
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 133-141.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220607
韦敏益1, 马增凤1, 黄大辉1, 秦媛媛2, 刘驰1, 卢颖萍1,3, 罗同平1, 李振经1, 张月雄1,*( ), 秦钢1,*(
), 秦钢1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-14
修回日期:2022-08-05
出版日期:2023-03-10
发布日期:2023-03-10
通讯作者:
张月雄,秦钢
基金资助:
WEI Minyi1, MA Zengfeng1, HUANG Dahui1, QIN Yuanyuan2, LIU Chi1, LU Yingping1,3, LUO Tongping1, LI Zhenjing1, ZHANG Yuexiong1,*( ), QIN Gang1,*(
), QIN Gang1,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-14
Revised:2022-08-05
Online:2023-03-10
Published:2023-03-10
Contact:
ZHANG Yuexiong, QIN Gang
摘要:
【目的】发掘水稻抗细菌性条斑病新基因,丰富抗病基因资源,为水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因克隆及分子育种提供依据。【方法】以抗病材料广西普通野生稻WP1和感病品种9311及其衍生的F8:9代RIL群体为研究材料,利用QTL-Seq初定位与细菌性条斑病抗性相关的区间,之后利用QTL Ici Mapping 4.1进行复合区间作图以验证结果并精细定位。【结果】分别在第4、8、10染色体上鉴定了一个与细菌性条斑病抗性相关的位点,复合区间作图验证了第4染色体抗细菌性条斑病QTL位点qBLS4.1,表型贡献率和LOD值分别为10.65%和5.03,并进一步将qBLS4.1精细定位在521 kb的范围内。抗感亲本序列比对分析发现,在41个基因的编码区共有252个非同义突变,可能与细菌性条斑病抗性相关。【结论】通过QTL-seq分析结合复合区间作图法可以更快速高效地对水稻QTL进行定位,鉴定了一个抗细菌性条斑病性QTL新位点qBLS4.1,为水稻抗细菌性条斑病新基因鉴定与克隆奠定基础。
韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢. 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 133-141.
WEI Minyi, MA Zengfeng, HUANG Dahui, QIN Yuanyuan, LIU Chi, LU Yingping, LUO Tongping, LI Zhenjing, ZHANG Yuexiong, QIN Gang. QTL-Seq Analysis for Identification of Resistance Locus to Bacterial Leaf Streak in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 133-141.
| 标记 | 物理位置 | 正向引物 | 反向引物 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | Position / bp | Forward primer(5’-3’) | Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
| C4M1 | 557 006 | TATACACGCAACTCCCCCTC | TGCCAATACCACAGTCCTGA |
| C4M2 | 1 332 530 | TTTCTCCAAACCGAACAAGC | CAGTGCAGCAGGGAAGTACA |
| C4M3 | 2 519 322 | CTCCCACCTGACAAGTTCGT | CAACCAGAGAAAAGCAAGCA |
| C4M5 | 4 314 270 | CGAAAGGTCAAAACGTTGGT | GTGCATCCGCCTTAATTTGT |
| C4M6 | 5 006 279 | CGTCATGGTCATCGTACGTC | CACGTAACGCAACGGATATG |
| C4M8 | 5 534 085 | AATCACCGAGAGCATTTTGG | GTGCAACTTTTACGTGGCCT |
| C4M9 | 6 070 782 | AGAGACTGTCGCTCCCAAAA | GGGAAAGCTCTGAAATGATCC |
| C4M10 | 6 888 374 | GAGAGCCCGTAAACATTCCA | ACCATCAACCGGATTATTCA |
| C4M13 | 11 782 373 | CCCTGGAAAGAACAAACCAA | ATGACCGAGCCTGATATTGC |
| C4M14 | 13 911 219 | AGCATGTTAAATCATCATCCCA | TGGCTTAACGAAAGAAGAGAGAA |
| C4MJ1 | 5 269 417 | GGTCTCTCTCTCATGCGTCC | ACCAGACCAGGCAGCTAAGA |
| C4MJ5 | 5 364 530 | TTCCCCTAAACCATTTTTCTCTC | AGGAGGAAGGGAGGTGCTAC |
| C4MJ2 | 5 691 595 | CGTCAAGGAACACAGCGATA | TGGGACGGATGGATTAGTTT |
| C4MJ3 | 5 790 460 | GCCTGAATCACGAAGCTCAT | GAGAAGGTTTGCTCCTGCAC |
表1 用于本研究基因定位的InDel标记
Table 1. InDel markers for gene mapping in this study.
