
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 373-386.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240515
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Huanhe1, WANG Lulu1,2, MA Weiyi1, ZHANG Xiang1, ZUO Boyuan1, GENG Xiaoyu1, ZHU Wang1,2, ZHU Jizou1, MENG Tianyao1,2, CHEN Yinglong1, GAO Pinglei1, XU Ke1, DAI Qigen1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-29
Revised:2024-10-15
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
*email: qgdai@yzu.edu.cn
韦还和1, 汪璐璐1,2, 马唯一1, 张翔1, 左博源1, 耿孝宇1, 朱旺1,2, 朱济邹1, 孟天瑶1,2, 陈英龙1, 高平磊1, 许轲1, 戴其根1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
*email: qgdai@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:WEI Huanhe, WANG Lulu, MA Weiyi, ZHANG Xiang, ZUO Boyuan, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHU Wang, ZHU Jizou, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, DAI Qigen. Grain-filling Characteristics and Its Relationship with Grain Yield Formation of japonica Rice Nanjing 9108 Under Combined Salinity-drought Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 373-386.
韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240515
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 单位面积穗数 NP (×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 SPP | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | 实产 Actual yield (t hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 304 a | 165 a | 89.3 a | 26.7 a | 11.6 a |
| 中度干旱 MD | 291 b | 152 b | 88.7 ab | 26.0 b | 10.3 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 273 c | 145 c | 87.2 b | 25.6 c | 8.9 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 271 c | 140 d | 84.3 c | 25.4 c | 8.5 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 256 d | 133 e | 82.8 d | 24.8 d | 7.4 e | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 238 e | 117 f | 79.7 e | 24.0 e | 5.7 f | ||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 307 a | 162 a | 89.7 a | 26.8 a | 11.7 a |
| 中度干旱 MD | 287 b | 154 b | 88.9 ab | 26.5 b | 10.2 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 271 c | 143 c | 86.7 b | 25.7 c | 9.1 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 267 cd | 137 d | 84.0 c | 25.6 c | 8.6 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 253 d | 134 e | 82.3 d | 24.8 d | 7.2 e | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 241 e | 119 f | 78.9 e | 24.2 e | 5.6 f | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×盐处理Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
Table 1. Grain yield and yield components of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 单位面积穗数 NP (×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 SPP | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | 实产 Actual yield (t hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 304 a | 165 a | 89.3 a | 26.7 a | 11.6 a |
| 中度干旱 MD | 291 b | 152 b | 88.7 ab | 26.0 b | 10.3 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 273 c | 145 c | 87.2 b | 25.6 c | 8.9 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 271 c | 140 d | 84.3 c | 25.4 c | 8.5 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 256 d | 133 e | 82.8 d | 24.8 d | 7.4 e | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 238 e | 117 f | 79.7 e | 24.0 e | 5.7 f | ||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 307 a | 162 a | 89.7 a | 26.8 a | 11.7 a |
| 中度干旱 MD | 287 b | 154 b | 88.9 ab | 26.5 b | 10.2 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 271 c | 143 c | 86.7 b | 25.7 c | 9.1 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 267 cd | 137 d | 84.0 c | 25.6 c | 8.6 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 253 d | 134 e | 82.3 d | 24.8 d | 7.2 e | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 241 e | 119 f | 78.9 e | 24.2 e | 5.6 f | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×盐处理Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 穗长 PL (cm) | 强势粒 SG | 弱势粒 IG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籽粒数 NG | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | 籽粒数 NG | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | |||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 13.9 a | 19.3 a | 92.6 a | 29.0 a | 35.0 a | 87.5 a | 24.6 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 12.7 b | 17.6 b | 91.7 ab | 28.5 ab | 31.8 b | 86.6 ab | 23.8 ab | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.1 bc | 16.9 b | 90.5 b | 27.9 b | 29.6 bc | 84.7 b | 23.7 ab | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.1 c | 15.7 c | 87.5 c | 27.6 bc | 28.3 c | 81.7 c | 23.2 b | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.7 cd | 14.8 d | 86.5 c | 27.2 bc | 26.5 d | 79.6 cd | 22.8 bc | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.2 d | 13.6 e | 84.1 d | 25.8 c | 22.9 e | 76.2 d | 22.2 c | |||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 14.1 a | 18.5 a | 92.2 a | 29.1 a | 34.5 a | 88.2 a | 24.8 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 13.0 b | 17.2 b | 91.5 ab | 28.9 ab | 32.2 ab | 86.9 ab | 24.7 a | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.3 bc | 17.0 b | 90.3 b | 27.9 b | 29.6 b | 83.7 b | 24.0 ab | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.7 c | 16.6 bc | 87.3 c | 27.9 b | 28.2 bc | 81.2 bc | 23.2 b | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 cd | 16.5 bc | 86.4 cd | 27.2 bc | 27.3 c | 78.4 c | 23.1 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.4 d | 15.0 c | 83.1 d | 26.4 c | 24.2 d | 74.4 d | 22.2 c | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
Table 2. Panicle traits of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 穗长 PL (cm) | 强势粒 SG | 弱势粒 IG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籽粒数 NG | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | 籽粒数 NG | 结实率 SSR (%) | 千粒重 1000-GW (g) | |||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 13.9 a | 19.3 a | 92.6 a | 29.0 a | 35.0 a | 87.5 a | 24.6 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 12.7 b | 17.6 b | 91.7 ab | 28.5 ab | 31.8 b | 86.6 ab | 23.8 ab | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.1 bc | 16.9 b | 90.5 b | 27.9 b | 29.6 bc | 84.7 b | 23.7 ab | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.1 c | 15.7 c | 87.5 c | 27.6 bc | 28.3 c | 81.7 c | 23.2 b | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.7 cd | 14.8 d | 86.5 c | 27.2 bc | 26.5 d | 79.6 cd | 22.8 bc | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.2 d | 13.6 e | 84.1 d | 25.8 c | 22.9 e | 76.2 d | 22.2 c | |||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 14.1 a | 18.5 a | 92.2 a | 29.1 a | 34.5 a | 88.2 a | 24.8 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 13.0 b | 17.2 b | 91.5 ab | 28.9 ab | 32.2 ab | 86.9 ab | 24.7 a | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.3 bc | 17.0 b | 90.3 b | 27.9 b | 29.6 b | 83.7 b | 24.0 ab | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.7 c | 16.6 bc | 87.3 c | 27.9 b | 28.2 bc | 81.2 bc | 23.2 b | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 cd | 16.5 bc | 86.4 cd | 27.2 bc | 27.3 c | 78.4 c | 23.1 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.4 d | 15.0 c | 83.1 d | 26.4 c | 24.2 d | 74.4 d | 22.2 c | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 干物质量 Dry matter weight (t/hm2) | 抽穗期至成熟期 干物重积累量 Dry weight accumulation from heading to maturity (t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.2 a | 20.4 a | 8.1 a | 0.493 d |
