
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 601-609.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7080
收稿日期:2018-06-19
修回日期:2018-07-31
出版日期:2018-11-27
发布日期:2018-05-10
通讯作者:
方福平
基金资助:
Zhongdu CHEN, Chunchun XU, Long JI, Fuping FANG*( )
)
Received:2018-06-19
Revised:2018-07-31
Online:2018-11-27
Published:2018-05-10
Contact:
Fuping FANG
摘要:
目的 长江中游地区是我国双季稻主产区,系统分析双季稻生产碳足迹构成对于该地区农业的固碳减排和发展低碳农业具有重要的意义。方法 基于农业碳足迹理论及生命周期评价法,采用问卷调查方式定量研究长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹,分析其构成因素,解析长江中游地区双季稻生产肥料、灌溉投入以及碳足迹与水稻产量的关系。【内容】长江中游地区双季稻单位产量、单位生物量、单位产值碳足迹分别为0.67 kg/kg、0.35 kg/kg和0.27 kg/元,随着产量的增加呈现显著降低的趋势。CH4排放、柴油、肥料为长江中游地区双季稻生产碳排放主要来源,分别占双季稻生产碳足迹的66.2%、13.1%和10.9%。早稻和晚稻生产分别有22.4%和36.7%的地块氮肥投入过量,28.4%和33.5%的地块灌溉投入过量且产量较低,存在着较大的节能减排潜力。种植规模与碳足迹呈现显著负相关关系。与小规模双季稻种植相比,大规模早稻和晚稻种植单位产量碳足迹分别降低了29.7%和37.2%。这项研究表明,作物生产的碳足迹可能受到农场规模、气候条件以及作物管理实践的影响。结论 因此,适当减少双季稻种植面积并发展水稻节肥节水及免耕技术,构建规模化的低碳种植模式必将成为未来长江流域双季稻生产应对气候变化发展低碳农业的重要举措。
中图分类号:
陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 方福平. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609.
Zhongdu CHEN, Chunchun XU, Long JI, Fuping FANG. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Double Cropping Rice Production in the Middle Yangtze River Valley Based on Household Surveys[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 601-609.
| 项目Item | 单位Unit | 系数Coefficient | 来源Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 柴油Diesel | kg/kg | 0.89 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 柴油燃烧Diesel combustion | kg/kg | 4.10 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 灌溉用电Electricity for irrigation | kg/kg | 0.82 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 氮肥N | kg/kg | 1.53 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 磷肥P2O5 | kg/kg | 1.63 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 钾肥K2O | kg/kg | 0.65 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 农膜Film | kg/kg | 22.72 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | kg/kg | 16.61 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 除草剂Herbicides | kg/kg | 10.15 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | kg/kg | 10.57 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 水稻种子Rice seed | kg/kg | 1.84 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
表1 农业投入资料的温室气体排放系数
Table 1 Index of greenhouse gas(GHG) emission of different material for agricultural production.
| 项目Item | 单位Unit | 系数Coefficient | 来源Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 柴油Diesel | kg/kg | 0.89 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 柴油燃烧Diesel combustion | kg/kg | 4.10 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 灌溉用电Electricity for irrigation | kg/kg | 0.82 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 氮肥N | kg/kg | 1.53 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 磷肥P2O5 | kg/kg | 1.63 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 钾肥K2O | kg/kg | 0.65 | CLCD 0.7 |
| 农膜Film | kg/kg | 22.72 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | kg/kg | 16.61 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 除草剂Herbicides | kg/kg | 10.15 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | kg/kg | 10.57 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
| 水稻种子Rice seed | kg/kg | 1.84 | Ecoinvent 2.2 |
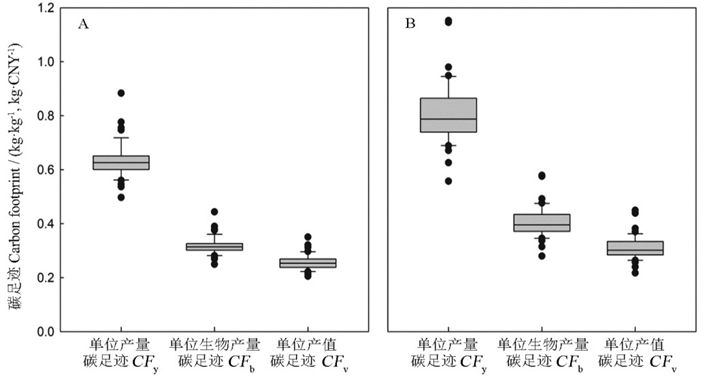
图2 长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹^ A-早稻单位产量、单位生物量、单位产值碳足迹;B-晚稻单位产量、单位生物量、单位产值碳足迹。
Fig. 2. Carbon footprint of double cropping rice production in the middle Yangtze River Valley. ^ A, Carbon footprint per unit yield(CFy), biomass(CFb), and output value(CFv) of early rice; B, Carbon footprint per unit yield(CFy), biomass(CFb), and output value(CFv) of late rice.
