
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 257-264.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6172 257
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guilian ZHANG, Bin LIAO, Wenbang TANG, Liyun CHEN*( ), Yinghui XIAO*(
), Yinghui XIAO*( )
)
Received:2016-12-25
Revised:2017-02-28
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-05-10
Contact:
Liyun CHEN, Yinghui XIAO
通讯作者:
陈立云,肖应辉
基金资助:CLC Number:
Guilian ZHANG, Bin LIAO, Wenbang TANG, Liyun CHEN, Yinghui XIAO. Identifying QTLs for Thermo-tolerance of Grain Chalkiness Trait in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 257-264.
张桂莲, 廖斌, 唐文帮, 陈立云, 肖应辉. 稻米垩白性状对高温耐性的QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 257-264.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6172 257
| 性状 Trait | 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | RIL群体RIL population | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 996 | 4628 | 平均值Mean | 变幅Range | |||||||
| 垩白粒率耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalky grain rate | 2014 | 30.65±1.07 | 70.25±1.76 | 55.11±1.65 | 2.54~84.56 | |||||
| 2015 | 31.45±0.66 | 75.68±2.27 | 56.12±1.96 | 0.00~90.91 | ||||||
| 垩白大小耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalkiness size | 2014 | 40.78±1.43 | 65.78±1.64 | 42.29±1.23 | 11.3~65.53 | |||||
| 2015 | 41.12±1.53 | 70.14±2.10 | 44.11±1.54 | 2.76~95.23 | ||||||
| 垩白度耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalkiness degree | 2014 | 40.43±1.54 | 67.53±2.03 | 48.82±1.71 | 5.03~72.70 | |||||
| 2015 | 41.39±1.45 | 73.42±2.57 | 50.77±1.78 | 7.66~91.47 | ||||||
Table 1 Heat tolerance index of chalky grain rate, chalkiness size and chalkiness degree of two parents and their RIL population.
| 性状 Trait | 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | RIL群体RIL population | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 996 | 4628 | 平均值Mean | 变幅Range | |||||||
| 垩白粒率耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalky grain rate | 2014 | 30.65±1.07 | 70.25±1.76 | 55.11±1.65 | 2.54~84.56 | |||||
| 2015 | 31.45±0.66 | 75.68±2.27 | 56.12±1.96 | 0.00~90.91 | ||||||
| 垩白大小耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalkiness size | 2014 | 40.78±1.43 | 65.78±1.64 | 42.29±1.23 | 11.3~65.53 | |||||
| 2015 | 41.12±1.53 | 70.14±2.10 | 44.11±1.54 | 2.76~95.23 | ||||||
| 垩白度耐热指数 Heat tolerance index of chalkiness degree | 2014 | 40.43±1.54 | 67.53±2.03 | 48.82±1.71 | 5.03~72.70 | |||||
| 2015 | 41.39±1.45 | 73.42±2.57 | 50.77±1.78 | 7.66~91.47 | ||||||
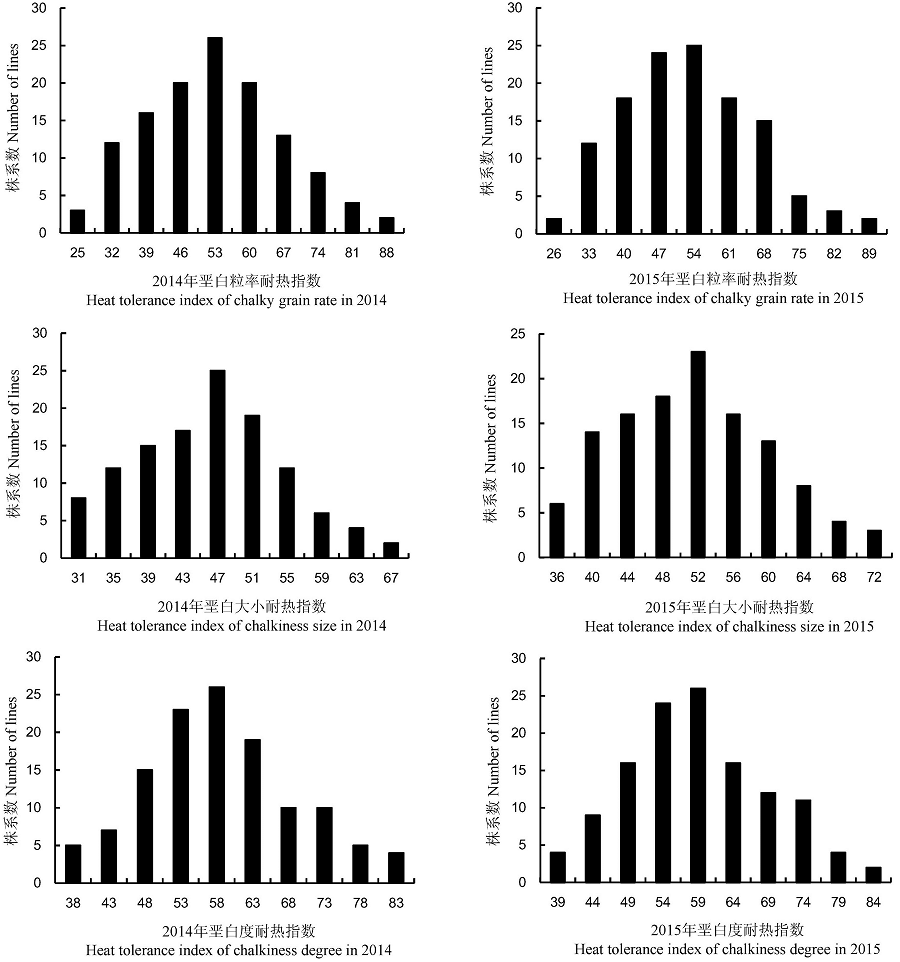
Fig. 1. Frequency distribution of heat tolerance index of chalky grain rate, chalkiness size and chalkiness degree in RIL population in 2014 and 2015.
