
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 187-199.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0710
章燕柳1, 邵在胜1, 杨阳2, 童楷程2, 王云霞2,*( ), 景立权1, 王余龙1, 杨连新1
), 景立权1, 王余龙1, 杨连新1
收稿日期:2020-07-17
修回日期:2020-09-29
出版日期:2021-03-10
发布日期:2021-03-10
通讯作者:
王云霞
基金资助:
Yanliu ZHANG1, Zaisheng SHAO1, Yang YANG2, Kaicheng TONG2, Yunxia WANG2,*( ), Liquan JING1, Yulong WANG1, Lianxin YANG1
), Liquan JING1, Yulong WANG1, Lianxin YANG1
Received:2020-07-17
Revised:2020-09-29
Online:2021-03-10
Published:2021-03-10
Contact:
Yunxia WANG
摘要:
【目的】研究不同类型水稻品种稻草饲用品质相关理化指标对臭氧胁迫的响应。【方法】利用新型自然光气体熏蒸平台,以 8个水稻品种为供试材料,设置室内对照和高臭氧浓度(80 nL/L)处理,于抽穗期、穗后20 d和成熟期分别测定叶片和茎鞘中饲用品质相关的理化指标。【结果】与对照相比,高浓度臭氧处理使稻草粗蛋白、木质素、纤维素、半纤维素和总酚含量分别增加7.07%(P <0.1)、10.88%(P <0.1)、1.98%、0.92%和5.01% (P<0.01),可溶性糖和淀粉含量分别下降15.07%(P <0.1)和18.55%(P <0.01)。多数情形下,叶片各指标含量对臭氧胁迫的响应大于茎鞘。所有测定指标的品种间差异均达极显著水平。不同生育期稻草木质素、纤维素、半纤维素和总酚含量表现为穗后20 d>成熟期>抽穗期,稻草可溶性糖和淀粉含量则表现为抽穗期>成熟期>穗后20 d,而粗蛋白含量随生育进程推进呈降低趋势。方差分析表明,臭氧胁迫与品种互作对所有测定指标的影响均达显著或极显著水平;除总酚含量外,臭氧与植株部位互作对所有测定指标的影响均达极显著水平;而臭氧与生育时期互作仅对植株粗蛋白、纤维素、可溶性糖和总酚含量有显著或极显著影响。【结论】稻草饲用品质相关理化指标因生育时期、供试品种和茎叶不同部位而异,高浓度臭氧环境下稻草饲用品质表现出变劣的趋势。
章燕柳, 邵在胜, 杨阳, 童楷程, 王云霞, 景立权, 王余龙, 杨连新. 全生育期臭氧胁迫对不同水稻品种稻草饲用品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 187-199.
Yanliu ZHANG, Zaisheng SHAO, Yang YANG, Kaicheng TONG, Yunxia WANG, Liquan JING, Yulong WANG, Lianxin YANG. Effects of Ozone Stress on Feeding Quality of Straw of Different Rice Varieties During the Whole Growth Period[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 187-199.
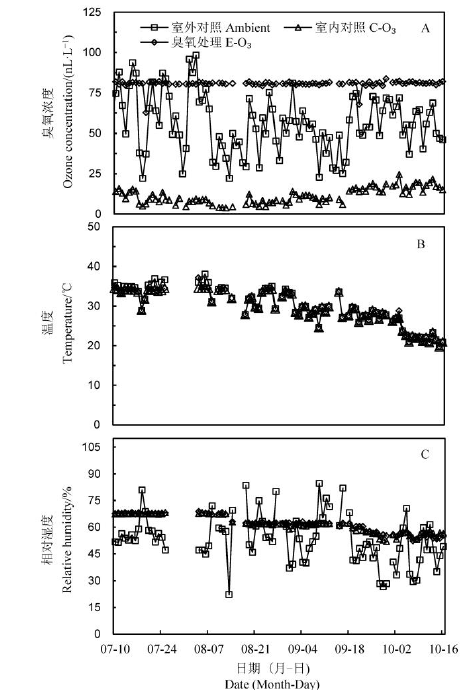
图1 2018年水稻生长季自然光气体熏蒸平台控制情况 Ambient–室外对照;C-O3–室内对照;E-O3–高臭氧浓度;臭氧浓度为熏蒸期间的日平均浓度。下同。
Fig. 1. Ozone concentration, temperature and relative humidity in the greenhouse-type gas fumigation device during rice growing season in 2018. C-O3, Control, E-O3, Elevated ozone concentration, Ozone concentration is the average daily concentration during fumigation; The same as below.
| 植株部位Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O₃ | 188±6 | 163±4 | 165±6 | 192±3 | 158±4 | 179±6 | 200±1 | 214±6 |
| E-O₃ | 189±6 | 176±7 | 172±6 | 164±5 | 159±8 | 183±5 | 184±2 | 223±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 113±6 | 120±6 | 106±6 | 88±4 | 82±4 | 108±2 | 110±7 | 127±3 | |
| E-O₃ | 124±5 | 126±6 | 100±3 | 95±4 | 87±6 | 117±4 | 111±4 | 119±3 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O₃ | 68±4 | 68±3 | 47±3 | 54±2 | 55±2 | 55±4 | 43±1 | 73±3 | |
| E-O₃ | 74±2 | 71±2 | 56±2 | 53±1 | 57±4 | 56±3 | 49±3 | 79±2 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O₃ | 68±3 | 52±2 | 59±3 | 53±1 | 40±1 | 58±2 | 69±4 | 59±3 |
| E-O₃ | 62±3 | 59±1 | 68±5 | 50±2 | 45±0 | 60±2 | 67±3 | 65±2 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 48±2 | 58±4 | 36±1 | 29±1 | 30±1 | 45±1 | 40±2 | 42±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 44±3 | 57±2 | 59±6 | 35±2 | 36±2 | 50±3 | 55±5 | 59±5 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O₃ | 48±1 | 35±3 | 33±1 | 37±3 | 35±1 | 39±2 | 33±1 | 42±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 50±2 | 43±2 | 48±4 | 39±1 | 36±1 | 45±3 | 44±3 | 55±1 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O₃ | 114±7 | 94±2 | 109±9 | 97±1 | 74±3 | 106±5 | 125±3 | 112±3 |
| E-O₃ | 104±4 | 103±5 | 116±8 | 84±3 | 79±3 | 107±4 | 117±2 | 119±1 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 69±1 | 78±1 | 57±2 | 47±1 | 45±1 | 66±2 | 64±3 | 59±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 70±4 | 78±3 | 73±3 | 53±2 | 51±2 | 74±1 | 77±5 | 74±3 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O₃ | 54±1 | 46±3 | 38±2 | 42±2 | 41±1 | 44±2 | 37±1 | 48±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 58±1 | 53±2 | 51±3 | 44±1 | 43±2 | 49±3 | 46±2 | 61±2 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.685 | 0.014 | 0.147 | 0.333 | 0.192 | 0.168 | 0.460 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.441 | 0.403 | 0.765 | <0.001 | 0.742 | 0.625 | 0.001 | 0.622 | ||
| O3×P | 0.056 | 0.586 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.765 | 0.972 | 0.007 | 0.010 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3× S×P | 0.633 | 0.475 | 0.062 | 0.004 | 0.859 | 0.591 | 0.536 | 0.007 | ||
表1 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草粗蛋白含量的影响
Table 1 Effects of ozone stress on crude protein concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. mg/g
| 植株部位Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O₃ | 188±6 | 163±4 | 165±6 | 192±3 | 158±4 | 179±6 | 200±1 | 214±6 |
| E-O₃ | 189±6 | 176±7 | 172±6 | 164±5 | 159±8 | 183±5 | 184±2 | 223±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 113±6 | 120±6 | 106±6 | 88±4 | 82±4 | 108±2 | 110±7 | 127±3 | |
| E-O₃ | 124±5 | 126±6 | 100±3 | 95±4 | 87±6 | 117±4 | 111±4 | 119±3 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O₃ | 68±4 | 68±3 | 47±3 | 54±2 | 55±2 | 55±4 | 43±1 | 73±3 | |
| E-O₃ | 74±2 | 71±2 | 56±2 | 53±1 | 57±4 | 56±3 | 49±3 | 79±2 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O₃ | 68±3 | 52±2 | 59±3 | 53±1 | 40±1 | 58±2 | 69±4 | 59±3 |
| E-O₃ | 62±3 | 59±1 | 68±5 | 50±2 | 45±0 | 60±2 | 67±3 | 65±2 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 48±2 | 58±4 | 36±1 | 29±1 | 30±1 | 45±1 | 40±2 | 42±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 44±3 | 57±2 | 59±6 | 35±2 | 36±2 | 50±3 | 55±5 | 59±5 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O₃ | 48±1 | 35±3 | 33±1 | 37±3 | 35±1 | 39±2 | 33±1 | 42±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 50±2 | 43±2 | 48±4 | 39±1 | 36±1 | 45±3 | 44±3 | 55±1 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O₃ | 114±7 | 94±2 | 109±9 | 97±1 | 74±3 | 106±5 | 125±3 | 112±3 |
| E-O₃ | 104±4 | 103±5 | 116±8 | 84±3 | 79±3 | 107±4 | 117±2 | 119±1 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O₃ | 69±1 | 78±1 | 57±2 | 47±1 | 45±1 | 66±2 | 64±3 | 59±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 70±4 | 78±3 | 73±3 | 53±2 | 51±2 | 74±1 | 77±5 | 74±3 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O₃ | 54±1 | 46±3 | 38±2 | 42±2 | 41±1 | 44±2 | 37±1 | 48±2 | |
| E-O₃ | 58±1 | 53±2 | 51±3 | 44±1 | 43±2 | 49±3 | 46±2 | 61±2 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.685 | 0.014 | 0.147 | 0.333 | 0.192 | 0.168 | 0.460 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.441 | 0.403 | 0.765 | <0.001 | 0.742 | 0.625 | 0.001 | 0.622 | ||
| O3×P | 0.056 | 0.586 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.765 | 0.972 | 0.007 | 0.010 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3× S×P | 0.633 | 0.475 | 0.062 | 0.004 | 0.859 | 0.591 | 0.536 | 0.007 | ||
