
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 69-79.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9045
李思平, 曾路生*( ), 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东*(
), 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-04-12
修回日期:2019-11-04
出版日期:2020-01-10
发布日期:2020-01-10
通讯作者:
曾路生,丁效东
基金资助:
Siping LI, Lusheng ZENG*( ), Lipeng WU, Yuxiao ZHANG, Junrui XIE, Xiaodong DING*(
), Lipeng WU, Yuxiao ZHANG, Junrui XIE, Xiaodong DING*( )
)
Received:2019-04-12
Revised:2019-11-04
Online:2020-01-10
Published:2020-01-10
Contact:
Lusheng ZENG, Xiaodong DING
摘要:
【目的】为解决水稻土壤保肥能力较弱,水稻产量较低,氮肥利用效率不高等问题,【方法】于山东省济宁市任城区水稻田设置氮肥水平与栽植密度双因素大田试验,设4个施氮量水平,即无氮(N1,0 kg/hm2)、低氮(N2,216 kg/hm2)、中氮(N3,288 kg/hm2)和高氮(N4,360 kg/hm2);栽植密度设3个梯度,即低密度(24万穴/hm2)、中密度(27万穴/hm2)和高密度(30万穴/hm2)。以探究不同氮肥水平和栽植密度下水稻成熟期土壤养分含量及氮肥利用效率的变化。【结果】随着土层加深,氮、磷、钾、有机质含量均明显下降。其中D3N4处理碱解氮含量下降了60.8%,D3N3处理速效磷含量降低了72.7%。随着施氮量增加,土壤pH值和有机质含量有所下降,速效钾含量升高,肥料偏生产力和氮肥农学利用效率降低,产量先升高后降低;随着栽植密度增加,土壤pH值与速效磷含量有所下降,表层土壤碱解氮含量略有升高,有机质含量与产量及肥料偏生产力均先升高后降低,氮肥农学利用效率降低。【结论】当栽植密度为27万穴/hm2时,氮肥用量288 kg/hm2,水稻产量最高,为14 615.3 kg/hm2;相同密度下氮肥按照216 kg/hm2施用,水稻产量、氮肥农学效率和肥料偏生产力均较高。研究结果可在实际生产中参考应用。
中图分类号:
李思平, 曾路生, 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东. 氮肥水平与栽植密度对植稻土壤养分含量变化与氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 69-79.
Siping LI, Lusheng ZENG, Lipeng WU, Yuxiao ZHANG, Junrui XIE, Xiaodong DING. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Level and Planting Density on Changes in Soil Nutrient contents and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 69-79.
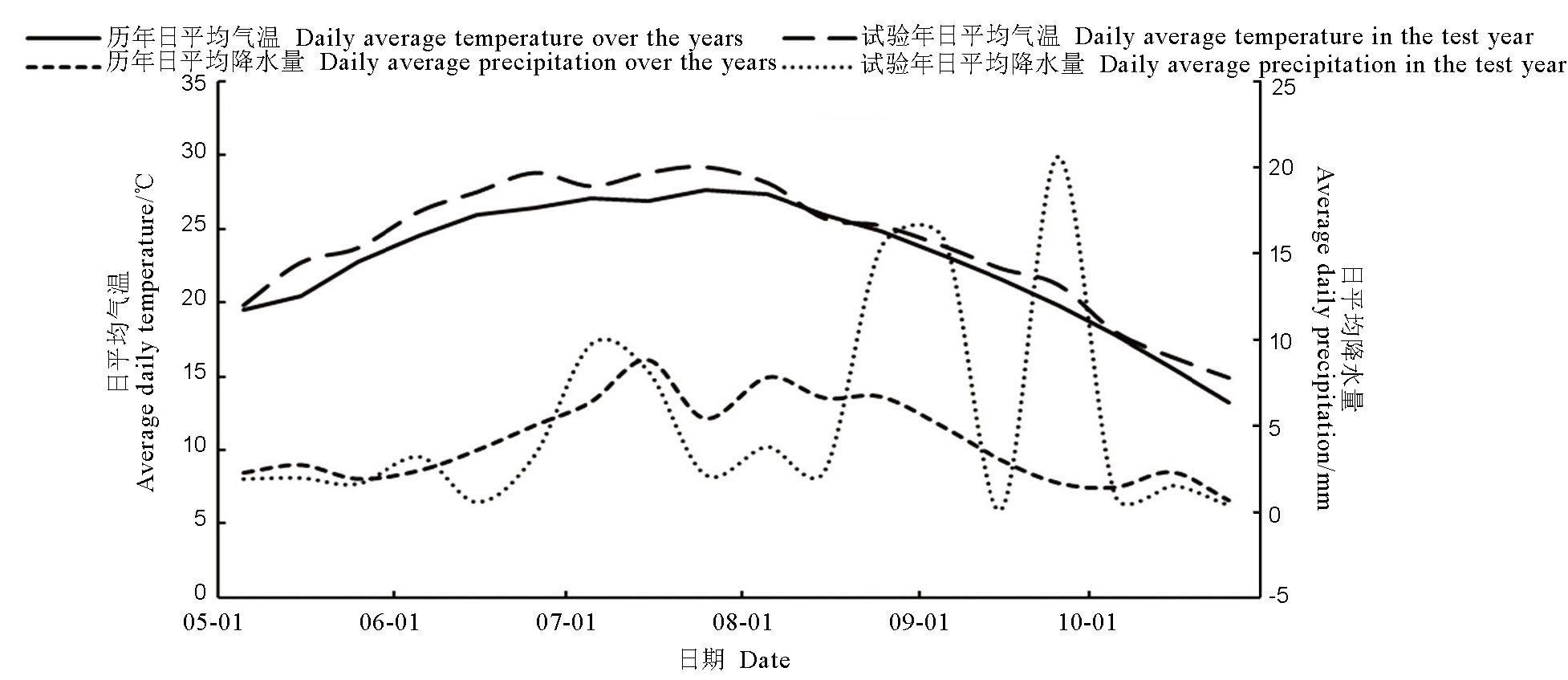
图1 山东济宁稻区水稻生育期日平均气温与日平均降水量变化趋势图中数据来自中国气象数据网地面气象资料。
Fig. 1. Trends of daily average temperature and daily average precipitation during rice growth period in Jining rice region of Shandong Province. The data in the figure are from China Meteorological Data Network.
