
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 249-258.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.01103
田铮1,2, 赵春芳2, 张亚东2, 赵庆勇2, 朱镇2, 赵凌2, 陈涛2, 姚姝2, 周丽慧2, 梁文化2, 路凯2, 王才林1,2,*( ), 张红生1,*
), 张红生1,*
收稿日期:2020-11-02
修回日期:2021-01-07
出版日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2021-05-10
通讯作者:
王才林,张红生
基金资助:
Zheng TIAN1,2, Chunfang ZHAO2, Yadong ZHANG2, Qingyong ZHAO2, Zhen ZHU2, Ling ZHAO2, Tao CHEN2, Shu YAO2, Lihui ZHOU2, Wenhua LIANG2, Kai LU2, Cailin WANG1,2,*( ), Hongsheng ZHANG1,*
), Hongsheng ZHANG1,*
Received:2020-11-02
Revised:2021-01-07
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-10
Contact:
Cailin WANG, Hongsheng ZHANG
摘要:
【目的】近两年江苏省选育了大量的半糯型粳稻品种。不同半糯型粳稻品种间的食味品质及稻米理化特性仍存在较大差异。探究影响半糯粳稻食味品质形成的原因,将为优良食味水稻育种提供理论依据。【方法】以2019年参加江苏省优良食味稻米评比的39个半糯型粳稻品种为试验材料,通过对蒸煮食味、外观、理化、RVA谱特征值等24个品质相关指标的测定,分析不同食味值组别间各性状指标的差异及与食味品质之间相关性。【结果】依据食味值高低将其分为高食味值(>80)、中食味值(70~80)和低食味值(<70)三组。与低食味值组相比,高食味值组品种具有较低的垩白粒率、垩白度、蛋白质含量和米饭硬度,较好的透明度,较高的胶稠度、米饭外观和黏度值。统计分析表明,直链淀粉含量、成糊温度、RVA谱特征值在三组间差异均不显著。相关性分析表明,米饭食味值与直链淀粉含量、胶稠度呈显著正相关,与蛋白质含量、成糊温度、透明度及垩白性状显著负相关。进一步分析表明高食味值组中各性状与食味值相关性均未达到显著水平,而中、低食味值组中直链淀粉含量与食味值均呈显著正相关。【结论】稻米外观和理化品质对半糯型粳稻食味品质的形成有重要影响,在半糯型粳稻中食味值较高的品种往往具有更好的外观品质、较高的直链淀粉含量和胶稠度、较低的蛋白质含量,因此在半糯型水稻育种过程中应重视这些指标的辅助选择。
田铮, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 陈涛, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林, 张红生. 江苏省半糯型粳稻蒸煮食味品质性状的差异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 249-258.
Zheng TIAN, Chunfang ZHAO, Yadong ZHANG, Qingyong ZHAO, Zhen ZHU, Ling ZHAO, Tao CHEN, Shu YAO, Lihui ZHOU, Wenhua LIANG, Kai LU, Cailin WANG, Hongsheng ZHANG. Differences in Eating and Cooking Quality Traits of Semi-waxy japonica Rice Cultivars in Jiangsu Province[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 249-258.
