
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 142-152.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220603
魏倩倩1,2, 徐青山2, 潘林2, 孔亚丽2, 朱练峰2, 曹小闯2, 田文昊2, 刘佳3, 金千瑜2, 项兴佳1, 张均华2,*( ), 朱春权2,*(
), 朱春权2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-08
修回日期:2022-08-31
出版日期:2023-03-10
发布日期:2023-03-10
通讯作者:
张均华,朱春权
基金资助:
WEI Qianqian1,2, XU Qingshan2, PAN Lin2, KONG Yali2, ZHU Lianfeng2, CAO Xiaochuang2, TIAN Wenhao2, LIU Jia3, JIN Qianyu2, XIANG Xingjia1, ZHANG Junhua2,*( ), ZHU Chunquan2,*(
), ZHU Chunquan2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-08
Revised:2022-08-31
Online:2023-03-10
Published:2023-03-10
Contact:
ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunquan
摘要:
【目的】阐明钙离子与硫化氢相互作用缓解水稻铝毒害的分子和生理机制。【方法】以Kasalath为试验材料,选取0 μmol/L和30 μmol/L AlCl3,0.1 mmol/L 和 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2,0.2 μmol/L NaHS和100 μmol/L硫化氢清除剂亚牛磺酸(HP)作为处理浓度,将种子置于30℃培养箱中黑暗培养24 h后取水稻根系,通过测定水稻根系伸长量、总铝含量、细胞汁液中铝含量、质外体中铝含量、细胞壁中铝含量、果胶含量、果胶甲酯酶活性以及OsSTAR2、OsNRAT1和OsFRDL4相对表达量,探究钙离子与硫化氢互作缓解铝对水稻根系伸长抑制作用的机制。【结果】铝胁迫下,相较于0.1 mmol/L CaCl2处理,0.5 mmol/L CaCl2处理显著提高了水稻根系伸长量、硫化氢含量、总钙含量和细胞质中钙含量,显著降低了水稻根系的总铝含量,细胞液、质外体和细胞壁中的铝含量。铝胁迫下,硫氢化钠预处理后,水稻根系的伸长量在两种钙浓度下均显著增加,水稻的根尖铝含量、根系总铝含量、细胞液中铝含量、质外体中铝含量和细胞壁中铝含量在两种钙浓度下均显著降低,OsSTAR2和OsFRDL4相对表达量在两种钙浓度下均显著提高,OsNRAT1相对表达量在两种钙浓度下均显著降低。铝胁迫下,添加HP则呈现相反的结果。【结论】铝胁迫下,钙离子通过增加水稻根系硫化氢的生成,降低水稻根系对铝的吸收和积累,最终缓解铝对水稻根系伸长的抑制作用。
魏倩倩, 徐青山, 潘林, 孔亚丽, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 田文昊, 刘佳, 金千瑜, 项兴佳, 张均华, 朱春权. 钙离子与硫化氢互作缓解铝对水稻根系伸长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 142-152.
WEI Qianqian, XU Qingshan, PAN Lin, KONG Yali, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, TIAN Wenhao, LIU Jia, JIN Qianyu, XIANG Xingjia, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunquan. Mechanism of Interaction Between Calcium Ion and Hydrogen Sulfide Alleviating the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum on Root Elongation in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 142-152.
| 引物 Primer | 序列Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsSTAR2-R | CCTCAGCTTCTTCATCGTCACC |
| OsSTAR2-F | ACCTCTTCATGGTCACCGTCG |
| OsFRDL4-R | TCATTTGCGAAGAAACTTCCACG |
| OsFRDL4-F | CGTCATCAGCACCATCCACAG |
| OsNRAT1-F | GAGGCCGTCTGCAGGAGAGG |
| OsNRAT1-R | GGAAGTATCTGCAAGCAGCTCTGATGC |
| OsHistone-R | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
| OsHistone-F | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT |
表1 本研究所选的引物及其序列
Table 1. Primers selected for this study and the sequences.
