
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 150-158.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210606
裘霖琳1, 刘窍1, 付亚萍2, 刘文真2, 胡国成2, 翟玉凤1, 庞礴1, 汪得凯1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-17
修回日期:2021-09-14
出版日期:2022-03-10
发布日期:2022-03-11
通讯作者:
汪得凯
基金资助:
QIU Linlin1, LIU Qiao1, FU Yaping2, LIU Wenzhen2, HU Guocheng2, ZHAI Yufeng1, PANG Bo1, WANG Dekai1,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-17
Revised:2021-09-14
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2022-03-11
Contact:
WANG Dekai
摘要:
【目的】 水稻株高和穗型在产量形成中发挥着重要作用。鉴定与克隆水稻株高和穗型发育相关基因,可以丰富水稻株高穗型发育调控的分子机理,为分子设计育种奠定理论基础和提供基因资源。【方法】 在粳稻日本晴T-DNA插入群体中筛选到矮化小穗突变体dsp2-D(dwarf and small panicle 2-Dominant),对其主要农艺性状进行了分析;采用图位克隆法结合T-DNA标签分离法进行了基因定位和克隆;利用半定量PCR和qRT-PCR进一步确定dsp2-D的候选基因;遗传转化实验验证了DSP2的功能。【结果】 与野生型日本晴相比,dsp2-D突变体表现为半矮化、穗轴和枝梗明显缩短、穗型直立、千粒重降低等特征;遗传分析表明该突变体受一对不完全显性单基因控制;利用图位克隆将DSP2定位于第2染色体标记RM208和RM7337之间,与RM3850共分离;随后遗传分析发现,T-DNA插入位点与dsp2-D表型共分离,利用TAIL-PCR分离T-DNA插入序列,显示T-DNA插入到上述RM208和RM7337之间的两个基因之间。RT-PCR检测发现,位于T-DNA插入位点下游的一个编码LOB家族转录因子基因的表达量明显增加,而其他5个基因的表达量变化不明显,表明该基因可能为DSP2的候选基因;在野生型日本晴中过量表达DSP2基因,转化植株出现半矮化、小穗的表型,与dsp2-D表型类似,从而验证了DSP2的功能。【结论】 DSP2基因的过量表达是产生dsp2-D突变表型的原因;DSP2基因对水稻株高和穗长发育具有负向调控作用;为进一步丰富株高和穗型的遗传调控网络打下了基础。
裘霖琳, 刘窍, 付亚萍, 刘文真, 胡国成, 翟玉凤, 庞礴, 汪得凯. 水稻矮化小穗基因DSP2的鉴定与克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 150-158.
QIU Linlin, LIU Qiao, FU Yaping, LIU Wenzhen, HU Guocheng, ZHAI Yufeng, PANG Bo, WANG Dekai. Identification and Gene Cloning of DSP2 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 150-158.
| 引物名称 | 正向引物序列 | 反向引物序列 | 实验目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer(5'-3') | Reverse primer(5'-3') | Purpose |
| ORF1-qPCR | AGATCAACCTCCAACTACTCTC | AAGCTCAGTAGTACACAGGC | RT-PCR |
| ORF2-qPCR | GTGGTTCCAGAAGATCGTGTC | TTGTCGATGGACAGGAGCTC | RT-PCR |
| ORF3-qPCR | CACGCCTACGACAACATGAAC | GTACTCGAACGCGTTGACATC | RT-PCR |
| ORF4-qPCR | CCGGTGATACAAAGAGGTGC | ATATGCTTCGGCCACCTTG | RT-PCR |
| ORF5-qPCR | AGCGGTTGTCTGGTGATATC | AGACAGAAAACCCCTTGACG | RT-PCR |
| ORF6-qPCR | CAGCTTCTGATCCTGCAGTAG | ATCTCCCTTACTGATGCTGAC | RT-PCR |
| UBQ5-qPCR | ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT | ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT | RT-PCR |
| HPTⅡ | CAGAAGAAGATGTTGGCGAC | ATGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | 共分离分析 Co-segregation |
| DSP2-ORF | ATGTCGACATGGCTGGTGCTACGGCTGC | ATCTGCAGCTGAGAGTAGTTGGAGGTTGAT | 全长ORF Full length ORF |
| NPTⅡ | TATGTCCTGATAGCGGTCCG | GTGCCCTGAATGAACTCCAG | 转化植株检测 Detection of transgenic plants |
表1 PCR鉴定及定量PCR所用的引物
Table 1 Primers used for PCR identification and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis.