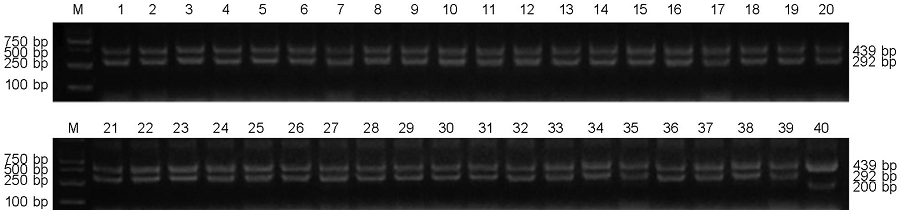
图1 39个样品的基因型检测M-DNA分子量标准;1-39代表39份半糯材料,从1到39分别代表泗稻17425、扬粳6084、常软19-3、淮粳669、武育052、镇稻3199、扬产1911、苏秀828、武科粳094、宝煌8865、南粳9108、泗稻18-40、17MGJ85、淮粳918、金粳8882、宁8874、扬粳8233、中江粳89014、天隆粳8407、武育377、华粳8855、金单粳8917、瑞华8911、武粳278、常软19-9、扬粳7016、镇稻5855、武703、苏4699、镇稻668、镇稻678、南粳5718、南粳2728、丰粳1606、徐稻9号、南粳3908、南粳晶谷、苏香粳100、南粳46;40-非Wxmp对照。
Fig. 1. Molecular detections of 39 varieties. M, DNA marker; 1-39, 39 semi-waxy varieties in sequence are Sidao 17425, Yangjing 6084, Changruan 19-3, Huaijing 669, Wuyu 052, Zhendao 3199, Yangchan 1911, Suxiu 828, Wukejing 094, Baohuang 8865, Nanjing 9108, Sidao 18-40, 17MGJ85, Huaijing 918, Jinjing 8882, Ning 8874, Yangjing 8233, Zhongjiangjing 89014, Tianlongjing 8407, Wuyu 377, Huajing 8855, Jindanjing 8917, Ruihua 8911, Wujing 278, Changruan 19-9, Yangjing 7016, Zhendao 5855, Wu 703, Su 4699, Zhendao 668, Zhendao 678, Nanjing 5718, Nanjing 2728, Fengjing 1606, Xudao 9, Nanjing 3908, Nanjing Jinggu, Suxiangjing 100, Nanjing 46; 40, The control without Wxmp gene.
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 粒长宽比 Length-width ratio | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% | 透明度 Transparency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.83±0.05 A | 2.72±0.03 A | 1.78±0.02 A | 46.71±6.77 A | 15.86±2.72 A | 4.3±0.3 A |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.48~5.05 | 2.52~2.92 | 1.65~1.87 | 16.13~81.16 | 4.68~30.34 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 59 | 23 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.60 | 0.23 | -0.62 | 0.02 | 0.40 | -1.65 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.37 | 0.55 | -1.44 | -1.70 | -1.28 | -0.81 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.80±0.05 A | 2.81±0.04 A | 1.71±0.03 A | 27.93±3.33 B | 7.89±1.10 B | 3.5±0.2 A |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.61~5.45 | 2.61~3.14 | 1.56~2.06 | 12.78~54.71 | 3.25~17.68 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 4 | 5 | 7 | 49 | 57 | 29 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 2.26 | 0.39 | 1.73 | 0.95 | 1.17 | -1.03 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 6.26 | -0.23 | 3.70 | -0.39 | 0.15 | 0.74 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.65±0.23 A | 2.77±0.06 A | 1.68±0.06 A | 26.33±17.08 B | 7.61±6.79 B | 3.3±0.8 B |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.15~5.07 | 2.66~2.85 | 1.56~1.77 | 8.61~63.94 | 2.71~25.82 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 2 | 4 | 65 | 89 | 25 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 3.31 | -0.90 | 1.50 | 1.57 | 7.11 | 1.24 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | -0.65 | -0.37 | -0.17 | 1.31 | 2.56 | 0.81 |
表1 不同组别间的稻米理化特性差异
Table 1 Differences in physicochemical properties between different groups.
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 粒长宽比 Length-width ratio | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% | 透明度 Transparency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.83±0.05 A | 2.72±0.03 A | 1.78±0.02 A | 46.71±6.77 A | 15.86±2.72 A | 4.3±0.3 A |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.48~5.05 | 2.52~2.92 | 1.65~1.87 | 16.13~81.16 | 4.68~30.34 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 59 | 23 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.60 | 0.23 | -0.62 | 0.02 | 0.40 | -1.65 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.37 | 0.55 | -1.44 | -1.70 | -1.28 | -0.81 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.80±0.05 A | 2.81±0.04 A | 1.71±0.03 A | 27.93±3.33 B | 7.89±1.10 B | 3.5±0.2 A |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.61~5.45 | 2.61~3.14 | 1.56~2.06 | 12.78~54.71 | 3.25~17.68 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 4 | 5 | 7 | 49 | 57 | 29 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 2.26 | 0.39 | 1.73 | 0.95 | 1.17 | -1.03 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 6.26 | -0.23 | 3.70 | -0.39 | 0.15 | 0.74 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 4.65±0.23 A | 2.77±0.06 A | 1.68±0.06 A | 26.33±17.08 B | 7.61±6.79 B | 3.3±0.8 B |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 4.15~5.07 | 2.66~2.85 | 1.56~1.77 | 8.61~63.94 | 2.71~25.82 | 2.0~5.0 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 2 | 4 | 65 | 89 | 25 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 3.31 | -0.90 | 1.50 | 1.57 | 7.11 | 1.24 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | -0.65 | -0.37 | -0.17 | 1.31 | 2.56 | 0.81 |