| 处理 Treatment | 土层深度 Soil layer | 均值 Average value | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| D1N1 | 7.72±0.06 b | 7.87±0.02 c | 7.80 | 0.014 |
| D1N2 | 7.69±0.01 bc | 7.75±0.01 e | 7.72 | 0.005 |
| D1N3 | 7.87±0.06 a | 7.99±0.09 ab | 7.93 | 0.011 |
| D1N4 | 7.91±0.05 a | 8.03±0.02 a | 7.97 | 0.011 |
| D2N1 | 7.69±0.01 bc | 7.98±0.02 ab | 7.84 | 0.026 |
| D2N2 | 7.65±0.04 bcd | 7.80±0.02 de | 7.73 | 0.014 |
| D2N3 | 7.63±0.05 cd | 7.74±0.06 e | 7.69 | 0.010 |
| D2N4 | 7.59±0.01 de | 7.66±0.07 f | 7.63 | 0.006 |
| D3N1 | 7.69±0.03 bc | 7.94±0.02 b | 7.82 | 0.023 |
| D3N2 | 7.71±0.03 b | 7.84±0.01 cd | 7.78 | 0.012 |
| D3N3 | 7.54±0.06 ef | 7.82±0.03 cd | 7.68 | 0.026 |
| D3N4 | 7.51±0.01 f | 7.99±0.03 ab | 7.75 | 0.044 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | * | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Planting density(D) | *** | *** | ||
| N×D | *** | *** | ||
表1 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻成熟期不同土层pH值的影响
Table 1 Effect of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on pH of different soil layers in rice maturity.
| 处理 Treatment | 土层深度 Soil layer | 均值 Average value | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| D1N1 | 7.72±0.06 b | 7.87±0.02 c | 7.80 | 0.014 |
| D1N2 | 7.69±0.01 bc | 7.75±0.01 e | 7.72 | 0.005 |
| D1N3 | 7.87±0.06 a | 7.99±0.09 ab | 7.93 | 0.011 |
| D1N4 | 7.91±0.05 a | 8.03±0.02 a | 7.97 | 0.011 |
| D2N1 | 7.69±0.01 bc | 7.98±0.02 ab | 7.84 | 0.026 |
| D2N2 | 7.65±0.04 bcd | 7.80±0.02 de | 7.73 | 0.014 |
| D2N3 | 7.63±0.05 cd | 7.74±0.06 e | 7.69 | 0.010 |
| D2N4 | 7.59±0.01 de | 7.66±0.07 f | 7.63 | 0.006 |
| D3N1 | 7.69±0.03 bc | 7.94±0.02 b | 7.82 | 0.023 |
| D3N2 | 7.71±0.03 b | 7.84±0.01 cd | 7.78 | 0.012 |
| D3N3 | 7.54±0.06 ef | 7.82±0.03 cd | 7.68 | 0.026 |