| 引物 Primer | 序列Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsSTAR2-R | CCTCAGCTTCTTCATCGTCACC |
| OsSTAR2-F | ACCTCTTCATGGTCACCGTCG |
| OsFRDL4-R | TCATTTGCGAAGAAACTTCCACG |
| OsFRDL4-F | CGTCATCAGCACCATCCACAG |
| OsNRAT1-F | GAGGCCGTCTGCAGGAGAGG |
| OsNRAT1-R | GGAAGTATCTGCAAGCAGCTCTGATGC |
| OsHistone-R | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
| OsHistone-F | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT |
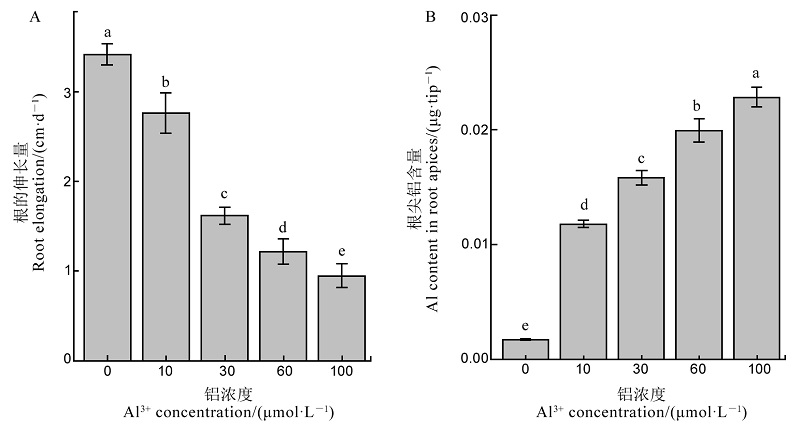
图1 不同铝浓度对水稻根系伸长(A)和根尖铝含量(B)的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 1. Effects of different Al3+ concentrations on root elongation (A) and Al content in root apices (B). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3).
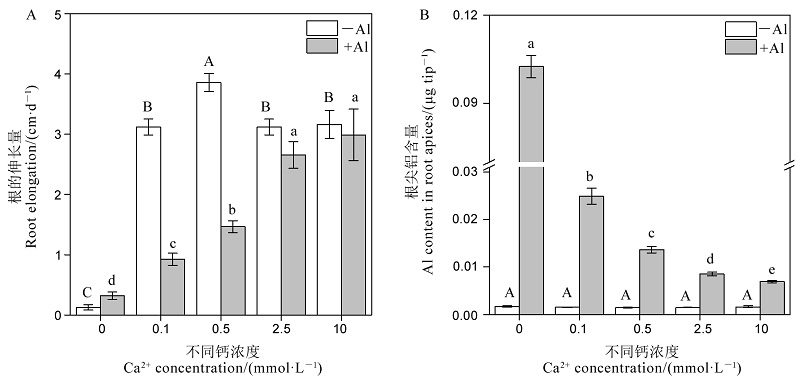
图2 不同钙浓度对水稻根系伸长(A)和根尖铝含量(B)的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。?Al表示不加Al;+Al表示Al3+浓度为30μmol/L。
Fig. 2. Effects of different Ca2+ concentrations on root elongation (A) and Al content in root apices (B). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). -Al, No Al3+ addition; +Al, 30μmol/L Al3+.
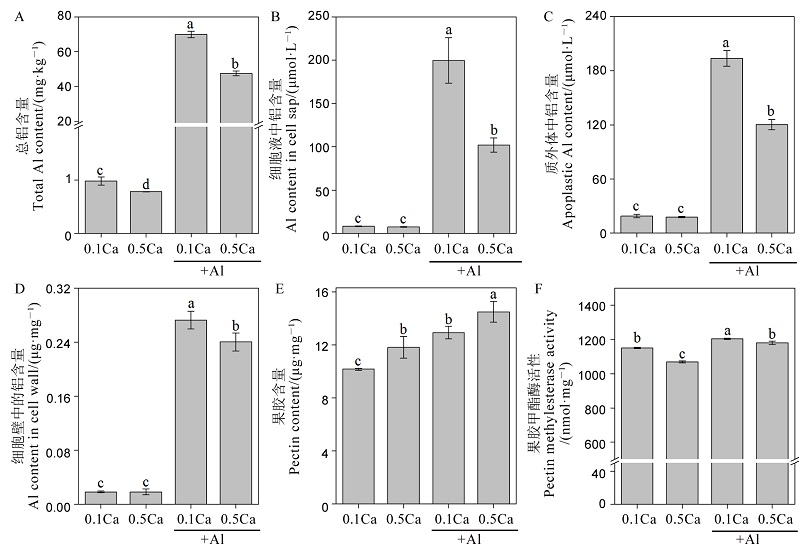
图3 不同钙处理对水稻根系总铝含量(A)、细胞液铝含量(B),质外体铝含量(C),细胞壁铝含量(D),果胶含量(E)和果胶甲酯酶活性(F)的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 3. Effects of different Ca2+ concentrations on total Al concentration (A), Al concentration in cell sap (B), apoplastic Al concentration (C), Al content in cell wall(D), pectin content (E), pectin methylesterase activity (F). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+Al, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3; 0.5Ca+Al, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3.
