
中国水稻科学 ›› 2026, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 95-105.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2026.241110
廖政明1,#, 郭梁2,3,#, 潘孝武2,3, 黎用朝2, 董铮2,3, 李小湘2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-18
修回日期:2025-01-06
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-21
通讯作者:
*email: xiaoxiang66196@126.com作者简介:第一联系人:共同第一作者
基金资助:
LIAO Zhengming1,#, GUO Liang2,3,#, PAN Xiaowu2,3, LI Yongchao2, DONG Zheng2,3, LI Xiaoxiang2,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-18
Revised:2025-01-06
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-21
About author:First author contact:These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】水稻种子耐储性对种质资源保护、粮食安全和可持续发展具有重要意义。本研究旨在挖掘控制水稻种子耐储性的QTL,并探索不同老化方式下耐储性的遗传基础。【方法】以籼稻93-11为背景的131个尼瓦拉野生稻渗入系为材料,分别采用自然老化和人工老化处理,测定发芽率进行QTL定位。通过转录组测序比较携带qASS1.1/qNSS1.1野生稻等位基因的耐储材料Ra32与不携带增效等位基因的不耐储材料Ra146,筛选差异表达基因(Differentially expressed genes, DEGs),并通过GO和KEGG分析挖掘候选基因。【结果】共检测到6个耐储性QTL,分布在1、3、6、7、9号染色体上,每个QTL可解释3.3%~21.0%的表型变异。其中,主效QTL qASS1.1/qNSS1.1在两种老化处理中均稳定检测到,且野生稻等位基因显著提高种子耐储性。转录组分析共鉴定出人工老化下2077个DEG、自然老化下1468个DEG,两种处理下共有733个DEG。GO富集和KEGG代谢途径分析显示,人工老化下DEG可富集到1428个GO条目和97个代谢途径;自然老化下分别为1199个条目和85个代谢途径。在最显著富集的10个生物学过程和30个代谢途径中,昼夜节律调控翻译和过氧化氢分解过程等生物学过程以及MAPK信号传导通路、细胞分裂素生物合成、组氨酸代谢、抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢等代谢是两种老化处理共有的富集通路,表明种子耐储性可能受抗氧化系统调控、能量代谢及种子储藏物质积累等机制影响。基于这些富集通路,经RT-qPCR验证,初步筛选到主效QTL qASS1.1/qNSS1.1的5个候选基因,包括Os01g0842400与Os01g0842500(编码漆酶前体蛋白)、Os01g0847800(编码醛酮还原酶家族蛋白)、Os01g0855900(编码CDC6-DNA复制起始蛋白)和Os01g0860400(编码糖基水解酶)。【结论】本研究挖掘到耐储性QTL并筛选出多个候选基因,揭示了不同老化处理下水稻种子主要通过调节抗氧化防御、维持细胞稳定性和代谢过程来提高其耐储性,为水稻耐储性改良提供了新的基因资源和理论支持。
廖政明, 郭梁, 潘孝武, 黎用朝, 董铮, 李小湘. 水稻种子耐储性基因的挖掘及不同老化方式的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 95-105.
LIAO Zhengming, GUO Liang, PAN Xiaowu, LI Yongchao, DONG Zheng, LI Xiaoxiang. Identification of Genes for Rice Seed Storability and Transcriptome Analysis Under Different Aging Conditions[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 95-105.
