
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 359-372.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.201205
杜成兴#, 张华丽#, 戴冬青, 吴明月, 梁敏敏, 陈俊宇*( ), 马良勇*(
), 马良勇*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-08
修回日期:2021-01-26
出版日期:2021-07-10
发布日期:2021-07-10
通讯作者:
陈俊宇,马良勇
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Chengxing DU#, Huali ZHANG#, Dongqing DAI, Mingyue WU, Minmin LIANG, Junyu CHEN*( ), Liangyong MA*(
), Liangyong MA*( )
)
Received:2020-12-08
Revised:2021-01-26
Online:2021-07-10
Published:2021-07-10
Contact:
Junyu CHEN, Liangyong MA
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】粒重粒形对水稻的产量和品质均有重要的影响。本研究通过开展水稻粒重粒形QTL的初步定位,并对新鉴定的第1染色体长臂qTGW1.2/qGL1.2区间进行验证,旨在进一步揭示水稻粒重粒形的遗传调控机制。【方法】以大粒的FM9为父本,小粒的EFT为母本,配组衍生遗传群体,先后获得包含277个株系的F2:3群体和211个株系的重组自交系群体(Recombinant Inbred Lines, RILs),测定千粒重、粒长和粒宽,采用完备区间作图法进行QTL初定位;针对新鉴定的qTGW1.2/qGL1.2区间,筛选2个剩余杂合体单株,自交衍生分离群体,开展QTL效应验证。【结果】初定位分析共检测到35个调控千粒重、粒长和粒宽的QTL,其中,11个能同时在两个群体中被检测到,18个仅在F2:3群体中被检测到,6个仅在RIL群体中被检测到;应用两个剩余杂合体衍生的两套分离群体验证了新鉴定的qTGW1.2/qGL1.2区间对千粒重和粒长的效应,并观察到颖壳细胞长度的显著变化。通过qPCR分析,观察到与细胞周期、生长素代谢和粒形相关基因表达发生了显著变化。【结论】初步定位的35个QTL以及验证的qTGW1.2/qGL1.2有利于进一步揭示水稻粒重粒形的遗传控制基础,也为后续的基因克隆及分子标记辅助选择奠定了基础。
杜成兴, 张华丽, 戴冬青, 吴明月, 梁敏敏, 陈俊宇, 马良勇. 水稻粒重粒形QTL的定位及qTGW1.2/qGL1.2的验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 359-372.
Chengxing DU, Huali ZHANG, Dongqing DAI, Mingyue WU, Minmin LIANG, Junyu CHEN, Liangyong MA. QTL Analysis for Grain Weight and Shape and Validation of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 359-372.
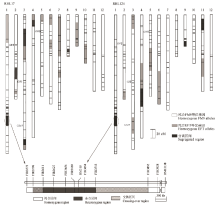
图2 两个剩余杂合体单株RHL17和RHL124与目标qTGW1.2/qGL1.2区间的基因型组成
Fig. 2. Schematic genotypes of two residual heterozygotes RHL17 and RHL124 and the targeted region of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2.
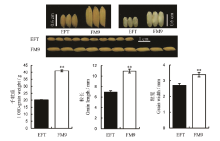
图3 两个亲本材料EFT和FM9的千粒重、粒长和粒宽的比较**表示在 0.01水平上显著。
Fig. 3. Comparison of 1000-grain weight, grain length and grain width of the parents EFT and FM9.** Significant at 0.01 level.
| 群体 Population | 性状Trait | F2:3-TGW | F2:3-GL | F2:3-GW | RIL-TGW | RIL-GL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2:3 | 粒长GL | 0.679** | ||||
| 粒宽GW | 0.725** | 0.279** | ||||
| RIL | 千粒重TGW | -0.053 | ||||
| 粒长GL | 0.020 | 0.753** | ||||
| 粒宽GW | -0.163 | 0.776** | 0.394** |
表1 EFT/FM9 F2:3和RIL群体粒型性状相关性分析
Table 1 Correlationship analysis on grain shape traits in EFT/FM9 F2:3 and RIL population.
