
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 427-438.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.210303
褚晓洁1, 芦涛1, 叶涵斐1, 王盛1, 林晗1, 吴先美2, 何瑞2, 严钢1, 王跃星2, 李三峰2, 路梅1, 胡海涛1,*( ), 杨窑龙2,*(
), 杨窑龙2,*( ), 饶玉春1,*(
), 饶玉春1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-04
修回日期:2021-04-12
出版日期:2021-09-10
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
胡海涛,杨窑龙,饶玉春
基金资助:
Xiaojie CHU1, Tao LU1, Hanfei YE1, Sheng WANG1, Han LIN1, Xianmei WU2, Rui HE2, Gang YAN1, Yuexing WANG2, Sanfeng LI2, Mei LU1, Haitao HU1,*( ), Yaolong YANG2,*(
), Yaolong YANG2,*( ), Yuchun RAO1,*(
), Yuchun RAO1,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-04
Revised:2021-04-12
Online:2021-09-10
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
Haitao HU, Yaolong YANG, Yuchun RAO
摘要:
【目的】早衰突变体是研究早衰机制的良好载体,对于探究早衰的遗传机理与作用机制及提高水稻的产量和品质具有重要作用。【方法】本研究利用EMS诱变获得了一个早衰突变体lps1,并对该突变体及其野生型进行表型观察、细胞学及组织化学分析、生理生化分析、遗传分析、基因定位和激素处理。【结果】lps1的叶片从3叶期开始发黄,成熟期株高、有效分蘖数、结实率、千粒重等极显著降低。电镜观察发现lps1叶表面光滑,硅质化突起和叶绿体数目减少、片层结构紊乱。生理生化分析表明lps1中有大量的活性氧积累,同时伴有蛋白质的降解、细胞膜的损伤以及大规模的细胞死亡。遗传分析表明该早衰表型受单隐性核基因控制,并且其在第5染色体上编码了一个泛素结合酶。亚细胞定位结果证明LPS1蛋白在细胞质与核中均有表达。外源激素处理发现,lps1对外源激素的处理更为敏感,且LPS1突变促进了ABA合成相关基因的表达。【结论】LPS1 突变使水稻ABA合成信号途径异常,进而引发H2O2等一系列与衰老相关生理指标的异常变动,导致lps1过早衰老,最终造成水稻产量严重降低。
褚晓洁, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 王盛, 林晗, 吴先美, 何瑞, 严钢, 王跃星, 李三峰, 路梅, 胡海涛, 杨窑龙, 饶玉春. 水稻叶片衰老基因LPS1的克隆与功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 427-438.
Xiaojie CHU, Tao LU, Hanfei YE, Sheng WANG, Han LIN, Xianmei WU, Rui HE, Gang YAN, Yuexing WANG, Sanfeng LI, Mei LU, Haitao HU, Yaolong YANG, Yuchun RAO. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Leaf Senescence Gene LPS1 in Oryza sativa[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 427-438.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | 用途 Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | CACACATTCTAAATTTGGAAAAAGG | TACGTGGCTACTTGGCGTTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M2 | GCTGAAGAGCCTCCTCGAA | GGTATCATGAGAGCGAGTCTGA | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M3 | ACCCATGACCATGAGACGAT | GGGTACTAGCCGTGCTTATCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M4 | AGCCATTAGGGGCTTAGGAA | CCCCTGAGTGATATGCTTGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M5 | TAAATTACATCGGCCGGAGA | CCCACCAAAGAAATCTCCAA | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M6 | ATTTGGGGGAAAGTTTGCTT | AATAGTATGCGTGCGCTGTG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| LPS1 | TCCTAAGAAGGGCTCGGAAA | CTGCCTCAACCACACTTACA | 载体构建Vector construction |
| LPS1-GFP | GCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGAT CTATATGCAATTGAC | TCGAGACGTCTCTAGACGGGCTGC AGGGGATGCCGG | 载体构建Vector construction |
| Q-YGL1 | AACCTTACCGTCCTATTCCTT | CCATACATCTAACAGAGCACC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-NYC3 | TCTATCTAGGTGCCAAAGGC | ATTCTGGCACCTGCTGTTTC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-DVR | CGAGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGTGC | CCTCCCGATCTTGCCGAACTC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-RLS1 | CTTGGGCTGTTGATGCAGC | CTTCAACACCCGCCTCGC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA1 | GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT | TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA2 | AGCAAACCTGAAAGGTGTGGA | AAAGCCACCATCCACCATGA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA3 | GGGCAAGATTTTGTTCGGCA | AAGGGTACACTTGTTGCCCC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED1 | ACCATGAAGTCCATGAGGCT | TCTCGTAGTCTTGGTCTTGG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED2 | ATGGAAACGAGGATAGTGGT | CTTATTGTTGTGCGAGAAGT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED3 | CTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCG | TGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED5 | TCCGAGCTCCTCGTCGTGAA | AGGTGTTTTGGAATGAACCA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsZEP | GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT | TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsZDS | CACGTGTTCTTCGGGTGTTA | ATGTAACGGAGCTCCCACAG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x1 | AAGCTGGCAAAACCAACATC | CCGTGCTAATACGGAATCCA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x2 | CTACTGCTGATGGTGGCTGA | CCCATGGCCTTTGCTTTAT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x3 | AGTACAGCCCATTCCCTGTG | ACGCCTAATCAAACCATTGC | qRT-PCR |
