
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 255-263.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240802
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHU Ao1,2, XIE Jiaxin1,2, CAO Wei3, ZHOU Chuanming1,2, LI Beilei1,2, CHEN Jiaxin1,2, LI Li1,2, CAO Fangbo1,2, CHEN Jiana1,2, HUANG Min1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-05
Revised:2024-11-25
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
HUANG Min
舒傲1,2, 解嘉鑫1,2, 曹威3, 周传名1,2, 李蓓蕾1,2, 陈嘉馨1,2, 李莉1,2, 曹放波1,2, 陈佳娜1,2, 黄敏1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
黄敏
基金资助:SHU Ao, XIE Jiaxin, CAO Wei, ZHOU Chuanming, LI Beilei, CHEN Jiaxin, LI Li, CAO Fangbo, CHEN Jiana, HUANG Min. Effect of Nitrogen Management Strategies on Yield and Grain Quality of High-quality Hybrid Mid-season Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 255-263.
舒傲, 解嘉鑫, 曹威, 周传名, 李蓓蕾, 陈嘉馨, 李莉, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 氮肥运筹对优质杂交中稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 255-263.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240802
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number(×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 群体颖花量 Total spikelets (×108/hm2) | 结实率 Grain filling rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 298 a | 200 ab | 5.98 ab | 77.2 cd | 24.6 a | 9.94 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 283 ab | 197 ab | 5.57 bc | 80.6 b | 25.0 a | 9.72 ab |
| N3 | 272 ab | 191 b | 5.21 c | 83.9 a | 24.8 a | 9.45 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 288 a | 219 a | 6.27 a | 76.9 d | 21.8 b | 9.74 ab |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 279 ab | 217 ab | 5.81 ab | 79.7 bc | 21.7 b | 9.38 bc |
| N3 | 261 b | 209 ab | 5.65 bc | 83.3 a | 21.5 b | 9.14 ac | |
| 方差分析ANOVA((F-value)) | |||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 1.42NS | 7.65* | 6.83* | 0.82NS | 257.86** | 5.24* | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 4.93* | 0.37NS | 10.46** | 32.13** | 0.42NS | 6.57* | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.13NS | 0.34NS | 0.22NS | 0.09NS | 0.90NS | 0.11NS |
Table 1. Effects of nitrogen management strategies on yield and its components of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2022)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number(×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 群体颖花量 Total spikelets (×108/hm2) | 结实率 Grain filling rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 298 a | 200 ab | 5.98 ab | 77.2 cd | 24.6 a | 9.94 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 283 ab | 197 ab | 5.57 bc | 80.6 b | 25.0 a | 9.72 ab |
| N3 | 272 ab | 191 b | 5.21 c | 83.9 a | 24.8 a | 9.45 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 288 a | 219 a | 6.27 a | 76.9 d | 21.8 b | 9.74 ab |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 279 ab | 217 ab | 5.81 ab | 79.7 bc | 21.7 b | 9.38 bc |
| N3 | 261 b | 209 ab | 5.65 bc | 83.3 a | 21.5 b | 9.14 ac | |
| 方差分析ANOVA((F-value)) | |||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 1.42NS | 7.65* | 6.83* | 0.82NS | 257.86** | 5.24* | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 4.93* | 0.37NS | 10.46** | 32.13** | 0.42NS | 6.57* | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.13NS | 0.34NS | 0.22NS | 0.09NS | 0.90NS | 0.11NS |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number(×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 群体颖花量 Total spikelets (×108/hm2) | 结实率 Grain filling rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 297 a | 188 b | 5.56 b | 78.1 c | 25.5 b | 9.73 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 266 b | 188 b | 5.03 d | 83.6 b | 25.7 ab | 9.44 ab |