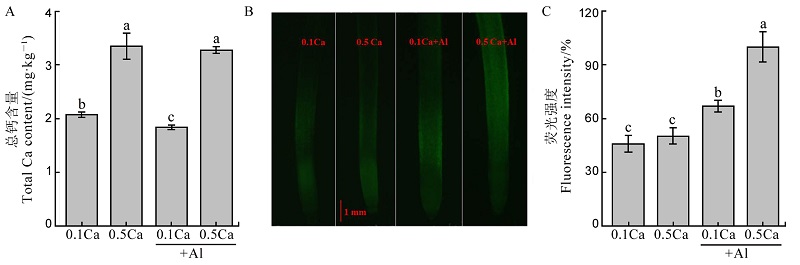
图4 不同钙处理对水稻根系总钙含量(A)和细胞质中钙含量(B和C)影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 4. Effects of different Ca2+ concentrations on total Ca concentration (A), Ca concentration in cell sap (B and C). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca: 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca: 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+Al: 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3; 0.5Ca+Al: 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3.
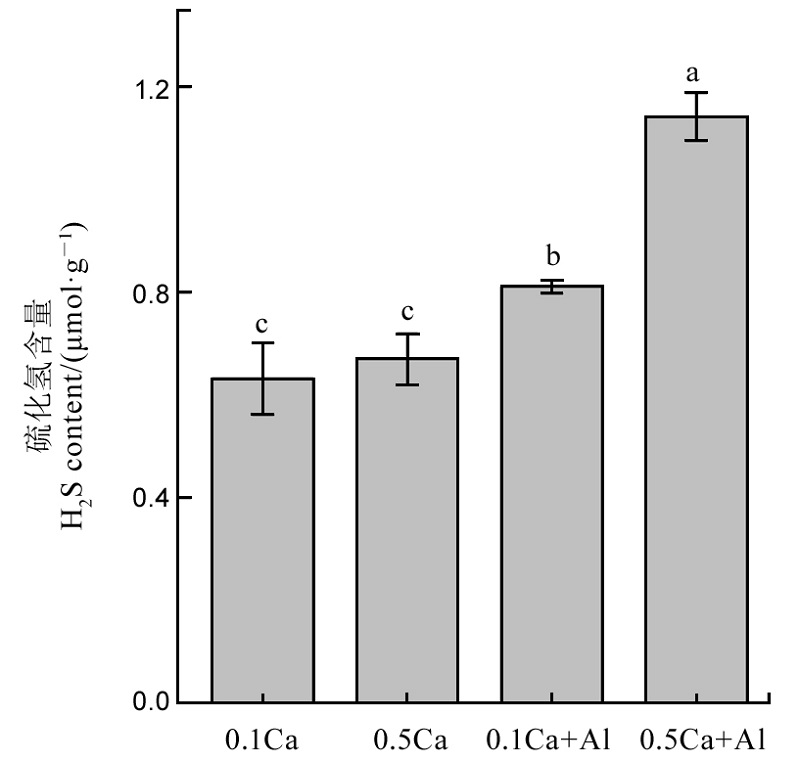
图5 不同钙处理对水稻根系内源性硫化氢含量的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 5. Effects of different Ca2+ concentrations on the content of endogenous H2S. Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca: 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca: 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+Al: 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3; 0.5Ca+Al: 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+30 μmol/L AlCl3.
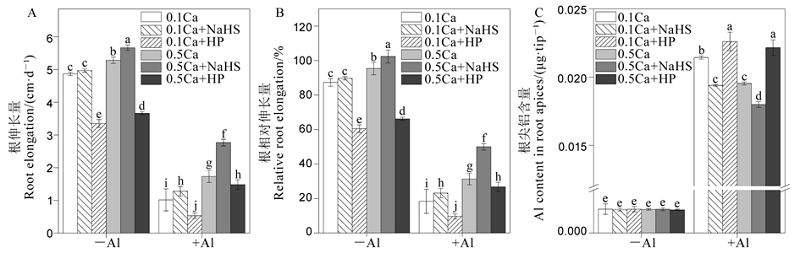
图6 钙离子与硫化氢相互作用对水稻根系伸长(A)、相对根系伸长(B)和根尖铝含量(C)的影响。 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 6. Effects of interaction between Ca2+ and H2S on root elongation (A), relative root elongation (B) and Al content in root apices (C). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+NaHS, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.1Ca+HP, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP; 0.5Ca, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca+NaHS, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.5Ca+HP, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP.
