
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 227-236.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210705
收稿日期:2021-07-13
修回日期:2021-08-24
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
王才林
基金资助:
YAO Shu, ZHANG Yadong, LU Kai, WANG Cailin( )
)
Received:2021-07-13
Revised:2021-08-24
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
WANG Cailin
摘要:
水稻淀粉合成对稻米品质的影响研究一直备受关注,是水稻基础科学研究的热点和难点之一。淀粉合成途径受众多酶催化调控,可溶性淀粉合成酶(soluble starch synthase, SSS)是其中较重要的一种,极大地影响稻米食味品质的形成。可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和SSⅢa是控制稻米糊化温度和胚乳支链淀粉生物合成途径中的两个关键基因。本文重点回顾并归纳了国内外关于SSⅡa和SSⅢa基因的功能、等位变异及其互作对稻米蒸煮食味品质影响的最新研究进展,同时对SSⅡa和SSⅢa基因的育种利用前景进行了展望,以期为稻米品质分子改良和育种提供参考依据。
姚姝, 张亚东, 路凯, 王才林. 水稻可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和SSⅢa的功能、等位变异及其互作研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 227-236.
YAO Shu, ZHANG Yadong, LU Kai, WANG Cailin. Progress in Functions, Allelic Variations and Interactions of Soluble Starch Synthases Genes SSⅡa and SSⅢa in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 227-236.
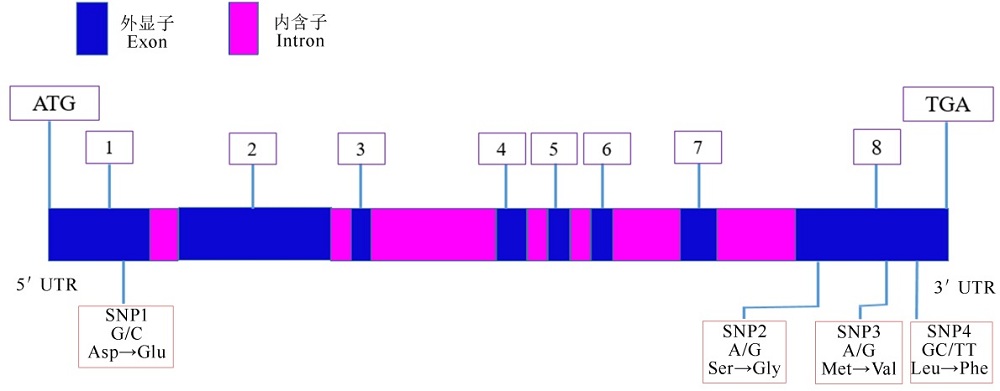
图1 水稻淀粉合成酶基因SSIIa的结构示意图(包括外显子,内含子及SNP)
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the gene that codes for rice starch synthase IIa (SSIIa) (showing the positions of exons, introns and single nucleotide polymorphisms).
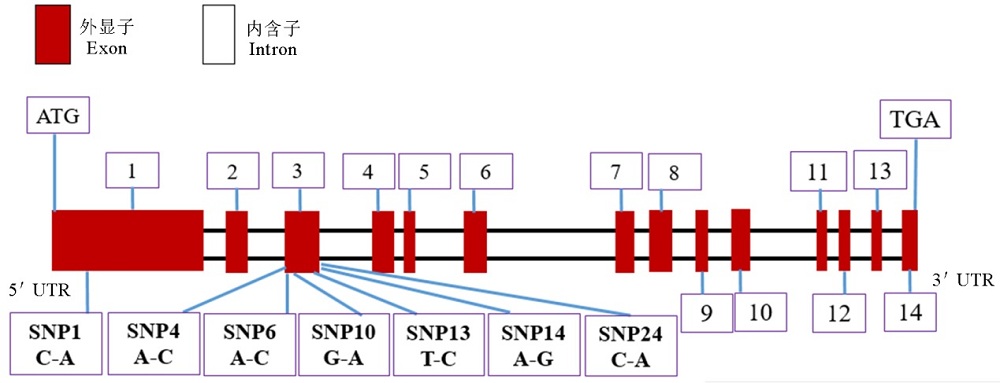
图2 水稻淀粉合成酶基因SSIIIa结构示意图(包括外显子,内含子及部分SNP)
Fig. 2. Schematic representation of the gene that codes for rice starch synthase IIIa (SSIIIa) (showing the positions of exons, introns and single nucleotide polymorphisms).
