
中国水稻科学 ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 610-618.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.06.007
张庆1, 王娟1, 景立权1, 杨连新1, 王云霞2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2015-07-25
修回日期:2015-09-26
出版日期:2015-10-25
发布日期:2015-11-10
通讯作者:
王云霞
作者简介:*通讯录作者:E-mail:yxwang@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Qing ZHANG1, Juan WANG1, Li-quan JING1, Lian-xin YANG1, Yun-xia WANG2,*( )
)
Received:2015-07-25
Revised:2015-09-26
Online:2015-10-25
Published:2015-11-10
Contact:
Yun-xia WANG
About author:*Corresponding author:E-mail:yxwang@yzu.edu.cn
摘要:
2014年土培条件下,以日本晴、L81和L71为供试材料,开花及花后1周叶面喷施硫酸锌、柠檬酸锌、葡萄糖酸锌和EDTA二钠锌(Zn2+浓度均为0.2%,以喷施等量清水为对照),研究叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对稻穗不同部位糙米锌浓度及有效性的影响。结果表明,稻穗不同部位糙米锌浓度差异显著,其中稻穗上部糙米锌浓度显著大于稻穗中部和下部,植酸、植酸与锌摩尔比则相反,不同处理趋势一致。与不施锌相比,硫酸锌、柠檬酸锌、葡萄糖酸锌和EDTA二钠锌使所有品种糙米锌浓度平均分别增加33%、31%、26%和27%,其中锌处理对稻穗上、中部糙米锌浓度的影响显著大于稻穗下部,供试材料中以日本晴的响应最大。锌处理对糙米植酸浓度影响较小,但对植酸与锌摩尔比影响较大。与对照相比,硫酸锌、柠檬酸锌、葡萄糖酸锌和EDTA二钠锌使所有品种糙米植酸与锌摩尔比平均分别下降25%、24%、22%和18%,其中稻穗上部和中部的降幅大于稻穗下部,日本晴和L71的降幅大于L81;锌处理×品种和锌处理×品种×部位间互作均达显著水平。以上数据说明,水稻籽粒生长早期喷锌处理可大幅增加糙米锌浓度及其生物有效性,增幅因锌化合物、供试品种以及籽粒在稻穗上的着生部位(以强势粒响应更大)而异。
张庆, 王娟, 景立权, 杨连新, 王云霞. 叶面施用不同形态锌化合物对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 610-618.
Qing ZHANG, Juan WANG, Li-quan JING, Lian-xin YANG, Yun-xia WANG. Effect of Foliar Application of Different Zn Compounds on Zn Concentration and Bioavailability in Brown Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(6): 610-618.
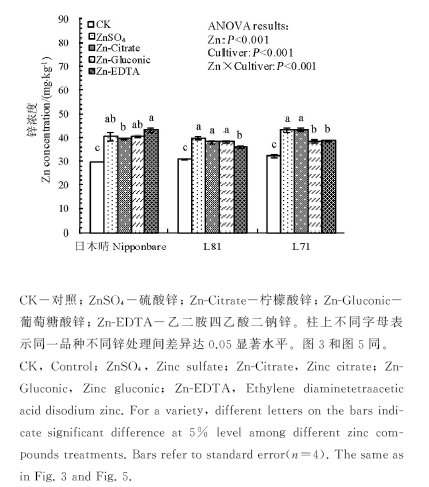
图1 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71糙米锌浓度的影响
Fig. 1. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on Zn concentration in brown rice of Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
| 参数 Parameters | 锌 Zn | 品种 Cultivar (C) | 部位 Part (P) | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锌浓度Zn concentration | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| 植酸浓度PA concentration | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.602 | <0.001 | 0.385 |
| 植酸与锌摩尔比Molar ratio of PA to Zn | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.049 |
表1 不同锌处理对稻米锌浓度、植酸浓度和植酸与锌摩尔比影响的显著性检验(P值)
Table 1 Significance test for Zn concentration, phytic acid (PA) concentration and the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) of brown rice among different Zn treatments (P value).
