
中国水稻科学 ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 501-510.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.05.007
收稿日期:2015-01-10
修回日期:2015-03-30
出版日期:2015-09-10
发布日期:2015-09-10
通讯作者:
张文忠
作者简介:*通讯录作者:E-mail:zwzhong@126.com
基金资助:
Ji-ping GAO, Yang-hui SUI, Wen-zhong ZHANG*( ), Chen YAO, Ming-chao GAO, Ming-hui ZHAO, Zheng-jin XU
), Chen YAO, Ming-chao GAO, Ming-hui ZHAO, Zheng-jin XU
Received:2015-01-10
Revised:2015-03-30
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-09-10
Contact:
Wen-zhong ZHANG
About author:*Corresponding author:E-mail:zwzhong@126.com
摘要:
在大田环境下,以辽粳294、开粳1号为材料,在灌浆期设置5个水分梯度处理,研究了水稻冠层温度日变化特征及其与土壤水分状况、产量生理特性、稻米品质之间的关系。结果表明:1)冠层温度低于气温,但与其显著正相关。梯度水分处理导致冠层温度和冠气温度差逐级升高,即土壤水势降低,冠层温度升高,冠气温度差绝对值增大;2)相同环境条件下,抗旱性弱的品种辽粳294的冠层温度低于抗旱性强的品种开粳1号;3)水分胁迫下水稻冠气温度差与每穗实粒数、千粒重、结实率、产量、整精米率、蛋白质含量、直链淀粉、脂肪酸和食味值呈显著负相关,与秕粒数、垩白度、垩白粒、碎米率呈显著正相关;4)光合速率、气孔导度及蒸腾速率随土壤水势降低而下降,且抗旱性强的品种开粳1号的光合性能较强。相关性分析表明,两个品种冠气温度差与其光合性能显著或极显著负相关;5)开粳1号的气孔密度显著大于辽粳294,而气孔长度和气孔宽度极显著小于辽粳294。综合分析表明,在灌浆期辽粳294和开粳1号在土壤水势为-0.02~-0.03 MP时,平均冠气温度差分别维持在0.9℃和0.8℃时对产量影响不显著(达到水分临界水平),可作为水稻灌浆期的节水灌溉指标。
中图分类号:
高继平, 隋阳辉, 张文忠, 姚晨, 高明超. 水稻灌浆期冠层温度对植株生理性状及稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 501-510.
Ji-ping GAO, Yang-hui SUI, Wen-zhong ZHANG, Chen YAO, Ming-chao GAO, Ming-hui ZHAO, Zheng-jin XU. Effect of Canopy Temperature on Physiological Characteristic and Grain Quality at Filling Stage in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(5): 501-510.
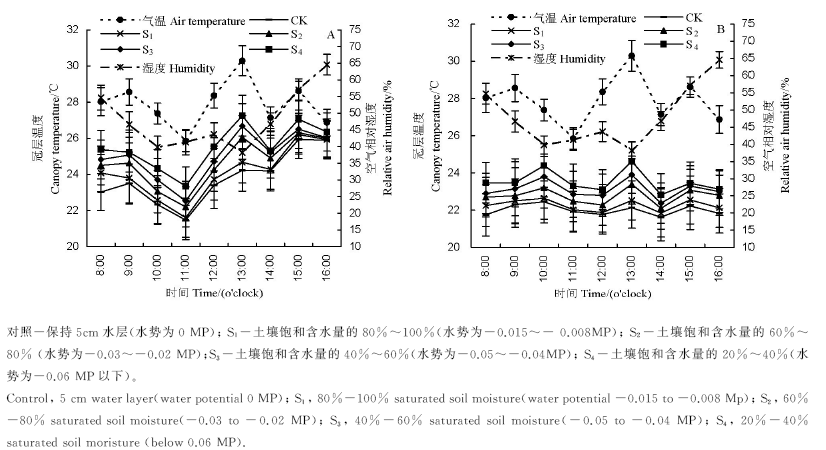
图1 不同水分胁迫条件下辽粳294(A)和开粳1号(B)冠层温度、气温和空气相对湿度的日变化特征
Fig. 1. Diurnal variation of canopy temperature,air temperature,relative air humidity for Liaojing 294(A) and Kaijing 1(B) under different water stress conditions.