| 项目Item | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | 双季稻Double rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| N₂O | 4.92 | 5.04 | 4.98 |
| CH₄ | 63.5 | 68.7 | 66.2 |
| 柴油Diesel fuel | 13.9 | 12.3 | 13.1 |
| 灌溉Irrigation | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 农膜Plastic film | 3.6 | 0.0 | 1.7 |
| 种子Seeds | 2.5 | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| 除草剂Herbicides | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 氮肥N | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.5 |
| 磷肥P₂O₅ | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| 钾肥K2O | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
表2 长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹构成
Table 2 Mean proportions of the carbon footprint of double cropping rice in the middle Yangtze River Valley.
| 项目Item | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | 双季稻Double rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| N₂O | 4.92 | 5.04 | 4.98 |
| CH₄ | 63.5 | 68.7 | 66.2 |
| 柴油Diesel fuel | 13.9 | 12.3 | 13.1 |
| 灌溉Irrigation | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 农膜Plastic film | 3.6 | 0.0 | 1.7 |
| 种子Seeds | 2.5 | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| 除草剂Herbicides | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 氮肥N | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.5 |
| 磷肥P₂O₅ | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| 钾肥K2O | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
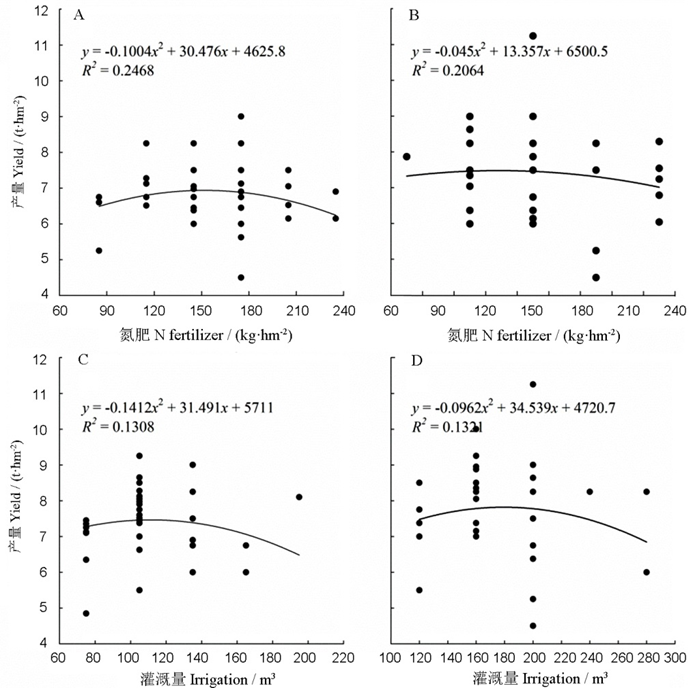
图3 长江中游地区双季稻氮肥和灌溉投入量与产量的关系^ A-早稻产量与氮肥施用量的关系;B-晚稻产量与氮肥施用量的关系;C-早稻产量与灌溉量的关系;D-晚稻产量与灌溉量的关系。
Fig. 3. Relationship of N-fertilizer and irrigation inputs with yield of double-cropping rice in the middle Yangtze River Valley.^A, Relationship of actual yield of early rice with N-fertilizer application rate; B, Relationship of actual yield of early rice with N-fertilizer application rate; C, Relationship of actual yield of early rice with irrigation amount; D, Relationship of actual yield of early rice with irrigation amount.
