
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 487-504.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211105
陈红阳, 贾琰( ), 赵宏伟(
), 赵宏伟( ), 瞿炤珺, 王新鹏, 段雨阳, 杨蕊, 白旭, 王常丞
), 瞿炤珺, 王新鹏, 段雨阳, 杨蕊, 白旭, 王常丞
收稿日期:2021-11-08
修回日期:2022-02-28
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
贾琰,赵宏伟
基金资助:
CHEN Hongyang, JIA Yan( ), ZHAO Hongwei(
), ZHAO Hongwei( ), QU Zhaojun, WANG Xinpeng, DUAN Yuyang, YANG Rui, BAI Xu, WANG Changcheng
), QU Zhaojun, WANG Xinpeng, DUAN Yuyang, YANG Rui, BAI Xu, WANG Changcheng
Received:2021-11-08
Revised:2022-02-28
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
JIA Yan, ZHAO Hongwei
摘要:
【目的】研究结实期低温胁迫对水稻强、弱势粒淀粉组分含量、积累速率及关键酶活性的影响,明确淀粉合成关键酶活性变化对淀粉积累速率的调控效应,探究强、弱势粒淀粉形成积累差异对水稻产量的影响。【方法】以耐冷型品种东农428和冷敏型品种松粳10为试验材料,设置1个常温处理(白天温度28℃,14h/夜间温度22℃,10 h,7 d)和4个低温处理(17℃,低温处理时间分别为1、3、5、7 d),分析了结实期低温胁迫对强、弱势粒淀粉组分积累、合成关键酶活性、水稻产量及构成因素的影响,并探讨了灌浆期各阶段淀粉积累差异与酶活性变化的关系。【结果】与对照相比,结实期低温胁迫降低了两个品种水稻强、弱势粒中腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶(AGPase)、可溶性淀粉合成酶(SSS)、淀粉分支酶(SBE)的峰值活性以及支链淀粉和总淀粉含量,提高了齐穗后28~38 d 低温处理3、5、7 d的颗粒结合型淀粉合成酶(GBSS)活性和直链淀粉含量。与对照相比,各低温处理酶活性最高和淀粉积累最快的时间均有不同程度的推迟,低温处理7 d的影响最大,强、弱势粒低温处理7 d的支链淀粉和总淀粉含量分别在齐穗后13、18 d降幅最大,直链淀粉含量在28 d增幅最大。相关分析表明,强、弱势粒直链淀粉含量及强势粒支链淀粉、总淀粉含量与其最大积累速率呈极显著正相关,弱势粒支链淀粉、总淀粉含量还受到其最大积累速率出现时间的影响。AGPase、GBSS、SSS、SBE活性变化与淀粉积累速率和积累时间早晚密切相关,对淀粉及淀粉组分含量的变化有着明显的影响。同时,结实期低温胁迫显著降低了水稻的千粒重、结实率和产量,且随低温处理天数的增加降幅逐渐增大。结实期低温胁迫对弱势粒中淀粉合成关键酶活性变化影响大于强势粒,弱势粒淀粉合成积累减慢,含量降低,导致水稻千粒重显著下降,产量降低。【结论】就品种而言,耐冷型东农428具有较高的淀粉合成关键酶活性,淀粉及其组分含量较高,在低温胁迫下产量能维持在较高的水平。因此,强、弱势粒淀粉合成关键酶活性对淀粉合成起着非常关键的调控作用,淀粉组分和含量及其变化对产量有着十分重要的影响。
陈红阳, 贾琰, 赵宏伟, 瞿炤珺, 王新鹏, 段雨阳, 杨蕊, 白旭, 王常丞. 结实期低温胁迫对水稻强、弱势粒淀粉形成与积累的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 487-504.
CHEN Hongyang, JIA Yan, ZHAO Hongwei, QU Zhaojun, WANG Xinpeng, DUAN Yuyang, YANG Rui, BAI Xu, WANG Changcheng. Effects of Low Temperature Stress During Grain Filling on Starch Formation and Accumulation of Superior and Inferior Grains in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 487-504.
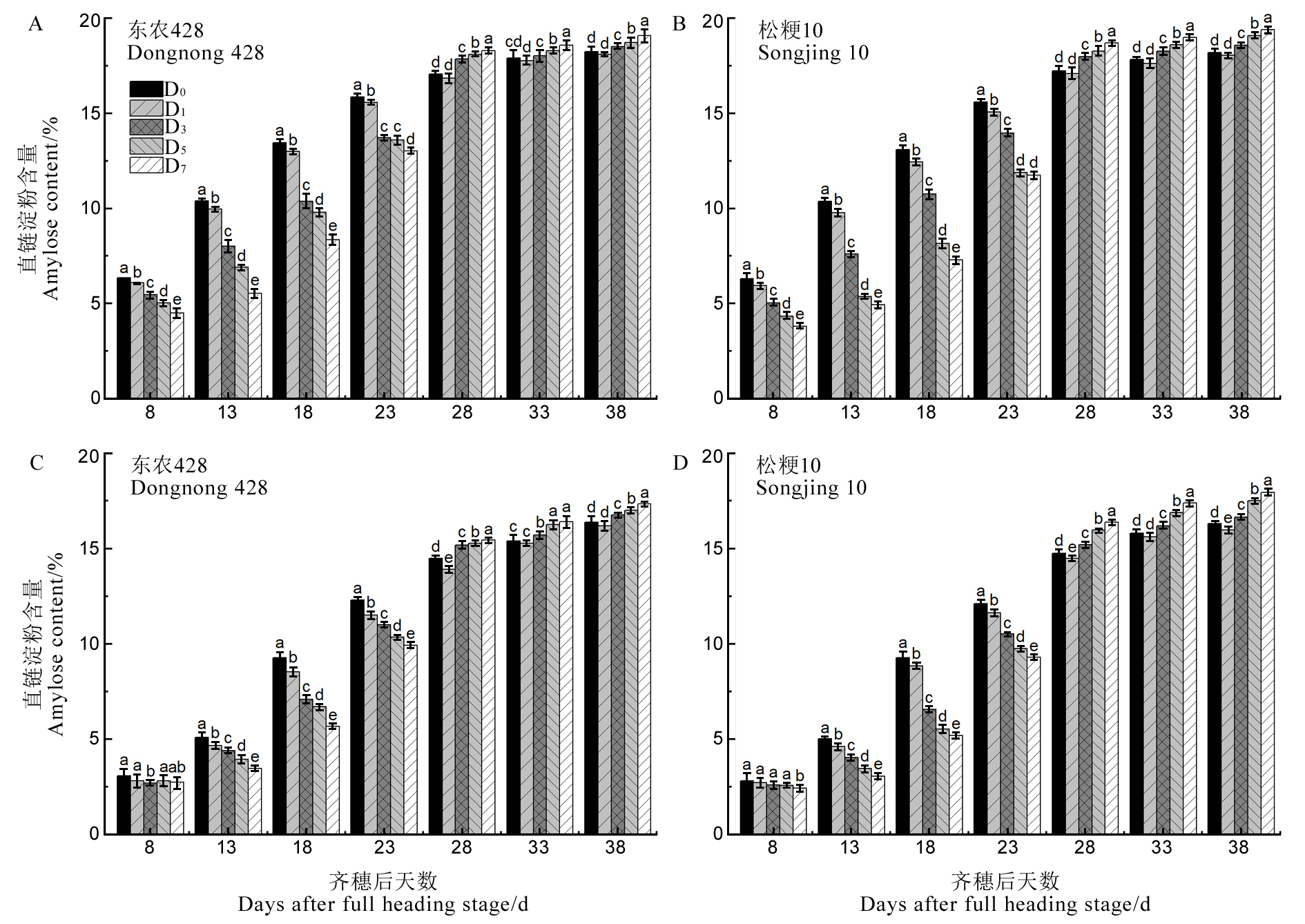
图1 结实期低温胁迫对强、弱势粒直链淀粉含量的影响 柱状图上不同小写字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平。A、B-强势粒,C、D-弱势粒。D0、D1、D3、D5、D7分别代表低温(17℃)处理0(对照)、1、3、5、7 d。下同。
Fig. 1. Effect of low temperature stress on amylose content of superior and inferior grains during grain filling period. Within a hitogram, different lowercase letters above the bars mean significant difference at P<0.05. A and B, superior grains; C and D, Inferior grains. D0, D1, D3, D5 and D7 represent 0(contrd), 1, 3, 5, and 7 days of treatment, low temperature(17℃) respectively. The same below.