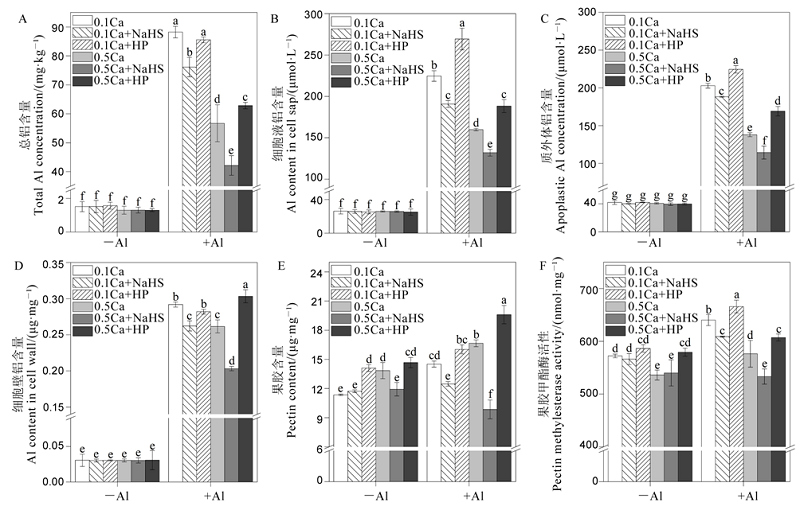
图7 钙离子与硫化氢相互作用对水稻根系中总铝含量(A),细胞液铝含量(B),质外体铝含量(C),细胞壁铝含量(D),果胶含量(E)和果胶甲酯酶活性(F)的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 7. Effects of interaction between Ca2+ and H2S on total Al concentration (A), Al concentration in cell sap (B), apoplastic Al concentration (C), Al content in cell wall(D), pectin content (E), pectin methylesterase activity (F). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+NaHS, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.1Ca+HP, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP; 0.5Ca, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca+NaHS, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.5Ca+HP, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP.
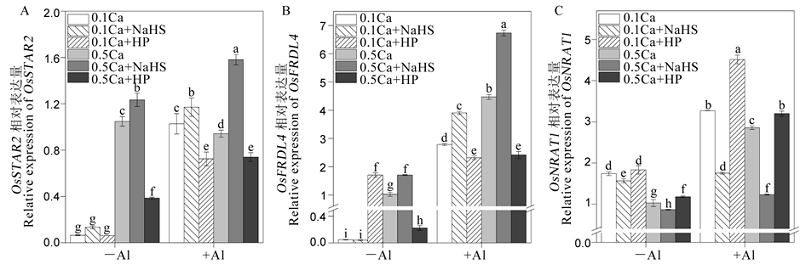
图8 钙离子与硫化氢相互作用对水稻根系OsSTAR2 (A)、OsFRDL4 (B)和OsNRAT1 (C)相对表达量的影响 不同字母代表处理间的差异达0.05显著水平。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 8. Effects of interaction between Ca2+ and H2S on relative expression of OsSTAR2 (A), OsFRDL4 (B) and OsNRAT1 (C). Different letters in the figure indicate that there is a significant difference in the results under the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the value is the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). 0.1Ca, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.1Ca+NaHS, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.1Ca+HP, 0.1 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP; 0.5Ca, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2; 0.5Ca+NaHS, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+0.2 μmol/L NaHS; 0.5Ca+HP, 0.5 mmol/L CaCl2+100 μmol/L HP.