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 时间 Time/(o’clock) | 平均 Average | 差值 Difference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:00 | 9:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | |||
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||||||
| 对照CK | -5.0±1.6 | -5.1±1.4 | -5.1±1.5 | -4.4±1.8 | -5.0±2.4 | -6.1±2.9 | -2.9±1.2 | -2.7±1.3 | -1.0±0.7 | -4.1±1.5 | 0.0 |
| S1 | -4.0±1.7 | -4.8±1.5 | -4.8±1.3 | -4.3±1.7 | -4.6±2.6 | -5.6±2.6 | -2.9±1.3 | -2.4±1.5 | -0.9±0.6 | -3.8±1.4 | 0.3 |
| S2 | -3.5±1.4 | -3.9±1.5 | -4.3±1.6 | -3.7±1.6 | -4.1±2.3 | -4.2±2.8 | -2.2±1.1 | -2.3±1.1 | -0.9±0.6 | -3.2±1.1 | 0.9 |
| S3 | -3.2±1.1 | -3.5±1.3 | -3.7±1.1 | -3.3±1.2 | -3.6±2.4 | -3.6±2.7 | -1.9±1.0 | -2.1±1.0 | -0.8±0.4 | -2.9±1.0 | 1.2 |
| S4 | -2.7±0.9 | -3.3±1.1 | -3.1±1.4 | -2.5±1.0 | -2.8±2.6 | -3.0±2.5 | -1.8±0.8 | -1.6±0.7 | -0.5±0.3 | -2.4±0.9 | 1.7 |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||||||
| 对照CK | -6.3±1.2 | -6.3±1.5 | -4.9±1.4 | -3.9±1.9 | -6.6±2.3 | -8.2±2.7 | -5.5±1.7 | -6.4±2.2 | -5.0±1.5 | -5.9±1.2 | 0.0 |
| S1 | -5.8±1.5 | -6.1±1.6 | -4.7±1.3 | -3.8±1.8 | -6.5±2.1 | -7.8±2.9 | -5.3±1.8 | -6.1±2.3 | -4.7±1.3 | -5.6±1.1 | 0.3 |
| S2 | -5.3±1.5 | -5.8±1.4 | -4.2±1.3 | -3.4±1.8 | -6.1±2.3 | -6.9±2.5 | -5.0±1.5 | -5.5±2.1 | -4.1±1.5 | -5.1±1.1 | 0.8 |
| S3 | -5.1±1.2 | -5.4±1.4 | -3.6±1.5 | -3.0±1.7 | -5.6±1.9 | -6.4±2.7 | -4.8±1.5 | -5.3±2.0 | -3.9±1.4 | -4.8±1.1 | 1.1 |
| S4 | -4.6±1.3 | -5.1±1.5 | -3.0±1.6 | -2.6±1.8 | -5.3±2.1 | -5.7±3.2 | -4.3±1.7 | -5.2±1.9 | -3.7±1.4 | -4.4±1.0 | 1.5 |
表1 水分胁迫对不同抗旱品种冠气温度差的影响
Table 1 Effect of water stress on canopy-air temperature difference of varieties with different drought resistance.℃
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 时间 Time/(o’clock) | 平均 Average | 差值 Difference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:00 | 9:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | |||
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||||||
| 对照CK | -5.0±1.6 | -5.1±1.4 | -5.1±1.5 | -4.4±1.8 | -5.0±2.4 | -6.1±2.9 | -2.9±1.2 | -2.7±1.3 | -1.0±0.7 | -4.1±1.5 | 0.0 |
| S1 | -4.0±1.7 | -4.8±1.5 | -4.8±1.3 | -4.3±1.7 | -4.6±2.6 | -5.6±2.6 | -2.9±1.3 | -2.4±1.5 | -0.9±0.6 | -3.8±1.4 | 0.3 |
| S2 | -3.5±1.4 | -3.9±1.5 | -4.3±1.6 | -3.7±1.6 | -4.1±2.3 | -4.2±2.8 | -2.2±1.1 | -2.3±1.1 | -0.9±0.6 | -3.2±1.1 | 0.9 |
| S3 | -3.2±1.1 | -3.5±1.3 | -3.7±1.1 | -3.3±1.2 | -3.6±2.4 | -3.6±2.7 | -1.9±1.0 | -2.1±1.0 | -0.8±0.4 | -2.9±1.0 | 1.2 |
| S4 | -2.7±0.9 | -3.3±1.1 | -3.1±1.4 | -2.5±1.0 | -2.8±2.6 | -3.0±2.5 | -1.8±0.8 | -1.6±0.7 | -0.5±0.3 | -2.4±0.9 | 1.7 |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||||||