| 染色体 Chromosome | 位点 QTL | 标记区间 Marker interval | LOD值 LOD score | 加性效应 Additive effect | 贡献率 Phenotypic variations explained/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||
| 垩白粒率高温耐性Heat tolerance of chalky grain rate (HTCGR) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCGR1.1 | RM297 | –RM6648 | 3.50 | 0.04 | 9.04 | |||||
| 1 | qHTCGR1.2 | RM6648 | –RM6387 | 3.48 | 0.04 | 8.48 | |||||
| 3 | qHTCGR3 | SFP3_1 | –RM231 | 3.30 | 0.04 | 7.91 | |||||
| 6 | qHTCGR6.1 | RM3353 | –RM1369 | 4.44 | 7.24 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 14.24 | 12.14 | ||
| 6 | qHTCGR6.2 | RM1369 | –RM190 | 4.78 | 7.47 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 17.89 | 14.25 | ||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.1 | RM3859 | 3.06 | 0.03 | 7.98 | ||||||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.2 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 3.56 | 0.06 | 10.30 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.3 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 3.44 | 0.05 | 7.66 | |||||
| 垩白大小高温耐性Heat tolerance of chalkiness size (HTCS) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCS1 | RM8003 | –RM237 | 3.19 | –0.10 | 15.08 | |||||
| 2 | qHTCS2.1 | RM7245 | –RM6366 | 3.99 | 0.17 | 10.90 | |||||
| 2 | qHTCS2.2 | RM6366 | –RM1367 | 3.75 | 0.16 | 10.31 | |||||
| 4 | qHTCS4 | RM3866 | 2.90 | 0.16 | 7.35 | ||||||
| 6 | qHTCS6.1 | RM3353 | –RM1369 | 2.76 | –0.15 | 6.91 | |||||
| 6 | qHTCS6.2 | RM1369 | –RM190 | 2.65 | –0.19 | 10.74 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCS7.1 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 3.03 | –0.17 | 7.86 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCS7.2 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 4.02 | –0.25 | 18.76 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.1 | RM6100 | –RM25678 | 4.07 | –0.14 | 11.60 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.2 | RM25678 | –RM6745 | 3.69 | 0.14 | 10.58 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.3 | RM6745 | –RM25681 | 4.00 | –0.14 | 11.40 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.4 | RM25681 | –RM7300 | 3.02 | –0.13 | 9.68 | |||||
| 垩白度高温耐性 Heat tolerance of chalkiness degree (HTCD) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCD1 | RM8003 | –RM237 | 2.98 | –0.10 | 11.54 | |||||
| 3 | qHTCD3 | RM6349 | –SFP31 | 4.81 | –0.17 | 36.34 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCD7.1 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 4.68 | 5.54 | –0.15 | –0.14 | 13.27 | 17.44 | ||
| 7 | qHTCD7.2 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 4.25 | 6.25 | –0.16 | –0.17 | 16.32 | 29.52 | ||
Table 2 Mapping of heat tolerance QTL associated with grain chalkiness traits.