| N3 | 251 bc | 187 bc | 4.73 e | 85.2 ab | 25.8 a | 9.22 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 290 a | 210 a | 5.96 a | 79.4 c | 21.9 c | 9.3 bc |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 264 bc | 206 ab | 5.38 c | 85.2 ab | 21.8 c | 9.02 cd |
| N3 | 248 c | 203 a | 5.23 c | 86.2 a | 21.8 c | 8.69 d | |
| 方差分析ANOVA(F-value) | |||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 0.80NS | 20.25** | 78.66** | 3.86NS | 3323.42** | 29.66** | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 32.25** | 0.30NS | 100.56** | 48.91** | 3.14NS | 14.50** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.11NS | 0.27NS | 0.91NS | 0.04NS | 2.06NS | 0.17NS |
Table 2. Effects of nitrogen management strategies on yield and its components of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2023)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number(×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 群体颖花量 Total spikelets (×108/hm2) | 结实率 Grain filling rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 297 a | 188 b | 5.56 b | 78.1 c | 25.5 b | 9.73 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 266 b | 188 b | 5.03 d | 83.6 b | 25.7 ab | 9.44 ab |
| N3 | 251 bc | 187 bc | 4.73 e | 85.2 ab | 25.8 a | 9.22 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 290 a | 210 a | 5.96 a | 79.4 c | 21.9 c | 9.3 bc |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 264 bc | 206 ab | 5.38 c | 85.2 ab | 21.8 c | 9.02 cd |
| N3 | 248 c | 203 a | 5.23 c | 86.2 a | 21.8 c | 8.69 d | |
| 方差分析ANOVA(F-value) | |||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 0.80NS | 20.25** | 78.66** | 3.86NS | 3323.42** | 29.66** | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 32.25** | 0.30NS | 100.56** | 48.91** | 3.14NS | 14.50** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.11NS | 0.27NS | 0.91NS | 0.04NS | 2.06NS | 0.17NS |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗前干物质积累量 Pre-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 抽穗后干物质积累量 Post-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 总干物质积累量 Total biomass production(t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 13.4 a | 6.31 a | 19.8 a | 0.49 ab |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 13.0 ab | 6.55 a | 19.5 ab | 0.49 ab |
| N3 | 12.7 b | 5.49 a | 18.2 c | 0.51 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 12.7 b | 5.96 a | 18.6 abc | 0.48 ab |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 12.5 bc | 6.03 a | 18.6 bc | 0.46 b |
| N3 | 12.0 c | 5.98 a | 18.0 c | 0.48 ab | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 17.3** | 0.15NS | 6.34* | 4.71NS | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 6.59* | 1.07NS | 4.93* | 0.72NS | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.40NS | 0.95NS | 0.82NS | 0.86NS |