| 对照CK | -6.3±1.2 | -6.3±1.5 | -4.9±1.4 | -3.9±1.9 | -6.6±2.3 | -8.2±2.7 | -5.5±1.7 | -6.4±2.2 | -5.0±1.5 | -5.9±1.2 | 0.0 |
| S1 | -5.8±1.5 | -6.1±1.6 | -4.7±1.3 | -3.8±1.8 | -6.5±2.1 | -7.8±2.9 | -5.3±1.8 | -6.1±2.3 | -4.7±1.3 | -5.6±1.1 | 0.3 |
| S2 | -5.3±1.5 | -5.8±1.4 | -4.2±1.3 | -3.4±1.8 | -6.1±2.3 | -6.9±2.5 | -5.0±1.5 | -5.5±2.1 | -4.1±1.5 | -5.1±1.1 | 0.8 |
| S3 | -5.1±1.2 | -5.4±1.4 | -3.6±1.5 | -3.0±1.7 | -5.6±1.9 | -6.4±2.7 | -4.8±1.5 | -5.3±2.0 | -3.9±1.4 | -4.8±1.1 | 1.1 |
| S4 | -4.6±1.3 | -5.1±1.5 | -3.0±1.6 | -2.6±1.8 | -5.3±2.1 | -5.7±3.2 | -4.3±1.7 | -5.2±1.9 | -3.7±1.4 | -4.4±1.0 | 1.5 |
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 每穗实粒数 FGP | 每穗秕粒数 UGP | 千粒重 TGW /g | 结实率 SSR /% | 理论产量 TY /(kg·667m-2) | 实测产量 AY /(kg·667m-2) | 实测增产率 AYGR /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 73.7±5.31 aA | 18.7±1.05 cC | 24.8±0.15 aA | 79.8±0.03 aA | 472.3±28.3 aA | 486.19 | - |
| S1 | 73.4±1.99 aA | 17.6±0.58 cC | 23.7±0.22 bcB | 80.6±0.01 aA | 453.3±14.0 aA | 494.63 | +1.74 |
| S2 | 76.1±4.53 aA | 18.8±1.36 cC | 23.9±0.21 bAB | 80.2±0.04 aA | 469.3±20.9 aAB | 494.19 | +1.65 |
| S3 | 66.2±3.34 bAB | 28.6±3.14 bB | 23.1±0.19 cB | 69.9±0.03 bB | 394.1±27.1 bB | 442.28 | -9.03 |
| S4 | 57.6±2.16 cB | 37.4±3.60 aA | 23.3±0.17 cB | 60.3±0.02 cC | 326.96±17.8 cC | 387.81 | -20.24 |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 70.7±2.89 abA | 16.8±0.01 cC | 27.4±0.13 aA | 80.7±0.01 aA | 556.6±15.3 aA | 518.06 | - |
| S1 | 76.2±0.63 aA | 18.3±0.0.1 cC | 26.8±0.13 bcAB | 80.5±0.01 aA | 559.3±28.8 aA | 536.75 | +3.61 |
| S2 | 68.7±7.62 bA | 17.4±0.02 cC | 26.9±0.13 abAB | 79.9±0.02 aA | 528.6±32.3 aA | 528.77 | +2.07 |
| S3 | 57.4±2.23 cB | 23.5±0.01 bB | 26.7±0.14 bcAB | 70.9±0.01 bB | 436.5±34.3 bB | 479.00 | -7.54 |
| S4 | 51.1±5.29 cB | 36.5±0.03 aA | 26.3±0.14 cB | 58.1±0.03 cC | 376.3±15.8 cB | 418.56 | -19.21 |
表2 水分胁迫对不同抗旱品种产量结构的影响
Table 2 Effect of water stress on yield components of different drought resistance varieties.
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 每穗实粒数 FGP | 每穗秕粒数 UGP | 千粒重 TGW /g | 结实率 SSR /% | 理论产量 TY /(kg·667m-2) | 实测产量 AY /(kg·667m-2) | 实测增产率 AYGR /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 73.7±5.31 aA | 18.7±1.05 cC | 24.8±0.15 aA | 79.8±0.03 aA | 472.3±28.3 aA | 486.19 | - |
| S1 | 73.4±1.99 aA | 17.6±0.58 cC | 23.7±0.22 bcB | 80.6±0.01 aA | 453.3±14.0 aA | 494.63 | +1.74 |
| S2 | 76.1±4.53 aA | 18.8±1.36 cC | 23.9±0.21 bAB | 80.2±0.04 aA | 469.3±20.9 aAB | 494.19 | +1.65 |
| S3 | 66.2±3.34 bAB | 28.6±3.14 bB | 23.1±0.19 cB | 69.9±0.03 bB | 394.1±27.1 bB | 442.28 | -9.03 |
