
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 447-458.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210714
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Rongtao1,2, WANG Jian1,2, CHEN Cheng1,2, ZHAO Liyu1, CHEN Xuejuan1, LU Daihua1,2( )
)
Received:2021-09-06
Revised:2021-11-10
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
LU Daihua
伏荣桃1,2, 王剑1,2, 陈诚1,2, 赵黎宇1, 陈雪娟1, 卢代华1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
卢代华
基金资助:FU Rongtao, WANG Jian, CHEN Cheng, ZHAO Liyu, CHEN Xuejuan, LU Daihua. Transcriptome Analysis of Young Rice Panicles in Early Response to Exposure to Mycotoxin of Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 447-458.
伏荣桃, 王剑, 陈诚, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 水稻幼穗响应稻曲病菌毒素胁迫早期的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 447-458.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210714
| 样品名 Sample | 过滤前数据 Total raw reads / bp | 过滤后数据 Total clean reads / bp | 过滤后数据Clean bases(G) / bp | Q30/% | N/% | GC/% | 总对比数据 Total mapped reads /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1-1 | 43 418 126 | 41 710 168 | 5.82 | 90.75 | 0.01 | 50.07 | 36 532 652(94.56%) |
| CK1-2 | 38 359 472 | 35 721 996 | 4.98 | 87.46 | 0.01 | 52.25 | 32 694 216(94.92%) |
| CK1-3 | 49 946 750 | 47 116 642 | 6.53 | 86.91 | 0.01 | 52.26 | 42 564 507(94.74%) |
| CL1-1 | 44 766 290 | 43 134 338 | 6.11 | 90.88 | 0.01 | 49.21 | 38 396 232(95.14%) |
| CL1-2 | 43 990 022 | 42 300 572 | 5.84 | 89.18 | 0.01 | 48.86 | 35 673 451(93.65%) |
| CL1-3 | 44 322 824 | 42 304 834 | 5.97 | 89.59 | 0.01 | 49.82 | 39 456 359(94.76%) |
Table 1. Statistics of transcriptone sequencing data.
| 样品名 Sample | 过滤前数据 Total raw reads / bp | 过滤后数据 Total clean reads / bp | 过滤后数据Clean bases(G) / bp | Q30/% | N/% | GC/% | 总对比数据 Total mapped reads /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1-1 | 43 418 126 | 41 710 168 | 5.82 | 90.75 | 0.01 | 50.07 | 36 532 652(94.56%) |
| CK1-2 | 38 359 472 | 35 721 996 | 4.98 | 87.46 | 0.01 | 52.25 | 32 694 216(94.92%) |
| CK1-3 | 49 946 750 | 47 116 642 | 6.53 | 86.91 | 0.01 | 52.26 | 42 564 507(94.74%) |
| CL1-1 | 44 766 290 | 43 134 338 | 6.11 | 90.88 | 0.01 | 49.21 | 38 396 232(95.14%) |
| CL1-2 | 43 990 022 | 42 300 572 | 5.84 | 89.18 | 0.01 | 48.86 | 35 673 451(93.65%) |
| CL1-3 | 44 322 824 | 42 304 834 | 5.97 | 89.59 | 0.01 | 49.82 | 39 456 359(94.76%) |
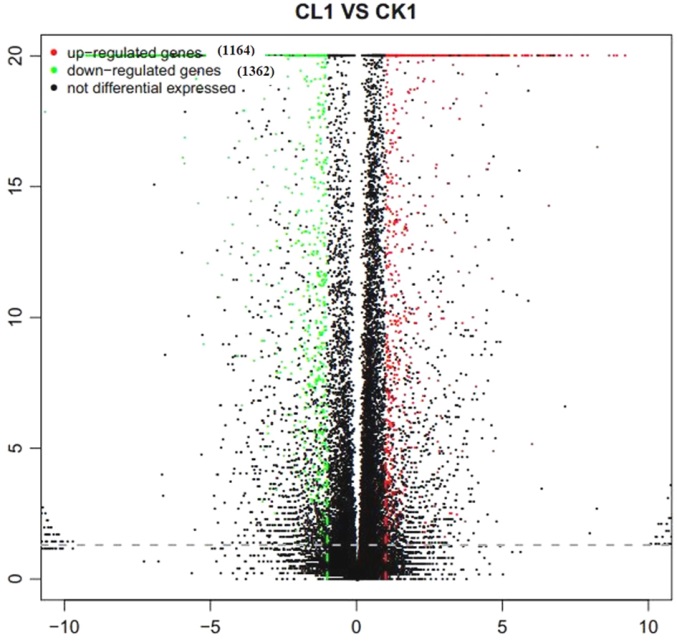
Fig. 2. Volcano-plot distribution of DEGs. Horizontal axis represents the multiple value of differetially expressed gene between different groups of samples; Vertical axis represents statistically significant degree(P value) of gene expression changes; Red, Up-regulated DEGs; Blue, Down-regulated DEGs; Black, Non-DEGs.