Table 3. Effect of nitrogen management strategies on dry matter production of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2022)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗前干物质积累量 Pre-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 抽穗后干物质积累量 Post-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 总干物质积累量 Total biomass production(t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 13.4 a | 6.31 a | 19.8 a | 0.49 ab |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 13.0 ab | 6.55 a | 19.5 ab | 0.49 ab |
| N3 | 12.7 b | 5.49 a | 18.2 c | 0.51 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 12.7 b | 5.96 a | 18.6 abc | 0.48 ab |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 12.5 bc | 6.03 a | 18.6 bc | 0.46 b |
| N3 | 12.0 c | 5.98 a | 18.0 c | 0.48 ab | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 17.3** | 0.15NS | 6.34* | 4.71NS | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 6.59* | 1.07NS | 4.93* | 0.72NS | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.40NS | 0.95NS | 0.82NS | 0.86NS |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗前干物质积累量 Pre-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 抽穗后干物质积累量 Post-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 总干物质积累量 Total biomass production(t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 14.5 a | 6.08 a | 20.6 a | 0.46 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 13.0 ab | 5.90 a | 19.9 ab | 0.49 a |
| N3 | 12.0 bc | 5.73 a | 17.7 b | 0.46 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 12.7 b | 5.89 a | 18.6 ab | 0.47 a |
| Huazhe you 261 | N2 | 11.4 cd | 6.36 a | 17.7 b | 0.49 a |
| N3 | 10.5 d | 6.16 a | 16.7 b | 0.50 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 25.86** | 0.11NS | 5.09NS | 0.04NS | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 18.85** | 0.02NS | 4.99* | 2.50NS | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.13NS | 0.09NS | 0.24NS | 0.16NS | |
Table 4. Effect of nitrogen management strategies on dry matter production of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2023)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗前干物质积累量 Pre-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 抽穗后干物质积累量 Post-heading biomass production(t/hm2) | 总干物质积累量 Total biomass production(t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 14.5 a | 6.08 a | 20.6 a | 0.46 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 13.0 ab | 5.90 a | 19.9 ab | 0.49 a |
| N3 | 12.0 bc | 5.73 a | 17.7 b | 0.46 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 12.7 b | 5.89 a | 18.6 ab | 0.47 a |
| Huazhe you 261 | N2 | 11.4 cd | 6.36 a | 17.7 b | 0.49 a |
| N3 | 10.5 d | 6.16 a | 16.7 b | 0.50 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 25.86** | 0.11NS | 5.09NS | 0.04NS | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 18.85** | 0.02NS | 4.99* | 2.50NS | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.13NS | 0.09NS | 0.24NS | 0.16NS | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering(t/hm2) | 幼穗分化期 Panicle initiation(t/hm2) | 抽穗期 Heading(t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 1.81 a | 6.18 a | 14.5 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 1.78 a | 5.35 ab | 13.0 b |
| N3 | 1.73 a | 4.72 bcd | 12.0 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 1.33 b | 4.97 bc | 12.8 b |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 1.26 b | 4.43 cd | 11.5 cd |
| N3 | 1.23 b | 3.91 d | 10.6 d | |
| 方差分析 ANOVA(F-value) | ||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 121.19** | 18.52** | 25.86** | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 1.36NS | 10.12** | 18.85** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.06NS | 0.27NS | 0.13NS |