| D3N4 | 7.51±0.01 f | 7.99±0.03 ab | 7.75 | 0.044 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | * | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Planting density(D) | *** | *** | ||
| N×D | *** | *** | ||
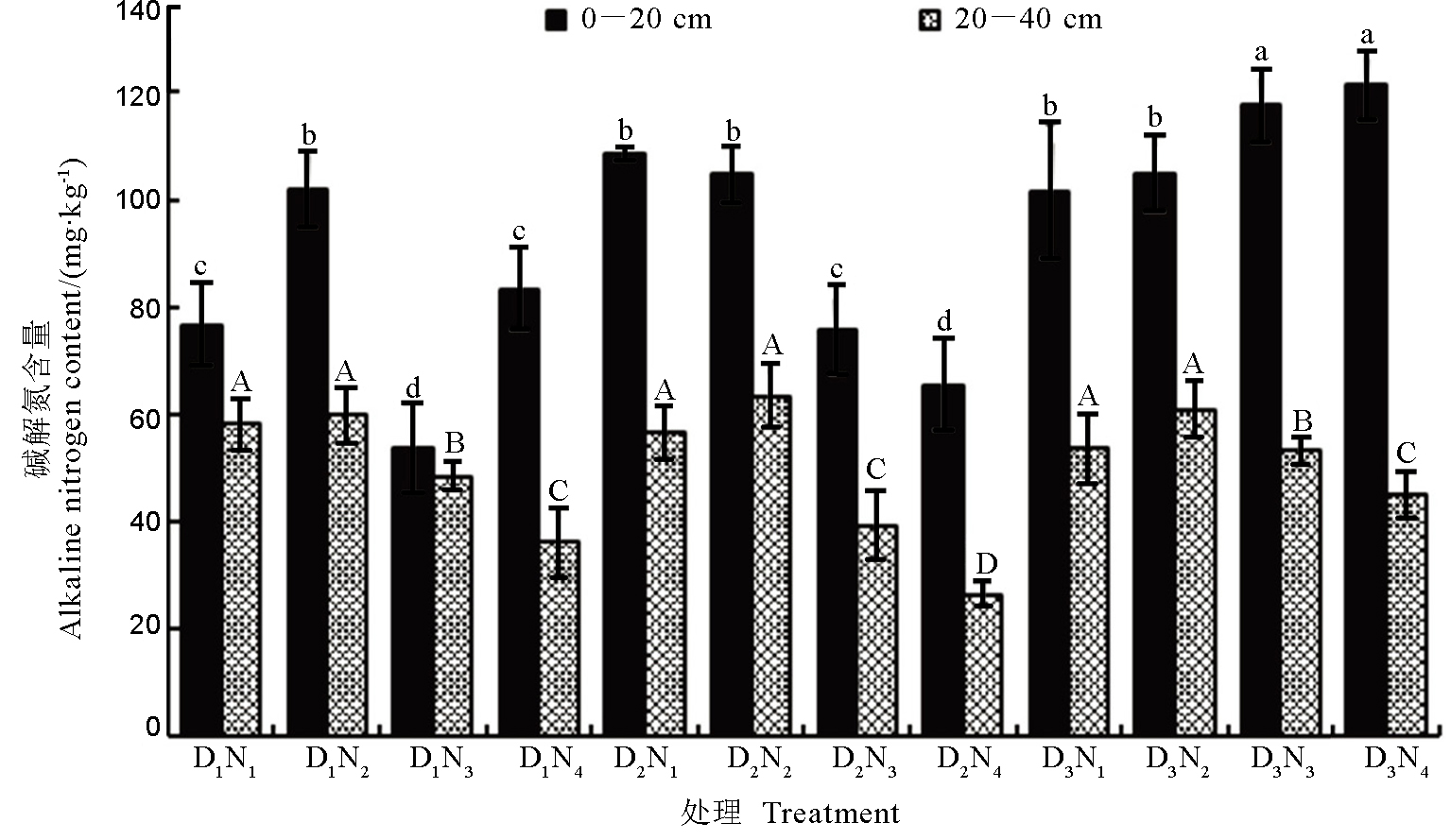
图2 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻成熟期不同土层碱解氮含量的影响图柱上方不同小写字母表示不同处理间0–20 cm土层在P<0.05水平上差异显著;不同大写字母表示不同处理间20–40cm土层在P<0.05上差异显著。图3~4同。
Fig. 2. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on alkali nitrogen content in different soil layers during rice maturity. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant difference between the 0-20cm soil layers at P<0.05 level, and different capital letters indicate significant difference between 20–40 cm soil layer at P <0.05 level. The same as in figures below.
| 因素分析 Factor analysis | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level | *** | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Density | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| N×D | *** | ** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ||
表2 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻土壤碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾含量的影响因素分析
Table 2 Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on the contents of alkali nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in rice soil.
| 因素分析 Factor analysis | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level | *** | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Density | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| N×D | *** | ** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ||
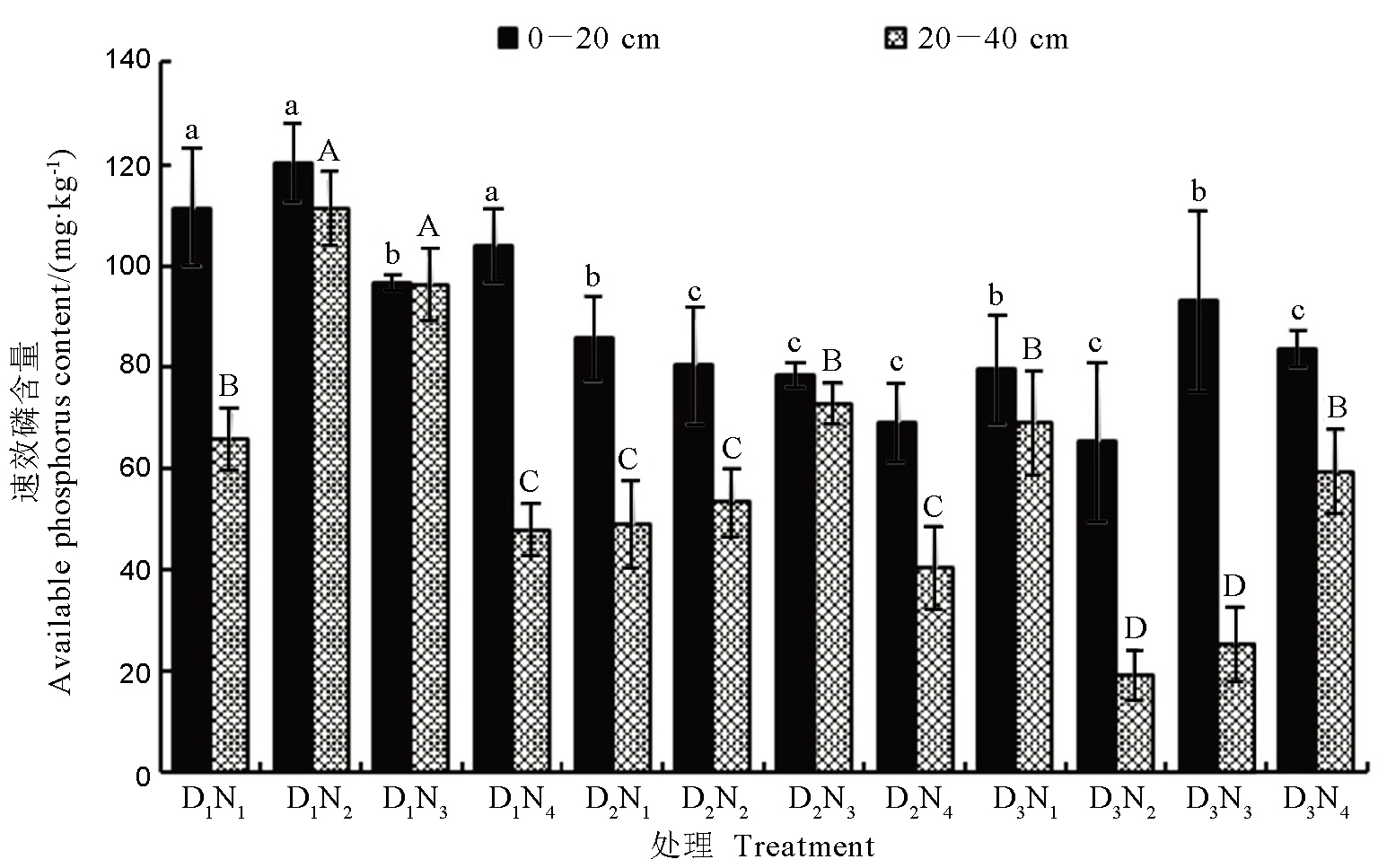
图3 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻成熟期不同土层速效磷含量的影响
Fig. 3. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on available phosphorus content in different soil layers during rice maturity.
