
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 95-107.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8083 95
• 综述 • 下一篇
苏达1,2, 吴良泉2, SørenKRasmussen3, 周庐建4, 程方民4,*
收稿日期:2018-07-16
修回日期:2018-12-31
出版日期:2019-03-10
发布日期:2019-03-10
通讯作者:
程方民
基金资助:Da SU1,2, Liangquan WU2, K Rasmussen Søren3, Lujian ZHOU4, Fangmin CHENG4,*
Received:2018-07-16
Revised:2018-12-31
Online:2019-03-10
Published:2019-03-10
Contact:
Fangmin CHENG
摘要:
提高或维持水稻产量的同时,提高稻米品质已成为目前水稻育种的首要目标之一。其中,通过降低籽粒中植酸等抗营养因子,增加锌、铁生物有效性以提升水稻营养品质,是目前水稻品质改良的一个重要方向。本文主要综述了水稻籽粒中植酸合成的代谢路径、低植酸水稻的筛选及相关功能基因的遗传特点、植酸生理代谢的调控网络、低植酸水稻农艺性状劣变和生态适应性降低的生理原因、籽粒植酸合成的环境调控效应等相关研究进展。可为低植酸水稻品质改良以及栽培调优提供借鉴。
中图分类号:
苏达, 吴良泉, SørenKRasmussen, 周庐建, 程方民. 低植酸水稻种质资源筛选、遗传生理调控与环境生态适应性 研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 95-107.
Da SU, Liangquan WU, K Rasmussen Søren, Lujian ZHOU, Fangmin CHENG. Research Advances on the Low Phytic Acid Rice Breeding and Their Genetic Physiological Regulation and Environmental Adaptability[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 95-107.
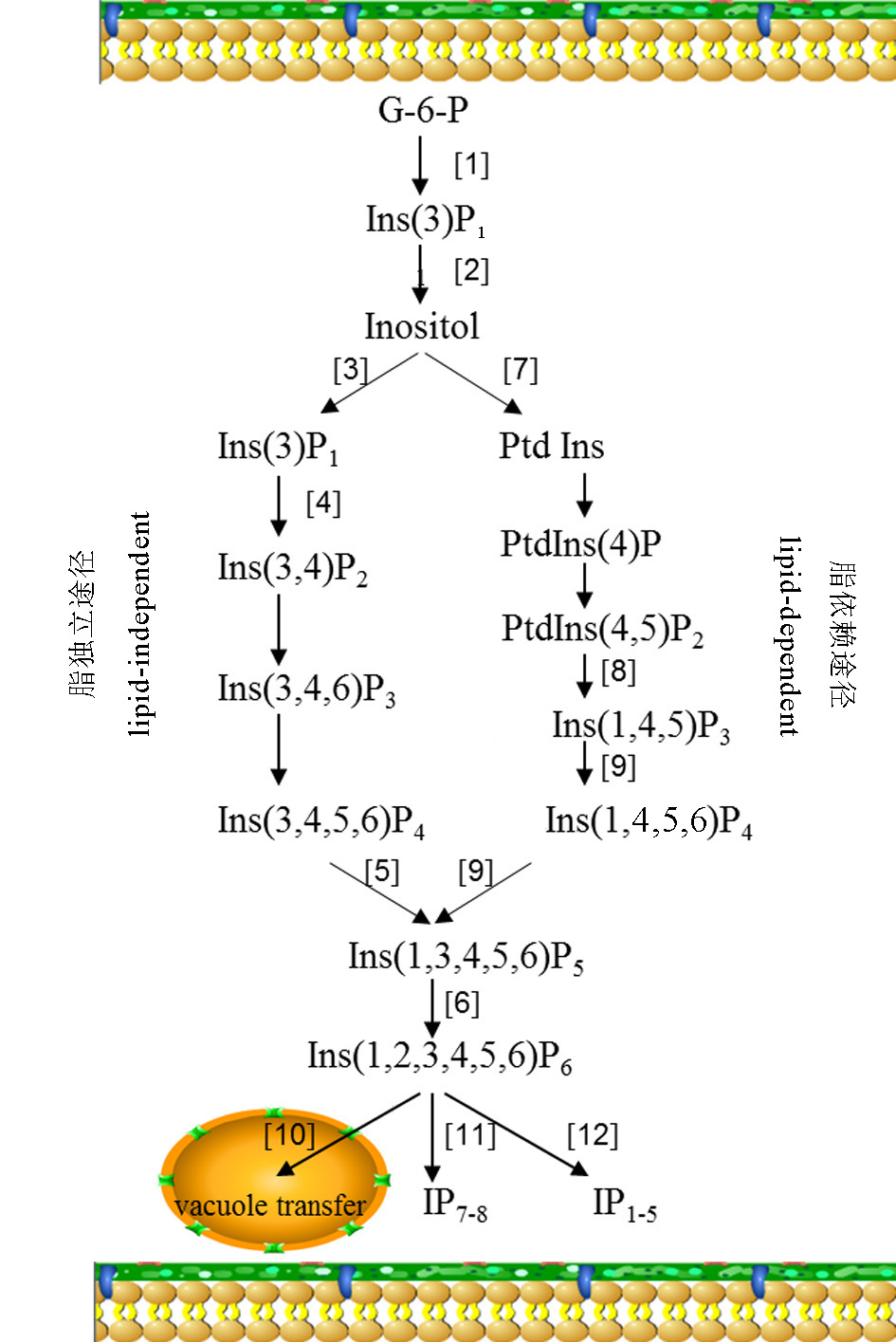
图1 植酸的生物合成 G-6-P,葡萄糖-6-磷酸; Inositol,肌醇;Ins(3)P1, 肌醇-3-单磷酸; Ins(3,4)P2,肌醇-3,4-二磷酸;Ins(3,4,6)P3,肌醇-3,4-6-三磷酸;Ins(3,4,5,6)P4,肌醇-3,4-5-6-四磷酸;Ptd Ins,磷酯酰肌醇;PtdIns(4)P,磷脂酰肌醇-4-单磷酸;PtdIns(4,5)P2,磷脂酰肌醇4,5二磷酸;Ins(1,4,5)P3,肌醇1,4,5三磷酸;Ins(1,4,5,6)P4,肌醇1,4,5,6四磷酸;Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5,肌醇1-3,4-5-6-五磷酸;Ins(1,2,3,4,5,6)P6,肌醇1-2-3-4-5-6-六磷酸(植酸)。[1]–肌醇-3-磷酸合成酶;[2]–肌醇-3-磷酸水解酶;[3]–肌醇激酶;[4]–磷酸甘油酸激酶;[5]–多磷酸-肌醇5,6-激酶;[6]–1,3,4,5,6-5-肌醇-2-磷酸激酶;[7]–磷脂酰肌醇合成酶;[8]–磷酸磷脂酶C;[9]–肌醇1,4,5-三磷酸激酶;[10]–ABC转运蛋白;MRP转运蛋白;[11]–六磷酸肌醇激酶;[12]–植酸酶或磷酸酶。
Fig. 1. Biosynthetic pathways of phytic acid. [1], MIPS,myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthase; [2], Ins(3)P1-monophosphatase IMP,myo-inositol-phosphate monophosphatase; [3], MIK,myo-inositol- kinase; [4], PGK,phosphoglycerate kinase; [5], ITP5/6K,inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate 5/6-kinase; [6], IPK1,inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase; [7], PtdIns Synthase,phosphatidy linositol synthase; [8], Phospholipase C; [9], Inositol 1,4,5-tris-phosphate kinase; [10], ABC transporter; MRP transporter; [11], InsP6 Kinase; [12], Phytases or phosphatase.