| 群体 Population | 性状Trait | F2:3-TGW | F2:3-GL | F2:3-GW | RIL-TGW | RIL-GL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2:3 | 粒长GL | 0.679** | ||||
| 粒宽GW | 0.725** | 0.279** | ||||
| RIL | 千粒重TGW | -0.053 | ||||
| 粒长GL | 0.020 | 0.753** | ||||
| 粒宽GW | -0.163 | 0.776** | 0.394** |
| 性状 | 数量性状基因座 | 标记区间 | F2:3 | RIL | 已克隆QTLa Cloned QTLa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | QTL | Marker interval | LOD | PVE/% | Add | LOD | PVE/% | Add | ||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1.1 | RM246-RM1061 | 3.97 | 3.25 | -0.92 | |||||
| TGW | qTGW1.2 | RM315-RM12138 | 5.28 | 3.95 | -1.08 | 4.51 | 4.15 | -0.94 | ||
| qTGW2 | RM145-RM71 | 59.83 | 38.33 | -3.70 | 31.8 | 34.24 | -3.00 | GW2[ | ||
| qTGW3.1 | THI351-THI468 | 4.25 | 4.24 | -1.07 | ||||||
| qTGW3.2 | THI1668-THI1701 | 16.05 | 6.74 | -1.49 | 8.68 | 7.60 | -1.41 | GS3[ | ||
| qTGW3.3 | RM168-RM3867 | 11.15 | 5.89 | -1.39 | 5.82 | 5.92 | -1.24 | GSA1[ | ||
| qTGW5.1 | FIF232-FIF345 | 8.53 | 3.67 | 0.95 | GS5[ | |||||
| qTGW5.2 | FIF426-FIF738 | 9.86 | 4.64 | 1.11 | 5.95 | 4.97 | 1.14 | GSE5/GW5/qSW5[ | ||
| qTGW6.1 | RM136-RM3 | 4.19 | 2.25 | -0.87 | ||||||
| qTGW6.2 | RM30-RM340 | 6.12 | 2.80 | -1.04 | ||||||
| qTGW7 | RM420-RM172 | 4.35 | 1.76 | -0.76 | ||||||
| qTGW9.1 | RM296-RM7424 | 4.97 | 2.68 | -0.96 | DEP1/DN1/qNGR9[ | |||||
| qTGW9.2 | RM7048-RM328 | 3.26 | 3.16 | -0.91 | ||||||
| qTGW10.1 | RM228-RM590 | 6.70 | 2.64 | -0.92 | ||||||
| qTGW10.2 | RM474-TEN400 | 4.12 | 3.43 | -0.96 | ||||||
| qTGW12 | RM1103-RM3226 | 6.26 | 2.62 | -0.93 | ||||||
| 粒长 | qGL1.1 | RM1061-RM128 | 8.29 | 4.05 | -0.16 | |||||
| GL | qGL1.2 | RM315-RM12138 | 7.47 | 3.83 | -0.15 | 9.10 | 8.25 | -0.21 | ||
| qGL1.3 | RM12283-RM12333 | 2.99 | 2.42 | -0.12 | ||||||
| qGL2 | RM145-RM71 | 12.09 | 6.35 | -0.21 | 12.82 | 18.24 | -0.32 | GW2[ | ||
| qGL3.1 | THI156-THI214 | 4.86 | 4.01 | -0.15 | ||||||
| qGL3.2 | THI301-THI351 | 5.06 | 2.36 | -0.12 | ||||||
| qGL3.3 | THI1668-THI1701 | 45.92 | 32.65 | -0.44 | 24.88 | 25.95 | -0.38 | GS3[ | ||
| qGL3.4 | RM168-RM3867 | 7.62 | 5.15 | -0.18 | 2.95 | 2.78 | -0.12 | GSA1[ | ||
| qGL5 | RM538-RM480 | 5.14 | 2.45 | 0.13 | ||||||
| qGL6 | RM589-RM587 | 4.26 | 2.27 | 0.12 | ||||||
| qGL7 | RM351-RM234 | 5.78 | 3.32 | -0.14 | ||||||
| qGL9 | RM296-RM7424 | 10.43 | 7.67 | -0.22 | DEP1/DN1/qNGR9[ | |||||
| qGL11 | RM1355-RM209 | 7.18 | 3.70 | -0.16 | ||||||
| 粒宽 | qGW2 | RM145-RM71 | 48.09 | 30.95 | -0.20 | 17.85 | 24.96 | -0.17 | GW2[ | |
| GW | qGW3 | RM3867-RM571 | 5.30 | 2.93 | -0.05 | GSA1[ | ||||
| qGW5.1 | FIF426-FIF738 | 29.68 | 19.25 | 0.15 | 10.84 | 15.49 | 0.13 | GSE5/GW5/qSW5[ | ||
| qGW5.2 | FIF738-FIF801 | 9.30 | 4.42 | 0.07 | ||||||
| qGW11 | RM21-RM254 | 4.44 | 3.10 | -0.06 | ||||||
| qGW12 | RM1103-RM3226 | 7.88 | 4.01 | -0.07 | ||||||
表2 F2:3和RIL群体中检测到的粒重粒形QTL
Table 2 QTLs for grain weight and shape detected in the F2:3 and RIL populations.
