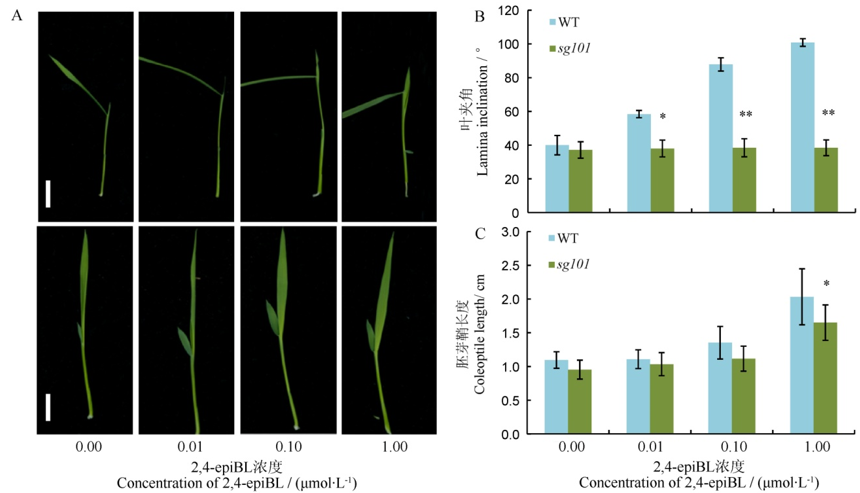
Fig. 4. Lamina joint test to 2,4-epiBL in Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. A, Performance of lamina joint to 2,4-epiBL in wild-type(up) and sg101(down). Scale bars, 2.0 cm; B and C, Changes of lamina inclination and coleoptile length to 2,4-epiBL, respectively. *, **Significant difference at 0.05 and 0.01 level between wild type and mutant sg101, respectively.
| 分离群体 Segregation population | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | P值 P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | ||||
| sg101/TN1 | 4 | 0 | 116 | 34 | 0.436 | 0.509 | |
| sg101/南京6号 sg101/Nanjing 6号 | 8 | 0 | 258 | 74 | 1.301 | 0.254 | |
| sg101/9311 | 5 | 0 | 154 | 43 | 1.058 | 0.304 | |
| TN1/sg101 | 4 | 0 | 128 | 38 | 0.394 | 0.530 | |
| 南京6号/sg101 Nanjing 6/sg101 | 3 | 0 | 102 | 29 | 0.573 | 0.449 | |
| 9311/sg101 | 6 | 0 | 178 | 56 | 0.143 | 0.076 | |
Table 3 Genetic analysis of SG101.
| 分离群体 Segregation population | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | P值 P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | ||||
| sg101/TN1 | 4 | 0 | 116 | 34 | 0.436 | 0.509 | |
| sg101/南京6号 sg101/Nanjing 6号 | 8 | 0 | 258 | 74 | 1.301 | 0.254 | |
| sg101/9311 | 5 | 0 | 154 | 43 | 1.058 | 0.304 | |
| TN1/sg101 | 4 | 0 | 128 | 38 | 0.394 | 0.530 | |
| 南京6号/sg101 Nanjing 6/sg101 | 3 | 0 | 102 | 29 | 0.573 | 0.449 | |
| 9311/sg101 | 6 | 0 | 178 | 56 | 0.143 | 0.076 | |
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | GCTAGGCTTGATCCGAGAGA | GTCCCGCTTCTTCCCCTA | |
| M2 | GACCACGTCAAGCATAAGTTCA | AGCCTTTCAGGGAGGAAGAA | |
| M3 | CTCCCTACTTCTCCTCTTCG | CATACGCAACACCGCATCTT | |
| M4 | GGTGTTTGATCCCATTTGCT | TGGATGAAGAACTGCGCATA | |
| S1 | GGAACGGGGTGACAATTCTA | GCCTGTTTGAGGGAATGGTA | |
| S2 | ATTCTTACTTAATAATCAATAC | TACCTAGCTCGACTCAGACCCA | |
| S3 | GAGCAGGCAGACCTGCATAA | AAAACACTGCCTGTGATTCTGT | |
| S4 | CGACGGTGGGAGCAGAAGAAA | TCGGACTATCTCTGCTGGAATT | |
| S5 | ACTCCTATGTTTCAACCTG | GTGACCATCAATGAACCTT | |
| S6 | AAATCTAGTCAACACGCCGT | ACATGAGTTTAATTCCAAAATT | |
Table 4 Primers used for fine mapping of SG101 in this study.