| 参数 Parameters | 锌 Zn | 品种 Cultivar (C) | 部位 Part (P) | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锌浓度Zn concentration | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| 植酸浓度PA concentration | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.602 | <0.001 | 0.385 |
| 植酸与锌摩尔比Molar ratio of PA to Zn | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.049 |
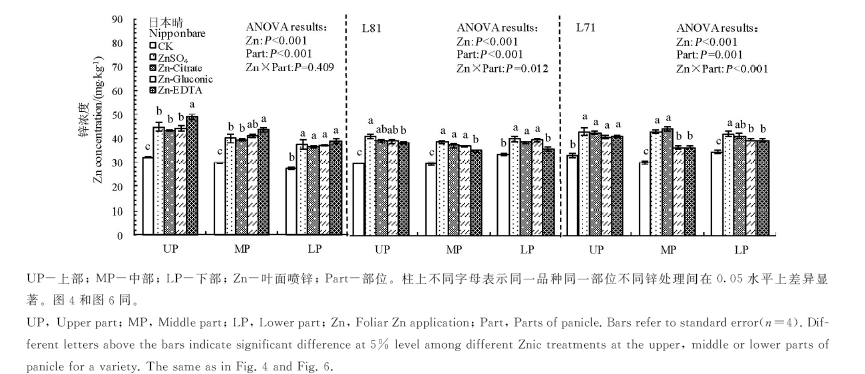
图2 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71稻穗上、中和下部糙米锌浓度的影响
Fig. 2. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on Zn concentrations in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
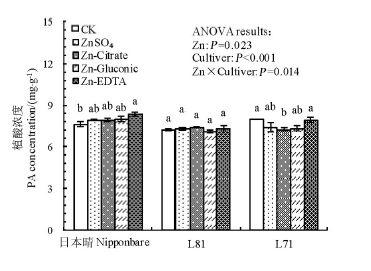
图3 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71糙米植酸浓度的影响
Fig. 3. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on concentration of phytic acid (PA) in brown rice of Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
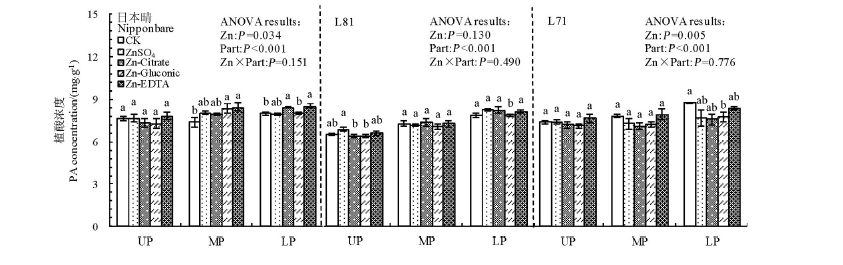
图4 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71稻穗上、中和下部糙米植酸浓度的影响
Fig. 4. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on phytic acid (PA) concentrations in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
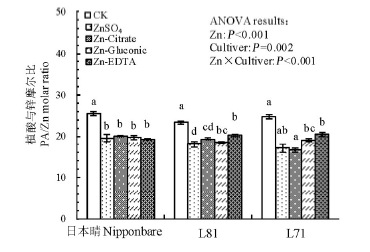
图5 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71糙米植酸与锌摩尔比的影响
Fig. 5. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn compounds on the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) in brown rice of Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
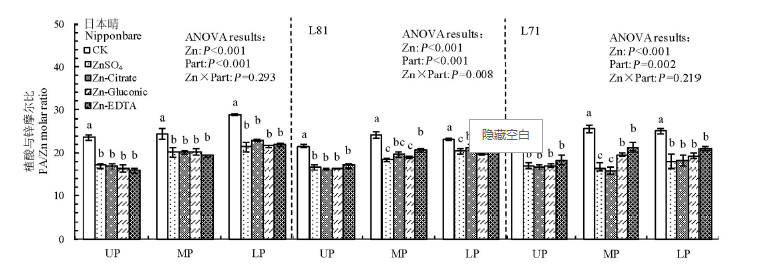
图6 叶面喷施不同形态锌化合物对日本晴、L81和L71稻穗不同部位糙米植酸与锌摩尔比的影响
Fig. 6. Effect of foliar application of different forms of Zn on the molar ratio of phytic acid to Zn (PA/Zn) in brown rice from the upper, middle and lower parts of panicles for Nipponbare, L81 and L71.
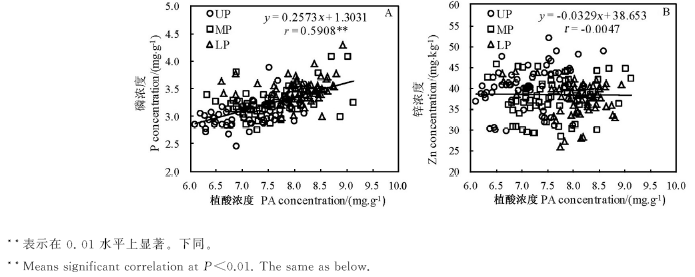
图7 供试材料稻穗不同部位糙米中植酸浓度与磷(A)或锌浓度(B)间的关系(n=180)
Fig. 7. Relationship between concentrations of phytic acid (PA) and P (A) or Zn (B) in brown rice from different parts of panicles of tested rice cultivars (n=180).