| 性状 | 数量性状基因座 | 标记区间 | F2:3 | RIL | 已克隆QTLa Cloned QTLa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | QTL | Marker interval | LOD | PVE/% | Add | LOD | PVE/% | Add | ||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1.1 | RM246-RM1061 | 3.97 | 3.25 | -0.92 | |||||
| TGW | qTGW1.2 | RM315-RM12138 | 5.28 | 3.95 | -1.08 | 4.51 | 4.15 | -0.94 | ||
| qTGW2 | RM145-RM71 | 59.83 | 38.33 | -3.70 | 31.8 | 34.24 | -3.00 | GW2[ | ||
| qTGW3.1 | THI351-THI468 | 4.25 | 4.24 | -1.07 | ||||||
| qTGW3.2 | THI1668-THI1701 | 16.05 | 6.74 | -1.49 | 8.68 | 7.60 | -1.41 | GS3[ | ||
| qTGW3.3 | RM168-RM3867 | 11.15 | 5.89 | -1.39 | 5.82 | 5.92 | -1.24 | GSA1[ | ||
| qTGW5.1 | FIF232-FIF345 | 8.53 | 3.67 | 0.95 | GS5[ | |||||
| qTGW5.2 | FIF426-FIF738 | 9.86 | 4.64 | 1.11 | 5.95 | 4.97 | 1.14 | GSE5/GW5/qSW5[ | ||
| qTGW6.1 | RM136-RM3 | 4.19 | 2.25 | -0.87 | ||||||
| qTGW6.2 | RM30-RM340 | 6.12 | 2.80 | -1.04 | ||||||
| qTGW7 | RM420-RM172 | 4.35 | 1.76 | -0.76 | ||||||
| qTGW9.1 | RM296-RM7424 | 4.97 | 2.68 | -0.96 | DEP1/DN1/qNGR9[ | |||||
| qTGW9.2 | RM7048-RM328 | 3.26 | 3.16 | -0.91 | ||||||
| qTGW10.1 | RM228-RM590 | 6.70 | 2.64 | -0.92 | ||||||
| qTGW10.2 | RM474-TEN400 | 4.12 | 3.43 | -0.96 | ||||||
| qTGW12 | RM1103-RM3226 | 6.26 | 2.62 | -0.93 | ||||||
| 粒长 | qGL1.1 | RM1061-RM128 | 8.29 | 4.05 | -0.16 | |||||
| GL | qGL1.2 | RM315-RM12138 | 7.47 | 3.83 | -0.15 | 9.10 | 8.25 | -0.21 | ||
| qGL1.3 | RM12283-RM12333 | 2.99 | 2.42 | -0.12 | ||||||
| qGL2 | RM145-RM71 | 12.09 | 6.35 | -0.21 | 12.82 | 18.24 | -0.32 | GW2[ | ||
| qGL3.1 | THI156-THI214 | 4.86 | 4.01 | -0.15 | ||||||
| qGL3.2 | THI301-THI351 | 5.06 | 2.36 | -0.12 | ||||||
| qGL3.3 | THI1668-THI1701 | 45.92 | 32.65 | -0.44 | 24.88 | 25.95 | -0.38 | GS3[ | ||
| qGL3.4 | RM168-RM3867 | 7.62 | 5.15 | -0.18 | 2.95 | 2.78 | -0.12 | GSA1[ | ||
| qGL5 | RM538-RM480 | 5.14 | 2.45 | 0.13 | ||||||