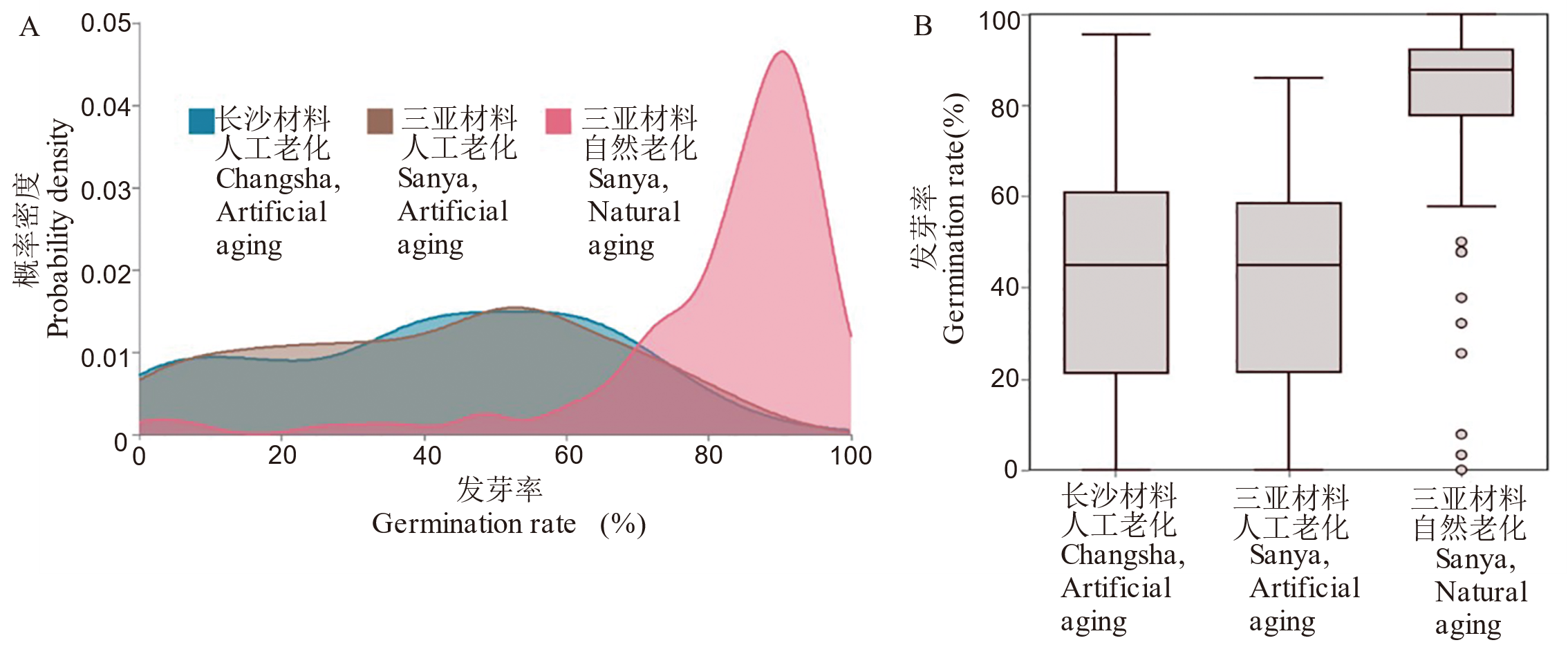
图2 不同老化方式与材料来源下种子发芽率的分布特征与统计概况 A:发芽率的核密度估计曲线;B:发芽率箱线图。
Fig. 2. Distribution and summary statistics of seed germination rate from different origins under different aging treatments A, Kernel density estimation (KDE) curves of germination rates; B, Boxplots of germination rate.
| 染色体 Chr | QTL | 处理 Treatment | 标记区间 Marker region | 物理区间 Interval (Mb) | LOD | R2 (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | 前人研究 Previous study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | qASS1.1 | 人工老化(三亚) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 7.28 | 19.0 | 0.13 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qASS1.1 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 11.60 | 15.5 | 0.16 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qASS1.2 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin154-Bin160 | 38.73-40.29 | 3.90 | 4.5 | −0.09 | |
| 1 | qNSS1.1 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 19.04 | 21.0 | 0.13 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qNSS1.2 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin154-Bin160 | 38.73-40.29 | 7.19 | 5.8 | −0.08 | |
| 3 | qASS3 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin333-Bin340 | 50.15-67.74 | 3.00 | 3.3 | 0.12 | |
| 6 | qNSS6 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin580-Bin612 | 1.56-13.19 | 9.76 | 9.2 | 0.40 | qSS-6[ |
| 7 | qNSS7 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin662-Bin669 | 6.16-17.35 | 8.40 | 8.1 | 0.15 | qSS7.1[ |
| 9 | qASS9 | 人工老化(三亚) | Bin813-Bin819 | 8.04-10.05 | 6.96 | 17.7 | 0.16 | qRC9-2[ |