| 项目Items | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大规模LZF | 中规模MZF | 小规模SZF | 大规模LZF | 中规模MZF | 小规模SZF | ||
| 柴油Diesel fuel | 484.7±65.2 b | 526.8±91.3 b | 676.2±44.1 a | 525.3±77.1 b | 571.5±102.1 b | 772.0±66.6 a | |
| 氮肥N | 255.6±31.1 c | 361.4±53.3 b | 470.9±50.2 a | 332.2±54.5 c | 412.5±20.1 b | 554.2±77.9 a | |
| 磷肥P2O5 | 19.2±8.2 b | 38.5±11.4 a | 42.9±10.5 a | 34.2±9.7 b | 36.9±16.4 b | 66.3±15.4 a | |
| 钾肥K2O | 65.5±20.1 a | 57.1±17.2 a | 67.1±15.9 a | 52.4±15.1 b | 85.1±16.8 a | 96.2±9.4 a | |
| 灌溉Irrigation | 15.3±5.1 b | 18.3±3.8 b | 25.3±1.8 a | 31.7±8.6 a | 23.8±7.1 a | 39.3±10.2 a | |
| 农膜Film | 153.9±39.1 a | 165.4±61.1 a | 167.2±38.6 a | - | - | - | |
| 种子Seed | 123.6±49.5 a | 118.8±55.3 a | 111.5±51.7 a | 132.3±66.1 a | 55.6±19.1 b | 74.5±21.9 b | |
| 除草剂Herbicides | 1.9±0.9 a | 2.0±1.1 a | 2.1±0.8 a | 3.1±1.2 a | 4.5±2.1 a | 2.6±1.3 a | |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | 7.0±2.7 a | 10.3±4.5 a | 5.2±3.9 a | 7.3±2.9 a | 10.8±3.1 a | 10.0±2.9 a | |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | 7.3±3.8 a | 8.3±2.9 a | 10.5±4.6 a | 6.0±3.3 a | 8.7±2.7 a | 7.3±2.5 a | |
| 甲烷CH4 | 2751.0±902.7 a | 2863.1±962.7 a | 3018.8±802.9 a | 3106.4±1009.1 a | 3403.8±1122.1 a | 3480.1±1245.4 a | |
| 氧化亚氮N2O | 149.9±31.1 c | 212.2±28.2 b | 276.3±28.2 a | 198.2±21.8 c | 252.2±32.9 c | 329.6±41.5 c | |
| 面积碳足迹Cf | 4035.1±302.7 b | 4382.2±232.1 b | 4874.0±202.1 a | 4429.3±333.1 b | 4865.3±298.1 b | 5532.2±442.1 a | |
| 产量Yield | 7500.0±511.2 a | 6653.2±302.7 b | 6222.0±441.2 b | 7800.0±311.1 a | 7403.6±413.2 a | 6037.5±849.1 b | |
| 产量碳足迹Cfy | 0.54±0.05 c | 0.66±0.02 b | 0.78±0.08 a | 0.57±0.05 b | 0.66±0.09 b | 0.92±0.13 a | |
表3 长江中游地区双季稻不同种植规模碳足迹投入及构成
Table 3 Carbon footprint of double cropping rice at different scales in the middle Yangtze River Valley. kg/hm2
| 项目Items | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大规模LZF | 中规模MZF | 小规模SZF | 大规模LZF | 中规模MZF | 小规模SZF | ||
| 柴油Diesel fuel | 484.7±65.2 b | 526.8±91.3 b | 676.2±44.1 a | 525.3±77.1 b | 571.5±102.1 b | 772.0±66.6 a | |
| 氮肥N | 255.6±31.1 c | 361.4±53.3 b | 470.9±50.2 a | 332.2±54.5 c | 412.5±20.1 b | 554.2±77.9 a | |
| 磷肥P2O5 | 19.2±8.2 b | 38.5±11.4 a | 42.9±10.5 a | 34.2±9.7 b | 36.9±16.4 b | 66.3±15.4 a | |
| 钾肥K2O | 65.5±20.1 a | 57.1±17.2 a | 67.1±15.9 a | 52.4±15.1 b | 85.1±16.8 a | 96.2±9.4 a | |
| 灌溉Irrigation | 15.3±5.1 b | 18.3±3.8 b | 25.3±1.8 a | 31.7±8.6 a | 23.8±7.1 a | 39.3±10.2 a | |
| 农膜Film | 153.9±39.1 a | 165.4±61.1 a | 167.2±38.6 a | - | - | - | |
| 种子Seed | 123.6±49.5 a | 118.8±55.3 a | 111.5±51.7 a | 132.3±66.1 a | 55.6±19.1 b | 74.5±21.9 b | |
| 除草剂Herbicides | 1.9±0.9 a | 2.0±1.1 a | 2.1±0.8 a | 3.1±1.2 a | 4.5±2.1 a | 2.6±1.3 a | |
| 杀虫剂Insecticides | 7.0±2.7 a | 10.3±4.5 a | 5.2±3.9 a | 7.3±2.9 a | 10.8±3.1 a | 10.0±2.9 a | |
| 杀菌剂Fungicides | 7.3±3.8 a | 8.3±2.9 a | 10.5±4.6 a | 6.0±3.3 a | 8.7±2.7 a | 7.3±2.5 a | |
| 甲烷CH4 | 2751.0±902.7 a | 2863.1±962.7 a | 3018.8±802.9 a | 3106.4±1009.1 a | 3403.8±1122.1 a | 3480.1±1245.4 a | |
| 氧化亚氮N2O | 149.9±31.1 c | 212.2±28.2 b | 276.3±28.2 a | 198.2±21.8 c | 252.2±32.9 c | 329.6±41.5 c | |
| 面积碳足迹Cf | 4035.1±302.7 b | 4382.2±232.1 b | 4874.0±202.1 a | 4429.3±333.1 b | 4865.3±298.1 b | 5532.2±442.1 a | |