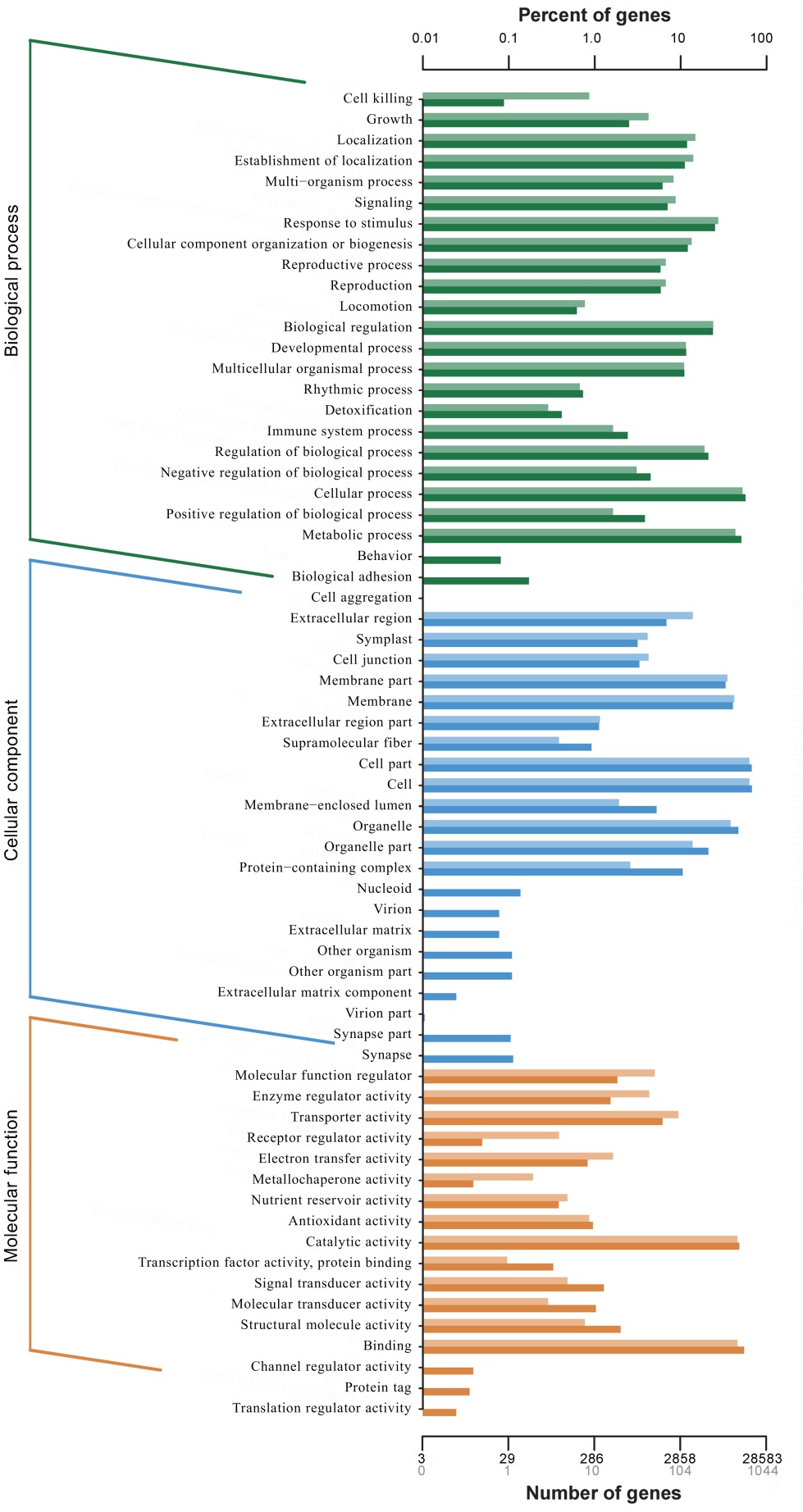
Fig. 3. GO function classification of DEGs. Vertical axis is function classification; Horizontal axis is the number of genes in the classification (bottom) and their percentage in the total number of annotated genes (top). Light colors represent differentially expressed genes and dark colors represent all genes.