| ANOVA | 粗蛋白 Crude protein | 结构性碳水化合物 Structural carbohydrates | 非结构性碳水化合物 Non-structured carbohydrates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 木质素 Lignin | 纤维素 Cellulose | 半纤维素 Hemicellulose | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 淀粉 Starch | 总酚 Total phenolic | |||||
| 臭氧胁迫 O3 stress | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.562 | 0.886 | 0.059 | 0.003 | 0.009 | |||
| 品种 Variety (V) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 植株部位 Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.718 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.015 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×S | 0.005 | 0.713 | 0.015 | 0.522 | <0.001 | 0.506 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×P | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.076 | |||
| V×S | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| V×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×S | 0.007 | 0.269 | 0.089 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×P | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.146 | 0.004 | 0.059 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×S×P | 0.804 | 0.001 | 0.480 | 0.007 | 0.085 | 0.149 | 0.001 | |||
| V×S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×S×P | 0.014 | 0.161 | 0.085 | 0.092 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | |||
表2 臭氧胁迫对不同水稻品种稻草饲用品质相关理化指标影响的汇总显著性检验 (P值)
Table 2 ANOVA results of the effect of ozone stress on feed value index of rice straw from different rice varieties (P value).
| ANOVA | 粗蛋白 Crude protein | 结构性碳水化合物 Structural carbohydrates | 非结构性碳水化合物 Non-structured carbohydrates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 木质素 Lignin | 纤维素 Cellulose | 半纤维素 Hemicellulose | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 淀粉 Starch | 总酚 Total phenolic | |||||
| 臭氧胁迫 O3 stress | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.562 | 0.886 | 0.059 | 0.003 | 0.009 | |||
| 品种 Variety (V) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 植株部位 Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.718 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.015 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×S | 0.005 | 0.713 | 0.015 | 0.522 | <0.001 | 0.506 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×P | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.076 | |||
| V×S | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| V×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×S | 0.007 | 0.269 | 0.089 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×P | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.146 | 0.004 | 0.059 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×S×P | 0.804 | 0.001 | 0.480 | 0.007 | 0.085 | 0.149 | 0.001 | |||
| V×S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| O3×V×S×P | 0.014 | 0.161 | 0.085 | 0.092 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | |||
| 植株部位Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 139±1 | 129±9 | 114±6 | 118±5 | 125±4 | 142±2 | 121±3 | 126±3 |
| E-O3 | 141±3 | 155±5 | 153±5 | 120±5 | 140±4 | 141±2 | 129±3 | 150±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 122±4 | 153±6 | 109±6 | 110±3 | 134±7 | 117±5 | 122±5 | 132±10 | |
| E-O3 | 145±10 | 164±9 | 142±2 | 138±6 | 155±4 | 154±5 | 145±7 | 150±8 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 122±5 | 138±4 | 118±3 | 111±2 | 130±3 | 120±4 | 125±2 | 117±4 | |
| E-O3 | 131±4 | 154±3 | 135±4 | 122±5 | 143±7 | 130±7 | 141±2 | 133±3 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 116±9 | 138±4 | 86±5 | 103±5 | 101±3 | 106±2 | 85±5 | 94±1 |
| E-O3 | 122±5 | 145±3 | 94±5 | 109±5 | 121±5 | 112±4 | 86±3 | 129±6 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 149±3 | 150±8 | 107±3 | 121±2 | 139±8 | 128±7 | 117±2 | 96±2 | |
| E-O3 | 148±6 | 163±5 | 110±6 | 116±6 | 157±3 | 128±11 | 117±4 | 109±4 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 120±3 | 141±7 | 99±4 | 103±5 | 116±9 | 103±6 | 100±1 | 97±4 | |
| E-O3 | 123±5 | 147±6 | 107±9 | 114±8 | 150±3 | 120±8 | 108±4 | 113±4 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 124±6 | 135±3 | 100±6 | 108±5 | 108±3 | 120±3 | 100±4 | 105±1 |
| E-O3 | 129±4 | 149±3 | 122±6 | 112±5 | 127±3 | 123±3 | 105±1 | 136±5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 140±4 | 151±8 | 107±3 | 117±2 | 137±8 | 124±5 | 119±1 | 104±1 | |
| E-O3 | 147±7 | 163±3 | 121±4 | 123±6 | 156±2 | 137±8 | 128±5 | 119±3 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 121±3 | 140±6 | 106±3 | 105±3 | 120±7 | 109±3 | 109±1 | 101±4 | |
| E-O3 | 125±4 | 149±4 | 118±6 | 117±7 | 147±3 | 124±4 | 122±2 | 118±3 | ||
| ANOVA 结果ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.115 | 0.285 | 0.047 | 0.179 | 0.111 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.289 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.024 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.242 | 0.597 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.022 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.647 | 0.796 | 0.208 | 0.386 | 0.774 | 0.112 | 0.349 | 0.098 | ||
| O3×P | 0.145 | 0.226 | <0.001 | 0.061 | 0.231 | 0.216 | 0.006 | 0.833 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | 0.982 | 0.001 | 0.486 | 0.005 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.035 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.155 | 0.478 | 0.139 | 0.014 | 0.254 | 0.011 | 0.248 | 0.549 | ||
| O3 | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.115 | 0.285 | 0.047 | 0.179 | 0.111 | <0.001 | ||
表3 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草木质素含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of ozone stress on lignin concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. g/kg
| 植株部位Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 139±1 | 129±9 | 114±6 | 118±5 | 125±4 | 142±2 | 121±3 | 126±3 |
| E-O3 | 141±3 | 155±5 | 153±5 | 120±5 | 140±4 | 141±2 | 129±3 | 150±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 122±4 | 153±6 | 109±6 | 110±3 | 134±7 | 117±5 | 122±5 | 132±10 | |
| E-O3 | 145±10 | 164±9 | 142±2 | 138±6 | 155±4 | 154±5 | 145±7 | 150±8 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 122±5 | 138±4 | 118±3 | 111±2 | 130±3 | 120±4 | 125±2 | 117±4 | |
| E-O3 | 131±4 | 154±3 | 135±4 | 122±5 | 143±7 | 130±7 | 141±2 | 133±3 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 116±9 | 138±4 | 86±5 | 103±5 | 101±3 | 106±2 | 85±5 | 94±1 |
| E-O3 | 122±5 | 145±3 | 94±5 | 109±5 | 121±5 | 112±4 | 86±3 | 129±6 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 149±3 | 150±8 | 107±3 | 121±2 | 139±8 | 128±7 | 117±2 | 96±2 | |
| E-O3 | 148±6 | 163±5 | 110±6 | 116±6 | 157±3 | 128±11 | 117±4 | 109±4 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 120±3 | 141±7 | 99±4 | 103±5 | 116±9 | 103±6 | 100±1 | 97±4 | |