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.1 b | 17.6 b | 6.5 b | 0.505 cd | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.5 c | 14.9 c | 5.4 cd | 0.515 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 8.8 d | 14.5 cd | 5.7 c | 0.508 cd | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 7.5 e | 12.2 d | 4.7 d | 0.525 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 f | 9.1 e | 3.4 e | 0.541 a | ||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.2 a | 20.6 a | 8.4 a | 0.492 e |
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.8 b | 17.4 b | 6.6 b | 0.508 d | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.4 c | 15.2 c | 5.9 c | 0.517 cd | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.0 cd | 14.7 cd | 5.7 c | 0.506 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 7.4 d | 11.9 d | 4.6 d | 0.522 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 e | 9.0 e | 3.3 e | 0.539 a | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
Table 3. Dry matter weight and harvest index of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 干物质量 Dry matter weight (t/hm2) | 抽穗期至成熟期 干物重积累量 Dry weight accumulation from heading to maturity (t/hm2) | 收获指数 Harvest index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.2 a | 20.4 a | 8.1 a | 0.493 d |
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.1 b | 17.6 b | 6.5 b | 0.505 cd | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.5 c | 14.9 c | 5.4 cd | 0.515 c | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 8.8 d | 14.5 cd | 5.7 c | 0.508 cd | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 7.5 e | 12.2 d | 4.7 d | 0.525 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 f | 9.1 e | 3.4 e | 0.541 a | ||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.2 a | 20.6 a | 8.4 a | 0.492 e |
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.8 b | 17.4 b | 6.6 b | 0.508 d | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.4 c | 15.2 c | 5.9 c | 0.517 cd | ||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.0 cd | 14.7 cd | 5.7 c | 0.506 d | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 7.4 d | 11.9 d | 4.6 d | 0.522 b | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 e | 9.0 e | 3.3 e | 0.539 a | ||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理 Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 叶片光合速率 Leaf photosynthetic rate (µmol m-2 s-1) | 叶片SPAD值 Leaf SPAD value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗后20 d 20 DAH | 抽穗后40 d 40 DAH | 抽穗后20 d 20 DAH | 抽穗后40 d 40 DAH | ||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.8 a | 13.2 a | 42.6 a | 34.0 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 20.3 ab | 12.2 b | 41.3 b | 31.0 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.6 c | 10.6 d | 39.0 c | 26.6 d | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.4 b | 11.2 c | 38.6 c | 28.6 c | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 18.2 cd | 9.9 e | 35.7 d | 24.8 e | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 17.7 d | 9.4 f | 33.1 e | 21.6 f | |||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.3 a | 12.6 a | 43.4 a | 34.1 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 21.7 ab | 12.1 b | 42.1 b | 31.3 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 20.9 b | 10.5 d | 39.0 cd | 26.7 c | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.4 bc | 11.3 c | 40.0 c | 30.2 bc | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 19.8 c | 9.5 e | 36.4 d | 26.1 c | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 19.1 d | 9.2 f | 32.1 e | 21.0 d | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ** | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
Table 4. Leaf photosynthetic rate and SPAD values of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 叶片光合速率 Leaf photosynthetic rate (µmol m-2 s-1) | 叶片SPAD值 Leaf SPAD value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗后20 d 20 DAH | 抽穗后40 d 40 DAH | 抽穗后20 d 20 DAH | 抽穗后40 d 40 DAH | ||||
| 2021 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.8 a | 13.2 a | 42.6 a | 34.0 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 20.3 ab | 12.2 b | 41.3 b | 31.0 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.6 c | 10.6 d | 39.0 c | 26.6 d | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.4 b | 11.2 c | 38.6 c | 28.6 c | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 18.2 cd | 9.9 e | 35.7 d | 24.8 e | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 17.7 d | 9.4 f | 33.1 e | 21.6 f | |||
| 2022 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.3 a | 12.6 a | 43.4 a | 34.1 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 21.7 ab | 12.1 b | 42.1 b | 31.3 b | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 20.9 b | 10.5 d | 39.0 cd | 26.7 c | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.4 bc | 11.3 c | 40.0 c | 30.2 bc | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 19.8 c | 9.5 e | 36.4 d | 26.1 c | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 19.1 d | 9.2 f | 32.1 e | 21.0 d | |||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | ** | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理 Salinity treatment(S) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 干旱处理 Drought treatment(D) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 年份×盐处理 Y×S | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×干旱处理 Y×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 盐处理×干旱处理 S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
| 年份×盐处理×干旱处理Y×S×D | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||
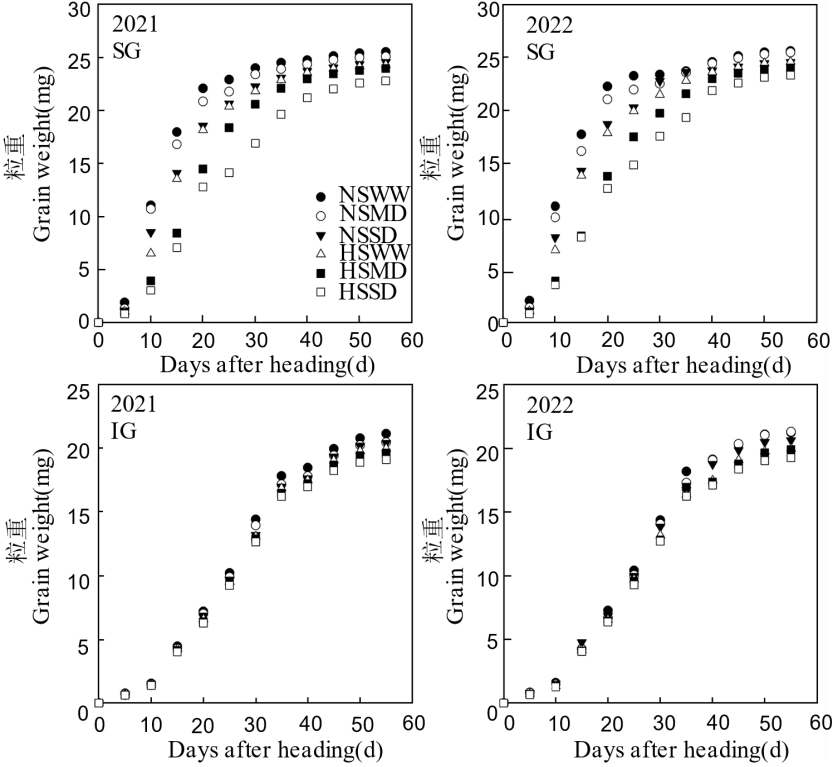
Fig. 1. Dynamics in grain weight of rice under salinity and drought stresses NS, Non-salinity; HS, High-salinity. WW, Well-watered conditions; MD, Moderate drought; SD, Severe drought. SG, Superior grains; IG, Inferior grains.