| [1] | Gadal N, Shrestha J, Poudel M N, Pokhrel B. A review on production status and growing environments of rice in Nepal and in the world[J]. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 2019, 4(1): 83-87. |
| [2] | 吴比, 胡伟, 邢永忠. 中国水稻遗传育种历程与展望[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(10): 841-857. |
| Wu B, Hu W, Xing Y Z. The history and prospect of rice genetic breeding in China[J]. Hereditas, 2018, 40(10): 841-857. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhong W G, Yang J, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Li Y S. Research progress on the breeding of japonica super rice varieties in Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(5): 992-999. |
| [4] | Fei C, Xu Q, Xu Z J, Chen W F. Effect of rice breeding process on improvement of yield and quality in China[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 363-367. |
| [5] | 张昌泉, 赵冬生, 李钱峰, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 稻米品质性状基因的克隆与功能研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283. |
| Zhang C Q, Zhao D S, Li Q F, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progresses in research on cloning and functional analysis of key genes involving in rice grain quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283.. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 张昌泉, 冯琳皓, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 江苏省水稻品质性状遗传和重要基因克隆研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(5): 425-441. |
| Zhang C Q, Ma L H, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progress on inheritance and gene cloning for rice grain quality in Jiangsu province[J]. Hereditas, 2021, 43(5): 425-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 康艺维, 陈玉宇, 张迎信. 水稻粒型基因克隆研究进展及育种应用展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. |
| Kang Y W, Chen Y Y, Zhang Y X. Research Progress and breeding prospects of grain size associated genes in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Yang G L, Chen S P, Chen L K, Gao W W, Huang Y T, Zhou D H, Wang J F, Liu Y Z, Huang M, Xiao W M, Wang H, Guo T, Chen Z Q. Development and utilization of functional KASP markers to improve rice eating and cooking quality through MAS breeding[J]. Euphytica, 2019, 215: 66. |
| [9] | Zhang C Q, Zhu J H, Chen S G, Fan X L, Li Q F, Lu Y, Wang M, Yu H X, Yi C D, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Wx, the ancestral allele of rice waxy gene[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1157-1166. |
| [10] | 孙涛, 同拉嘎, 赵书宇, 王海微, 韩云飞, 张忠臣, 金正勋. 氮肥对水稻胚乳淀粉品质、相关酶活性及基因表达量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 475-484. |
| Sun T, Tong L G, Zhao S Y, Wang H W, Han Y F, Zhang Z C, Jin Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on starch quality, activities and gene expression levels of related enzymes in rice endosperm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 475-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 陈雅玲, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关酶的结构、功能及其互作研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 1-12. |
| Chen Y L, Bao J S, Progress in structures, functions and interactions of starch synthesis related enzymes in rice endosperm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Yang F, Chen Y L, Tong C, Huang Y, Xu F F, Li K H, Corke H, Sun M, Bao J S. Association mapping of starch physicochemical properties with starch synthesis-related gene markers in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 34(4): 1747-1763. |
| [13] | 赵春芳, 岳红亮, 黄双杰, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林. 南粳系列水稻品种的食味品质与稻米理化特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52: 909-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| Zhao C F, Yue H L, Huang S J, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Liang W H, Lu K, Wang C L. Study on eating quality and physicochemical properties in Nanjing rice varieties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52: 909-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Tian Z X, Yan C J, Qian Q. Development of gene-tagged molecular markers for starch synthesis-related genes in rice[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(66): 2591-2601. |
| [15] | Tian Z, Qian Q, Liu Q, Yan M, Liu X, Yan C, Liu G, Gao Z, Tang S, Zeng D L, Wang Y, Yu J, Gu M, Li J. Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(51): 21760-21765. |