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 直链淀粉含量AC Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量PC Protein content/% | 胶稠度GC Gel consistency / mm | 成糊温度PaT Pasting temp/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 10.33±0.58 A | 8.17±0.20 A | 70.6±2.4 B | 74.8±0.9 A |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 7.23~13.76 | 7.21~9.38 | 56.0~81.0 | 71.2~81.5 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 19 | 9 | 12 | 4 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.91 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.47 | -0.88 | 1.01 | 0.13 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 11.23±0.41 A | 7.78±0.14 A | 75.3±2.4 B | 72.6±0.3 A |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 6.73~13.87 | 6.44~9.06 | 46.0~90.0 | 70.4~75.2 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 15 | 8 | 13 | 2 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -1.10 | -0.05 | -1.44 | 0.25 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 2.01 | 1.26 | 4.06 | -0.24 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 12.02±1.89 A | 6.56±0.56 B | 85.8±7.9 A | 71.5±1.3 B |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 8.45~14.16 | 5.86~7.35 | 76.0~102.5 | 68.9~73.6 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 16 | 9 | 9 | 2 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.02 | -1.61 | 1.09 | 1.03 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | -0.91 | 0.34 | 0.97 | -0.53 |
表2 不同组别间的稻米理化特性差异
Table 2 Differences in physicochemical properties between groups with various ECQ.
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 直链淀粉含量AC Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量PC Protein content/% | 胶稠度GC Gel consistency / mm | 成糊温度PaT Pasting temp/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 10.33±0.58 A | 8.17±0.20 A | 70.6±2.4 B | 74.8±0.9 A |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 7.23~13.76 | 7.21~9.38 | 56.0~81.0 | 71.2~81.5 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 19 | 9 | 12 | 4 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.91 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.47 | -0.88 | 1.01 | 0.13 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 11.23±0.41 A | 7.78±0.14 A | 75.3±2.4 B | 72.6±0.3 A |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 6.73~13.87 | 6.44~9.06 | 46.0~90.0 | 70.4~75.2 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 15 | 8 | 13 | 2 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -1.10 | -0.05 | -1.44 | 0.25 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 2.01 | 1.26 | 4.06 | -0.24 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 12.02±1.89 A | 6.56±0.56 B | 85.8±7.9 A | 71.5±1.3 B |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 8.45~14.16 | 5.86~7.35 | 76.0~102.5 | 68.9~73.6 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 16 | 9 | 9 | 2 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.02 | -1.61 | 1.09 | 1.03 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | -0.91 | 0.34 | 0.97 | -0.53 |
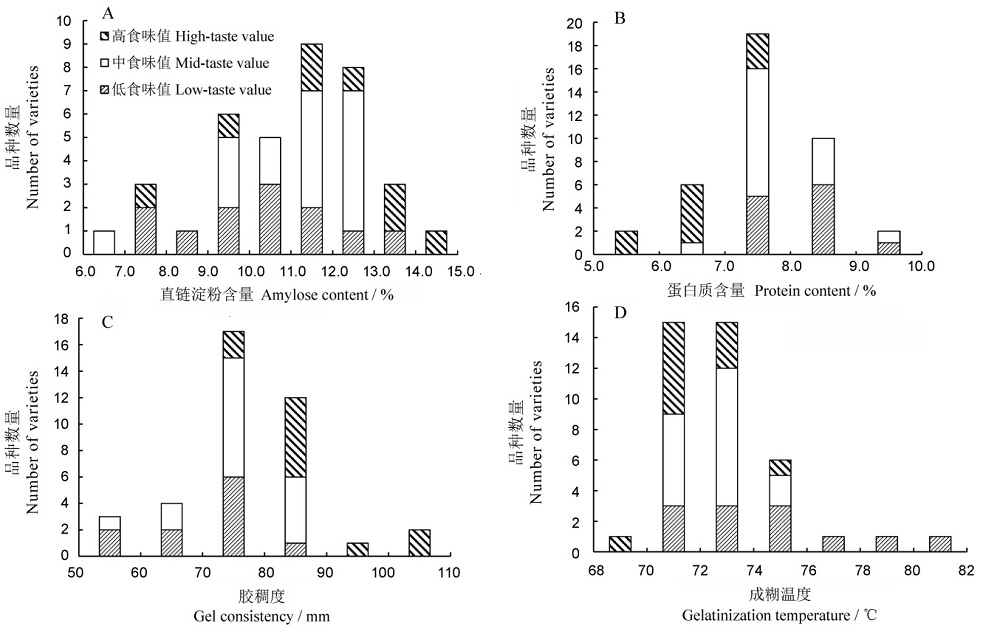
图4 39份样品稻米理化特性的频率分布A-直链淀粉含量的频率分布; B-蛋白质含量的频率分布; C-胶稠度的频率分布; D-成糊温度的频率分布。
Fig. 4. Frequency distribution of physicochemical properties. A, Frequency distribution of amylose content, B, Frequency distribution of protein content, C, Frequency distribution of gel consistency, D, Frequency distribution of gelatinization temperature.