表1 利用IL群体在人工或自然老化处理后检测到的耐储性QTL
Table 1. Identified QTLs for seed storability under natural or artificial aging treatments in an IL population
| 染色体 Chr | QTL | 处理 Treatment | 标记区间 Marker region | 物理区间 Interval (Mb) | LOD | R2 (%) | 加性效应 Additive effect | 前人研究 Previous study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | qASS1.1 | 人工老化(三亚) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 7.28 | 19.0 | 0.13 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qASS1.1 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 11.60 | 15.5 | 0.16 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qASS1.2 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin154-Bin160 | 38.73-40.29 | 3.90 | 4.5 | −0.09 | |
| 1 | qNSS1.1 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin147-Bin152 | 37.73-38.68 | 19.04 | 21.0 | 0.13 | qSS1.1[ |
| 1 | qNSS1.2 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin154-Bin160 | 38.73-40.29 | 7.19 | 5.8 | −0.08 | |
| 3 | qASS3 | 人工老化(长沙) | Bin333-Bin340 | 50.15-67.74 | 3.00 | 3.3 | 0.12 | |
| 6 | qNSS6 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin580-Bin612 | 1.56-13.19 | 9.76 | 9.2 | 0.40 | qSS-6[ |
| 7 | qNSS7 | 自然老化(三亚) | Bin662-Bin669 | 6.16-17.35 | 8.40 | 8.1 | 0.15 | qSS7.1[ |
| 9 | qASS9 | 人工老化(三亚) | Bin813-Bin819 | 8.04-10.05 | 6.96 | 17.7 | 0.16 | qRC9-2[ |
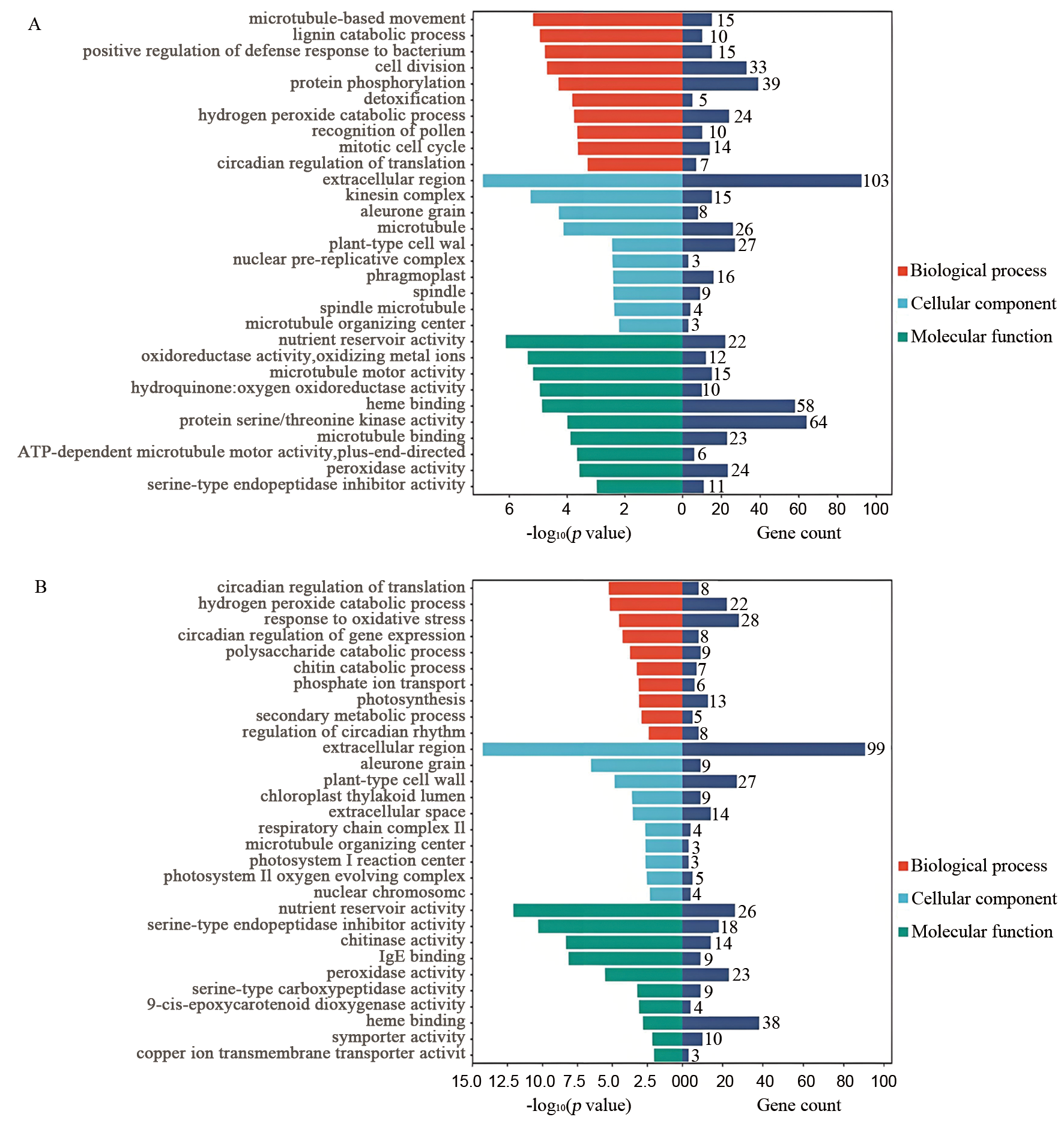
图3 差异表达基因的GO富集分析 A:人工老化后Ra32与Ra146的DEGs;B:自然老化后Ra32与Ra146的DEGs。
Fig. 3. GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes A, DEGs of Ra32 vs. Ra146 after artificial aging; B, DEGs of Ra32 vs. Ra146 after natural aging.