| 标记 | 物理位置 | 正向引物 | 反向引物 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | Position / bp | Forward primer(5’-3’) | Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
| C4M1 | 557 006 | TATACACGCAACTCCCCCTC | TGCCAATACCACAGTCCTGA |
| C4M2 | 1 332 530 | TTTCTCCAAACCGAACAAGC | CAGTGCAGCAGGGAAGTACA |
| C4M3 | 2 519 322 | CTCCCACCTGACAAGTTCGT | CAACCAGAGAAAAGCAAGCA |
| C4M5 | 4 314 270 | CGAAAGGTCAAAACGTTGGT | GTGCATCCGCCTTAATTTGT |
| C4M6 | 5 006 279 | CGTCATGGTCATCGTACGTC | CACGTAACGCAACGGATATG |
| C4M8 | 5 534 085 | AATCACCGAGAGCATTTTGG | GTGCAACTTTTACGTGGCCT |
| C4M9 | 6 070 782 | AGAGACTGTCGCTCCCAAAA | GGGAAAGCTCTGAAATGATCC |
| C4M10 | 6 888 374 | GAGAGCCCGTAAACATTCCA | ACCATCAACCGGATTATTCA |
| C4M13 | 11 782 373 | CCCTGGAAAGAACAAACCAA | ATGACCGAGCCTGATATTGC |
| C4M14 | 13 911 219 | AGCATGTTAAATCATCATCCCA | TGGCTTAACGAAAGAAGAGAGAA |
| C4MJ1 | 5 269 417 | GGTCTCTCTCTCATGCGTCC | ACCAGACCAGGCAGCTAAGA |
| C4MJ5 | 5 364 530 | TTCCCCTAAACCATTTTTCTCTC | AGGAGGAAGGGAGGTGCTAC |
| C4MJ2 | 5 691 595 | CGTCAAGGAACACAGCGATA | TGGGACGGATGGATTAGTTT |
| C4MJ3 | 5 790 460 | GCCTGAATCACGAAGCTCAT | GAGAAGGTTTGCTCCTGCAC |
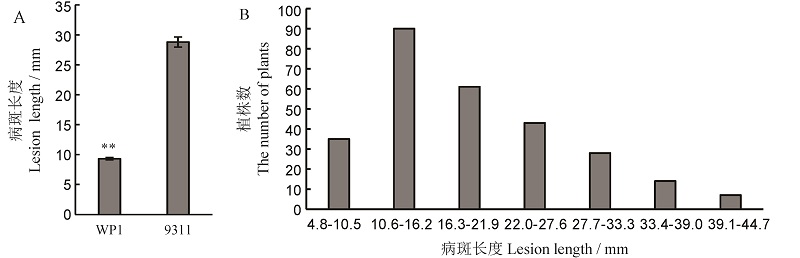
图2 亲本对细菌性条斑病的抗性鉴定结果(A)和F8:9群体(B)病斑长度分布频率 **亲本间的差异达0.01显著水平。
Fig. 2. Resistance of parents to bacterial leaf streak(A) and distribution frequency of lesion length in F8:9 population(B). ** Difference between the parents was significant at 0.01 level.
| 关联分析方法 Association analysis method | 染色体 Chromosome | 起始Start | 终止End | 片段大小 Size/Mb | 基因数量 Gene number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于SNP的ED方法关联结果 Results of ED method based on SNP | 10 | 16,070,000 | 21,090,000 | 5.02 | 925 |
| 4 | 6,170,000 | 6,840,000 | 0.67 | 99 | |
| 8 | 20,840,000 | 24,160,000 | 3.32 | 547 | |
| 基于SNP的ΔSNP-index方法关联结果 Results of ΔSNP-index method based on SNP | 10 | 17,060,000 | 20,860,000 | 3.80 | 697 |
| 基于InDel的ED方法关联结果 Results of ED method based on InDel | 10 | 16,180,000 | 21,160,000 | 4.98 | 919 |
| 4 | 5,640,000 | 7,520,000 | 1.88 | 244 | |
| 8 | 20,650,000 | 24,170,000 | 3.52 | 575 | |
| 基于InDel的ΔSNP-index方法关联结果 Results of SNP-index method based on InDel | 10 | 17,280,000 | 21,000,000 | 3.72 | 693 |
表2 QTL-seq结果统计
Table 2. Results of QTL-seq.