| S4 | 57.6±2.16 cB | 37.4±3.60 aA | 23.3±0.17 cB | 60.3±0.02 cC | 326.96±17.8 cC | 387.81 | -20.24 |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 70.7±2.89 abA | 16.8±0.01 cC | 27.4±0.13 aA | 80.7±0.01 aA | 556.6±15.3 aA | 518.06 | - |
| S1 | 76.2±0.63 aA | 18.3±0.0.1 cC | 26.8±0.13 bcAB | 80.5±0.01 aA | 559.3±28.8 aA | 536.75 | +3.61 |
| S2 | 68.7±7.62 bA | 17.4±0.02 cC | 26.9±0.13 abAB | 79.9±0.02 aA | 528.6±32.3 aA | 528.77 | +2.07 |
| S3 | 57.4±2.23 cB | 23.5±0.01 bB | 26.7±0.14 bcAB | 70.9±0.01 bB | 436.5±34.3 bB | 479.00 | -7.54 |
| S4 | 51.1±5.29 cB | 36.5±0.03 aA | 26.3±0.14 cB | 58.1±0.03 cC | 376.3±15.8 cB | 418.56 | -19.21 |
| 相关因子 Correlation factor | 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 开粳1号Kaijing 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 | 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 | ||
| 产量 TY | y= -78.196x +166.54 | 0.7801* | y = -124.23x - 150.2 | 0.8998* | |
| 实粒数FGP | y = -8.8358x+40.355 | 0.6833* | y = -15.108x - 13.214 | 0.8371* | |
| 秕粒数UGP | y = 10.958x +60.191 | 0.8041* | y = 11.389x +81.319 | 0.7331* | |
| 千粒重TGW | y = -0.7716x +21.207 | 0.6689* | y = -0.5363x +24.047 | 0.7710* | |
| 结实率SSR | y = -11.24x +37.29 | 0.7830* | y = -14.02x +1.59 | 0.7935* | |
| 糙米率BR | y = -0.5213x+79.043 | 0.9873** | y = -0.408x +78.847 | 0.5235 | |
| 精米率MR | y = -0.723x +71.657 | 0.8426* | y = -0.3668x+71.835 | 0.5113 | |
| 整精米率HR | y = -7.7346x +35.767 | 0.8297* | y = -3.1471x +54.985 | 0.7960* | |
| 碎米率BRR | y = 1.0368x+14.29 | 0.6265 | y = 1.5927x +14.74 | 0.9640** | |
| 长宽比LWR | y = 0.0063x+1.5951 | 0.0477 | y = 0.0127x +1.5762 | 0.5485 | |
| 垩白度C | y = 1.1694x+5.8116 | 0.9204** | y = 0.8064x +8.7585 | 0.9457** | |
| 垩白粒率CR | y = 2.2246x+10.902 | 0.8607* | y = 0.9724x +13.216 | 0.7139* | |
| 蛋白质含量PC | y = -0.3563x+7.264 | 0.7126* | y = 0.2855x+10.008 | 0.9452** | |
| 直链淀粉含量AC | y = -0.6927x +17.326 | 0.9848** | y = -0.5704x +16.607 | 0.9370** | |
| 脂肪酸含量 FA | y = -3.1777x +1.9234 | 0.8865** | y = -3.3232x - 4.6111 | 0.9281** | |
| 食味值Score | y = -1.7435x +66.644 | 0.9155** | y = -2.5037x +56.242 | 0.8692** | |
表3 水分胁迫下水稻冠气温度差与产量因素、碾米、外观及食味品质的相关关系
Table 3 Relationship between canopy-air temperature difference and yield components,appearance ,eating quality of rice under different water stresses.
| 相关因子 Correlation factor | 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 开粳1号Kaijing 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 | 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 | ||
| 产量 TY | y= -78.196x +166.54 | 0.7801* | y = -124.23x - 150.2 | 0.8998* | |
| 实粒数FGP | y = -8.8358x+40.355 | 0.6833* | y = -15.108x - 13.214 | 0.8371* | |