| 染色体 Chromosome | 位点 QTL | 标记区间 Marker interval | LOD值 LOD score | 加性效应 Additive effect | 贡献率 Phenotypic variations explained/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||
| 垩白粒率高温耐性Heat tolerance of chalky grain rate (HTCGR) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCGR1.1 | RM297 | –RM6648 | 3.50 | 0.04 | 9.04 | |||||
| 1 | qHTCGR1.2 | RM6648 | –RM6387 | 3.48 | 0.04 | 8.48 | |||||
| 3 | qHTCGR3 | SFP3_1 | –RM231 | 3.30 | 0.04 | 7.91 | |||||
| 6 | qHTCGR6.1 | RM3353 | –RM1369 | 4.44 | 7.24 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 14.24 | 12.14 | ||
| 6 | qHTCGR6.2 | RM1369 | –RM190 | 4.78 | 7.47 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 17.89 | 14.25 | ||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.1 | RM3859 | 3.06 | 0.03 | 7.98 | ||||||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.2 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 3.56 | 0.06 | 10.30 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCGR7.3 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 3.44 | 0.05 | 7.66 | |||||
| 垩白大小高温耐性Heat tolerance of chalkiness size (HTCS) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCS1 | RM8003 | –RM237 | 3.19 | –0.10 | 15.08 | |||||
| 2 | qHTCS2.1 | RM7245 | –RM6366 | 3.99 | 0.17 | 10.90 | |||||
| 2 | qHTCS2.2 | RM6366 | –RM1367 | 3.75 | 0.16 | 10.31 | |||||
| 4 | qHTCS4 | RM3866 | 2.90 | 0.16 | 7.35 | ||||||
| 6 | qHTCS6.1 | RM3353 | –RM1369 | 2.76 | –0.15 | 6.91 | |||||
| 6 | qHTCS6.2 | RM1369 | –RM190 | 2.65 | –0.19 | 10.74 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCS7.1 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 3.03 | –0.17 | 7.86 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCS7.2 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 4.02 | –0.25 | 18.76 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.1 | RM6100 | –RM25678 | 4.07 | –0.14 | 11.60 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.2 | RM25678 | –RM6745 | 3.69 | 0.14 | 10.58 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.3 | RM6745 | –RM25681 | 4.00 | –0.14 | 11.40 | |||||
| 10 | qHTCS10.4 | RM25681 | –RM7300 | 3.02 | –0.13 | 9.68 | |||||
| 垩白度高温耐性 Heat tolerance of chalkiness degree (HTCD) | |||||||||||
| 1 | qHTCD1 | RM8003 | –RM237 | 2.98 | –0.10 | 11.54 | |||||
| 3 | qHTCD3 | RM6349 | –SFP31 | 4.81 | –0.17 | 36.34 | |||||
| 7 | qHTCD7.1 | RM21327 | –RM21364 | 4.68 | 5.54 | –0.15 | –0.14 | 13.27 | 17.44 | ||
| 7 | qHTCD7.2 | RM21364 | –RM3859 | 4.25 | 6.25 | –0.16 | –0.17 | 16.32 | 29.52 | ||
| [1] | 林海, 庞乾林, 王志刚, 鄂志国. 2015年我国审定的水稻品种基本特性分析. 中国稻米, 2016, 22(6): 4-9. |
| Lin H, Pang G L, Wang Z G, E Z G. Analysis on characteristics of rice varieties registered in China in 2015.China Rice, 2016,22(6): 4-9. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 闵捷, 朱智伟, 章林平, 陈能, 许立, 牟仁祥. 中国超级杂交稻组合的稻米品质分析. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 206-210 |
| Min J, Zhu Z W, Zhang L P, Chen N, Xu L, Mou R X.Analysis on milled rice quality of super hybrid rice combinations in China.Chin J Rice Sci, 2014, 28(2): 206-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | IPCC. Climate Change 2001: Scientific Basis. New York, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2001. |
| [4] | 夏明元, 戚华雄. 高温热害对四个不育系配制的杂交组合结实率的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2004(2): 21-22. |
| Xia M Y, Qi H X.Effect of high temperature heat stress on seed setting rate of hybrid combinations from four sterile lines.Hubei Agric Sci, 2004 (2): 21-22. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 杨惠成, 黄仲青, 蒋之埙, 王相文. 2003年安徽早中稻花期热害及防御技术. 安徽农业科学, 2004, 32(1): 3-4. |
| Yang H C, Huang Z Q, Jiang Z X, Wang X W.Heat damage and defense technology of early and middle rice at flowering stage in Anhui in 2003.Anhui Agric Sci, 2004, 32(1): 3-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 郑建初, 张彬, 陈留根, 杜群, 秦永生, 宋健, 张卫建. 抽穗期高温对水稻产量构成要素和稻米品质的影响及其基因型差异. 江苏农业学报, 2005, 21(4):249-254. |