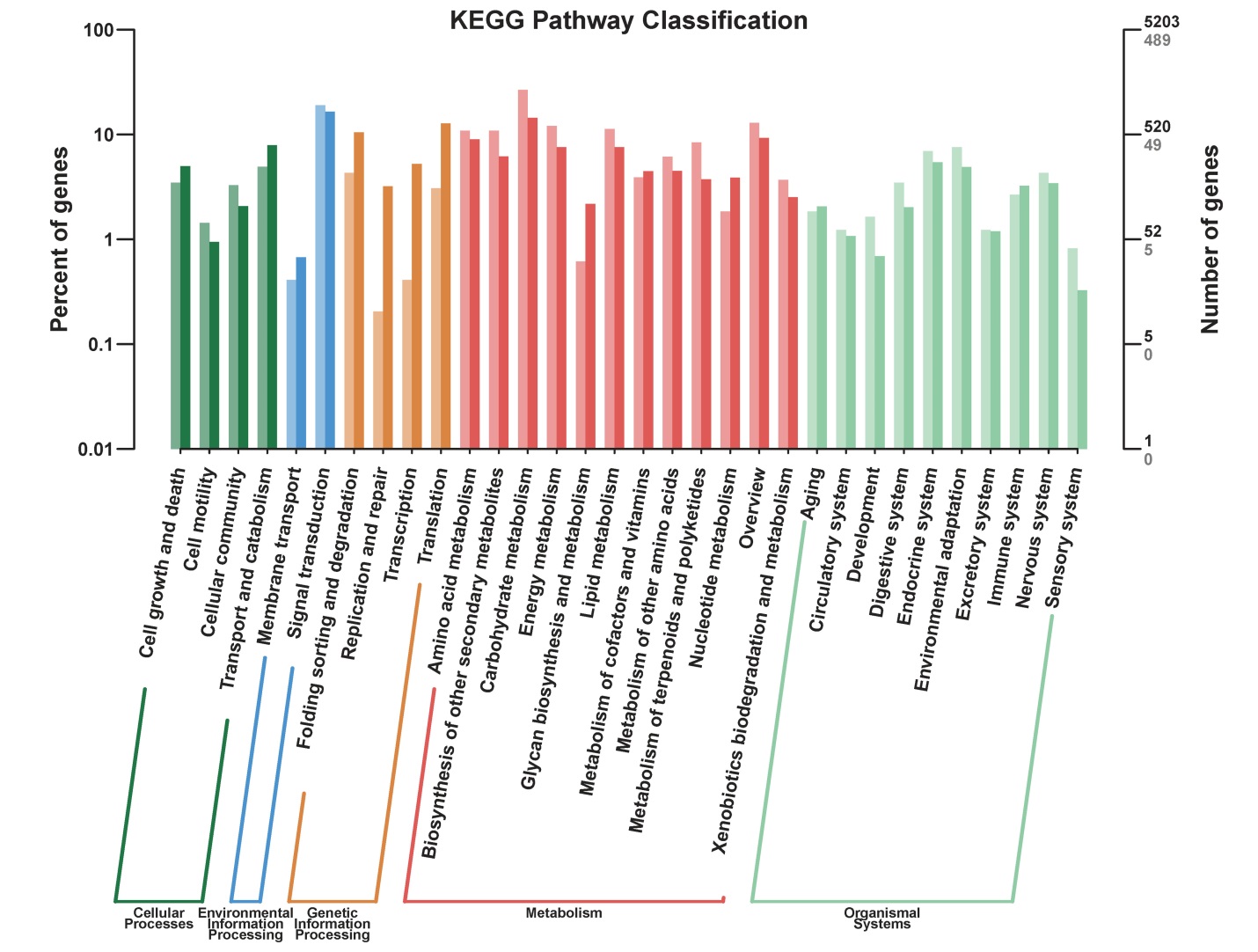
Fig. 4. KEGG pathway classification of DEGs. The horizontal axis represents different pathways; The left vertical axis represents the percentage of the number of genes in this pathway in the total number of annotated genes (left), the right vertical axis represents the number of genes (light color represents differentially expressed genes, dark color represents all genes).