| 样品类型 Type | 峰值黏度PKV | 热浆黏度TV | 崩解值BDV | 最终黏度FV | 回复值CSV | 消减值SBV | 峰值时间 Pt/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Mean | 2706.91±121.85 A | 1477.33±95.88 A | 1229.58±79.69 A | 2110.17±102.77 A | 616.18±86.91 A | -596.75±88.51 A | 6.07±0.08 A |
| 变幅 Range | 1994~3472 | 994~2094 | 888~1776 | 1584~2699 | 454~724 | -1181~-212 | 5.53~6.40 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 16 | 22 | 22 | 17 | 14 | 51 | 4 |
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.64 | 0.25 | -0.73 | -0.53 | -0.53 |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.07 | -0.58 | -0.32 | -1.10 | -0.57 | -0.66 | -0.22 |
| 平均值 Mean | 2813.76±57.24 A | 1641.47±44.54 A | 1172.29±33.58 A | 2289.18±43.10 A | 647.71±54.35 A | -524.59±39.68 A | 6.24±0.03 A |
| 变幅 Range | 2420~3067 | 1396~1952 | 921~1348 | 1962~2549 | 566~719 | -768~-268 | 6.07~6.53 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 8 | 11 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 31 | 2 |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.06 | 0.26 | -0.54 | -0.30 | -0.23 | 0.430 | 0.82 |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -1.22 | -1.35 | -0.86 | -1.04 | -1.60 | -1.123 | 1.33 |
| 平均值 Mean | 2724.20±182.07 A | 1490.30±229.92 A | 1233.90±173.78 A | 2122.70±272.49 A | 632.40±71.96 A | -601.50±235.71 A | 6.13±0.26 A |
| 变幅 Range | 2438~3128 | 999~1757 | 1035~1525 | 1539~2341 | 500~724 | -1025~-311 | 5.6~6.4 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 7 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 4 |
| 偏度 Skewness | 2.46 | 1.33 | -1.24 | 1.51 | -0.42 | -0.60 | 1.32 |
| 峰度Kurtosis | 0.87 | -1.16 | 0.44 | -1.59 | -0.73 | -0.66 | -1.51 |
表3 不同食味值组稻米外观品质的比较
Table 3 Differences in physicochemical properties between groups with various ECQ. cP
| 样品类型 Type | 峰值黏度PKV | 热浆黏度TV | 崩解值BDV | 最终黏度FV | 回复值CSV | 消减值SBV | 峰值时间 Pt/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Mean | 2706.91±121.85 A | 1477.33±95.88 A | 1229.58±79.69 A | 2110.17±102.77 A | 616.18±86.91 A | -596.75±88.51 A | 6.07±0.08 A |
| 变幅 Range | 1994~3472 | 994~2094 | 888~1776 | 1584~2699 | 454~724 | -1181~-212 | 5.53~6.40 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 16 | 22 | 22 | 17 | 14 | 51 | 4 |
| 偏度 Skewness | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.64 | 0.25 | -0.73 | -0.53 | -0.53 |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.07 | -0.58 | -0.32 | -1.10 | -0.57 | -0.66 | -0.22 |
| 平均值 Mean | 2813.76±57.24 A | 1641.47±44.54 A | 1172.29±33.58 A | 2289.18±43.10 A | 647.71±54.35 A | -524.59±39.68 A | 6.24±0.03 A |
| 变幅 Range | 2420~3067 | 1396~1952 | 921~1348 | 1962~2549 | 566~719 | -768~-268 | 6.07~6.53 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 8 | 11 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 31 | 2 |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.06 | 0.26 | -0.54 | -0.30 | -0.23 | 0.430 | 0.82 |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -1.22 | -1.35 | -0.86 | -1.04 | -1.60 | -1.123 | 1.33 |
| 平均值 Mean | 2724.20±182.07 A | 1490.30±229.92 A | 1233.90±173.78 A | 2122.70±272.49 A | 632.40±71.96 A | -601.50±235.71 A | 6.13±0.26 A |
| 变幅 Range | 2438~3128 | 999~1757 | 1035~1525 | 1539~2341 | 500~724 | -1025~-311 | 5.6~6.4 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 7 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 4 |
| 偏度 Skewness | 2.46 | 1.33 | -1.24 | 1.51 | -0.42 | -0.60 | 1.32 |
| 峰度Kurtosis | 0.87 | -1.16 | 0.44 | -1.59 | -0.73 | -0.66 | -1.51 |