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒 Superior grains | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 0.81 a | 0.61 a | 0.48 e | 0.24 e | 0.17 a | 0.07 b | |
| D1 | 0.77 b | 0.60 b | 0.52 d | 0.25 d | 0.19 a | 0.06 b | |||
| D3 | 0.51 c | 0.47 d | 0.67 c | 0.83 c | 0.03 c | 0.10 a | |||
| D5 | 0.38 d | 0.58 c | 0.76 b | 0.90 b | 0.04 b | 0.09 a | |||
| D7 | 0.21 e | 0.57 c | 0.93 a | 1.05 a | 0.06 b | 0.10 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 0.81 a | 0.54 c | 0.50 e | 0.32 e | 0.12 a | 0.07 b | ||
| D1 | 0.76 b | 0.53 c | 0.52 d | 0.40 d | 0.11 a | 0.09 a | |||
| D3 | 0.51 c | 0.63 a | 0.64 c | 0.88 c | 0.06 b | 0.06 b | |||
| D5 | 0.20 e | 0.56 b | 0.74 b | 1.28 b | 0.07 b | 0.10 a | |||
| D7 | 0.23 d | 0.47 d | 0.89 a | 1.39 a | 0.06 b | 0.08 a | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 0.40 a | 0.79 a | 0.60 d | 0.44 e | 0.19 b | 0.20 a | |
| D1 | 0.37 b | 0.78 a | 0.59 d | 0.48 d | 0.27 a | 0.18 b | |||
| D3 | 0.34 c | 0.54 b | 0.78 b | 0.83 c | 0.11 c | 0.21 a | |||
| D5 | 0.22 d | 0.55 b | 0.73 c | 0.99 b | 0.19 b | 0.15 c | |||
| D7 | 0.15 e | 0.44 c | 0.85 a | 1.10 a | 0.19 b | 0.19 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 0.44 a | 0.85 a | 0.56 d | 0.53 e | 0.21 b | 0.10 b | ||
| D1 | 0.38 b | 0.85 a | 0.56 d | 0.57 d | 0.23 a | 0.07 c | |||
| D3 | 0.29 c | 0.51 b | 0.79 c | 0.94 c | 0.20 b | 0.09 b | |||
| D5 | 0.18 d | 0.41 d | 0.84 a | 1.25 b | 0.18 c | 0.12 a | |||
| D7 | 0.13 e | 0.43 c | 0.82 b | 1.42 a | 0.20 b | 0.11 a | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 166.11** | 50.95** | 142.15** | 276.34** | 109.63** | 1.25 | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 92.37** | 51.36** | 168.62** | 223.58** | 199.02** | 1.06 | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 15.38** | 9.37** | 11.72** | 20.02** | 17.05** | 0.72 | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 369.01** | 167.58** | 101.97** | 525.66** | 51.84** | 66.18** | ||
| 品种(V) | 121.30** | 32.17* | 96.38** | 310.01** | 34.79* | 325.93** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 31.10** | 22.26** | 24.67** | 52.01** | 9.13* | 13.18** | |||
表1 结实期低温胁迫下直链淀粉积累速率
Table 1. Accumulation rate of amylose under low temperature treatment during grain-filling period. %/d
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒 Superior grains | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 0.81 a | 0.61 a | 0.48 e | 0.24 e | 0.17 a | 0.07 b | |
| D1 | 0.77 b | 0.60 b | 0.52 d | 0.25 d | 0.19 a | 0.06 b | |||
| D3 | 0.51 c | 0.47 d | 0.67 c | 0.83 c | 0.03 c | 0.10 a | |||
| D5 | 0.38 d | 0.58 c | 0.76 b | 0.90 b | 0.04 b | 0.09 a | |||
| D7 | 0.21 e | 0.57 c | 0.93 a | 1.05 a | 0.06 b | 0.10 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 0.81 a | 0.54 c | 0.50 e | 0.32 e | 0.12 a | 0.07 b | ||
| D1 | 0.76 b | 0.53 c | 0.52 d | 0.40 d | 0.11 a | 0.09 a | |||
| D3 | 0.51 c | 0.63 a | 0.64 c | 0.88 c | 0.06 b | 0.06 b | |||
| D5 | 0.20 e | 0.56 b | 0.74 b | 1.28 b | 0.07 b | 0.10 a | |||
| D7 | 0.23 d | 0.47 d | 0.89 a | 1.39 a | 0.06 b | 0.08 a | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 0.40 a | 0.79 a | 0.60 d | 0.44 e | 0.19 b | 0.20 a | |
| D1 | 0.37 b | 0.78 a | 0.59 d | 0.48 d | 0.27 a | 0.18 b | |||
| D3 | 0.34 c | 0.54 b | 0.78 b | 0.83 c | 0.11 c | 0.21 a | |||
| D5 | 0.22 d | 0.55 b | 0.73 c | 0.99 b | 0.19 b | 0.15 c | |||
| D7 | 0.15 e | 0.44 c | 0.85 a | 1.10 a | 0.19 b | 0.19 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 0.44 a | 0.85 a | 0.56 d | 0.53 e | 0.21 b | 0.10 b | ||
| D1 | 0.38 b | 0.85 a | 0.56 d | 0.57 d | 0.23 a | 0.07 c | |||
| D3 | 0.29 c | 0.51 b | 0.79 c | 0.94 c | 0.20 b | 0.09 b | |||
| D5 | 0.18 d | 0.41 d | 0.84 a | 1.25 b | 0.18 c | 0.12 a | |||
| D7 | 0.13 e | 0.43 c | 0.82 b | 1.42 a | 0.20 b | 0.11 a | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 166.11** | 50.95** | 142.15** | 276.34** | 109.63** | 1.25 | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 92.37** | 51.36** | 168.62** | 223.58** | 199.02** | 1.06 | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 15.38** | 9.37** | 11.72** | 20.02** | 17.05** | 0.72 | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 369.01** | 167.58** | 101.97** | 525.66** | 51.84** | 66.18** | ||
| 品种(V) | 121.30** | 32.17* | 96.38** | 310.01** | 34.79* | 325.93** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 31.10** | 22.26** | 24.67** | 52.01** | 9.13* | 13.18** | |||
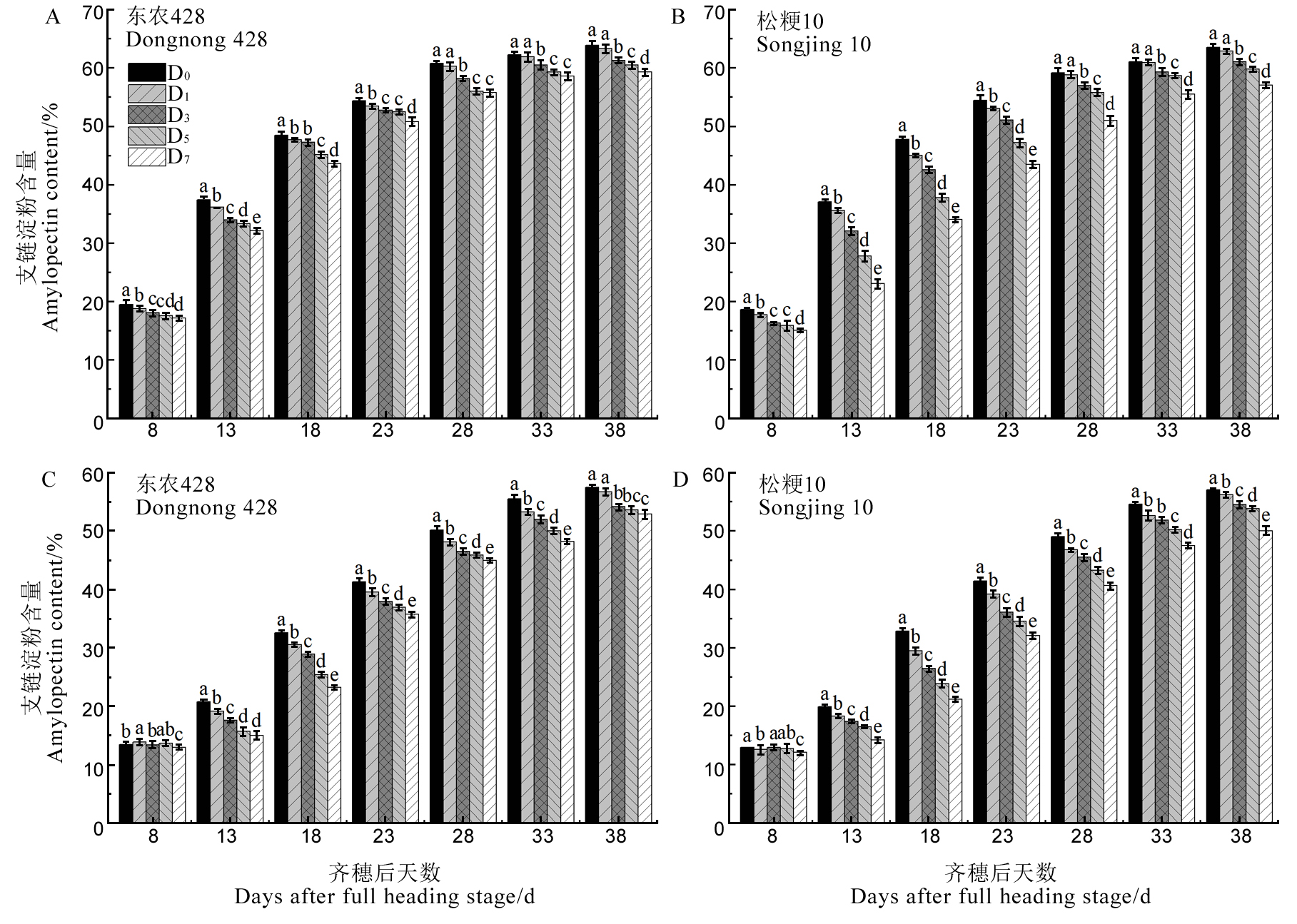
图2 结实期低温胁迫对强、弱势粒支链淀粉含量的影响
Fig. 2. Effect of low temperature stress on amylopectin content of superior and inferior grains during grain filling period.