| 秕粒数UGP | y = 10.958x +60.191 | 0.8041* | y = 11.389x +81.319 | 0.7331* | |
| 千粒重TGW | y = -0.7716x +21.207 | 0.6689* | y = -0.5363x +24.047 | 0.7710* | |
| 结实率SSR | y = -11.24x +37.29 | 0.7830* | y = -14.02x +1.59 | 0.7935* | |
| 糙米率BR | y = -0.5213x+79.043 | 0.9873** | y = -0.408x +78.847 | 0.5235 | |
| 精米率MR | y = -0.723x +71.657 | 0.8426* | y = -0.3668x+71.835 | 0.5113 | |
| 整精米率HR | y = -7.7346x +35.767 | 0.8297* | y = -3.1471x +54.985 | 0.7960* | |
| 碎米率BRR | y = 1.0368x+14.29 | 0.6265 | y = 1.5927x +14.74 | 0.9640** | |
| 长宽比LWR | y = 0.0063x+1.5951 | 0.0477 | y = 0.0127x +1.5762 | 0.5485 | |
| 垩白度C | y = 1.1694x+5.8116 | 0.9204** | y = 0.8064x +8.7585 | 0.9457** | |
| 垩白粒率CR | y = 2.2246x+10.902 | 0.8607* | y = 0.9724x +13.216 | 0.7139* | |
| 蛋白质含量PC | y = -0.3563x+7.264 | 0.7126* | y = 0.2855x+10.008 | 0.9452** | |
| 直链淀粉含量AC | y = -0.6927x +17.326 | 0.9848** | y = -0.5704x +16.607 | 0.9370** | |
| 脂肪酸含量 FA | y = -3.1777x +1.9234 | 0.8865** | y = -3.3232x - 4.6111 | 0.9281** | |
| 食味值Score | y = -1.7435x +66.644 | 0.9155** | y = -2.5037x +56.242 | 0.8692** | |
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 糙米率 BR/% | 精米率 MR/% | 整精米率 HR/% | 碎米率 BRR/% | 长宽比 LWR | 垩白度 C/% | 垩白粒率 CR/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 81.23±0.27 aA | 74.86±0.17 aA | 67.03±4.36 aA | 10.07±0.29 bA | 1.57±0.03 aA | 1.10±0.20 cB | 1.63±0.25 cB |
| S1 | 81.01±0.50 abAB | 74.15±0.90 abA | 63.67±5.45 aAB | 10.87±1.21 abA | 1.57±0.03 aA | 1.37±0.25 cAB | 2.90±0.61 bB |
| S2 | 80.67±0.60 bcAB | 74.12±1.07 abA | 62.90±2.27 aAB | 10.03±0.61 bA | 1.60±0.02 aA | 1.63±0.42 bcAB | 2.73±0.85 bB |
| S3 | 80.55±0.34 bcAB | 73.52±0.50 bA | 60.97±1.63 aAB | 11.20±0.50 abA | 1.55±0.07 aA | 2.73±0.43 abAB | 5.20±0.44 aA |
| S4 | 80.31±0.32 cB | 73.51±0.19 bA | 51.20±5.74 bB | 12.27±0.65 aA | 1.59±0.01 aA | 3.03±0.51 aA | 5.53±0.15 aA |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 81.08±0.34 abA | 73.89±0.36 aA | 73.13±1.66 aA | 5.27±0.32 cC | 1.49±0.02 aA | 3.90±0.35 cB | 7.53±0.40 cB |
| S1 | 81.48±0.15 aA | 74.13±0.49 aA | 72.17±4.15 aA | 5.77±0.23 cBC | 1.52±0.03 aA | 4.37±0.12 bcAB | 8.03±0.06 bB |
| S2 | 80.67±0.26 bA | 73.44±0.17 aA | 72.60±0.80 aA | 6.53±0.25 bB | 1.51±0.01 aA | 4.63±0.71 abAB | 7.83±0.25 bcB |
| S3 | 80.92±0.31 abA | 73.81±0.42 aA | 70.60±1.25 abA | 7.43±0.31 aA | 1.52±0.03 aA | 4.77±0.15 abAB | 8.17±0.12 bB |
| S4 | 80.61±0.52 bA | 73.37±0.82 aA | 67.70±1.47 bA | 7.57±0.35 aA | 1.52±0.03 aA | 5.30±0.10 aB | 9.40±0.10 aA |
表4 水分胁迫对不同抗旱品种碾米及外观品质的影响
Table 4 Effect of water stress on rice milling and appearance quality of different drought resistance varieties.