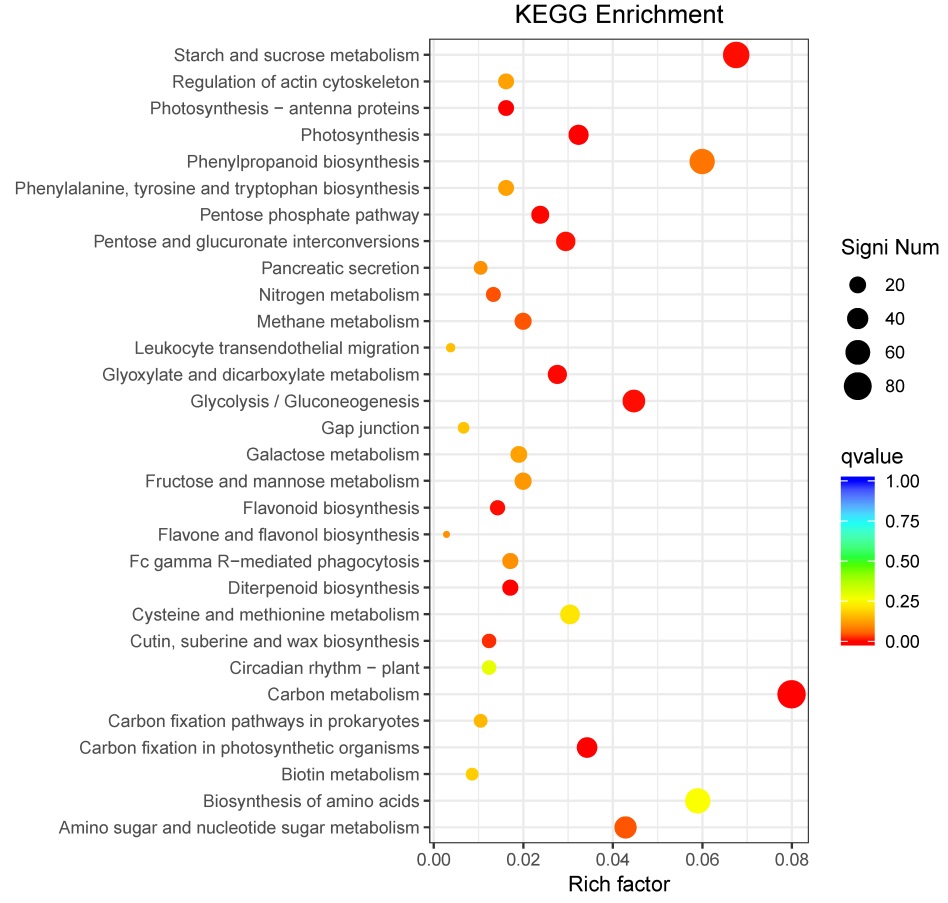
Fig. 5. Scatter plot of enriched KEGG pathways for DEGs. Vertical axis represents functional information; Horizontal axis shows the rich factor corresponding to pathway, and the greater the rich factor, the greater the enrichment degree. The size of the dots represents the number of DEGs under the term, and the larger the dots, the more genes (the top 30 pathways with the highest enrichment).
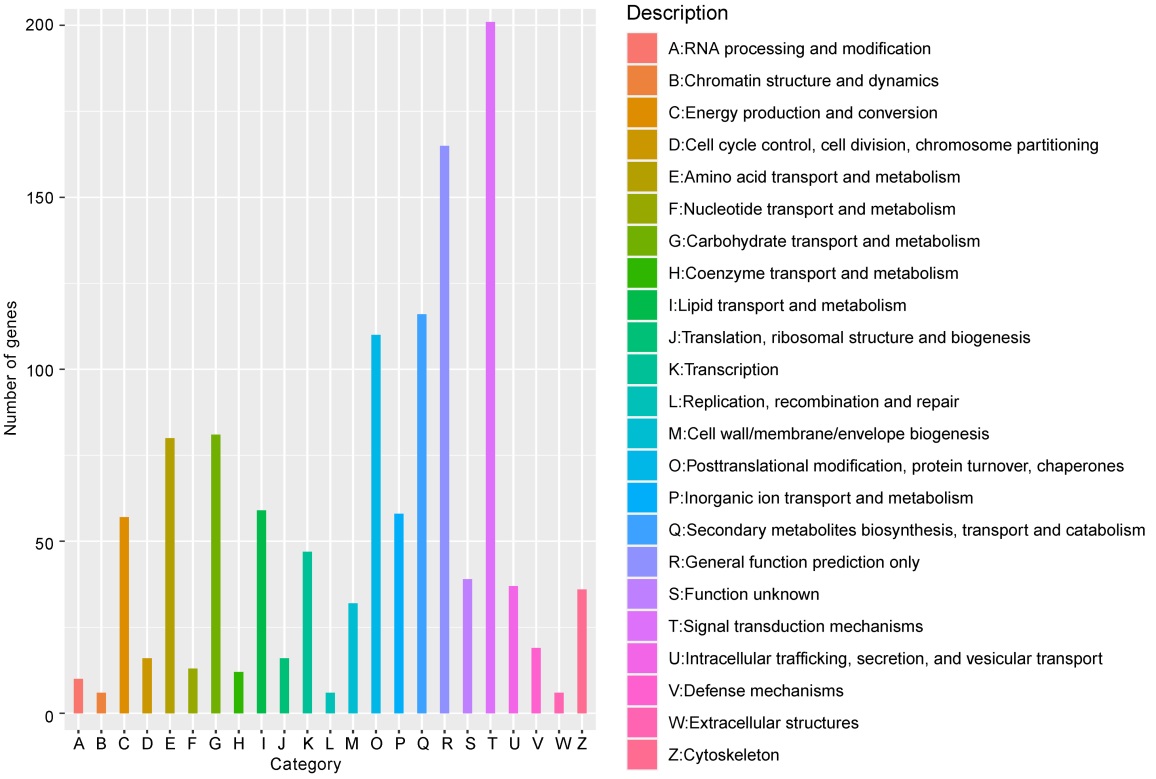
Fig. 6. KOG function classification of DEGs. Each color on the horizontal axis represents a functional classification of KOG; Vertical axis is number of genes annotated under the classification.
| 转录因子家族 Transcription factor family | 受影响的转录因子数量 Number of affected transcription factors | 主要的植物调控功能 Main regulatory functions in plants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上调 Up-regulated | 下调 Down-regulated | 总数 Total | ||
| Myb | 8 | 7 | 15 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| WRKY | 2 | 0 | 2 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| HSF(Heat shock transcription factor) | 6 | 3 | 9 | 抵御生物、非生物胁迫b, c |
| bHLH(basic Helix loop helix) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| MADS-box | 3 | 9 | 12 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| GATA | 2 | 7 | 9 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| HOX | 6 | 9 | 15 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| 总数Total | 28 | 38 | 66 | |
Table 2. Plant transcription factors affected by mycotoxin from U. virens.
