
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 253-264.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220808
王文婷1,#, 马佳颖1,#, 李光彦1,3, 符卫蒙1, 李沪波1, 林洁1, 陈婷婷1, 奉保华1, 陶龙兴1, 符冠富1, 秦叶波2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-25
修回日期:2022-12-05
出版日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-05-16
通讯作者:
*email: qyb.leaf@163.com
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
WANG Wenting1,#, MA Jiaying1,#, LI Guangyan1,3, FU Weimeng1, LI Hubo1, LIN Jie1, CHEN Tingting1, FENG Baohua1, TAO Longxing1, FU Guanfu1, QIN Yebo2,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-25
Revised:2022-12-05
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: qyb.leaf@163.com
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】近年来极端高温天气频发,严重抑制水稻产量品质形成,优化植株营养状态,改善能量代谢可减缓高温热害,但高温下不同施肥量对籽粒能量代谢的影响及其与产量、品质及耐热性形成的影响仍未见报道,其作用机制的阐明可为水稻耐热性抗风险栽培技术研发提供重要理论依据。【方法】以浙江省推广大面积较大的单季杂交籼稻品种中浙优8号为材料,采用人工气候室盆栽的试验方法开展研究。设置不施肥(0-NPK)、1/2肥料(1/2-NPK)和正常施肥(1-NPK)三个肥料用量处理,开花当天移至人工气候室高温处理15d(高温处理设置昼/夜分别为36/28℃,常温对照设置昼/夜分别为28/25℃)。【结果】无论常温或高温下,在供试肥料水平下随着施肥量增加,中浙优8号产量、结实率及千粒重均呈逐渐增加的趋势;高温下,结实率、千粒重的下降幅度随施肥量增加而下降。然而,整精米率随施肥量增加而下降,垩白度则呈增加的趋势。高温处理后籽粒可溶性糖、MDA、H2O2、腺苷三磷酸酶(ATPase)及PARP [poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase]含量高于常温对照处理,淀粉、非结构性碳水化合物、抗氧化酶活性及ATP含量则低于常温对照。无论常温或高温下非结构性碳水化合物、抗氧化酶活性、ATP及ATPase均随着施肥量的增加而提高,而MDA、H2O2及PARP含量则呈下降趋势。常温下,能量感受器基因SnRK1A及SnRK1B相对表达量随施肥量增加而下降,而TOR则呈增长趋势。与常温对照相比,高温处理后SnRK1A上调表达,而TOR相对表达量随施肥量增加而上调。【结论】增施肥料能有效缓解花期高温对水稻结实率及千粒重的影响,但外观品质与加工品质存在变劣的趋势。常温下,增施肥料品质变劣可能与籽粒灌浆速率加快有关,而高温导致品质下降主要在于能量不足,难以满足产量及品质形成的需求。
王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264.
WANG Wenting, MA Jiaying, LI Guangyan, FU Weimeng, LI Hubo, LIN Jie, CHEN Tingting, FENG Baohua, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu, QIN Yebo. Effect of Different Fertilizer Application Rates on Rice Yield and Quality Formation and Its Relationship with Energy Metabolism at High Temperature[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 253-264.
| 气象条件 Meteorological condition | 六月 June | 七月 July | 八月 August | 九月 September | 十月 October | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨量Precipitation/mm 日照时长Sunshine/h 平均气温Temperature/°C | 221.8 141.2 26.6 | 317.9 246.7 29.3 | 315.6 254.2 28.6 | 125.0 237.8 26.8 | 68.6 196.8 20.0 | ||
表1 水稻生长期降雨量、日照时长以及平均气温的变化
Table 1. Monthly total precipitation, sunshine hours, and average temperature during the rice growing seasons.