| 引物名称 | 正向引物序列 | 反向引物序列 | 实验目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer(5'-3') | Reverse primer(5'-3') | Purpose |
| ORF1-qPCR | AGATCAACCTCCAACTACTCTC | AAGCTCAGTAGTACACAGGC | RT-PCR |
| ORF2-qPCR | GTGGTTCCAGAAGATCGTGTC | TTGTCGATGGACAGGAGCTC | RT-PCR |
| ORF3-qPCR | CACGCCTACGACAACATGAAC | GTACTCGAACGCGTTGACATC | RT-PCR |
| ORF4-qPCR | CCGGTGATACAAAGAGGTGC | ATATGCTTCGGCCACCTTG | RT-PCR |
| ORF5-qPCR | AGCGGTTGTCTGGTGATATC | AGACAGAAAACCCCTTGACG | RT-PCR |
| ORF6-qPCR | CAGCTTCTGATCCTGCAGTAG | ATCTCCCTTACTGATGCTGAC | RT-PCR |
| UBQ5-qPCR | ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT | ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT | RT-PCR |
| HPTⅡ | CAGAAGAAGATGTTGGCGAC | ATGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | 共分离分析 Co-segregation |
| DSP2-ORF | ATGTCGACATGGCTGGTGCTACGGCTGC | ATCTGCAGCTGAGAGTAGTTGGAGGTTGAT | 全长ORF Full length ORF |
| NPTⅡ | TATGTCCTGATAGCGGTCCG | GTGCCCTGAATGAACTCCAG | 转化植株检测 Detection of transgenic plants |
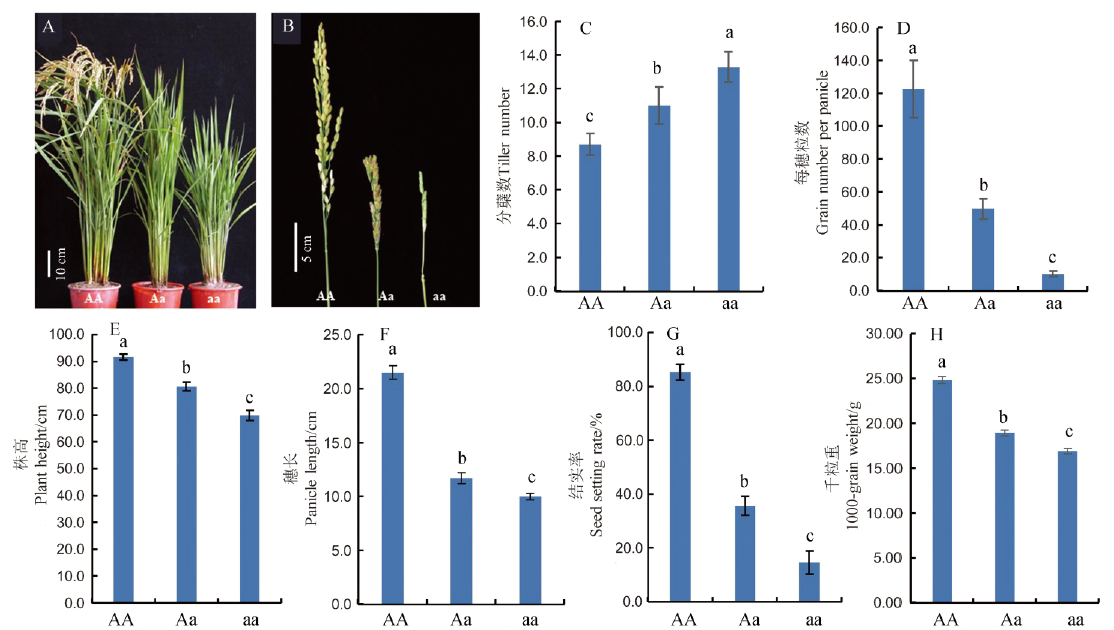
图1 突变体dsp2-D的表型 AA、Aa、aa分别代表野生型日本晴植株、杂合体和dsp2-D纯合体。不同字母代表差异极显著(P<0.01,Tukey检验),n=10。
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of the dsp2-D mutant. AA, Wild-type ‘Nipponbare’ plants; Aa, dsp2-D heterozygous plants; aa, dsp2-D homozygous plants. Values are mean ± SD of ten biological replicates. Samples with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.01; Tukey’s test).