Table 5. Effect of nitrogen management strategies on dry matter production of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice at various growth stages prior to tillering (2023)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering(t/hm2) | 幼穗分化期 Panicle initiation(t/hm2) | 抽穗期 Heading(t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 1.81 a | 6.18 a | 14.5 a |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 1.78 a | 5.35 ab | 13.0 b |
| N3 | 1.73 a | 4.72 bcd | 12.0 bc | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 1.33 b | 4.97 bc | 12.8 b |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 1.26 b | 4.43 cd | 11.5 cd |
| N3 | 1.23 b | 3.91 d | 10.6 d | |
| 方差分析 ANOVA(F-value) | ||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 121.19** | 18.52** | 25.86** | |
| 氮肥运筹N management strategy(N) | 1.36NS | 10.12** | 18.85** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.06NS | 0.27NS | 0.13NS |
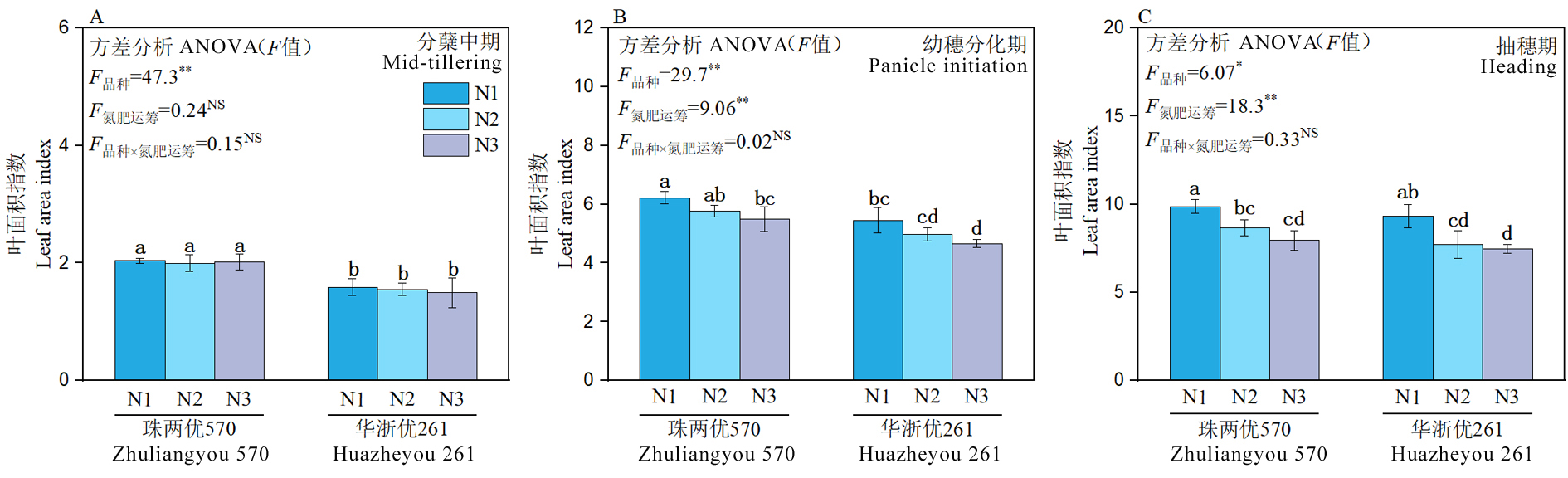
Fig. 1. Leaf area index of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice under different nitrogen management strategies(2023) * and ** denote significance at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively; NS denotes no significant difference at the 0.05 probability level. N split-application regimes at basal, early tillering, and panicle initiation stages, N1, 5:2:3; N2, 4:2:4; N3, 3:2:5. The same below.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate(%) | 精米率 Milled rice rate(%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness(%) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 蛋白质含量Protein content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 79.5 a | 59.5 a | 44.0 c | 8.43 a | 1.76 a | 16.1 abc | 6.9 ab |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 79.8 a | 61.8 a | 48.5 abc | 7.82 a | 1.78 a | 17.0 ab | 7.31 ab |
| N3 | 78.4 a | 62.7 a | 52.7 a | 3.94 a | 1.39 a | 17.9 a | 7.4 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 80.5 a | 60.5 a | 43.4 c | 6.01 a | 1.57 a | 14.3 cd | 6.65 b |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 80.1 a | 62.5 a | 46.6 bc | 5.46 a | 1.43 a | 14.2 d | 6.83 ab |
| N3 | 80.5 a | 63.9 a | 49.3 ab | 5.73 a | 1.33 a | 15.8 bcd | 7.49 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | ||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 1.65NS | 0.42NS | 2.23NS | 0.58NS | 0.34NS | 20.99** | 1.45NS | |
| 氮肥运筹 N management strategy(N) | 0.13NS | 0.25NS | 9.80** | 1.19NS | 0.31NS | 4.43* | 4.92* | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.33NS | 0.77NS | 0.38NS | 1.12NS | 0.06NS | 0.39NS | 0.86NS |
Table 6. Effect of nitrogen management strategies on rice quality of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2022)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate(%) | 精米率 Milled rice rate(%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness(%) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 蛋白质含量Protein content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 79.5 a | 59.5 a | 44.0 c | 8.43 a | 1.76 a | 16.1 abc | 6.9 ab |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 79.8 a | 61.8 a | 48.5 abc | 7.82 a | 1.78 a | 17.0 ab | 7.31 ab |