| 转录因子家族 Transcription factor family | 受影响的转录因子数量 Number of affected transcription factors | 主要的植物调控功能 Main regulatory functions in plants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上调 Up-regulated | 下调 Down-regulated | 总数 Total | ||
| Myb | 8 | 7 | 15 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| WRKY | 2 | 0 | 2 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| HSF(Heat shock transcription factor) | 6 | 3 | 9 | 抵御生物、非生物胁迫b, c |
| bHLH(basic Helix loop helix) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 植物生长发育,抵御生物、非生物胁迫a, b, c |
| MADS-box | 3 | 9 | 12 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| GATA | 2 | 7 | 9 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| HOX | 6 | 9 | 15 | 植物生长发育,抵御非生物胁迫a, c |
| 总数Total | 28 | 38 | 66 | |
| 序号No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WRKY71 | BGIOSGA007670 | F: TGCAGGTGGTGAAAGATGGG |
| R: GAAACAGGCTCGAATTTGCACT | |||
| 2 | WRKY24 | BGIOSGA004722 | F: AGAGATGGTGAGTGCCCTGT |
| R: CGATGTCGCTCATGGTTTGG | |||
| 3 | Myb | BGIOSGA004072 | F: CATCTCGCAAAACGGCGAAG |
| R: GTTCGGACATCACATAGTCGC | |||
| 4 | Myb | BGIOSGA006005 | F: TGCCTTGGATACGCGAAAGA |
| R: CCGCTTCTTGAGGTGAGTGT | |||
| 5 | UGPase | BGIOSGA007245 | F: TCTGGGATGGCCATAGAAAAACA |
| R: GTACTGGACCAACAACGTGC | |||
| 6 | Chitinase | BGIOSGA006087 | F: GTACTGGACCAACAACGTGC |
| R: TTAGCAGGTGAGGTTGCTGC | |||
| 7 | Peroxidase | BGIOSGA037333 | F: GGGATTTGCCATAAGCGAAACA |
| R:CCACATTCTCGGTTGTTGCC | |||
| 8 | SBEII | BGIOSGA018719 | F: GAGTCGAGCTGGAATTGTGTTG |
| R: GCAGAGTGCCCACATTCATC | |||
| 9 | NADPH oxidase | BGIOSGA037531 | F: AGATGAATTCGCTCCAATGATTTGT |
| R: GGCCAAGCTGAAATTGTGGC | |||
| UBI | F: CGCAAGAAGAAGTGTGGTCA | ||
| R: ACGATTGATTTAACCAGTCCATGA |
Table 3. Primers used for qRT-PCR verifying.