| 突变方法 Origin of mutation | 基因位点 Locus | 低植酸突变体名称 Name of lpa | 植酸含量降幅 Reduction in Phytic acid /% | 无机磷变化 Pi variation | 总磷变化 Total P variation | 产量劣变 Yield inferiority | 其他 Other phenotypic changes | 参考文献 Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| antisense under Ole18 | MIPS (RION1) | -- | 68-75 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | 否 | 植酸变化仅影响胚乳和糊粉层 | [ | ||
| antisense under 35S | MIPS (RION1) | -- | -- | -- | 不变 | -- | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi under GluB-1 | MIPS (RION1) | lpa1 | 17 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | -- | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi | MIPS | -- | -- | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | -- | MIPS基因下调4.59倍;阳离子含量增加, 其中精米中铁含量增加1.6倍;肌醇和抗坏血酸含量降低 | [ | ||
| RNAi under Oleosin 18 | IPK1 | -- | 69(T4代) | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | IPK1 转录表达下调3.85倍;胚乳中铁含量增加1.8倍 | [ | ||
| EMS | ITPK | -- | 46-68 | -- | -- | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MIK | Os-lpa-XS110-1 | 34-64 | -- | -- | 是. | 23个蛋白表达量增加;肌醇,果聚糖, 半乳糖和半乳糖苷含量增加;低价磷酸肌醇盐未检出 | [ | ||
| EMS | MIK | lpa N15-186 | 34-75 | -- | -- | -- | -- | [ | ||
| Gene silence (amiMIK) | MIK | -- | 37.0-50.7, | 增加 3.2-4.8倍 | -- | -- | OsMIK转录表达降低,不同株系总磷含量变化不一致 | [ | ||
| Gene silence (hpMIK) | MIK | -- | 14.9-50.2 | 增加 1.8-4.4倍 | -- | -- | OsMIK转录表达降低,不同株系总磷含量变化不一致 | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MRP | Os-lpa-XS110-2 | 20 | -- | -- | 是 | 肌醇和寡聚糖降低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MRP | Os-lpa-XS110-3 | 约100 | 增加10倍 | 不变 | 致死 | 肌醇含量增加400%;植酸量<0.20 mg/g | [ | ||
| T-DNA insertion | MRP | -- | 90 | 增加10倍 | 不变 | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi under Oleosin 18 | MRP | -- | 35.8-71.9 | 增加 7.5 倍 | -- | 是 | 脂和核酸中的磷含量降低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Os-lpa-XQZ-3 | -- | -- | -- | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | -- | 44 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | lpa-Z9B-1 | 45 | -- | 降低 | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | lpa-MH86-1 | 43.9-35.2 | 增加108%-170% | 降低 | 是 | 糖、小分子籽粒内含物、丝氨酸、赖氨酸、硫、磷酸、 GABA活性增加;植酸、硫酸盐和磷酸盐基因表达量改变 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | 2-PGK | KBNT lpa1-1 | 39-71 | 增加5%-32% | -- | 减产10% | 植酸蛋白体体积减小;低价肌醇磷酸盐增加 | [ | ||
| 60Co-γ | 2-PGK | DR1331-2 | 45 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | lpa1 | 45 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | 胚中植酸降幅高于糊粉层;钙, 锰降低、锌增加; 无低价磷酸盐 | [ [ | ||
| 60Co-γ+ NaN3 | -- | Os-lpa-R6547-3 | -- | -- | -- | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Dontokoi176 | 15 | -- | 增加12% | 否 | 垩白增幅率较低,铁,钼含量降低,其它矿质元素增加 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari2623 | 45 | -- | 不变 | 否 | 垩白增幅率较高,萌发前期活性较低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Koshihikari4019 | 36 | -- | 不变 | 否 | 垩白增幅率较高 | [ | ||
| Callus culture | -- | NC1857 | 17.1 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜、锰、钠、锌增加,钼降低41.9% | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Dontokoil 76 | 14.7 | 增加 | 增加 22% | 小幅降低 | 增加了43.4%的铜,33.4%的钾,20.4%的镁,11.5%的钠, 39.1%的磷,23.6%的硫,10.8%的二氧化硅,44.2%的锌。 而降低铁13.8%,钼17.5% | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Koshihikari49 | 5.9 | 增加 | 增加 9.4% | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari2623 | 44.7 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari3847 Koshihikari | 47.9 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari4019 | 35.9 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
表1 水稻低植酸突变类型及其特点
Table 1 Different lpa rice mutants and their characteristics.