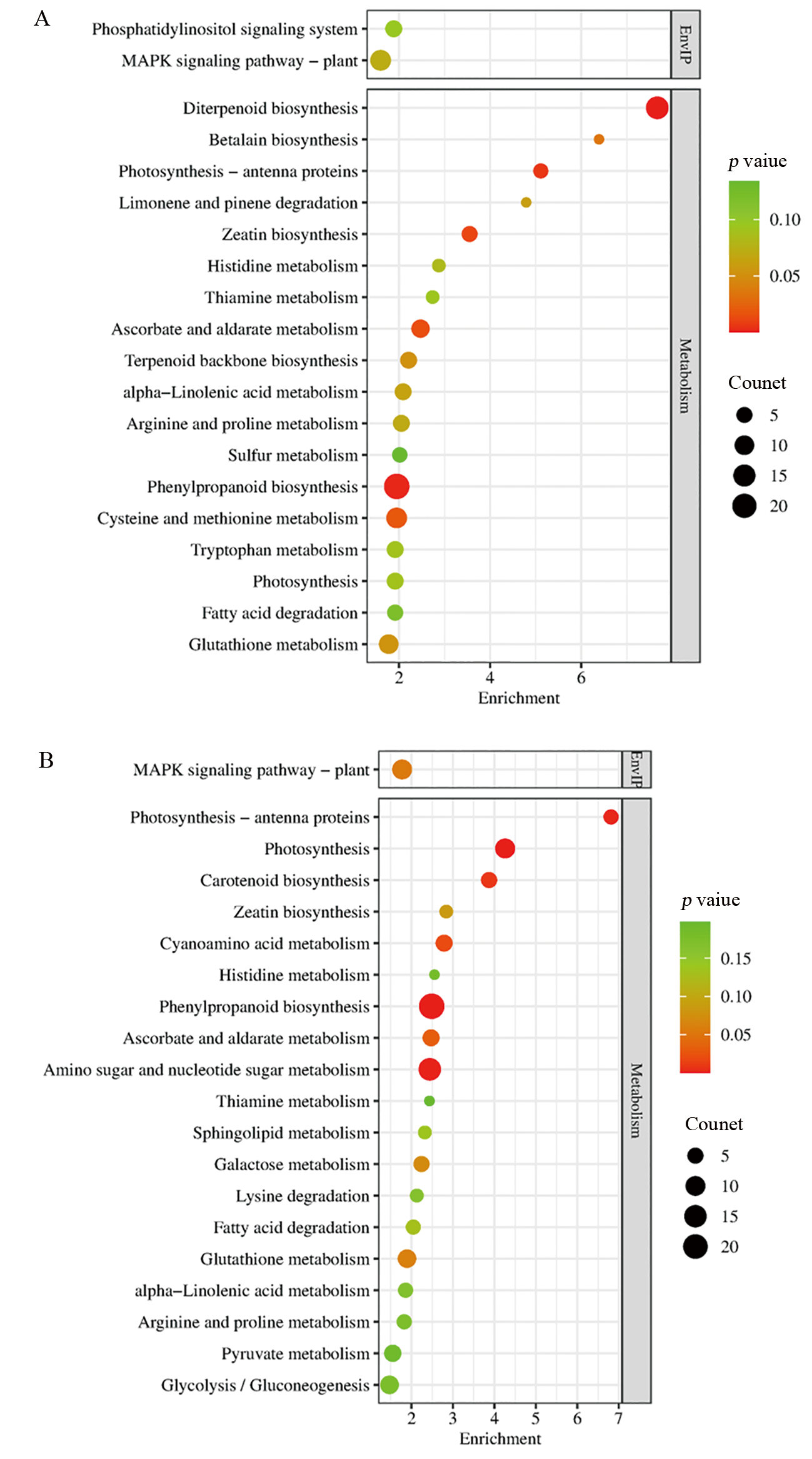
图4 差异表达基因的KEGG富集分析 A:人工老化后Ra32与Ra146的DEG;B:自然老化后Ra32与Ra146的DEG;EnvIP, Environmental information processing.