| 气象条件 Meteorological condition | 六月 June | 七月 July | 八月 August | 九月 September | 十月 October | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨量Precipitation/mm 日照时长Sunshine/h 平均气温Temperature/°C | 221.8 141.2 26.6 | 317.9 246.7 29.3 | 315.6 254.2 28.6 | 125.0 237.8 26.8 | 68.6 196.8 20.0 | ||
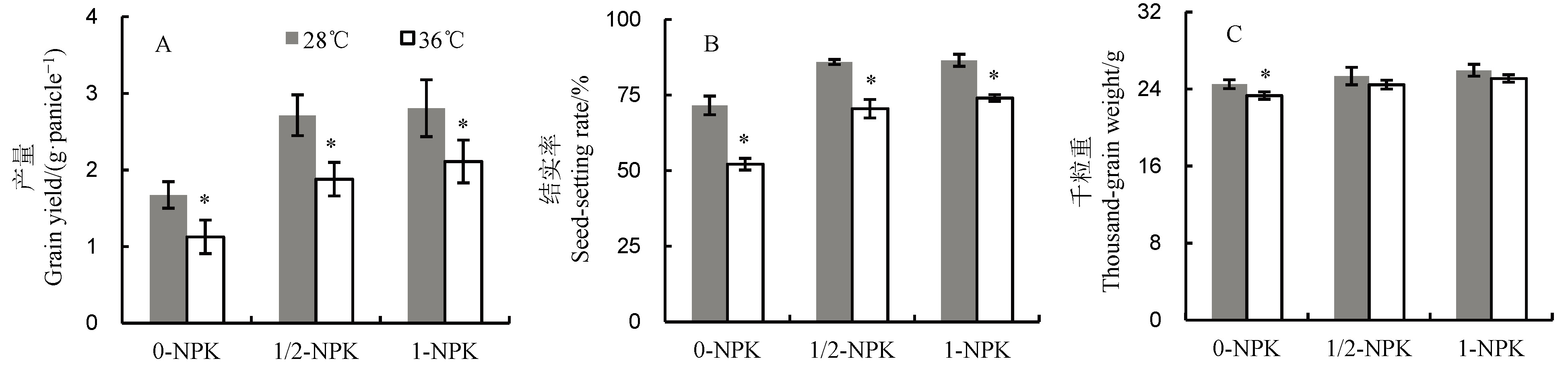
图1 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量、结实率和千粒重的影响 0-NPK、1/2-NPK和1-NPK分别表示NPK施肥量分别为0、1/2正常用量和正常用量。*表示t检验比较分析显著差异。下同。
Fig. 1. Effects of different fertilizer application on grain yield, seed setting rate and thousand-grain weight of rice under heat stress. 0-NPK, Zero fertilizer application rate; 1/2-NPK, 1/2 application level of normal practice; 1-NPK, Normal application level. * denotes significant difference at P < 0.05 by t-test. The same below
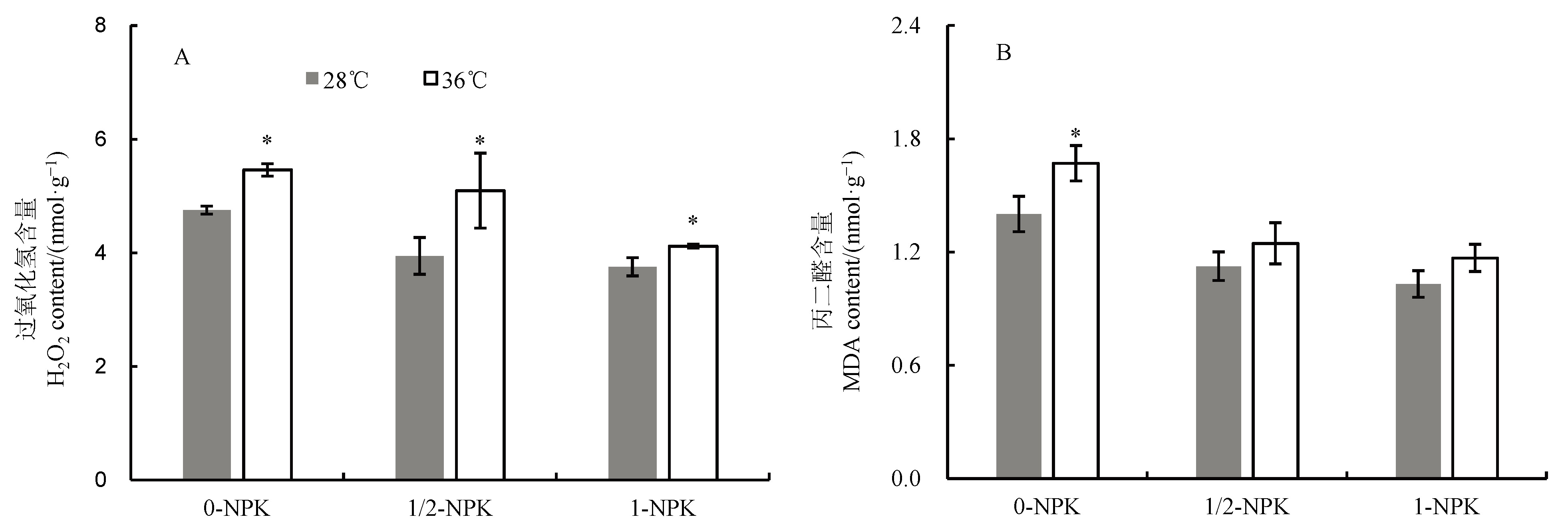
图4 高温下不同施肥量对籽粒H2O2和MDA含量的影响
Fig. 4. Effects of different fertilizer application levels on contents of MDA and H2O2 in grains of rice under heat stress.