| Zheng J C, Zhang B, Chen L G, Du Q, Qin Y S, Song J, Zhang W J.Genotypic differences in effects of high temperature in field on rice yield components and grain quality during heading stage.Jiangsu J Agric Sci, 2005, 21(4): 249-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 谢晓金, 李秉柏, 李映雪, 李昊宇, 赵小艳, 杨沈斌, 王志明. 抽穗期高温胁迫对水稻产量构成要素和品质的影响.中国农业气象, 2010, 31(3): 411-415. |
| Xie X J, Li B B, Li Y X, Li H Y, Zhao X Y, Yang S B, Wang Z M.Effects of high temperature on rice yield components and grain quality during heading stage.Chin Agric Agrometeorol, 2010, 31(3): 411-415. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 石军, 褚旭东, 王志, 黄廷友, 李春财. 自然高温对15个籼稻杂交组合稻米品质的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(5): 897-899. |
| Shi J, Chu X D, Wang Z, Huang T Y, Li C C.Effect of natural high temperature on rice quality of 15 indica hybrid combinations.Hubei Agric Sci, 2011, 50(5): 897-899. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | Saghai-Maroof M A, Biyashev R M, Yang G P, Zhang Q. Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barley: Species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91(12): 5466-5470. |
| [10] | Chen X, Temnyk H S, Xu Y, Cho Y G, McCouch S R. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice(Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 1997, 95: 553-567. |
| [11] | Temnykh S, Park W D, Ayres N, Sam Cartinhour, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho Y G, Ishii T, McCouch S R. Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 100: 697-712. |
| [12] | McCouch S R, Teytelman L, Xu Y B, Lobos K B, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B Y, Maghirang R, Li Z K, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice(Oryza sativa L.).DNA Res, 2002, 9:199-207. |
| [13] | International Rice Genome Sequencing Project.The map-based of the rice genome.Nature, 2005, 436: 793-800. |
| [14] | Edwards J D, Janda J, Sweeney M T, Gaikwad A B, Liu B, Leung H, Galbraith D W.Development and evaluation of a high-throughput, low-cost genotyping platform based on oligonucleotide microarrays in rice.Plant Meth, 2008, 4: 13. |
| [15] | Lincoln S, Daley M, Lander E.Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0//Whitehead Institute Technical Report. 3rd ed. Cambridge: Whitehead Institute, 1992. |
| [16] | 何云丽, 叶乃忠, 郝明, 罗丽华, 肖应辉. 多环境下早籼稻重组自交系群体的抽穗期QTL分析. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 389-397. |
| He Y L, Ye N Z, Hao M, Lu L H, Xiao Y H.QTL analysis for heading date by using recombinant inbred lines derived from early-season indica rice across multi-environments.Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 27(4): 389-397. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Zeng Z B.Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci.Genetics, 1994, 136: 1457-1468. |
| [18] | Mei D Y, Zhu Y J, Yu Y H, Fan Y Y, Huang D R, Zhuang J Y.Quantitative trait loci for grain chalkiness and endosperm transparency detected in three recombinant inbred line populations of indica rice.J Integr Agric, 2013, 12: 1-11. |
| [19] | 周立军, 刘喜, 江玲, 郑蕾娜, 陈亮明, 刘世家, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 利用CSSL和BIL群体分析稻米垩白粒率QTL及互作效应. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(4): 1129-1135. |
| Zhou L J, Liu X, Jiang L, Zheng L N, Chen L M, Liu S J, Zhai F Q, Wan J M.Analysis of QTL and GE effects on PGWC in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using CSSL and BIL populations.Sci Agric Sin, 2009, 42(4): 1129-1135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Liu X, Wang Y and Wang S W. QTL analysis of percentage of grains with chalkiness in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L).Gen Mol Res, 2012, 11: 717-724. |
| [21] | 晁园, 冯付春, 高冠军, 朱雪萍,何予卿.利用重组自交系群体定位水稻品质相关性状的QTL. 华中农业大学学报, 2012, 31(4): 397-403. |
| Chao Y, Feng F C, Gao G J, Zhu X P, He Y Q.Mapping QTLs related with rice qualities of appearance, cooking and eating using a recombinant inbred line population. J Huangzhong Agric Univ, 2012, 31(4): 397-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 杨亚春, 倪大虎, 宋丰顺, 李泽福, 易成新, 杨剑波. 不同生态地点下稻米外观品质性状的QTL定位分析. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 43-51. |