| [1] | 郑爱珍, 李春喜. 酸性红壤铝毒对植物的影响及其改良[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2004(6): 38-40. |
| Zheng A Z, Li C X. Influences and improvement of Al toxin on plant in acid red soil[J]. Huibei Agricultural Sciences, 2004(6): 38-40. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Poschenrieder C, Gunsé B, Corrales I, Barceló J J. A glance into aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 400(1-3): 356-368. |
| [3] | Zhen Y, Qi J L, Wang S S, Su J, Xu G H, Zhang M S, Miao L, Peng X X, Tian D C, Yang Y H. Comparative proteome analysis of differentially expressed proteins induced by Al toxicity in soybean[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2007, 131: 542-554. |
| [4] |
Zhu C Q, Zhang J H, Sun L M, Zhu L F, Abliz B, Hu W J, Zhong C, Bai Z G, Sajid H, Cao X C, Jin Q Y. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity via decreasing apoplast and symplast Al contents in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 294
PMID |
| [5] | 沈仁芳. 铝在土壤-植物中的行为及植物的适应机制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. |
| Shen R F. The Behavior of Aluminum in Soil Plant and the Adaptive Mechanism of Plants[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | Ma J F, Chen Z C, Shen R F. Molecular mechanisms of Al tolerance in gramineous plants[J]. Plant and Soil, 2014, 381: 1-12. |
| [7] | Huang W J, Oo T L, He H Y, Wang A Q, Zhan J, Wei S Q, He L F. Aluminum induces rapidly mitochondria- dependent programmed cell death in Al sensitive peanut root tips[J]. Botanical Studies, 2014, 55: 67. |
| [8] | Hepler P K. Calcium: A central regulator of plant growth and development[J]. The Plant Cell, 2005: 2142-2155. |
| [9] | Tang R H, Han S C, Zheng H L, Cook C W, Choi C S, Woerner T E, Jackson R B, Pei Z M. Coupling diurnal cytosolic Ca2+ oscillations to the CAS-IP3 pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. Science, 2007, 315: 1423-1426. |
| [10] | Zhu J K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(2): 313-324. |
| [11] | Wan U L, Najeeb U, Jilani G, Naeem M S, Zhou W J. Calcium invigorates the cadmium-stressed Brassica napus L. Plants by strengthening their photosynthetic system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2011, 18: 1478-1486. |
| [12] | Bashir K, Rasheed S, Kobayashi T, Seki M, Nishizawa N K. Regulating subcellular metal homeostasis: The key to crop improvement[J]. Front Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1192. |
| [13] | Lu H P, Li Z, Wu J T, Shen Y, Li Y W, Zou B, Tang Y T, Zhuang P. Influences of Calcium silicate on chemical forms and subcellular distribution of cadmium in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40583. |
| [14] | 王爱勤, 何龙飞, 沈振国, 刘友良, 李杨瑞. 铝胁迫下钙对小麦幼苗营养元素吸收和转运的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2002, 15 (2): 42-47. |
| Wang A Q, He L F, Shen Z G, Liu Y L, Li Y R. Effects of calcium on the absorption and distribution of nutrient elements of wheat seedlings under aluminum stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2002, 15(2): 42-47. | |
| [15] | Chen J, Duan R X, Hu W J, Zhang N N, Lin X Y, Zhang J H, Zheng H L. Unravelling calcium-alleviated aluminium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana: Insights into regulatory mechanisms using proteomics[J]. Journal of Proteomic, 2019, 199: 15-30. |
| [16] | Fang H H, Jing T, Liu Z Q, Zhang L Q, Jin Z P, Pei Y X. Hydrogen sulfide interacts with calcium signaling to enhance the chromium tolerance in Setaria italica[J]. Cell Calcium, 2014, 56(6): 472-481. |
| [17] | Bont L D, Mu X J, Wei B, Han Y. Abiotic stress-triggered oxidative challenges: Where does H2S act?[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2022, 49(8): 748-755. |
| [18] | Peng R Y, Bian Z Y, Zhou L, Cheng W, Hai N, Yang C Q, Yang T, Wang X Y, Wang C Y. Hydrogen sulfide enhances nitric oxide-induced tolerance of hypoxia in maize (Zea mays L.)[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2016, 35(11): 2325-2340. |
| [19] | Wang H H, Ji F, Zhang Y Y, Hou J J, Liu W W, Huang J J, Liang W H. Interactions between hydrogen sulphide and nitric oxide regulate two soybean citrate transporters during the alleviation of aluminium toxicity[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2019, 42(8): 2340-2356. |
| [20] |
Zhu C Q, Wei Q Q, Hu W J, Kong Y L, Xiang X J, Zhang H, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Liu J, Tian W H, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Unearthing the alleviatory mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide in aluminum toxicity in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 182: 133-144.