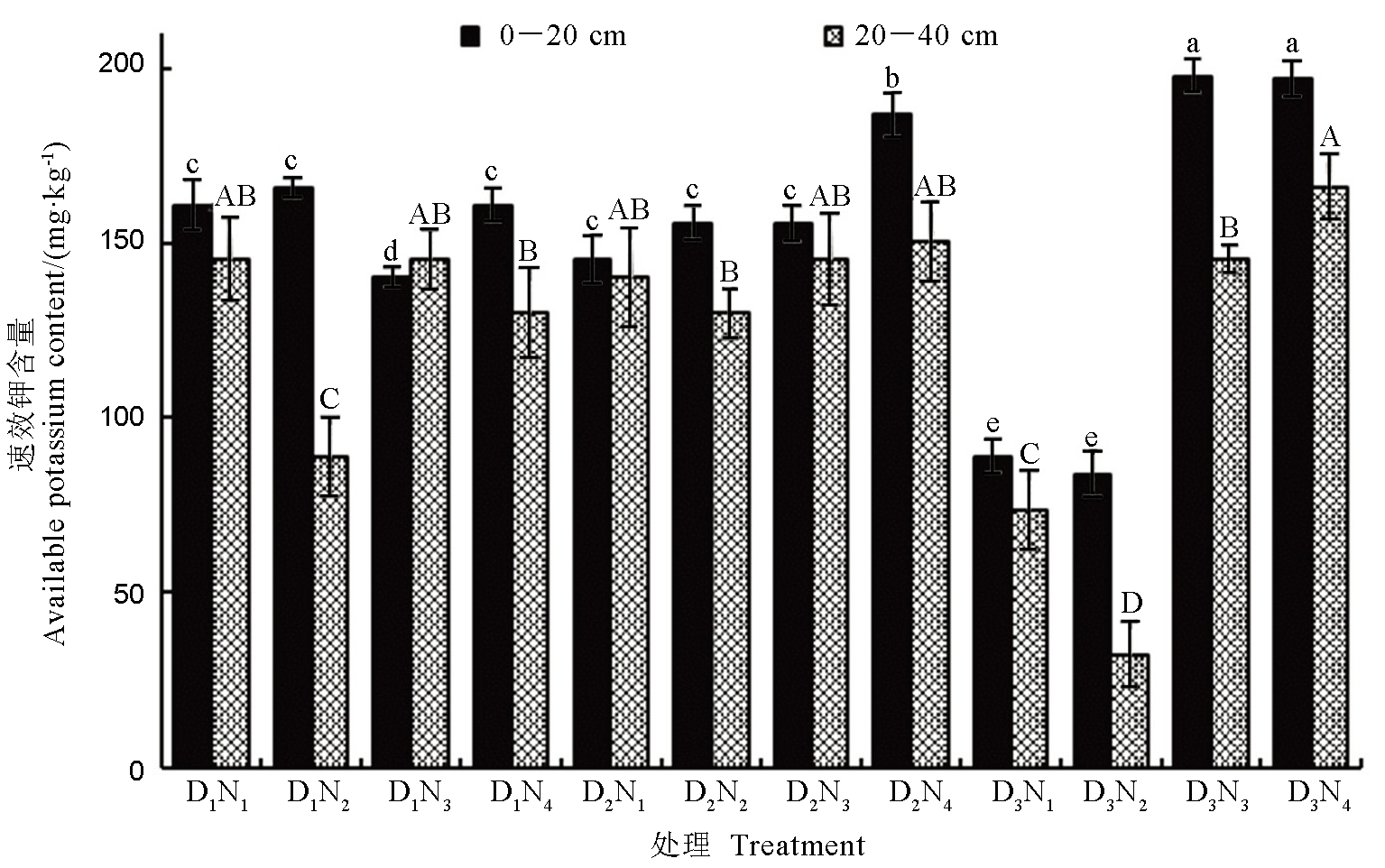
图4 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻成熟期不同土层速效钾含量的影响
Fig. 4. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on available potassium content in different soil layers during rice maturity.