| Yang Y C, Ni D H, Song F S, Li Z F, Yi C X, Yang J B.Identification of QTLs of rice appearance quality traits across different ecological sites.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(1): 43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王林森, 陈亮明, 王沛然, 王卓然, 郑海, 马宏阳, 江玲, 赵志刚, 万建民. 利用高世代回交群体检测水稻垩白相关性状QTL.南京农业大学学报,2016, 39(2): 183-190. |
| Wang L S, Chen L M,Wang P R, Wang Z R, Zheng H, Ma H Y, Jiang L, Zhao Z G, Wan J M.Detecting the QTL of rice chalkiness traits using advanced backcrossing population.J Nanjing Agric Univ, 2016, 39(2): 183-190.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 朱昌兰. 稻低直链淀粉含量的遗传及品质形成对高温耐性的QTL分析. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2004. |
| Zhu C L.Identifying QTLs for thermo-tolerance of quality formation and inheritance of low amylose content in rice. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 李健陵, 林育炯, 张晓艳, 杜尧东, 王华, 吴丽姬, 胡飞. 抽穗期和乳熟期高温对水稻剑叶理化特性以及产量和品质的影响. 农业现代化研究, 2013, 34(11): 109-113. |
| Li J L, Lin Y J, Zhang X Y, Du Y D, Wang H, Wu L J, Hu F.Effects of high temperature on physiological and biochemical characteristics of flag leaves, grain yield and quality of rice in heading and milk stage. Res Agric Mod, 2013, 34(11): 109-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张桂莲, 陈立云, 张顺堂, 黄明, 唐文邦, 雷东阳, 李梅华, 贺治洲. 高温胁迫对水稻花器官和产量构成要素及稻米品质的影响. 湖南农业大学学报, 2007, 33(2): 132-136. |
| Zhang G L, Chen L Y, Zhang S T, Huang M, Tang W B, Lei D Y, Li M H, He Z Z.Effects of high temperature stress on rice flower organ and yield components and grain quality. J Hunan Agric Univ, 2007, 33(2): 132-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 张国发, 王绍华, 尤娟, 王强盛, 丁艳锋, 吉志军. 结实期不同时段高温对稻米品质的影响. 作物学报, 2006, 32(2): 283-287. |
| Zhang G F, Wang S H, You J, Wang Q S, Ding Y F, Ji Z J.Effect of higher temperature in different filling stages on rice qualities.Acta Agron Sin, 2006, 32(2): 283-287.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 盛婧, 陶红娟, 陈留根. 灌浆结实期不同时段温度对水稻结实与稻米品质的影响.中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(4): 396-402. |
| Sheng Q, Tao H J, Chen L G.Response of seed-setting and grain quality of rice to temperature at different time during grain filling period.Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(4): 396-402.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 赵飞, 尹维娜, 曲丽君, 东丽, 华泽田. 水稻外观品质与产量构成因素的QTL解析. 核农学报, 2014, 28(6): 990-997. |
| Zhao F, Yin W N, Qu L J, Dong L, Hua Z T.Correlation and QTL analysis of the rice appearance quality and processing quality.J Nuclear Agric Sci, 2014, 28(6): 990-997. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 陶亚军, 徐梦彬, 王飞, 陈达, 周勇, 梁国华. 利用染色体单片段代换系定位水稻垩白QTL. 华北农学报, 2015, 30(1): 1-8. |
| Tao Y J, Xu M B, Wang F, Chen D, Zhou Y, Liang G H.QTL mapping of chalkiness using chromosome single segment substituted lines in rice.Acta Agric Boreali-sin, 2015, 30(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 盘毅, 罗丽华, 邓化冰, 张桂莲, 唐文邦, 陈立云, 肖应辉. 水稻开花期高温胁迫下的花粉育性QTL定位. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 99-102. |
| Pan Y, Luo L H, Deng H B, Zhang G L, Tang W B, Chen L Y, Xiao Y H.Quantitative trait loci associated with pollen fertility under high temperature stress at flowering stage in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(1): 99-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Yamakawa H, Ebitani T, Terao T.Comparison between locations of QTLs for grain chalkiness and genes responsive to high temperature during grain filling on the rice chromosome map.Breeding Sci, 2008, 58(3): 337-343. |
| [33] | 高方远, 邱玲, 陆贤军, 任鄄胜, 吴贤婷, 任光俊, 曾礼华. 杂交籼稻骨干保持系岗46B稻谷粒形及垩白的QTL分析. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3): 235-242. |
| Gao F Y, Qiu L, Lou XJ, Ren Z S, Wu X T, Ren G J, Zeng L H.QTL analysis on grain shape and chalkiness of an elite maintainer line Gang 46B in hybrid rice(Oryza sativa L.).Chin J Rice Sci, 2014, 28(3): 235-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||