| qGL6 | RM589-RM587 | 4.26 | 2.27 | 0.12 | ||||||
| qGL7 | RM351-RM234 | 5.78 | 3.32 | -0.14 | ||||||
| qGL9 | RM296-RM7424 | 10.43 | 7.67 | -0.22 | DEP1/DN1/qNGR9[ | |||||
| qGL11 | RM1355-RM209 | 7.18 | 3.70 | -0.16 | ||||||
| 粒宽 | qGW2 | RM145-RM71 | 48.09 | 30.95 | -0.20 | 17.85 | 24.96 | -0.17 | GW2[ | |
| GW | qGW3 | RM3867-RM571 | 5.30 | 2.93 | -0.05 | GSA1[ | ||||
| qGW5.1 | FIF426-FIF738 | 29.68 | 19.25 | 0.15 | 10.84 | 15.49 | 0.13 | GSE5/GW5/qSW5[ | ||
| qGW5.2 | FIF738-FIF801 | 9.30 | 4.42 | 0.07 | ||||||
| qGW11 | RM21-RM254 | 4.44 | 3.10 | -0.06 | ||||||
| qGW12 | RM1103-RM3226 | 7.88 | 4.01 | -0.07 | ||||||
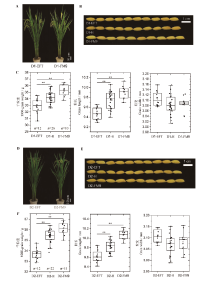
图6 高世代分离群体D1(A-C)和D2群体(D-F)中qTGW1.2/qGL1.2不同基因型间的株型、粒形和粒重的比较**表示在0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 6. Comparison of plant architecture, grain shape and grain weight among different genotypes of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2 in the D1 population (A-C) and the D2 population (D-F) of advanced generations. **Significant at 0.01 level.
| 群体 Population | 分离区别 Segregated region | 性状 Trait | qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT | qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9 | P值 P value | 加性效应 Additive effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | FIR3596-FIR3892 | 千粒重TGW/g | 33.00±1.09 | 34.77±1.03 | 0.0014 | -0.89 |
| 粒长GL/mm | 9.42±0.17 | 9.85±0.13 | <0.0001 | -0.21 | ||
| 粒宽GW/mm | 3.09±0.02 | 3.08±0.02 | 0.1703 | |||
| E2 | FIR3596-FIR3892 | 千粒重TGW/g | 33.63±0.87 | 35.99±0.88 | <0.0001 | -1.19 |
| 粒长GL/mm | 9.67±0.17 | 10.11±0.11 | <0.0001 | -0.22 | ||
| 粒宽GW/mm | 3.10±0.03 | 3.09±0.04 | 0.7305 |
表3 高世代分离群体E1和E2中qTGW1.2/qGL1.2的效应分析
Table 3 Effect of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2 estimated in E1 and E2 populations of advanced generations.