| 突变方法 Origin of mutation | 基因位点 Locus | 低植酸突变体名称 Name of lpa | 植酸含量降幅 Reduction in Phytic acid /% | 无机磷变化 Pi variation | 总磷变化 Total P variation | 产量劣变 Yield inferiority | 其他 Other phenotypic changes | 参考文献 Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| antisense under Ole18 | MIPS (RION1) | -- | 68-75 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | 否 | 植酸变化仅影响胚乳和糊粉层 | [ | ||
| antisense under 35S | MIPS (RION1) | -- | -- | -- | 不变 | -- | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi under GluB-1 | MIPS (RION1) | lpa1 | 17 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | -- | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi | MIPS | -- | -- | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | -- | MIPS基因下调4.59倍;阳离子含量增加, 其中精米中铁含量增加1.6倍;肌醇和抗坏血酸含量降低 | [ | ||
| RNAi under Oleosin 18 | IPK1 | -- | 69(T4代) | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | IPK1 转录表达下调3.85倍;胚乳中铁含量增加1.8倍 | [ | ||
| EMS | ITPK | -- | 46-68 | -- | -- | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MIK | Os-lpa-XS110-1 | 34-64 | -- | -- | 是. | 23个蛋白表达量增加;肌醇,果聚糖, 半乳糖和半乳糖苷含量增加;低价磷酸肌醇盐未检出 | [ | ||
| EMS | MIK | lpa N15-186 | 34-75 | -- | -- | -- | -- | [ | ||
| Gene silence (amiMIK) | MIK | -- | 37.0-50.7, | 增加 3.2-4.8倍 | -- | -- | OsMIK转录表达降低,不同株系总磷含量变化不一致 | [ | ||
| Gene silence (hpMIK) | MIK | -- | 14.9-50.2 | 增加 1.8-4.4倍 | -- | -- | OsMIK转录表达降低,不同株系总磷含量变化不一致 | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MRP | Os-lpa-XS110-2 | 20 | -- | -- | 是 | 肌醇和寡聚糖降低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays + sodium zide | MRP | Os-lpa-XS110-3 | 约100 | 增加10倍 | 不变 | 致死 | 肌醇含量增加400%;植酸量<0.20 mg/g | [ | ||
| T-DNA insertion | MRP | -- | 90 | 增加10倍 | 不变 | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| RNAi under Oleosin 18 | MRP | -- | 35.8-71.9 | 增加 7.5 倍 | -- | 是 | 脂和核酸中的磷含量降低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Os-lpa-XQZ-3 | -- | -- | -- | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | -- | 44 | 增加 (等摩尔) | -- | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | lpa-Z9B-1 | 45 | -- | 降低 | 是 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | Sultr3;3 | lpa-MH86-1 | 43.9-35.2 | 增加108%-170% | 降低 | 是 | 糖、小分子籽粒内含物、丝氨酸、赖氨酸、硫、磷酸、 GABA活性增加;植酸、硫酸盐和磷酸盐基因表达量改变 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | 2-PGK | KBNT lpa1-1 | 39-71 | 增加5%-32% | -- | 减产10% | 植酸蛋白体体积减小;低价肌醇磷酸盐增加 | [ | ||
| 60Co-γ | 2-PGK | DR1331-2 | 45 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | -- | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | lpa1 | 45 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 否 | 胚中植酸降幅高于糊粉层;钙, 锰降低、锌增加; 无低价磷酸盐 | [ [ | ||
| 60Co-γ+ NaN3 | -- | Os-lpa-R6547-3 | -- | -- | -- | 致死 | -- | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Dontokoi176 | 15 | -- | 增加12% | 否 | 垩白增幅率较低,铁,钼含量降低,其它矿质元素增加 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari2623 | 45 | -- | 不变 | 否 | 垩白增幅率较高,萌发前期活性较低 | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Koshihikari4019 | 36 | -- | 不变 | 否 | 垩白增幅率较高 | [ | ||
| Callus culture | -- | NC1857 | 17.1 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜、锰、钠、锌增加,钼降低41.9% | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Dontokoil 76 | 14.7 | 增加 | 增加 22% | 小幅降低 | 增加了43.4%的铜,33.4%的钾,20.4%的镁,11.5%的钠, 39.1%的磷,23.6%的硫,10.8%的二氧化硅,44.2%的锌。 而降低铁13.8%,钼17.5% | [ | ||
| γ-rays | -- | Koshihikari49 | 5.9 | 增加 | 增加 9.4% | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari2623 | 44.7 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari3847 Koshihikari | 47.9 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| EMS | -- | Koshihikari4019 | 35.9 | 增加 (等摩尔) | 不变 | 小幅降低 | 铜,锰,钠和锌增加,钼降低 | [ | ||
| [1] | Raboy V.Seeds for a better future: 'Low phytate', grains help to overcome malnutrition and reduce pollution.Trends Plant Sci, 2001, 6(10): 458-462. |
| [2] | Borg S, Brinch-Pedersen H, Tauris B, Holm P B.Iron transport, deposition and bioavailability in the wheat and barley grain.Plant Soil, 2009, 325(1-2): 15-24. |
| [3] | Rosa-Sibakov N, Kaisa P, Valérie M.How does wheat grain, bran and aleurone structure impact their nutritional and technological properties?Trends Food Sci Technol, 2015, 41(2): 118-134. |
| [4] | 张倩雯, 丁广大, 王效华, Liu L, King J G, 徐芳森, 石磊. 植物种子植酸研究进展. 植物科学学报, 2016, 34(5): 814-820. |
| Zhang Q W, Ding G D, Wang X H, Liu L, King J G, Xu F S, Shi L.Research progress on plant seed phytate.Plant Sci J, 2016, 34(5): 814-820. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Brinch-Pedersen H, Sorensen L D, Holm P B.Engineering crop plants: Getting a handle on phosphate.Trends Plant Sci, 2002, 7(3): 118-125. |
| [6] | Welch R M, Graham R D.Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J Exp Bot, 2004, 55(396): 353-364. |
| [7] | Boncompagni E, Gregorio O, Eleonora C, Prakash I G, Stefania G, Theophilus T K Z, Maria G D, Erik N, Francesca S. Antinutritional factors in pearl millet grains: Phytate and goitrogens content variability and molecular characterization of genes involved in their pathways.PloS One, 2018, 13(6): e0198394. |
| [8] | Loewus F A, Murthy P. Myo-inositol metabolism in plants. Plant Sci, 2000, 150(1): 1-19. |
| [9] | Raboy V.Low-phytic-acid grains.Food Nutr Bull, 2000, 21(4): 423-427. |
| [10] | Suzuki M, Tanaka K, Kuwano M, Yoshida K T.Expression pattern of inositol phosphate-related enzymes in rice (Oryza sartiva L.): Implications for the phytic acid biosynthetic pathway. Gene, 2007, 405(1-2): 55-64. |