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 外观 Appearance | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度 Stickiness | 平衡度 Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 5.81±0.31 C | 7.04±0.14 A | 6.09±0.30 C | 5.73±0.31 C |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 3.0~6.7 | 6.6~8.3 | 3.5~7.0 | 2.9~6.6 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 18 | 7 | 17 | 18 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -2.00 | 1.95 | -1.78 | -2.00 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 4.15 | 4.29 | 3.09 | 4.00 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 7.15±0.09 B | 6.43±0.04 B | 7.72±0.13 B | 7.22±0.09 B |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 6.5~7.6 | 6.1~6.7 | 6.9~8.5 | 6.6~7.8 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 3 | 7 | 5 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.35 | 0.01 | -0.09 | -0.12 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.92 | -0.43 | -1.34 | -1.06 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 8.58±0.40 A | 5.72±0.25 C | 8.94±0.49 A | 8.64±0.44 A |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 8.0~9.2 | 5.2~6.0 | 8.3~9.7 | 8.0~9.3 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.65 | 0.63 | -1.19 | -0.80 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | 0.48 | -1.15 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
表4 不同食味值组间米饭质地的差异
Table 4 Differences in cooked rice texture between groups with various ECQ.
| 样品类型 Type | 参数 Parameter | 外观 Appearance | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度 Stickiness | 平衡度 Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 5.81±0.31 C | 7.04±0.14 A | 6.09±0.30 C | 5.73±0.31 C |
| Low taste value | 变幅 Range | 3.0~6.7 | 6.6~8.3 | 3.5~7.0 | 2.9~6.6 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 18 | 7 | 17 | 18 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -2.00 | 1.95 | -1.78 | -2.00 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | 4.15 | 4.29 | 3.09 | 4.00 | |
| 中食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 7.15±0.09 B | 6.43±0.04 B | 7.72±0.13 B | 7.22±0.09 B |
| Mid-taste value | 变幅 Range | 6.5~7.6 | 6.1~6.7 | 6.9~8.5 | 6.6~7.8 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 3 | 7 | 5 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.35 | 0.01 | -0.09 | -0.12 | |
| 峰度 Kurtosis | -0.92 | -0.43 | -1.34 | -1.06 | |
| 高食味值 | 平均值 Mean | 8.58±0.40 A | 5.72±0.25 C | 8.94±0.49 A | 8.64±0.44 A |
| High taste value | 变幅 Range | 8.0~9.2 | 5.2~6.0 | 8.3~9.7 | 8.0~9.3 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| 偏度 Skewness | -0.65 | 0.63 | -1.19 | -0.80 | |
| 峰度Kurtosis | 0.48 | -1.15 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 性状参数 Property | 米饭食味值Taste value of cooked rice | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总样本 Total sample | 高食味值组 High taste group | 中食味值组 Middle taste group | 低食味值组 Low taste group | |
| 直链淀粉含量 AC | 0.495** | -0.126 | 0.537* | 0.633* |
| 蛋白质含量 PC | -0.694** | -0.343 | -0.244 | -0.312 |
| 胶稠度GC | 0.421** | 0.352 | 0.218 | -0.528 |
| 成糊温度 PaT | -0.601** | -0.409 | -0.229 | -0.371 |
| 峰值黏度PKV | 0.140 | 0.479 | -0.023 | 0.284 |
| 热浆黏度 TV | 0.210 | 0.369 | -0.168 | 0.562* |
| 崩解值 BDV | -0.060 | 0.014 | 0.183 | -0.243 |
| 最终黏度 FV | 0.220 | 0.377 | -0.196 | 0.580* |
| 消减值 SBV | 0.080 | 0.067 | -0.180 | 0.284 |
| 回复值 CSV | 0.310 | 0.217 | -0.076 | 0.337 |
| 峰值时间 PeT | 0.100 | 0.251 | -0.238 | 0.696** |
| 透明度 Transparency | 0.378* | 0.273 | -0.028 | 0.082 |
| 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | -0.330* | -0.119 | -0.088 | -0.340 |
| 垩白度 Chalkiness | -0.438** | 0.129 | -0.120 | -0.379 |
表5 不同食味值组中稻米外观、理化及RVA特征值与米饭食味值间的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis between taste value and rice appearance, physicochemical properties and RVA parameters.