| [1] | IPCC. Summary for policymakers//Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pirani A. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 1-41 |
| [2] | Muthayya S, Sugimoto J D, Montgomery S, Maberly G F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2014, 1324: 7-14. |
| [3] | Bhagirath S, Khawar J, Gulshan M. Rice Production Worldwide[M]. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG, 2017. |
| [4] | Rahaman M M, Shehab M K, Islam A. Total production and water consumption of major crops in south asia during 1988-2013[c]// Conference on Water Security and Climate Change: Challenges and Opportunities in Asia, 28 November - 01 December, 2016. 2016. |
| [5] | Perkins-Kirkpatrick S E, Lewis S C. Increasing trends in regional heatwaves[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3357. |
| [6] | 黄福灯, 李春寿, 刘鑫, 程方民. 高温胁迫对水稻花粉活力的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2010, (6): 1272-1274. |
| Huang F D, Li C S, Liu X, Cheng F M. Effects of high temperature stress on pollen viability of rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2010, (6): 1272-1274. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 程方民, 刘正辉, 张嵩午. 稻米品质形成的气候生态条件评价及我国地域分布规律[J]. 生态学报, 2002(5): 636-642. |
| Cheng F M, Liu Z H, Zhang S W. Evaluation on climatic ecological conditions of rice quality formation and regional distribution of our country[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002(5): 636-642. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Zhang C X, Li G Y, Chen T T, Feng B H, Fu W M, Yan J X, Islam M R, Jin Q Y, Tao L X, Fu G F. Heat stress induces spikelet sterility in rice at anthesis through inhibition of pollen tube elongation interfering with auxin homeostasis in pollinated pistils[J]. Rice, 2018, 11(1): 1-12. |
| [9] | Jiang N, Yu P H, Fu W M, Li G Y, Feng B H, Chen T T, Li H B, Tao L X, Fu G F. Acid invertase confers heat tolerance in rice plants by maintaining energy homoeostasis of spikelets[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2020, 43(5): 1273-1287. |
| [10] | 符冠富, 张彩霞, 杨雪芹, 杨永杰, 陈婷婷, 赵霞, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 章秀福, 陶龙兴, 金千瑜. 水杨酸减轻高温抑制水稻颖花分化的作用机理研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 637-647. |
| Fu G F, Zhang C X, Yang X Q, Yang Y J, Chen T T, Zhao X, Fu W M, Feng B H, Zhang X F, Tao L X, Jin Q Y. Effect of salicylic acid on inhibition of spikelet differentiation at high temperature in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(6): 637-647. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Zhang C X, Feng B H, Chen T T, Zhang X F, Tao L X, Fu G F. Sugars, antioxidant enzymes and IAA mediate salicylic acid to prevent rice spikelet degeneration caused by heat stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 2017, 83: 313-323. |
| [12] | Feng B, Zhang C, Chen T, Zhang X, Tao L, Fu G. Salicylic acid reverses pollen abortion of rice caused by heat stress[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2018, 18(1): 245. |
| [13] | Sousa J S, Calisto F, Langer J D, Mills D J, Refojo P N, Teixeira M, Kuhlbrandt W, Vonck J, Pereira M M. Structural basis for energy transduction by respiratory alternative complex III[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1728. |
| [14] | Li G Y, Zhang C X, Zhang G H, Fu W M, Feng B H, Chen T T, Peng S B, Tao L X, Fu G F. Abscisic acid negatively modulates heat tolerance in rolled leaf rice by increasing leaf temperature and regulating energy homeostasis[J]. Rice (N Y), 2020a, 13(1): 18. |
| [15] | Chen T T, Li G Y, Islam M R, Fu W M, Feng B H, Tao L X, Fu G F. Abscisic acid synergizes with sucrose to enhance grain yield and quality of rice by improving the source-sink relationship[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 525. |
| [16] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 徐徽, 杨志远, 秦俭, 彭玉, 马均. 水氮管理模式与磷钾肥配施对杂交水稻冈优725养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(7): 1335-1346. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yang Z Y, Qin J, Peng Y, Ma J. Effects of water and nitrogen management mode and combined application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on nutrient uptake of hybrid rice Gangyou 725[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(7): 1335-1346. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 姜红芳, 兰宇辰, 王鹤璎, 徐令旗, 李猛, 赵洋, 李晓蕾, 刘旭莹, 吕艳东, 郭晓红. 氮肥运筹对苏打盐碱地水稻养分积累、转运及分配的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020, (5): 45-55. |