| 群体 Population | 分离区别 Segregated region | 性状 Trait | qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT | qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9 | P值 P value | 加性效应 Additive effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | FIR3596-FIR3892 | 千粒重TGW/g | 33.00±1.09 | 34.77±1.03 | 0.0014 | -0.89 |
| 粒长GL/mm | 9.42±0.17 | 9.85±0.13 | <0.0001 | -0.21 | ||
| 粒宽GW/mm | 3.09±0.02 | 3.08±0.02 | 0.1703 | |||
| E2 | FIR3596-FIR3892 | 千粒重TGW/g | 33.63±0.87 | 35.99±0.88 | <0.0001 | -1.19 |
| 粒长GL/mm | 9.67±0.17 | 10.11±0.11 | <0.0001 | -0.22 | ||
| 粒宽GW/mm | 3.10±0.03 | 3.09±0.04 | 0.7305 |
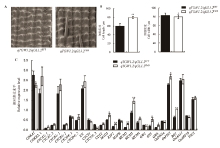
图7 携带qTGW1.2/qGL1.2的FM9纯合型(qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9)和EFT纯合型(qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT)材料的颖壳表皮细胞扫描电镜观察和相关基因的表达分析A- qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9和qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT的颖壳细胞(标尺:200 μm);B-外颖细胞长度和宽度的比较(*, **分别表示在 0.05 和 0.01 水平上显著相关,n=30);C- qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9和qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT幼穗中细胞周期与粒形相关基因的表达水平比较。CDKA1-A型细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1;CDKB2;1-B型周期蛋白依赖性激酶2;CYCA1;1- A型周期蛋白依赖性激酶1-1;CYCA2; 2-A型周期蛋白依赖性激酶2-1;CYCB1;1-B型周期蛋白依赖性激酶1-1;CYCB2; 2-B型周期蛋白依赖性激酶2-2;CYCD4;1-D型周期蛋白依赖性激酶4-1;CYCD4; 2-D型周期蛋白依赖性激酶4-2;KN-突触融合蛋白相关蛋白KNOLLE;CYCT1- T型细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1;CYCU4; 3-U型细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4-3;CDT2-U型细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4-1;MAD2-细胞扩增相关基因MAD2;E2F2- E2F转录因子2;MAPK-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶;MCM2-微型染色体维持蛋白2;MCM3-微型染色体维持蛋白3;MCM4-微型染色体维持蛋白4;GW2-粒宽基因;GS3-粒长基因;GW5 -粒宽基因;OsPIN1a-PIN蛋白1a;OsPIN1- PIN蛋白1;BG1-大粒基因;OsIAA11-Aux/IAA蛋白11;OsARF19-生长素应答因子19;TSG1-色氨酸转氨酶。
Fig. 7. Scanning electron observation and quantitative expression analysis of related genes in qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9 and qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT. A, Local outer surfaces of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9 and qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT spikelet hulls. (Bars = 200 µm); B, Comparison of the cell length and width of outer glume cells (*, **Significant at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively, n=30); C, Two parental homozygous genotypes qTGW1.2/qGL1.2FM9 and qTGW1.2/qGL1.2EFT are involved in the expression levels of cell cycle- and grain shape-related genes in young panicles. CDKA1, Cyclin-dependent kinase A-1; CDKB2;1, B-type cyclin-dependent kinase 2;1; CYCA1;1, A-type cyclin 1;1; CYCA2; 2, A-type cyclin 3;1; CYCB1;1, B-type cyclin 1; CYCB2; 2, B-type cyclin 2;2; CYCD4;1, D-type cyclin 4;1; CYCD4; 2, D-type cyclin 4;2; KN, Syntaxin-related protein KNOLLE; CYCT1, T-type cyclin 1; CYCU4; 3, U-type cyclin 4;3; CDT2, Cadmium tolerant 2; MAD2, Cell expansion-related gene MAD2; E2F2, E2F transcription factor 2; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCM2, Mini-chromosome maintenance protein 2; MCM3, Mini-chromosome maintenance protein 3; MCM4, Mini-chromosome maintenance protein 4; GW2, Grain weight 2; GS3, Grain size 3; GW5, Grain width 5; OsPIN1a, Pin protein 1a; OsPIN1, Pin-formed 1b; BG1, Big grain 1; OsIAA11, Aux/IAA protein 11; OsARF19, Auxin response factor 19; TSG1, Tillering and small grain 1.