| [11] | Coelho C M, Tsai S M, Vitorello V A.Dynamics of inositol phosphate pools (tris-, tetrakis- and pentakisphosphate) in relation to the rate of phytate synthesis during seed development in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Plant Physiol, 2005, 162(1): 1-9. |
| [12] | Shi J, Wang H, Wu Y, Hazebroek J, Meeley R B, Ertl D S.The maize low-phytic acid mutant lpa2 is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene. Plant Physiol, 2003, 131(2): 507-515. |
| [13] | Cui M, Liang D, Ma F W.Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding kiwifruit L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase, a key gene of inositol formation. Mol Biol Rep, 2013, 40(1): 697-705. |
| [14] | Perera I, Saman S, Naoki H.Manipulating the phytic acid content of rice grain toward improving micronutrient bioavailability.Rice, 2018, 11(1): 4. |
| [15] | Coelho C M, Benedito V A, Figueira A, Vitorello V A, Azevedo R A.Variation in the enzyme activity and gene expression of myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthase and phytate accumulation during seed development in common bean(Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Acta Physiol Plant, 2007, 190(3): 24-39. |
| [16] | Larson S R, Rutger J N, Young K A, Raboy V.Isolation and genetic mapping of a non-lethal rice (Oryza sativa L.) low phytic acid 1 mutation. Crop Sci, 2000, 40(5): 1397-1405. |
| [17] | Wilcox J R, Premachandra G S, Young K A, Raboy V.Isolation of high seed inorganic P, low-phytate soybean mutants.Crop Sci, 2000, 40(6): 1601-1605. |
| [18] | Yuan F J, Zhao H J, Ren X L, Zhu S L, Fu X J, Shu Q Y.Generation and characterization of two novel low phytate mutations in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor Appl Genet, 2007, 115(7): 945-957. |
| [19] | Hambidge K M, Krebs N F, Westcott J L, Sian L, Miller L V, Peterson K L, Raboy V.Absorption of calcium from tortilla meals prepared from low-phytate maize.Am J Clin Nutr, 2005, 82(1): 84-87. |
| [20] | Poulsen H D, Johansen K S, Hatzack F, Boisen S, Rasmussen S R K. Nutritional value of low-phytate barley evaluated in rats.Acta Agr Scand A-An, 2001, 51(1): 53-58. |
| [21] | Petry N, Egli I, Campion B, Nielsen E, Hurrell R.Genetic reduction of phytate in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds increases iron absorption in young women. J Nutr, 2013, 143(8): 1219-1224. |
| [22] | Hambidge K M, Huffer J W, Raboy V, Grunwald G K, Westcott J L, Sian L, Miller L V, Dorsch J A, Krebs N F.Zinc absorption from low-phytate hybrids of maize and their wild-type isohybrids.Am J Clin Nutr, 2004, 79(6): 1053-1059. |
| [23] | Kuwano M, Mimura T, Takaiwa F, Yoshida K T.Generation of stable 'low phytic acid' transgenic rice through antisense repression of the 1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate synthase gene(RINO1) using the 18-kDa oleosin promoter. Plant Biotechnol J, 2009, 7(1): 96-105. |
| [24] | Feng X, Yoshida K T.Molecular approaches for producing low-phytic-acid grains in rice.Plant Biotechnol, 2004, 21(3): 183-189. |
| [25] | Li W X, Huang J Z, Zhao H J, Tan Y Y, Cui H R, Poirier Y, Shu Q Y.Production of low phytic acid rice by hairpin RNA- and artificial microRNA-mediated silencing of OsMIK in seeds. Plant Cell Tiss Org, 2014, 119(1): 15-25. |
| [26] | Kuwano M, Ohyama A, Tanaka Y, Mimura T, Takaiwa F, Yoshida K T.Molecular breeding for transgenic rice with low-phytic-acid phenotype through manipulating myo-inositol 3-phosphate synthase gene. Mol Breeding, 2006, 18(3): 263-272. |
| [27] | Ali N, Paul S, Gayen D, Sarkar S N, Datta S K, Datta K.RNAi mediated down regulation of myo-inositol-3- phosphate synthase to generate low phytate rice. Rice, 2013, 6(1): 1-12. |
| [28] | Kim S I, Andaya C B, Newman J W, Goyal S S, Tai T H.Isolation and characterization of a low phytic acid rice mutant reveals a mutation in the rice orthologue of maize MIK. Theor Appl Genet, 2008, 117(8): 1291-1301. |
| [29] | Kim S I, Andaya C B, Goyal S S, Tai T H.The rice OsLpa1 gene encodes a novel protein involved in phytic acid metabolism. Theor Appl Genet, 2008, 117(5): 769-779. |
| [30] | Zhao H J, Liu Q L, Ren X L, Wu D X, Shu Q Y.Gene identification and allele-specific marker development for two allelic low phytic acid mutations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding, 2008, 22(4): 603-612. |
| [31] | Kim S, Tai T H.Identification of novel rice low phytic acid mutations via TILLING by sequencing.Mol Breeding, 2014, 34(4): 1717-1729. |
| [32] | Ali N, Paul S, Gayen D, Sarkar S N, Datta K, Datta S K.Development of low phytate rice by RNAi mediated seed-specific silencing of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakis phosphate 2-kinase gene (IPK1). PloS One, 2013, 8(7): e68161. |
| [33] | Nagy R, Grob H, Weder B, Green P, Klein M, Frelet-Barrand A, Schjoerring J K, Brearley C, Martinoia E. The Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette protein ATMRP5/ATABCC5 is a high-affinity inositol hexakisphosphate transporter involved in guard cell signaling and phytate storage. J Biol Chem, 2009: jbc. M109. 030247. |
| [34] | Xu X H, Zhao H J, Liu Q L, Frank T, Engel K H, An G H, Shu Q Y.Mutations of the multi-drug resistance-associated protein ABC transporter gene 5 result in reduction of phytic acid in rice seeds.Theor Appl Genet, 2009, 119(1): 75-83. |