| E-O3 | 123±5 | 147±6 | 107±9 | 114±8 | 150±3 | 120±8 | 108±4 | 113±4 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 124±6 | 135±3 | 100±6 | 108±5 | 108±3 | 120±3 | 100±4 | 105±1 |
| E-O3 | 129±4 | 149±3 | 122±6 | 112±5 | 127±3 | 123±3 | 105±1 | 136±5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 140±4 | 151±8 | 107±3 | 117±2 | 137±8 | 124±5 | 119±1 | 104±1 | |
| E-O3 | 147±7 | 163±3 | 121±4 | 123±6 | 156±2 | 137±8 | 128±5 | 119±3 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 121±3 | 140±6 | 106±3 | 105±3 | 120±7 | 109±3 | 109±1 | 101±4 | |
| E-O3 | 125±4 | 149±4 | 118±6 | 117±7 | 147±3 | 124±4 | 122±2 | 118±3 | ||
| ANOVA 结果ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.115 | 0.285 | 0.047 | 0.179 | 0.111 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.289 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.024 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.242 | 0.597 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.022 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.647 | 0.796 | 0.208 | 0.386 | 0.774 | 0.112 | 0.349 | 0.098 | ||
| O3×P | 0.145 | 0.226 | <0.001 | 0.061 | 0.231 | 0.216 | 0.006 | 0.833 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | 0.982 | 0.001 | 0.486 | 0.005 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.035 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.155 | 0.478 | 0.139 | 0.014 | 0.254 | 0.011 | 0.248 | 0.549 | ||
| O3 | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.115 | 0.285 | 0.047 | 0.179 | 0.111 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 379±15 | 395±18 | 408±13 | 403±12 | 406±8 | 409±3 | 435±7 | 351±13 |
| E-O3 | 368±17 | 408±12 | 384±8 | 427±4 | 416±4 | 400±5 | 453±9 | 387±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 425±5 | 452±14 | 459±18 | 464±18 | 477±10 | 429±5 | 453±4 | 417±15 | |
| E-O3 | 407±12 | 436±14 | 426±14 | 442±10 | 460±9 | 431±11 | 475±7 | 392±15 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 523±6 | 479±10 | 501±14 | 511±5 | 511±14 | 523±8 | 520±7 | 477±7 | |
| E-O3 | 506±7 | 508±19 | 501±5 | 508±4 | 525±9 | 514±12 | 500±6 | 464±2 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 433±13 | 480±6 | 408±13 | 426±9 | 358±18 | 418±8 | 454±7 | 381±10 |
| E-O3 | 430±4 | 498±10 | 448±5 | 421±9 | 368±10 | 416±10 | 457±8 | 449±18 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 489±9 | 534±13 | 508±5 | 503±11 | 480±5 | 532±12 | 501±10 | 439±13 | |
| E-O3 | 498±10 | 543±13 | 495±17 | 495±5 | 546±9 | 505±12 | 501±10 | 430±17 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 427±13 | 458±9 | 481±6 | 455±5 | 396±14 | 463±7 | 481±11 | 366±5 | |
| E-O3 | 425±13 | 460±14 | 473±15 | 480±17 | 464±21 | 499±15 | 486±11 | 411±21 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 413±8 | 448±8 | 405±5 | 419±3 | 372±13 | 414±6 | 446±5 | 372±5 |
| E-O3 | 408±8 | 465±10 | 415±6 | 423±7 | 382±8 | 410±4 | 455±3 | 428±13 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 468±13 | 507±6 | 494±11 | 491±9 | 479±5 | 497±8 | 484±7 | 434±10 | |
| E-O3 | 469±9 | 511±11 | 470±14 | 480±7 | 520±6 | 479±12 | 491±9 | 421±15 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 455±10 | 464±6 | 488±5 | 471±5 | 427±9 | 483±20 | 496±9 | 389±4 | |
| E-O3 | 451±11 | 476±10 | 483±11 | 489±13 | 484±13 | 504±14 | 492±8 | 424±15 | ||
| ANOVA结果ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.403 | 0.419 | 0.451 | 0.873 | 0.144 | 0.917 | 0.344 | 0.241 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | 0.000 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.060 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.465 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.136 | 0.763 | ||
| O3×S | 0.966 | 0.544 | 0.341 | 0.102 | 0.171 | 0.309 | 0.194 | 0.002 | ||
| O3×P | 0.308 | 0.951 | 0.142 | 0.679 | 0.002 | 0.602 | 0.648 | 0.016 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.875 | 0.417 | 0.249 | 0.096 | 0.436 | 0.118 | 0.103 | 0.502 | ||
表4 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草纤维素含量的影响
Table 4 Effects of ozone stress on cellulose concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. g/kg
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 379±15 | 395±18 | 408±13 | 403±12 | 406±8 | 409±3 | 435±7 | 351±13 |
| E-O3 | 368±17 | 408±12 | 384±8 | 427±4 | 416±4 | 400±5 | 453±9 | 387±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 425±5 | 452±14 | 459±18 | 464±18 | 477±10 | 429±5 | 453±4 | 417±15 | |
| E-O3 | 407±12 | 436±14 | 426±14 | 442±10 | 460±9 | 431±11 | 475±7 | 392±15 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 523±6 | 479±10 | 501±14 | 511±5 | 511±14 | 523±8 | 520±7 | 477±7 | |
| E-O3 | 506±7 | 508±19 | 501±5 | 508±4 | 525±9 | 514±12 | 500±6 | 464±2 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 433±13 | 480±6 | 408±13 | 426±9 | 358±18 | 418±8 | 454±7 | 381±10 |
| E-O3 | 430±4 | 498±10 | 448±5 | 421±9 | 368±10 | 416±10 | 457±8 | 449±18 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 489±9 | 534±13 | 508±5 | 503±11 | 480±5 | 532±12 | 501±10 | 439±13 | |
| E-O3 | 498±10 | 543±13 | 495±17 | 495±5 | 546±9 | 505±12 | 501±10 | 430±17 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 427±13 | 458±9 | 481±6 | 455±5 | 396±14 | 463±7 | 481±11 | 366±5 | |
| E-O3 | 425±13 | 460±14 | 473±15 | 480±17 | 464±21 | 499±15 | 486±11 | 411±21 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 413±8 | 448±8 | 405±5 | 419±3 | 372±13 | 414±6 | 446±5 | 372±5 |
| E-O3 | 408±8 | 465±10 | 415±6 | 423±7 | 382±8 | 410±4 | 455±3 | 428±13 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 468±13 | 507±6 | 494±11 | 491±9 | 479±5 | 497±8 | 484±7 | 434±10 | |
| E-O3 | 469±9 | 511±11 | 470±14 | 480±7 | 520±6 | 479±12 | 491±9 | 421±15 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 455±10 | 464±6 | 488±5 | 471±5 | 427±9 | 483±20 | 496±9 | 389±4 | |
| E-O3 | 451±11 | 476±10 | 483±11 | 489±13 | 484±13 | 504±14 | 492±8 | 424±15 | ||
| ANOVA结果ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.403 | 0.419 | 0.451 | 0.873 | 0.144 | 0.917 | 0.344 | 0.241 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | 0.000 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.060 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.465 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.136 | 0.763 | ||
| O3×S | 0.966 | 0.544 | 0.341 | 0.102 | 0.171 | 0.309 | 0.194 | 0.002 | ||
| O3×P | 0.308 | 0.951 | 0.142 | 0.679 | 0.002 | 0.602 | 0.648 | 0.016 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.875 | 0.417 | 0.249 | 0.096 | 0.436 | 0.118 | 0.103 | 0.502 | ||
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 190±4 | 184±5 | 182±4 | 197±3 | 196±2 | 182±6 | 186±6 | 171±5 |