| 关联分析方法 Association analysis method | 染色体 Chromosome | 起始Start | 终止End | 片段大小 Size/Mb | 基因数量 Gene number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于SNP的ED方法关联结果 Results of ED method based on SNP | 10 | 16,070,000 | 21,090,000 | 5.02 | 925 |
| 4 | 6,170,000 | 6,840,000 | 0.67 | 99 | |
| 8 | 20,840,000 | 24,160,000 | 3.32 | 547 | |
| 基于SNP的ΔSNP-index方法关联结果 Results of ΔSNP-index method based on SNP | 10 | 17,060,000 | 20,860,000 | 3.80 | 697 |
| 基于InDel的ED方法关联结果 Results of ED method based on InDel | 10 | 16,180,000 | 21,160,000 | 4.98 | 919 |
| 4 | 5,640,000 | 7,520,000 | 1.88 | 244 | |
| 8 | 20,650,000 | 24,170,000 | 3.52 | 575 | |
| 基于InDel的ΔSNP-index方法关联结果 Results of SNP-index method based on InDel | 10 | 17,280,000 | 21,000,000 | 3.72 | 693 |
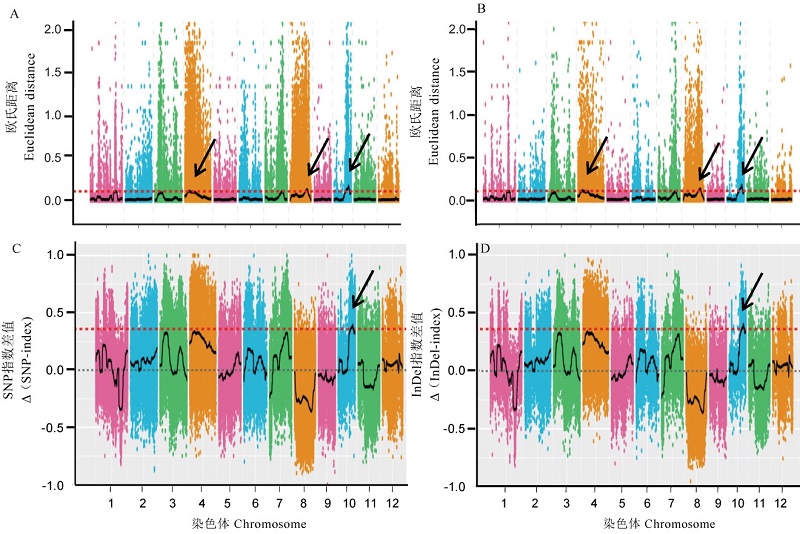
图3 BSA-seq 基于SNP和InDel的ED和△(SNP-index)关联分析 A图和B图分别是基于SNP和InDel的ED关联分析;C图和D图分别是基于SNP和InDel的△(SNP-index)关联分析,红色的虚线为99%的阈值线。
Fig. 3. ED and △(SNP-index) correlation analysis based on SNP and InDel of BSA-seq. A and B, ED association analysis figures based on SNP and InDel, respectively. C and D, △ (SNP-index) correlation analysis diagram based on SNP and InDel, respectively. The red dotted line is the 99% threshold line.
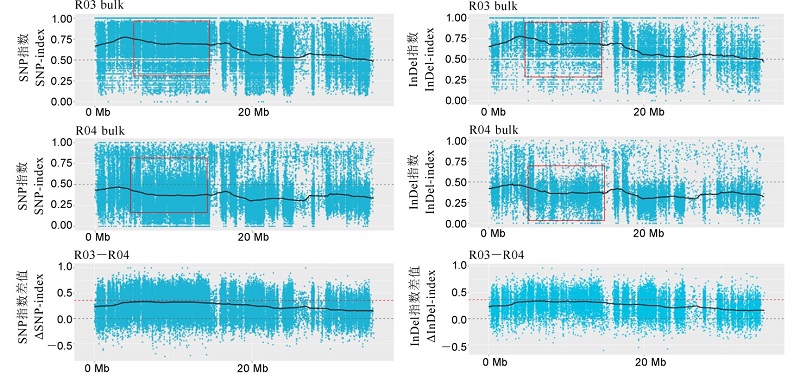
图4 第4染色体上抗病池、感病池的SNP和InDel指数分析 A图和B图分别为抗、感病混池的SNP指数的分布图;C图为Δ(SNP-index)值的分布图,红色的虚线为99%的阈值线。R03为抗病池,R04为感病池。
Fig. 4. SNP-index and InDel -index of the resistant pool and the susceptible pool on chromosome 4. A, B are the distribution of SNP-index values in resistant and susceptible mixed pools, respectively; C shows the distribution of Δ(SNP-index) value. The red dotted line is the 99% threshold line. R03, Resistant pool; R04, Susceptible pool.