| [35] | Wanke D, Üner Kolukisaoglu H.An update on the ABCC transporter family in plants: Many genes, many proteins, but how Many functions?Plant Biol, 2010, 12: 15-25. |
| [36] | Maroof M A, Glover N M, Biyashev R M, Buss G R, Grabau E A.Genetic basis of the low-phytate trait in the soybean line CX1834.Crop Sci, 2009, 49(1): 69-76. |
| [37] | Panzeri D, Cassani E, Doria E, Tagliabue G, Fort L, Campion B, Bollini R, Brearley C A, Pilu R, Nielsen E, Sparvoli F.A defective ABC transporter of the MRP family, responsible for the bean lpa1 mutation, affects the regulation of the phytic acid pathway, reduces seed myo-inositol and alters ABA sensitivity. New Phytol, 2011, 191(1): 70-83. |
| [38] | Cerino B F, Amelotti M, Cassani E, Pilu R.Study of low phytic acid1-7 (lpa1-7), a new ZmMRP4 mutation in maize. J Hered, 2012, 103(4): 598-605. |
| [39] | Shi J, Wang H, Hazebroek J, Harp T.The maize low-phytic acid 3 encodes a myo-inositol kinase that plays a role in phytic acid biosynthesis in developing seeds. Plant J, 2005, 42(5): 708-719. |
| [40] | Pilu R, Panzeri D, Cassani E, Cerino B F, Landoni M, Nielsen E.A paramutation phenomenon is involved in the genetics of maize low phytic acid 1-241 (lpa1-241) trait. Heredity, 2009, 102(3): 236-245. |
| [41] | Bhati K K, Alok A, Kumar A, Kaur J, Tiwari S, Pandey A K, Notes A.Silencing of ABCC13 transporter in wheat reveals its involvement in grain development, phytic acid accumulation and lateral root formation. J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(14): 4379-4389. |
| [42] | Bhati K K, Aggarwal S, Sharma S, Mantri S, Singh S P, Bhalla S, Kaur J, Tiwari S, Roy J K, Tuli R, Pandey A K.Differential expression of structural genes for the late phase of phytic acid biosynthesis in developing seeds of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci, 2014, 224: 74-85. |
| [43] | Mitsuhashi N, Kondo M, Nakaune S, Ohnishi M, Hayashi M, Hara-Nishimura I, Richardson A, Fukaki H, Nishimura M, Mimura T.Localization of myo-inositol-1- phosphate synthase to the endosperm in developing seeds of Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot, 2008, 59(11): 3069-3076. |
| [44] | Chiera J M, Grabau E A.Localization of myo-inositol phosphate synthase(GmMIPS-1) during the early stages of soybean seed development. J Exp Bot, 2007, 58: 2261-2268. |
| [45] | Li W X, Zhao H J, Pang W Q, Cui H R, Poirier Y, Shu Q Y.Seed-specific silencing of OsMRP5 reduces seed phytic acid and weight in rice. Transgen Res, 2014, 23(4): 585-599. |
| [46] | Sparvoli F, Cominelli E.Seed biofortification and phytic acid reduction: a conflict of interest for the plant? Plants, 2015, 4(4): 728-755. |
| [47] | Borghi L, Kang J, Ko D, Lee Y, Marinoia E.The role of ABCG-type ABC transporters in phytohormone transport.Biochem Soc T, 2015, 43(5): 924-930. |
| [48] | Cominelli E, Confalonieri M, Carlessi M, Cortinovisa G, Daminati M G, Porch T G, Losa A, Sparvoli F.Phytic acid transport in Phaseolus vulgaris: A new low phytic acid mutant in the PvMRP1 gene and study of the PvMRPs promoters in two different plant systems.Plant Sci, 2018, 270: 1-12. |
| [49] | Israel D W, Taliercio E, Kwanyuen P, Burton J W, Dean L.Inositol metabolism in developing seed of low and normal phytic acid soybean lines.Crop Sci, 2011, 51: 282-289. |
| [50] | Redekar N, Pilot G, Raboy V, Song L, Saghai-Maroof M A. Inference of transcription regulatory network in low phytic acid soybean seeds.Front Plant Sci, 2017, 8: 2029. |
| [51] | Redekar N R, Biyashev R M, Jensen R V, Helm R, Grabau E A, Maroof M A.Genome-wide transcriptome analyses of developing seeds from low and normal phytic acid soybean lines.BMC Genom, 2015, 16(1): 1074. |
| [52] | Liu K S, Xu X H, Ren X L, Fu H W, Wu D X, Shu Q Y.Generation and characterization of low phytic acid germplasm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 2007, 114(5): 803-814. |
| [53] | Zhao H J, Liu Q L, Fu H W, Xu X H, Wu D X, Shu Q Y.Effect of non-lethal low phytic acid mutations on grain yield and seed viability in rice.Field Crop Res, 2008, 108(3): 206-211. |
| [54] | Zhao H, Frank T, Tan Y.Disruption of OsSULTR3;3 reduces phytate and phosphorus concentrations and alters the metabolite profile in rice grains. New Phytol, 2016, 211(3): 926-939. |
| [55] | Ye H, Zhang X Q, Broughton S, Westcott S, Wu D, Lance R, Li C.A nonsense mutation in a putative sulphate transporter gene results in low phytic acid in barley.Funct Integr Genom, 2011, 11(1): 103-110. |
| [56] | Takahashi H, Buchner P, Yoshimoto N, Hawkesford M J, Shiu S H.Evolutionary relationships and functional diversity of plant sulfate transporters.Front Plant Sci, 2012, 2: 119. |
| [57] | Zhang S, Yang W, Zhao Q, Zhou X, Jiang L, Ma S, Liu X, Li Y, Zhang C, Fan Y, Chen R.Analysis of weighted co-regulatory networks in maize provides insights into new genes and regulatory mechanisms related to inositol phosphate metabolism. BMC Genom, 2016, 17(1): 129. |
| [58] | Frank T, Norenberg S, Engel K H.Metabolite profiling of two novel low phytic acid (lpa) soybean mutants. J Agric Food Chem, 2009, 57(14): 6408-6416. |