| Actin | CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG | qRT-PCR |
表1 本研究所用引物及序列
Table 1 Primers and sequences used in this study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | 用途 Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | CACACATTCTAAATTTGGAAAAAGG | TACGTGGCTACTTGGCGTTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M2 | GCTGAAGAGCCTCCTCGAA | GGTATCATGAGAGCGAGTCTGA | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M3 | ACCCATGACCATGAGACGAT | GGGTACTAGCCGTGCTTATCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M4 | AGCCATTAGGGGCTTAGGAA | CCCCTGAGTGATATGCTTGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M5 | TAAATTACATCGGCCGGAGA | CCCACCAAAGAAATCTCCAA | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| M6 | ATTTGGGGGAAAGTTTGCTT | AATAGTATGCGTGCGCTGTG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| LPS1 | TCCTAAGAAGGGCTCGGAAA | CTGCCTCAACCACACTTACA | 载体构建Vector construction |
| LPS1-GFP | GCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGAT CTATATGCAATTGAC | TCGAGACGTCTCTAGACGGGCTGC AGGGGATGCCGG | 载体构建Vector construction |
| Q-YGL1 | AACCTTACCGTCCTATTCCTT | CCATACATCTAACAGAGCACC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-NYC3 | TCTATCTAGGTGCCAAAGGC | ATTCTGGCACCTGCTGTTTC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-DVR | CGAGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGTGC | CCTCCCGATCTTGCCGAACTC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-RLS1 | CTTGGGCTGTTGATGCAGC | CTTCAACACCCGCCTCGC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA1 | GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT | TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA2 | AGCAAACCTGAAAGGTGTGGA | AAAGCCACCATCCACCATGA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA3 | GGGCAAGATTTTGTTCGGCA | AAGGGTACACTTGTTGCCCC | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED1 | ACCATGAAGTCCATGAGGCT | TCTCGTAGTCTTGGTCTTGG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED2 | ATGGAAACGAGGATAGTGGT | CTTATTGTTGTGCGAGAAGT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED3 | CTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCG | TGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsNCED5 | TCCGAGCTCCTCGTCGTGAA | AGGTGTTTTGGAATGAACCA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsZEP | GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT | TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsZDS | CACGTGTTCTTCGGGTGTTA | ATGTAACGGAGCTCCCACAG | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x1 | AAGCTGGCAAAACCAACATC | CCGTGCTAATACGGAATCCA | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x2 | CTACTGCTGATGGTGGCTGA | CCCATGGCCTTTGCTTTAT | qRT-PCR |
| Q-OsABA80x3 | AGTACAGCCCATTCCCTGTG | ACGCCTAATCAAACCATTGC | qRT-PCR |
| Actin | CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG | qRT-PCR |
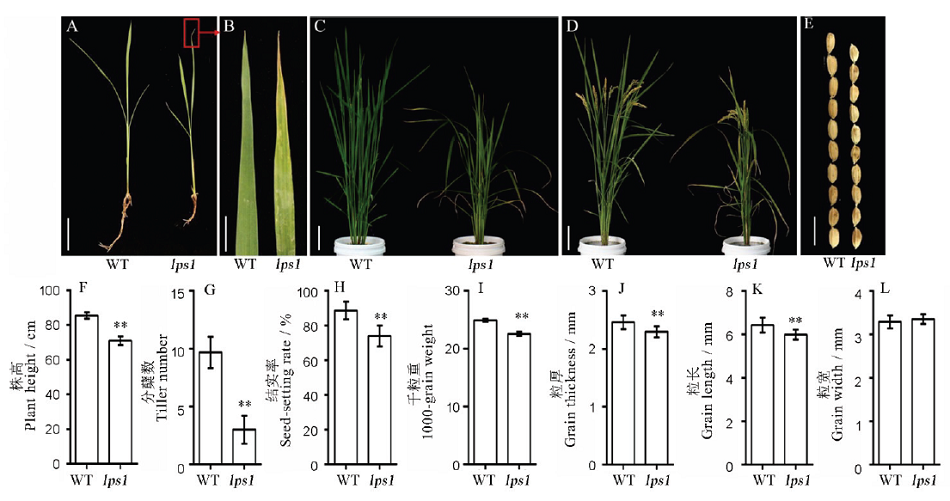
图1 水稻早衰突变体lps1及其野生型的表型及农艺性状A-3叶期植株表型(标尺=3 cm);B-3叶期叶片表型(标尺=1 cm);C-分蘖期表型(标尺=6 cm);D-成熟期表型(标尺=8 cm);E-籽粒表型(标尺=10 cm); F~I-野生型与lps1的农艺性状(株高、分蘖、结实率、千粒重);J~L, 粒厚、粒长和粒宽。*和**分别表示野生型与lps1在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 1. Phenotype and agronomic traits of the wild type and lps1. A, Plant phenotype(Bar=3 cm); B, Leaf phenotype at the three-leaf stage(Bar=1 cm); C, Tillering stage(Bar=6 cm); D, Maturity stage(Bar=8 cm); E, Seed phenotype of wild type and lps1(Bar=10 cm); F-I, Agronomic traits of wild type and lps1; J-L, Statistics of seed thickness, length and width of the wild type and lps1. * and ** indicate that the wild-type and mutant lps1 are significantly different at the levels of 0.05 and 0.01, respectively.
