
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 367-376.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210805
黄奇娜1,#, 江苏2,#, 汪利民2, 张燕1, 俞林飞1, 李春福1, 丁利群2, 邵国胜1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-09
修回日期:2021-10-02
出版日期:2022-07-10
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
邵国胜
基金资助:
HUANG Qina1,#, JIANG Su2,#, WANG Limin2, ZHANG Yan1, YU Linfei1, LI Chunfu1, DING Liqun2, SHAO Guosheng1,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-09
Revised:2021-10-02
Online:2022-07-10
Published:2022-07-12
Contact:
SHAO Guosheng
摘要:
【目的】为了探究低温冷害胁迫后水分/湿度对水稻幼苗根系活力和水分运输等的影响,【方法】以具有低温耐性差异的嘉籼7号和辐8329两个水稻品种为研究材料进行低温胁迫处理后,在进行实验Ⅰ(不同湿度梯度,正常温度培养条件下)和实验Ⅱ(快速回温处理实验,以正常温度恢复为对照)。【结果】实验Ⅰ结果表明,与较低湿度(30%)相比,较高的湿度(60%和90%)可以提高根系活力,有效保证水稻幼苗的存活率并缓解其遭受的低温冷害。水孔蛋白基因OsPIP2;5和OsPIP2;6的表达水平与根系活力密切相关,对水稻的抗寒和低温耐性具有显著的调控作用。实验Ⅱ结果表明,与对照组(CK)相比,快速回温处理后水稻幼苗的含水量和根系活力显著降低;且正常自然恢复状态下,两个水稻品种的存活率明显高于快速回温组幼苗。【结论】低温胁迫显著影响水稻幼苗的生长发育过程。较高的湿度环境有助于缓解幼苗的低温冷害损伤,保证存活率。