| [59] | Emami K, Morris N J, Cockell S J, Golebiowska G, Shu Q Y, Gatehouse A M R. Changes in protein expression profiles between a low phytic acid rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica) line and its parental line: a proteomic and bioinformatic approach. J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 58(11): 6912-6922. |
| [60] | Rutger J N, Raboy V, Moldenhauer K A K, Bryant R J, Lee F N, Gibbons J W. Registration of KBNT lpa1-1 low phytic acid germplasm of rice. Crop Sci, 2004, 44(1): 363-364. |
| [61] | Lott J N A, Liu J C, Ockenden I, Truax M. Phytic acid-phosphorus and other nutritionally important mineral nutrient elements in grains of wild-type and low phytic acid (lpa1-1) rice. Seed Sci Res, 2004, 14(2): 109-116. |
| [62] | Andaya C B, Tai T H.Fine mapping of the rice low phytic acid (Lpa1) locus.Theor Appl Genet, 2005, 111(3): 489-495. |
| [63] | Yatou O, Aoki H, Aii J, Tanaka H.Selection of novel non-lethal, low phytic acid mutants and evaluation of their agronomic traits/mineral compositions in rice (Oryza sativa). Jarq-jpn Agr Res Q: Jarq, 2018, 52(1): 39-47. |
| [64] | Hitz W D, Carlson T J, Kerr P S, Sebastian S A.Biochemical and molecular characterization of a mutation that confers a decreased raffinosaccharide and phytic acid phenotype on soybean seeds.Plant Physiol, 2002, 128(2): 650-660. |
| [65] | Edwards J D, Jackson A K, McClung A M. Genetic architecture of grain chalk in rice and interactions with a low phytic acid locus.Field Crop Res, 2017, 205: 116-123. |
| [66] | Zhou L, Ye Y, Zhao Q, Du X, Zakari S A, Su D, Pan G, Cheng F M.Suppression of ROS generation mediated by higher InsP3 level is critical for the delay of seed germination in lpa rice. Plant Growth Regul, 2018, 85(3): 411-424. |
| [67] | Oltmans S E, Fehr W R, Welke G A, Raboy V, Peterson K L.Agronomic and seed traits of soybean lines with low-phytate phosphorus.Crop Sci, 2005, 45(2): 593-598. |
| [68] | Bregitzer P, Raboy V.Effects of four independent low-phytate mutations in barley on (Hordeum vulgare L.) seed phosphorus characteristics and malting quality. Cereal Chem, 2006, 83: 460-464. |
| [69] | Meis S J, Fehr W R, Schnebly S R.Seed source effect on field emergence of soybean lines with reduced phytate and raffinose saccharides.Crop Sci, 2003, 43(4): 1336-1339. |
| [70] | Hulke B S, Fehr W R, Welke G A.Agronomic and seed characteristics of soybean with reduced phytate and palmitate.Crop Sci, 2004, 44: 2027-2031. |
| [71] | Su D, Lei B T, Li Z W, Cao Z Z, Huang F D, Pan G, Ding Y, Cheng F M.Influence of high temperature during filling period on grain phytic acid and its relation to spikelet sterility and grain weight in non-lethal low phytic acid mutations in rice.J Cereal Sci, 2014, 60(2): 331-338. |
| [72] | Pilu R, Landoni M, Cassani E, Doria E, Nielsen E.The maize lpa241 mutation causes a remarkable variability of expression and some pleiotropic effects. Crop Sci, 2005, 45: 2096-2105. |
| [73] | Raboy V, Gerbasi P F, Young K A, Stoneberg S D, Pickett S G, Bauman A T, Murthy P, Sheridan W F, Ertl D S.Origin and seed phenotype of maize low phytic acid 1-1 and low phytic acid 2-1.Plant Physiol, 2000, 124(1): 355-368. |
| [74] | David E B, Edward J S, Mary J G, Victor R, Jianming F.A low phytic acid barley mutation alters seed gene expression.Crop Sci, 2007, 47: S149. |
| [75] | Ertl D S, Young K A, Raboy V.Plant genetic approaches to phosphorus management in agricultural production.J Environ Qual, 1998, 27(2): 299-304. |
| [76] | Nunes A C, Vianna G R, Cuneo F, Amayafarf A, De-Capdeville G, Rech L, Arag A.RNAi-mediated silencing of the myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene(GmMIPS1) in transgenic soybean inhibited seed development and reduced phytate content. Planta, 2006, 224(1): 125-132. |
| [77] | Raboy V, Peterson K.A substantial fraction of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) low phytic acid mutations have little or no effect on yield across diverse production environments. Plants, 2015, 4(2): 225-239. |
| [78] | Naidoo R, Tongoona P, Derera J, Laing M D, Watson G M F. Combining ability of low phytic acid (lpa1-1) and quality protein maize (QPM) lines for seed germination and vigour under stress and non-stress conditions. Euphytica, 2012, 185(3): 529-541. |
| [79] | Ockenden I, Dorsch J A, Reid M M, Lin L, Grant L K, Raboy V, Lott J N A. Characterization of the storage of phosphorus, inositol phosphate and cations in grain tissues of four barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) low phytic acid genotypes. Plant Sci, 2004, 167(5): 1131-1142. |
| [80] | Sheard L B, Tan X, Mao H, Withers J, Ben-Nissan G, Hinds T R, Kobayashi Y, Hsu F F, Sharon M.Jasmonate perception by inositol-phosphate-potentiated COI1-JAZ co-receptor.Nature, 2010, 468(7322): 400-405. |
| [81] | Ananieva E, Gillaspy G.Switches in nutrient and inositol signaling.Plant Signal Behav, 2009, 4(4): 304-306. |
| [82] | Lemtiri-Chlieh F, MacRobbie E, Webb A, Manison N F, Brownlee C, Skeppe J N, Chen J, Prestwich G D, Brearley C A. Inositol hexakisphosphate mobilizes an endomembrane store of calcium in guard cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A, 2003, 100(17): 10091-10095. |
| [83] | Murphy A M, Otto B, Brearley C A, Carr J P, Hanke D E.A role for inositol hexakisphosphate in the maintenance of basal resistance to plant pathogens.Plant J, 2008, 56(4): 638-652. |
| [84] | Munnik T, Vermeer J E.Osmotic stress-induced phosphoinositide and inositol phosphate signalling in plants.Plant Cell Environ, 2010, 33(4): 655-669. |