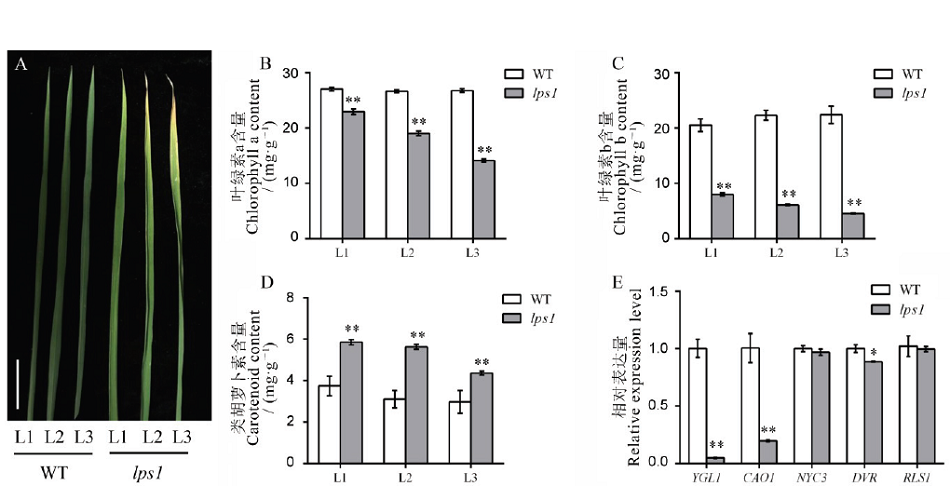
图2 水稻早衰突变体lps1及其野生型分蘖期叶绿素含量及相关基因表达分析A-分蘖期野生型与lps1不同部位叶表型,标尺为2 cm;B~D-野生型与lps1叶绿素a、叶绿素b和类胡萝卜素含量测定;E-叶绿素合成与代谢相关基因表达水平。L1―倒1叶;L2―倒2叶;L3―倒3叶。*和**分别表示野生型与lps1在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著
Fig. 2. Chlorophyll contents and related gene expression analysis at the tillering stage.A, Leaf phenotype of the wild type and lps1 in the tillering stage, bar=2 cm; B-D, Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid contents of the wild type and lps1; E, Chlorophyll synthesis and metabolism-related gene expression level. L1, First leaf from the top; L2, Second leaf from the top; L3, Third leaf from the top. * and ** indicate that the wild type and lps1 are significantly different at the levels of 0.05 and 0.01, respectively.
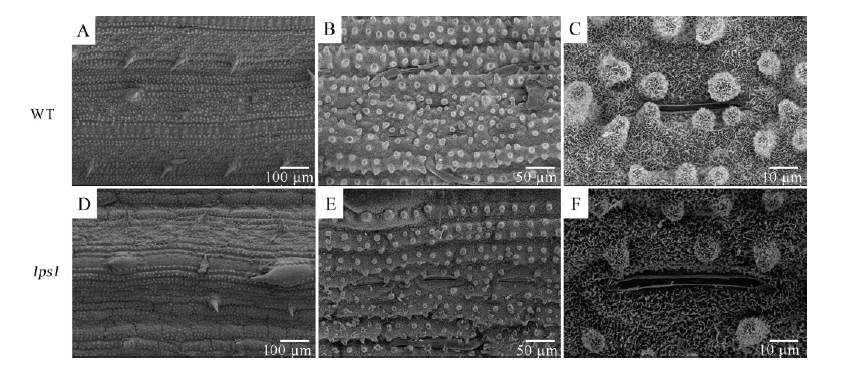
图3 水稻野生型(A~C)和早衰突变体lps1(D~F)叶片下表皮的扫描电镜(SEM)观察
Fig. 3. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations of the epidermis of the wild type (A-C) and lps1(D-F).