| [1] | Wang A H, Hou Q Q, Si L Z, Huang X H, Luo J H, Lu D F, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Miao J S, Xie Y F, Wang Y C, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou C C, Li Y, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Tian Q L, Wang Z X, Han B.The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180(4): 2077-2090. |
| [2] | 罗玉坤, 朱智伟, 陈能, 段彬伍, 章林平. 中国主要稻米的粒型及其品质特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2004(2): 49-53. |
| Luo Y K, Zhu Z W, Chen N, Duan B W, Zhang L P.Grain types and related quality characteristics of rice in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2004(2): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 杨联松, 白一松, 张培江, 许传万, 胡兴明, 王伍梅, 佘德红, 陈桂芝. 谷粒形状与稻米品质相关性研究[J]. 杂交水稻, 2001(4): 51-53, 57. |
| Yang L S, Bai Y S, Zhang P J, Xu C W, Hu X M, Wang W M.Studies on the correlation between grain shape and grain quality in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2001(4): 51-53, 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Huang R Y, Jiang L R, Zheng J S, Wang T S, Wang H C, Huang Y M, Hong Z L.Genetic bases of rice grain shape: So many genes, so little known[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2013, 18(4): 218-226. |
| [5] | Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F.Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61(1): 421-442. |
| [6] | Chan A N, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y, Zhuang Z H. Identification through fine mapping and verification using CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis for a minor QTL controlling grain weight in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2021, 134: 327-337. . |
| [7] | Li N, Xu R, Duan P, Li Y H.Control of grain size in rice[J]. Plant Reproduction, 2018, 31: 237-251. |
| [8] | 康艺维, 陈玉宇, 张迎信. 水稻粒型基因克隆研究进展及育种应用展望[J]. 中国水稻学, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. |
| Kang Y W, Chen Y Y, Zhang Y X.Research progress and breeding prospects of grain size associated genes in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Yamamoto T, Yonemaru J, Yano M.Towards the understanding of complex traits in rice: Substantially or superficially[J]. DNA Research, 2009, 16: 141-154. |
| [10] | Takai T, Ikka T, Kondo K, Nonoue Y, Ono N, Arai-Sanoh Y, Yoshinaga S, Nakano H, Yano M, Kondo M, Yamamoto T.Genetic mechanisms underlying yield potential in the rice high-yielding cultivar Takanari, based on reciprocal chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2014, 14(1): 295. |
| [11] | Nagata K, Ando T, Nonoue Y, Mizubayashi T, Kitazawa N, Shomura A, Matsubara K, Ono N, Mizobuchi R, Shabaya T, Ogisotanaka E, Hori K, Yano M, Fukuoka S.Advanced backcross QTL analysis reveals complicated genetic control of rice grain shape in a japonica ×indica cross[J]. Breeding Science, 2015, 65(4): 308-318. |
| [12] | 王琳琳, 陈玉宇, 郭梁, 张宏伟, 樊叶杨, 庄杰云. 水稻第1染色体qTGW1.2区域粒重组分性状QTL的剖析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 232-240. |
| Wang L L, Chen Y Y, Guo L, Zhang H W, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of quantitative trait loci for grain weight and its component traits in the qTGW1.2 region on chromosome 1 of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(3): 232-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 朱安东, 孙志超, 朱玉君, 张荟, 牛小军, 樊叶杨, 张振华, 庄杰云. 应用剩余杂合体衍生群体定位水稻粒重粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 144-151. |
| Zhu A D, Sun Z C, Zhu Y J, Zhang H, N X J, Fan Y Y, Zhang Z H, Zhuang J Y. Identification of QTL for grain weight and grain shape using populations derived from residual heterozygous lines of indica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 144-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Ye H, Foley M E, Gu X Y.New seed dormancy loci detected from weedy rice-derived advanced populations with major QTL alleles removed from the background[J]. Plant Science, 2010, 179(6): 612-619. |
| [15] | Bai X, Wu B, Xing Y.Yield-related QTLs and their applications in rice genetic improvement[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2012, 54: 300-311. |
| [16] | Wang Z, Chen J Y, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Validation of qGS10, a quantitative trait locus for grain size on the long arm of chromosome 10 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(1): 16-26. |
| [17] | Zhang H W, Fan Y Y, Zhu Y J, Chen J Y, Yu S B, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of the qTGW1.1 region into two tightly-linked minor QTLs having stable effects for grain weight in rice[J]. BMC Genetics, 2016, 17: 98. |
| [18] | 王建康. 数量性状基因的完备区间作图方法[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(2): 239-245. |