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒SG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 3.58 a | 2.21 d | 1.18 c | 1.29 b | 0.29 e | 0.32 a | |
| D1 | 3.47 b | 2.31 c | 1.16 d | 1.36 a | 0.33 d | 0.28 b | |||
| D3 | 3.16 c | 2.65 a | 1.10 e | 1.09 c | 0.46 c | 0.16 d | |||
| D5 | 3.14 c | 2.37 b | 1.46 a | 0.70 e | 0.65 a | 0.25 c | |||
| D7 | 2.99 d | 2.29 e | 1.44 b | 0.99 d | 0.57 b | 0.14 d | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 3.69 a | 2.14 b | 1.33 d | 0.95 d | 0.38 e | 0.49 a | ||
| D1 | 3.58 b | 1.88 e | 1.61 c | 1.15 c | 0.42 d | 0.39 b | |||
| D3 | 3.15 c | 2.10 c | 1.70 b | 1.18 c | 0.46 c | 0.34 c | |||
| D5 | 2.38 d | 2.00 d | 1.88 a | 1.72 a | 0.57 b | 0.22 d | |||
| D7 | 1.60 e | 2.19 a | 1.89 a | 1.51 b | 0.89 a | 0.32 c | |||
| 弱势粒IG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 1.46 a | 2.36 a | 1.75 d | 1.76 c | 1.07 b | 0.41 e | |
| D1 | 1.06 b | 2.28 b | 1.79 c | 1.72 d | 1.04 c | 0.69 c | |||
| D3 | 0.85 c | 2.26 b | 1.80 c | 1.71 d | 1.10 a | 0.43 d | |||
| D5 | 0.40 d | 1.95 c | 2.29 b | 1.79 b | 0.83 d | 0.71 b | |||
| D7 | 0.40 d | 1.64 d | 2.51 a | 1.84 a | 0.84 d | 0.95 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 1.39 a | 2.59 a | 1.72 d | 1.52 d | 1.11 c | 0.48 c | ||
| D1 | 1.14 b | 2.24 b | 1.94 c | 1.52 d | 1.08 c | 0.71 a | |||
| D3 | 0.89 c | 1.81 c | 1.94 c | 1.87 a | 1.28 b | 0.33 d | |||
| D5 | 0.74 d | 1.48 d | 2.14 b | 1.74 b | 1.39 a | 0.46 c | |||
| D7 | 0.42 e | 1.40 e | 2.18 a | 1.72 c | 1.37 a | 0.51 b | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 205.62** | 359.23** | 296.56** | 126.65** | 119.98** | 86.34* | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 392.38** | 452.06** | 296.76** | 256.46** | 206.26** | 195.14** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 35.18** | 49.29** | 43.06** | 30.12** | 19.35** | 10.72* | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 134.45** | 296.52** | 104.46** | 117.96** | 96.88** | 76.14** | ||
| 品种(V) | 164.42** | 203.80* | 88.46** | 102.44** | 169.75** | 103.42** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 26.43** | 33.45** | 16.31** | 12.11* | 19.23** | 10.78* | |||
表2 结实期低温胁迫下支链淀粉积累速率
Table 2. Accumulation rate of amylopectin under low temperature treatment during grain-filling period. %/d
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒SG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 3.58 a | 2.21 d | 1.18 c | 1.29 b | 0.29 e | 0.32 a | |
| D1 | 3.47 b | 2.31 c | 1.16 d | 1.36 a | 0.33 d | 0.28 b | |||
| D3 | 3.16 c | 2.65 a | 1.10 e | 1.09 c | 0.46 c | 0.16 d | |||
| D5 | 3.14 c | 2.37 b | 1.46 a | 0.70 e | 0.65 a | 0.25 c | |||
| D7 | 2.99 d | 2.29 e | 1.44 b | 0.99 d | 0.57 b | 0.14 d | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 3.69 a | 2.14 b | 1.33 d | 0.95 d | 0.38 e | 0.49 a | ||
| D1 | 3.58 b | 1.88 e | 1.61 c | 1.15 c | 0.42 d | 0.39 b | |||
| D3 | 3.15 c | 2.10 c | 1.70 b | 1.18 c | 0.46 c | 0.34 c | |||
| D5 | 2.38 d | 2.00 d | 1.88 a | 1.72 a | 0.57 b | 0.22 d | |||
| D7 | 1.60 e | 2.19 a | 1.89 a | 1.51 b | 0.89 a | 0.32 c | |||
| 弱势粒IG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 1.46 a | 2.36 a | 1.75 d | 1.76 c | 1.07 b | 0.41 e | |
| D1 | 1.06 b | 2.28 b | 1.79 c | 1.72 d | 1.04 c | 0.69 c | |||
| D3 | 0.85 c | 2.26 b | 1.80 c | 1.71 d | 1.10 a | 0.43 d | |||
| D5 | 0.40 d | 1.95 c | 2.29 b | 1.79 b | 0.83 d | 0.71 b | |||
| D7 | 0.40 d | 1.64 d | 2.51 a | 1.84 a | 0.84 d | 0.95 a | |||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 1.39 a | 2.59 a | 1.72 d | 1.52 d | 1.11 c | 0.48 c | ||
| D1 | 1.14 b | 2.24 b | 1.94 c | 1.52 d | 1.08 c | 0.71 a | |||
| D3 | 0.89 c | 1.81 c | 1.94 c | 1.87 a | 1.28 b | 0.33 d | |||
| D5 | 0.74 d | 1.48 d | 2.14 b | 1.74 b | 1.39 a | 0.46 c | |||
| D7 | 0.42 e | 1.40 e | 2.18 a | 1.72 c | 1.37 a | 0.51 b | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 205.62** | 359.23** | 296.56** | 126.65** | 119.98** | 86.34* | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 392.38** | 452.06** | 296.76** | 256.46** | 206.26** | 195.14** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 35.18** | 49.29** | 43.06** | 30.12** | 19.35** | 10.72* | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 134.45** | 296.52** | 104.46** | 117.96** | 96.88** | 76.14** | ||
| 品种(V) | 164.42** | 203.80* | 88.46** | 102.44** | 169.75** | 103.42** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 26.43** | 33.45** | 16.31** | 12.11* | 19.23** | 10.78* | |||
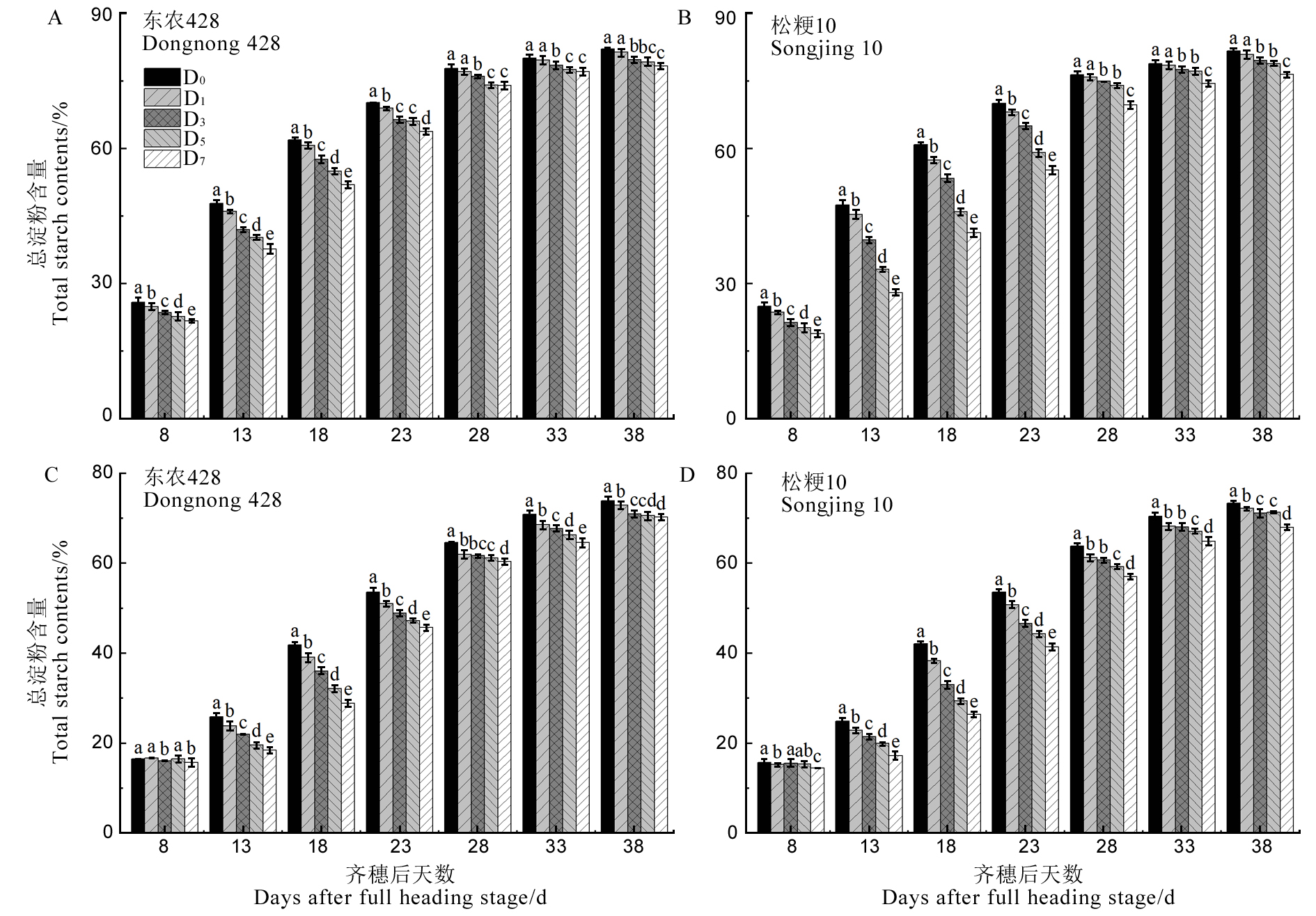
图3 结实期低温胁迫对强、弱势粒总淀粉含量的影响
Fig. 3. Effect of low temperature stress on total starch contents of superior and inferior grains during grain filling period.