| [16] | 姚姝, 于新, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 张亚东, 赵春芳, 赵凌, 王才林. 氮肥用量和播期对优良食味粳稻直链淀粉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 535-549. |
| Yao S, Yu X, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Zhang Y D, Zhao C F, Zhao L, Wang C L. Effects of nitrogen and sowing date on amylose content in good eating quality rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 535-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Pfister B, Zeeman S C. Formation of starch in plant cells[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2016, 73(14): 2781-2807. |
| [18] | Li C, Powell P O, Gilbert R G. Recent progress toward understanding the role of starch biosynthetic enzymes in the cereal endosperm[J]. De Gruyter, 2017, 1(1): 59-74. |
| [19] | Singh N, Kaur L, Sandhu K S, Kaur J, Nishinari K. Relationships between physicochemical, morphological, thermal, rheological properties of rice starches[J]. Food Hydrocolloid, 2006, 20(4): 532-542. |
| [20] | Jeon J S, Ryoo N, Hahn T R, Walia H, Nakamura Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2010, 48(6): 383-392. |
| [21] | Fan X Y, Guo M, Li R D, Yang Y H, Liu M, Zhu Q, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Xu R G, Yan C J. Allelic variations in the soluble starch synthase II gene family result in changes of grain quality and starch properties in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 2017, 155(1): 129-140. |
| [22] | Jiang H W, Dian W M, Liu F Y, Wu P. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of three genes encoding starch synthase II in rice[J]. Planta, 2004, 218: 1062-1070. |
| [23] | Fujita N, Yoshida M, Kondo T, Saito K, Utsumi Y, Tokunaga T, Nishi H, Satoh J H, Park J L, Jane A, Miyao A, Hirochika Y, Nakamura Y. Characterization of SSⅡa-deficient mutants of rice: The function of SSⅡa and pleiotropic effects by SSⅡa deficiency in the rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 144(4): 2009-2023. |
| [24] | Hirose T, TeraoT A. Comprehensive expression analysis of the starch synthase gene family in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Planta, 2004, 220: 9-16. |
| [25] | Chen Z Z, Lu Y, Feng L H, Hao W Z, Li C, Yang Y, Fan X L, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Liu Q Q. Genetic dissection and functional differentiation of ALKa and ALKb, two natural alleles of the ALK/SSⅡa gene, responding to low gelatinization temperature in rice[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 39. |
| [26] | Fujita N, Yoshida M, Asakura N, Ohdan T, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Nakamyra Y. Functional and characterization of starch synthase I using mutants in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140: 1070-1084. |
| [27] | Zhou H J, Wang L J, Liu G F, Meng X B, Jing Y H, Shu X L, Kong X L, Sun J, Yu H, Smith S M, Wu D X, Li J Y. Critical roles of soluble starch synthase SSⅢa and granule-bound starch synthase Waxy in synthesizing resistant starch in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(45): 12844-12849. |
| [28] | Takahashi T, Fujita N. Thermal and rheological characteristics of mutant rice starches with widespread variation of amylose content and amylopectin structure[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2017, 62: 83-93. |
| [29] | Zhu J, Zhang S, Zhang B, Qiao D, Pu H, Liu S, Li L. Structural features and thermal property of propionylated starches with different amylose/amylopectin ratio[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 97: 123-130. |
| [30] | Nakamura Y, Aihara S, Crofts N, Sawada T, Fujita N. In vitro studies of enzymatic properties of starch synthases I and interactions between starch synthase Iandstarch branching enzymes from rice[J]. Plant Science, 2014, 224: 1-8. |
| [31] | Gao Z Y, Zeng D L, Cui X, Zhou Y H, Yan M X, Huang D N, Li J Y, Qian Q. Map-based cloning of the ALK gene, which controls the gelatinization temperature of rice[J]. Science in China: Series C, 2003, 46(6): 661-668. |
| [32] | Umemoto T, Aoki N. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in rice starch synthase IIa that alter starch gelatinisation and starch association of the enzyme[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2005, 32: 763-768. |
| [33] | Wang K, Hasjim J, Wu A C, Li E, Henry R J, Gilbert R G. Roles of GBSSI and SSⅡa in determining amylose fine structure[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 127: 264-274. |