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 方程参数 Equation parameter | 方程拟合 Simulated equation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | K | N | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 24.38 | 6107.27 | 0.5664 | 3.0308 | Y=24.38 |
| SG | 中度干旱 MD | 23.79 | 8607.28 | 0.5637 | 3.2093 | Y=23.79 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 23.24 | 9336.26 | 0.4808 | 3.4410 | Y=23.24 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 23.03 | 7951.21 | 0.4742 | 3.0184 | Y=23.03 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 23.00 | 3160.03 | 0.3391 | 2.8003 | Y=23.00 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 21.80 | 4246.39 | 0.2936 | 3.1752 | Y=21.80 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.26 | 11274.68 | 0.2949 | 2.9366 | Y=20.26 | |
| IG | 中度干旱 MD | 19.68 | 9977.78 | 0.2934 | 2.8548 | Y=19.68 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 19.63 | 10484.08 | 0.2878 | 2.8548 | Y=19.63 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.29 | 11237.63 | 0.2908 | 2.8821 | Y=19.29 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 18.92 | 10053.42 | 0.2898 | 2.8003 | Y=18.92 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.47 | 9707.16 | 0.2903 | 2.7730 | Y=18.47 | |||
| 2022 | 强势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 24.27 | 6107.27 | 0.5634 | 3.0593 | Y=24.27 |
| SG | 中度干旱 MD | 23.86 | 8179.72 | 0.5446 | 3.1547 | Y=23.86 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 23.34 | 7318.14 | 0.4809 | 3.1274 | Y=23.34 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 23.04 | 7951.20 | 0.4680 | 3.1274 | Y=23.04 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 23.02 | 2586.37 | 0.3154 | 2.8003 | Y=23.02 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.24 | 4265.16 | 0.2946 | 3.2638 | Y=22.24 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.59 | 12001.81 | 0.2960 | 2.9364 | Y=20.59 | |
| IG | 中度干旱 MD | 20.62 | 12553.42 | 0.2910 | 2.9093 | Y=20.62 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 20.08 | 12553.42 | 0.2906 | 3.0184 | Y=20.08 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.23 | 11237.63 | 0.2908 | 2.8821 | Y=19.23 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 19.16 | 9957.77 | 0.2873 | 2.8412 | Y=19.16 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.60 | 10053.42 | 0.2902 | 2.8003 | Y=18.60 | |||
Table 5. Stimulation equations of grain-filling process of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 方程参数 Equation parameter | 方程拟合 Simulated equation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | K | N | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 24.38 | 6107.27 | 0.5664 | 3.0308 | Y=24.38 |
| SG | 中度干旱 MD | 23.79 | 8607.28 | 0.5637 | 3.2093 | Y=23.79 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 23.24 | 9336.26 | 0.4808 | 3.4410 | Y=23.24 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 23.03 | 7951.21 | 0.4742 | 3.0184 | Y=23.03 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 23.00 | 3160.03 | 0.3391 | 2.8003 | Y=23.00 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 21.80 | 4246.39 | 0.2936 | 3.1752 | Y=21.80 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.26 | 11274.68 | 0.2949 | 2.9366 | Y=20.26 | |
| IG | 中度干旱 MD | 19.68 | 9977.78 | 0.2934 | 2.8548 | Y=19.68 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 19.63 | 10484.08 | 0.2878 | 2.8548 | Y=19.63 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.29 | 11237.63 | 0.2908 | 2.8821 | Y=19.29 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 18.92 | 10053.42 | 0.2898 | 2.8003 | Y=18.92 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.47 | 9707.16 | 0.2903 | 2.7730 | Y=18.47 | |||
| 2022 | 强势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 24.27 | 6107.27 | 0.5634 | 3.0593 | Y=24.27 |
| SG | 中度干旱 MD | 23.86 | 8179.72 | 0.5446 | 3.1547 | Y=23.86 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 23.34 | 7318.14 | 0.4809 | 3.1274 | Y=23.34 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 23.04 | 7951.20 | 0.4680 | 3.1274 | Y=23.04 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 23.02 | 2586.37 | 0.3154 | 2.8003 | Y=23.02 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.24 | 4265.16 | 0.2946 | 3.2638 | Y=22.24 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 20.59 | 12001.81 | 0.2960 | 2.9364 | Y=20.59 | |
| IG | 中度干旱 MD | 20.62 | 12553.42 | 0.2910 | 2.9093 | Y=20.62 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 20.08 | 12553.42 | 0.2906 | 3.0184 | Y=20.08 | |||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 19.23 | 11237.63 | 0.2908 | 2.8821 | Y=19.23 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 19.16 | 9957.77 | 0.2873 | 2.8412 | Y=19.16 | |||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.60 | 10053.42 | 0.2902 | 2.8003 | Y=18.60 | |||
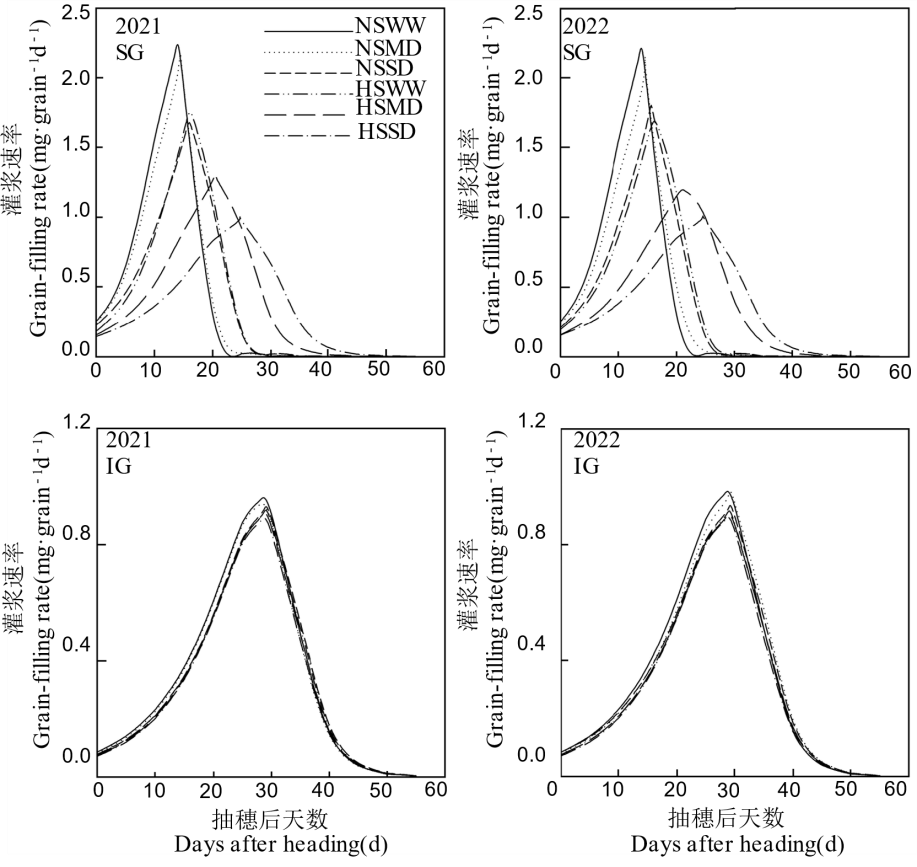
Fig. 2. Dynamics of grain-filling rate of rice under salinity and drought stresses SG, Superior grains; IG, Inferior grains. NS, Non-salinity; HS, High-salinity. WW, Well-watered conditions; MD, Moderate drought; SD, Severe drought.