同时,低温胁迫后的外界环境湿度对水稻幼苗的含水量、根系活力和水孔蛋白相关基因表达有显著影响,其中OsPIP2;5和OsPIP2;6的表达水平与根系活力正相关,在水稻幼苗抵御外界低温冷害过程中起重要作用。因此,与低温胁迫后田间大量灌溉相比,正常温度下土壤缓慢的温度上升对幼苗的根系活力影响较小,有助于其在低温冷害后恢复生命活动。
黄奇娜, 江苏, 汪利民, 张燕, 俞林飞, 李春福, 丁利群, 邵国胜. 低温胁迫后水分对水稻幼苗根系活力和水孔蛋白相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 367-376.
HUANG Qina, JIANG Su, WANG Limin, ZHANG Yan, YU Linfei, LI Chunfu, DING Liqun, SHAO Guosheng. Effects of Moisture Content on Root Vigor and the Expression of Aquaporin-related Genes in Rice Seedlings Under Low Temperature Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 367-376.
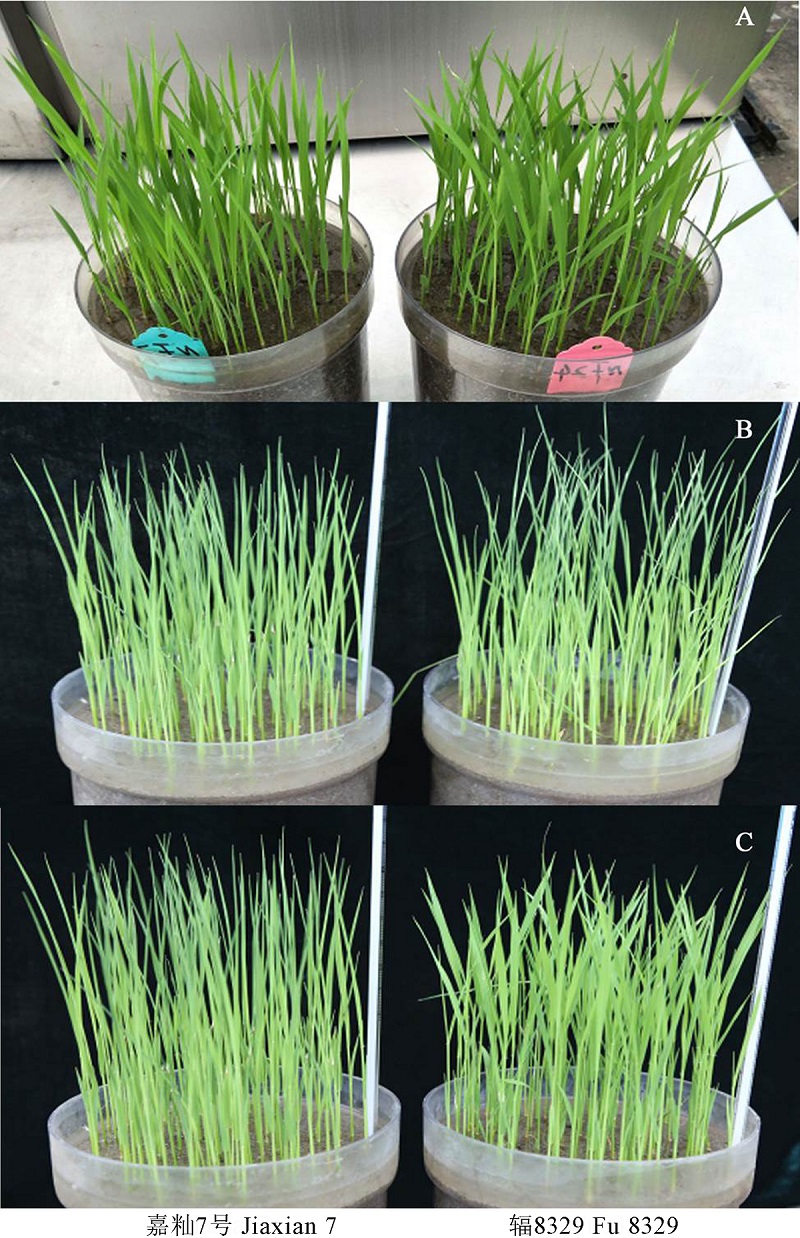

图1 低温处理3 d后的嘉籼7号和辐8329表型变化 A―低温处理前;B―低温处理1 d后;C―低温处理3 d后。
Fig. 1. Phenotype of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 after 3 days of low temperature treatment. A, Before low temperature treatment; B, 1 d of low temperature treatment; C, 3 d of low temperature treatment.
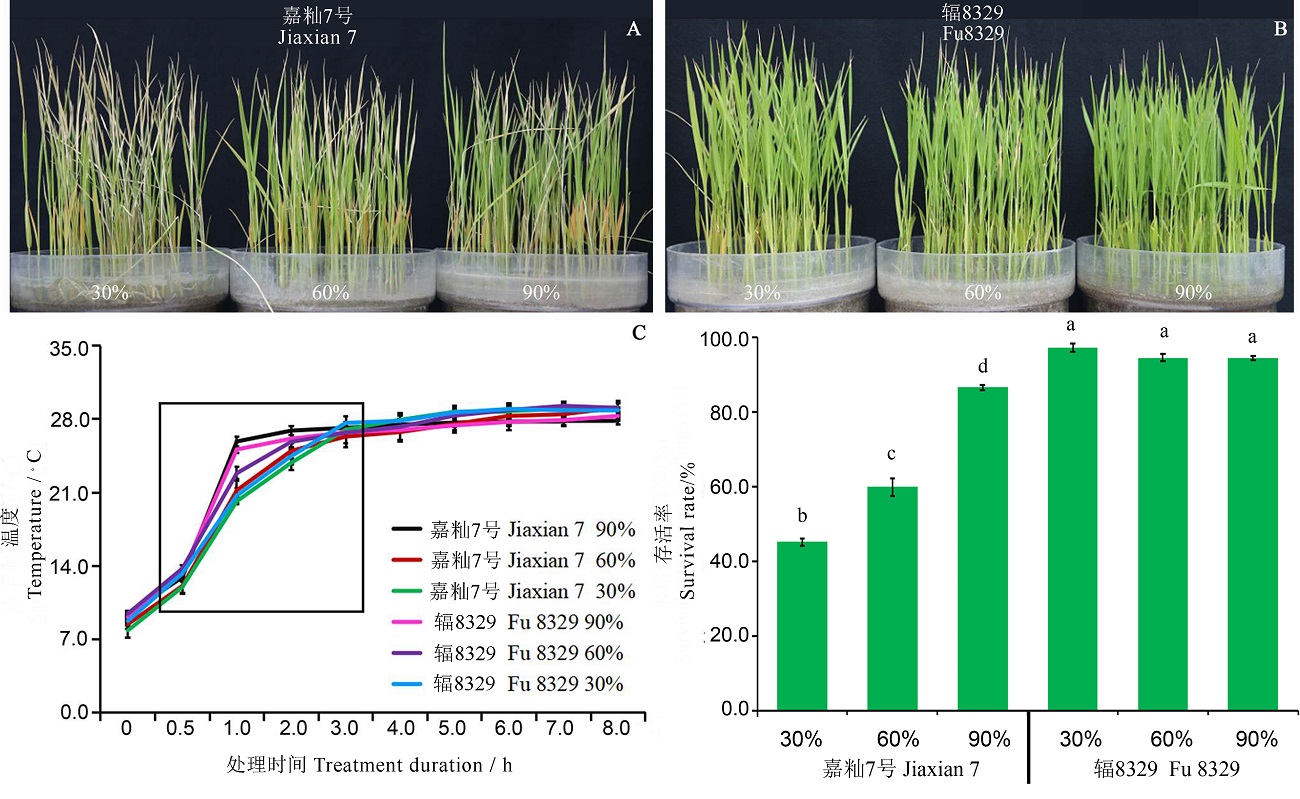