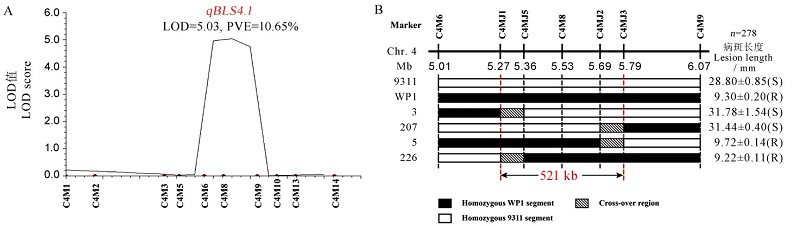
图5 抗细条病基因qBLS4.1验证和精细定位 A图为qBLS4.1在染色体上的位置与遗传效应;B图为重组单株的基因型和表型。
Fig. 5. Verification and fine mapping of the resistance locus qBLS4.1. A, Location and genetic effect of qBLS4.1; B, Graphical genotypes and resistance phenotypes of the recombinants.
| ORF编号 | 基因 | 突变类型 | 基因功能注释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Gene | Mutation type | Putative function |
| 1 | LOC_Os04g09870 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 2 | LOC_Os04g09880 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 3 | LOC_Os04g09900 | SNP | 贝壳杉烯合酶,叶绿体前体 Ent-kaurene synthase, chloroplast precursor |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g09910 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 5 | LOC_Os04g09920 | InDel/SNP | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| 6 | LOC_Os04g09950 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 7 | LOC_Os04g09960 | InDel | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 8 | LOC_Os04g09990 | InDel | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 9 | LOC_Os04g10010 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 10 | LOC_Os04g10070 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 11 | LOC_Os04g10100 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 12 | LOC_Os04g10110 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 13 | LOC_Os04g10120 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 14 | LOC_Os04g10140 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 15 | LOC_Os04g10160 | SNP | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| 16 | LOC_Os04g10170 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 17 | LOC_Os04g10180 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 18 | LOC_Os04g10190 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 19 | LOC_Os04g10200 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 20 | LOC_Os04g10214 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 21 | LOC_Os04g10219 | InDel | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 22 | LOC_Os04g10230 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 23 | LOC_Os04g10240 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 24 | LOC_Os04g10260 | SNP | 含碱性亮氨酸拉链结构域的蛋白 Basic region leucine zipper domain containing protein |
| 25 | LOC_Os04g10270 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 26 | LOC_Os04g10290 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 27 | LOC_Os04g10300 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 28 | LOC_Os04g10320 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 29 | LOC_Os04g10330 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 30 | LOC_Os04g10390 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 31 | LOC_Os04g10400 | SNP | 电子转运黄素蛋白亚单位β Electron transfer flavoprotein subunit beta |
| 32 | LOC_Os04g10410 | SNP | 酰胺酶 Amidase |
| 33 | LOC_Os04g10420 | InDel/SNP | CW7 |
| 34 | LOC_Os04g10450 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 35 | LOC_Os04g10500 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 36 | LOC_Os04g10550 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 37 | LOC_Os04g10569 | SNP | 谷氨酰-tRNA酰胺转移酶 Glutamyl-tRNA amidotransferase |
| 38 | LOC_Os04g10590 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 39 | LOC_Os04g10620 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 40 | LOC_Os04g10630 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 41 | LOC_Os04g10650 | SNP | CDT1A-DNA复制起始蛋白 CDT1A-DNA replication initiation protein |
表3 定位区间内的候选基因注释
Table 3. Candidate gene annotation in the location interval.