| 产量Yield | 7500.0±511.2 a | 6653.2±302.7 b | 6222.0±441.2 b | 7800.0±311.1 a | 7403.6±413.2 a | 6037.5±849.1 b | |
| 产量碳足迹Cfy | 0.54±0.05 c | 0.66±0.02 b | 0.78±0.08 a | 0.57±0.05 b | 0.66±0.09 b | 0.92±0.13 a | |
| [1] | 于兴安. 当代国际环境法发展面临的内外问题与对策分析. 鄱阳湖学刊, 2017: 75-82. |
| Yu X A.Internal and external problems and countermeasures in the development of contemporary international environmental law.J Poyang Lake, 2017: 75-82. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Statistical Yearbook 2013: World Food and Agriculture. Rome,Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2013. |
| [3] | West T O, Marland G.Net carbon flux from agriculture: Carbon emissions, carbon sequestration, crop yield, and land-use change.Biogeochemistry, 2003, 63(1): 73-83. |
| [4] | Hammod G.Time to give due weight to the ‘carbon footprint’ issue.Nature, 2007, 445(7125): 256. |
| [5] | Cheng K, Pan G, Smith P, Luo T, Li L, Zheng J.Carbon footprint of China’s crop production: An estimation using agro-statistics data over 1993-2007.Agric Ecosyst Environ, 2011, 142(3-4): 231-237 |
| [6] | 米松华, 黄祖辉, 朱奇彪, 黄莉莉. 农户低碳减排技术采纳行为研究. 浙江农业学报, 2014, 26(3): 797-804 |
| Mi S H, Huang Z H, Zhu Q F, Huang L L.Study on factors influencing farmers' adoption of low-carbon technologies.Acta Agric Zhejiang, 2014, 26(3): 797-804. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王占彪, 陈静, 张立峰, 陈阜, 孙红春, 李连涛. 河北省棉花生产碳足迹分析. 棉花学报, 2016, 28(6): 594-601. |
| Wang Z B, Chen J, Zhang L F, Chen B, Sun L H, Li L T.Carbon footprint analysis of cotton production in Hebei Province.Cotton Sci, 2016, 28(6): 594-601. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 刘夏璐, 王洪涛, 陈建, 何琴, 张浩, 姜睿, 陈雪雪, 侯萍. 中国生命周期参考数据库的建立方法与基础模型. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(10): 2136-2144. |
| Liu X L, Wang H C, Chen J, He Q, Zhang H, Jiang R, Chen X X, Hou P.Method and basic model for development of Chinese reference life cycle database.Acta Sci Circumst, 2010, 30(10): 2136-2144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Röös E, Sundberg C, Hansson P A.Carbon Footprint of Food Products//Assessment of Carbon Footprint in Different Industrial Sectors, Volume 1. Springer Singapore, 2014: 85-112. |
| [10] | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change2006:Synthesis Report. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006 |
| [11] | Yan X, Yagi K, Akiyama H, Akimoto H.Statistical analysis of the major variables controlling methane emission from rice fields.Global Change Biol, 2005, 11: 1131-1141. |
| [12] | 肖玉. 中国稻田生态系统服务功能及其经济价值研究. 北京: 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所, 2005. |
| Xiao Y.Study on the service function and economic value of rice field ecosystem in China. Beijing: Institute of Geographical Science and Resources,Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 逯非, 王效科, 韩冰, 欧阳志云, 郑华. 稻田秸秆还田: 土壤固碳与甲烷增排. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(1): 99-108. |
| Lu F, Wang X K, Han B, Ouyang Z Y, Zheng H.Straw return to rice paddy: Soil carbon sequestration and increased methane emission.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2010, 21(1): 99-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Xue J F, Pu C, Liu S L, Zhao X, Zhang R, Chen F.Carbon and nitrogen footprint of double rice production in Southern China.Ecol Indic, 2016, 64: 249-257. |