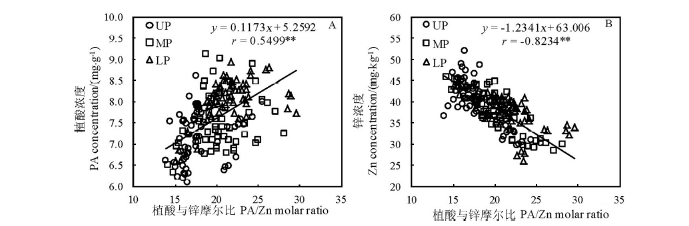
图8 供试材料稻穗不同部位糙米中植酸与锌摩尔比与植酸浓度(A)或Zn(B)之间的相关性(n=180)
Fig. 8. Relationship between PA/Zn molar ratios and concentrations of Zn or PA in brown rice from different parts of panicles of tested cultivars (n=180)
| 参数 Parameter | 锌 Zn | 品种 C | 部位 P | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 0.337 | 0.056 | 0.256 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.513 | 1.000 |
| 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 0.845 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.096 | 0.279 | <0.001 | 0.993 |
表2 不同处理对水稻糙米率和单位面积产量影响的显著性检验(P值)
Table 2 Significance test for brown rice rate and grain yield of rice among different treatments (P value).
| 参数 Parameter | 锌 Zn | 品种 C | 部位 P | 锌×品种 Zn×C | 锌×部位 Zn×P | 品种×部位 C×P | 锌×品种×部位 Zn×C×P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 0.337 | 0.056 | 0.256 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.513 | 1.000 |
| 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 0.845 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.096 | 0.279 | <0.001 | 0.993 |
| [1] | 黄秋蝉, 韦友欢, 石景芳. 微量元素锌对人体健康的生理效应及其防治途径. 微量元素与健康研究, 2009, 26(1): 68-70. |
| [2] | WHO. Reducing risks, promoting healthy life//World Health Organization. The World Health Report. Geneva, Switzerland:WHO, 2002. |
| [3] | Cakmak I.Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification.Plant Soil, 2008, 302: 1-17. |
| [4] | 邹春琴, 张福锁. 籽粒铁、锌营养与人体健康研究进展. 广东微量元素科学, 2006, 13(7): 1-8. |
| [5] | 郭九信, 廖文强, 孙玉明, 等. 锌肥施用方法对水稻产量及籽粒氮锌含量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 185-192. |
| [6] | Cakmak I, Pfeiffer W H, McClafferty B, et al. Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron.Cereal Chem, 2010, 87: 10-20. |
| [7] | Cakmak I.Enrichment of fertilizers with zinc: An excellent investment for humanity and crop production in India.J Trace Elem Med Bio, 2009, 23: 281-289. |
| [8] | Wang Y X, Specht A, Horst W J.Stable isotope labelling and zinc distribution in grains studied by laser ablation ICP-MS in an ear culture system reveals zinc transport barriers during grain filling in wheat.New Phytol, 2011, 189: 428-437. |
| [9] | 曹玉贤, 田霄鸿, 李秀丽, 等.土施和喷施锌肥对冬小麦子粒锌含量及生物有效性的影响.植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(6): 1394-1401. |
| [10] | 李辛, 李志洪, 孙建华, 等.土壤施锌和叶面喷锌对风沙土玉米Zn吸收与积累的影响.西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 42(1):144-150. |
| [11] | ZhangY Q, Sun Y X, Ye Y L,et al. Zinc biofortification of wheat through fertilizer applications in different locations of China.Field Crops Res, 2012, 125: 1-7. |
| [12] | Wei Y Y,Shohag M J I,Yang X E. Biofortification and bioavailability of rice grain zinc asaffected by different forms of foliar zinc fertilization.PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(9): 1-10. |
| [13] | Haslett B S, Reid R J, Rengel Z.Zinc mobility in wheat: Uptake and distribution of zinc applied to leaves or roots.AnnBot, 2001, 87: 379-386. |
| [14] | Wu C, Lu L, Yang X, et al.Uptake, translocation, and remobilization of zinc absorbed at different growth stages by rice genotypes of different Zn densities.J Agric Food Chem, 58: 6767-6773. |
| [15] | Harris N S, Taylor G J.Remobilization of cadmium in maturing shoots of near isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium accumulation.J Exp Bot, 2001, 52: 1473-1481. |
| [16] | 王云霞, 杨连新, Horst W J.重金属复合处理对小麦铜锌镍镉积累和分布的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(11):2145-2151. |
| [17] | 王云霞, 杨连新, Horst W J.用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱研究小麦籽粒元素的共分布. 作物学报, 2012, 38(3): 514-521. |