| 处理 Treatment | 土壤层次 Soil level | 均值 Average value | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| D1N1 | 25.1±1.2 ab | 14.7±0.3 de | 19.9 | 0.37 |
| D1N2 | 20.8±2.7 d | 18.8±1.1 ab | 19.8 | 0.07 |
| D1N3 | 21.2±0.6 cd | 12.7±1.6 e | 17.0 | 0.35 |
| D1N4 | 25.7±0.9 a | 16.0±2.0 cd | 20.9 | 0.33 |
| D2N1 | 22.4±0.5 bcd | 19.6±0.7 a | 21.0 | 0.09 |
| D2N2 | 25.0±2.8 ab | 17.3±1.0 abc | 21.2 | 0.26 |
| D2N3 | 23.7±0.5 abc | 17.9±1.8 abc | 20.8 | 0.20 |
| D2N4 | 24.1±0.7 ab | 19.0±1.6 ab | 21.6 | 0.17 |
| D3N1 | 23.2±0.5 bc | 16.7±0.4 bcd | 20.0 | 0.23 |
| D3N2 | 24.8±1.9 ab | 16.2±0.5 cd | 20.5 | 0.30 |
| D3N3 | 22.6±2.7 bcd | 16.8±1.9 bcd | 19.7 | 0.21 |
| D3N4 | 22.9±0.3 bc | 12.9±2.3 e | 17.9 | 0.40 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | * | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Planting density(D) | NS | * | ||
| N×D | ** | *** | ||
表3 氮肥水平与栽植密度对水稻成熟期不同土层有机质含量的影响
Table 3 Effect of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on organic matter content in different soil layers during rice maturity. g/kg
| 处理 Treatment | 土壤层次 Soil level | 均值 Average value | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | |||
| D1N1 | 25.1±1.2 ab | 14.7±0.3 de | 19.9 | 0.37 |
| D1N2 | 20.8±2.7 d | 18.8±1.1 ab | 19.8 | 0.07 |
| D1N3 | 21.2±0.6 cd | 12.7±1.6 e | 17.0 | 0.35 |
| D1N4 | 25.7±0.9 a | 16.0±2.0 cd | 20.9 | 0.33 |
| D2N1 | 22.4±0.5 bcd | 19.6±0.7 a | 21.0 | 0.09 |
| D2N2 | 25.0±2.8 ab | 17.3±1.0 abc | 21.2 | 0.26 |
| D2N3 | 23.7±0.5 abc | 17.9±1.8 abc | 20.8 | 0.20 |
| D2N4 | 24.1±0.7 ab | 19.0±1.6 ab | 21.6 | 0.17 |
| D3N1 | 23.2±0.5 bc | 16.7±0.4 bcd | 20.0 | 0.23 |
| D3N2 | 24.8±1.9 ab | 16.2±0.5 cd | 20.5 | 0.30 |
| D3N3 | 22.6±2.7 bcd | 16.8±1.9 bcd | 19.7 | 0.21 |
| D3N4 | 22.9±0.3 bc | 12.9±2.3 e | 17.9 | 0.40 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | * | *** | ||
| 栽植密度Planting density(D) | NS | * | ||
| N×D | ** | *** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 千粒重 Thousand seed weight/g | 穗数 Number of panicles per 667m2/(×104) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agricultural utilization efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 肥料偏生产力 Fertilizer partial productivity/( kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1N1 | 11124.1±799.2 b | 22.5±0.3 cd | 220.3±16.7 d | 224.7±12.3 abc | 89.0±1.2 abc | / | 49.44 |
| D1N2 | 11957.9±299.7 b | 21.2±0.4 f | 246.0±13.8 cd | 229.7±8.7 a | 89.3±1.1 ab | 3.86 | 27.12 |
| D1N3 | 12331.7±949.1 b | 24.1±0.7 a | 248.6±7.9 cd | 205.9±10.8 cd | 87.5±0.7 cde | 4.19 | 24.04 |
| D1N4 | 11338.7±49.9 c | 21.3±1.2 ef | 241.8±15.6 cd | 220.0±11.3 abc | 88.5±1.0 bc | 0.60 | 19.38 |
| D2N1 | 13037.5±1398.6 ab | 22.9±0.5 bc | 253.6±22.1 c | 224.6±6.9 abc | 88.3±0.4 bcd | / | 57.94 |
| D2N2 | 14366.2±699.3 a | 22.2±0.4 cdef | 311.0±14.7 b | 207.9±15.2 bcd | 86.8±0.7 de | 6.15 | 32.58 |
| D2N3 | 14615.3±1098.9 a | 22.2±0.6 cdef | 376.7±20.7 a | 174.8±13.7 e | 89.3±1.3 ab | 5.47 | 28.49 |
| D2N4 | 13165.6±449.6 b | 22.4±0.7 cde | 321.1±19.3 b | 182.9±12.2 e | 86.5±0.5 e | 0.36 | 22.51 |
| D3N1 | 8221.1±499.5 d | 22.2±0.8 cdef | 164.4±9.5 e | 224.9±10.9 abc | 90.1±0.6 a | / | 36.54 |
| D3N2 | 9259.1±749.3 cd | 23.7±1.1 ab | 172.4±14.5 e | 226.4±7.3 ab | 88.9±0.8 abc | 4.81 | 21.00 |
| D3N3 | 9466.7±499.5 c | 21.1±0.2 f | 233.7±18.9 cd | 191.9±16.0 de | 86.4±0.7 e | 4.33 | 18.45 |
| D3N4 | 11999.5±1148.9 b | 21.7±0.3 def | 236.2±26.7 cd | 233.9±14.8 a | 89.2±1.3 ab | 10.49 | 20.51 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | *** | NS | *** | *** | * | ||
| 密度Growing density(D) | * | NS | *** | *** | * | ||
| N×D | *** | *** | *** | * | *** |
表4 氮肥水平与栽植密度互作对水稻产量、构成因子及肥料利用效率的影响
Table 4 Effects of interaction between nitrogen level and planting density on rice yield, its components and fertilizer use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 千粒重 Thousand seed weight/g | 穗数 Number of panicles per 667m2/(×104) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agricultural utilization efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 肥料偏生产力 Fertilizer partial productivity/( kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1N1 | 11124.1±799.2 b | 22.5±0.3 cd | 220.3±16.7 d | 224.7±12.3 abc | 89.0±1.2 abc | / | 49.44 |
| D1N2 | 11957.9±299.7 b | 21.2±0.4 f | 246.0±13.8 cd | 229.7±8.7 a | 89.3±1.1 ab | 3.86 | 27.12 |
| D1N3 | 12331.7±949.1 b | 24.1±0.7 a | 248.6±7.9 cd | 205.9±10.8 cd | 87.5±0.7 cde | 4.19 | 24.04 |
| D1N4 | 11338.7±49.9 c | 21.3±1.2 ef | 241.8±15.6 cd | 220.0±11.3 abc | 88.5±1.0 bc | 0.60 | 19.38 |
| D2N1 | 13037.5±1398.6 ab | 22.9±0.5 bc | 253.6±22.1 c | 224.6±6.9 abc | 88.3±0.4 bcd | / | 57.94 |
| D2N2 | 14366.2±699.3 a | 22.2±0.4 cdef | 311.0±14.7 b | 207.9±15.2 bcd | 86.8±0.7 de | 6.15 | 32.58 |
| D2N3 | 14615.3±1098.9 a | 22.2±0.6 cdef | 376.7±20.7 a | 174.8±13.7 e | 89.3±1.3 ab | 5.47 | 28.49 |
| D2N4 | 13165.6±449.6 b | 22.4±0.7 cde | 321.1±19.3 b | 182.9±12.2 e | 86.5±0.5 e | 0.36 | 22.51 |
| D3N1 | 8221.1±499.5 d | 22.2±0.8 cdef | 164.4±9.5 e | 224.9±10.9 abc | 90.1±0.6 a | / | 36.54 |