| [15] | 王兴, 赵鑫, 王钰乔, 薛建福, 张海林. 中国水稻生产的碳足迹分析. 资源科学, 2017, 39(4): 713-722. |
| Wang X, Zhao X, Wang Y Q, Xue J F, Zhang H L.Carbon footprint analysis of rice production in China.Resour Sci, 2017, 39(4): 713-722. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 史磊刚, 陈阜, 孔凡磊, 范士超. 华北平原冬小麦-夏玉米种植模式碳足迹研究. 中国人口资源与环境, 2011, 21(9): 93-98. |
| Shi L G, Chen F, Kong F L, Fang S C.The Carbon footprint of winter wheat-summer maize cropping pattern on North China.China Popul, Resour Environ, 2011, 21(9): 93-98. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 陈中督. 农作措施对双季稻田固碳减排效应与农户低碳技术采纳行为研究. 北京:中国农业大学, 2017. |
| Chen Z D.Impacts of farming practices on carbon sequestration and emission mitigation in double rice field and farmers’ adoption behavior of low carbon technology. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Cheng K, Pan G, Smith P, Luo T, Li L, Zheng J.Carbon footprint of China's crop production: An estimation using agro statistics data over 1993-2007.Agric Ecosyst Environ, 2011, 142: 231-237. |
| [19] | 卢小宏. 不同农作措施下冬小麦-夏玉米碳足迹及优化潜力评价. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2013. |
| Lu X.Carbon footprint and optimization potential of winter wheat and summer maize under different agricultural measures. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Nelson R G, Hellwinckel C M, Brandt C C, Energy Use and Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Cropland Production in the United States, 1990-2004.J Environ Qual, 2009, 38(2): 418-425 |
| [21] | Shang Q, Yang X, Gao C.Net annual global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in Chinese double rice-cropping systems: A 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments.Global Change Biol, 2011, 17: 2196-2210. |
| [22] | 周胜, 宋祥甫, 颜晓元. 水稻低碳生产研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2013 , 27(2): 213-222. |
| Zhou S, Song X F, Yan X Y.Progress in research on low-carbon rice production technology.Chin J Rice Sci, 2013 , 27(2): 213-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Yagi K, Tsuruta H, Kanda K I,Minami K.Effect of water management on methane emission from a Japanese rice paddy field: Automated methane monitoring.Global Biogeochem Cycles, 1996, 10(2): 255-267. |
| [24] | 董红敏, 李玉娥, 陶秀萍, 彭小培, 李娜, 朱志平. 中国农业源温室气体排放与减排技术对策. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(10): 269-273. |
| Dong H M, Li Y E, Tao X P, Peng X P, Li N, Zhu Z P.China greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities and its mitigation strategy. TChin Soc Agric Eng, 2008, 24(10): 269-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 曹凑贵, 李成芳, 展茗, 汪金平. 稻田管理措施对土壤碳排放的影响. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(1): 93-98. |
| Cao C G, Li C F, Zhang M, Wang J P.Effects of agricultural management practices on carbon emissions in paddy fields.Sci Agric Sin, 2011, 44(1): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 李晶, 王明星, 陈德章. 水稻田甲烷的减排方法研究及评价. 大气科学, 1998, 22(3): 99-107. |
| Li J, Wang M X, Chen D Z.Studies on mitigation methods of methane emission from rice paddies.Acta Seismol Sin, 1998, 22(3): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 黄耀. 中国的温室气体排放、减排措施与对策. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(5): 722-732. |