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒SG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 4.39 a | 2.83 d | 1.66 d | 1.53 d | 0.46 d | 0.39 a | |
| D1 | 4.25 b | 2.91 c | 1.67 d | 1.61 c | 0.51 c | 0.35 b | |||
| D3 | 3.70 c | 3.12 a | 1.76 c | 1.92 b | 0.49 c | 0.25 d | |||
| D5 | 3.51 d | 2.95 b | 2.22 b | 1.60 c | 0.69 a | 0.33 c | |||
| D7 | 3.20 e | 2.86 e | 2.37 a | 2.05 a | 0.62 b | 0.24 d | |||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 4.50 a | 2.68 b | 1.84 e | 1.27 e | 0.50 d | 0.56 a | ||
| D1 | 4.35 b | 2.42 d | 2.14 d | 1.56 d | 0.53 c | 0.52 b | |||
| D3 | 3.66 c | 2.73 a | 2.34 c | 1.98 c | 0.52 c | 0.50 b | |||
| D5 | 2.59 d | 2.56 c | 2.63 b | 2.99 a | 0.64 b | 0.32 c | |||
| D7 | 1.83 e | 2.66 b | 2.79 a | 2.90 b | 0.95 a | 0.28 d | |||
| 弱势粒IG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 1.86 a | 3.19 a | 2.36 e | 2.20 d | 1.26 b | 0.60 c | |
| D1 | 1.42 b | 3.05 b | 2.39 d | 2.20 d | 1.31 a | 0.87 b | |||
| D3 | 1.19 c | 2.79 c | 2.58 c | 2.55 c | 1.21 c | 0.64 c | |||
| D5 | 0.63 d | 2.50 d | 3.03 b | 2.78 b | 1.02 d | 0.86 b | |||
| D7 | 0.55 e | 2.26 e | 3.19 a | 2.94 a | 1.03 d | 1.13 a | |||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 1.83 a | 3.44 a | 2.29 d | 2.05 d | 1.33 d | 0.58 e | ||
| D1 | 1.52 b | 3.08 b | 2.50 c | 2.09 d | 1.40 c | 0.79 b | |||
| D3 | 1.17 c | 2.31 c | 2.73 b | 2.81 c | 1.48 b | 0.41 d | |||
| D5 | 0.92 d | 1.89 d | 2.99 a | 2.99 b | 1.57 a | 0.84 a | |||
| D7 | 0.55 e | 1.82 d | 3.00 a | 3.14 a | 1.56 a | 0.63 c | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 298.35** | 202.65** | 168.64** | 245.40** | 96.14** | 79.64* | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 205.46** | 462.62** | 246.13** | 301.14** | 196.45** | 106.54** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 36.65** | 29.35** | 20.02** | 44.54** | 11.69** | 9.47** | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 163.49** | 341.48** | 116.45** | 99.84** | 67.69** | 56.74** | ||
| 品种(V) | 196.35** | 160.36* | 156.23** | 134.06** | 106.99** | 70.25** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 22.64** | 22.13** | 19.47** | 12.22** | 9.15** | 6.88** | |||
表3 结实期低温处理下总淀粉积累速率
Table 3. Accumulation rate of total starch under low temperature treatment during grain-filling period. %/d
| 粒位 Grain position | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 齐穗后天数Days after full heading stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8~13 | 13~18 | 18~23 | 23~28 | 28~33 | 33~38 | ||||
| 强势粒SG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 4.39 a | 2.83 d | 1.66 d | 1.53 d | 0.46 d | 0.39 a | |
| D1 | 4.25 b | 2.91 c | 1.67 d | 1.61 c | 0.51 c | 0.35 b | |||
| D3 | 3.70 c | 3.12 a | 1.76 c | 1.92 b | 0.49 c | 0.25 d | |||
| D5 | 3.51 d | 2.95 b | 2.22 b | 1.60 c | 0.69 a | 0.33 c | |||
| D7 | 3.20 e | 2.86 e | 2.37 a | 2.05 a | 0.62 b | 0.24 d | |||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 4.50 a | 2.68 b | 1.84 e | 1.27 e | 0.50 d | 0.56 a | ||
| D1 | 4.35 b | 2.42 d | 2.14 d | 1.56 d | 0.53 c | 0.52 b | |||
| D3 | 3.66 c | 2.73 a | 2.34 c | 1.98 c | 0.52 c | 0.50 b | |||
| D5 | 2.59 d | 2.56 c | 2.63 b | 2.99 a | 0.64 b | 0.32 c | |||
| D7 | 1.83 e | 2.66 b | 2.79 a | 2.90 b | 0.95 a | 0.28 d | |||
| 弱势粒IG | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | D0 | 1.86 a | 3.19 a | 2.36 e | 2.20 d | 1.26 b | 0.60 c | |
| D1 | 1.42 b | 3.05 b | 2.39 d | 2.20 d | 1.31 a | 0.87 b | |||
| D3 | 1.19 c | 2.79 c | 2.58 c | 2.55 c | 1.21 c | 0.64 c | |||
| D5 | 0.63 d | 2.50 d | 3.03 b | 2.78 b | 1.02 d | 0.86 b | |||
| D7 | 0.55 e | 2.26 e | 3.19 a | 2.94 a | 1.03 d | 1.13 a | |||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | D0 | 1.83 a | 3.44 a | 2.29 d | 2.05 d | 1.33 d | 0.58 e | ||
| D1 | 1.52 b | 3.08 b | 2.50 c | 2.09 d | 1.40 c | 0.79 b | |||
| D3 | 1.17 c | 2.31 c | 2.73 b | 2.81 c | 1.48 b | 0.41 d | |||
| D5 | 0.92 d | 1.89 d | 2.99 a | 2.99 b | 1.57 a | 0.84 a | |||
| D7 | 0.55 e | 1.82 d | 3.00 a | 3.14 a | 1.56 a | 0.63 c | |||
| F值 F value | 强势粒 Superior grains | 处理Treatment(T) | 298.35** | 202.65** | 168.64** | 245.40** | 96.14** | 79.64* | |
| 品种Variety(V) | 205.46** | 462.62** | 246.13** | 301.14** | 196.45** | 106.54** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 36.65** | 29.35** | 20.02** | 44.54** | 11.69** | 9.47** | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 处理(T) | 163.49** | 341.48** | 116.45** | 99.84** | 67.69** | 56.74** | ||
| 品种(V) | 196.35** | 160.36* | 156.23** | 134.06** | 106.99** | 70.25** | |||
| 处理×品种T×V | 22.64** | 22.13** | 19.47** | 12.22** | 9.15** | 6.88** | |||
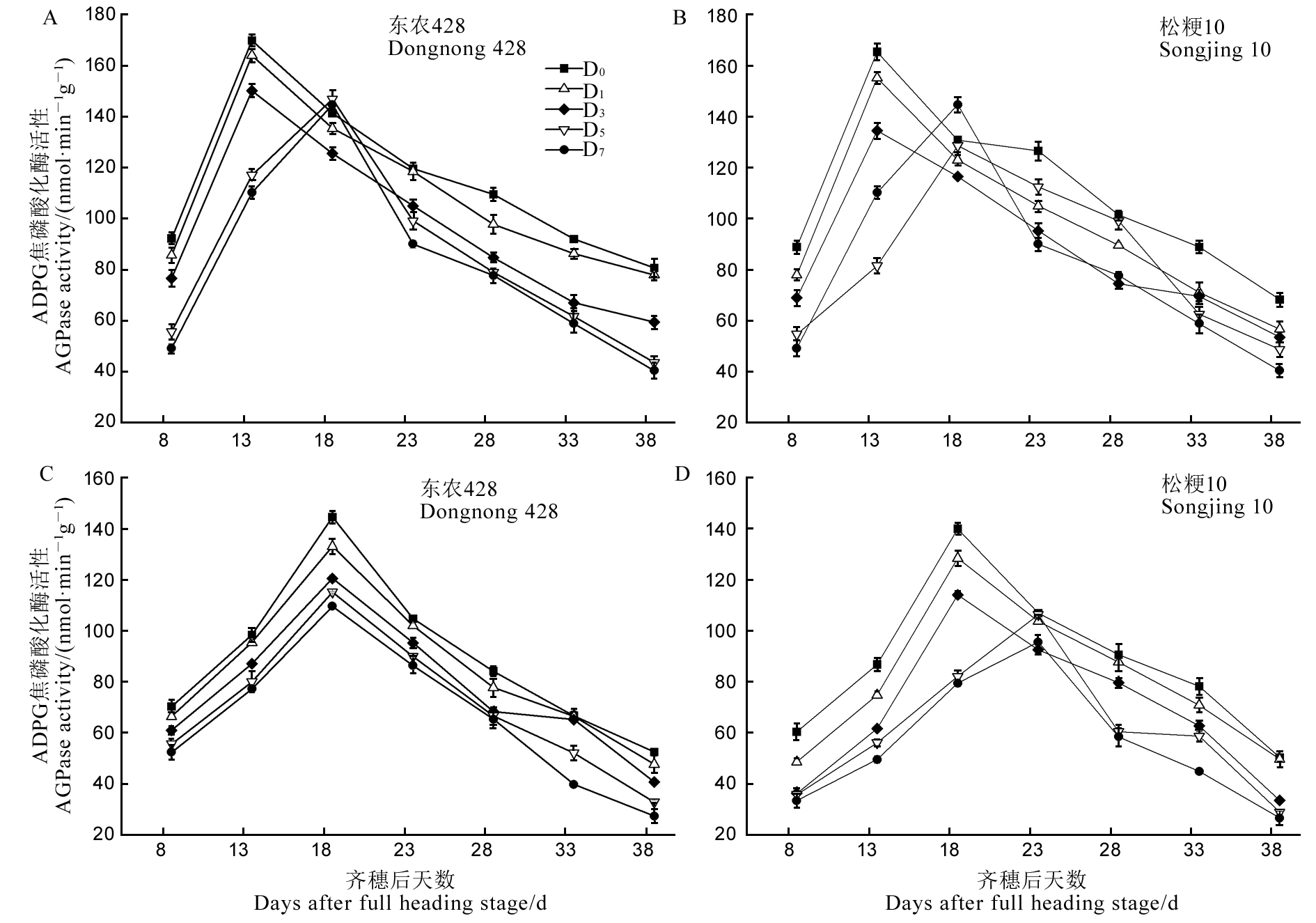
图4 结实期低温胁迫下强、弱势粒AGPase活性的变化
Fig. 4. Changes of AGPase activity of superior and inferior grains under low temperature treatment during grain filling period.