| D3N2 | 9259.1±749.3 cd | 23.7±1.1 ab | 172.4±14.5 e | 226.4±7.3 ab | 88.9±0.8 abc | 4.81 | 21.00 |
| D3N3 | 9466.7±499.5 c | 21.1±0.2 f | 233.7±18.9 cd | 191.9±16.0 de | 86.4±0.7 e | 4.33 | 18.45 |
| D3N4 | 11999.5±1148.9 b | 21.7±0.3 def | 236.2±26.7 cd | 233.9±14.8 a | 89.2±1.3 ab | 10.49 | 20.51 |
| 氮肥水平Nitrogen level(N) | *** | NS | *** | *** | * | ||
| 密度Growing density(D) | * | NS | *** | *** | * | ||
| N×D | *** | *** | *** | * | *** |
| 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 土壤pH Soil pH | 土壤碱解氮 Soil alkaline nitrogen | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus | 土壤速效钾 Soil available potassium | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agricultural utilization efficiency | 肥料偏生产力 Fertilizer partial productivity | 水稻产量 Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH value | 1.00 | |||||||
| 土壤碱解氮Soil alkaline nitrogen | -0.31 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 土壤速效磷Soil available phosphorus | 0.38 | -0.09 | 1.00 | |||||
| 土壤速效钾Soil available potassium | -0.33 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 1.00 | ||||
| 土壤有机质Soil organic matter | 0.13 | -0.08 | -0.29 | -0.13 | 1.00 | |||
| 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agronomy utilization efficiency | -0.38 | 0.58* | -0.15 | 0.02 | -0.24 | 1.00 | ||
| 肥料偏生产力Fertilizer partial productivity | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.52* | -0.22 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 1.00 | |
| 水稻产量Yield | -0.32 | -0.25 | 0.57* | 0.44* | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 1.00 |
表5 水稻成熟期0–20 cm植稻土壤养分与水稻产量及肥料利用率的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis between soil nutrient contents and rice yield and fertilizer utilization rate in 0–20 cm rice soil layer during rice maturity.
| 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 土壤pH Soil pH | 土壤碱解氮 Soil alkaline nitrogen | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus | 土壤速效钾 Soil available potassium | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agricultural utilization efficiency | 肥料偏生产力 Fertilizer partial productivity | 水稻产量 Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH value | 1.00 | |||||||
| 土壤碱解氮Soil alkaline nitrogen | -0.31 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 土壤速效磷Soil available phosphorus | 0.38 | -0.09 | 1.00 | |||||
| 土壤速效钾Soil available potassium | -0.33 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 1.00 | ||||
| 土壤有机质Soil organic matter | 0.13 | -0.08 | -0.29 | -0.13 | 1.00 | |||
| 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen fertilizer agronomy utilization efficiency | -0.38 | 0.58* | -0.15 | 0.02 | -0.24 | 1.00 | ||
| 肥料偏生产力Fertilizer partial productivity | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.52* | -0.22 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 1.00 | |
| 水稻产量Yield | -0.32 | -0.25 | 0.57* | 0.44* | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| [1] | 邓明君, 邓俊杰, 刘佳宇. 中国粮食作物化肥施用的碳排放时空演变与减排潜力[J]. 资源科学, 2016, 38(3): 534-544. |
| Deng M J, Deng J J, Liu J Y.On the space-time evolution of carbon emissions and reduction potential in Chinese grain crop fertilizer application[J]. Resources Science, 2016, 38(3): 534-544. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 刘书通, 李春生, 方福平, 张小惠, 毛一剑, 孔宪琴, 张克勤, 吴荣梁. 我国水稻生产区域变化及其比较优势分析[J]. 中国稻米, 2014, 20(4): 9-13. |
| Liu S T, Li C S, Fang F P, Zhang X H, Mao Y J, Kong X Q, Zhang K Q, Wu R L.Study on the variation and comparative advantage of regional rice production structure in China[J]. China Rice, 2014, 20(4): 9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Ladha J K, Gjd K, Bennett J, Peng S, Reddy C K, Reddy P M, Singh U.Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved lowland rice germplasm[J]. Field Crops Research, 1998, 56(1-2): 41-71. |
| [4] | Ju X T, Xing G X, Chen X P, Zhang S L, Zhang L J, Liu X J, Cui Z L, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu Z L, Zhang F S.Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2009, 106(9): 3041-3046. |
| [5] | Zheng X, Han S, Huang Y, Wang Y S, Wang M X.Re-quantifying the emission factors based on field measurements and estimating the direct N2O emission from Chinese croplands[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2004, 18(2), DOI: 10.102912003GB002167, 2004. |
| [6] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯. 中国水稻高产栽培技术创新与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K.Innovation and practice of high-yield rice cultivation technology in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Huang M, Yang C L, Ji Q M, Jiang L G, Tan J L, Li Y Q.Tillering responses of rice to plant density and nitrogen rate in a subtropical environment of southern China.Field Crops Research, 2013, 149: 187-192. |
| [8] | 邓中华, 明日, 李小坤, 郑磊, 徐维明, 杨运清, 任涛, 丛日环, 鲁剑巍. 不同密度和氮肥用量对水稻产量、构成因子及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(1): 20-25. |