| E-O3 | 188±7 | 184±6 | 191±2 | 198±7 | 196±5 | 179±5 | 183±2 | 167±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 197±2 | 187±5 | 207±9 | 209±5 | 221±9 | 196±3 | 198±3 | 176±8 | |
| E-O3 | 195±6 | 202±3 | 204±0 | 197±6 | 219±4 | 204±2 | 198±3 | 180±8 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 220±4 | 217±1 | 208±4 | 205±4 | 211±5 | 226±4 | 212±7 | 199±6 | |
| E-O3 | 198±5 | 213±8 | 212±3 | 202±5 | 205±3 | 209±4 | 208±5 | 178±6 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 182±1 | 196±12 | 212±4 | 157±7 | 200±4 | 184±4 | 170±1 | 200±6 |
| E-O3 | 169±5 | 192±4 | 193±6 | 181±5 | 197±5 | 194±1 | 195±1 | 186±5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 208±7 | 210±6 | 206±3 | 224±4 | 200±5 | 214±5 | 197±6 | 177±11 | |
| E-O3 | 209±6 | 227±2 | 211±4 | 204±7 | 216±4 | 207±2 | 207±1 | 183±9 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 208±3 | 204±2 | 210±5 | 170±5 | 194±10 | 206±5 | 190±5 | 186±11 | |
| E-O3 | 193±9 | 206±5 | 204±7 | 186±6 | 217±13 | 218±3 | 224±5 | 180±8 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 185±2 | 191±9 | 198±2 | 169±5 | 199±3 | 184±3 | 176±2 | 191±5 |
| E-O3 | 176±2 | 189±4 | 192±4 | 186±5 | 196±4 | 188±2 | 190±1 | 179±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 205±5 | 202±3 | 207±2 | 219±3 | 206±5 | 208±2 | 197±4 | 177±10 | |
| E-O3 | 205±6 | 219±1 | 209±3 | 202±5 | 217±4 | 206±2 | 204±2 | 182±8 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 211±2 | 208±2 | 210±5 | 180±3 | 199±7 | 213±3 | 198±5 | 188±9 | |
| E-O3 | 195±6 | 208±3 | 206±5 | 191±4 | 212±8 | 215±3 | 218±3 | 180±7 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.341 | 0.587 | 0.721 | 0.674 | 0.452 | 0.839 | <0.001 | 0.586 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.347 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.283 | 0.011 | 0.047 | <0.001 | 0.296 | 0.060 | 0.898 | 0.091 | ||
| O3×S | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.639 | 0.002 | 0.459 | 0.559 | 0.290 | 0.168 | ||
| O3×P | 0.852 | 0.887 | 0.059 | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.057 | <0.001 | 0.787 | ||
| S×P | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.279 | 0.009 | 0.457 | 0.014 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.395 | 0.836 | 0.025 | 0.101 | 0.208 | 0.002 | 0.091 | 0.444 | ||
表5 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草半纤维素含量的影响
Table 5 Effects of ozone stress on hemicellulose concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. g/kg
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片 Leaf | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 190±4 | 184±5 | 182±4 | 197±3 | 196±2 | 182±6 | 186±6 | 171±5 |
| E-O3 | 188±7 | 184±6 | 191±2 | 198±7 | 196±5 | 179±5 | 183±2 | 167±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 197±2 | 187±5 | 207±9 | 209±5 | 221±9 | 196±3 | 198±3 | 176±8 | |
| E-O3 | 195±6 | 202±3 | 204±0 | 197±6 | 219±4 | 204±2 | 198±3 | 180±8 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 220±4 | 217±1 | 208±4 | 205±4 | 211±5 | 226±4 | 212±7 | 199±6 | |
| E-O3 | 198±5 | 213±8 | 212±3 | 202±5 | 205±3 | 209±4 | 208±5 | 178±6 | ||
| 茎秆 Stem | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 182±1 | 196±12 | 212±4 | 157±7 | 200±4 | 184±4 | 170±1 | 200±6 |
| E-O3 | 169±5 | 192±4 | 193±6 | 181±5 | 197±5 | 194±1 | 195±1 | 186±5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 208±7 | 210±6 | 206±3 | 224±4 | 200±5 | 214±5 | 197±6 | 177±11 | |
| E-O3 | 209±6 | 227±2 | 211±4 | 204±7 | 216±4 | 207±2 | 207±1 | 183±9 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 208±3 | 204±2 | 210±5 | 170±5 | 194±10 | 206±5 | 190±5 | 186±11 | |
| E-O3 | 193±9 | 206±5 | 204±7 | 186±6 | 217±13 | 218±3 | 224±5 | 180±8 | ||
| 稻草 Straw | 抽穗期 Heading | C-O3 | 185±2 | 191±9 | 198±2 | 169±5 | 199±3 | 184±3 | 176±2 | 191±5 |
| E-O3 | 176±2 | 189±4 | 192±4 | 186±5 | 196±4 | 188±2 | 190±1 | 179±4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 205±5 | 202±3 | 207±2 | 219±3 | 206±5 | 208±2 | 197±4 | 177±10 | |
| E-O3 | 205±6 | 219±1 | 209±3 | 202±5 | 217±4 | 206±2 | 204±2 | 182±8 | ||
| 成熟期 Maturity | C-O3 | 211±2 | 208±2 | 210±5 | 180±3 | 199±7 | 213±3 | 198±5 | 188±9 | |
| E-O3 | 195±6 | 208±3 | 206±5 | 191±4 | 212±8 | 215±3 | 218±3 | 180±7 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.341 | 0.587 | 0.721 | 0.674 | 0.452 | 0.839 | <0.001 | 0.586 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.347 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.283 | 0.011 | 0.047 | <0.001 | 0.296 | 0.060 | 0.898 | 0.091 | ||
| O3×S | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.639 | 0.002 | 0.459 | 0.559 | 0.290 | 0.168 | ||
| O3×P | 0.852 | 0.887 | 0.059 | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.057 | <0.001 | 0.787 | ||
| S×P | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.279 | 0.009 | 0.457 | 0.014 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.395 | 0.836 | 0.025 | 0.101 | 0.208 | 0.002 | 0.091 | 0.444 | ||
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 58±3.2 | 89±2.2 | 88±9.0 | 66±5.3 | 128±1.6 | 101±4.9 | 68±1.8 | 84±1.1 |
| E-O3 | 63±0.9 | 59±4.8 | 55±2.8 | 60±2.6 | 113±3.2 | 79±2.0 | 72±5.1 | 69±2.4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 31±1.5 | 30±2.1 | 30±3.2 | 51±7.2 | 94±1.9 | 83±2.5 | 49±3.4 | 79±5.5 | |
| E-O3 | 34±4.9 | 27±1.4 | 22±1.5 | 39±6.3 | 45±3.4 | 64±2.6 | 49±2.9 | 53±3.3 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 80±6.0 | 70±3.7 | 61±3.9 | 54±4.3 | 76±3.0 | 47±7.5 | 44±5.0 | 68±5.4 | |
| E-O3 | 48±4.9 | 39±3.7 | 39±1.0 | 27±1.8 | 40±2.7 | 33±2.3 | 20±1.9 | 42±2.8 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 60±2.0 | 54±2.0 | 78±7.1 | 137±4.8 | 141±4.6 | 120±2.3 | 92±0.4 | 131±4.5 |
| E-O3 | 56±3.7 | 73±0.7 | 72±6.3 | 137±14 | 127±5.9 | 120±1.0 | 96±0.8 | 84±2.6 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 22±0.5 | 67±2.5 | 78±5.7 | 90±9.2 | 81±2.7 | 39±5.0 | 30±2.6 | 97±5.6 | |
| E-O3 | 27±4.9 | 65±1.1 | 66±3.8 | 84±4.8 | 53±6.0 | 20±2.1 | 24±2.0 | 95±3.2 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 70±1.5 | 79±4.0 | 120±8.2 | 137±4.3 | 96±3.9 | 121±10.5 | 85±2.3 | 100±5.8 | |
| E-O3 | 73±2.6 | 71±5.9 | 99±7.1 | 118±4.7 | 85±7.7 | 105±11.3 | 74±6.1 | 93±2.8 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 60±2.0 | 67±1.9 | 83±5.1 | 114±4.4 | 137±3.5 | 112±2.7 | 82±0.9 | 115±4.4 |
| E-O3 | 58±2.7 | 67±1.9 | 64±4.0 | 113±10.4 | 122±4.0 | 104±0.4 | 86±2.0 | 79±1.9 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 25±0.8 | 55±2.3 | 64±4.4 | 77±8.9 | 84±1.7 | 53±4.1 | 37±0.9 | 93±4.8 | |
| E-O3 | 29±4.7 | 54±0.4 | 51±1.9 | 70±5.7 | 51±5.0 | 36±2.6 | 33±1.9 | 86±2.9 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 73±2.3 | 76±1.7 | 100±5.6 | 113±4.8 | 91±3.3 | 96±7.4 | 69±1.7 | 94±5.2 | |