| Wang J K.Inclusive composite interval mapping of quantitative trait genes[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(2): 239-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | McCouch S R, CGSNL (Committee on Gene Symbolization, Nomenclature and Linkage, Rice Genetics Cooperative). Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1(1): 72-84. |
| [20] | Ruan B P, Shang L S, Zhang B, Hu J, Wang Y X, LIN H, Zhang A P, Liu C L, P Y L, Zhu L, Ren D Y, Shen L, Dong G J, Zhang G H, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. Natural variation in the promoter of TGW2 determines grain width and weight in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2020, 227(2): 629-640. |
| [21] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X.A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39: 623-630. |
| [22] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112: 1164-1171. |
| [23] | Mao H L, Sun S Y, Yao J L, Wang C R, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107: 19579-19584. |
| [24] | Dong N Q, Sun Y W, Guo T, Shi C L, Zhang Y M, Kan Y, Xiang Y H, Zhang H, Yang Y B, Li Y C, Zhao H Y, Yu H X, Lu Z Q, Wang Y, Ye W W, Shan J X, Lin H X.UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic fux redirection in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2629. |
| [25] | Li Y B, Fan CC, Xing Y Z, Jiang Y H, Luo L J, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J H, He Y Q, Zhang Q F. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2011, 43(12): 1266-1269. |
| [26] | Xu C J, Liu Y, Li Y B, Xu X B, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J H, Zhang Q F.Differential expression of GS5 regulates grain size in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(9): 2611-2623. |
| [27] | Duan P G, Xu J S, Zeng D L, Zhang B L, Geng M F, Zhang G Z, Huang K, Huang L J, Xu R, Ge S, Qian Q, Li Y H.Natural variation in the promoter of GSE5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10: 685-694. |
| [28] | Liu J, Chen J, Zheng X, Wu F, Lin Q, Heng Y, Cheng Z, Zhou K, Lin Q, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Wang H, Wan J.GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signaling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17043. |
| [29] | Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M.Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40: 1023-1028. |
| [30] | Wan X Y, Weng J F, Zhai H Q, Wang J K, Lei C L, Liu X L, Guo T, Jiang L, Su N, Wan J M.Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for rice grain width and fine mapping of an identified QTL allele gw-5 in a recombination hotspot region on chromosome 5[J]. Genetics, 2008, 179: 2239-2252. |
| [31] | Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wan J.Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight[J]. Cell Research, 2008, 18: 1199-1209. |
| [32] | Yan C J, Zhou J H, Yan S, Chen F, Yeboah M, Tang S Z, Liang G H, Gu M H.Identification and characterization of a major QTL responsible for erect panicle trait in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2007, 115(8): 1093-1100. |
| [33] | Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X.Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009, 41(4): 494-497. |
| [34] | Fumio T S, Yasushi K, Hiroshi K, Haruko O, Akemi T, Naho H, Akio M, Hirohiko H, Hidemi K, Masahiro Y, Seiichi T.A loss-of-function mutation of rice DENSE PANICLE 1 causes semi-dwarfness and slightly increased number of spikelets[J]. Breeding Science, 2011, 61(1): 17-25. |
| [35] | Sun H, Qian Q, Wu K, Luo J, Wang S, Zhang C, Ma Y, Liu Q, Huang X, Yuan Q, Han R, Zhao M, Dong G, Guo L, Zhu X, Gou Z, Wang W, Wu Y, Lin H, Fu X.Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate nitrogen-use efficiency in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(4): 652-656. |
| [36] | Li M, Li X, Zhou Z, Wu P, Fang M, Pan X, Lin Q, Luo W, Wu G, Li H.Reassessment of the four yield-related genes Gn1a, DEP1, GS3, and IPA1 in rice using a CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 377. |
| [37] | Liu Q, Han R, Wu K, Zhang J, Ye Y, Wang S, Chen J, Pan Y, Li Q, Xu X, Zhou J, Tao D, Wu Y, Fu X.G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 852. |
| [38] | Sun S, Wang L, Mao H, Shao L, Li X, Xiao J, Ouyang Y, Zhang Q.A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 851. |
| [39] | Li N, Li Y H. Signaling pathways of seed size control in plants[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 33: 23-32. |
| [40] | Yu S. B, Li J. X, Xu C. G, Tan Y. F, Gao Y. J, Li X. H, Zhang Q F, Maroof S. Importance of epistasis as the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 1997, 94: 9226-9231. |