| 品种与处理 Variety and treatment | 糙米率 BR/% | 精米率 MR/% | 整精米率 HR/% | 碎米率 BRR/% | 长宽比 LWR | 垩白度 C/% | 垩白粒率 CR/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 81.23±0.27 aA | 74.86±0.17 aA | 67.03±4.36 aA | 10.07±0.29 bA | 1.57±0.03 aA | 1.10±0.20 cB | 1.63±0.25 cB |
| S1 | 81.01±0.50 abAB | 74.15±0.90 abA | 63.67±5.45 aAB | 10.87±1.21 abA | 1.57±0.03 aA | 1.37±0.25 cAB | 2.90±0.61 bB |
| S2 | 80.67±0.60 bcAB | 74.12±1.07 abA | 62.90±2.27 aAB | 10.03±0.61 bA | 1.60±0.02 aA | 1.63±0.42 bcAB | 2.73±0.85 bB |
| S3 | 80.55±0.34 bcAB | 73.52±0.50 bA | 60.97±1.63 aAB | 11.20±0.50 abA | 1.55±0.07 aA | 2.73±0.43 abAB | 5.20±0.44 aA |
| S4 | 80.31±0.32 cB | 73.51±0.19 bA | 51.20±5.74 bB | 12.27±0.65 aA | 1.59±0.01 aA | 3.03±0.51 aA | 5.53±0.15 aA |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | |||||||
| 对照CK | 81.08±0.34 abA | 73.89±0.36 aA | 73.13±1.66 aA | 5.27±0.32 cC | 1.49±0.02 aA | 3.90±0.35 cB | 7.53±0.40 cB |
| S1 | 81.48±0.15 aA | 74.13±0.49 aA | 72.17±4.15 aA | 5.77±0.23 cBC | 1.52±0.03 aA | 4.37±0.12 bcAB | 8.03±0.06 bB |
| S2 | 80.67±0.26 bA | 73.44±0.17 aA | 72.60±0.80 aA | 6.53±0.25 bB | 1.51±0.01 aA | 4.63±0.71 abAB | 7.83±0.25 bcB |
| S3 | 80.92±0.31 abA | 73.81±0.42 aA | 70.60±1.25 abA | 7.43±0.31 aA | 1.52±0.03 aA | 4.77±0.15 abAB | 8.17±0.12 bB |
| S4 | 80.61±0.52 bA | 73.37±0.82 aA | 67.70±1.47 bA | 7.57±0.35 aA | 1.52±0.03 aA | 5.30±0.10 aB | 9.40±0.10 aA |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 蛋白质含量 PC/% | 直链淀粉含量 AC/% | 脂肪酸含量 FFA/% | 食味值 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 对照CK | 8.63±0.12 aAB | 20.20±0.26 aA | 14.43±0.61 aA | 73.47±1.14 aA |
| S1 | 8.60±0.30 aAB | 19.90±0.70 abA | 14.13±1.53 aA | 73.37±1.27 aA | |
| S2 | 8.70±0.00 aA | 19.67±0.21 abcA | 13.57±0.55 aA | 72.80±0.60 aAB | |
| S3 | 8.20±0.10 bBC | 19.27±0.21 bcA | 10.43±1.00 bB | 71.80±0.26 abAB | |
| S4 | 8.03±0.06 bC | 18.97±0.49 cA | 9.20±0.36 bB | 70.40±0.69 bB | |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | 对照CK | 8.30±0.00 cA | 20.03±0.40 aA | 14.43±0.86 aA | 71.80±1.85 aA |
| S1 | 8.43±0.12 bcA | 19.70±0.46 aAB | 14.27±1.86 aA | 69.67±0.06 bAB | |
| S2 | 8.50±0.20 abcA | 19.57±0.45 abAB | 13.13±0.23 abAB | 68.60±0.10 bcB | |
| S3 | 8.70±0.20 abA | 19.43±0.06 abAB | 11.67±0.82 bB | 68.37±0.47 bcB | |
| S4 | 8.73±0.06 aA | 19.03±0.06 bB | 9.27±0.23 cC | 67.43±0.55cB |
表5 水分胁迫对不同抗旱品种食味品质的影响
Table 5 Effect of water stress on eating quality of different drought resistance varieties.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 蛋白质含量 PC/% | 直链淀粉含量 AC/% | 脂肪酸含量 FFA/% | 食味值 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 对照CK | 8.63±0.12 aAB | 20.20±0.26 aA | 14.43±0.61 aA | 73.47±1.14 aA |
| S1 | 8.60±0.30 aAB | 19.90±0.70 abA | 14.13±1.53 aA | 73.37±1.27 aA | |
| S2 | 8.70±0.00 aA | 19.67±0.21 abcA | 13.57±0.55 aA | 72.80±0.60 aAB | |
| S3 | 8.20±0.10 bBC | 19.27±0.21 bcA | 10.43±1.00 bB | 71.80±0.26 abAB | |
| S4 | 8.03±0.06 bC | 18.97±0.49 cA | 9.20±0.36 bB | 70.40±0.69 bB | |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | 对照CK | 8.30±0.00 cA | 20.03±0.40 aA | 14.43±0.86 aA | 71.80±1.85 aA |
| S1 | 8.43±0.12 bcA | 19.70±0.46 aAB | 14.27±1.86 aA | 69.67±0.06 bAB | |
| S2 | 8.50±0.20 abcA | 19.57±0.45 abAB | 13.13±0.23 abAB | 68.60±0.10 bcB | |
| S3 | 8.70±0.20 abA | 19.43±0.06 abAB | 11.67±0.82 bB | 68.37±0.47 bcB | |
| S4 | 8.73±0.06 aA | 19.03±0.06 bB | 9.27±0.23 cC | 67.43±0.55cB |
| 品种 Variety | 气孔长度 Stomatal length/μm | 气孔宽度 Stomatal width/μm | 气孔密度 Stomatal density/mm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 28.4±1.87 aA | 14.9±1.43 aA | 322.6±6.69 bA |
| 开粳1号Kaijing 1 | 23.9±2.86 bB | 11.1±1.38 bB | 375.5±4.32 aA |
表6 不同抗旱性水稻品种剑叶气孔性状比较
Table 6 The flag leaf stomatal characteristics of rice with various drought tolerance.