| 序号No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WRKY71 | BGIOSGA007670 | F: TGCAGGTGGTGAAAGATGGG |
| R: GAAACAGGCTCGAATTTGCACT | |||
| 2 | WRKY24 | BGIOSGA004722 | F: AGAGATGGTGAGTGCCCTGT |
| R: CGATGTCGCTCATGGTTTGG | |||
| 3 | Myb | BGIOSGA004072 | F: CATCTCGCAAAACGGCGAAG |
| R: GTTCGGACATCACATAGTCGC | |||
| 4 | Myb | BGIOSGA006005 | F: TGCCTTGGATACGCGAAAGA |
| R: CCGCTTCTTGAGGTGAGTGT | |||
| 5 | UGPase | BGIOSGA007245 | F: TCTGGGATGGCCATAGAAAAACA |
| R: GTACTGGACCAACAACGTGC | |||
| 6 | Chitinase | BGIOSGA006087 | F: GTACTGGACCAACAACGTGC |
| R: TTAGCAGGTGAGGTTGCTGC | |||
| 7 | Peroxidase | BGIOSGA037333 | F: GGGATTTGCCATAAGCGAAACA |
| R:CCACATTCTCGGTTGTTGCC | |||
| 8 | SBEII | BGIOSGA018719 | F: GAGTCGAGCTGGAATTGTGTTG |
| R: GCAGAGTGCCCACATTCATC | |||
| 9 | NADPH oxidase | BGIOSGA037531 | F: AGATGAATTCGCTCCAATGATTTGT |
| R: GGCCAAGCTGAAATTGTGGC | |||
| UBI | F: CGCAAGAAGAAGTGTGGTCA | ||
| R: ACGATTGATTTAACCAGTCCATGA |
| [1] | Tanaka E, Ashizawa T, Sonoda R, Sonoda R, Tanka C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens,the causal agent of rice false smut[J]. Mycotaxon, 2008, 106(1): 491-501. |
| [2] | Fan J, Yang J, Wang Y Q, Li G B, Li Y, Huang F, Wang W M. Current understanding on Villosiclava virens, a unique flower-infecting fungus causing rice false smut disease[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2016, 17(9): 1321-1330. |
| [3] | 伏荣桃, 王剑, 卢代华, 张鸿, 龚学书, 陈雪娟, 任鸿志, 毛建辉. 水稻稻曲病抗性鉴定技术及影响因子研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(18): 266-272. |
| Fu R T, Wang J, Lu D H, Zhang H, Gong X S, Chen X J, Ren H Z, Mao J H. Resistance identification and influence factor of rice false smut[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(18): 266-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Hu M L, Luo L X, Wang S, Liu Y F, Li J Q. Infection processes of Ustilaginoidea virens during artificial inoculation of rice panicles[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2014, 139: 67-77. |
| [5] | Meng J J, Sun W B, Mao Z L, Dan X, Wang X, Lu S, Yang L, Zhou L, Zhang G. Main ustilaginoidins and their distribution in rice false smut balls[J]. Toxins, 2015, 7(10): 4023-4034. |
| [6] | Lai D W, Meng J J, Zhang X P, Xu D, Dai J G, Zhou L G. Ustilobisorbicillinol A, a cytotoxic sorbyl-containing aromatic polyketide from Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Organic Letters, 2019, 21(5): 1311-1314. |
| [7] | Fu X X, Xie R S, Wang J. Development of colloidal gold-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis of ustiloxins A and B in rice samples[J]. Toxins, 2017, 9(3): 79. |
| [8] | Meng J J, Gu G, Dang P Q, Zhang X P, Wang W X, Dai J G, Liu Y, Lai D W, Zhou L G. Sorbicillinoids from the fungus Ustilaginoidea virens and their phytotoxic, cytotoxic, and antimicrobial activities[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2019, 7: 435. |
| [9] | Li Y, Koiso Y, Kobayashi H, Hashimoto Y, Iwasaki S. Ustiloxins, new antimitotic cyclic peptides: Interaction with porcine brain tubulin[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 1995, 49(10): 1367-1372. |
| [10] | Hu Z, Dang Y, Liu C S, Zhou L, Liu H. Acute exposure to ustiloxin A affects growth and development of early life zebrafish, Danio rerio[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 226: 851-857. |
| [11] | 陈美军, 胡东维, 徐颖. 稻曲病菌毒素的活性测定、抗体制备与细胞定位[J]. 实验生物学报, 2004, 37(4): 310-314. |
| Chen M J, Hu D W, Xu Y. Activity assay, antiserum preparation and cellular localization of ustiloxins[J]. Acta Biologiae Experimentalis Sinica, 2004, 37(4): 310-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Hamed K A, Wayne T S, Cartwright R D, Sciumbato G L. Ustilaginoidea virens infection of rice in Arkansas: Toxicity of false smut galls, their extracts and the ustiloxin fraction[J]. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2014, 5(21): 3166-3176. |
| [13] | Wang X H, Wang J, Lai D W, Wang W X, Liu Y. Ustiloxin G, a new cyclopeptide mycotoxin from rice false smut balls[J]. Toxins, 2017, 9(2): 54-63. |