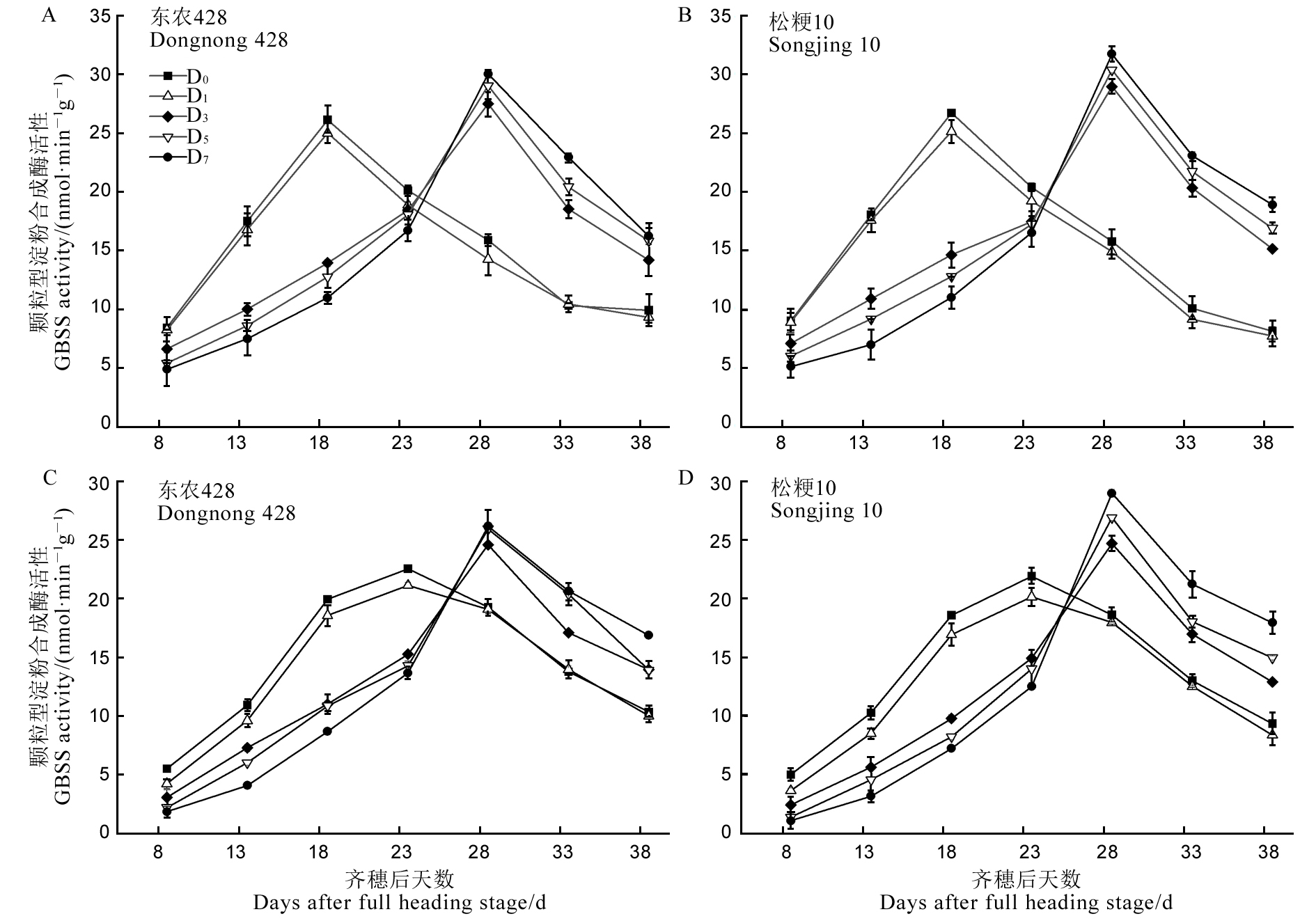
图5 结实期低温胁迫下强、弱势粒GBSS活性的变化
Fig. 5. Changes of GBSS activity of superior and inferior grains under low temperature treatment during grain filling period.
| 粒位 Grain position | 参数 Parameters | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | 松粳10 Songjing 10 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直链淀粉 含量 Amylose content | 支链淀粉 含量 Amylopectin content | 总淀粉 含量 Total starch content | 直链淀粉 含量 Amylose content | 支链淀粉 含量 Amylopectin content | 总淀粉 含量 Total starch content | ||||
| 强势粒 Superior grains | 直链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylose | 0.968** | 0.978** | ||||||
| 支链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylopectin | −0.825 | 0.977** | −0.869 | 0.984** | |||||
| 总淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of total starch | −0.762 | 0.962** | 0.998** | −0.857 | 0.945* | 0.958* | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 直链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylose | 0.947* | 0.983** | ||||||
| 支链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylopectin | 0.564 | −0.349 | 0.497 | 0.464 | |||||
| 总淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of total starch | 0.435 | −0.259 | 0.065 | 0.553 | 0.023 | 0.326 | |||
表4 淀粉含量与最大积累速率之间的相关分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis between starch content and maximum accumulation rate.
| 粒位 Grain position | 参数 Parameters | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | 松粳10 Songjing 10 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直链淀粉 含量 Amylose content | 支链淀粉 含量 Amylopectin content | 总淀粉 含量 Total starch content | 直链淀粉 含量 Amylose content | 支链淀粉 含量 Amylopectin content | 总淀粉 含量 Total starch content | ||||
| 强势粒 Superior grains | 直链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylose | 0.968** | 0.978** | ||||||
| 支链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylopectin | −0.825 | 0.977** | −0.869 | 0.984** | |||||
| 总淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of total starch | −0.762 | 0.962** | 0.998** | −0.857 | 0.945* | 0.958* | |||
| 弱势粒 Inferior grains | 直链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylose | 0.947* | 0.983** | ||||||
| 支链淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of amylopectin | 0.564 | −0.349 | 0.497 | 0.464 | |||||
| 总淀粉最大积累速率 Maximum accumulation rate of total starch | 0.435 | −0.259 | 0.065 | 0.553 | 0.023 | 0.326 | |||
| 积累速率 Accumulation rate | 参数 Parameter | 齐穗后天数 DAFH/d | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | 松粳10 Songjing 10 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase | GBSS | SSS | SBE | AGPase | GBSS | SSS | SBE | ||||
| 总淀粉积累速率 Total starch accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.913* | 0.982** | 0.892* | 0.964** | 0.968** | 0.882* | 0.979** | 0.969** | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | −0.431 | −0.224 | 0.590 | 0.738 | 0.076 | −0.328 | 0.065 | 0.148 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.964** | 0.732 | 0.772 | 0.865 | −0.508 | 0.964** | −0.628 | 0.934* | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.242 | 0.608 | −0.385 | −0.132 | 0.642 | 0.951** | 0.876 | −0.521 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | −0.352 | −0.143 | 0.484 | 0.956** | −0.856 | −0.339 | 0.886* | 0.905* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | 0.199 | 0.679 | 0.772 | −0.706 | −0.845 | 0.848 | 0.886* | 0.857 | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.885* | 0.889* | 0.877 | 0.418 | 0.918* | 0.966** | 0.891* | −0.216 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.800 | 0.788 | 0.955** | 0.930* | 0.831 | 0.922* | 0.971** | 0.868 | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.777 | 0.763 | 0.966** | 0.215 | 0.874 | 0.876 | 0.924* | 0.359 | ||
| R4 | 28~28 | 0.090 | 0.979** | −0.827 | 0.861 | −0.704 | 0.992** | −0.967* | 0.890* | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | 0.679 | −0.884* | 0.753 | 0.936* | 0.480 | −0.915* | 0.877 | −0.772 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | 0.491 | −0.514 | 0.604 | 0.968** | −0.065 | 0.255 | 0.016 | 0.986** | ||
| 直链淀粉积累速率 Amylose accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.940* | 0.955* | 0.925* | 0.932* | 0.972** | 0.945* | 0.941* | 0.976** | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | 0.033 | 0.698 | −0.849 | −0.824 | −0.420 | −0.022 | −0.516 | −0.081 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.904* | 0.883* | 0.866 | 0.772 | −0.259 | 0.911* | −0.699 | 0.843 | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.108 | 0.998** | −0.888* | −0.834 | 0.564 | 0.972** | 0.846 | −0.545 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | 0.694 | 0.897* | −0.665 | −0.740 | 0.413 | 0.904* | −0.130 | −0.930* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | −0.392 | −0.826 | −0.930* | 0.949* | 0.473 | −0.213 | 0.137 | −0.521 | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.855 | 0.950* | 0.888* | 0.118 | 0.921* | 0.951** | 0.945* | −0.288 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.893* | 0.942* | 0.790 | 0.826 | 0.792 | 0.981** | 0.986** | 0.889* | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.839 | 0.987** | 0.653 | 0.026 | 0.767 | 0.891* | 0.095 | 0.505 | ||
| R4 | 23~28 | −0.030 | 0.996** | −0.769 | 0.798 | −0.812 | 0.943* | −0.887* | 0.774 | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | −0.355 | 0.248 | −0.486 | −0.136 | −0.764 | 0.900* | −0.838 | 0.830 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | −0.174 | 0.972** | −0.609 | −0.223 | −0.226 | 0.931* | −0.318 | 0.188 | ||
| 支链淀粉积累速率 Amylopectin accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.785 | 0.795 | 0.990** | 0.761 | 0.949* | 0.845 | 0.974** | 0.949* | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | −0.593 | 0.102 | 0.977** | 0.473 | 0.279 | −0.323 | 0.913* | 0.190 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.750 | 0.447 | 0.906* | 0.899* | −0.613 | 0.956* | −0.571 | 0.945* | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.120 | −0.931* | 0.821 | 0.924* | 0.776 | 0.882* | 0.910* | −0.458 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | −0.396 | −0.613 | 0.883* | 0.902* | −0.871 | −0.458 | 0.902* | 0.904* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | 0.281 | 0.899* | 0.981** | −0.899* | −0.710 | 0.985** | 0.660 | 0.970** | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.880* | 0.861 | 0.862 | 0.483 | 0.911* | 0.966** | 0.867 | −0.189 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.670 | 0.617 | 0.998** | 0.932* | 0.836 | 0.883* | 0.951** | 0.847 | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.683 | 0.609 | 0.997** | 0.267 | 0.879* | 0.833 | 0.887* | 0.215 | ||
| R4 | 23~28 | 0.724 | 0.601 | −0.910* | 0.956** | −0.253 | 0.874 | −0.935* | 0.969** | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | 0.782 | −0.953** | 0.894* | 0.972** | 0.533 | −0.940* | 0.897* | −0.803 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | 0.485 | −0.587 | 0.636 | 0.943* | 0.094 | −0.065 | 0.100 | 0.866 | ||
表5 淀粉积累速率与酶活性变化的相关分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis of starch accumulation rate and enzyme activity change.