| [34] | Jiang H W, Dian W M, Wu P. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of three genes encoding starch synthaseII in rice[J]. Planta, 2004, 218: 1062-1070. |
| [35] | Huang L C, Gu Z W, Chen Z Z, Yu J W, Chu R, Tan H Y, Zhao D S, Fan X L, Zhang C Q, Li Q F, Liu Q Q. Improving rice eating and cooking quality by coordinated expression of the major starch synthesis-related genes, SSII and Wx, in endosperm[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2021, 106(4-5): 419-432. |
| [36] | 高振宇, 黄大年, 钱前. 植物支链淀粉生物合成研究进展[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2004, 30(5):489-495. |
| Gao Z Y, Huang D N, Qian Q. Progress on the biosynthesis of amylopectin in plants[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2004, 30(5): 489-495. (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | Miura S, Crofts N, Saito Y, Hosaka Y, Oitome N F, Watanabe T, Kumamaru T, Fujita N. Starch Synthase IIa-deficient mutant rice line produces endosperm starch with lower gelatinization temperature than japonica rice cultivars[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 645 |
| [38] | Waters D, Henry R J, Reinke R F, Fitzgeraid M A. Gelatinization temperature of rice explained by polymorphisms in starch synthase[J]. Plant Biotechnolgy, 2006, 4: 115-122. |
| [39] | Dian W, Jiang H, Wu P. Evolution and expression analysis of starch synthase III and IV in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56: 623-632. |
| [40] | Li S F, Wei X T, Ren Y L, Qiu J H, Jiao G A, Guo X P, Tang S Q, Wan J M, Hu P S. OsBT1 encodes an ADP-glucose transporter involved in starch synthesis and compound granule formation in rice endosperm[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(40124): 1-13. |
| [41] | Nuzhdin S V, Friesen M L, Mcintyre L M. Genotype phenotype mapping in a post-GWAS world[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2012, 28(9): 421-426. |
| [42] | Kong X, Zhu P, Sui Z, Bao J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 172: 433-440. |
| [43] | Crofts N, Abe N, Oitome N F, Matsushima R, Hayashi M, Tetlow I J, Emes M J, Nakamura Y, Fujita N. Amylopectin biosynthetic enzymes from developing rice seed form enzymatcally active protein complexes[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66: 4469-4482. |
| [44] | Ryoo N, Yu C, Park C S, Baik M Y, Park I M, Cho M H, Bhoo S H, An G, Hahn T R, Jeon J S. Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSⅢa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2007, 26(7): 1083-1095. |
| [45] | Naoko F, Naoko C, Katsumi A. Lack of starch synthase IIIa and high expression of granule-bound starch synthase I synergistically increase the apparent amylose content in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Science, 2012, 193-194: 62-69. |
| [46] | Zhang G, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Guo X, Su N, Jiang L, Mao L, Wan J. Double repression of soluble starch synthase genes SSⅡa and SSⅢa in rice (Oryza sativa L.) uncovers interactive effects on the physicochemical properties of starch[J]. Genome, 2011, 54(6): 448-459. |
| [47] | 周慧颖. 水稻胚乳支链淀粉结构及其与品质和淀粉合成相关基因的关联分析[D]. 江西农业大学, 2017. |
| Zhou H Y. Studies on endosperm amylopectin structure and its association with quality and starch synthesis-related genes of rice[D]. Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | Nakamura Y, Ono M, Utsumi C, Steup M. Functional interaction between plastidial starch phosphorylase and starch branching enzymes from rice during the synthesis of branched maltodextrins[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(5): 869-878. |
| [49] | Bao J S, Corke H, Sun M. Nucleotide diversity in starch synthase IIa and validation of single nucleotide polymorphisms in relation to starch gelatinization temperature and other physicochemical properties in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 113: 1171-1183. |
| [50] | Jr V M B, Luo J X, Li Z Y, Gidley M J, Bird A R, Tetlow I J, Fitzgerald M, Jobling S A, Rahman S. Functional genomic validation of the roles of soluble starch synthase IIa in japonica rice endosperm[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 2(11): 1-12. |
| [51] | Gao Z Y, Zeng D L, Cheng F M, Tian Z X, Guo L B, Su Y, Yan M X, Jiang H, Dong G J, Huang Y C, Han B, Li J Y, Qian Q. ALK, the key gene for gelatinization temperature is a modifier gene for gel consistency in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2011, 53: 756-765. |