| E-O3 | 65±3.3 | 60±3.6 | 78±5.5 | 87±4.3 | 70±6.4 | 79±8.3 | 52±3.4 | 79±2.8 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.603 | <0.001 | 0.059 | 0.288 | 0.019 | 0.107 | 0.005 | 0.029 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.453 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.301 | 0.055 | 0.012 | 0.581 | 0.000 | 0.009 | ||
| O3×P | 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.194 | 0.301 | 0.003 | 0.269 | 0.608 | 0.397 | ||
| S×P | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.098 | ||
| O3×S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.124 | 0.999 | 0.089 | 0.208 | 0.175 | <0.001 | ||
表6 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草可溶性糖含量的影响
Table 6 Effects of ozone stress on soluble sugar concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. mg/g
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 58±3.2 | 89±2.2 | 88±9.0 | 66±5.3 | 128±1.6 | 101±4.9 | 68±1.8 | 84±1.1 |
| E-O3 | 63±0.9 | 59±4.8 | 55±2.8 | 60±2.6 | 113±3.2 | 79±2.0 | 72±5.1 | 69±2.4 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 31±1.5 | 30±2.1 | 30±3.2 | 51±7.2 | 94±1.9 | 83±2.5 | 49±3.4 | 79±5.5 | |
| E-O3 | 34±4.9 | 27±1.4 | 22±1.5 | 39±6.3 | 45±3.4 | 64±2.6 | 49±2.9 | 53±3.3 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 80±6.0 | 70±3.7 | 61±3.9 | 54±4.3 | 76±3.0 | 47±7.5 | 44±5.0 | 68±5.4 | |
| E-O3 | 48±4.9 | 39±3.7 | 39±1.0 | 27±1.8 | 40±2.7 | 33±2.3 | 20±1.9 | 42±2.8 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 60±2.0 | 54±2.0 | 78±7.1 | 137±4.8 | 141±4.6 | 120±2.3 | 92±0.4 | 131±4.5 |
| E-O3 | 56±3.7 | 73±0.7 | 72±6.3 | 137±14 | 127±5.9 | 120±1.0 | 96±0.8 | 84±2.6 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 22±0.5 | 67±2.5 | 78±5.7 | 90±9.2 | 81±2.7 | 39±5.0 | 30±2.6 | 97±5.6 | |
| E-O3 | 27±4.9 | 65±1.1 | 66±3.8 | 84±4.8 | 53±6.0 | 20±2.1 | 24±2.0 | 95±3.2 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 70±1.5 | 79±4.0 | 120±8.2 | 137±4.3 | 96±3.9 | 121±10.5 | 85±2.3 | 100±5.8 | |
| E-O3 | 73±2.6 | 71±5.9 | 99±7.1 | 118±4.7 | 85±7.7 | 105±11.3 | 74±6.1 | 93±2.8 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 60±2.0 | 67±1.9 | 83±5.1 | 114±4.4 | 137±3.5 | 112±2.7 | 82±0.9 | 115±4.4 |
| E-O3 | 58±2.7 | 67±1.9 | 64±4.0 | 113±10.4 | 122±4.0 | 104±0.4 | 86±2.0 | 79±1.9 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 25±0.8 | 55±2.3 | 64±4.4 | 77±8.9 | 84±1.7 | 53±4.1 | 37±0.9 | 93±4.8 | |
| E-O3 | 29±4.7 | 54±0.4 | 51±1.9 | 70±5.7 | 51±5.0 | 36±2.6 | 33±1.9 | 86±2.9 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 73±2.3 | 76±1.7 | 100±5.6 | 113±4.8 | 91±3.3 | 96±7.4 | 69±1.7 | 94±5.2 | |
| E-O3 | 65±3.3 | 60±3.6 | 78±5.5 | 87±4.3 | 70±6.4 | 79±8.3 | 52±3.4 | 79±2.8 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.603 | <0.001 | 0.059 | 0.288 | 0.019 | 0.107 | 0.005 | 0.029 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | 0.453 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.301 | 0.055 | 0.012 | 0.581 | 0.000 | 0.009 | ||
| O3×P | 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.194 | 0.301 | 0.003 | 0.269 | 0.608 | 0.397 | ||
| S×P | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.098 | ||
| O3×S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.124 | 0.999 | 0.089 | 0.208 | 0.175 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 43±0.9 | 52±0.7 | 53±0.1 | 45±0.8 | 40±1.0 | 50±2.4 | 40±1.3 | 45±0.8 |
| E-O3 | 47±1.3 | 49±1.3 | 49±1.3 | 44±1.1 | 41±1.1 | 46±2.4 | 35±1.0 | 42±1.5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 42±2.3 | 36±0.3 | 41±1.2 | 45±2.3 | 36±1.5 | 44±2.6 | 36±1.4 | 34±0.5 | |
| E-O3 | 43±0.9 | 34±0.7 | 37±1.0 | 33±1.4 | 36±1.3 | 37±3.1 | 33±1.7 | 33±1.1 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 40±3.3 | 39±0.4 | 42±1.7 | 42±1.5 | 39±1.7 | 38±0.4 | 38±2.0 | 46±1.0 | |
| E-O3 | 42±0.4 | 37±1.2 | 39±0.5 | 39±0.4 | 36±1.3 | 37±1.4 | 35±1.5 | 42±0.9 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 181±5.3 | 99±2.8 | 150±9.5 | 190±3.1 | 239±3.8 | 184±3.7 | 143±0.6 | 206±7.2 |
| E-O3 | 174±5.9 | 89±1.1 | 102±4.9 | 170±1.7 | 227±9.6 | 158±3.5 | 125±10.1 | 134±3.5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 127±2.4 | 49±2.3 | 63±2.5 | 74±2.8 | 98±7.0 | 45±1.1 | 61±1.4 | 193±5.9 | |
| E-O3 | 91±3.8 | 39±0.9 | 42±1.9 | 56±4.2 | 60±0.4 | 39±3.2 | 55±1.6 | 145±2.0 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 189±3.2 | 98±2.6 | 93±5.1 | 141±3.5 | 216±6.2 | 122±9.5 | 93±2.4 | 204±2.1 | |
| E-O3 | 170±2.8 | 89±3.2 | 80±6.3 | 112±0.9 | 174±8.1 | 98±4.0 | 69±3.8 | 140±1.4 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 129±4.2 | 81±1.9 | 106±8.5 | 144±2.1 | 181±4.3 | 131±5.8 | 99±0.9 | 151±6.9 |
| E-O3 | 132±6.7 | 74±1.0 | 77±3.5 | 132±1.1 | 170±7.3 | 115±3.0 | 87±5.9 | 102±1.8 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 100±2.2 | 45±1.7 | 56±2.1 | 65±1.7 | 80±5.2 | 45±1.3 | 52±0.8 | 161±5.3 | |
| E-O3 | 75±2.4 | 38±0.8 | 40±1.6 | 49±3.2 | 53±0.3 | 39±2.9 | 46±0.6 | 119±0.7 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 146±3.7 | 79±1.2 | 76±3.5 | 112±4.0 | 167±4.0 | 94±6.7 | 72±2.2 | 170±2.1 | |
| E-O3 | 128±2.6 | 71±2.6 | 65±4.2 | 87±1.4 | 126±8.8 | 76±3.8 | 55±1.8 | 113±1.0 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.127 | <0.001 | 0.106 | 0.012 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.057 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.011 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.002 | 0.801 | 0.002 | 0.214 | 0.036 | 0.237 | 0.153 | 0.017 | ||
| O3×P | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | <0.001 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.104 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.010 | 0.905 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.088 | 0.056 | 0.147 | 0.061 | ||
表7 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草淀粉含量的影响
Table 7 Effects of ozone stress on starch concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. mg/g
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 43±0.9 | 52±0.7 | 53±0.1 | 45±0.8 | 40±1.0 | 50±2.4 | 40±1.3 | 45±0.8 |
| E-O3 | 47±1.3 | 49±1.3 | 49±1.3 | 44±1.1 | 41±1.1 | 46±2.4 | 35±1.0 | 42±1.5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 42±2.3 | 36±0.3 | 41±1.2 | 45±2.3 | 36±1.5 | 44±2.6 | 36±1.4 | 34±0.5 | |
| E-O3 | 43±0.9 | 34±0.7 | 37±1.0 | 33±1.4 | 36±1.3 | 37±3.1 | 33±1.7 | 33±1.1 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 40±3.3 | 39±0.4 | 42±1.7 | 42±1.5 | 39±1.7 | 38±0.4 | 38±2.0 | 46±1.0 | |
| E-O3 | 42±0.4 | 37±1.2 | 39±0.5 | 39±0.4 | 36±1.3 | 37±1.4 | 35±1.5 | 42±0.9 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 181±5.3 | 99±2.8 | 150±9.5 | 190±3.1 | 239±3.8 | 184±3.7 | 143±0.6 | 206±7.2 |