| 积累速率 Accumulation rate | 参数 Parameter | 齐穗后天数 DAFH/d | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | 松粳10 Songjing 10 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase | GBSS | SSS | SBE | AGPase | GBSS | SSS | SBE | ||||
| 总淀粉积累速率 Total starch accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.913* | 0.982** | 0.892* | 0.964** | 0.968** | 0.882* | 0.979** | 0.969** | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | −0.431 | −0.224 | 0.590 | 0.738 | 0.076 | −0.328 | 0.065 | 0.148 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.964** | 0.732 | 0.772 | 0.865 | −0.508 | 0.964** | −0.628 | 0.934* | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.242 | 0.608 | −0.385 | −0.132 | 0.642 | 0.951** | 0.876 | −0.521 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | −0.352 | −0.143 | 0.484 | 0.956** | −0.856 | −0.339 | 0.886* | 0.905* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | 0.199 | 0.679 | 0.772 | −0.706 | −0.845 | 0.848 | 0.886* | 0.857 | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.885* | 0.889* | 0.877 | 0.418 | 0.918* | 0.966** | 0.891* | −0.216 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.800 | 0.788 | 0.955** | 0.930* | 0.831 | 0.922* | 0.971** | 0.868 | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.777 | 0.763 | 0.966** | 0.215 | 0.874 | 0.876 | 0.924* | 0.359 | ||
| R4 | 28~28 | 0.090 | 0.979** | −0.827 | 0.861 | −0.704 | 0.992** | −0.967* | 0.890* | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | 0.679 | −0.884* | 0.753 | 0.936* | 0.480 | −0.915* | 0.877 | −0.772 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | 0.491 | −0.514 | 0.604 | 0.968** | −0.065 | 0.255 | 0.016 | 0.986** | ||
| 直链淀粉积累速率 Amylose accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.940* | 0.955* | 0.925* | 0.932* | 0.972** | 0.945* | 0.941* | 0.976** | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | 0.033 | 0.698 | −0.849 | −0.824 | −0.420 | −0.022 | −0.516 | −0.081 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.904* | 0.883* | 0.866 | 0.772 | −0.259 | 0.911* | −0.699 | 0.843 | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.108 | 0.998** | −0.888* | −0.834 | 0.564 | 0.972** | 0.846 | −0.545 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | 0.694 | 0.897* | −0.665 | −0.740 | 0.413 | 0.904* | −0.130 | −0.930* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | −0.392 | −0.826 | −0.930* | 0.949* | 0.473 | −0.213 | 0.137 | −0.521 | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.855 | 0.950* | 0.888* | 0.118 | 0.921* | 0.951** | 0.945* | −0.288 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.893* | 0.942* | 0.790 | 0.826 | 0.792 | 0.981** | 0.986** | 0.889* | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.839 | 0.987** | 0.653 | 0.026 | 0.767 | 0.891* | 0.095 | 0.505 | ||
| R4 | 23~28 | −0.030 | 0.996** | −0.769 | 0.798 | −0.812 | 0.943* | −0.887* | 0.774 | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | −0.355 | 0.248 | −0.486 | −0.136 | −0.764 | 0.900* | −0.838 | 0.830 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | −0.174 | 0.972** | −0.609 | −0.223 | −0.226 | 0.931* | −0.318 | 0.188 | ||
| 支链淀粉积累速率 Amylopectin accumulation rate | 强势粒Superior grains | ||||||||||
| Q1 | 8~13 | 0.785 | 0.795 | 0.990** | 0.761 | 0.949* | 0.845 | 0.974** | 0.949* | ||
| Q2 | 13~18 | −0.593 | 0.102 | 0.977** | 0.473 | 0.279 | −0.323 | 0.913* | 0.190 | ||
| Q3 | 18~23 | −0.750 | 0.447 | 0.906* | 0.899* | −0.613 | 0.956* | −0.571 | 0.945* | ||
| Q4 | 23~28 | −0.120 | −0.931* | 0.821 | 0.924* | 0.776 | 0.882* | 0.910* | −0.458 | ||
| Q5 | 28~33 | −0.396 | −0.613 | 0.883* | 0.902* | −0.871 | −0.458 | 0.902* | 0.904* | ||
| Q6 | 33~38 | 0.281 | 0.899* | 0.981** | −0.899* | −0.710 | 0.985** | 0.660 | 0.970** | ||
| 弱势粒Inferior grains | |||||||||||
| R1 | 8~13 | 0.880* | 0.861 | 0.862 | 0.483 | 0.911* | 0.966** | 0.867 | −0.189 | ||
| R2 | 13~18 | 0.670 | 0.617 | 0.998** | 0.932* | 0.836 | 0.883* | 0.951** | 0.847 | ||
| R3 | 18~23 | 0.683 | 0.609 | 0.997** | 0.267 | 0.879* | 0.833 | 0.887* | 0.215 | ||
| R4 | 23~28 | 0.724 | 0.601 | −0.910* | 0.956** | −0.253 | 0.874 | −0.935* | 0.969** | ||
| R5 | 28~33 | 0.782 | −0.953** | 0.894* | 0.972** | 0.533 | −0.940* | 0.897* | −0.803 | ||
| R6 | 33~38 | 0.485 | −0.587 | 0.636 | 0.943* | 0.094 | −0.065 | 0.100 | 0.866 | ||
| 年份 Year | 品种/处理Variety /Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per hill | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | ||||||||
| D0 | 13.96 a | 101.37 a | 93.02 a | 23.49 a | 7728.81 a | ||||
| D1 | 13.03 a | 100.90 a | 91.79 b | 23.40 a | 7058.57 b | ||||
| D3 | 12.85 a | 99.83 a | 87.82 c | 22.47 b | 6328.40 c | ||||
| D5 | 13.23 a | 99.87 a | 84.05 d | 20.93 c | 5811.78 d | ||||
| D7 | 12.88 a | 99.97 a | 81.58 e | 19.67 d | 5164.90 e | ||||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | |||||||||
| D0 | 12.86 a | 99.57 a | 92.74 a | 22.84 a | 6781.19 a | ||||
| D1 | 12.20 a | 99.07 a | 89.27 b | 21.65 b | 5838.55 b | ||||
| D3 | 11.82 a | 98.90 a | 86.74 c | 20.58 c | 5217.13 c | ||||
| D5 | 12.16 a | 98.52 a | 81.28 d | 19.11 d | 4651.47 d | ||||
| D7 | 11.68 a | 97.67 a | 78.31 e | 18.35 e | 4097.28 e | ||||
| 2021 | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | ||||||||
| D0 | 13.26 a | 99.59 a | 95.25 a | 23.17 a | 7286.92 a | ||||
| D1 | 12.83 a | 99.02 a | 92.79 b | 22.84 a | 6729.61 b | ||||
| D3 | 12.85 a | 98.93 a | 86.57 c | 21.80 b | 5997.54 c | ||||
| D5 | 13.03 a | 98.77 a | 83.07 d | 20.93 c | 5593.39 d | ||||
| D7 | 12.68 a | 98.25 a | 80.84 e | 19.38 d | 4899.06 e | ||||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | |||||||||
| S0 | 13.09 a | 98.71 a | 93.67 a | 22.92 a | 6934.78 a | ||||
| S1 | 12.86 a | 98.20 a | 90.08 b | 21.69 b | 6168.00 b | ||||
| S3 | 12.72 a | 98.06 a | 85.26 c | 20.14 c | 5353.79 c | ||||
| S5 | 12.96 a | 98.01 a | 80.65 d | 19.04 d | 4876.06 d | ||||
| S7 | 12.48 a | 97.67 a | 77.14 e | 18.03 e | 4237.58 e | ||||
表6 结实期低温胁迫对水稻产量构成因素的影响
Table 6. Effect of low temperature stress on rice yield components during grain filling period.