Fig. 4. KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes A, DEGs of Ra32 vs. Ra146 after artificial aging; B, DEGs of Ra32 vs. Ra146 after natural aging; EnvIP, Environmental Information Processing.
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 功能注释 Functional annotation | Ra32 vs Ra146 1) | GO富集通路 GO enriched pathways | KEGG富集通路 KEGG enriched pathways |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0842400 | 漆酶前体蛋白 Laccase precursor protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 木质素分解过程、 氧化还原酶活性 Lignin catabolic process, oxidoreductase activity | |
| Os01g0842500 | 漆酶前体蛋白 Laccase precursor protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 木质素分解过程、 氧化还原酶活性 Lignin catabolic process, oxidoreductase activity | |
| Os01g0847800 | 醛酮还原酶家族蛋白 Aldo-keto reductase family protein | 上调 Up-regulated | 糖酵解/糖异生、抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, pyruvate metabolism | |
| Os01g0855900 | CDC6-DNA复制起始蛋白 CDC6-DNA replication initiation protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 细胞分裂、 有丝分裂细胞周期 Cell division, mitotic cell cycle | |
| Os01g0860400 | 糖基水解酶 Glycoside hydrolase | 上调 Up-regulated | 壳聚糖分解过程、 多糖分解过程 Chitosan catabolic process, polysaccharide catabolic process | 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
表2 耐储性QTL qASS1.1/qNSS1.1候选基因
Table 2. Candidate genes for qASS1.1/qNSS1.1 controlling seed storability
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 功能注释 Functional annotation | Ra32 vs Ra146 1) | GO富集通路 GO enriched pathways | KEGG富集通路 KEGG enriched pathways |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0842400 | 漆酶前体蛋白 Laccase precursor protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 木质素分解过程、 氧化还原酶活性 Lignin catabolic process, oxidoreductase activity | |
| Os01g0842500 | 漆酶前体蛋白 Laccase precursor protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 木质素分解过程、 氧化还原酶活性 Lignin catabolic process, oxidoreductase activity | |
| Os01g0847800 | 醛酮还原酶家族蛋白 Aldo-keto reductase family protein | 上调 Up-regulated | 糖酵解/糖异生、抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, pyruvate metabolism | |
| Os01g0855900 | CDC6-DNA复制起始蛋白 CDC6-DNA replication initiation protein | 下调 Down-regulated | 细胞分裂、 有丝分裂细胞周期 Cell division, mitotic cell cycle | |
| Os01g0860400 | 糖基水解酶 Glycoside hydrolase | 上调 Up-regulated | 壳聚糖分解过程、 多糖分解过程 Chitosan catabolic process, polysaccharide catabolic process | 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer | 反向引物 Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Os01g0842400 | ATCTTCGGCGAGTGGTGGA | TGTCTTGGGCAGAGCAGTTG |
| Os01g0842500 | CTTCTCCGTTCCTCCATCCT | ACGTTCGTCGTTTTCACATCGA |
| Os01g0847800 | TGGCGTTCATCTCTCTGCGTA | CTGACCCTGCTGAAGACCC |
| Os01g0855900 | CCATACCCGCGAAGCATTAAG | AGAGCCAAGCCCGCCAAAG |
| Os01g0860400 | GACCTCGCCAGGGATCTGA | CGAACAGCCCCGTGCTGAT |
表3 RT-qPCR验证的引物序列
Table 3. Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR validation of candidate genes
| 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer | 反向引物 Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Os01g0842400 | ATCTTCGGCGAGTGGTGGA | TGTCTTGGGCAGAGCAGTTG |
| Os01g0842500 | CTTCTCCGTTCCTCCATCCT | ACGTTCGTCGTTTTCACATCGA |
| Os01g0847800 | TGGCGTTCATCTCTCTGCGTA | CTGACCCTGCTGAAGACCC |
| Os01g0855900 | CCATACCCGCGAAGCATTAAG | AGAGCCAAGCCCGCCAAAG |
| Os01g0860400 | GACCTCGCCAGGGATCTGA | CGAACAGCCCCGTGCTGAT |
| [1] | 朱俊峰. 我国粮食产后损失的现状、影响因素及改进对策[J]. 江西社会科学, 2023, 43(9): 29-40. |
| Zhu J F. The current situation, influencing factors, and improvement strategies of post-harvest losses in grain production in China[J]. Jianxi Social Sciences, 2023, 43(9): 29-40. (in Chinese with Chinese abstract) | |