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 籽粒灌浆特征参数 Grain-filling parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax (mg grain-1 d-1) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 达最大灌浆速率的时间 Tmax (d) | 有效灌浆天数 EGP (d) | ||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.163 | 1.373 | 13.4 | 21.5 |
| SG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 2.036 | 1.287 | 14.0 | 22.1 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 1.631 | 1.027 | 16.4 | 26.0 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 1.714 | 1.088 | 16.6 | 26.3 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.274 | 0.813 | 20.7 | 34.2 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.978 | 0.619 | 24.5 | 40.1 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.952 | 0.605 | 28.0 | 43.5 | |
| IG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.934 | 0.595 | 27.8 | 43.4 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.914 | 0.582 | 28.5 | 44.4 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.903 | 0.575 | 28.4 | 44.2 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.896 | 0.571 | 28.2 | 44.1 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.880 | 0.562 | 28.1 | 43.9 | |||
| 2022 | 强势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.131 | 1.351 | 13.5 | 21.6 |
| SG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.992 | 1.261 | 14.4 | 22.8 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 1.729 | 1.095 | 16.1 | 25.7 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 1.661 | 1.052 | 16.8 | 26.5 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.186 | 0.756 | 21.6 | 36.2 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.985 | 0.622 | 24.4 | 39.9 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.971 | 0.618 | 28.1 | 43.6 | |
| IG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.961 | 0.611 | 28.8 | 44.5 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.916 | 0.581 | 28.7 | 44.4 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.900 | 0.573 | 28.4 | 44.2 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.892 | 0.569 | 28.4 | 44.4 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.882 | 0.562 | 28.2 | 44.0 | |||
Table 6. Grain-filling parameters of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 籽粒灌浆特征参数 Grain-filling parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax (mg grain-1 d-1) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 达最大灌浆速率的时间 Tmax (d) | 有效灌浆天数 EGP (d) | ||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.163 | 1.373 | 13.4 | 21.5 |
| SG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 2.036 | 1.287 | 14.0 | 22.1 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 1.631 | 1.027 | 16.4 | 26.0 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 1.714 | 1.088 | 16.6 | 26.3 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.274 | 0.813 | 20.7 | 34.2 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.978 | 0.619 | 24.5 | 40.1 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.952 | 0.605 | 28.0 | 43.5 | |
| IG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.934 | 0.595 | 27.8 | 43.4 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.914 | 0.582 | 28.5 | 44.4 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.903 | 0.575 | 28.4 | 44.2 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.896 | 0.571 | 28.2 | 44.1 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.880 | 0.562 | 28.1 | 43.9 | |||
| 2022 | 强势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.131 | 1.351 | 13.5 | 21.6 |
| SG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.992 | 1.261 | 14.4 | 22.8 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 1.729 | 1.095 | 16.1 | 25.7 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 1.661 | 1.052 | 16.8 | 26.5 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 1.186 | 0.756 | 21.6 | 36.2 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.985 | 0.622 | 24.4 | 39.9 | |||
| 弱势粒 | 无盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.971 | 0.618 | 28.1 | 43.6 | |
| IG | NS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.961 | 0.611 | 28.8 | 44.5 | |
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.916 | 0.581 | 28.7 | 44.4 | |||
| 高盐 | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 0.900 | 0.573 | 28.4 | 44.2 | ||
| HS | 中度干旱 MD | 0.892 | 0.569 | 28.4 | 44.4 | ||
| 重度干旱 SD | 0.882 | 0.562 | 28.2 | 44.0 | |||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 前期 Early stage | 中期 Middle stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.3 | 0.899 | 178.9 | 6.2 | 1.919 | 231.3 | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.8 | 0.860 | 163.6 | 6.4 | 1.808 | 203.0 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.6 | 0.744 | 158.7 | 7.6 | 1.449 | 187.2 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.9 | 0.678 | 137.1 | 7.4 | 1.521 | 177.8 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 15.6 | 0.538 | 124.5 | 10.2 | 1.130 | 170.2 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.4 | 0.461 | 115.3 | 12.2 | 0.868 | 144.2 | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.0 | 0.344 | 265.2 | 11.9 | 0.844 | 350.7 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 21.9 | 0.332 | 230.8 | 11.8 | 0.828 | 311.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.5 | 0.322 | 214.3 | 12.1 | 0.810 | 289.2 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.4 | 0.319 | 202.3 | 12.0 | 0.800 | 271.1 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.3 | 0.310 | 183.0 | 11.9 | 0.794 | 250.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.2 | 0.303 | 154.1 | 11.9 | 0.780 | 212.2 | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.3 | 0.896 | 171.1 | 6.3 | 1.891 | 219.8 | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.1 | 0.830 | 159.5 | 6.6 | 1.768 | 200.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.4 | 0.725 | 153.3 | 7.4 | 1.534 | 193.8 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.9 | 0.687 | 147.4 | 7.6 | 1.474 | 186.3 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 16.2 | 0.520 | 138.7 | 10.9 | 1.051 | 189.7 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.2 | 0.481 | 131.4 | 12.3 | 0.875 | 161.0 | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.2 | 0.348 | 266.0 | 11.8 | 0.862 | 351.7 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.8 | 0.338 | 247.3 | 12.0 | 0.852 | 329.1 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.6 | 0.337 | 225.4 | 12.2 | 0.813 | 292.3 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.4 | 0.318 | 201.2 | 12.0 | 0.798 | 269.7 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.4 | 0.315 | 192.9 | 12.1 | 0.791 | 261.1 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.3 | 0.306 | 164.3 | 11.9 | 0.782 | 224.7 | ||||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 后期 Late stage | ||||||