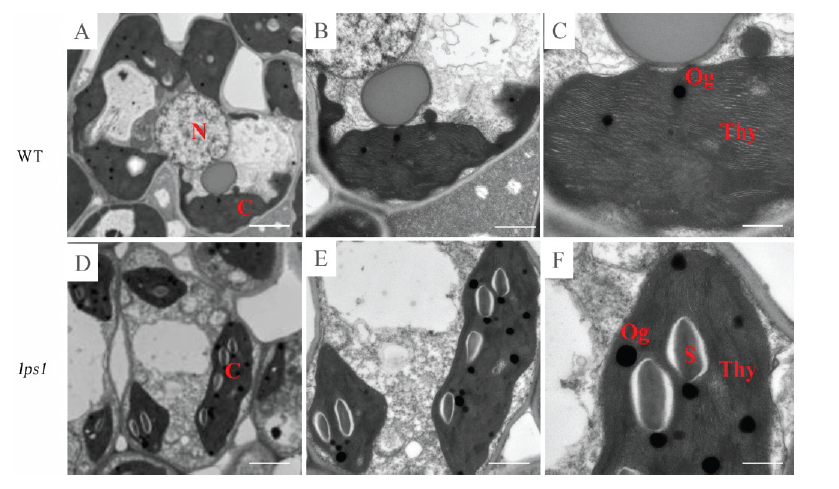
图4 水稻野生型(A~C)和早衰突变体lps1(D~F)叶片的透射电镜(TEM)观察N-细胞核; C-叶绿体; Thy-类囊体; S-淀粉颗粒; Og-嗜锇颗粒。
Fig. 4. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation of the wild type (A-C) and lps1(D-F) leaves. N, Nucleus; C, Chloroplast; Thy, Thylakoid; S, Starch granules; Og, Osmophilic granules.
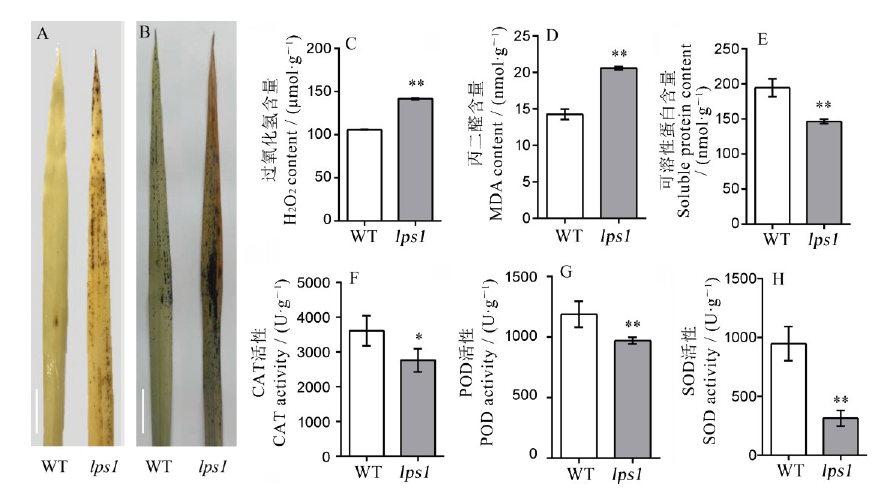
图5 水稻早衰突变体lps1及其野生型生理生化检测A-DAB染色; 标尺为2 cm;B-NBT染色, 标尺为2 cm;C-衰老相关生理指标(过氧化氢、丙二醛、可溶性蛋白含量、过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶活性)的测定。*和**分别表示野生型与lps1在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 5. Physiological and biochemical detection of the wild type and lps1.A, DAB staining; bar=2 cm; B, NBT staining, bar=2 cm; C, Determination of aging-related physiological indicators (H2O2, MDA, SP, CAT, POD, SOD). * and ** indicate that the wild-type and lps1 are significantly different at the levels of 0.05 and 0.01, respectively.