图2 低温胁迫后不同湿度恢复处理嘉籼7号和辐8329的表型、沙子温度变化和存活率 A-嘉籼7号在低湿度(30%)、中湿度(60%)和高湿度(90%)三个湿度处理5 d的表型;B―辐8329在三个湿度处理5 d的表型;C―嘉籼7号和辐8329在不同湿度处理下沙子温度变化;D,嘉籼7号和辐8329在三个湿度处理5 d后的幼苗存活率。数值表示平均值±标准差(n=3)。不同小写字母表示幼苗存活率在处理之间的差异达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 2. Phenotype, sand temperature and survival rate of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 under different humidity after low temperature stress. A, Phenotype of Jiaxian 7 under different humidity conditions(30%,60%,90%); B, Phenotype of Fu 8329 under different humidity conditions; C, Sand temperature of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329; D, Survival rate of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329. Data were means ± standard deviation (SD) from three replicated experiments (n = 3). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P < 0.05).
| 品种 Variety | 低湿度 Low humidity | 中湿度 Medium humidity | 高湿度 High humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 嘉籼7号Jiaxian 7 | 129.75 ± 5.34 d | 170.92 ± 2.60 b | 97.48 ± 3.36 e |
| 辐8329 Fu 8329 | 144.84 ± 1.78 c | 404.19 ± 18.53 a | 161.63 ± 2.88 b |
表1 嘉籼7号和辐8329三个不同湿度处理5 d后的根系活力
Table 1. Root vigor of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 exposed to different humidity for 5 d. mg/(g·h)
| 品种 Variety | 低湿度 Low humidity | 中湿度 Medium humidity | 高湿度 High humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 嘉籼7号Jiaxian 7 | 129.75 ± 5.34 d | 170.92 ± 2.60 b | 97.48 ± 3.36 e |
| 辐8329 Fu 8329 | 144.84 ± 1.78 c | 404.19 ± 18.53 a | 161.63 ± 2.88 b |
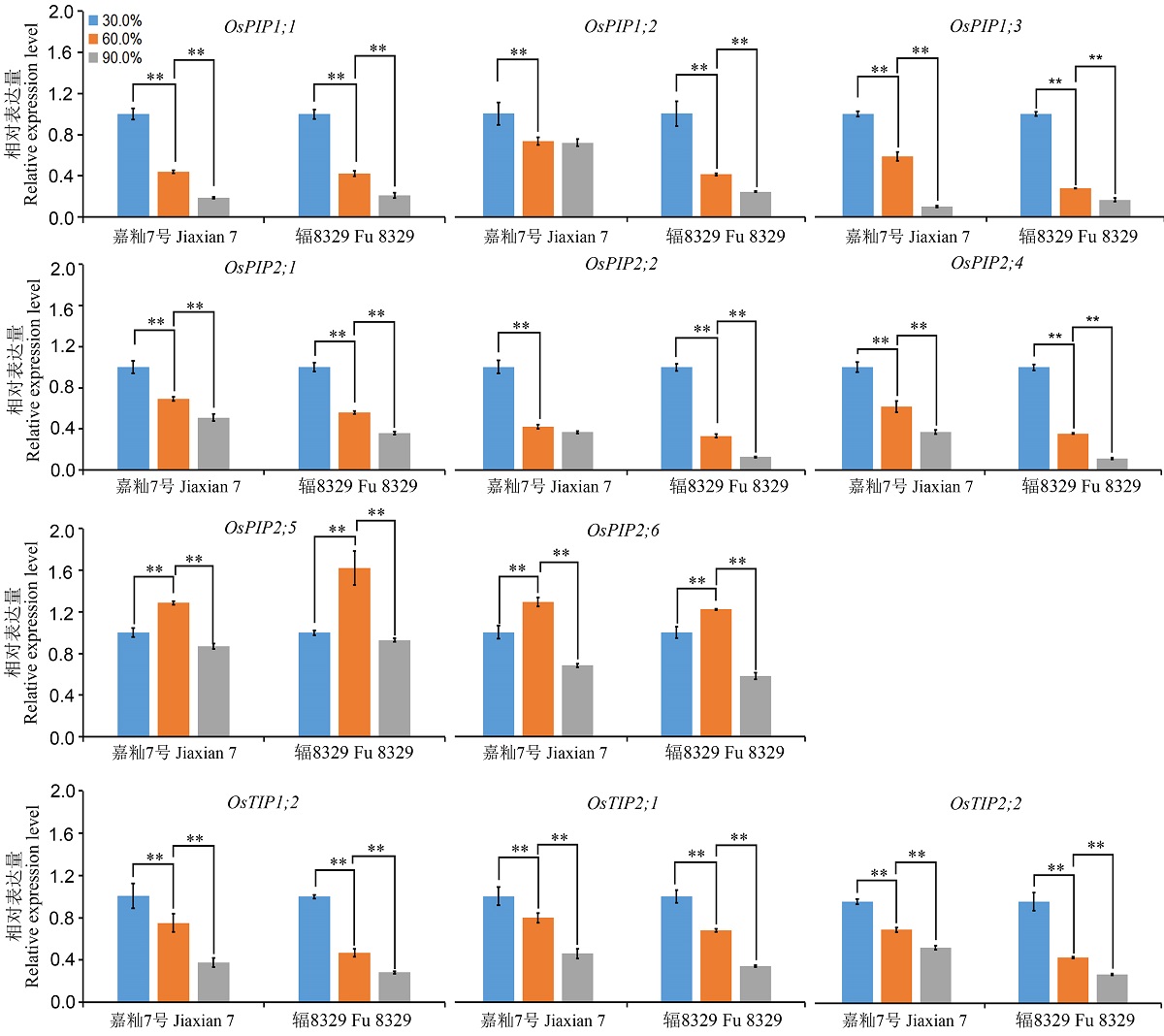
图3 低温胁迫后不同湿度恢复处理对嘉籼7号和辐8329根系中水孔蛋白相关基因表达量影响。 数值表示±SD(n=3)(t-test);**,表示极显著差异P < 0.01。
Fig. 3. Effect of humidity treatments after chilling stress on relative expression levels of aquaporin-related genes in roots of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329. Data were means ± standard deviation (SD) from three replicated experiments (n = 3)(t-test); **, Significant at P < 0.01.