| N3 | 78.4 a | 62.7 a | 52.7 a | 3.94 a | 1.39 a | 17.9 a | 7.4 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 80.5 a | 60.5 a | 43.4 c | 6.01 a | 1.57 a | 14.3 cd | 6.65 b |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 80.1 a | 62.5 a | 46.6 bc | 5.46 a | 1.43 a | 14.2 d | 6.83 ab |
| N3 | 80.5 a | 63.9 a | 49.3 ab | 5.73 a | 1.33 a | 15.8 bcd | 7.49 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA (F-value) | ||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 1.65NS | 0.42NS | 2.23NS | 0.58NS | 0.34NS | 20.99** | 1.45NS | |
| 氮肥运筹 N management strategy(N) | 0.13NS | 0.25NS | 9.80** | 1.19NS | 0.31NS | 4.43* | 4.92* | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.33NS | 0.77NS | 0.38NS | 1.12NS | 0.06NS | 0.39NS | 0.86NS |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate(%) | 精米率 Milled rice rate(%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness (%) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 蛋白质含量Protein content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 80.3 a | 66.3 a | 46.6 c | 4.61 a | 1.30 ab | 14.3 c | 6.66 cd |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 80.5 a | 66.2 a | 50.0 bc | 2.94 a | 0.94 ab | 15.5 abc | 7.22 ab |
| N3 | 81.1 a | 66.0 a | 53.1 ab | 2.89 a | 0.81 b | 16.5 ab | 7.46 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 79.4 a | 66.8 a | 52.2 ab | 7.56 a | 1.98 a | 13.8 c | 6.33 d |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 79.1 a | 66.6 a | 53.4 ab | 6.06 a | 1.69 ab | 15.1 bc | 6.82 bcd |
| N3 | 81.8 a | 65.7 a | 55.0 a | 4.83 a | 1.36 ab | 17.2 a | 7.13 abc | |
| 方差分析ANOVA(F-value) | ||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 0.56NS | 0.08NS | 9.08* | 4.42NS | 5.50* | 0.01NS | 6.43* | |
| 氮肥运筹 N management strategy(N) | 2.25NS | 0.33NS | 4.85* | 1.09NS | 1.30NS | 10.92** | 11.55** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.85NS | 0.12NS | 0.82NS | 0.08NS | 0.04NS | 0.63NS | 0.02NS |
Table 7. Effect of nitrogen management strategies on rice quality of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice (2023)
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate(%) | 精米率 Milled rice rate(%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness (%) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 蛋白质含量Protein content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珠两优570 | N1 | 80.3 a | 66.3 a | 46.6 c | 4.61 a | 1.30 ab | 14.3 c | 6.66 cd |
| Zhuliangyou 570 | N2 | 80.5 a | 66.2 a | 50.0 bc | 2.94 a | 0.94 ab | 15.5 abc | 7.22 ab |
| N3 | 81.1 a | 66.0 a | 53.1 ab | 2.89 a | 0.81 b | 16.5 ab | 7.46 a | |
| 华浙优261 | N1 | 79.4 a | 66.8 a | 52.2 ab | 7.56 a | 1.98 a | 13.8 c | 6.33 d |
| Huazheyou 261 | N2 | 79.1 a | 66.6 a | 53.4 ab | 6.06 a | 1.69 ab | 15.1 bc | 6.82 bcd |
| N3 | 81.8 a | 65.7 a | 55.0 a | 4.83 a | 1.36 ab | 17.2 a | 7.13 abc | |
| 方差分析ANOVA(F-value) | ||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 0.56NS | 0.08NS | 9.08* | 4.42NS | 5.50* | 0.01NS | 6.43* | |
| 氮肥运筹 N management strategy(N) | 2.25NS | 0.33NS | 4.85* | 1.09NS | 1.30NS | 10.92** | 11.55** | |
| 品种×氮肥运筹V×N | 0.85NS | 0.12NS | 0.82NS | 0.08NS | 0.04NS | 0.63NS | 0.02NS |
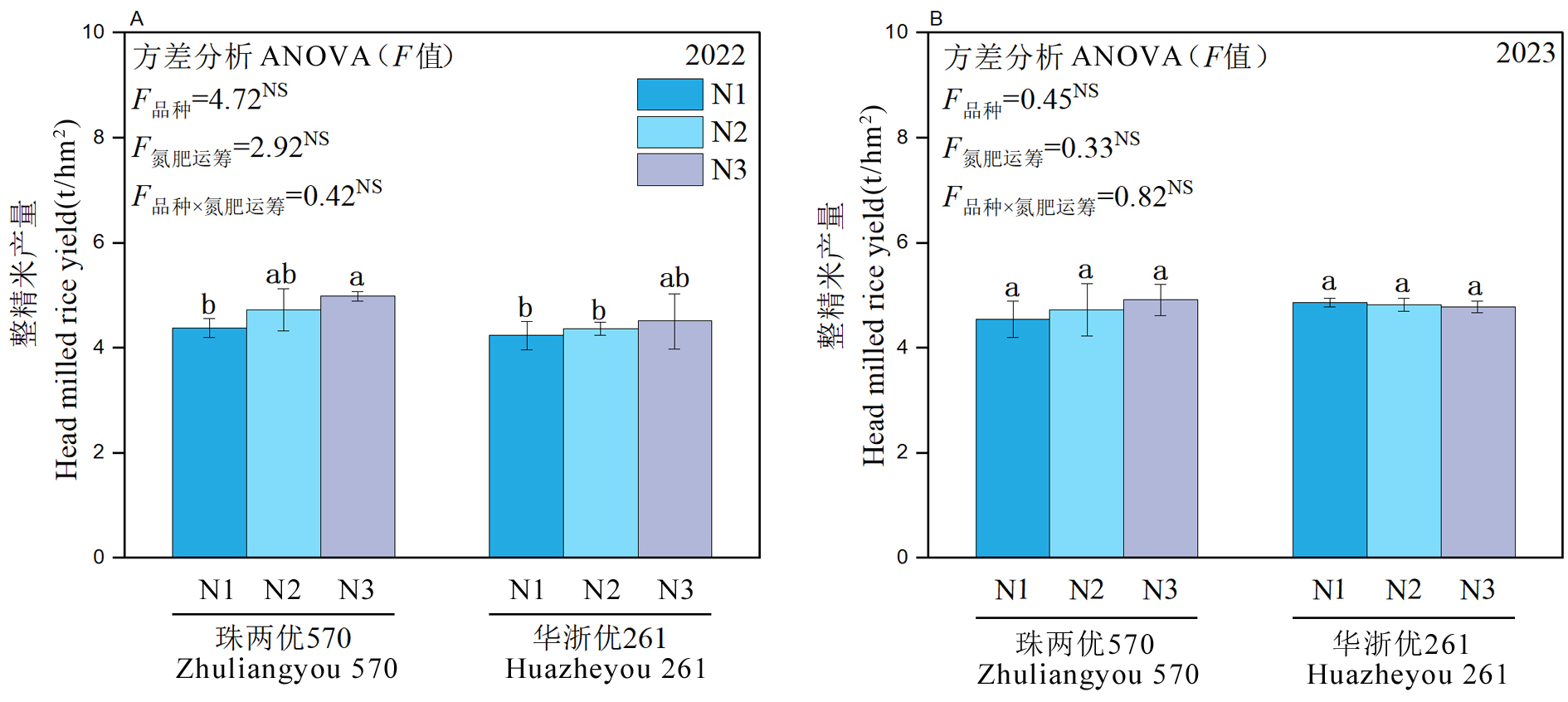
Fig. 2. Head rice rate of high-quality hybrid mid-season rice under different nitrogen management strategies * and ** denote significance at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively; NS denotes non-significant the 0.05 probability level.