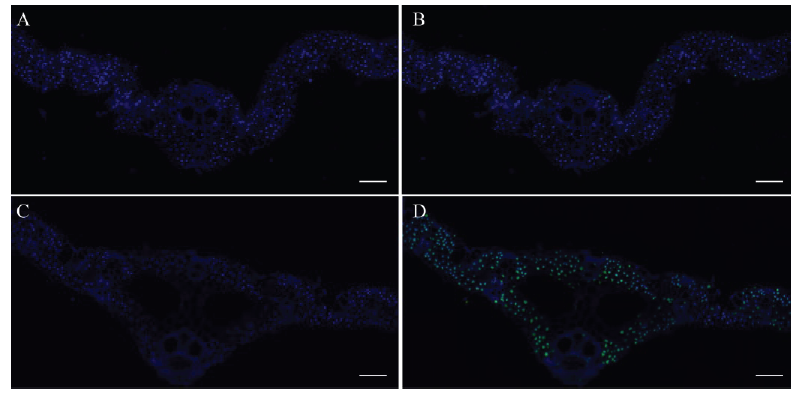
图6 野生型(A、B)和lps1(C、D)叶片的TUNEL处理 A-D,标尺为100 μm。蓝色荧光代表正常细胞,绿色荧光代表凋亡细胞。
Fig. 6. TUNEL treatment results of the wild type (A and B) and lps1 (C and D) leaves. A-D, bar=100 μm. Blue fluorescence represents normal cells, green fluorescence represents apoptotic cells.
| 杂交组合 Combination | F1表型 Phenotype of F1 | F2表型 Phenotype of F2 | χ2(3:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Normal | 突变表型 Mutant | 总株数 Total | |||
| lps1/浙辐802 lps1/Zhefu 802 | 正常表型 Normal | 253 | 82 | 335 | 0.049 |
| 浙辐802/lps1 Zhefu 802/lps1 | 正常表型 Normal | 233 | 76 | 309 | 0.027 |
表2 F2代分离群体统计结果
Table 2 Statistical results of F2 segregating population.
| 杂交组合 Combination | F1表型 Phenotype of F1 | F2表型 Phenotype of F2 | χ2(3:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Normal | 突变表型 Mutant | 总株数 Total | |||
| lps1/浙辐802 lps1/Zhefu 802 | 正常表型 Normal | 253 | 82 | 335 | 0.049 |
| 浙辐802/lps1 Zhefu 802/lps1 | 正常表型 Normal | 233 | 76 | 309 | 0.027 |
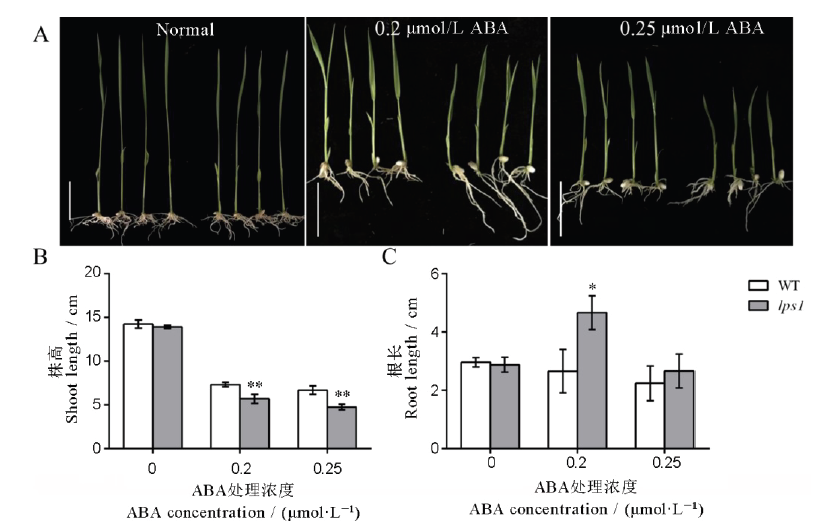
图9 外源激素处理对野生型和lps1幼苗的影响 A-外源激素处理对野生型WT(左)和lps1(右)表型的影响,标尺为3 cm;B-激素处理后地上部分长度;C-激素处理后地下部分长度。*和**分别表示野生型与lps1在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 9. Effect of exogenous hormone treatment on the wild type and lps1 seedlings. A, Effect of exogenous hormone treatment on the phenotype of the wild type(left) and lps1(right), bar=3 cm; B, Length of the aerial part after hormone treatment; C, Length of the underground part after hormone treatment. * and ** indicate significant difference between the wild type and lps1 at 0.05 and 0.01 level, respectively.