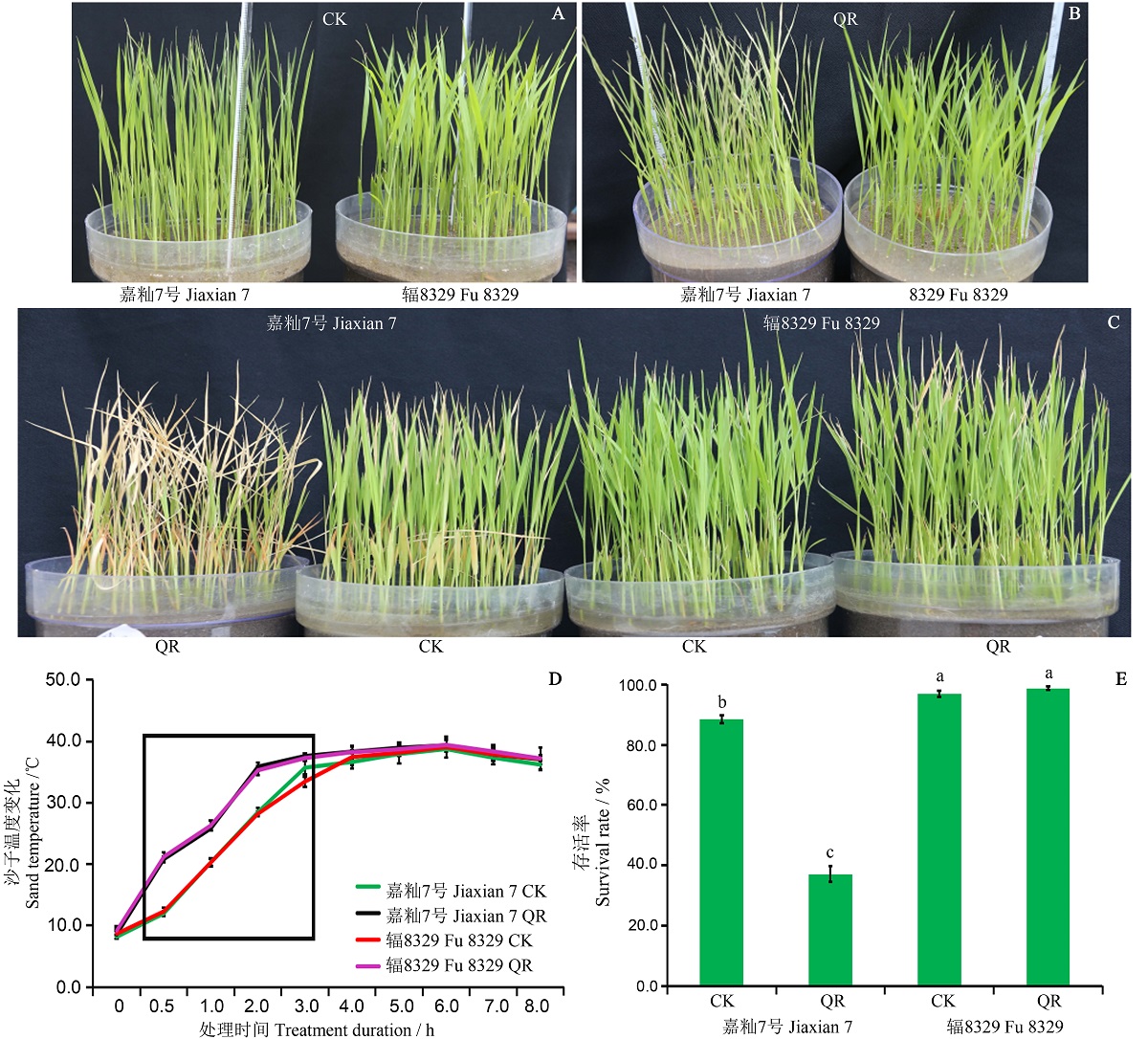
图4 快速回温后嘉籼7号和辐8329的表型、沙子温度变化和存活率 A-对照组(CK);B-快速回温组(QR)处理5 h后;C,常温恢复3 d后的表型;D,快速回温处理后沙子温度变化;E,快速回温处理后的幼苗存活率。数值表示平均值±标准差(n=3),不同的小写字母表示水稻幼苗率在处理之间的显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4. Phenotype, sand temperature and survival rate of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 after quick rewarming. A, Controls; B, Quick rewarming after 5 h of treatment; C, Phenotype of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 with water change test after 3 d; D, Sand temperature of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329; E, Survival rate. Data were means ±SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P < 0.05).