| 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean(mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | ||||||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.0 | 0.581 | 55.8 | ||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 4.9 | 0.550 | 47.9 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 | 0.445 | 42.9 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.9 | 0.460 | 43.0 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.4 | 0.339 | 42.4 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.5 | 0.264 | 34.1 | |||||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.6 | 0.255 | 85.6 | |||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.7 | 0.249 | 76.9 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.244 | 71.4 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.8 | 0.241 | 66.7 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.9 | 0.239 | 62.3 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.234 | 53.0 | |||||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.0 | 0.573 | 52.8 | ||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 5.1 | 0.537 | 47.5 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.8 | 0.466 | 46.1 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 6.0 | 0.448 | 44.4 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.1 | 0.316 | 47.2 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.4 | 0.267 | 37.7 | |||||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.6 | 0.260 | 85.9 | |||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.8 | 0.257 | 80.7 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.7 | 0.246 | 70.6 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.8 | 0.240 | 66.3 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.9 | 0.238 | 64.6 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.235 | 55.9 | |||||||
Table 7. Grain-filling characteristics of early, middle and late stages of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 前期 Early stage | 中期 Middle stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean (mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.3 | 0.899 | 178.9 | 6.2 | 1.919 | 231.3 | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.8 | 0.860 | 163.6 | 6.4 | 1.808 | 203.0 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.6 | 0.744 | 158.7 | 7.6 | 1.449 | 187.2 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.9 | 0.678 | 137.1 | 7.4 | 1.521 | 177.8 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 15.6 | 0.538 | 124.5 | 10.2 | 1.130 | 170.2 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.4 | 0.461 | 115.3 | 12.2 | 0.868 | 144.2 | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.0 | 0.344 | 265.2 | 11.9 | 0.844 | 350.7 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 21.9 | 0.332 | 230.8 | 11.8 | 0.828 | 311.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.5 | 0.322 | 214.3 | 12.1 | 0.810 | 289.2 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.4 | 0.319 | 202.3 | 12.0 | 0.800 | 271.1 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.3 | 0.310 | 183.0 | 11.9 | 0.794 | 250.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.2 | 0.303 | 154.1 | 11.9 | 0.780 | 212.2 | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.3 | 0.896 | 171.1 | 6.3 | 1.891 | 219.8 | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.1 | 0.830 | 159.5 | 6.6 | 1.768 | 200.4 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.4 | 0.725 | 153.3 | 7.4 | 1.534 | 193.8 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.9 | 0.687 | 147.4 | 7.6 | 1.474 | 186.3 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 16.2 | 0.520 | 138.7 | 10.9 | 1.051 | 189.7 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 18.2 | 0.481 | 131.4 | 12.3 | 0.875 | 161.0 | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.2 | 0.348 | 266.0 | 11.8 | 0.862 | 351.7 | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.8 | 0.338 | 247.3 | 12.0 | 0.852 | 329.1 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.6 | 0.337 | 225.4 | 12.2 | 0.813 | 292.3 | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 22.4 | 0.318 | 201.2 | 12.0 | 0.798 | 269.7 | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 22.4 | 0.315 | 192.9 | 12.1 | 0.791 | 261.1 | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 22.3 | 0.306 | 164.3 | 11.9 | 0.782 | 224.7 | ||||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | 后期 Late stage | ||||||
| 天数 Days (d) | 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean(mg grain-1 d-1) | 灌浆量 GFA (mg) | ||||||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.0 | 0.581 | 55.8 | ||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 4.9 | 0.550 | 47.9 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.7 | 0.445 | 42.9 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.9 | 0.460 | 43.0 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.4 | 0.339 | 42.4 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.5 | 0.264 | 34.1 | |||||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.6 | 0.255 | 85.6 | |||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.7 | 0.249 | 76.9 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.244 | 71.4 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.8 | 0.241 | 66.7 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.9 | 0.239 | 62.3 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.234 | 53.0 | |||||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 5.0 | 0.573 | 52.8 | ||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 5.1 | 0.537 | 47.5 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 5.8 | 0.466 | 46.1 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 6.0 | 0.448 | 44.4 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.1 | 0.316 | 47.2 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.4 | 0.267 | 37.7 | |||||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.6 | 0.260 | 85.9 | |||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.8 | 0.257 | 80.7 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.7 | 0.246 | 70.6 | |||||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.8 | 0.240 | 66.3 | ||||||