| [85] | Stevenson-Paulik J, Bastidas R J, Chiou S T, Frye R A, York J D.Generation of phytate-free seeds in Arabidopsis through disruption of inositol polyphosphate kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A, 2005, 102(35): 12612-12617. |
| [86] | Kuo H, Chang T, Chiang S.Arabidopsis inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase, AtIPK1, is required for growth and modulates phosphate homeostasis at the transcriptional level. Plant J, 2014, 80(3): 503-515. |
| [87] | Qin Z, Chen Q, Tong Z.The Arabidopsis inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6 kinase, AtItpk-1, is involved in plant photomorphogenesis under red light conditions, possibly via interaction with COP9 signalosome. Plant Physiol Bioch, 2005, 43(10-11): 947-954. |
| [88] | Latrasse D, Jegu T, Meng P H, Mazubert C, Hudik E, Delarue M, Charon C, Crespi M, Hirt H, Raynaud C, Bergounioux C, Benhamed M.Dual function of MIPS1 as a metabolic enzyme and transcriptional regulator.Nuc Acids Res, 2013, 41(5): 2907-2917. |
| [89] | Loewus F A, Loewus M W.Myo-inositol: its biosynthesis and metabolism.Ann Rev Plant Physiol, 1983, 34(1): 137-161. |
| [90] | Gumber S C, Loewus M W, Loewus F A.Further studies on myo-Inositol-1-phosphatase from the pollen of Lilium longiflorum Thunb. Plant Physiol, 1984, 76(1): 40-44. |
| [91] | Irvine R F, Schell M J.Back in the water: The return of the inositol phosphates.Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 2001, 2(5): 327-338. |
| [92] | Hui Q, Yang R, Shen C, Zhou Y, Gu Z.Mechanism of calcium lactate facilitating phytic acid degradation in soybean during germination. J Agric Food Chem, 2016, 64(27): 5564-5573. |
| [93] | Nelson D E, Rammesmayer G, Bohnert H J.Regulation of cell-specific inositol metabolism and transport in plant salinity tolerance.Plant Cell, 1998, 10(5): 753-764. |
| [94] | Patra B, Ray S, Richter A, Majumder A L.Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants by co-expression of PcINO1 and McIMT1 is accompanied by increased level of myo-inositol and methylated inositol. Protoplasma, 2010, 245(1-4): 143-152. |
| [95] | Majee M, Maitra S, Dastidar K G, Pattnaik S, Chatterjee A, Hait N C, Das K P, Majumder A L.A novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka, a halophytic wild rice molecular cloning, bacterial overexpression, characterization, and functional introgression into tobacco-conferring salt tolerance phenotype.J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(27): 28539-28552. |
| [96] | Ishitani M, Majumder A L, Bornhouser A, Michalowski C B, Jensen R G, Bohnert H J.Coordinate transcriptional induction of myo-inositol metabolism during environ mental stress. Plant J, 1996, 9(4): 537-548. |
| [97] | Boominathan P, Shukla R, Kumar A, Manna D, Negi D, Verma P K, Chattopadhyay D.Long term transcript accumulation during the development of dehydration adaptation in Cicer arietinum.Plant Physiol, 2004, 135(3): 1608-1620. |
| [98] | Abreu E, Aragao F.Isolation and characterization of a myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene from yellow passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa) expressed during seed development and environmental stress. Ann Bot-London, 2007, 99(2): 285-292. |
| [99] | Iwai T, Takahashi M, Oda K, Terada Y, Yoshida K T.Dynamic changes in the distribution of minerals in relation to phytic acid accumulation during rice seed development.Plant Physiol, 2012, 160(4): 2007-2014. |
| [100] | Kaur H, Shukla R K, Yadav G, Chattopadhyay D, Majee M.Two divergent genes encoding L -myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase1(CaMIPS1) and 2 (CaMIPS2) are differentially expressed in chickpea.Plant Cell Environ, 2008, 31(11): 1701-1716. |
| [101] | Das-Chatterjee A, Goswami L, Maitra S, Dastidar K G, Ray S, Majumder A L.Introgression of a novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka(PcINO1) confers salt tolerance to evolutionary diverse organisms. FEBS Lett, 2006, 580(16): 3980-3988. |
| [102] | Plaxton W C, Preiss J.Purification and properties of nonproteolytic degraded ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase from maize endosperm.Plant Physiol, 1987, 83(1): 105-112. |
| [103] | Bilgrami S S, Houshmand S, Kadivar M, Fakheri B, Zandi P, Shariati V, Razavi K, Tavakol E, Mahdinezhad N, Sabouri S J, Kumar B S, Możdżeń K.Phytic acid, iron and zinc content in wheat ploidy levels and amphiploids: The impact of genotype and planting seasons. Arch Acker Pfl Boden, 2018, 64(3): 331-346. |
| [104] | Miller G A, Youngs V L.Environmental and cultivar effects on oat phytic acid concentration.Cereal Chem, 1980, 57: 189-191. |
| [105] | Batten G D, Lott J.The influence of phosphorus nutrition on the appearance and composition of globoid crystals in wheat aleurone cells.Cereal Chem, 1986, 63(1): 14-18. |
| [106] | Feil B, Fossati D.Phytic acid in triticale grains as affected by cultivar and environment.Crop Sci, 1997, 37(3): 916-921. |
| [107] | Jaksomsak P, Tuiwong P, Rerkasem B, Guild G, Palmer L, Stangoulis J, Prom-u-thai C T. The impact of foliar applied zinc fertilizer on zinc and phytate accumulation in dorsal and ventral grain sections of four Thai rice varieties with different grain zinc.,J Cereal Sci, 2018 79: 6-12. |