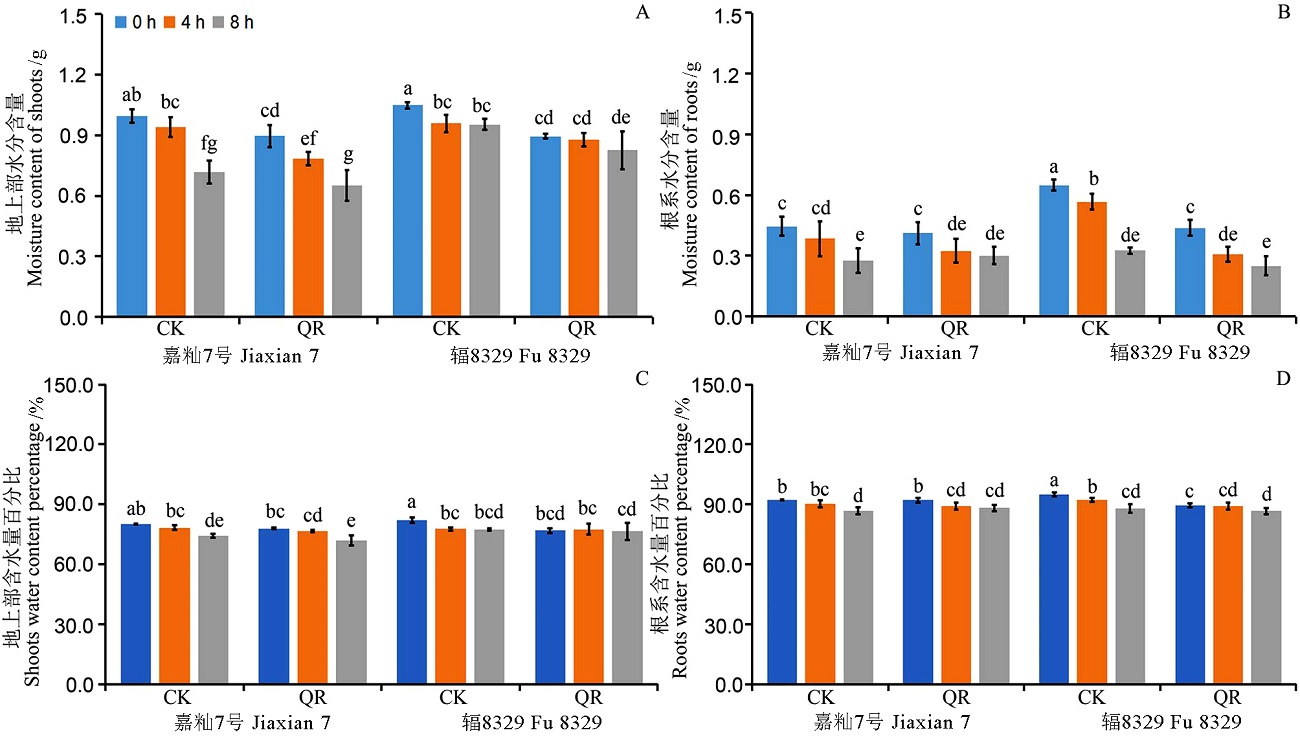
图5 快速回温实验常温恢复0,4和8 h后嘉籼7号和辐8329地上部、根系水分含量和含水量百分比 CK表示对照,QR表示快速回温处理,数值表示±SD(n=3),柱形图上不同的小写字母表示P < 0.05。A和B表示地上部和根系的水分含量(g);C和D表示地上部和根系的含水量(%)。
Fig. 5. Moisture content and water content in shoots and roots of Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329 after 0, 4 and 8 h of treatment. CK, Control; QR, Quick rewarming. Data were means ± standard deviation (SD) from three replicated experiments (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the error bars represented significant differences (P < 0.05). A, Moisture content of shoots; B, Moisture content of roots; C, Water content (%) of shoots; D, Water content (%) of roots.
| 品种 Variety | 处理后0 h 0 h after treatment/ (mg·g−1·h−1) | 处理后3 d Three days after treatment/ (mg·g−1·h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 CK | 快速回温组 Quick rewarming | 对照组 CK | 快速回温组 Quick rewarming | |
| 嘉籼7号 Jiaxian 7 | 12.68 ± 0.66 b | 25.40 ± 5.59 a | 181.66 ± 1.85 b | 43.12 ± 2.52 d |
| 辐8329 Fu 8329 | 9.74 ± 1.49 b | 13.17 ± 1.03 b | 308.67 ± 5.95 a | 87.40 ± 2.97 c |
表2 快速回温和常温恢复对低温胁迫处理后的嘉籼7号和辐8329根系活力的影响
Table 2. Effect of quick rewarming and normal rewarming on root vigor of chilled Jiaxian 7 and Fu 8329.