| ORF编号 | 基因 | 突变类型 | 基因功能注释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Gene | Mutation type | Putative function |
| 1 | LOC_Os04g09870 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 2 | LOC_Os04g09880 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 3 | LOC_Os04g09900 | SNP | 贝壳杉烯合酶,叶绿体前体 Ent-kaurene synthase, chloroplast precursor |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g09910 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 5 | LOC_Os04g09920 | InDel/SNP | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| 6 | LOC_Os04g09950 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 7 | LOC_Os04g09960 | InDel | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 8 | LOC_Os04g09990 | InDel | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 9 | LOC_Os04g10010 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 10 | LOC_Os04g10070 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 11 | LOC_Os04g10100 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 12 | LOC_Os04g10110 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 13 | LOC_Os04g10120 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 14 | LOC_Os04g10140 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 15 | LOC_Os04g10160 | SNP | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| 16 | LOC_Os04g10170 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 17 | LOC_Os04g10180 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 18 | LOC_Os04g10190 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 19 | LOC_Os04g10200 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 20 | LOC_Os04g10214 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 21 | LOC_Os04g10219 | InDel | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 22 | LOC_Os04g10230 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 23 | LOC_Os04g10240 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 24 | LOC_Os04g10260 | SNP | 含碱性亮氨酸拉链结构域的蛋白 Basic region leucine zipper domain containing protein |
| 25 | LOC_Os04g10270 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 26 | LOC_Os04g10290 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 27 | LOC_Os04g10300 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 28 | LOC_Os04g10320 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 29 | LOC_Os04g10330 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 30 | LOC_Os04g10390 | InDel/SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 31 | LOC_Os04g10400 | SNP | 电子转运黄素蛋白亚单位β Electron transfer flavoprotein subunit beta |
| 32 | LOC_Os04g10410 | SNP | 酰胺酶 Amidase |
| 33 | LOC_Os04g10420 | InDel/SNP | CW7 |
| 34 | LOC_Os04g10450 | SNP | 假设蛋白 Hypothetical protein |
| 35 | LOC_Os04g10500 | SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 36 | LOC_Os04g10550 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 37 | LOC_Os04g10569 | SNP | 谷氨酰-tRNA酰胺转移酶 Glutamyl-tRNA amidotransferase |
| 38 | LOC_Os04g10590 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白 Retrotransposon protein, unclassified |
| 39 | LOC_Os04g10620 | SNP | 反转录转座子蛋白,Ty3-gypsy亚类 Retrotransposon protein, Ty3-gypsy subclass |
| 40 | LOC_Os04g10630 | InDel/SNP | 表达蛋白 Expressed protein |
| 41 | LOC_Os04g10650 | SNP | CDT1A-DNA复制起始蛋白 CDT1A-DNA replication initiation protein |
| [1] |
Yang W, Ju Y H, Zuo L P, Shang L Y, Li X R, Li X M, Feng S Z, Ding X H, Chu Z H. OsHsfB4d binds the promoter and 11/11 regulates the expression of OsHsp18.0-CI to resistant against Xanthomonas oryzae[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 28.
PMID |
| [2] | Liu W, Liu J, Triplett L, Leach J E, Wang G L. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2013, 52: 213-241. |
| [3] | He W A, Huang D H, Li R B, Qiu Y F, Song J D, Yang H N, Zheng J X, Huang Y Y, Liu C, Zhang Y X, Ma Z F, Yang Y. Identification of a resistance gene bls1 to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2012, 11: 962-969. |
| [4] | Ma Z F, Qin G, Zhang Y X, Liu C, Wei M Y, Cen Z L, Yan Y, Luo T P, Li Z J, Liang H F, Huang D H, Deng G F. Bacterial Leaf Streak 1 encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase confers the rice resistance to bacterial leaf streak[J]. The Plant Journal, 2021, 107(4): 1084-1101. |
| [5] | 吴为人, 唐定中, 李维明, 卢浩然, Worland A J. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性基因定位[J]. 高技术通讯, 1998(7): 47-50. |
| Wu W R, Tang D Z, Li W M, Lu H R, Worland A J. Mapping of genes underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 1998(7): 47-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Tang D Z, Wu W R, Li W M, Lu H R, Worland A J. Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2000, 101: 286-291. |
| [7] | 陈志伟, 景艳军, 李小辉, 周元昌, 刁志娟, 李生平, 吴为人. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性QTL qBlsr5a的验证和更精确定位[J]. 福建农林大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 35(6): 619-622. |
| Chen Z W, Jing Y J, Li X H, Zhou Y C, Diao Z J, Li S P, Wu W R. Verification and more precise mapping of a QTL qBIsr5a underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Natural Science, 2006, 35(6): 619-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Han Q D, Chen Z W, Deng Y L, Lan T, Guan H Z, Guan Y L, Zhou Y C, Lin M C, Wu W R. Fine mapping of qBlsr5a, a QTL controlling resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(4): 587-590. |
| [9] | Xie X F, Chen Z W, Cao J L, Guan H Z, Lin D G, Li C L, Lan T, Duan Y L, Mao D M, Wu W R. Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping sub-CSSLs in rice[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(4): e95751. |
| [10] |
Triplett L R, Cohen S P, Heffelfinger C, Schmidt C L, Huerta A I, Tekete C, Verdier V, Bogdanove A J, Leach J E. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety carolina gold select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(5): 472-483.