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | GCTAGGCTTGATCCGAGAGA | GTCCCGCTTCTTCCCCTA | |
| M2 | GACCACGTCAAGCATAAGTTCA | AGCCTTTCAGGGAGGAAGAA | |
| M3 | CTCCCTACTTCTCCTCTTCG | CATACGCAACACCGCATCTT | |
| M4 | GGTGTTTGATCCCATTTGCT | TGGATGAAGAACTGCGCATA | |
| S1 | GGAACGGGGTGACAATTCTA | GCCTGTTTGAGGGAATGGTA | |
| S2 | ATTCTTACTTAATAATCAATAC | TACCTAGCTCGACTCAGACCCA | |
| S3 | GAGCAGGCAGACCTGCATAA | AAAACACTGCCTGTGATTCTGT | |
| S4 | CGACGGTGGGAGCAGAAGAAA | TCGGACTATCTCTGCTGGAATT | |
| S5 | ACTCCTATGTTTCAACCTG | GTGACCATCAATGAACCTT | |
| S6 | AAATCTAGTCAACACGCCGT | ACATGAGTTTAATTCCAAAATT | |
| [1] | Xing Y, Zhang Q.Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield.Ann Rev Plant Biol, 2010, 61: 421-442. |
| [2] | Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Shi C.Identification and characterization ofdwarf 62, a loss-of-function mutation in DLT/OsGRAS-32 affecting gibberellin metabolism in rice. Planta, 2010, 232(6): 1383-1396. |
| [3] | Mao H, Sun S, Yao J, Wang C, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q.Linking differential domain functions of theGS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2010, 107(45): 19579-19584. |
| [4] | 茆海亮. 水稻粒形基因GS3的功能研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010. |
| Mao H L.Functional study of rice grain shape gene GS3. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 石珍源. 水稻粒型QTL qGW12的精细定位和粒长调控基因SG4的克隆与功能验证. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2015. |
| Shi Z Y.Fine mapping of rice width locus GW12 and functional verification of a grain length gene SG4 in rice. Beijing: Chinese Academic of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Zuo J, Li J.Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size.Ann Rev Genet, 2014, 48: 99-118. |
| [7] | Zhang X, Wang J, Huang J, Lan H, Wang C, Yin C, Wu Y, Tang H, Qian Q, Li J, Zhang H.Rare allele ofOsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2012, 109(52): 21534-21539. |
| [8] | Qi P, Lin Y, Song X, Shen J, Huang W, Shan J, Zhu M, Jiang L, Gao J, Lin H.The novel quantitative trait locusGL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3. Cell Res, 2012, 22(12): 1666-1680. |
| [9] | Wang Y, Xiong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Xu J, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, Jing Y, Wang Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q.Copy number variation at theGL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [10] | Hu, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, Xie L, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q. A rare allele ofGS2 Enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant, 2015, 8(10): 1455-1465. |
| [11] | Song X, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M, Lin H,. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase.Nat Genet, 2007, 39: 623-630. |
| [12] | Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y.Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2011, 123(7): 1173-1181. |
| [13] | Weng J F, Gu S H, Wan X Y, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C L, Zhang X, Cheng Z J, Guo X P, Wang J L, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Isolation and initial characterization ofGW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res, 2008, 18(12): 1199-1209. |
| [14] | Li Y, Fan Ch, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q.Natural variation inGS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet, 2011, 43(12): 1266-1269. |
| [15] | Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X.Control of grain size, shape and quality byOsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet, 2012, 44: 950-954. |
| [16] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint.Plant Cell, 2000, 12(9): 1591-1605. |
| [17] | Tanaka A, Nakagawa H, Tomita C, Shimatani Z, Ohtake M, Nomura T, Jiang , Dubouzet J, Kikuchi S, Sekimoto H, Yokota T, Asami T, Kamakura T, Mori M.BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol, 2009, 151(2): 669-680. |
| [18] | Duan P, Rao Y, Zeng D, Yang Y, Xu R, Zhang B, Dong G, Qian Q, Li Y.SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J, 2014, 77(4): 547-557. |
| [19] | Liu S, Hua L, Dong S, Chen H, Zhu X, Jiang J, Zhang F, Li Y, Fang X, Chen F.OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J, 2015, 84(4): 672-681. |
| [20] | Liu L, Tong H, Xiao Y, Che R, Xu F, Hu B, Liang C, Chu J, Li J, Chu C.Activation ofBig Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(35): 11102-11107. |
| [21] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4326. |
| [22] | Horiguchi G, Ferjani A, Fujikura U, Tsukaya H.Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion in the control of leaf size inArabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res, 2006,119: 37-42. |
| [23] | Horvath BM, Magyar Z, Zhang Y, Hamburger AW, Bako L, Visser RG, Bachem CW, Bogre L.EBP1 regulates organ size through cell growth and proliferation in plants. EMBO J. 2006, 25: 4909-4920. |
| [24] | Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E.Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase geneTGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(6): 707-711. |
| [25] | Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A.Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant geneDwarf 1 encodes the α-subunit of GTP-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1999, 96(18): 10284-10289. |
| [26] | Fujisawa Y, Kato T, Ohki S, Ishikawa A, Kitano H, Sasaki T, Asahi T, Iwasaki Y.Suppression of the heterotrimeric G protein causes abnormal morphology, including dwarfism, in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1999, 96(13): 7575-7580. |
| [27] | Andrzej B.Metabolism of brassinosteroids in plants.Plant Physiol Biochem, 2007, 45(2): 95-107. |
| [28] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, Inukai Y, Fujioka S, Shimada Y, Takatsuto S, Agetsuma M, Yoshida S, Watanabe Y, Uozu S, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem.Plant J, 2002, 32(4): 495-508. |
| [29] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujiok S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisudwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(12): 2900-2910. |
| [30] | Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y.A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant,dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(3): 776-790. |
| [31] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.The rice brassinosteroid deficientdwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2243-2254. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||