PMID |
| [21] | Liu Z Q, Fang H H, Pei Y X, Jin Z P, Zhang L P, Liu D M. WRKY transcription factors down-regulate the expression of H2S-generating genes, LCD and DES in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(11): 995-1001. |
| [22] | Kaur H, Hussain S J, Al-Huqail A A, Siddiqui M H, Al-Huqail A A, Khan M I R. Hydrogen sulphide and salicylic acid regulate antioxidant pathway and nutrient balance in mustard plants under cadmium stress[J]. Plant Biology, 2022, 24(4): 660-669. |
| [23] | Singh S, Prasad S M, Singh V P. Additional calcium and sulfur manages hexavalent chromium toxicity in Solanum lycopersicum L. and Solanum melongena L. seedlings by involving nitric oxide[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 398: 122607. |
| [24] | Husain T, Suhel M, Prasa S M, Singh V P. Ethylene needs endogenous hydrogen sulfide for alleviating hexavalent chromium stress in Vigna mungo L. and Vigna radiata L[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 290: 117968. |
| [25] | Khan M N, Siddiqui M H, AlSolami M A, Alamri S, Hu Y, Ali H M, Al-Amri A A, Alsubaie Q D, Al-Munqedhi B M A, Al-Ghamdi A. Crosstalk of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide requires calcium to mitigate impaired photosynthesis under cadmium stress by activating defense mechanisms in Vigna radiata[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 156: 278-290. |
| [26] | Yang J L, Zhu X F, Peng Y X, Zheng C, Li G X, Liu Y, Shi Y Z, Zheng S J. Cell wall hemicellulose contributes significantly to aluminum adsorption and root growth in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 155(4): 1885-1892. |
| [27] |
Xia J X, Yamaji N, Kasai T, Ma J F. Plasma membrane-localized transporter for aluminum in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107: 18381-18385.
PMID |
| [28] | Hossain M A, Ban K, Hossain A K M Z, Koyama H, Hara T. Combined effects of Mg and Ca supply on alleviation of Al toxicity in wheat plants[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50: 283-286. |
| [29] | 周索, 王绍杰, 余晓丽. 拟南芥花粉细胞质游离钙离子荧光测定法[J]. 生物技术, 2005(5): 55-57. |
| Zhou S, Wang S J, Yu X L. Measurement of cytoplasmic calcium fluorescence in Arabidopsis thaliana pollen cells[J]. Biotechnology, 2005(5): 55-57. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | Dubois M, Gilles K A, Hamilton J K, Rebers P A, Smith F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28: 350-356. |
| [31] | 朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华. 硫化氢提高水稻磷吸收转运的生理和分子机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 532-540. |
| Zhu C Q, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Bai Z G, Huang J, Liang Q D, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide enhancing phosphorus absorption and transportation in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33 (6): 532-540. | |
| [32] | Blamey F P C, Nishizawa N K, Yoshimura E. Timing, magnitude, and location of initial soluble aluminum injuries to mungbean roots[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50: 67-76. |
| [33] | Ma J F. Plant root responses to three abundant soil minerals: Silicon, aluminum and iron[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2005, 24: 267-281. |
| [34] | Hossain M A, Ashrafuzzaman M, Hossain A K, Ismail M R, Koyama H. Role of accumulated calcium in alleviating aluminum injury in wheat plants[J]. Scientific World Journal, 2014: 457187. |
| [35] | Ligaba-Osena A, Fei Z J, Liu J P, Xu Y M, Shaff Y, Lee S C, Luan S, Kudla J, Kochian L, Pineros M. Loss-of-function mutation of the calcium sensor CBL1 in-creases aluminum sensitivity in Arabidopsis[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 214(2): 830-841. |
| [36] | Rudd J J, Franklin-Tong V E. Unravelling response-specificity in Ca2+ signalling pathways in plant cells[J]. New Phytologist, 2001, 151(1): 7-33. |
| [37] |
Rengel Z, Zhang W H. Role of dynamics of intracellular Calcium in aluminium-toxicity syndrome[J]. New Phytologist, 2003, 159: 295-314.
PMID |
| [38] | Zhang H, Tan Z Q, Hu L Y, Wang S H, Luo J P, Jones R L. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in germinating wheat seedlings[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2010, 52(6): 556-567. |
| [39] | Clarkson D T. Interactions between aluminium and phosphorus on root surfaces and cell wall material[J]. Plant Soil 1967, 27: 347-356. |
| [40] |
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Kashino-Fujii M, Ma J F. Retrotransposonmediated aluminum tolerance through enhanced expression of the citrate transporter OsFRDL4[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 172: 2327-2336.
PMID |
| [41] | Huang C F, Yamaji N, Chen Z, Ma J F. A tonoplast-localized half-size ABC transporter is required for internal detoxification of aluminum in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 69: 857-867. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||