| Jang H F, Lan Y C, Wang H Y, Xu L Q, Li M, Zhao Y, Li X L, Liu X Y, Lü Y D, Guo X H. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer operation on nutrient accumulation, transport and distribution of rice in soda-alkali soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2020, (5): 45-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Fahad S, Hussain S, Saud S, Hassan S, Tanveer M, Ihsan M Z, Shah A N, Ullah A, Nasrullah, Khan F, Ullah S, Alharby H, Nasim W, Wu C, Huang J L. A combined application of biochar and phosphorus alleviates heat-induced adversities on physiological, agronomical and quality attributes of rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 103: 191-198. |
| [19] | Xu Y Q, Guan X Y, Han Z Y, Zhou L J, Zhang Y, Asad M, Wang Z W, Jin R, Pan G, Cheng F M. Combined effect of nitrogen fertilizer application and high temperature on grain quality properties of cooked rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 874033. |
| [20] | Tang S, Zhang H X, Liu W Z, Dou Z, Zhou Q Y, Chen W Z, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 455-462. |
| [21] | Wang X Q, Wang K L, Yin T Y, Zhao Y F, Liu W Z, Shen Y Y, Ding Y F, Tang S. Nitrogen fertilizer regulated grain storage protein synthesis and reduced chalkiness of rice under actual field warming[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 12: 715436. |
| [22] | Ma J Y, Chen T T, Lin J, Fu W M, Feng B H, Li G Y, Li H B, Li J C, Wu Z H, Tao L X, Fu G F. Functions of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in energy status and their influences on rice growth and development[J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(2): 166-178. |
| [23] | Xu H X, Weng X Y, Yang Y. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthetic characteristics of rice plants[J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2007, 54(6): 741-748. |
| [24] | Chaudhary M I, Adu-Gyamfi J J, Saneoka H, Nguyen N T, Suwa R, Kanai S, El-Shemy H A, Lightfoot D A, Fujita K. The effect of phosphorus deficiency on nutrient uptake, nitrogen fixation and photosynthetic rate in mashbean, mungbean and soybean[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2008, 30(4): 537-544. |
| [25] | Shabala S. Regulation of potassium transport in leaves: from molecular to tissue level[J]. Annals of Botany, 2003, 92(5): 627-634. |
| [26] | Britto D T, Kronzucker H J. Cellular mechanisms of potassium transport in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 133(4): 637-650. |
| [27] | Yoshida S, Fornd D A, Cock J H, Gomez K A. Determination of sugar and starch in plant tissue[M]//Yoshida S. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Los Baños, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 1976: 46-49. |
| [28] | Giannopolitis C N, Ries S K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 59(2), 1977, 309-314. |
| [29] | Maehly A C, Chance B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases[J]. Methods of Biochemical Analysis, 1954, 1: 357-424. |
| [30] | Bonnecarrère V, Borsani O, Pedro Díaz, Fabián Capdevielle, Blanco P, Monza J. Response to photoxidative stress induced by cold in japonica rice is genotype dependent[J]. Plant Science, 2011, 180(5): 726-732. |
| [31] | Brennan T, Frenkel C. Involvement of hydrogen peroxide in the regulation of senescence in pear. Plant Physiology, 1977, 59(3): 411-416. |
| [32] | Dhindsa R S, Pamela P D, Thorpe T A. Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1981(1): 93-101. |
| [33] | 赵庆雷, 吴修, 王瑜, 李曰鹏, 陈博聪, 王佳, 马加清. 扬花期高温条件下施肥量对水稻高位分蘖及产量性状的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2016, 48(8): 61. |
| Zhao Q L, Wu X, Wang Y, Li Y P, Chen B C, Wang J, Ma J Q. Effects of fertilizer application on high tillering and yield characters of rice at high temperature during flowering stage[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 48(8): 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 闫娜. 增施氮素穗肥对幼穗分化期高温下水稻产量的影响及生理机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| Yan N. Effects of increased nitrogen panicle fertilizer on rice yield at high temperature during young panicle differentiation and its physiological mechanism[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 赵决建. 氮磷钾施用量及比例对水稻抗高温热害能力的影响[J]. 土壤肥料, 2005(5): 13-16. |