| 性状参数 Property | 米饭食味值Taste value of cooked rice | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总样本 Total sample | 高食味值组 High taste group | 中食味值组 Middle taste group | 低食味值组 Low taste group | |
| 直链淀粉含量 AC | 0.495** | -0.126 | 0.537* | 0.633* |
| 蛋白质含量 PC | -0.694** | -0.343 | -0.244 | -0.312 |
| 胶稠度GC | 0.421** | 0.352 | 0.218 | -0.528 |
| 成糊温度 PaT | -0.601** | -0.409 | -0.229 | -0.371 |
| 峰值黏度PKV | 0.140 | 0.479 | -0.023 | 0.284 |
| 热浆黏度 TV | 0.210 | 0.369 | -0.168 | 0.562* |
| 崩解值 BDV | -0.060 | 0.014 | 0.183 | -0.243 |
| 最终黏度 FV | 0.220 | 0.377 | -0.196 | 0.580* |
| 消减值 SBV | 0.080 | 0.067 | -0.180 | 0.284 |
| 回复值 CSV | 0.310 | 0.217 | -0.076 | 0.337 |
| 峰值时间 PeT | 0.100 | 0.251 | -0.238 | 0.696** |
| 透明度 Transparency | 0.378* | 0.273 | -0.028 | 0.082 |
| 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | -0.330* | -0.119 | -0.088 | -0.340 |
| 垩白度 Chalkiness | -0.438** | 0.129 | -0.120 | -0.379 |
| [1] | Shi Y S, Wei H, Hong X L.Identification of QTLs for cooking and eating quality of rice grain[J]. Rice Science, 2006, 13(3): 161-169. |
| [2] | Rao Y C, Li Y Y, Qian Q.Recent progress on molecular breeding of rice in China[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(4): 551-564. |
| [3] | Cheng S H, Zhan X D, Cao L Y.Breeding strategies for increasing yield potential in super hybrid rice[J]. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2015, 2(4): 277-282. |
| [4] | Yu S B, Jauhar A, Zhang C P, Li Z, Zhang Q.Correction to: Genomic breeding of green super rice varieties and their deployment in Asia and Africa[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2020, 133(4): 1337. |
| [5] | 张亚东, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 冯凯华, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林. 优良食味粳稻南粳5718的选育及主要特征特性[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(4): 100-102. |
| Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Feng K H, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Liang W H, Lu K, Wang C L.Breeding and characteristics of a new japonica rice variety Nanjing 5718 with good eating quality[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(4): 100-102. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 李凌, 田麟, 王涛涛, 蒋其根, 罗治靖, 陈明姣, 张建中, 张大兵, 袁政. 优质稻米‘青香软粳’低直链淀粉含量形成分子机制的初步研究[J]. 植物生理学报, 2012, 48(2): 147-155. |
| Li L, Tian L, Wang T T, Jiang J G, Luo Z J, Chen M J, Zhang J Z, Zhang D B, Yuan Z.Preliminary study for the molecular mechanism of low amylose content in high-quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety Qingxiangruanjing[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2012, 48(2): 147-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 陈智慧, 王芳权, 许扬, 王军, 李文奇, 范方军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 软米基因Wxmp在部分粳稻品种资源中的分布[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. |
| Chen Z H, Wang F Q, Xu Y, Wang J, Li W Q, Fan F J, Zhong W G, Yang J.The distribution of low amylose content allele Wxmp in japonica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Wang S Y, Yang Y H, Guo M, Zhong C Y, Yan C J, Sun S Y.Targeted mutagenesis of amino acid transporter genes for rice quality improvement using the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. The Crop Journal, 2020, 8(3): 457-464. |
| [9] | Yang Y, Guo M, Sun S, Zou Y, Yin S, Liu Y, Tang S, Gu M, Yang Z, Yan C.Natural variation of OsGluA2 is involved in grain protein content regulation in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 138-141. |
| [10] | Yang Y H, Shen Z Y, Xu C D, Guo M, Li Y G, Zhang Y X, Zhong C Y, Sun S Y, Yan C J.Genetic improvement of panicle-erectness japonica rice toward both yield and eating and cooking quality[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2020, 40(5): 51. |
| [11] | Hamaker B R, Griffin V K.Effect of disulfide bond-containing protein on rice starch gelatinization and pasting[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 1993, 70(4): 377-380. |
| [12] | 王鹤璎. 寒地水稻水直播品种筛选及与常规种植方式下的产质量比较[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2020. |