| [14] | Fu R T, Wang J, Chen C, Gong X S, Lu D H. Effect of crude toxins of Ustilaginoidea virens on rice seed germination[J]. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 2017, 11(32): 1267-1273. |
| [15] | Luduena R F, Roach M C, Prasad V. Interaction of ustiloxin A with bovine brain tubulin[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 1994, 47(9): 1593-1599. |
| [16] | 武斌, 温雪玮, 李衫衫, 胡东维, 梁五生. 稻曲病菌毒素对水稻幼根转录组的影响[J]. 农业生物技术报, 2018, 26(7):1093-1106. |
| Wu B, Wen X W, Li S S, Hu D W, Lang W S. Influences of mycotoxins of Villosiclava virens on the transcriptome of rice (Oryza sativa) seedling roots[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2018, 26(7): 1093-1106. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Xu G, Bi D, Qu H, Zou X, Gao X, Yang H, He H, Wang X, Bao J, Zuo S, Pan X, Zhou B, Wang G, Qu S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Rhizoctonia solani-resistant and -susceptible rice cultivars reveals the importance of pathogen recognition and active immune responses in host resistance[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2018, 61(3):143-158. |
| [18] | 楚乐乐, 罗成科, 李芳兰, 路旭平, 马天利, 李培富. 盐胁迫下OsDSR2 RNAi转基因水稻的生理特性及转录组学分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(4): 954-965. |
| Chu L L, Luo C K, Li F L, Lu X P, Ma T L, Li P F. Analysis of the physiological characteristics and transcriptome profiles of OsDSR2 RNAi transgenic rice under salt stress[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(4): 954-965. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(4): 1165-1188. |
| [20] | Chao J, Jin J, Wang D, Han R, Zhu R S, Zhu Y G, Li S Q, Sun M X. Cytological and transcriptional dynamics analysis of host plant revealed stages specific biological processes related to compatible rice Ustilaginoidea virens interaction[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(3): e91391. |
| [21] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [22] | Ismaiel A, Papenbrock J. Mycotoxins: Producing fungi and mechanisms of phytotoxicity[J]. Agriculture, 2015, 5: 492-537. |
| [23] | Janardhanan K K, Husain A. Phytotoxic activity of tenuazonic acid isolated from Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler causing leaf blight of Datura innoxia Mill. and its effect on host metabolism[J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 1984, 111(3-4): 305-311. |
| [24] | McLean M. The phytotoxicity of Fusarium metabolites: An update since 1989. Mycopathologia, 1996, 133: 163-179. |
| [25] | Ismaiel A A, Tharwat N A. Antifungal activity of silver ion on ultrastructure and production aflatoxin B1 and patulin by two mycotoxigenic strains, Aspergillus flavus OC1 and Penicillium vulpinum CM1[J]. Journal de Mycologie Medical, 2014, 24(3): 193-204. |
| [26] | Fujita K, Arase S, Hiratsuka H, Honda Y, Nozu M. The role of toxin(s) produced by germinating spores of Pyricularia oryzae in pathogenesis[J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 1994, 142(3-4): 245-252. |
| [27] | Vidhyasekaran P, Ruby Ponmalar T, Samiyappan R, Velazhahan R, Muthukrishnan S. Host-specific toxin production by Rhizoctonia solani, the rice sheath blight pathogen[J]. Phytopathology, 1997, 87(12): 1258-1263. |
| [28] | Samuel A T, Valentine I T. Effect of total aflatoxin on the growth characteristics and chlorophyll level of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)[J]. New York Science Journal, 2014, 7: 8-13. |
| [29] | Aver’yanov A A, Lapikova V P, Lebrun M H. Tenuazonic acid, toxin of rice blast fungus, induces disease resistance and reactive oxygen production in plants[J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2007, 54: 749-754. |
| [30] | 齐俊生, 李怀方. 一种检测棉花黄萎菌毒素致萎性的新方法: 叶片针刺涂抹法[J]. 棉花学报, 2006, 18(4): 228-232. |
| Qi J S, Li H F. A new detection method of wilting induction by phytotoxin from V. dahliae on cotton through leaf pricking and spreading[J]. Cotton Science, 2006, 18(4): 228-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 杨艳丽, 肖浪涛, 胡先奇. 马铃薯晚疫病菌与寄主品种抗性关系研究. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(6): 2202-2210. |