| [1] | Ma G H, Yuan L P. Hybrid rice achievements, development and prospect in China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(2): 197-205. |
| [2] | Huang M, Cao J L, Zhang R C, Chen J N, Cao F B, Fang S L, Zhang M, Liu L S. Late-stage vigor contributes to high grain yield in high-quality hybrid rice[J]. Crop and Environment, 2022, 1(2): 115-118. |
| [3] | Jiang P, Xie X B, Huang M, Zhou X F, Chen J N, Wu D D, Xia B, Xiong H, Xu F X, Zou Y B. Potential yield increase of hybrid rice at five locations in southern China[J]. Rice, 2016, 9(1): 1-14. |
| [4] | Feng F, Li Y J, Qin X L, Liao Y C, Siddique K H M. Changes in rice grain quality of indica and japonica type varieties released in China from 2000 to 2014[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1863. |
| [5] | Li X, Zhang R C, Chen G, Xie J X, Xiao Z W, Cao F B, Ali I, Iqbal A, Wahab A, Huang M, Chen J N. Increasing grain weight and yield stability by increasing pre-heading non-structural carbohydrate reserves per spikelet in short-growth duration rice[J]. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(6): 1912-1920. |
| [6] | 潘孝武, 何强, 张武汉, 舒服, 邢俊杰, 孙平勇, 邓华凤. 新形势下长江流域稻作发展的思考[J]. 杂交水稻, 2015, 30(6): 1-5. |
| Pan X W, He Q, Zhang W H, Shu F, Xing J J, Sun P Y, Deng H F. Reflection of rice development in Yangtze River Basin under the new situation[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2015, 30(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Shrestha J, Karki T B, Hossain M A. Application of nitrogenous fertilizer in rice production: A review[J]. Journal of Nepal Agricultural Research Council, 2022(8): 16-26. |
| [8] | 张四海, 吴文革, 李泽福, 王元垒, 黄义德, 赵决建, 方文杰. 氮肥运筹对双季晚稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2008(3): 28-31. |
| Zhang S H, Wu W G, Li Z F, Wang Y L, Huang Y D, Zhao J J, Fang W J. The effect of different proportion of nitrogen application on yield and quality of double cropping late rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2008(3): 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 吴朝晖. 超级杂交中籼稻高产生理生态及其调控研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2008. |
| Wu C W. Research on the physiological ecology of super hybrid indica rice for high yield and its regulation[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 王新其, 程灿, 方军, 朱元宏, 曹黎明. 氮肥运筹对杂交粳稻‘申优17’主要品质性状效应分析[J]. 上海农业学报, 2020, 36(4): 25-30. |
| Wang X Q, Cheng C, Fang J, Zhu Y H, Cao L M. Analysis of the effect of nitrogen fertilizer transport on major quality traits of hybrid japonica rice Shenyou 17[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2020, 36(4): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| Xiao D K, Hu R, Han T F, Zhang W F, Hou J, Ren K Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer consumption and operation on rice yield and its components in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 林义月, 李阳, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 杨晓龙, 张作林, 程建平. 氮肥运筹对机直播水稻产量、品质及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2023, 42(2): 93-98. |
| Lin Y Y, Li Y, Wang B F, Zhang Z S, Yang X L, Zhang Z L, Cheng J P. Effects of nitrogen management on yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency of rice with machine direct seeding[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023, 42(2): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 石丽红, 纪雄辉, 朱校奇, 李洪顺, 彭华, 刘昭兵. 提高超级杂交稻库容量的施氮数量和时期运筹[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(6): 1274-1281. |
| Shi L H, Ji X H, Zhu X H, Li H S, Peng H, Liu Z B. A preliminary study on optimizing nitrogen fertilization amount at different phases to enhance the storage capacity of super hybrid rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(6): 1274-1281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 陈本洋. 氮肥运筹对水稻生长、产量及品质特性的影响[J]. 乡村科技, 2024, 15(1): 68-70. |
| Chen B Y. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer transportation on growth, yield and quality characteristics of rice[J]. Rural Science and Technology, 2024, 15(1): 68-70. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 范立慧, 徐珊珊, 侯朋福, 薛利红, 李刚华, 丁艳锋, 杨林章. 不同地力下基蘖肥运筹比例对水稻产量及氮肥吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(10): 1872-1884. |
| Fan L H, Xu S S, Hou P F, Xue L H, Li G H, Ding Y F, Yang L Z. Effect of different ratios of basal to tiller nitrogen on rice yield and nitrogen utilization under different soil fertility[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(10): 1872-1884. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 苏雨婷, 袁帅, 李永松, 崔璨, 陈平平, 王晓玉, 易镇邪. 氮肥运筹对湘南双季杂交稻产量与抗倒伏特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2022(3): 225-232. |
| Su Y T, Yuan S, Li Y S, Cui C, Chen P P, Wang X Y, Yi Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on yield and lodging resistance properties of double-cropping hybrid rice in southern Hunan[J]. Crops, 2022(3): 225-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 王曙光, 谢成林, 谢仁康, 张文杰, 张菊芳, 王汝利. 杂交中籼稻产量与主要经济性状关系的分析[J]. 中国稻米, 2009, 15(2): 11-14. |
| Wang S G, Xie C L, Xie R K, Zhang W J, Zhang J F, Wang R L. Analysis on the relationship between grain yield and major economic characteristics of middle-season hybrid indica rice[J]. China Rice, 2009, 15(2): 11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 潘胜才, 陈余波, 简叙, 卢沙沙, 秦建权. 光照、氮素对杂交水稻干物质积累、分配和产量形成的影响[J]. 作物研究, 2024, 38(1): 1-9, 15. |