PMID |
| [11] | 施力军, 罗登杰, 赵严, 岑贞陆, 刘芳, 李容柏. 普通野生稻抗细菌性条斑病基因的遗传分析与定位[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(2): 1-5. |
| Shi L J, Luo D J, Zhao Y, Cen Z L, Liu F, Li R B. Genetic analysis and mapping of bacterial leaf streak resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(2): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 罗登杰, 万瑶, 覃雪梅, 施力军, 张慧, 李容柏, 刘芳. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性基因bls2 SSR分子标记开发[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(5): 1167-1173. |
| Luo D J, Wan Y, Qin X M, Shi L J, Zhang H, Li R B, Liu F. Development of SSR molecular markers for bacterial leaf streak resistance gene bls2 in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(5): 1167-1173. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Wu T, Peng C, Li B B, Wu W, Kong L G, Li F C, Chu Z H, Liu F, Ding X H. OsPGIP1-mediated resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice is beyond responsive to the polygalacturonase of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. Rice, 2019, 12: 90. |
| [14] | Shen X L, Yuan B, Liu H B, Li X H, Wang S P. Opposite functions of a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase during the process of resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae[J]. The Plant Journal, 2010, 64(1): 86-99. |
| [15] | Feng C S, Zhang X, Wu T, Yuan B, Ding X H, Yao F Y, Chu Z H. The polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein 4 (OsPGIP4), a potential component of the qBlsr5a locus, confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Planta, 2016, 243: 1297-1308. |
| [16] |
Ma H G, Chen J, Zhang Z Z, Ma L, Yang Z Y, Zhang Q L, Li X H, Xiao J H, Wang S P. MAPK kinase 10.2 promotes disease resistance and drought tolerance by activating different MAPKs in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2017, 92: 557-570.
PMID |
| [17] | Ju Y H, Tian H J, Zhang R H, Zuo L P, Jin G X, Xu Q, Ding X H, Li X K, Chu Z H. Overexpression of OsHSP18.0-CI enhances resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Rice, 2017, 10: 12. |
| [18] |
Yang W, Zhang B G, Qi G H, Shang L Y, Chu Z H. Identification of the phytosulfokine receptor 1 (OsPSKR1) confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Planta, 2019, 250: 1603-1612.
PMID |
| [19] |
Jiang N, Yan J, Liang Y, Shi Y L, He Z Z, Wu Y T, Zeng Q, Liu X L, Peng J H. Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.): An updated review[J]. Rice, 2020, 13: 3.
PMID |
| [20] | Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 14(1): 1754-1760. |
| [21] |
Mckenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristol M A. The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297-1303.
PMID |
| [22] | Mansfeld B N, Grumet R. QTLseqr: An R package for bulk segregant analysis with next-generation sequencing[J]. Plant Genome, 2018, 11(2): 1-5. |
| [23] |
Paterson A H, DeVerna J W, Lanini B, Tanksley S D. Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes, in an interspecies cross of tomato[J]. Genetics, 1990, 124: 735-742.
PMID |
| [24] | 彭小群, 王梦龙. 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(3): 472-482. |
| Peng X Q, Wang M L. Research advances on resistance genes to bacterial blight disease in rice[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2022, 58(3): 472-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 李仲惺, 楼珏, 卢华金. 水稻细菌性条斑病发病程度与发病因子关系探讨[J]. 中国稻米, 2016, 22(4): 62-64. |
| Li Z X, Lou J, Lu H. Relationship between incidence and disease factors of bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(4): 62-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Xie X F, Zheng Y, Lu L B, Yuan J Z, Hu J, Bu S H, Lin Y Y, Liu Y S, Guan H Z, Wu W R. Genome-wide association study of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Plants (Basel), 2021, 10(10): 2039. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||