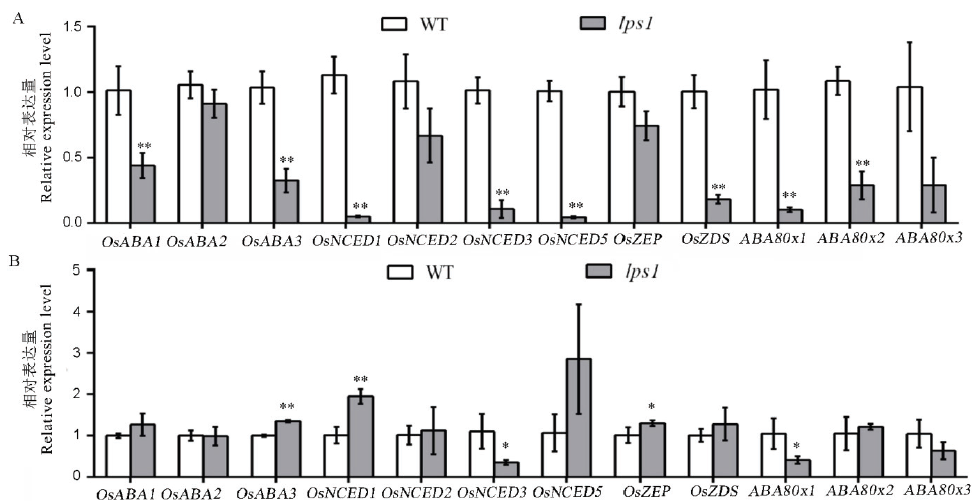
图10 ABA合成与降解相关基因表达水平 A-处理前野生型(WT)和lps1中ABA相关基因表达水平;B-处理后野生型(WT)和lps1中ABA相关基因表达水平;*和**分别表示野生型与lps1在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 10. ABA synthesis and degradation related gene expression levels. A, ABA-related gene expression levels in the wild type and lps1 before treatment; B, ABA-related gene expression levels in the wild type and lps1 after treatment; * and ** indicate significant difference between the wild type and lps1 at 0.05 and 0.01 level, respectively.
| [1] | Cao J, Jiang F, Sodmergen, Cui K M. Time-course of programmed cell death during leaf senescence in Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Journal of Plant Research, 2003, 116(1): 7-12. |
| [2] | Vicky B W. The molecular biology of leaf senescence[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1997, 48(2): 181-199. |
| [3] | Lim P O, Kim H J, Nam H G. Leaf senescence[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2007, 58(1): 115-136. |
| [4] | Zhang H S, Zhou C J. Signal transduction in leaf senescence[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2013, 82(6): 539-545. |
| [5] | Panda D, Sarkar R K. Natural leaf senescence: Probed by chlorophyll fluorescence, CO2 photosynthetic rate and antioxidant enzyme activities during grain filling in different rice cultivars[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2013, 19(3): 43-51. |
| [6] | Li Z H, Zhang Y, Zou D, Zhao Y, Wang H L, Zhang Y, Xia X L, Luo J C, Zhang Z. LSD 3.0: A comprehensive resource for the leaf senescence research community[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(D1): D1069-D1075. |
| [7] | Mao C J, Lu S C, Lü B, Zhang B, Shen J B, He J M, Luo L Q, Xi D D, Chen X, Ming F. A rice NAC transcription factor promotes leaf senescence via ABA biosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2017, 174(3): 1747-1763. |
| [8] | Liang C Z, Wang Y Q, Zhu Y N, Tang J Y, Hu B, Liu L C, Ou S J, Sun X H, Chu J F, Chu C C. OsNAP connects abscisic acid and leaf senescence by fine-tuning abscisic acid biosynthesis and directly targeting senescence-associated genes in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(27): 10013-10018. |
| [9] | Han M, Kim C Y, Lee J, Lee S K, Jeon J S. OsWRKY42 represses OsMT1d and induces reactive oxygen species and leaf senescence in rice[J]. Molecular Cells, 2014, 37(7): 532-539. |
| [10] | Uji Y, Akimitsu K, Gomi K. Identification of OsMYC2-regulated senescence-associated genes in rice[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(6): 1241-1246. |
| [11] | Lu G W, Casaretto J A, Ying S, Mahmood K, Liu F, Bi Y M, Rothstein S J. Overexpression of OsGATA12 regulates chlorophyll content, delays plant senescence and improves rice yield under high density planting[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2017, 94(1): 215-227. |
| [12] | Liu W Z, Fu Y P, Hu G C, Si H M, Wu C, Sun Z X. Identification and fine mapping of a thermo-sensitive chlorophyll deficient mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Planta, 2007, 226(3): 785-795. |
| [13] | Liu C H, Zhu H T, Xing Y, Tan J J, Chen X H, Zhang J J, Peng H F, Xie Q J, Zhang Z M. Albino Leaf 2 is involved in the splicing of chloroplast group I and II introns in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(18): 5339-5347. |
| [14] | Kusaba M, Ito H, Morita R, Iida S, Sato Y, Fujimoto M, Kawasaki S, Tanaka R, Hirochika H, Nishimura M, Tanaka A. Rice NON-YELLOW COLORING1 is involved in light-harvesting complex II and grana degradation during leaf senescence[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4): 1362-1375. |
| [15] | Rong H, Tang Y Y, Zhang H, Wu P Z, Chen Y P, Li M R, Wu G J, Jiang H W. The Stay-Green Rice like (SGRL) gene regulates chlorophyll degradation in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2013, 170(15): 1367-1373. |
| [16] | Fang C Y, Zhang H, Wan J, Wu Y Y, Chen W, Wang S C, Wang W S, Zhang H W, Zhang F, Qu L H, Liu X Q, Zhou D X, Luo J. Control of leaf senescence by an MeOH-jasmonates cascade that is epigenetically regulated by OsSRT1 in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(10): 1366-1378. |