| 年份 Year | 品种/处理Variety /Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per hill | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | ||||||||
| D0 | 13.96 a | 101.37 a | 93.02 a | 23.49 a | 7728.81 a | ||||
| D1 | 13.03 a | 100.90 a | 91.79 b | 23.40 a | 7058.57 b | ||||
| D3 | 12.85 a | 99.83 a | 87.82 c | 22.47 b | 6328.40 c | ||||
| D5 | 13.23 a | 99.87 a | 84.05 d | 20.93 c | 5811.78 d | ||||
| D7 | 12.88 a | 99.97 a | 81.58 e | 19.67 d | 5164.90 e | ||||
| 松粳10 Songjing 10 | |||||||||
| D0 | 12.86 a | 99.57 a | 92.74 a | 22.84 a | 6781.19 a | ||||
| D1 | 12.20 a | 99.07 a | 89.27 b | 21.65 b | 5838.55 b | ||||
| D3 | 11.82 a | 98.90 a | 86.74 c | 20.58 c | 5217.13 c | ||||
| D5 | 12.16 a | 98.52 a | 81.28 d | 19.11 d | 4651.47 d | ||||
| D7 | 11.68 a | 97.67 a | 78.31 e | 18.35 e | 4097.28 e | ||||
| 2021 | 东农428 Dongnong 428 | ||||||||
| D0 | 13.26 a | 99.59 a | 95.25 a | 23.17 a | 7286.92 a | ||||
| D1 | 12.83 a | 99.02 a | 92.79 b | 22.84 a | 6729.61 b | ||||
| D3 | 12.85 a | 98.93 a | 86.57 c | 21.80 b | 5997.54 c | ||||
| D5 | 13.03 a | 98.77 a | 83.07 d | 20.93 c | 5593.39 d | ||||
| D7 | 12.68 a | 98.25 a | 80.84 e | 19.38 d | 4899.06 e | ||||
| 松梗10 Songjing 10 | |||||||||
| S0 | 13.09 a | 98.71 a | 93.67 a | 22.92 a | 6934.78 a | ||||
| S1 | 12.86 a | 98.20 a | 90.08 b | 21.69 b | 6168.00 b | ||||
| S3 | 12.72 a | 98.06 a | 85.26 c | 20.14 c | 5353.79 c | ||||
| S5 | 12.96 a | 98.01 a | 80.65 d | 19.04 d | 4876.06 d | ||||
| S7 | 12.48 a | 97.67 a | 77.14 e | 18.03 e | 4237.58 e | ||||
| [1] | 周明旭. 黑龙江省水稻生产可持续发展研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. |
| Zhou M X. Study on sustainable development of rice production in heilongjiang province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Shimono H, Okada M, Kanda E, Arakawa I. Low temperature-induced sterility in rice: Evidence for the effects of temperature before panicle initiation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 101(2): 221-231. |
| [3] | 王主玉, 申双和. 水稻低温冷害研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 22: 11971-11973. |
| Wang Z Y, Shen S H. Research progress on low temperature and chilling injury of rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 22: 11971-11973. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Zhang J, Dong P, Zhang H Y, Meng C R, Zhang X J, Hou J W, Wei C Z. Low soil temperature reducing the yield of drip irrigated rice in arid area by influencing anther development and pollination[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2019, 11(3): 103-114. |
| [5] | 窦志. 灌浆期开放式增温对水稻籽粒灌浆和品质的影响及氮素粒肥的调控效应[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. |
| Dou Z. Effects of Free-air during grain filling stage on grain filling and quality of rice and regulation effect of nitrogen spikelet fertilizer[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 张荣萍, 马均, 王贺正, 李艳, 李旭毅, 汪仁全. 不同灌水方式对水稻籽粒灌浆特性的影响[J]. 西昌学院学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 21(4): 23-27. |
| Zhang R P, Ma J, Wang H Z, Li Y, Li X Y, Wang R Q. Effects of different irrigation methods on grain filling characteristics of rice[J]. Journal of Xichang University: Natural Science Edition, 2007, 21(4): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 黄锦文, 梁义元, 梁康迳, 林文雄. 不同类型水稻籽粒灌浆的生理生化特性研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2003, 11(1): 10-13. |
| Huang J W, Liang Y Y, Liang K J, Lin W X. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of grain filling in different types of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2003, 11(1): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 徐富贤, 郭晓艺, 张林, 熊洪, 朱永川, 刘茂, 周兴兵. 杂交中稻库源结构对弱势粒灌浆结实的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2013, 15(1): 96-101. |
| Xu F X, Guo X Y, Zhang L, Xiong H, Zhu Y C, Liu M, Zhou X B. Effects of sink-source structure of hybrid middle rice on grain filling of weak grains[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013, 15(1): 96-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 谈桂露, 张耗, 付景, 王志琴, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 超级稻花后强、弱势粒多胺浓度变化及其与籽粒灌浆的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(12): 2225-2233. |
| Tan G L, Zhang H, Fu J, Wang Z Q, Liu L J, Yang J C. Variation of polyamine concentration in strong and weak grains of super rice after flowering and its relationship with grain filling[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(12): 2225-2233. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 杨建昌, 袁莉民, 唐成, 王志琴, 刘立军, 朱庆森. 结实期干湿交替灌溉对稻米品质及籽粒中一些酶活性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(8): 1052-1057. |
| Yang J C, Yuan L M, Tang C, Wang Z Q, Liu L J, Zhu Q S. Effects of alternate wet and dry irrigation on rice quality and some enzyme activities in grain[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2005, 31(8): 1052-1057. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Du X D, Zhao H W, Wang J G, Liu H L, Yang L, Xu J, Song J T. Changes in starch accumulation and activity of enzymes associated with starch synthesis under different nitrogen applications in Japonica rice in cold region[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(1): 159-167. |
| [12] | Yan Z, Ding J, Song J, Humphreys G, Peng Y X, Li C Y, Zhu X K, Guo W S. Author correction: Grain yield, starch content and activities of key enzymes of waxy and non-waxy wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 12-16. |
| [13] | 胡博文, 谷娇娇, 贾琰, 沙汉景, 张君颜, 黄书勤, 赵宏伟. 盐胁迫对寒地粳稻籽粒淀粉形成积累及产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(1): 119-127. |
| Hu B W, Gu J J, Jia Y, Sha H J, Zhang J Y, Huang S Q, Zhao H W. Effects of salt stress on grain starch formation, accumulation and yield of japonica rice in cold regions[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(1): 119-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Maung T Z, Yoo J M, Chu S H, Kim K W, Chung I M, Park Y J. Haplotype variations and evolutionary analysis of the granule-bound starch synthase I gene in the Korean World Rice Collection[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12(1708): 707237. |
| [15] | 刘奇华, 蔡建, 李天. 水稻籽粒中的淀粉合成关键酶及其与籽粒灌浆和稻米品质的关系[J]. 植物生理学报, 2006, 42(6): 1211-1216. |
| Liu Q H, Cai J, Li T. Key enzymes of starch synthesis in rice grains and their relationship with grain filling and rice quality[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2006, 42(6): 1211-1216. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Liu J, Qian Z, Zhou L, Cao Z Z, Shi C H, Cheng F M. Influence of environmental temperature during grain filling period on granule size distribution of rice starch and its relation to gelatinization properties[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2017, 76: 42-55 |
| [17] | Kato T, Shinmura D, Taniguchi A. Activities of enzymes for sucrose-starch conversion in developing endosperm of rice and their association with grain filling in extra-heavy panicle types[J]. Plant Production Science, 2007, 10(4): 442-450. |
| [18] | 夏楠, 赵宏伟, 吕艳超, 赵振东, 邹德堂, 刘化龙, 王敬国, 贾琰. 灌浆结实期冷水胁迫对寒地粳稻籽粒淀粉积累及相关酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(1): 62-74. |
| Xia N, Zhao H W, Lv Y C, Zhao Z D, Zou D T, Liu H L, Wang J G, Jia Y. Effects of cold water stress on grain starch accumulation and related enzyme activities of japonica rice in cold regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(1): 62-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 沈鹏, 金正勋, 罗秋香, 金学泳, 孙艳丽. 水稻灌浆过程中籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性与蒸煮食味品质的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(1): 58-64. |
| Shen P, Jin Z X, Luo Q X, Jin X Y, Sun Y L. The relationship between key enzyme activities of grain starch synthesis and cooking and eating quality during rice filling process[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(1): 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 宋兴年. 夜间温度对水稻弱势籽粒灌浆充实的作用机制研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2011. |
| Song X N. Mechanism of nighttime temperature on grain filling and enrichment of weak grains in rice[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 钟连进, 程方民. 水稻籽粒灌浆过程直链淀粉的积累及其相关酶的品种类型间差异[J]. 作物学报, 2003, 29(3): 452-456. |
| Zhong L J, Cheng F M. The accumulation of amylose during grain filling in rice and the differences in related enzymes among cultivars[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2003, 29(3): 452-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 王士强, 宋晓慧, 赵海红, 孙明明, 萧长亮, 顾春梅, 那永光, 解保胜, 曹立勇, 程式华. 孕穗期低温胁迫对寒地水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2016, 37(3): 579-586. |
| Wang S Q, Song X H, Zhao H H, Sun M M, Xiao C L, Gu C M, Na Y G, Xie B S, Cao L Y, Cheng S H. Effects of low temperature stress at booting stage on yield and quality of rice in cold regions[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2016, 37(3): 579-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王艳华. 持续低温对沈阳地区水稻的影响及品种搭配决策研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2013. |
| Wang Y H. Effects of persistent low temperature on rice in Shenyang area and research on variety combination decision[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Ali I, Tang L, Dai J. Responses of grain yield and yield related parameters to post-heading low-temperature stress in Japonica rice[J]. Plants, 2021, 10(7): 1425. |
| [25] | 付景, 徐云姬, 陈露, 袁莉民, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 超级稻花后强、弱势粒淀粉合成相关酶活性和激素含量变化及其与籽粒灌浆的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3): 302-310. |
| Fu J, Xu Y J, Chen L, Yuan L M, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Changes of enzyme activities and hormone contents related to starch synthesis in strong and weak grains of super rice after flowering and their relationship with grain filling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(3): 302-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 沈直, 唐设, 张海祥, 陈文珠, 丁艳锋, 王绍华. 灌浆期开放式增温对水稻强势粒和弱势粒淀粉代谢关键酶相关基因表达水平的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39: 906. |
| Shen Z, Tang S, Zhang H Y, Chen W Z, Ding Y F, Wang S H. Effects of open warming at grain filling stage on the expression levels of genes related to key enzymes in starch metabolism in superior and inferior grains of rice[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016, 39: 906. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 李健陵, 霍治国, 吴丽姬, 朱庆华, 胡飞. 孕穗期低温对水稻产量的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3): 277-288. |
| Li J L, Huo Z G, Wu L J, Zhu Q H, Hu F. Effects of low temperature at booting stage on rice yield and its physiological mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(3): 277-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Seyede S, Fallah A. Corrigendum to "temperature effect on yield and yield components of different rice cultivars in flowering stage"[J]. International Journal of Agronomy, 2020, 2020: 1-1. |