| 中度干旱 MD | 9.9 | 0.238 | 64.6 | |||||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.9 | 0.235 | 55.9 | |||||||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | AGPase酶活性 Activity of AGPase (mol min-1 mg-1) | GBSS酶活性 Activity of GBSS (mol min-1 mg-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 16.3 a | 44.6 a | 13.9 a | 6.9 a | 17.2 a | 5.6 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 14.9 b | 40.7 b | 13.1 b | 6.6 ab | 15.6 b | 5.1 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 13.2 c | 39.0 bc | 12.6 bc | 6.2 b | 13.5 cd | 4.5 b | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 13.0 c | 36.3 c | 13.1 b | 6.6 ab | 13.9 c | 4.2 c | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.5 d | 34.2 cd | 11.3 c | 5.6 c | 12.0 d | 3.6 cd | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.2 e | 31.4 d | 10.2 d | 4.1 d | 10.1 e | 2.4 d | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.1 a | 32.3 a | 10.6 a | 4.3 a | 12.7 a | 4.4 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 b | 30.2 b | 10.0 b | 4.1 ab | 11.8 b | 3.8 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.6 cd | 28.9 c | 9.4 c | 3.7 bc | 10.9 c | 3.3 bc | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.0 c | 29.0 c | 10.0 b | 4.1 ab | 10.4 cd | 3.2 bc | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.6 d | 26.8 d | 7.9 d | 3.3 bc | 9.1 d | 2.1 c | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 7.9 e | 22.6 e | 6.9 e | 2.5 c | 7.9 e | 1.3 d | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 15.3 a | 48.4 a | 14.5 a | 5.9 a | 17.4 a | 6.0 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 14.2 b | 45.2 b | 14.1 ab | 5.5 ab | 16.2 b | 5.5 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.3 cd | 44.6 bc | 13.2 c | 4.7 b | 13.9 c | 4.9 c | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.7 c | 43.4 c | 13.7 b | 4.5 b | 14.2 c | 4.8 c | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 d | 41.3 d | 11.6 d | 3.5 c | 12.8 d | 3.6 d | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.3 e | 38.1 e | 9.3 e | 2.4 d | 11.2 e | 2.4 e | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.7 a | 35.7 a | 11.1 a | 4.5 a | 13.1 a | 4.1 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.7 b | 32.5 b | 10.8 ab | 4.1 ab | 11.9 b | 3.8 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.2 c | 31.3 c | 9.8 c | 3.4 b | 11.1 bc | 3.5 b | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.3 c | 29.0 d | 10.5 b | 3.3 b | 10.6 cd | 3.3 bc | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.6 cd | 26.4 e | 8.4 d | 2.8 c | 9.2 d | 2.5 c | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 7.8 d | 23.5 f | 7.1 e | 2.1 d | 7.6 e | 1.3 d | ||||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | SSS酶活性 Activity of SSS(mol min-1 mg-1) | SBE酶活性 Activity of SBE(U g-1) | |||||
| 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.4 a | 6.5 a | 2.2 a | 4.5 a | 7.1 a | 3.1 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.3 a | 5.9 b | 2.0 ab | 4.5 a | 6.7 ab | 2.8 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.3 a | 4.7 c | 1.9 b | 4.4 a | 5.9 b | 2.6 ab | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.2 ab | 5.2 bc | 1.8 b | 4.3 a | 5.8 b | 2.5 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.2 ab | 4.5 c | 1.7 bc | 4.2 a | 4.7 c | 2.3 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.1 b | 3.8 d | 1.5 c | 4.1 a | 3.6 d | 2.0 b | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.2 a | 4.2 a | 1.5 a | 3.1 a | 4.8 a | 2.1 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.2 a | 3.7 b | 1.4 a | 3.1 a | 4.5 ab | 2.0 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.1 a | 3.1 cd | 1.4 a | 3.0 a | 3.8 b | 1.8 a | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.1 a | 3.3 c | 1.3 a | 2.9 a | 4.3 ab | 1.7 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.1 a | 2.5 d | 1.3 a | 2.9 a | 3.5 bc | 1.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.0 a | 1.7 e | 1.2 a | 2.8 a | 2.6 c | 1.5 b | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.3 a | 6.3 a | 2.5 a | 5.1 a | 7.8 a | 3.4 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.3 a | 5.9 ab | 2.3 a | 5.1 a | 7.5 ab | 3.2 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.2 a | 5.5 b | 2.3 a | 5.0 a | 6.7 b | 2.9 ab | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.1 a | 5.2 bc | 2.2 a | 4.8 ab | 6.5 b | 2.8 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.1 a | 4.6 c | 2.2 a | 4.8 ab | 5.3 c | 2.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.0 a | 3.6 d | 2.0 a | 4.6 b | 4.1 d | 2.4 b | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.4 a | 4.4 a | 1.7 a | 3.4 a | 5.1 a | 2.3 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.3 a | 4.0 ab | 1.5 a | 3.4 a | 4.8 ab | 2.1 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.3 a | 3.5 b | 1.5 a | 3.3 a | 4.4 b | 1.9 a | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.3 a | 3.6 b | 1.4 a | 3.2 a | 3.8 c | 1.9 a | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.2 a | 2.9 c | 1.3 a | 3.2 a | 3.4 cd | 1.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.2 a | 2.3 d | 1.2 a | 3.1 a | 2.5 d | 1.5 b | ||||
Table 8. Key enzymes activities involved in starch synthesis of rice grains under salinity and drought stresses
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | AGPase酶活性 Activity of AGPase (mol min-1 mg-1) | GBSS酶活性 Activity of GBSS (mol min-1 mg-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 16.3 a | 44.6 a | 13.9 a | 6.9 a | 17.2 a | 5.6 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 14.9 b | 40.7 b | 13.1 b | 6.6 ab | 15.6 b | 5.1 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 13.2 c | 39.0 bc | 12.6 bc | 6.2 b | 13.5 cd | 4.5 b | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 13.0 c | 36.3 c | 13.1 b | 6.6 ab | 13.9 c | 4.2 c | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.5 d | 34.2 cd | 11.3 c | 5.6 c | 12.0 d | 3.6 cd | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.2 e | 31.4 d | 10.2 d | 4.1 d | 10.1 e | 2.4 d | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.1 a | 32.3 a | 10.6 a | 4.3 a | 12.7 a | 4.4 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 b | 30.2 b | 10.0 b | 4.1 ab | 11.8 b | 3.8 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.6 cd | 28.9 c | 9.4 c | 3.7 bc | 10.9 c | 3.3 bc | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 10.0 c | 29.0 c | 10.0 b | 4.1 ab | 10.4 cd | 3.2 bc | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.6 d | 26.8 d | 7.9 d | 3.3 bc | 9.1 d | 2.1 c | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 7.9 e | 22.6 e | 6.9 e | 2.5 c | 7.9 e | 1.3 d | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 15.3 a | 48.4 a | 14.5 a | 5.9 a | 17.4 a | 6.0 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 14.2 b | 45.2 b | 14.1 ab | 5.5 ab | 16.2 b | 5.5 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 12.3 cd | 44.6 bc | 13.2 c | 4.7 b | 13.9 c | 4.9 c | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 12.7 c | 43.4 c | 13.7 b | 4.5 b | 14.2 c | 4.8 c | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 11.2 d | 41.3 d | 11.6 d | 3.5 c | 12.8 d | 3.6 d | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 10.3 e | 38.1 e | 9.3 e | 2.4 d | 11.2 e | 2.4 e | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 11.7 a | 35.7 a | 11.1 a | 4.5 a | 13.1 a | 4.1 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 10.7 b | 32.5 b | 10.8 ab | 4.1 ab | 11.9 b | 3.8 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 9.2 c | 31.3 c | 9.8 c | 3.4 b | 11.1 bc | 3.5 b | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 9.3 c | 29.0 d | 10.5 b | 3.3 b | 10.6 cd | 3.3 bc | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 8.6 cd | 26.4 e | 8.4 d | 2.8 c | 9.2 d | 2.5 c | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 7.8 d | 23.5 f | 7.1 e | 2.1 d | 7.6 e | 1.3 d | ||||