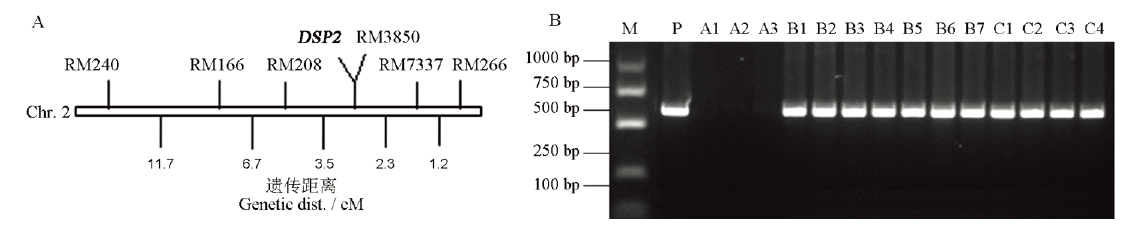
图2 DSP2基因在第2染色体上的定位和T-DNA共分离分析 A―DSP2基因的初步定位;B―T-DNA插入位点共分离分析。M, 1 kb ladder; P为质粒阳性对照; A1~A3为野生型;B1~B7为杂合体;C1~C4为纯合体。
Fig. 2. Location of DSP2 on chromosome 2 and co-segregation analysis of T-DNA. A, Preliminary localization of DSP2 gene; B, Co-segregation analysis of T-DNA and dsp2-D phenotypes. M, 1 kb ladder, P, Plasmid positive control; A1-A3, Wild type; B1-B7, Heterozygote; C1-C4, Homozygous mutant.
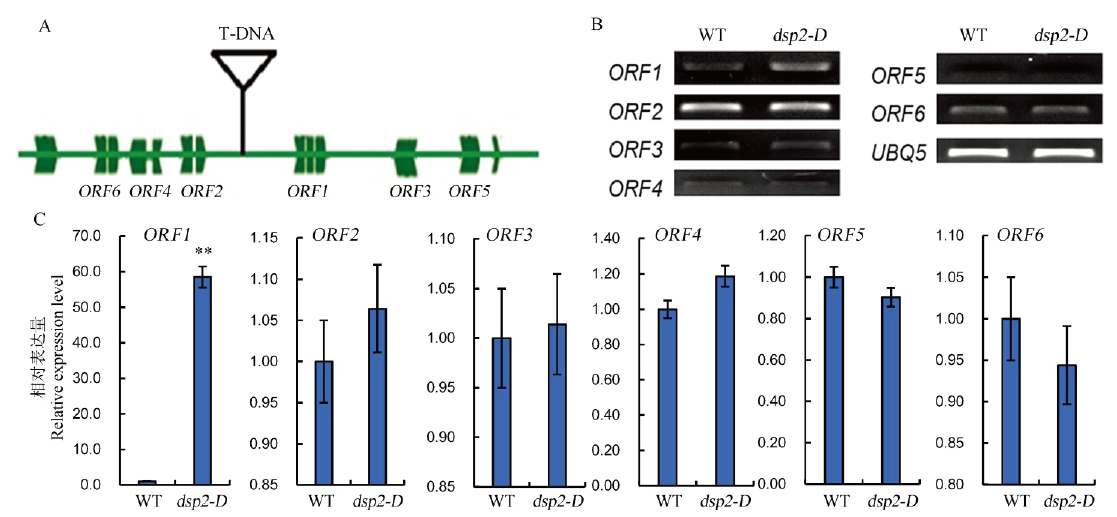
图3 候选基因DSP2的表达分析 A―T-DNA插入位点;B, C―6个基因在突变体dsp2-D和野生型中的表达水平,水稻OsUBQ5为内参基因。Bar值表示3个生物学重复的平均值±SD;**表示0.01极显著水平。
Fig. 3. Expression analysis of candidate gene DSP2. A, Schematic diagram of T-DNA insertion sites; B and C, Expression levels of six candidate genes in dsp2-D and wild type analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and real time PCR; OsUBQ5 was amplified as a control. Bars represent standard deviation (n=3). ** indicates significant difference between Nipponbare and dsp2-D by t-test (P<0.01).