| [2] | Zhou T S, Yu D, Wu L B, Xu Y S, Duan M J, Yuan D Y. Seed storability in rice: Physiological foundations, molecular mechanisms, and applications in breeding[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(4): 401-416. |
| [3] | 王雪彬, 张健, 韦燕燕, 罗继景, 梁云涛, 蔡中全. 基于BSA-seq的水稻籽粒耐陈化QTL定位分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(16): 5337-5347. |
| Wang X B, Zhang J, Wei Y Y, Luo J J, Liang Y T, Cai Z Q. QTLs mapping analysis of rice grain aging tolerance based on BSA-seq[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(16): 5337-5347. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 曹玉洁, 费月新, 赵文佳, 侯璐燕, 王越, 吴敏, 许珊, 吴洪恺. 以种子电导率为指标定位水稻耐储藏QTL[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(1): 46-49. |
| Cao Y J, Fei Y X, Zhao W J, Hou L Y, Wang Y, Wu M, Xu S, Wu H K. Mapping of QTL for rice storability based on seed electric conductivity[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(1): 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Jin B C, Qi H N, Jia L Q, Tang Q Z, Gao L, Li Z N, Zhao G W. Determination of viability and vigor of naturally-aged rice seeds using hyperspectral imaging with machine learning[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 122: 104097. |
| [6] | Song P, Wang Z Y, Song P, Yue X, Bai Y H, Feng L L. Evaluating the effect of aging process on the physicochemical characteristics of rice seeds by low field nuclear magnetic resonance and its imaging technique[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2021, 99: 103190. |
| [7] | Ye J, Wang C J, Chen L, Zhai R R, Wu M M, Lu Y T, Yu F M, Zhang X M, Zhu G F, Ye S H. Golden hull: A potential biomarker for assessing seed aging tolerance in rice[J]. Agronomy. 2024, 14(10): 2357. |
| [8] | Wang W Q, He A B, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. The effect of storage condition and duration on the deterioration of primed rice seeds[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 172. |
| [9] | 吴方喜, 罗曦, 魏毅东, 郑燕梅, 林强, 谢国生, 谢华安, 张建福. 世界水稻核心种质的耐储藏特性鉴定[J]. 福建稻麦科技, 2021, 39(1): 1-5. |
| Wu F X, Luo X, Wei Y D, Zheng Y M, Lin Q, Xie G S, Xie H A, Zhang J F. Identification of seed storability in rice core collections from 47 countries worldwide[J]. Fujian Science and Technology of Rice and Wheat, 2021, 39(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 黄祎雯, 张维谊, 王霞, 王敏, 沈斯文, 高猛峰, 梅博, 汪弘康, 童金蓉, 曹黎明, 丰东升, 孙滨. 33份不同基因型水稻耐储性比较[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 1-13[2025-03-13]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20240202.1646.010.html |
| Huang Y W, Zhang W Y, Wang X, Wang M, Shen S W, Gao M F, Mei B, Wang H K, Tong J R, Cao L M, Feng D S, Sun B. Comparison of storage tolerance among 33 different genotypes of rice[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20240202.1646.010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 黄祎雯, 孙滨, 程灿, 牛付安, 周继华, 张安鹏, 涂荣剑, 李瑶, 姚瑶, 代雨婷, 谢开珍, 陈小荣, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 对水稻种子耐储性QTL的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(9): 2255-2264. |
| Huang Y W, Sun B, Chen C, Niu F A, Zhou J H, Zhang A P, Tu R J, Li Y, Yao Y, Dai Y T, Xie K Z, Chen X R, Cao L M, Chu H W. QTL mapping of seed storage tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2255-2264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 余丽琴, 李慧, 周慧颖, 王嘉宇, 黎毛毛. 水稻耐储藏特性三年动态鉴定与QTL分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 464-473. |
| Liu J, Yao X Y, Yu L Q, Li H, Zhou H Y, Wang J Y, Li M M. Detection and analysis of dynamic quantitative trait loci at three years for seed storability in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 464-473. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Wu F X, Luo X, Wang L Q, Wei Y D, Li J G, Xie H A, Zhang J F, Xie G S. Genome-wide association study reveals the QTLs for seed storability in world rice core collections[J]. Plants (Basel), 2021, 10(4): 812. |