| Pan S C, Chen Y B, Jian X, Lu S S, Qin J Q. Effects of photo and nitrogen on yield, yield composition, dry matter accumulation and distribution of hybrid rice[J]. Crop Research, 2024, 38(1): 1-9, 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 李超, 肖小平, 唐海明, 汤文光, 程凯凯, 郭立君, 汪柯, 唐友云. 减氮增密对机插双季稻生物学特性及周年产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(12): 2451-2459. |
| Li C, Xiao X P, Tang H M, Tang W G, Cheng K K, Guo L J, Wang K, Tang Y Y. Biological characteristics and annual yield of double machine-transplanted rice under nitrogen-reduction and density-increase measures[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(12): 2451-2459. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Yang W, Peng S B, Laza R C, Laza R C, Visperas R M, Dionision-Sese M L. Yield gap analysis between dry and wet season rice crop grown under high-yielding management conditions[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2008, 100(5): 1390-1395. |
| [21] | 陈雷, 韦宇, 张晓丽, 李冬秀, 高国庆, 粟学俊, 吕荣华, 陶伟, 唐茂艳, 梁天锋. 施氮量对优质杂交稻丰田优553干物质生产及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(6): 42-47. |
| Chen L, Wei Y, Zhang X L, Li D X, Gao G Q, Su X J, Lü R H, Tao W, Tang M Y, Liang T F. Effects of nitrogen rate on dry matter production and nitrogen use efficiency of high-quality hybrid rice combination Fengtianyou 553[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(6): 42-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 杨安中, 吴文革, 李泽福, 段素梅, 陈刚, 许有尊. 氮肥运筹对超级稻库源关系、干物质积累及产量的影响[J]. 土壤, 2016, 48(2): 254-258. |
| Yang A Z, Wu W G, Li Z F, Duan S M, Chen G, Xu Y Z. Effects of nitrogen application on source-sink relationship, dry matter accumulation and yield of super hybrid rice[J]. Soils, 2016, 48(2): 254-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘风, 石爱龙, 祝海竣, 段玉婷, 关常铮, 罗龙欣, 彭涛, 王学华. 施氮量与肥料配比对水稻群体生长和产量的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2024, 39(3): 117-126. |
| Liu F, Shi A L, Zhu H J, Duan Y T, Guan C Z, Luo L X, Peng T, Wang X H. Effects of nitrogen application rate and fertilizer ratio on population growth and yield of rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2024, 39(3): 117-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 王雪艳. 施氮量对优质水稻产量和品质的影响[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2022. |
| Wang X. Effects of nitrogen application on yield and quality of high quality rice[D]. Jingzhou: Changjiang University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Hu Q, Liu Q Y, Jiang W Q, Qiu S, Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Liu G D, Xing Z P, Hu Y J, Guo B W, Gao H. Effects of mid-stage nitrogen application timing on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of japonica rice starch[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2021, 101(6): 2463-2471. |
| [26] | 赵学智, 杨金娟, 郭燕萍. 氮肥运筹对宁夏水稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2020, 61(4): 12-14. |
| Zhao X Z, Yang J J, Guo Y P. Effect of nitrogen application on yield and quality of rice in Ningxia[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2020, 61(4): 12-14. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 葛金鑫. 增密减氮对水稻产量及稻米食味品质的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| Ge J X. Effects of densification and nitrogen reduction on rice yield and rice flavor quality[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Xiong F, Wang Z, Gu Y J, Chen G, Zhou P. Effects of nitrogen application time on caryopsis development and grain quality of rice variety Yangdao 6[J]. Rice Science, 2008, 15(1): 57-62. |
| [29] | Huang M, Cao J L, Chen J N, Cao F B, Zhou C M. Slimming the grain through breeding is a practical way to reduce the chalky grain rate of middle-season hybrid rice[J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(8): 1886. |
| [30] | Thu T T P, Yamakawa T, Moe K. Effect of nitrogen application timing on growth, grain yield and eating quality of the KD18 and TH3-3 rice varieties[J]. Kyushu University Institutional Repository, 2014, 59(1): 55-64. |
| [31] | Tang W, Ye J, Yao X, Zhao P, Xuan W, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Xu S, An H, Chen G, Yu J, Wu W, Ge Y, Liu X, Li J, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Yang B, Jiang X, Peng C, Zhou C, Terzaghi W, Wang C, Wan J. Genome-wide associated study identifies NAC42-activated nitrate transporter conferring high nitrogen use efficiency in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5279. |
| [32] | 潘圣刚, 翟晶, 曹凑贵, 蔡明历, 王若涵, 黄胜奇, 李进山. 氮肥运筹对水稻养分吸收特性及稻米品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 522-527. |
| Pan S G, Zhai J, Cao C G, Cai M L, Wang R H, Huang S Q, Li J S. Effects of nitrogen management practices on nutrition uptake and grain qualities of rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(3): 522-527. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] |
WEI Huanhe, WANG Lulu, MA Weiyi, ZHANG Xiang, ZUO Boyuan, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHU Wang, ZHU Jizou, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, DAI Qigen.