| 品种 Variety | 气孔长度 Stomatal length/μm | 气孔宽度 Stomatal width/μm | 气孔密度 Stomatal density/mm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 28.4±1.87 aA | 14.9±1.43 aA | 322.6±6.69 bA |
| 开粳1号Kaijing 1 | 23.9±2.86 bB | 11.1±1.38 bB | 375.5±4.32 aA |
| 品种 Variety | 相关因子 Correlation factor | 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 光合速率 Pn | y = -4.7236x +6.146 | 0.9114** |
| 气孔导度 Gs | y = -0.1155x - 0.1198 | 0.8177* | |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci | y = -60.399x+22.581 | 0.6929* | |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | y = -1.4349x+0.4392 | 0.7947* | |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | 光合速率 Pn | y = -5.4643x - 4.8945 | 0.9523** |
| 气孔导度 Gs | y = -0.1734x - 0.551 | 0.8396* | |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci | y = -58.873x - 39.633 | 0.7408* | |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | y = -1.6623x - 3.0062 | 0.9106** |
表7 水分胁迫下水稻冠气温度差与光合指标的相关关系
Table 7 Relationship between anopy-air temperature difference and photosynthetic indexes of rice under water stress.
| 品种 Variety | 相关因子 Correlation factor | 回归方程 Regression equation | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 辽粳294 Liaojing 294 | 光合速率 Pn | y = -4.7236x +6.146 | 0.9114** |
| 气孔导度 Gs | y = -0.1155x - 0.1198 | 0.8177* | |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci | y = -60.399x+22.581 | 0.6929* | |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | y = -1.4349x+0.4392 | 0.7947* | |
| 开粳1号 Kaijing 1 | 光合速率 Pn | y = -5.4643x - 4.8945 | 0.9523** |
| 气孔导度 Gs | y = -0.1734x - 0.551 | 0.8396* | |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci | y = -58.873x - 39.633 | 0.7408* | |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | y = -1.6623x - 3.0062 | 0.9106** |
| [1] | González-Dugo M P, Moran M S, Mateos L, et al. Canopy temperature variability as an indicator of crop water stress severity.Irrig Sci, 2006, 24: 233-240. |
| [2] | Mahn J R, Young A W, Payton P.Deficit irrigation in a production setting: Canopy temperature as an adjunct to ET estimates.Irrig Sci, 2012, 30: 127-137. |
| [3] | Tumer N C, O'Toole J C, Cruz R T, et al. Response of seven diverse rice cultivars to water deficits: Ⅰ.Stress development, canopy temperature, leaf rolling and growth.Fileld Crops Res, 1986, 13: 257-271. |
| [4] | Balota M, Payne W A, Evett S R, et al.Canopy temperature depression sampling to assess grain yield variation and genotypicdifferentiation in winter wheat.Crop Sci,2007, 47: 1518-1529. |
| [5] | Feng B L, Yu H, Hu Y G, et al.The physiological characteristics of the low canopy temperature wheat genotypes under simulated drought condition.Acta Physiol Plant, 2009, 31: 1229-1235. |
| [6] | 张嵩午, 王长发. 小麦低温基因型的研究现状和未来发展. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(9): 2573-2580. |
| [7] | Jackson R D, Idso S B, Reginato R J.Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator.Water Resce Res, 1981, 17: 1133-1138. |
| [8] | Idso S B, Jackson R D, Pinter P J J, et al. Normalizing the stress degree day for environmental variability.Agric Meteorol, 1981, 24: 45-55. |