| 品种 Variety | 处理后0 h 0 h after treatment/ (mg·g−1·h−1) | 处理后3 d Three days after treatment/ (mg·g−1·h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 CK | 快速回温组 Quick rewarming | 对照组 CK | 快速回温组 Quick rewarming | |
| 嘉籼7号 Jiaxian 7 | 12.68 ± 0.66 b | 25.40 ± 5.59 a | 181.66 ± 1.85 b | 43.12 ± 2.52 d |
| 辐8329 Fu 8329 | 9.74 ± 1.49 b | 13.17 ± 1.03 b | 308.67 ± 5.95 a | 87.40 ± 2.97 c |
| [1] | 王亚男, 范思静. 低温胁迫对水稻幼苗叶片生理生化特性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(5): 8-9. |
| Wang Y N, Fang S J. Effects of low-temperature stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice seedling leaves[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2017, 45(5): 8-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 庞蓝青, 陈晨, 侯婉婷. 不同时期低温对水稻产量的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020, 22: 14-15, 20. |
| Pang L Q, Chen C, Hou W T. Effects of low temperature at different stages on rice yield[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22: 14-15, 20. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 易子豪. 水分亏缺对水稻秧苗生长的影响及调控[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. |
| Yi Z H. Effect of water deficit on rice seedling growth and its regulation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 江福英, 李延, 翁伯琦. 植物低温胁迫及其抗性生理[J]. 福建农业学报, 2002, 17(3): 190-195. |
| Jiang F Y, Li Y, Weng B Q. Review on physiology of chilling stress and chilling resistance of plants[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2002, 17(3): 190-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 张进忠, 韦华芳, 林贵美, 李小泉, 韦绍龙. 不同湿度环境下香蕉苗对低温胁迫响应[J]. 农学学报, 2011(9): 7-12. |
| Zhang J, Wei H, Lin G, Li X, Wei S. Effect of low temperature stress on banana seedlings under different humidity environment[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2011(9): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李响珍. 水稻发芽期亚干旱对苗期、孕穗期与开花期耐冷性的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2019. |
| Li X Z. Effects of sub-drought at germination stage on cold tolerance at seedling stage, booting stage and flowering stage in rice[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 胡涛. 低温对水稻根系生理特性及其基因表达的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. |
| Hu T. Effects of low temperature on physiological characteristics and gene expression of rice roots[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 向丹. 水稻苗期低温耐性差异及其调控研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. |
| Xiang D. The difference in low temperature tolerance of Rice Seedlings and its regulation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 李健陵, 霍治国, 吴丽姬, 朱庆华, 胡飞. 孕穗期低温对水稻产量的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3): 277-288. |
| Li J L, Huo Z G, Wu L J, Zhu Q H, Hu F. Effects of low temperature on grain yield of rice and its physiological mechanism at the booting stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(3): 277-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Tyerman S D, Bohnert H J, Maurel C, Steudle E, Smith J A C. Plant aquaporins: Their molecular biology, biophysics and significance for plant water relations[J]. Journal Of Experimental Botany, 1999, 50: 1055-1071. |
| [11] | Ahamed A, Murai-Hatano M, Ishikawa-Sakurai J, Hayashi H, Kawamura Y, Uemura M. Cold stress-induced acclimation in rice is mediated by root-specific aquaporins[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(8): 1445-1456. |
| [12] | Jang J Y, Kim D G, Kim Y O, Kim J S, Kang H. An expression analysis of a gene family encoding plasma membrane aquaporins in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2004, 54(5):713-25. |
| [13] | Danielson J A H, Johanson U. Unexpected complexity of the aquaporin gene family in the moss Physcomitrella patens[J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2008, 8: 45. |
| [14] | Forrest K L, Bhave M. Major intrinsic proteins (MIPs) in plants: A complex gene family with major impacts on plant phenotype[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2007, 7(4): 263-289. |
| [15] | Li L G, Li SF, Tao Y, Kitagawa Y. Molecular cloning of a novel water channel from rice: Its products expression in Xenopus oocytes and involvement in chilling tolerance[J]. Plant Science, 2000, 154: 43-51. |
| [16] | Yu X, Peng Y H, Zhang M H, Shao Y J, Su W A, Tang Z C. Water relations and an expression analysis of plasma membrane intrinsic proteins in sensitive and tolerant rice during chilling and recovery[J]. Cell Research, 2006, 16: 599-608. |