| Deng Z H, Ming R, Li X K, Zheng L, Xu W M, Yang Y Q, Ren T, Cong R H, Lu J W.Effects of nitrogen application rate and planting density on grain yields, yield components and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(1): 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 陈小荣,肖自京,孙嘉,钟蕾,朱昌兰,彭小松,贺晓鹏,傅军如,欧阳林娟. 不同产量晚稻品种分蘖期动态密度稀化下群体自动调节力的差异与生理机制. 中国水稻科学[J], 2013, 27(4): 405-412. |
| Chen X R, Xiao Z J, Sun J, Zhong L, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He X P, Fu J R, Ou-Yang L J. Discrepancy and its physiological mechanism of population self regulatory ability for late rice varieties under treatment of dynamic thinning of seedlings during tillering stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(4): 405-412. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 林洪鑫, 肖运萍, 袁展汽, 刘仁根, 汪瑞清. 水稻合理密植及其优质高产机理研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(9): 1-4. |
| Lin H X, Xiao Y P, Yuan Z Q, Liu R Y, Wang R Q.Advance in rational colse planting and its mechanism of superior quality and high yield in rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(9): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王成瑷, 王伯伦, 张文香, 赵磊, 赵秀哲, 高连文. 栽培密度对水稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2004, 35(4): 318-322. |
| Wang C A, Wang B L, Zhang W X, Zhao L, Zhao X Z, Gao L W.Effect of planting density on grain yield and quality of rice[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2004, 35(4): 318-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 周江明, 赵琳, 董越勇, 徐进, 边武英, 毛杨仓, 章秀福. 氮肥和栽植密度对水稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. |
| Zhou J M, Zhao L, Dong Y Y, Xu J, Bian W Y, Mao Y C, Zhang X F.Nitrogen and transplanting density interactions on the rice yield and N use rate[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 徐新朋, 周卫, 梁国庆, 孙静文, 王秀斌, 何萍, 徐芳森, 余喜初. 氮肥用量和密度对双季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(3): 1279-1286. |
| Xu X P, Zhou W, Liang G Q, Sun J W, Wang X B, He P, Xu F S, Yu X C.Effects of nitrogen and density interactions on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-rice systems[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2015, 21(3): 1279-1286. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 吴培, 陈天晔, 袁嘉琦, 黄恒, 邢志鹏, 胡雅杰, 朱明, 李德剑, 刘国林, 张洪程. 施氮量和直播密度互作对水稻产量形成特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 269-281. |
| Wu P, Chen T Y, Yuan J Q, Huang H, Xing Z P, Hu Y J, Zhu M, Li D J, Liu G L, Zhang H C.Effects of interaction between nitrogen application rate and direct-sowing density on yield formation characteristics of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 269-281.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 陈军, 黄珊瑜, 刘冰,吴林坤,林文雄. 不同氮肥运筹对水稻根际土壤理化性质及代谢物质的影响[J]. 福建农业学报, 2015, 30(11): 1082-1089. |
| Chen J, Huang S Y, Liu B, Wu L K, Lin W X.Effects of different nitrogen regimes on soil physico-chemical properties and metabolites in rice rhizosphere[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 30(11): 1082-1089. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 张玉,秦华东,黄敏,江立庚,徐世宏. 氮肥运筹对免耕水稻根系生长、根际土壤特性及产量的影响[J]. 广西植物, 2014(5): 681-685, 621. |
| Zhang Y, Qin H D, Huang M, Jiang L G, Xu S H.Effect of different nitrogen application modes on root growth, rhizosphere soil characteristics and rice yield under no-tillage[J]. Guihaia, 2014(5): 681-685, 621. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M].第三版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| Bao S D.Soil Agro-chemistrical Analysis[M]. 3rd. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [18] | 吕丽华, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 赵明, 赵久然, 鲁来清. 施氮量对夏玉米碳、氮代谢和氮利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(4): 630-637. |
| Lv L H, Tao H B, Wang P, Zhao M, Zhao J R, Lu L Q.The effect of nitrogen application rate on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(4): 630-637. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 谢金兰, 王维赞, 朱秋珍, 刘晓燕, 梁强, 李毅杰, 罗亚伟, 梁阗. 氮肥施用方式对甘蔗产量及土壤养分变化的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2013, 44(4): 607-610. |
| Xie J L, Wang W Z, Zhu Q Z, Liu X Y, Liang Q, Li Y J, Luo Y W, Liang T.Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application mode on sugarcane yield and soil nutrient change[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2013, 44(4): 607-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 侯云鹏, 韩立国, 孔丽丽, 尹彩侠, 秦裕波, 李前, 谢佳贵. 不同施氮水平下水稻的养分吸收、转运及土壤氮素平衡[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(4): 836-845. |
| Hou Y P, Han L G, Kong L L, Yin C X, Qin Y B, Li Q, Xie J G.Nutrient absorption,translocation in rice and soil nitrogen equilibrium under different nitrogen application doses[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition & Fertilizer, 2015, 21(4): 836-845. | |
| [21] | 姚小萌, 周正朝, 田霄鸿, 王淑娟, 党珍珍. 长期机械化秸秆全量还田对土壤养分分层的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2015, 46(1): 198-202. |