| Wang H Y.Selection of direct seeding rice varieties in cold area and comparison of yield and quality with conventional planting methods[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Land Reclamation University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 朱满山, 汤述翥, 顾铭洪. RVA谱在稻米蒸煮食用品质评价及遗传育种方面的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 8(8): 59-64. |
| Zhu M S, Tang S Z, Gu M H.Research progress of RVA spectrum in rice cooking and eating quality evaluation and genetic breeding[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 8(8): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 邹茜, 邵源梅, 黄平, 李华慧, 辜琼瑶, 郭咏梅, 李少明. 不同生态型低AC稻米蒸煮和食味品质特性研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(11): 2514-2520. |
| Zou Q, Shao Y M, Huang P, Li H H, Gu Q Y, Guo Y M, Li S M.Eating and cooking qualities in low amylose content rice with different ecotypes[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 2514-2520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 陆建忠, 张亚静, 沈超群. 米饭食味计与人工评鉴稻米食味品质比较试验[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2020, 26(16): 57-59. |
| Lu J Z, Zhang Y J, Shen C Q.Comparative test of RVA and artificial evaluation of rice eating quality[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 26(16): 57-59. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 苏光辉, 张洪伟, 张丽娜, 张泽洲. 米饭食味检测仪器评价优质稻米食味品质[J]. 北方水稻, 2019, 49(4): 34-35. |
| Su G H, Zhang H W, Zhang L N, Zhang Z Z.Evaluation of eating quality of high quality rice by rice taste detector[J]. North Rice, 2019, 49(4): 34-35. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 隋炯明, 李欣, 严松, 严长杰, 张蓉, 汤述翥, 陆驹飞, 陈宗祥, 顾铭洪. 稻米淀粉RVA谱特征与品质性状相关性研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(4): 657-663. |
| Sui J M, Li X, Yan S, Yan C J, Zhang R, Shang S Z, Lu J F, Chen Z X, Gu M H.Studies on the rice RVA profile characteristics and its correlation with the quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(4): 657-663. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 岳红亮, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 田铮, 陈涛, 梁文化, 张亚东, 王忠红, 王才林. 江苏省半糯粳稻食味品质特征及其与感官评价的关系[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2020, 35(6): 7-14, 22. |
| Yue H L, Zhao Q Y, Zhao C F, Tian Z, Chen T, Liang W H, Zhang Y D, Wang Z H, Wang C L.Characteristics of edible quality and their relationship with sensory evaluation of semi-waxy japonica rice varieties from Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2020, 35(6): 7-14, 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 朱昌兰, 沈文飚, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 水稻低直链淀粉含量基因育种利用的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(2): 157-162. |
| Zhu C L, Shen W B, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Advances in researches of the application of low-amylose content rice gene for breeding[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(2): 157-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 陈涛, 骆名瑞, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 于新. 利用四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR技术检测水稻低直链淀粉含量基因Wx-mq[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. |
| Chen T, Luo M R, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao L, Zhao Q Y, Zhou L H, Yao S, Yu X.Detection of wx-mq gene for low-amylose content by tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system PCR in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 稻米直链淀粉的测定分光光度法NY/T2639-2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of amylose content in rice: Spectrophotometry method NY/T2639-2014[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品中蛋白质的测定方法GB 5009.5-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. |
| National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. Method for determination of protein in food GB 5009.5-2016[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 米质测定方法NY/T83-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of rice quality NY/T83-2017[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | Tian Z, Qian Q, Liu Q, Yan M, Liu X, Yan C, Liu G, Gao Z, Tang S, Zeng D, Wang Y, Yu J, Gu M, Li J.Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(51): 21 760-21 765. |
| [25] | 朱霁晖, 张昌泉, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 水稻Wx基因的等位变异及育种利用研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. |