| [14] | Sasaki K, Fukuta Y, Sato T. Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling seed longevity of rice (Oryza sativa L.) after various periods of seed storage[J]. Plant Breeding, 2005, 124(4): 361-366. |
| [15] | Li L F, Lin Q Y, Liu S J, Liu X, Wang W Y, Hang N T, Liu F, Zhao Z G, Jiang L, Wan J M. Identification of quantitative trait loci for seed storability in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Breeding, 2012, 131(6): 739-743. |
| [16] | Long Q Z, Zhang W W, Wang P, Shen W B, Zhou T, Liu N N, Wang R, Jiang L, Huang J X, Wang Y H, Liu Y Q, Wan J M. Molecular genetic characterization of rice seed lipoxygenase 3 and assessment of its effects on seed longevity[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2013, 56(4): 232-242. |
| [17] | Yuan Z Y, Fan K, Wang Y T, Tian L, Zhang C P, Sun W Q, He H Z, Yu S B. OsGRETCHENHAGEN3-2 modulates rice seed storability via accumulation of abscisic acid and protective substances[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 186(1): 469-482. |
| [18] | 黄娟, 梁云涛, 陈成斌, 徐志健, 梁世春, 潘英华. 普通野生稻遗传分化及水稻起源关系研究进展[J]. 南方农业学报, 2015, 46(10): 1756-1760. |
| Huang J, Liang Y T, Chen C B, Xu Z J, Liang S C, Pan Y H. Advances in origin of Oryza sativa in terms of genetic differentiation of Oryza fufipogon[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(10): 1756-1760. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王世林, 吴婷, 周诗琪, 宋思铭, 胡标林. 结合BSA-seq和QTL分析鉴定东乡野生稻耐储性QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 789-800. |
| Wang S L, Wu T, Zhou S Q, Song S M, Hu B L. Identification of QTL for seed storability in Dongxiang wild rice by integrating BSA-seq and QTL analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 789-800. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Ma X, Fu Y C, Zhao X H, Jiang L Y, Zhu Z F, Gu P, Xu W Y, Su Z, Sun C Q, Tan L B. Genomic structure analysis of a set of Oryza nivara introgression lines and identification of yield-associated QTLs using whole-genome resequencing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27425. |
| [21] | Meng L, Li H H, Zhang L Y, Wang J K. QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations[J]. The Crop Journal, 2015, 3: 269-283. |
| [22] | McCouch S R, CGSNL (Committee on Gene Symbolization, Nomenclature and Linkage, Rice Genetics Cooperative). Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1: 72-84. |
| [23] | Chen S F, Zhou Y Q, Chen Y, Chen Y R, Gu J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i884-i890. |
| [24] | Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg S L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(4): 357-360. |
| [25] | Roberts A, Trapnell C, Donaghey J, Rinn J L, Pachter L. Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias[J]. Genome Biology, 2011, 12(3): R22. |
| [26] | Anders S, Pyl P T, Huber W. HTSeq: A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(2): 166-169. |
| [27] | Love M I, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(12): 550. |
| [28] | Dietz K-J, Mittler R, Noctor G. Recent progress in understanding the role of reactive oxygen species in plant cell signaling[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(3): 1535-1539. |
| [29] | Xue J S, Feng Y F, Zhang M Q, Xu Q L, Xu Y M, Shi J Q, Liu L F, Wu X F, Wang S, Yang Z N. The regulatory mechanism of rapid lignification for timely anther dehiscence[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2024, 66(8): 1788-1800. |
| [30] | 张盛春, 鞠常亮, 王小菁. 拟南芥漆酶基因AtLAC4参与生长及非生物胁迫响应[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(4): 357-365. |