| [9] | 杨建昌, 王维, 王志琴, 等.水稻旱秧大田期需水特性与节水灌溉指标研究. 中国农业科学, 2000, 33(2): 34-42. |
| [10] | 陶龙兴, 王熹, 黄效林, 等. 水稻灌浆期间土壤含水量对根系生理活性的影响. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(11): 1616-1620. |
| [11] | 蔡焕杰, 康绍忠. 棉花冠层温度的变化规律及其用于缺水诊断研究. 灌溉排水, 1997, 16(1): 1-5. |
| [12] | 程旺大, 姚海根, 赵国平, 等. 冠层温度在作物水分状况探测中的应用. 中国农学通报, 2000, 16(5): 42-44. |
| [13] | 梁银丽, 张成娥. 冠层温度-气温差与作物水分亏缺关系的研究. 生态农业研究, 2000, 8(1): 24-26. |
| [14] | 袁国富, 罗毅, 孙晓敏, 等. 作物冠层表面温度诊断冬小麦水分胁迫的试验研究. 农业工程学报, 2002, 18(6): 13-17. |
| [15] | 王纯枝, 宇振荣, 孙丹峰, 等. 夏玉米冠气温差及其影响因素探析. 土壤通报, 2006, 37(4): 651-657. |
| [16] | Patel N R, Mehta A N, Shekh A M.Canopy temperature and water stress quantification in rainfed pigeonpea.Agric Forest Meteorol, 2001, 109(3): 223-232. |
| [17] | 张文忠, 韩亚东, 杜宏娟, 等. 水稻开花期冠层温度与土壤水分及产量结构的关系. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(1): 99-102. |
| [18] | 韩亚东, 张文忠, 杨梅, 等. 孕穗期水稻叶温与水分状况关系的研究. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(2): 214-216. |
| [19] | 高继平, 韩亚东, 王晓通, 等. 水稻齐穗期冠层温度分异及其相关特性的研究. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2011, 42(4): 399-405. |
| [20] | 陈佳, 张文忠, 赵晓彤, 等. 水稻灌浆期冠气温差与土壤水分及气象因子关系初探. 江苏农业科学, 2009(2): 284-285. |
| [21] | 赵晓彤, 韩亚东, 高继平, 等. 水稻穗分化期不同土壤水势叶温及生理性状变化. 湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(1): 33-36. |
| [22] | 高明超. 水稻冠层温度特性及基于冠层温度的水分胁迫指数研究. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2013. |
| [23] | 刘云鹏, 申思, 潘余强, 等. 干旱胁迫下玉米叶-气温差与叶温差日变化特征及其品种差异. 中国农业大学学报, 2014, 19(5): 13-21. |
| [24] | 刘婵, 范兴科. 基于冠层叶-气温差的温室土壤水分诊断. 干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(1): 90-93. |
| [25] | 樊廷录, 宋尚有, 徐银萍, 等. 旱地冬小麦灌浆期冠层温度与产量和水分利用效率的关系. 生态学报, 2007, 27(11): 4491-4497. |
| [26] | 彭致功, 杨培岭, 段爱旺, 等. 日光温室茄子冠气温差与环境因子之间的关系研究. 华中农学报, 2003, 18(4): 111-113. |
| [27] | 冯佰利, 王长发, 苗芳, 等. 抗旱小麦的冷温特性研究. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 30(2): 6-10. |
| [28] | 周春菊, 张嵩午, 王林权, 等. 施肥对小麦冠层温度的影响及其与生物学性状的关联. 生态学报, 2005, 25(1): 18-22. |
| [29] | 刘亚, 丁俊强, 苏巴钱德, 等. 基于远红外热成像的叶温变化与玉米苗期耐旱性的研究. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(6): 2192-2201. |
| [30] | 胡单, 王长发. 大麦冠层温度及其与光合性能的关联. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(2): 62-67. |
| [31] | 赵刚, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 等. 不同品种冬小麦冠层温度与抗旱性和水分利用效率的关系研究. 农业现代化研究, 2010, 31(3): 334-337. |
| [32] | Liu Y, Subhash C, Yan J, et al.Maize leaf temperature responses to dought: Thermal imaging and quantitative traitloci(QTL)mapping.Environ Exp Bot, 2011, 71(2): 158-165. |
| [33] | 李向阳, 朱云集, 郭天财. 不同小麦基因型灌浆期冠层和叶面温度与产量和品质关系的初步分析. 麦类作物学报, 2004, 24(2): 88-91. |
| [34] | 董朋飞, 张绍芬, 刘天学, 等. 玉米灌浆期间气冠温差与产量的关系. 河南农业大学学报, 2007, 41(5): 487-491. |
| [35] | 彭世彰, 徐俊增, 丁加丽, 等. 节水灌溉条件下水稻叶气温差变化规律与水分亏缺诊断试验研究. 水利学报, 2006, 37(12): 1503-1508. |
| [36] | 张喜英, 裴冬, 陈素英. 用冠气温差指导冬小麦灌溉的指标研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2002, 10(2): 102-105. |
| [37] | 刘凯, 张耗, 张慎凤, 等. 结实期土壤水分和灌溉方式对水稻产量与品质的影响及其生理原因. 作物学报, 2008, 34(2): 268-276. |
| [38] | 董明辉, 谢裕林, 刘晓斌, 等. 结实期土壤水势对水稻籽粒品质及其粒间差异的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(2): 305-311. |
| [39] | 郑桂萍, 李金峰, 钱永德, 等. 土壤水分对水稻产量与品质的影响. 作物学报, 2006, 32(8): 1261-1264. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||