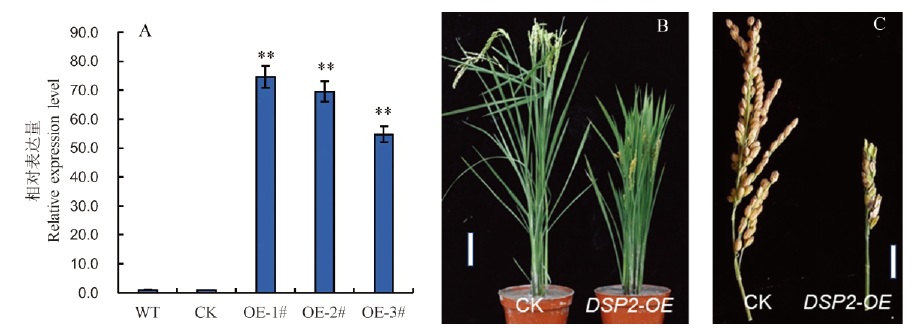
图4 DSP2基因的过量表达和功能验证 A―DSP2基因在野生型和转基因植株中的表达水平,其中WT代表野生型日本晴,CK代表空载体转化植株,OE-1#~OE-3#代表DSP2-OE转化植株;Bar值表示3个生物学重复的平均值±SD;**表示0.01极显著水平。B, C―DSP2过表达转基因植株的表型,CK为空载体转化植株。B图中标尺表示10 cm; C图中标尺表示5 cm。
Fig. 4. Overexpression of DSP2 gene and functional identification. A, Expression levels of DSP2 gene in wild-type and transgenic plants. WT, Wild type Nipponbare; CK, Control plasmid transgenic plants; OE-1#-OE-3#, DSP2-OE transgenic plants; Bars represent standard deviation (n=3). **indicates significant difference between Nipponbare and dsp2-D by t-test (P<0.01). B and C, Phenotype of the dsp2-D mutant and transgenic plant. B, Bar=10 cm; C, Bar=5 cm.
| [1] | 刘坚, 陶红剑, 施思, 叶卫军, 钱前, 郭龙彪. 水稻穗型的遗传和育种改良[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012,26(2):227-234. |
| Liu J, Tao H J, Shi S, Ye W J, Qian Q, Guo L B. Genetics and breeding improvement for panicle type in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012,26(2):227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 冷语佳, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻理想株型的遗传基础研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2014,20(2):1-6. |
| Leng Y J, Qian Q, Zeng D L. Progress on genetic basis of rice ideal plant type[J]. China Rice, 2014,20(2):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 淳雁, 李学勇. 水稻穗型的遗传调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017,52(1):19-29. |
| Chun Y, Li X Y. Research progress in genetic regulation of rice panicle architecture[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017,52(1):19-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A mutant gibberellin-synjournal gene in rice[J]. Nature, 2002,416(6882):701-702. |
| [5] | Peng J, Richards D E, Hartley N M, Murphy G P, Devos K M, Flintham J E, Beales J, Fish L J, Worland A J, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape J W, Gale M D, Harberd N P. “Green revolution” genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators[J]. Nature, 1999,400(6741):256-261. |
| [6] | Ogawa S, Toyomasu T, Yamane H, Murofushi N, Ikeda R, Morimoto Y, Nishimura Y, Omori T. A step in the biosynjournal of gibberellins that is controlled by the mutation in the semi-dwarf rice cultivar Tan-Ginbozu[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1996,37(3):363-368. |
| [7] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Itoh H, Kayano T, Iwahori S, Matsuoka M, Tanaka H. Genetic manipulation of gibberellin metabolism in transgenic rice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003,21(8):909-913. |
| [8] | Zhu Y, Nomura T, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Mao B, Hanada A, Zhou H, Wang R, Li P, Zhu X, Mander L N, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S, He Z. ELONGATED UPPERMOST INTERNODE encodes a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that epoxidizes gibberellins in a novel deactivation reaction in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2006,18(2):442-456. |
| [9] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow T, Hsing Y, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M. GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin[J]. Nature, 2005,437(7059):693-698. |
| [10] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450[J]. Plant Cell, 2003,15(12):2900-2910. |
| [11] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006,24(1):105-109. |
| [12] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone[J]. Plant Cell, 2005,17(8):2243-2254. |
| [13] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint[J]. Plant Cell, 2000,12(9):1591-1605. |
| [14] | Tong H, Jin Y, Liu W, Li F, Fang J, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2009,58(5):803-816. |
| [15] | Lin H, Wang R, Qian Q, Yan M, Meng X, Fu Z, Yan C, Jiang B, Su Z, Li J, Wang Y. DWARF27, an iron-containing protein required for the biosynjournal of strigolactones, regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth[J]. Plant Cell, 2009,21(5):1512-1525. |