| [41] | Zeng Y X, Ji Z J, Wen Z H, Liang Y, Yang C D.Combination of eight alleles at four quantitative trait loci determines grain length in rice[J]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11: 3. |
| [42] | Odonkor S, Choi S, Chakraborty D, Martinez-Bello L, Wang X, Bahri B A, Tenaillon M I, Panaud O, Devos K M.QTL mapping combined with comparative analyses identified candidate genes for reduced shattering in Setaria italica[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 918. |
| [43] | Li J X, Yu S B, Xu C G, Xu C G, Tan Y F, Gao Y J, Li X H, Zhang Q F.Analyzing quantitative trait loci for yield using a vegetatively replicated F2 population from a cross between the parents of an elite rice hybrid[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2000, 101: 248-254. |
| [44] | 庄杰云, 樊叶杨, 吴建利, 夏英武, 郑康乐. 应用二种定位法比较不同世代水稻产量性状QTL的检测结果[J]. 遗传学报, 2001(5): 458-464. |
| Zhuang J Y, Fan Y Y, Wu J L, Xia Y W, Zheng K L.Comparison of the detection of QTL for yield traits in different generations of a rice cross using two mapping approaches[J]. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2001(5): 458-464. | |
| [45] | 姜树坤, 张喜娟, 黄成, 邢亚南, 郑旭, 徐正进, 陈温福. 基于粳稻F2和F2:6群体的连锁图谱及剑叶性状QTL比较分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 372-378. |
| Jiang S K, Zhang X J, Huang C, Xing Y N, Zheng X, Xu Z J, Chen W F.Comparison of genetic linkage map and QTLs controlling flag leaf traits based on F2 and F2:6 populations derived from japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(4): 372-378. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 郭小蛟, 张涛, 蒋开锋, 杨莉, 曹应江, 杨乾华, 游书梅, 万先齐, 罗婧, 李昭祥, 高磊, 郑家奎. 水稻籼粳交F8、F2群体穗长QTL比较分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(23): 4849-4857. |
| Guo X J, Zhang T, Jiang K F, Yang L, Cao Y J, Yang Q H, You S M, Wan X Q, Luo J, Li Z X, Gao L, Zheng J K.Comparison of panicle length QTL based on F2 and F8 populations derived from rice subspecies cross[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(23): 4849-4857. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | Mackay T F C, Stone E A, Ayroles J F. The genetics of quantitative traits: Challenges and prospects[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2009, 10: 565-577. |
| [48] | Kumar J, Gupta D S, Gupta S, Dubey S, Gupta P, Kumar S.Quantitative trait loci from identification to exploitation for crop improvement[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2017, 36: 1187-1213. |
| [49] | 李盼盼, 朱玉君, 郭梁, 庄杰云, 樊叶杨. 利用剩余杂合体衍生的近等基因系精细定位水稻粒长微效QTL qGL1.1[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 125-134. |
| Li P P, Zhu Y J, Guo L, Zhuang J Y, Fan Y Y.Fine mapping of qGL1.1, a minor QTL for grain length, using near isogenic lines derived from residual heterozygotes in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 125-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | Zhang B, Shang L G, Ruan B P, Zhang A P, Yang S L, Jiang H Z, Liu C L, Hong K, Lin H, Gao Z Y, Hu J, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q.Development of three sets of high-throughput genotyped rice chromosome segment substitution lines and QTL mapping for eleven traits[J]. Rice, 2019, 12: 33. |
| [51] | Ma F Y, Du J, Wang D C, Wang H, Zhao B B,. He G H, Yang Z L, Zhang T, Wu R H, Zhao F M.Identification of long-grain chromosome segment substitution line Z744 and QTL analysis for agronomic traits in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19(5): 1163-1169. |
| [52] | Wang L L, Chen Y Y, Guo L, Zhang H W, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of qTGW1.2 to three QTLs for grain weight and grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Euphytica, 2015, 202: 119-127. |
| [53] | Wang W H, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Fine-mapping of qTGW1.2a, a quantitative trait locus for 1000-grain weight in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 220-228. |
| [54] | Dong Q, Zhang Z H, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Mou T M, Ma L Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection and fine-mapping of two QTL for grain size linked in a 460-kb region on chromosome 1 of rice[J]. Rice, 2018, 11: 44. |
| [55] | Yan S, Zou G H, Li S J, Wang H, Li·H Q, Zhai G W, Guo P, Song H M, Yan C H, Tao Y Z. Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011 123: 1173-1181. |
| [56] | Lu L, Shao D, Qiu X J, Sun L, Yan W H, Zhou X C, Yang L, He Y Q, Yu S B, Xing W Z.Natural variation and artificial selection in four genes determine grain shape in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 200(4): 1269-1280. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||