| [29] | 韩涛. 孕穗期冷水胁迫对水稻碳水化合物形成积累规律的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2014. |
| Han T. Booting stage cold water stress on rice carbohydrates form accumulation pattern[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 武琦. 不同生育时期低温胁迫下寒地粳稻淀粉积累规律的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2013. |
| Wu Q. Research on starch accumulation rule in different growth stages of japonica rice in cold region[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 何照范. 谷物淀粉组份分离及测试方法评述[J]. 粮食储藏, 1985, 6: 32-38. |
| He Z F. Review on separation and testing methods of grain starch components[J]. Grain Storage, 1985, 6: 32-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 李太贵, 沈波, 陈能, 罗玉坤. Q酶在水稻籽粒垩白形成中作用的研究[J]. 作物学报, 1997, 23(3): 338-344. |
| Li T G, Shen B, Chen N, Luo Y K. Study on the role of Q enzyme in the formation of chalky rice grains[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1997, 23(3): 338-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Doehlert D C, Kuo T M, Felker F C. Enzymes of sucrose and hexose metabolism in developing kernels of two inbreds of maize[J]. Plant Physiology, 1988, 86(4): 1013-1019. |
| [34] | 程方民, 蒋德安, 吴平, 石春海. 早籼稻籽粒灌浆过程中淀粉合成酶的变化及温度效应特征[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(2): 201-206. |
| Cheng F M, Jiang D A, Wu P, Shi C H. Changes and temperature effects of starch synthase during grain filling in early indica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(2): 201-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 杨志奇, 杨春刚, 汤翠凤, 郭桂珍, 余腾琼, 张俊国, 曹桂兰, 阿新祥, 徐福荣, 张三元, 戴陆园, 韩龙植. 中国粳稻地方品种孕穗期耐冷性评价及聚类分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(4): 485-491. |
| Yang Z Q, Yang C G, Yang C F, Guo G Z, Yu T Q, Zhang J G, Cao G L, A X F, Xu F R, Zhang S Y, Dai L Y, Han L Z. Evaluation and cluster analysis of cold tolerance of Chinese japonica rice landraces at booting stage[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2008, 9(4): 485-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 张文倩. 昼夜高温对水稻颖花发育及籽粒结实的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019. |
| Zhang W Q. Effects of day and night high temperature on rice spikelet development and grain setting[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Yang J, Peng S, Visperas R M. Grain filling pattern and cytokinin content in the grains and roots of rice plants[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2000, 30(3): 261-270. |
| [38] | 王新鹏. 孕穗期干旱胁迫对寒地粳稻碳代谢及产量形成影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020. |
| Wang X P. Effects of drought stress at booting stage on carbon metabolism and yield formation of japonica rice in cold regions[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Hu Y, Li L, Tian J. Effects of dynamic low temperature during the grain filling stage on starch morphological structure, physicochemical properties, and eating quality of soft japonica rice[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2020, 97(2): 540-550. |
| [40] | 李晓光, 刘海英, 金正勋, 刘洪亮, 黄星, 徐美兰. 水稻杂交后代灌浆成熟期籽粒淀粉合成关键酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性变化的初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 4: 443-446. |
| Li X G, Liu H Y, Jin Z X, Liu H L, Huang X, Xu M L. Preliminary study on the changes of key enzymes in grain starch synthesis and glutamine synthase activities during grain filling and maturity of rice hybrid offspring[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 4: 443-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 李银银, 陈静, 周群, 许更文, 芮梦凯, 徐心杰, 张耗. 水稻籽粒灌浆的研究进展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(4): 20-24. |
| Li Y Y, Chen J, Zhou Q, Xu G W, Rui M K, Xu X J, Zhang H. Research progress and prospect of rice grain filling[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(4): 20-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | Weng F, Zhang W, Wu X. Impact of low-temperature, overcast and rainy weather during the reproductive growth stage on lodging resistance of rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 9983-10004. |
| [43] | 郭连安, 胡运高, 杨国涛, 鄢圣敏, 易军. 不同直链淀粉含量水稻籽粒淀粉积累及其相关酶的活性变化研究[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 36(6): 942-949. |
| Guo L A, Hu Y G, Yang G T, Yan S M, Yi J. Study on the accumulation of starch in rice grains with different amylose contents and changes in the activities of related enzymes[J]. Journal of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2014, 36(6): 942-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 金正勋, 杨静, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金学泳, 秋太权. 灌浆成熟期温度对水稻籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. |
| Jin Z X, Yang J, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin X Y, Qiu T Q. Effects of temperature at grain filling maturity on the activities and quality of key enzymes for starch synthesis in rice grains[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 王军可, 王亚梁, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯, 朱德峰, 张玉屏. 灌浆初期高温影响水稻籽粒碳氮代谢的机理[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(12): 32-42. |
| Wang J K, Wang Y L, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K, Zhu D F, Zhang Y P. Mechanism of high temperature affecting rice grain carbon and nitrogen metabolism at the early stage of grain filling[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(12): 32-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | Hao Z, Li H W, Yang L M. Post-anthesis alternate wetting and moderate soil drying enhances activities of key enzymes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in inferior spikelets of rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(1): 215-227. |
| [47] | Chen L, Deng Y, Zhu H L, Hu Y X, Jiang Z G, Tang S, Wang S H, Ding Y F. The initiation of inferior grain filling is affected by sugar translocation efficiency in large panicle rice.[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 75. |
| [48] | 朱红. 抽穗后低温胁迫对水稻若干生理特性的影响[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2015. |
| Zhu H. Effects of low temperature stress after heading on some physiological characteristics of rice[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 杨建昌, 彭少兵, 顾世梁, Visperas R M. 水稻灌浆期籽粒中3个与淀粉合成有关的酶活性变化[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(2): 157-164. |
| Yang J C, Peng S B, Gu S L, Visperas R M. Changes in the activities of three enzymes related to starch synthesis in rice grains at grain filling stage[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(2): 157-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | 赵步洪, 张文杰, 常二华, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻灌浆期籽粒中淀粉合成关键酶的活性变化及其与灌浆速率和蒸煮品质的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004(8): 1123-1129. |
| Zhao B H, Zhang W J, Chang E H, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Activity changes of key enzymes in starch synthesis in rice grains during grain filling and their relationship with grain filling rate and cooking quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004(8): 1123-1129. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | Dobo M, Ayres N, Walker G. Polymorphism in the GBSS gene affects amylose content in US and European rice germplasm[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2010, 52(3): 450-456. |
| [52] | Du X D, Zhao H W, Wang J G. Changes in starch accumulation and activity of enzymes associated with starch synthesis under different nitrogen applications in japonica rice in cold region[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(1): 159-167. |
| [53] | 徐云姬. 三种禾谷类作物强、弱势粒灌浆差异机理及其调控技术[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016. |
| Xu Y J. Mechanisms of grain filling differences between strong and weak grains of three cereal crops and their control techniques[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | Okamura M, Arai-sanoh Y, Yoshida H. Characterization of high-yielding rice cultivars with different grain-filling properties to clarify limiting factors for improving grain yield[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 219, 139-147. |
| [55] | Ahmadi A, Baker D A. The effect of water stress on the activities of key regulatory enzymes of the sucrose to starch pathway in wheat[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2001, 35(1): 81-91. |
| [56] | 朱宽宇, 展明飞, 陈静, 王志琴, 杨建昌, 赵步洪. 不同氮肥水平下结实期灌溉方式对水稻弱势粒灌浆及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(2): 155-168. |
| Zhu K Y, Zhan M F, Chen J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhao B H. Effects of irrigation methods at fruiting stage on grain filling and yield of weak grains in rice under different nitrogen fertilizer levels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(2): 155-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [57] | 张诚信. 灌浆结实期低温弱光复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. |
| Zhang C X. Effects of low temperature and low light compound stress on rice yield and quality at grain filling stage[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [58] | Tanno H, Kiuchi H, Hirayama Y, Kikuchi H. Development of a simple testing method for cool weather tolerance at the flowering stage of rice using an air conditioned room[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 2000, 69(1): 43-48. |
| [59] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 潘晓华, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张义凯. 花后低温对水稻籽粒灌浆与内源激素含量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1551-1559. |
| Zeng Y H, Zhang Y P, Pan X H, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y K. Effects of low temperature after flowering on grain filling and endogenous hormone content in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1551-1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [60] | Chu G, Wang Z, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Agronomic and physiological performance of rice under integrative crop management[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2016, 108(1): 117-128. |
| [61] | Xue Y, Duan H, Liu L, Xue Y, Duan H, Liu L,. An improved crop management increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in rice[J]. Crop Science, 2013, 53(1): 271-284. |
| [62] | Fang M S, Song J B, Yang L M, Fan M, Shen J, Yuan L, Jiang R, Chen X, Davies W J, Zhang F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(1): 13-24. |
| [63] | Chand J U, Abhishek B, Rintu J. Breeding approaches and genomics technologies to increase crop yield under low-temperature stress.[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2017, 36(1): 1-35. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||