| [16] | Zou J, Chen Z, Zhang S, Zhang W, Jiang G, Zhao X, Zhai W, Pan X, Zhu L. Characterizations and fine mapping of a mutant gene for high tillering and dwarf in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Planta, 2005,222(4):604-612. |
| [17] | Arite T, Iwata H, Ohshima K, Maekawa M, Nakajima M, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Kyozuka J. DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2007,51(6):1019-1029. |
| [18] | Wang Y, Shang L, Yu H, Zeng L, Hu J, Ni S, Rao Y, Li S, Chu J, Meng X, Wang L, Hu P, Yan J, Kang S, Qu M, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu X, Chen H, Wang B, Gao Z, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhu X, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q. A strigolactone biosynjournal gene contributed to the green revolution in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020,13(6):923-932. |
| [19] | Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G, Liu H, Chen F, Wang L, Meng X, Liu G, Yu H, Yuan Y, Yi W, Zhao L, Ma H, He Y, Wu Z, Melcher K, Qian Q, Xu H E, Wang Y, Li J. DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signaling in rice[J]. Nature, 2013,504(7480):401-405. |
| [20] | Zhou F, Lin Q, Zhu L, Ren Y, Zhou K, Shabek N, Wu F, Mao H, Dong W, Gan L, Ma W, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen W, Chu J, Yan C, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Zhai H, Wu C, Wang H, Zheng N, Wan J. D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling[J]. Nature, 2013,504(7480):406-410. |
| [21] | Yao R, Ming Z, Yan L, Li S, Wang F, Ma S, Yu C, Yang M, Chen L, Li Y, Yan C, Miao D, Sun Z, Yan J, Sun Y, Wang L, Chu J, Fan S, He W, Deng H, Nan F, Li J, Rao Z, Lou Z, Xie D. DWARF14 is a non-canonical hormone receptor for strigolactone[J]. Nature, 2016,536(7617):469-473. |
| [22] | Wang L, Wang B, Yu H, Guo H, Lin T, Kou L, Wang A, Shao N, Ma H, Xiong G, Li X, Yang J, Chu J, Li J. Transcriptional regulation of strigolactone signalling in Arabidopsis[J]. Nature, 2020,583(7815):277-281. |
| [23] | Sazuka T, Kamiya N, Nishimura T, Ohmae K, Sato Y, Imamura K, Nagato Y, Koshiba T, Nagamura Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos[J]. Plant Journal, 2009,60(2):227-241. |
| [24] | Song Y, You J, Xiong L. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2009,70(3):297-309. |
| [25] | Qi W, Sun F, Wang Q, Chen M, Huang Y, Feng Y Q, Luo X, Yang J. Rice ethylene-response AP2/ERF factor OsEATB restricts internode elongation by down-regulating a gibberellin biosynthetic gene[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011,157(1):216-228. |
| [26] | Luan W, Liu Y, Zhang F, Song Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Sun Z. OsCD1 encodes a putative member of the cellulose synthase-like D sub-family and is essential for rice plant architecture and growth[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2011,9(4):513-524. |
| [27] | Tabuchi M, Sugiyama K, Ishiyama K, Inoue E, Sato T, Takahashi H, Yamaya T. Severe reduction in growth rate and grain filling of rice mutants lacking OsGS1;1, a cytosolic glutamine synthetase1;1[J]. Plant Journal, 2005,42(5):641-651. |
| [28] | Sato Y, Sentoku N, Miura Y, Hirochika H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Loss-of-function mutations in the rice homeobox gene OSH15 affect the architecture of internodes resulting in dwarf plants[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1999,18(4):992-1002. |
| [29] | Zhu Z Z, Fu Y P, Xiao H, Hu G C, Si H M, Yu Y H, Sun Z X. Ac/Ds Transposition activity in transgenic rice population and DNA flanking sequence of Ds insertion sites[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2003(1):102-107. |
| [30] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J. Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1985,5(2):69-76. |
| [31] | Michelmore R W, Kesseli I. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1991,88(21):9828-9832. |
| [32] | Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch S R. Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular & General Genetics, 1996,259(5):597-607. |