| 年份 Year | 粒位 Grain position | 盐处理 Salinity treatment | 干旱处理 Drought treatment | SSS酶活性 Activity of SSS(mol min-1 mg-1) | SBE酶活性 Activity of SBE(U g-1) | |||||
| 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | 15 DAH | 30 DAH | 45 DAH | |||||
| 2021 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.4 a | 6.5 a | 2.2 a | 4.5 a | 7.1 a | 3.1 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.3 a | 5.9 b | 2.0 ab | 4.5 a | 6.7 ab | 2.8 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.3 a | 4.7 c | 1.9 b | 4.4 a | 5.9 b | 2.6 ab | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.2 ab | 5.2 bc | 1.8 b | 4.3 a | 5.8 b | 2.5 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.2 ab | 4.5 c | 1.7 bc | 4.2 a | 4.7 c | 2.3 b | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.1 b | 3.8 d | 1.5 c | 4.1 a | 3.6 d | 2.0 b | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.2 a | 4.2 a | 1.5 a | 3.1 a | 4.8 a | 2.1 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.2 a | 3.7 b | 1.4 a | 3.1 a | 4.5 ab | 2.0 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.1 a | 3.1 cd | 1.4 a | 3.0 a | 3.8 b | 1.8 a | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.1 a | 3.3 c | 1.3 a | 2.9 a | 4.3 ab | 1.7 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.1 a | 2.5 d | 1.3 a | 2.9 a | 3.5 bc | 1.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.0 a | 1.7 e | 1.2 a | 2.8 a | 2.6 c | 1.5 b | ||||
| 2022 | 强势粒 SG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.3 a | 6.3 a | 2.5 a | 5.1 a | 7.8 a | 3.4 a | |
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.3 a | 5.9 ab | 2.3 a | 5.1 a | 7.5 ab | 3.2 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.2 a | 5.5 b | 2.3 a | 5.0 a | 6.7 b | 2.9 ab | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 3.1 a | 5.2 bc | 2.2 a | 4.8 ab | 6.5 b | 2.8 ab | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 3.1 a | 4.6 c | 2.2 a | 4.8 ab | 5.3 c | 2.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 3.0 a | 3.6 d | 2.0 a | 4.6 b | 4.1 d | 2.4 b | ||||
| 弱势粒 IG | 无盐 NS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.4 a | 4.4 a | 1.7 a | 3.4 a | 5.1 a | 2.3 a | ||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.3 a | 4.0 ab | 1.5 a | 3.4 a | 4.8 ab | 2.1 a | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.3 a | 3.5 b | 1.5 a | 3.3 a | 4.4 b | 1.9 a | ||||
| 高盐 HS | 浅水层灌溉 WW | 2.3 a | 3.6 b | 1.4 a | 3.2 a | 3.8 c | 1.9 a | |||
| 中度干旱 MD | 2.2 a | 2.9 c | 1.3 a | 3.2 a | 3.4 cd | 1.7 ab | ||||
| 重度干旱 SD | 2.2 a | 2.3 d | 1.2 a | 3.1 a | 2.5 d | 1.5 b | ||||
| 项目 Item | 产量 Grain yield | 成熟期干物质量 Dry matter weight at maturity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单位面积穗数 NP | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||
| 每穗粒数 SPP | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 结实率 SSR | 0.97** | 0.96** | ||
| 千粒重 1000-GW | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 抽穗期干物重 Dry matter weight at heading | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||
| 抽穗期至成熟期干物重积累量 Dry matter accumulation from heading to maturity | 0.98** | 0.99** | ||
| 收获指数 Harvest index | −0.95** | −0.96** | ||
| 强势粒 SG | 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax | 0.98** | 0.97** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 达最大灌浆速率的时间Tmax | −0.96** | −0.95** | ||
| 有效灌浆天数 EGP | −0.95** | −0.94** | ||
| 弱势粒 IG | 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax | 0.93** | 0.93** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.93** | 0.92** | ||
| 达最大灌浆速率的时间Tmax | −0.07 | −0.09 | ||
| 有效灌浆天数 EGP | −0.37 | −0.39 | ||
| 强势粒 SG | 前期 Early stage | 天数Days | −0.97** | −0.96** |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.97** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.93** | 0.93** | ||
| 中期 Middle stage | 天数Days | −0.94** | −0.93** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.94** | 0.94** | ||
| 后期 Late stage | 天数Days | −0.92** | −0.91** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.90** | 0.90** | ||
| 弱势粒 IG | 前期 Early stage | 天数Days | −0.14 | −0.16 |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.95** | 0.94** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 中期 Middle stage | 天数Days | −0.18 | −0.20 | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.93** | 0.93** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 后期 Late stage | 天数Days | −0.86** | −0.87** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.94** | 0.93** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
Table 9. Correlation analysis between grain yield, biomass weight at maturity and grain-filling characteristics of rice under salinity and drought stresses
| 项目 Item | 产量 Grain yield | 成熟期干物质量 Dry matter weight at maturity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单位面积穗数 NP | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||
| 每穗粒数 SPP | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 结实率 SSR | 0.97** | 0.96** | ||
| 千粒重 1000-GW | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 抽穗期干物重 Dry matter weight at heading | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||
| 抽穗期至成熟期干物重积累量 Dry matter accumulation from heading to maturity | 0.98** | 0.99** | ||
| 收获指数 Harvest index | −0.95** | −0.96** | ||
| 强势粒 SG | 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax | 0.98** | 0.97** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 达最大灌浆速率的时间Tmax | −0.96** | −0.95** | ||
| 有效灌浆天数 EGP | −0.95** | −0.94** | ||
| 弱势粒 IG | 最大灌浆速率 MGRmax | 0.93** | 0.93** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.93** | 0.92** | ||
| 达最大灌浆速率的时间Tmax | −0.07 | −0.09 | ||
| 有效灌浆天数 EGP | −0.37 | −0.39 | ||
| 强势粒 SG | 前期 Early stage | 天数Days | −0.97** | −0.96** |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.97** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.93** | 0.93** | ||
| 中期 Middle stage | 天数Days | −0.94** | −0.93** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.94** | 0.94** | ||