| [18] | Frossard E, Bucher M, Mächler F, et al.Potential for increasing the content and bioavailability of Fe, Zn and Ca in plants for human nutrition.JSci Food Agr, 2000, 80: 861-879. |
| [19] | Palmgren M G, Clemens S, Williams L E, et al.Zinc biofortification of cereals: Problems and solutions.Trends Plant Sci,2008,13: 464-473. |
| [20] | Fang Y, Wang L, Xin Z, et al.Effect of foliar application of zinc, selenium, and iron fertilizers on nutrients concentration and yield of rice grain in China.J Agric Food Chem,2008,56: 2079-2084. |
| [21] | Wissuwa M, Ismail A M, Graham R D.Rice grain zinc concentrations as affected by genotype, native soil-zinc availability, and zinc fertilization.Plant Soil,2008,306: 37-48. |
| [22] | Phattarakul N, Rerkasem B, Li L, et al.Biofortification of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries.Plant Soil,2012, 361: 131-141. |
| [23] | 周三妮, 赖上坤, 吴艳珍, 等. 大气CO2浓度升高和叶面施锌对武运粳23稻米不同部位锌浓度和有效性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(9):1689-1692. |
| [24] | 周三妮, 王云霞, 赖上坤, 等. FACE下二氧化碳、施氮量、密度和锌肥对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响.中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3):289-296. |
| [25] | Colle C, Madoz-Escande C, Leclerc E.Foliar transfer into the biosphere: Review of translocation factors to cereal grains.J Environ Radioactiv,2009, 100: 683-689. |
| [26] | Amrani M, Westfall D, Peterson G.Influence of water solubility of granular zinc fertilizers on plant uptake and growth.J Nutr, 1999, 22(12): 1815-1827. |
| [27] | Karak T, Singh U, Das S, et al.Comparative efficacy of ZnSO4 and Zn-EDTA application for fertilization of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Arch Agron Soil Sci, 2005,51(3): 253-264. |
| [28] | Wang Y X, Yang L X, Höller M, et al.Pyramiding of ozone tolerance QTLs OzT8 and OzT9 confers improved tolerance to season-long ozone exposure in rice.Environ Exp Bot, 2014,104: 26-33. |
| [29] | 周三妮. 不同条件下结实期叶面施锌对稻米锌浓度及有效性的影响. 扬州:扬州大学, 2015:1-91. |
| [30] | Lapteva N A.Colorimetric determination of phytate in unpurified extracts of seeds and the products of their processing.Anal Biochem, 1988, 175: 227-230. |
| [31] | 付力成, 王人民, 孟杰, 等. 叶面锌、铁配施对水稻产量、品质及铁锌分布的影响及其品种差异.中国农业科学, 2010, 43(24): 5009-5018. |
| [32] | 李宏云, 王少霞, 李萌, 等. 不同水氮管理下锌与氮磷肥配合喷施对冬小麦锌营养品质的影响.中国农业科学, 2014, 47(20): 4016-4026. |
| [33] | 李燕婷, 李秀英, 肖艳, 等. 叶面肥的营养机理及应用研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(1):162-172. |
| [34] | 杨芸, 周坤, 徐卫红, 等. 外源铁对不同品种番茄光合特性、品质及镉积累的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(4):1006-1015. |
| [35] | 付景, 徐云姬, 陈露, 等. 超级稻花后强弱势粒淀粉合成相关酶活性和激素含量变化及其与籽粒灌浆的关系. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3):302-310. |
| [36] | Cheryan M, Rackis J.Phytic acid interactions in food systems.Int J Food SciNutr, 1980,13(4): 297-335. |
| [37] | Lonnerdal B.Dietary factors influencing zinc absorption.J Nutr,2000,130: 1378S-1383S. |
| [38] | Ockenden I,Dorsch J A, Reid M M, et al.Characterization of the storage of phosphorus, inositol phosphate and cations in grain tissues of four barley low phytic acid genotypes.Plant Sci, 2004, 167(5):1131-1142. |
| [39] | Persson D P, Hansen T H, Laursen K H, et al.Simultaneous iron, zinc, sulfur and phosphorus speciation analysis of barley grain tissues using SEC-ICP-MS and IP-ICP-MS.Metallomics, 2009, 5: 418-426. |
| [40] | Morris E R, Ellis R.Usefulness of the dietary phyticacid/zinc molar ratio as an index of zinc bioavailabi1ity to rats and humans.Biol Trace Elem Res,1989,19:107-117. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||