| Zhao J J. Effects of application amount and proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on resistance to high temperature heat damage of rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer, 2005(5): 13-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 胡秋倩. 幼穗分化期高温影响水稻产量形成的机理及氮素调控研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| Hu Q Q. Effect of high temperature on rice yield Formation and Nitrogen regulation during young panicle differentiation[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 孙丽平, 李笑, 苏雪娇. 中华牛肝菌多糖的性质及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 2016, 37(24): 173-175. |
| Sun L P, Li X, Su X J. Properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Porcini sinensis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(24): 173-175. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 缪乃耀. 氮素粒肥对水稻灌浆前期高温胁迫的缓解效应及其生理机制[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. |
| Miao N Y. Alleviating effect and physiological mechanism of nitrogen granule fertilizer on high temperature stress in early filling stage of rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Xiong D L, Yu T T, Ling X X, Fahad S, Peng S B, Li Y, Huang J L. Sufficient leaf transpiration and nonstructural carbohydrates are beneficial for high-temperature tolerance in three rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars and two nitrogen treatments[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2015, 42(4): 347-356. |
| [40] | 王慧, 张从合, 严志, 申广勒, 周桂香, 杨韦, 方玉, 黄艳玲, 庞战士, 李方宝. 荃两优系列杂交稻品种耐热性与稻米品质的相关性研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(4): 79-83. |
| Wang H, Zhang C H, Yan Z, Shen G L, Zhou G X, Yang W, Fang Y, Huang Y L, Pang Z S, Li F B. Study on the correlation between heat resistance and rice quality of QuanLiangyou Series hybrid rice[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(4): 79-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 韩展誉, 吴春艳, 许艳秋, 黄福灯, 熊义勤, 管弦悦, 周庐建, 潘刚, 程方民. 不同施氮水平下灌浆期高温对水稻贮藏蛋白积累及其合成代谢影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1439-1454. |
| Han Z Y, Wu C Y, Xu Y Q, Huang F D, Xiong Y Q, Guan X Y, Zhou L J, Pan G, Cheng F M. Effects of high temperature on storage protein accumulation and anabolic metabolism of rice under different nitrogen application levels[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1439-1454. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 郭银燕, 张云康, 蒋美明, 胡秉民, 陈昆荣. 浙江省早籼稻区试品种(系)碾磨品质研究[J]. 生物数学学报, 1996(1): 85-88. |
| Guo Y Y, Zhang Y K, Jiang M M, Hu B M, Chen K R. Study on milling quality of early indica rice varieties (lines) in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Biomathematics, 1996(1): 85-88. | |
| [43] | 周培南, 冯惟珠, 许乃霞, 张亚洁, 苏祖芳. 施氮量和移栽密度对水稻产量及稻米品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业研究, 2001(1): 27-31. |
| Zhou P N, Feng W Z, Xu N X, Zhang Y J, Su Z F. Effects of nitrogen application rate and transplanting density on rice yield and quality[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Agricultural Research, 2001(1): 27-31. | |
| [44] | 杨志根. 不同施肥量对水稻产量及经济性状的影响[J]. 上海农业科技, 2011(4): 94. |
| Yang Z G. Effects of different fertilizer application rates on rice yield and economic characters[J]. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011(4): 94. | |
| [45] | Chen T T, Yang X Q, Fu W M, Li G Y, Feng B H, Fu G F, Tao L X. Strengthened assimilate transport improves yield and quality of super rice[J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(4): 753. |
| [46] | Li G Y, Chen T T, Feng B H, Peng S B, Tao L X, Fu G F. Respiration, rather than photosynthesis, determines rice yield loss under moderate high-temperature conditions[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 1287-. |
| [47] | Robaglia C, Thomas M, Meyer C. Sensing nutrient and energy status by SnRK1 and TOR kinases[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2012, 15(3): 301-7. |
| [48] | Rodriguez M, Parola R, Andreola S, Pereyra C, Martínez-Noël G. TOR and SnRK1 signaling pathways in plant response to abiotic stresses: Do they always act according to the "yin-yang" model?[J]Plant Science, 2019, 288: 110220. |
| [49] | 李志刚, 叶正钱, 杨肖娥, V.V. Virmani. 不同养分管理对杂交稻生育后期功能叶生理活性和籽粒灌浆的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2003(3): 31-36. |
| LI Z G, YE Z Q, YANG X E, Virmani V V. Effects of different nutrient management on physiological activities of functional leaves and grain filling in late growth period of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Agriculture & Life Sciences Edition, 2003(3): 31-36. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||