| [33] | Lander E S, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M J, Lincoln S E, Newburg L. Mapmaker: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations[J]. Genomics, 1987,1(2):174-181. |
| [34] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001,25(4):402-408. |
| [35] | Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA[J]. Plant Journal, 1994,6(2):271-282. |
| [36] | 郭龙彪, 程式华, 钱前. 水稻基因设计育种的研究进展与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008,22(6):650-657. |
| Guo L B, Chen S H, Qian Q. Progress and prospects of breeding by gene design in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2008,22(6):650-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Wang Y H, Li J Y. Molecular basis of plant architecture[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008,59(1):253-279. |
| [38] | Gurdv K. Productivity improvements in rice[J]. Nutrition Reviews, 2010,61(6):S114-116. |
| [39] | Majer C, Hochholdinger F. Defining the boundaries: structure and function of LOB domain proteins[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2011,16(1):47-52. |
| [40] | Zhang Y, Li Z, Ma B, Hou Q, Wan X. Phylogeny and functions of LOB domain proteins in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020,21(7):2278. |
| [41] | Yang Y, Yu X, Wu P. Comparison and evolution analysis of two rice subspecies LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES domain gene family and their evolutionary characterization from Arabidopsis[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2006,39(1):248-262. |
| [42] | Liu H, Wang S, Yu X, Yu J, He X, Zhang S, Shou H, Wu P. ARL1, a LOB-domain protein required for adventitious root formation in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2005,43(1):47-56. |
| [43] | Inukai Y, Sakamoto T, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shibata Y, Gomi K, Umemura I, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Crown rootless1, which is essential for crown root formation in rice, is a target of an Auxin Response Factor in auxin signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2005,17(5):1387-1396. |
| [44] | Li A, Zhang Y, Wu X, Tang W, Wu R, Dai Z, Liu G, Zhang H, Chen G, Pan X. DH1, a LOB domain-like protein required for glume formation in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2008,66(5):491-502. |
| [45] | Zhang J, Tang W, Huang Y, Niu X, Zhao Y, Han Y, Liu Y. Down-regulation of a LBD-like gene, OsIG1, leads to occurrence of unusual double ovules and developmental abnormalities of various floral organs and megagametophyte in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015,66(1):99-112. |
| [46] | Lu H, Dai Z, Li L, Wang J, Miao X, Shi Z. OsRAMOSA2 shapes panicle architecture through regulating pedicel length[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017,8(12):1538. |
| [47] | Li C, Zhu S, Zhang H, Chen L, Cai M, Wang J, Chai J, Wu F, Cheng Z, Guo X, Zhang X, Wan J. OsLBD37 and OsLBD38, two class II type LBD proteins, are involved in the regulation of heading date by controlling the expression of Ehd1 in rice[J]. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2017,486(3):720-725. |
| [48] | Huang X Z, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009,41(4):494-497. |
| [49] | Zhou Y, Zhu J, Li Z, Yi C, Liu J, Zhang H, Tang S, Gu M, Liang G. Deletion in a quantitative trait gene qPE9-1 associated with panicle erectness improves plant architecture during rice domestication[J]. Genetics, 2009,183(1):315-324. |
| [50] | Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song X J, Ito M, Asano K J, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M. OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):545-549. |
| [51] | Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, Dong G, Zeng D, Lu Z, Zhu X, Qian Q, Li J. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):541-544. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||