| E-O3 | 174±5.9 | 89±1.1 | 102±4.9 | 170±1.7 | 227±9.6 | 158±3.5 | 125±10.1 | 134±3.5 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 127±2.4 | 49±2.3 | 63±2.5 | 74±2.8 | 98±7.0 | 45±1.1 | 61±1.4 | 193±5.9 | |
| E-O3 | 91±3.8 | 39±0.9 | 42±1.9 | 56±4.2 | 60±0.4 | 39±3.2 | 55±1.6 | 145±2.0 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 189±3.2 | 98±2.6 | 93±5.1 | 141±3.5 | 216±6.2 | 122±9.5 | 93±2.4 | 204±2.1 | |
| E-O3 | 170±2.8 | 89±3.2 | 80±6.3 | 112±0.9 | 174±8.1 | 98±4.0 | 69±3.8 | 140±1.4 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 129±4.2 | 81±1.9 | 106±8.5 | 144±2.1 | 181±4.3 | 131±5.8 | 99±0.9 | 151±6.9 |
| E-O3 | 132±6.7 | 74±1.0 | 77±3.5 | 132±1.1 | 170±7.3 | 115±3.0 | 87±5.9 | 102±1.8 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 100±2.2 | 45±1.7 | 56±2.1 | 65±1.7 | 80±5.2 | 45±1.3 | 52±0.8 | 161±5.3 | |
| E-O3 | 75±2.4 | 38±0.8 | 40±1.6 | 49±3.2 | 53±0.3 | 39±2.9 | 46±0.6 | 119±0.7 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 146±3.7 | 79±1.2 | 76±3.5 | 112±4.0 | 167±4.0 | 94±6.7 | 72±2.2 | 170±2.1 | |
| E-O3 | 128±2.6 | 71±2.6 | 65±4.2 | 87±1.4 | 126±8.8 | 76±3.8 | 55±1.8 | 113±1.0 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.127 | <0.001 | 0.106 | 0.012 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.057 | <0.001 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.011 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.002 | 0.801 | 0.002 | 0.214 | 0.036 | 0.237 | 0.153 | 0.017 | ||
| O3×P | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | <0.001 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.104 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.010 | 0.905 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.088 | 0.056 | 0.147 | 0.061 | ||
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.3±0.02 | 2.1±0.00 | 2.3±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.7±0.02 | 2.6±0.05 | 2.8±0.03 | 3.0±0.04 |
| E-O3 | 2.4±0.03 | 2.2±0.03 | 2.5±0.03 | 2.8±0.02 | 2.8±0.02 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.01 | 3.2±0.01 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 2.2±0.05 | 2.3±0.04 | 2.0±0.02 | 2.4±0.02 | 2.4±0.03 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.5±0.03 | 2.9±0.05 | |
| E-O3 | 2.4±0.05 | 2.7±0.03 | 2.1±0.03 | 2.5±0.05 | 2.6±0.04 | 2.6±0.01 | 2.6±0.01 | 3.0±0.05 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 2.0±0.03 | 1.9±0.02 | 1.8±0.05 | 2.0±0.01 | 2.2±0.04 | 1.9±0.06 | 2.0±0.00 | 2.7±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 2.2±0.04 | 2.1±0.02 | 1.9±0.05 | 2.1±0.01 | 2.4±0.04 | 2.0±0.06 | 2.1±0.04 | 2.9±0.05 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.7±0.02 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.4±0.02 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.9±0.05 | 2.9±0.03 | 3.1±0.01 |
| E-O3 | 2.9±0.01 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.9±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.9±0.01 | 3.1±0.04 | 3.3±0.03 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 3.4±0.03 | 3.7±0.03 | 3.6±0.05 | 3.6±0.03 | 3.9±0.02 | 4.0±0.04 | 4.1±0.02 | 4.4±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.7±0.04 | 4.0±0.06 | 3.7±0.04 | 3.8±0.05 | 4.0±0.03 | 4.0±0.02 | 4.2±0.03 | 4.5±0.02 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 3.3±0.03 | 3.1±0.06 | 3.0±0.07 | 3.0±0.05 | 2.7±0.03 | 3.0±0.03 | 3.1±0.08 | 3.4±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.4±0.02 | 3.4±0.05 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.3±0.02 | 3.1±0.06 | 3.1±0.03 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.7±0.05 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.5±0.00 | 2.3±0.01 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.02 | 3.1±0.02 |
| E-O3 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.00 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.8±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.8±0.01 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.3±0.02 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.2±0.04 | 3.1±0.05 | 3.2±0.03 | 3.5±0.01 | 3.5±0.03 | 3.5±0.01 | 4.1±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.6±0.05 | 3.1±0.03 | 3.4±0.04 | 3.6±0.02 | 3.5±0.03 | 3.6±0.01 | 4.2±0.04 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 2.9±0.03 | 2.7±0.06 | 2.6±0.06 | 2.7±0.04 | 2.6±0.03 | 2.6±0.03 | 2.7±0.07 | 3.3±0.01 | |
| E-O3 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.0±0.04 | 2.8±0.03 | 2.9±0.02 | 2.8±0.03 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.02 | 3.5±0.06 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.034 | 0.020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.026 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.713 | 0.006 | 0.571 | 0.104 | 0.263 | ||
| O3×P | 0.010 | 0.085 | 0.011 | 0.064 | 0.763 | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.639 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.211 | 0.359 | 0.358 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.034 | 0.817 | 0.098 | ||
表8 臭氧胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片、茎秆和稻草总酚含量的影响
Table 8 Effects of ozone stress on total phenolic concentrations in leaves, stems and straw of different rice varieties. mg/g
| 植株部位 Plant parts | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理Treatment | 淮稻5号 HD5 | 武运粳27 WYJ27 | 扬稻6号 YD6 | 丰优香占 FYXZ | 甬优1540 YY1540 | 桂农占 GNZ | 深两优136 SLY136 | 中早39 ZZ39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片Leaf | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.3±0.02 | 2.1±0.00 | 2.3±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.7±0.02 | 2.6±0.05 | 2.8±0.03 | 3.0±0.04 |
| E-O3 | 2.4±0.03 | 2.2±0.03 | 2.5±0.03 | 2.8±0.02 | 2.8±0.02 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.01 | 3.2±0.01 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 2.2±0.05 | 2.3±0.04 | 2.0±0.02 | 2.4±0.02 | 2.4±0.03 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.5±0.03 | 2.9±0.05 | |
| E-O3 | 2.4±0.05 | 2.7±0.03 | 2.1±0.03 | 2.5±0.05 | 2.6±0.04 | 2.6±0.01 | 2.6±0.01 | 3.0±0.05 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 2.0±0.03 | 1.9±0.02 | 1.8±0.05 | 2.0±0.01 | 2.2±0.04 | 1.9±0.06 | 2.0±0.00 | 2.7±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 2.2±0.04 | 2.1±0.02 | 1.9±0.05 | 2.1±0.01 | 2.4±0.04 | 2.0±0.06 | 2.1±0.04 | 2.9±0.05 | ||
| 茎秆Stem | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.7±0.02 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.4±0.02 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.9±0.05 | 2.9±0.03 | 3.1±0.01 |