| Zhang S C, Ju C L, Wang X Q. Arabidopsis laccase gene AtLAC4 regulates plant growth and responses to abiotic stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(4): 357-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 徐小萍, 曹清影, 蔡柔荻, 官庆栩, 张梓浩, 陈裕坤, 徐涵, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 龙眼miR408与DlLAC12克隆及其在球形胚发生和非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. |
| Xu X P, Cao Q Y, Cai R D, Guan Q X, Zhang Z H, Chen Y K, Xu H, Lin Y L, Lai Z X. Gene cloning and expression analysis of miR408 and its target DlLAC12 in globular embryo development and abiotic stress in Dimocarpus longan[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Simpson P J, Tantitadapitak C, Reed A M, Mather O C, Bunce C M, White S A, Ride J P. Characterization of two novel aldo-keto reductases from Arabidopsis: Expression patterns, broad substrate specificity, and an open active-site structure suggest a role in toxicant metabolism following stress[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 392(2): 465-480. |
| [33] | Saito R, Shimakawa G, Nishi A, Iwamoto T, Sakamoto K, Yamamoto H, Amako K, Makino A, Miyake C. Functional analysis of the AKR4C subfamily of Arabidopsis thaliana: model structures, substrate specificity, acrolein toxicity, and responses to light and [CO2][J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2013, 77(10): 2038-2045. |
| [34] | Yu X H, Liu Y H, Yin L L, Peng Y B, Peng Y C, Gao Y X, Yuan B W, Zhu Q L, Cao T Y, Xie B W, Sun L Q, Chen Y, Gong Z C, Qiu Y Z, Fan X G, Li X. Radiation-promoted CDC6 protein stability contributes to radioresistance by regulating senescence and epithelial to mesenchymal transition[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38: 549-563. |
| [35] | Abeles F B, Bosshart R P, Forrence L E, Habig W H. Preparation and purification of glucanase and chitinase from bean leaves[J]. Plant Physiology, 1971, 47(1): 129-134. |
| [1] | 张城, 邵国军, 张雪, 田书军, 孙驰, 郭艳颖, 周燃, 韩勇, 郑文静, 孙廉平. 粳稻花时性状QTL定位与聚合效应分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 106-117. |
| [2] | 王世林, 吴婷, 周诗琪, 宋思铭, 胡标林. 结合BSA-seq和QTL分析鉴定东乡野生稻耐储性QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 789-800. |
| [3] | 李荣欣, 王波, 肖素勤, 殷富有, 张建红, 钟巧芳, 陈玲, 李金璐, 杨和生, 程在全, 刘丽. 野生稻叶绿体基因组组装与密码子偏好性分析及系统发育研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 801-812. |
| [4] | 丁国华, 李鑫, 曹良子, 周劲松, 雷蕾, 白良明, 洛育, 杨光, 崔志波, 赵明辉, 孙世臣. 孕穗期低温对寒地不同水稻材料光合系统的影响研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 679-689. |
| [5] | 陈嘉乐, 于清涛, 郑琛凡, 汪庆, 谭瑗瑗, 陈百翠, 李承欣, 蒋萌, 舒庆尧. 水稻OsNF-YC10自然变异及其与谷粒宽度的相关性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 552-562. |
| [6] | 黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-574. |
| [7] | 梁楚炎, 曾维, 王洁冰, 叶靖, 巫明明, 翟荣荣, 张小明, 张恒木, 叶胜海. 一个浙粳99短穗小粒突变体的鉴定及转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 67-81. |
| [8] | 杜彦修, 孙文玉, 袁泽科, 张倩倩, 李富豪, 李俊周, 孙红正. 利用QTL-Seq结合分子标记定位粳稻垩白粒率控制位点qChalk8[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 665-671. |
| [9] | 伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 转录组和代谢组联合分析揭示稻曲病菌的致病因子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 侯本福, 杨传铭, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 王嘉宇, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 利用龙稻5号/中优早8号RIL群体定位粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 13-24. |
| [12] | 胡佳晓, 刘进, 崔迪, 勒思, 周慧颖, 韩冰, 孟冰欣, 余丽琴, 韩龙植, 马小定, 黎毛毛. 利用东乡野生稻染色体片段置换系鉴定穗部性状主效QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 597-608. |
| [13] | 谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [14] | 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 熊运华, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 尹建华. 水稻加工和外观品质性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. |
| [15] | 韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢. 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||