| Yang Y L, Xiao L T, Hu X Q. Study on the relationship between the toxin of Phytophthora infestans and resistance of potato[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(6): 2202-2210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Ambawat S, Sharma P, Yadav N R. MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: An overview[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2013, 19(3): 307-321. |
| [33] | Wang Y M, Kwon S J, Wu J N, Choi J Y, Lee Y H, Agrawai G K, Tamogami S, Rakwal R, Park S R, Kim B G, Jung K H, Kang K Y, Kim S G, Kim S T. Transcriptome analysis of early responsive genes in rice during Magnaporthe oryzae infection[J]. The Plant Pathology Journal, 2014, 30(4): 343-354. |
| [34] | Han Y Q, Zhang K, Yang J, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Liu Y F, Chen Z Y, Hsiang T, Sun W X. Differential expression profiling of the early response to Ustilaginoidea virens between false smut resistant and susceptible rice varieties[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 955. |
| [35] | 张艺丹, 曾英, 卢山. 水稻二萜合成途径中代谢流调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(12): 1762-1768. |
| Zhang Y D, Zeng Y, Lu S. Recent progress in the study of metabolic flux regulation in rice diterpene biosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2019, 55(12): 1762-1768. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Peters R J. Uncovering the complex metabolic network underlying diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis in rice and other cereal crop plants[J]. Phytochemistry, 2006, 67: 2307-2317 |
| [37] | Zi J, Mafu S, Peters R J. To gibberellins and beyond Surveying the evolution of (di)terpenoid metabolism[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2014, 65: 259-286. |
| [38] | 韩彦卿, 韩渊怀, 张春来, 孙文献. 水稻幼穗与Ustilaginoidea virens互作早期的转录组分析[J]. 植物病理学报, 2019, 49(3): 296-305. |
| Han Y Q, Han Y H, Zhang C L, Sun W X. Transcriptomic analysis of early interaction between rice young spikelets and Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2019, 49(3): 296-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 彭波, 彭宇, 彭娟, 孔冬艳, 何璐璐, 孙艳芳, 黄雅琴, 宋世枝. 水稻种子主要营养物质合成及调控研究与展望. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(6): 1241-1251. |
| Peng B, Peng Y, Peng J, Kong D M, He L L, Sun Y F, Huang Y Q, Song S Z. Research advancement and prospects of main nutritious substances synthesis and regulation in rice seeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(6): 1241-1251. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Thitisaksakul M, Jiménez R C, Arias M C, Beckles D M. Effects of environmental factors on cereal starch biosynthesis and composition[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2012, 56(1): 67-80. |
| [41] | Fujita N. Starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm[J]. Agri-bioscience Monographs, 2014, 4(1): 1-18. |
| [42] | Fan J, Yang L, Zheng A P, Wang W M, Guo X Y, Li L, Huang F, Sun W X, Yan L, Huang Y Y. Infection of Ustilaginoidea virens intercepts rice seed formation but activates grain-filling-related genes[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2015, 57(6): 577-590. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | FU Rongtao, CHEN Cheng, WANG Jian, ZHAO Liyu, CHEN Xuejuan, LU Daihua. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveals the Pathogenic Factors of Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [5] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [6] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [7] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [8] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [9] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [10] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [11] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [12] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [13] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [14] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [15] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||