| Zhu J H, Zhang C Q, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.Progress in the allelic variation of Wx gene and its application in rice breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Mohapatra D, Bal S.Cooking quality and instrumental textural attributes of cooked rice for different milling fractions[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2006, 73(3): 253-259. |
| [27] | Li H, Gilbert R G.Starch molecular structure: The basis for an improved understanding of cooked rice texture[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 195: 9-17. |
| [28] | 陈莹莹. 江苏早熟晚粳品种稻米品质对氮肥的响应及其类型[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2012. |
| Chen Y Y.Response and types of rice quality of early maturing and late japonica varieties in Jiangsu Province to nitrogen fertilizer [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王鹏跃, 沈庆霞, 路兴花, 庞林江, 陈忠秀. 米蛋白及其组分与米饭物性及感官的关联特征研究[J]. 食品与机械, 2016, 32(3): 24-27. |
| Wang T Y, Shen Q X, Lu X H, Pang L J, Chen Z X.Relevance features of rice protein and its components to physical and sensory properties of cooked rice[J]. Food & Machinery, 2016, 32(3): 24-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 石吕, 张新月, 孙惠艳, 曹先梅, 刘建, 张祖建. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. |
| Dan L, Zhang X Y, Sun H Y, Cao X M, Liu J, Zhang Z J.Relationship of grain protein content with cooking and eating quality as affected by Nitrogen fertilizer at late growth stage for different types of rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 石彦国, 贺殷媛, 陈凤莲, 管哲贤, 孙贵尧, 郑梦彤, 张红玉. 大米蛋白与蒸煮品质相关性研究进展[J]. 食品科学技术学报, 2020, 38(4): 1-9. |
| Dan Y G, He Y Y, Chen F L, Guan Z X, Sun G Y, Zheng M T, Zhang H Y.Research progress on relationship between rice protein and cooking quality[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 38(4): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 赵春芳, 岳红亮, 黄双杰, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝. 南粳系列水稻品种的食味品质与稻米理化特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. |
| Zhao C F, Yue H L, Huang S J, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhang Y D, Chen C, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S.Eating quality and physicochemical properties in Nanjing rice varieties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Kong X, Zhu P, Sui Z, Bao J.Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinization temperature combinations[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 172(1): 433-440. |
| [34] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Pillay B, 王才林. Wxmp基因背景下可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和去分支酶基因PUL对水稻蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. |
| Yao S, Zhang Y D, Liu Y Q, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Pillay B, Wang C L.Allelic effects on eating and cooking quality of SSⅡa and PUL genes under Wxmp background in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Pillay B, 王才林. 水稻Wxmp背景下SSⅡa和SSⅢa等位变异及其互作对蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(11): 1690-1702. |
| Yao S, Zhang Y D, Liu Y Q, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Pillay B, Wang C L.Effects of SSⅡa and SSⅢa alleles and their interaction on eating and cooking quality under Wxmp background of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(11): 1690-1702. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 赵春芳, 岳红亮, 田铮, 顾明超, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 陈涛, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 梁文化, 路凯, 张亚东, 王才林. 江苏和东北粳稻稻米理化特性及Wx和OsSSIIa基因序列分析[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(6): 878-888. |
| Zhao C F, Yue H L, Tian Z, Gu M C, Zhao L, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhou L H, Yao S, Liang W H, Lu K, Zhang Y D, Wang C L.Physicochemical properties and sequence analysis of Wx and OsSSIIa genes in japonica rice cultivars from Jiangsu Province and Northeast of China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 878-888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [14] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [15] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||