| [108] | Dost K, Tokul O.Determination of phytic acid in wheat and wheat products by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography.Anal Chim Acta, 2006, 558(1-2): 22-27. |
| [109] | Dai F, Wang J, Zhang S, Xu Z, Zhang G.Genotypic and environmental variation in phytic acid content and its relation to protein content and malt quality in barley.Food Chem, 2007, 105(2): 606-611. |
| [110] | Thavarajah D, Thavarajah P, See C T, Vandenberg A.Phytic acid and Fe and Zn concentration in lentil (Lens culinaris L.) seeds is influenced by temperature during seed filling period. Food Chem, 2010, 122(1): 254-259. |
| [111] | Fernando N, Panozzo J, Tausz M, Norton R M, Fitzgerald G J, Myers S, Nicolas M E, Seneweera S.Intra-specific variation of wheat grain quality in response to elevated [CO2] at two sowing times under rain-fed and irrigation treatments.J Cereal Sci, 2014, 59(2): 137-144. |
| [112] | Dhole V J, Reddy K S.Genetic variation for phytic acid content in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). The Crop J, 2015, 3(2): 157-162. |
| [113] | 赵宁春, 张小明, 叶胜海, 程方民. 不同栽培方式和施氮量对稻米营养品质及植酸积累的影响. 浙江农业学报, 2009, 21(3): 259-263. |
| Zhao N C, Zhang X M, Ye S H, Cheng F M.Effects of different cultivation methods and nitrogen application on grain phytic acid contents and nutritional quality for japonica rice.Acta Agric Zhejiang, 2009, 21(3): 259-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [114] | 赵宁春, 张其芳, 程方民, 周伟军. 氮、磷、锌营养对水稻籽粒植酸含量的影响及与几种矿质元素间的相关性. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(2): 185-190. |
| Zhao N C, Zhang Q F, Cheng F M.Phosphorus and zinc supply levels on grain phytic acid content and its correlation with several mineral nutrients in rice grain.Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(2): 185-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [115] | Steiner T, Mosenthin R, Zimmermann B, Greiner R, Roth S.Distribution of phytase activity, total phosphorus and phytate phosphorus in legume seeds, cereals and cereal by-products as influenced by harvest year and cultivar.Anim Feed Sci Tech, 2007, 133(3-4): 320-334. |
| [116] | Liu Z H, Cheng F M, Zhang G P.Grain phytic acid content in japonica rice as affected by cultivar and environment and its relation to protein content.Food Chem, 2005, 89(1): 49-52. |
| [117] | Magallanes-López A M, Hernandez-Espinosa N, Velu G, Posadas-Romano G, Ordoñez-Villegas V M G, Crossa J, Ammar K, Guzmán C. Variability in iron, zinc and phytic acid content in a worldwide collection of commercial durum wheat cultivars and the effect of reduced irrigation on these traits.Food Chem, 2017, 237: 499-505. |
| [118] | Hummel M, Hallahan B F, Brychkova G, Ramirez-Villegas J, Guwela V, Chataika B, Curley E, McKeown P C, Morrison L, Talsma E F, Beebe S, Jarvis A, Chirwa R, Spillane C. Reduction in nutritional quality and growing area suitability of common bean under climate change induced drought stress in Africa.Sci Rep, 2018, 8: 16187. |
| [119] | Gibson L R, Mullen R E.Mineral concentrations in soybean seed produced under high day and night temperature.Can J Plant Sci, 2001, 81(4): 595-600. |
| [120] | Ning H, Liu Z, Wang Q, Lin Z, Chen S, Li G, Wang S, Ding Y.Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on grain phytic acid and protein concentrations in japonica rice and its variations with genotypes.J Cereal Sci, 2009, 50(1): 49-55. |
| [121] | Khan A M, Hussain S, Rengel Z, Shah M A A. Zinc bioavailability and nitrogen concentration in grains of wheat crop sprayed with zinc sulfate, ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride, and urea.J Plant Nutr, 2018, 41(15): 1926-1936. |
| [122] | Wang Z M, Liu Q, Pan F, Yuan L X, Yin X B.Effects of increasing rates of zinc fertilization on phytic acid and phytic acid/zinc molar ratio in zinc bio-fortified wheat.Field Crop Res, 2015, 184: 58-64. |
| [123] | 张其方, 刘奎刚, 苏达, 王复标, 程方民. 氮素和水分处理对稻米植酸含量和蛋白组分的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(3): 542-550. |
| Zhang Q F, Liu K G, Su D, Wang F B, Cheng F M.Effects of different nitrogen and water treatments on phytic acid contents and protein components in rice grain.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2012, 18(3): 542-550. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [124] | Su D, Zhou L J, Zhao Q, Pan G, Cheng F M.Different phosphorus supplies altered the accumulations and quantitative distributions of phytic acid, zinc, and iron in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Grains. J Agric Food Chem, 2018, 66(7): 1601-1611. |
| [125] | Raboy V, Dickinson D B.Phytic acid levels in seeds of Glycine max and G. soja as influenced by phosphorus status.Crop Sci, 1993, 33(6): 1300-1305. |
| [126] | Buerkert A, Haake C, Ruckwied M, Marschner H.Phosphorus application affects the nutritional quality of millet grain in the Sahel. Field Crop Res, 1998, 57(2): 223-235. |
| [127] | Zhang W, Liu D Y, Liu Y M, Chen X P, Zou C Q.Overuse of phosphorus fertilizer reduces the grain and flour protein contents and zinc bioavailability of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Agric Food Chem, 2017, 65(8):1473-1482. |
| [128] | Lickfett T, Matthaus B, Velasco L, Mollers C.Seed yield, oil and phytate concentration in the seeds of two oilseed rape cultivars as affected by different phosphorus supply.Eur J Agron, 1999, 11(3-4): 293-299. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||