| Huang Y.Emissions of greenhouse gases in china and its reduction strategy.Quatern Sci, 2006, 26(5): 722-732. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 展茗, 曹凑贵, 汪金平, 袁伟玲, 江洋, 高大伟. 稻鸭共作对甲烷排放的影响. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(12): 2666-2672. |
| Zhang M, Chao C G, Wang J P, Yuan W L, Jiang Y, Gao D W.Effects of rice-duck farming on paddy field's methane emission.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2008, 19(12): 2666-2672. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 文再坤. 发展湖南低碳农业科技创新体系建设的思考. 作物研究, 2010, 24(4): 244-245. |
| Wen Z K, Thoughts on developing hunan low-carbon agricultural science and technology innovation system.Crop Res, 2010, 24(4): 244-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 刘巽浩, 徐文修, 李增嘉, 褚庆全, 杨晓琳, 陈阜. 农田生态系统碳足迹法: 误区、改进与应用——兼析中国集约农作碳效率. 中国农业资源与区划, 2013, 35(6): 1-11. |
| Liu J H, Xu W X, Li Z J, Chu Q Q, Yang X L, Chen F.The missteps, improvement and application of carbon footprint methodology in farmland ecosystems with the case study of analyzing the carbon efficiency of china's intensive farming.Chin J Agric Resour Reg Plann, 2013, 35(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 朱相成, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 水分调控下绿肥种植和石灰施用对双季稻稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [2] | 陈丽明, 杨陶陶, 熊若愚, 谭雪明, 黄山, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊, 曾研华. 开放式主动增温对双季优质籼稻籽粒淀粉积累及其关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 166-177. |
| [3] | 杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77. |
| [4] | 王丰, 廖亦龙, 柳武革, 刘迪林, 曾学勤, 傅友强, 朱满山, 李金华, 付崇允, 马晓智, 霍兴. 籼型杂交稻恢复系动态株型与光能利用率评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 141-154. |
| [5] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| [6] | 叶春, 李艳大, 曹中盛, 黄俊宝, 孙滨峰, 舒时富, 吴罗发. 不同育秧盘对机插双季稻株型与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 435-442. |
| [7] | 钟雪梅, 黄铁平, 彭建伟, 卢文璐, 康兴蓉, 孙梦飞, 宋思明, 唐启源, 陈裕新, 湛冬至, 周旋. 机插同步一次性精量施肥对双季稻养分累积及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 436-446. |
| [8] | 陈中督 徐春春 纪龙 方福平*. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [9] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| [10] | 田昌, 周旋, 谢桂先, 刘强, 荣湘民, 张玉平, 谭力彰, 彭建伟. 控释尿素减施对双季稻田氨挥发损失和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 387-397. |
| [11] | 张浪, 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 成小琳, 徐华勤, 肖志祥, 唐启源, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对双季稻生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 226-236. |
| [12] | 吕伟生, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 黄山, 商庆银, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡水秀, 曾研华. 近30年江西双季稻安全生产期及温光资源变化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 323-334. |
| [13] | 陈佳娜, 谢小兵, 伍丹丹, 曹放波, 单双吕, 高伟, 李志斌, 邹应斌. 机插密度与氮肥运筹对中嘉早17产量形成及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 628-636. |
| [14] | 吴萍萍,.刘金剑.杨秀霞.商庆银.周 毅.谢小立.沈其荣.郭世伟,. 不同施肥制度对红壤地区双季稻田氨挥发的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(1): 85-85~93 . |
| [15] | 齐国君,秦冉冉,肖满开,郑兆阳,江潮,程遐年,张孝羲,翟保平,. 安徽安庆混作稻区稻纵卷叶螟第三、四代发生规律研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(5): 513-518 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||