| E-O3 | 2.9±0.01 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.9±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.9±0.01 | 3.1±0.04 | 3.3±0.03 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 3.4±0.03 | 3.7±0.03 | 3.6±0.05 | 3.6±0.03 | 3.9±0.02 | 4.0±0.04 | 4.1±0.02 | 4.4±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.7±0.04 | 4.0±0.06 | 3.7±0.04 | 3.8±0.05 | 4.0±0.03 | 4.0±0.02 | 4.2±0.03 | 4.5±0.02 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 3.3±0.03 | 3.1±0.06 | 3.0±0.07 | 3.0±0.05 | 2.7±0.03 | 3.0±0.03 | 3.1±0.08 | 3.4±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.4±0.02 | 3.4±0.05 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.3±0.02 | 3.1±0.06 | 3.1±0.03 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.7±0.05 | ||
| 稻草Straw | 抽穗期Heading | C-O3 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.5±0.00 | 2.3±0.01 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.01 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.02 | 3.1±0.02 |
| E-O3 | 2.7±0.01 | 2.5±0.00 | 2.5±0.02 | 2.8±0.01 | 2.6±0.02 | 2.8±0.01 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.3±0.02 | ||
| 穗后20 d 20DAH | C-O3 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.2±0.04 | 3.1±0.05 | 3.2±0.03 | 3.5±0.01 | 3.5±0.03 | 3.5±0.01 | 4.1±0.03 | |
| E-O3 | 3.3±0.04 | 3.6±0.05 | 3.1±0.03 | 3.4±0.04 | 3.6±0.02 | 3.5±0.03 | 3.6±0.01 | 4.2±0.04 | ||
| 成熟期Maturity | C-O3 | 2.9±0.03 | 2.7±0.06 | 2.6±0.06 | 2.7±0.04 | 2.6±0.03 | 2.6±0.03 | 2.7±0.07 | 3.3±0.01 | |
| E-O3 | 3.0±0.02 | 3.0±0.04 | 2.8±0.03 | 2.9±0.02 | 2.8±0.03 | 2.8±0.04 | 2.9±0.02 | 3.5±0.06 | ||
| ANOVA结果 ANOVA results | ||||||||||
| 臭氧胁迫O3 stress | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.034 | 0.020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.026 | ||
| 生育期 Growth stage (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 植株部位Plant parts (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.713 | 0.006 | 0.571 | 0.104 | 0.263 | ||
| O3×P | 0.010 | 0.085 | 0.011 | 0.064 | 0.763 | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.639 | ||
| S×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| O3×S×P | 0.211 | 0.359 | 0.358 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.034 | 0.817 | 0.098 | ||
| [1] | The Royal Society.Ground-level ozone in the 21st century: Future trends, impacts and policy implications[C]. London: The Royal Society, 2008. |
| [2] | Shon Z H, Kim K H, Song S K.Long-term trend in NO2 and NOx levels and their emission ratio in relation to road traffic activities in East Asia[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(18): 3120-3131. |
| [3] | Wang Y X, Zhang Y Q, Hao J, Luo M.Seasonal and spatial variability of surface ozone over China: Contributions from background and domestic pollution[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11: 3511-3525. |
| [4] | Xing J, Wang S X, Chatani S, Zhang C Y, Wei W, Hao J M, Klimont Z, Cofala J, Amann M.Projections of air pollutant emissions and its impacts on regional air quality in China in 2020[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11: 3119-3136. |
| [5] | Lai D M, Ghude S D, Patil S D, Kulkarni S H, Jena C, Tiwari S, Srivastava M K.Tropospheric ozone and aerosol long-term trends over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2012, 116(10): 82-92. |
| [6] | Liu Q, Lam K S, Jiang F, Wang T J, Xie M, Zhuang B L, Jiang X Y.A numerical study of the impact of climate and emission changes on surface ozone over South China in autumn time in 2000-2050[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 76: 227-237. |
| [7] | Wang Y X, Shen L L, Wu S L, Wu S L, Mickley L, He J W, Hao J M.Sensitivity of surface ozone over China to 2000-2050 global changes of climate and emissions[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 75: 374-382. |
| [8] | Wang X P, Mauzerall D L.Characterizing distributions of surface ozone and its impact on grain production in China, Japan, and South Korea: 1990 and 2020[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(26): 4383-4402. |
| [9] | Wang X K, Manning W, Feng Z W, Zhu Y G.Ground-level ozone in China: Distribution and effects on crop yields[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(2): 394-400. |
| [10] | 冯兆忠, 彭金龙. 地表臭氧对中国主要粮食作物产量与品质的影响:现状与展望[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 797-804. |
| Feng Z Z, Peng J L.Effects of ground-level ozone on grain yield and quality of cereal crops in China:Status and perspectives[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 797-804. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王云霞, 杨连新. 水稻品质对主要气候变化因子的响应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4):822-833. |
| Wang Y X,Yang L X.Response of rice quality to major climate change factors[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 822-833. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Kangasjarvi J, Jaspers P, Kollist H.Signalling and cell death in ozone exposed plants[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2005, 28(8): 1021-1036. |
| [13] | Ueda Y, Uehara N, Sasaki H, Kobayashi K, Yamakawa T.Impacts of acute ozone stress on superoxide dismutase (SOD) expression and reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in rice leaves[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 70: 396-402. |
| [14] | Fiscus E L, Booker F L, Burkey K O.Crop responses to ozone: Uptake, modes of action, carbon assimilation and partitioning[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2005, 28(8): 997-1011. |
| [15] | Ainsworth E A, Yendrek C R, Sitch S, Collins W J, Emberson L D.The effects of tropospheric ozone on net primary productivity and implications for climate change[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63(1): 637-661. |
| [16] | Binod P, Sindhu R, Singhania R R, Vikram S, Devi L, Nagalakshmi S, Kurien N, Sukumaran R K, Pandey A.Bioethanol production from rice straw: An overview[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(13): 4767-4774. |
| [17] | 董臣飞, 丁成龙, 许能祥, 程云辉, 沈益新, 顾洪如. 稻草饲用品质及茎秆形态特征的研究[J].草业学报, 2013(4): 86-89. |
| Dong C F, Ding C L, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, Shen Y X, Gu H R.Research on the feeding quality and related stem morphological traits of rice straw[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013(4): 86-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Van Soest P J. Rice straw, the role of silica and treatments to improve quality[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2006, 130(3-4): 137-171. |
| [19] | Frei M, Kohno Y, Wissuwa M, Makkar H P S, Becker K, Negative effects of tropospheric ozone on the feed value of rice straw are mitigated by an ozone tolerance QTL[J]. Global Change Biology, 2011, 17(7): 2319-2329. |