| [52] | Kharabian-Masouleh A, Waters D L E, Reinke R F. SNP in starch biosynthesis genes associated with nutritional and functional properties of rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 557. |
| [53] | Nakamura Y, Sakurai A, Inaba Y, Kimura K, Iwasawa N, Nagamine T. The fine structure of amylopectin in endosperm from asian cultivated rice can be largely classified into two classes[J]. Strch/starke, 2002, 54(3-4): 117-131. |
| [54] | Umemoto T, Yano M, Satoh H, Shomura A, Nakamura Y. Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104: 1-8. |
| [55] | Waters D, Henry R J, Reinke R F, Fitzgeraid M A. Gelatinization temperature of rice explained by polymorphisms in starch synthase[J]. Plant Biotechnolgy, 2006, 4: 115-122. |
| [56] | Bao J S, Sun M, Corke H. Analysis of the genetic behavior of some starch properties in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.): Thermal properties, gel texture, swelling volume[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104: 408-413. |
| [57] | Zhang C Q, Yang Y, Chen Z Z, Chen F, Pan L X, Lu Y, Li Q F, Fan X L, Sun Z Z, Liu Q Q. Characteristics of grain physicochemical properties and the starch structure in rice carrying a mutated ALK/SSⅡa gene[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68: 13950-13959. |
| [58] | Takashi O, Francisco P B, S Takayuki, Tatsuro H, Tomio T, Hikaru S, Yasunori N. Expression profiling of genes involved in starch synthesis in sink and source organs of rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(422): 3229-3244. |
| [59] | 林华. 水稻可溶性淀粉合酶基因SSⅡa、SSⅢa等位变异及其与稻米品质的关联分析[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2011. |
| Lin H. The research of allelic diversification of soluble starch synthase gene SSⅡa and SSⅢa and its association with quality[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [60] | 朱霁晖, 张昌泉, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 水稻Wx基因的等位变异及育种利用研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. |
| Zhu J H, Zhang C Q, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progress in the allelic variation of Wx gene and its application in rice breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [61] | 包劲松, 何平, 夏英武, 陈英, 朱立煌. 稻米淀粉RVA谱特征主要受Wx基因控制[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(18): 1973-1976. |
| Bao J S, He P, Xia Y W, Chen Y, Zhu L H. The RVA profile characteristics of rice controlled by Wx gene[J]. Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(18): 1973-1976. (in Chinese) | |
| [62] | Xiang X C, Kang C F, Xu S J, Yang B W. Combined effects of Wx and SSⅡa haplotypes on rice starch physicochemical properties[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2016, 97(4): 1229-1234. |
| [63] | 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许顺菊, 许亮, 王茜. Wx基因与SSⅢ-2基因互作对稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37: 879-884. |
| Yang B W, Xiang X C, Xu S J, Xu L, Wang X. Effects for interaction of Wx and SSⅢ-2 on rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2017, 37: 879-884. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [64] | Yang B W, Xu S J, Xu L, You H, Xiang X C. Effects of Wx and its interaction with SSⅢ-2 on rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9(456): 1-10. |
| [65] | 陈专专, 杨勇, 冯琳皓, 孙晔, 张昌泉, 范晓磊, 李钱峰, 刘巧泉. Wx与ALK主要等位基因不同组合对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 228-236. |
| Chen Z Z, Yang Y, Ma L H, Su Y, Zhang C Q, Liu Q Q. Effects of different combinations of Wx and ALK main alleles on rice grain quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 228-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [66] | Peng Y, Mao B, Zhang C, Shao Y, Wu T, Hu L, Hu Y, Tang L, Li Y, Zhao B, Tang W, Xiao Y. Corrigendum: Correlations between parental lines and indica hybrid rice in terms of eating quality traits[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2021, 8: 1-12. |
| [67] | Li Q F, Zhang G Y, Dong Z W, Yu H X, Gu M H, Sun S M, Liu Q Q. Characterization on of expression of the OsPUL gene encoding a pullulanase-type debranching enzyme during seed development and germination in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(5): 351-358. |
| [68] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Balakrishna P, 王才林. Wxmp基因背景下SSⅡa和PUL基因对水稻蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. |