| [17] | Matsumoto T, Lian H L, Su W A, Tanaka D, Liu C, Iwasaki I, Kitagawa Y. Role of the aquaporin PIP1 subfamily in the chilling tolerance of rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50: 216-229. |
| [18] | Kuwagata T, Ishikawa-Sakurai J, Hayashi H, Nagasuga K, Fukushi K, Ahamed A, Takasugi K, Katsuhara M, Murai-Hatano M. Influence of low air humidity and low root temperature on water uptake, growth and aquaporin expression in rice plants[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(8): 1418-1431. |
| [19] | Sakurai J, Ishikawa F, Yamaguchi T, Uemura M, Maeshima M. Identification of 33 rice aquaporin genes and analysis of their expression and function[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2005, 46(9): 1568-1577. |
| [20] | 孙天旭, 李玉花, 张旸. 逆境条件下水孔蛋白PIPs作用的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(6): 749-757. |
| Sun T X, Li Y H, Zhang Y. Advance in a role of PIP aquaporins under adversity condition[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50 (6): 749-757. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2002. |
| Zhao S J, Shi G A, Dong X C. Plant Physiology Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2002. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | Sakurai-Ishikawa J, Murai-Hatano M, Hayashi H, Ahamed A, Fukushi K, Matsumoto T, Kitagawa Y. Transpiration from shoots triggers diurnal changes in root aquaporin expression[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34(7): 1150-1163. |
| [23] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25: 402-408. |
| [24] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 潘晓华, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张义凯, 曾勇军. 花后不同时段低温对籼粳杂交稻稻米品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(2): 166-174. |
| Zeng Y, Zhang Y, Pan X, Zhu D, Xiang J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Zeng Y,. Effect of low temperature after flowering on grain quality of indica-japonica hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(2): 166-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 王文霞, 陈丽明, 王海霞, 刘有清, 吴自明, 曾勇军, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 曾研华. 淹水缓解直播早籼稻苗期低温冷害的生理特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 166-176. |
| Wang W, Chen L, Wang H, Liu Y, Wu Z, Zeng Y, Tan X, Pan X, Shi Q, Zeng Y,. Study on physiological characteristics behind mitigative effects of flooding on low temperature-caused chilling damage to direct seeded early indica rice at the seedling Stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 166-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Uemura M, Tominaga Y, Nakagawara C, Shigematsu S, Minami A, Kawamura Y. Responses of the plasma membrane to low temperatures[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2006, 126: 81-89. |
| [27] | Lee S H, Chung G C, Jang J Y, Ahn S J, Zwiazek J J. Overexpression of PIP2;5 aquaporin alleviates effects of low root temperature on cell hydraulic conductivity and growth in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(1): 479-488. |
| [28] | Javot H, Maurel C. The role of aquaporins in root water uptake[J]. Annual Botany, 2002, 90: 301-313. |
| [29] | Kramer P J, Boyer J S//Water Relations of Plants and Soils[J]. California: Academic Press, 1995. |
| [30] | 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 张义凯, 朱德峰. 淹涝条件下水温对水稻幼苗形态和生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 525-531. |
| Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Zhang Y K, Zhu D F. Effects of on morphological and physiological response of rice seedlings to water temperature under complete submergence[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 525-531. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Gunawardena T A, Fukai B. The interaction of nitrogen application and temperature during reproductive stage on spikelet sterility infield-grown rice[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 2005, 56: 625-636. |
| [32] | Farrell T C, Fox K M, Williams R L, Fukai S. Genotypic variation for cold tolerance during reproductive development in rice: Screening with cold air and cold water[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 98(2): 178-194. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||