Grain-filling Characteristics and Its Relationship with Grain Yield Formation of japonica Rice Nanjing 9108 Under Combined Salinity-drought Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [2] |
SHEN Zhida, YU Qiuhua, ZHANG Bin, CAO Yudong, WANG Shaohua, WANG Hongfei, WU Yongqing, DAI Zhigang, LI Xiaokun.
Effects of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rate on Grain Yield, Phosphorus Accumulation and Utilization of Direct-seeded Rice in Hubei Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [3] | MA Weiyi, ZHU Jizou, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, DIAO Liuyun, WANG Lulu, MENG Tianyao, GAO Pinglei, CHEN Yinglong, DAI Qigen, WEI Huanhe. Research Progress in Effects of Salt and Drought Stresses on Rice Quality Formation and Associated Physiological Mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [4] | XU Yuemei, PENG Shiyan, SUN Zhiwei, WANG Zhiqin, ZHU Kuanyu, YANG Jianchang. Differences in Endogenous Hormone Levels and Their Relationship with Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency in Rice Varieties With Various Tolerance to Low Phosphorus Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 231-244. |
| [5] | TANG Chenghan, WANG Jingqing, CHEN Huizhe, ZHANG Yuping, XIANG Jing, ZHANG Yikai, WANG Zhigang, HUAI Yan, CHEN Jiafeng, WANG Yaliang. Effects of Hybrid Rice Seedling Quality in Drill-seeding Nursery on Grain Yield in Mechanical Transplanting [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 245-254. |
| [6] | CHEN Shurong, ZHU Lianfeng, QIN Birong, WANG Jie, Zhu Xuhua, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Chunquan, CAO Xiaochuang, KONG Yali, ZHANG Junhua, JIN Qianyu. Effects of Nitrification Inhibitors on Rice Growth, Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Under Oxygenated Irrigation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 92-100. |
| [7] | FENG Xiangqian, WANG Aidong, HONG Weiyuan, LI Ziqiu, QIN Jinhua, ZHAN Lichuan, CHEN Lipeng, ZHANG Yunbo, WANG Danying, CHEN Song. Research Progress in Rice Yield Estimation Method Based on Low-altitude Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 604-616. |
| [8] | LIU Junfeng, MOU Jingyi, ZHAO Hongyan, GUO Shimeng, LI Yimeng, LIANG Chao, ZHOU Chanchan, WANG Shu, HUANG Yuancai. Effects of Nitrogen Application Practice and Row Spacing on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in japonica Rice With Different Panicle Types [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 672-684. |
| [9] | CAO Yudong, WU Penghao, DAI Zhigang, WANG Guibing, HE Shuai, GONG Ximin, LI Xiaokun. Effect of Side-deep Fertilization on Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Economic Benefits of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 695-708. |
| [10] | JIANG Peng, ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Xingbing, GUO Xiaoyi, ZHU Yongchuan, LIU Mao, GUO Chanchun, XIONG Hong, XU Fuxian. Yield Formation Characteristics of Ratooning Hybrid Rice Under Simplified Cultivation Practices in Winter Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [11] | XIONG Jiahuan, ZHANG Yikai, XIANG Jing, CHEN Huizhe, XU Yicheng, WANG Yaliang, WANG Zhigang, YAO Jian, ZHANG Yuping. Effect of Biochar-based Fertilizer Application on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Utilization in Film- mulched PaddyFields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [12] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [13] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [14] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||