| [17] | Xu W Y, Kong Z S, Li M N, Yang W Q, Xue Y B. A novel nuclear-localized CCCH-type ainc finger protein, OsDOS, is involved in delaying leaf senescence in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 141(4): 1376-1388. |
| [18] | Chen Y, Xu Y Y, Luo W, Li W X, Chen N, Zhang D J, Chong K. The F-Box protein OsFBK12 targets OsSAMS1 for degradation and affects pleiotropic phenotypes, including leaf senescence, in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 163(4): 1673-1685. |
| [19] | Zhao Y, Chan Z L, Gao J H, Xing L, Cao M J, Yu C M, Hu Y L, You J, Shi H T, Zhu Y F, Gong Y H, Mu Z X, Wang H Q, Deng X, Wang P C, Bressan R A, Zhu J K. ABA receptor PYL9 promotes drought resistance and leaf senescence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America, 2016, 113(7): 1949-1954. |
| [20] | Yang X, Gong P, Li K Y, Huang F D, Cheng F M, Pan G. A single cytosine deletion in the OsPLS1 gene encoding vacuolar-type H+-ATPase subunit A1 leads to premature leaf senescence and seed dormancy in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(9): 2761-2776. |
| [21] | Zhou Y, Liu L, Huang W F, Yuan M, Zhou F, Li X H, Lin Y J. Overexpression of OsSWEET5 in rice causes growth retardation and precocious senescence[J]. PloS One, 2014, 9(4): e94210. |
| [22] | Singh S, Singh A, Nandi A K. The rice OsSAG12-2 gene codes for a functional protease that negatively regulates stress-induced cell death[J]. Journal of Biosciences, 2016, 41(3): 445-453. |
| [23] | Wu L W, Ren D Y, Hu S K, Li G M, Dong G J, Jiang L, Hu X M, Ye W J, Cui Y T, Zhu J, Zhang G H, Gao Z Y, Zeng D L, Qian Q, Guo L B. Down-regulation of a nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase gene OsNaPRT1 leads to withered leaf tips[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(2): 1085-1098. |
| [24] | Lee R H, Hsu J H, Huang H J, Lo S F, Grace S C. Alkaline α-galactosidase degrades thylakoid membranes in the chloroplast during leaf senescence in rice[J]. New Phytology, 2009, 184(3): 596-606. |
| [25] | Kang K, Kim Y S, Park S, Back K. Senescence-induced serotonin biosynthesis and its role in delaying senescence in rice leaves[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 150(3): 1380-1393. |
| [26] | Kudo T, Makita N, Kojima M, Tokunaga H, Sakakibara H. Cytokinin activity of cis-zeatin and phenotypic alterations induced by overexpression of putative cis-zeatin glucosyltransferase in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 160(1): 319-331. |
| [27] | Wiseman B R. Plant-resistance to insects in integrated pest-management[J]. Plant Disease, 1994, 78(9): 927-932. |
| [28] | Liang C Z, Chu C C. Towards understanding abscisic acid-mediated leaf senescence[J]. Science China: Life Sciences, 2015, 58(5): 506-508. |
| [29] | Pan H R, Liu S M, Tang D Z. HPR1, a component of the THO/TREX complex, plays an important role in disease resistance and senescence in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Journal, 2012, 69(5): 831-843. |
| [30] | Hu Y N, Jiang Y J, Han X, Wang H P, Pan J J, Yu D Q. Jasmonate regulates leaf senescence and tolerance to cold stress: Crosstalk with other phytohormones[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(6): 1361-1369. |
| [31] | Dani K G S, Fineschi S, Michelozzi M, Loreto F. Do cytokinins, volatile isoprenoids and carotenoids synergically delay leaf senescence[J]. Plant Cell Environment, 2016, 39(5): 1103-1111. |
| [32] | Kim J I, Murphy A S, Baek D, Lee S W, Yun D J, Bressan R A, Narasimhan M L. YUCCA6 over-expression demonstrates auxin function in delaying leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(11): 3981-3992. |
| [33] | Chen L G, Xiang S Y, Chen Y L, Li D B, Yu D Q. Arabidopsis WRKY45 interacts with the DELLA protein RGL1 to positively regulate age-triggered leaf senescence[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10, 1174-1189. |
| [34] | Riefler M, Novak O, Strnad M, Schmülling T. Arabidopsis cytokinin receptor mutants reveal functions in shoot growth, leaf senescence, seed size, germination, root development, and cytokinin metabolism[J]. Plant Cell, 2006, 18(1): 40-54. |
| [35] | Wang T, Li C X, Wu Z H, Jia Y C, Wang H, Sun S Y, Mao C Z, Wang X L. Abscisic acid regulates auxin homeostasis in rice root tips to promote root hair elongation[J]. Frontier in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1121-1138. |