| Yao X M, Zhou Z C, Tian X H, Wang S J, Dang Z Z.Effects of long-term all straw return to field with machine on the stratifications of soil nutrients[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 46(1): 198-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 王若水, 康跃虎, 万书勤, 孙甲霞. 水分调控对盐碱地土壤盐分与养分含量及分布的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(14): 96-104. |
| Wang R S, Kang Y H, Wan S Q, Sun J X.Effects of water regulation methods on soil salt, nutrient content and its distribution in overlying saline wasteland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(14): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 葛顺峰, 许海港, 季萌萌, 姜远茂. 土壤碳氮比对平邑甜茶幼苗生长和碳氮分配的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(10): 942-949. |
| Ge S F, Xu H G, Ji M M, Jiang Y M.Effects of soil C:N on growth and distribution of nitrogen and carbon of Malus hupehensis seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2013, 37(10): 942-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 郑克武, 邹江石, 吕川根. 氮肥和栽插密度对杂交稻"两优培九"产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(6): 885-893. |
| Zheng K W, Zou J S, Lv C G.Effects of Transplanting Density and nitrogen fertilizer on yield formation and N absorption in a two-line intersubspecific hybrid rice "Liangyoupeijiu"[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(6): 885-893. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 曹胜彪, 张吉旺, 董树亭, 刘鹏, 赵斌, 杨今胜. 施氮量和种植密度对高产夏玉米产量和氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6): 1343-1353. |
| Cao S B, Zhang J W, Dong S T, Liu P, Zhao B, Yang J S.Effects of nitrogen rate and planting density on grain yield and nitrogen utilization efficiency of high yield summer maize[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition & Fertilizer, 2012, 18(6): 1343-1353. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 晏娟, 尹斌, 张绍林, 沈其荣, 朱兆良. 不同施氮量对水稻氮素吸收与分配的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(5): 835-839. |
| Yan J, Yin B, Zhang S L, Shen Q R, Zhu Z L.Effect of nitrogen application rate on nitrogen uptake and distribution in rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(5): 835-839. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 李旭毅, 郭翔, 马均. 水氮互作下水稻氮代谢关键酶活性与氮素利用的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(11): 2055-2063. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Li X Y, Guo X, Ma J.Relationship of activities of key enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism with nitrogen utilization in rice under water-nitrogen interaction[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(11): 2055-2063. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 李鹏程, 董合林, 刘爱忠, 刘敬然, 孙淼, 王国平, 刘绍东, 赵新华, 李亚兵. 种植密度氮肥互作对棉花产量及氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(23): 122-130. |
| Li P C, Dong H L, Liu A Z, Liu J R, Sun M, Wang G P, Liu S D, Zhao X H, Li Y B.Effects of planting density and nitrogen fertilizer interaction on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of cotton[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(23): 122-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 鲁叶江, 王开运, 杨万勤, 吴福忠. 缺苞箭竹群落密度对土壤养分库的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(6):996-1001. |
| Lu Y J, Wang K Y, Yang W Q, Wu F Z.Effects of Fargesia denudata density on soil nutrient pool[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(6): 996-1001. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 赵双, 朱小荣. 不同栽培密度对水稻产量影响的研究[J]. 中国盐业, 2016(15): 56-57. |
| ZHAO S, ZHU X R.Study on the influence of different cultivation density on rice yield[J]. China Salt Industry, 2016(15): 56-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 何虎, 曾勇军, 贾维强, 潘晓华, 石庆华. 栽插密度对天优华占辐射利用及产量的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2015, 30(4): 65-70. |
| He H, Zeng Y J, Jia W Q, Pan X H, Shi Q H.Effects of planting density on radiation use and grain yield of tianyou huazhan[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2015, 30(4): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 刘洁, 胡冬华. 水稻基础产量与土壤速效养分含量的相关性[J]. 作物研究, 2015(3): 277-280. |
| Liu J, Hu D H.Correlation between basic yield of rice and soil available nutrient content[J]. Crop Research, 2015(3): 277-280. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 曹倩, 贺明荣, 代兴龙, 门洪文, 王成雨. 密度、氮肥互作对小麦产量及氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 815-822. |
| Cao Q, He M R, Dai X L, Men H W, Wang C Y.Effects of interaction between density and nitrogen on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(4): 815-822. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 张娟, 武同华, 代兴龙, 王西芝, 李洪梅, 蒋明洋, 贺明荣. 种植密度和施氮水平对小麦吸收利用土壤氮素的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(6): 1727-1734. |
| Zhang J, Wu T H, Dai X L, Wang X Z, Li H M, Jiang M Y, He M R.Effects of plant density and nitrogen level on nitrogen uptake and utilization of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(6): 1727-1734. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [7] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [13] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [14] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [15] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||