| [20] | Frei M, Makkar H P S, Becker K, Wissuwa M. Ozone exposure during growth affects the feeding value of rice shoots[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2010, 155(1): 74-79. |
| [21] | Shao Z S, Zhang Y L, Mu H R, Wang Y X, Yang L X.Ozone-induced reduction in rice yield is closely related to the response of spikelet density under ozone stress[J/OL].Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 712: 136560. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136560. |
| [22] | Shiro S, Yoshie S, Naoki Y, Takefumi H, Masahiro S, Toshiaki U.High-throughput determination of thioglycolic acid lignin from rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2009, 26(3): 337-340. |
| [23] | Brenner E A, Salazar A M, Zabotina O A, Thomas L. Characterization of European forage maize lines for stover composition and associations with polymorphisms within O-methyltransferase genes[J]. Journal of Experimental Plant Biology, 2012, 185-186: 281-287. |
| [24] | 赵轶鹏, 赵新勇. 植物体可溶性糖测定方法的优化[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(4): 184-185. |
| Zhao Y P, Zhao X Y.Optimization of classical measuring method of soluble sugars in plant[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(4): 184-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 胡宏纹. 有机化学[M]. 北京. 高等教育出版社, 1990: 652. |
| Hu H W. Organic Chemistry [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990: 652. | |
| [26] | Makkar H P S, Blummel M, Borowy N K, Becke K. Gravimetric determination of tannins and their correlations with chemical and protein precipitation methods[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1993, 61(2): 161-165. |
| [27] | Piepho H P, Buchse A, Emrich K.A hitchhiker’s guide to mixed models for randomized experiments[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2003, 189(5): 310-322. |
| [28] | Sanz J, Muniferting R B, Bermejo V, Gimeno B S, Elvira S.Ozone and increased nitrogen supply effects on the yield and nutritive quality of Trifolium subterraneum[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(32): 5899-5907. |
| [29] | 郑飞翔, 王效科, 侯培强, 张巍巍, 逯非, 欧阳志云. 臭氧胁迫对水稻生长以及C、N、S元素分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(6): 1479-1486. |
| Zheng F X, Wang X K, Hou P Q, Zhang W W, Lu F, Ouyang Z Y.Influences of elevated ozone on growth and C, N, S allocations of rice[J]. Acta Oecologica, 2011, 31(6): 1479-1486. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 邵在胜, 沈士博, 贾一磊, 穆海蓉, 王云霞, 杨连新, 王余龙. 臭氧浓度增加对不同敏感型水稻元素吸收与分配的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(9): 1642-1652. |
| Shao Z S, Sheng S B, Jia Y L, Mu H R, Wang Y X, Yang L X, Wang Y L.Impact of ozone stress on element absorption and distribution of rice genotypes with different ozone sensitivities[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(9): 1642-1652. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Cho K, Shibato J, Agrawal G K, Jung Y H, Kubo A, Jwa N S, Tamogami S, Satoh K, Kikuchi S, Higashi T, Kimuar S, Saji H, Tanaka Y, Iwahashi H, Masuo Y, Rakwal R.Integrated transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics analyses to survey ozone responses in the leaves of rice seedlings[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2008, 7(7): 2980-2998. |
| [32] | Wang Y X, Michael F.Stressed food: The impact of abiotic environmental stresses on crop quality[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2011, 141(3-4): 271-286. |
| [33] | Mould F L.Predicting the feed quality: Chemical analysis and in vitro evaluation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2003, 84(1-2): 31-44. |
| [34] | Sarnklong C, Cone J W, Pellikaan W F, Hendriks W H.Utilization of rice straw and different treatments to improve its feed value for ruminants: A review[J]. AsianAustralian Journal of Animal Science, 2010, 23(5): 680-692. |
| [35] | Muntifering R B, Chappelka A H, Lin J C, Karnosky D F, Somers G L.Chemical composition and digestibility of Trifolium exposed to elevated ozone and carbon dioxide in a free-air (FACE) fumigation system[J]. Functional Ecology, 2010, 20(2): 269-275. |
| [36] | Bender J, Muntifering R B, Lin J C, Weigel H J.Growth and nutritive quality of Poa pratensis as influenced by ozone and competition[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 142(1): 109-115. |
| [37] | Makkar H P S. In vitro gas methods for evaluation of feeds containing phytochemicals[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2005, 123-124(part-P1): 291-302. |
| [38] | Nussbaum S, Geissmann M, Fuhrer J.Ozone exposure-response relationships for mixtures of perennial ryegrass and white clover depend on ozone exposure patterns[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1995, 29(9): 989-995. |
| [39] | Fuhrer J, SkRby L, Ashmore M R. Critical levels for ozone effects on vegetation in Europe[J]. Environmental Pollution, 1997, 97(1-2): 91-106. |
| [40] | 董臣飞, 顾洪如, 许能祥, 程云辉, 张文洁, 丁成龙. 赤霉素对不同收获时间的稻草中非结构性碳水化合物含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 53-64. |
| Dong C F, Gu H R, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, Zhang W J, Ding C L.Effects of gibberellic acid on nonstructural carbohydrates content in rice Oryza sativa straw harvested at different times[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(8): 53-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Dong C F, Ding C L, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, Shen Y X, Gu H R.Double-purpose rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety selection and their morphological traits[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 149: 276-282. |
| [42] | Dong C F, Shen Y X, Ding C L, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, Gu H R.The feeding quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw at different cutting heights and the related stem morphological traits[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 141: 1-8. |
| [43] | Dong C F, Ding C L, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, Shen Y X, Gu H R.Research on the feeding quality and related stem morphological traits of rice(Oryza sativa) straw[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(4): 83-88. |
| [44] | 章燕柳, 穆海蓉, 邵在胜, 王云霞, 景立权, 王余龙, 杨连新. 臭氧胁迫对稻穗不同部位糙米直链淀粉含量和RVA谱特征值的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(12): 4211-4221. |
| Zhang Y L, Mu H R, Shao Z S, Wang Y X, Jing L Q, Wang Y L, Yang L X.Effects of ozone stress on amylose content and RVA profile in superior and inferior grains of different rice varieties[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(12): 4211-4221. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [14] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [15] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||