| [36] | Xu N, Chu Y L, Chen H L, Li X X, Wu Q, Jin L, Wang G X, Huang J L. Rice transcription factor OsMADS25 modulates root growth and confers salinity tolerance via the ABA-mediated regulatory pathway and ROS scavenging[J]. PLoS Genet, 2018, 14(10): e1007662. |
| [37] | Chang Y, Nguyen B H, Xie Y J, Xiao B Z, Tang N, Zhu W L, Mou T M, Xiong L Z. Co-overexpression of the constitutively active form of OsbZIP46 and ABA-activated protein kinase SAPK6 improves drought and temperature stress resistance in rice[J]. Frontier in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1102-1117. |
| [38] | Promchuea S, Zhu Y J, Chen Z Z, Zhang J, Gong Z Z. ARF2 coordinates with PLETHORAs and PINs to orchestrate ABA-mediated root meristem activity in Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2017, 59(1): 30-43. |
| [39] | Sun L R, Wang Y B, He S B, Hao F S. Mechanisms for abscisic acid inhibition of primary root growth[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2018, 13(9): e1500069. |
| [40] | Hung K T, Yi T H, Kao C H. Hydrogen peroxide is involved in methyl jasmonate-induced senescence of rice leaves[J]. Physiology Plantarum, 2006, 127(2): 293-303. |
| [41] | 李兆伟. 水稻叶片早衰突变体的糖代谢基因表达与抗氧化生理调控[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. |
| Li Z W. The expression alteration of various genes related to sugar metabolism in senescing leaves and its antioxidation modulation for esl mutant[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. | |
| [42] | Lichtenthaler H K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 1987, 148: 350-382. |
| [43] | 游均, 方玉洁, 熊立仲. 活性氧检测[J/OL].Bio-101, 2018: e1010170. |
| You J, Fang Y J, Xiong L Z. Reactive oxygen detection [J/OL]. Bio-101, 2018: e1010170. (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | Rao Y C, Jiao R, Wang S, Wu X M, Ye H F, Pan C Y, Li S F, Xin D D, Zhou W Y, Dai G X, Hu J, Ren D Y, Wang Y X. SPL36 encodes a receptor-like protein kinase that regulates programmed cell death and defense responses in rice[J]. Rice, 2021, 14(1): 34-47. |
| [45] | 沈恒胜, 陈君琛, 黄进华, 汤葆莎. 水稻叶表皮硅体显微结构及其分布[J]. 福建农业大学学报, 2005, 34(2): 137-140. |
| Shen H S, Chen J C, Huang J H, Tang B S. Microtructure and distribution of silica bodies rice epidermis[J]. Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 34(2): 137-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 杨秉耀, 陈新芳, 刘向东, 郭海滨. 水稻不同品种叶表面硅质细胞的扫描电镜观察[J]. 电子显微学报, 2006, 25(2): 68-72. |
| Yang B Y, Chen X F, Liu X D, Guo H B. Scanning electron microscopic observation of silicon cells on the leaf surface of different rice varieties[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2005, 25(2): 68-72. | |
| [47] | Christopher E. A possible mechanism of biological silicification in plants[J]. Frontier in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 853-859. |
| [48] | Yang L, Han Y Q, Li P, Li F, Ali S, Hou M L. Silicon amendment is involved in the induction of plant defense responses to a phloem feeder[J]. Scientific Report, 2017, 7(1): 4232-4240. |
| [49] | Hideg E, Kálai T, Kós P B, Asada K, Hideg K. Singletoxygen in plants: Its significance and possible detection with double (fluorescent and spin) indicator reagents[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2006, 82(5): 1211-1218. |
| [50] | 华春, 王仁雷. 杂交稻及其三系叶片衰老过程中SOD、CAT活性和MDA含量的变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2003, 23(3): 406-409. |
| Hua C, Wang R L. Changes of SOD and CAT activities and MDA content during senescence of hybrid rice and three lines leaves[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali- Occidentalia Sinica, 2003, 23(3): 406-409. | |
| [51] | Hu B, Zhu C G, Li F, Tang J Y, Wang Y Q, Liu L C, Che R H, Chu C C. LEAF TIP NECROSIS1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of multiple phosphate starvation responses in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1101-1115. |
| [52] | Lee I C, Hong S W, Whang S S, Lim P O, Nam H G, Koo J C. Age-dependent action of an ABA-inducible receptor kinase, RPK1, as a positive regulator of senescence in Arabidopsis leaves[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(4): 651-662. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||