| Yao S, Zhang Y D, Liu Y Q, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Pillay B, Wang C L. Allelic effects on eating and cooking quality of SSⅡa and PUL genes under Wxmp background in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [69] | Yang F, Chen Y L, Tong C, Huang Y, Xu F F, Li K H, Corke H, Sun M, Bao J S. Association mapping of starch physicochemical properties with starch synthesis-related gene markers in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 34(4): 1747-1763. |
| [70] | He P, Li S G, Qian Q, Ma Y Q, Li J Z, Wang W M, Chen Y, Zhu L H. Genetic analysis of rice grain quality[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1999, 98: 502-508. |
| [71] | 祖启东. 利用近等基因系研究水稻淀粉合成相关基因等位变异的效应[D]. 扬州大学, 2012. |
| Zu Q D. Investigation on the effects of allelic variation of starch synthesis-related genes by using near-isogenic lines[D]. Yangzhou University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [72] | 徐卫. 水稻可溶性淀粉合酶基因与产量和稻米品质性状的关联分析[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2013. |
| Xu W. The association analysis of rice soluble starch synthase gene with yield and quality traits[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [73] | 吴洪恺, 梁国华, 顾燕娟, 单丽丽, 王芳, 韩月澎, 顾铭洪. 水稻淀粉合成相关基因对稻米RVA谱特征的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(11): 159-163. |
| Wu H K, Liang G H, Gu Y J, Shan L L, Wang F, Han Y P, Gu M H. The effect of the starch-synthesizing genes on RVA profile characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(11): 159-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [74] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Balakrishna P, 王才林. 水稻Wxmp背景下 SSⅡa和SSⅢa等位变异及其互作对蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(11): 1690-1702. |
| Yao S, Zhang Y D, Liu Y Q, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Pillay B, Wang C L. Effects of SSⅡa and SSⅢa alleles and their interaction on eating and cooking quality under Wxmp background of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(11): 1690-1702. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [75] | Kuroha T, Nagai K, Gamuyao R, Wang D R, Furuta T, Nakamori M, Kitaoka T, Adachi K, Minami A, Mori Y, Mashiguchi K, Seto Y, Yamaguchi S, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Wu J Z, Ebana K, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M, Yanagisawa S, Yamasaki M, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K, Mochizuki T, Tamiya G, McCouch S R, Ashikari M. Ethylene-gibberellin signaling underlies adaptation of rice to periodic flooding[J]. Science, 2018, 361: 181-186. |
| [76] | 徐正进, 陈温福. 中国北方粳型超级稻研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(2): 239-250. |
| Xu Z J, Chen W F. Research progress and related problems on japonica super rice in northern China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(2): 239-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [77] | 吴清清. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统编辑水稻淀粉合成相关的SSⅢa与PPDK的定点突变研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2019. |
| Wu Q Q. Research of orientation mutation of SSⅢa and PPDK related to starch synthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by CRISPR/Cas9 system[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [78] | Toyosawa Y, Kawagoe Y, Matsushima R, Crofts N, Fujita N. Deficiency of starch synthase IIIa and IVb alters starch granule morphology from polyhedral to spherical in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(3): 1255-1270. |
| [79] | 苏文丽, 向珣朝, 徐艳芳, 龙小林, 康翠芳, 许顺菊. 水稻SSⅡa基因型对成糊温度校准的影响及糊化温度与直链淀粉含量的关系分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2014, 15(2): 348-353. |
| Su W L, Xiang X C, Xu Y F, Long X L, Kang C F, Xu S J. The influence of SSⅡa genotype on the calibration of pasting temperature of rice and the relationship between gelatinization temperature and amylose content[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2014, 15(2): 348-353. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [80] | 陈专专, 李先锋, 仲敏, 葛家奇, 范晓磊, 张昌泉, 刘巧泉. 籼稻背景下抑制不同ALK等位基因表达对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 513-522. |
| Chen Z Z, Li X F, Zhong M, Ge J Q, Fan X L, Zhang C Q, Liu Q Q. Effects on grain quality by down-regulation of the expression of different ALK allele in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 513-522.. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||