| 后期 Late stage | 天数Days | −0.92** | −0.91** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.98** | 0.97** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.90** | 0.90** | ||
| 弱势粒 IG | 前期 Early stage | 天数Days | −0.14 | −0.16 |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.95** | 0.94** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 中期 Middle stage | 天数Days | −0.18 | −0.20 | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.93** | 0.93** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| 后期 Late stage | 天数Days | −0.86** | −0.87** | |
| 平均灌浆速率 MGRmean | 0.94** | 0.93** | ||
| 灌浆量 GFA | 0.98** | 0.98** | ||
| [1] | Ford T W, Quiring S M. Comparison of contemporary in situ, model, and satellite remote sensing soil moisture with a focus on drought monitoring[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(2): 1565-1582. |
| [2] | Yoruk E, Keles E N, Sefer O, Eraslan M. Salinity and drought stress on barley and wheat cultivars planted in Turkey[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2018, 39(6): 943-950. |
| [3] | Yang J T, Wang J F, Xu C D, Liu Y, Yin Q, Wang X M, Wang L, Wu Y N, Xiao G X. Rice supply flows and their determinants in China[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 174: 105812. |
| [4] | 王才林, 张亚东, 赵凌, 路凯, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 梁文化, 孙明法, 严国红. 耐盐碱水稻研究现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国稻米, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhao L, Lu K, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Liang W H, Sun M F, Yan G H. Research status, problems and suggestions on salt-alkali tolerant rice[J]. China Rice, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Meng T Y, Zhang X B, Ge J L, Chen X, Yang Y L, Zhu G L, Chen Y L, Zhou G S, Wei H H, Dai Q G. Agronomic and physiological traits facilitating better yield performance of japonica/indica hybrids in saline fields[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 271: 108255. |
| [6] | Wei H H, Geng X Y, Zhu W, Zhang X, Zhang X B, Chen Y L, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Zhou G S, Meng T Y, Dai Q G. Individual and combined influences of salinity and drought stress on the agro-physiological traits and grain yield of rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2023, 304: 109172. |
| [7] | Wei H H, Geng X Y, Zhang X, Zhu W, Zhang X B, Chen Y L, Huo Z Y, Zhou G S, Meng T Y, Dai Q G. Grain yield, biomass accumulation, and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of rice under combined salinity-drought stress[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 118-128. |
| [8] | Zhang J, Zhang Y Y, Song N Y, Chen Q L, Sun H Z, Peng T, Huang S, Zhao Q Z. Response of grain-filling rate and grain quality of mid-season indica rice to nitrogen application[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(6): 1465-1473. |
| [9] | Ma B, Zhang L, He Z H. Understanding the regulation of cereal grain filling: The way forward[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2023, 65(2): 526-547. |
| [10] | Teng Z N, Chen Y K, Yuan Y Q, Peng Y Q, Yi Y K, Yu H H, Yi Z X, Yang J C, Peng Y, Duan M J, Zhang J H, Ye N H. Identification of microRNAs regulating grain filling of rice inferior spikelets in response to moderate soil drying post-anthesis[J]. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(4): 962-971 |
| [11] | Peng Y Q, Chen Y K, Yuan Y M, Liu B H, Yu P, Song S H, Yi Y K, Teng Z N, Yi Z X, Zhang J H, Meng S, Ye N H, Duan M J. Post-anthesis saline-alkali stress inhibits grain filling by promoting ethylene production and signal transduction[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2022, 11(3): e384. |
| [12] | 韦还和, 张翔, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 马唯一, 左博源, 孟天瑶, 高平磊, 陈英龙, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐胁迫对水稻籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2024, 50(3): 734-746. |
| Wei H H, Zhang X, Zhu W, Geng X Y, Ma W Y, Zuo B Y, Meng T Y, Gao P L, Chen Y L, Xu K, Dai Q G. Effects of salinity stress on grain-filling characteristics and yield of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(3): 734-746. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Chen T T, Xu G W, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Expression of proteins in superior and inferior spikelets of rice during grain filling under different irrigation regimes[J]. Proteomics, 2016, 16(1): 102-121. |
| [14] | Vijayaraghavareddy P, Akula N N, Vemanna R S, Math R G H, Shinder D D, Yin X Y, Struik P C, Makarla U, Sreeman S. Metabolome profiling reveals impact of water limitation on grain filling in contrasting rice genotypes[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 162: 690-698. |
| [15] | 朱庆森, 曹显祖, 骆亦其. 水稻籽粒灌浆的生长分析[J]. 作物学报, 1988, 14(3): 182-193. |
| Zhu Q S, Cao X Z, Luo Y Q. Growth analysis on the process of grain filling in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1988, 14(3): 182-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Zheng C, Liu C T, Liu L, Tan Y N, Sheng X B, Yu D, Sun Z Z, Sun X W, Chen J, Yuan D Y, Duan M J. Effect of salinity stress on rice yield and grain quality: A meta-analysis[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2023, 144: 126765. |
| [17] | Marcos M, Sharifi H, Grattan S R, Linquist B A. Spatio-temporal salinity dynamics and yield response of rice in water-seeded rice fields[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 195: 37-46. |
| [18] | Tong H, Duan H, Wang S J, Su J P, Sun Y, Liu Y Q, Tang L, Liu X J, Chen W F. Moderate drought alleviates the damage to grain quality at high temperatures by improving the starch synthesis of inferior grains in japonica rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21(10): 3094-3101. |
| [19] | 张晨, 戴良香, 张冠初, 丁红, 徐扬, 郭庆, 张智猛, 石书兵. 旱盐复合胁迫对花生荚果发育特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 花生学报, 2023, 52(1): 72-79. |
| Zhang C, Dai L X, Zhang G C, Ding H, Xu Y, Guo Q, Zhang Z M, Shi S B. Effects of drought-salt combined stress on pod development, yield and quality of peanut[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2023, 52(1): 72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 翁亚伟, 张磊, 张姗, 田中伟, 靳雪莹, 李梦雅, 余钟毓, 姜东, 戴廷波. 盐旱复合胁迫对小麦幼苗生长和水分吸收的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(7): 2244-2252. |
| Weng Y W, Zhang L, Zhang S, Tian Z W, Jin X Y, Li M Y, Yu Z Y, Jiang D, Dai T B. Effects of salt with drought stress on growth and water uptake of wheat seedlings[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(7): 2244-2252. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Kumar G, Basu S, Singla-Pareek S L, Pareek A. Unraveling the contribution of OsSOS2 in conferring salinity and drought tolerance in a high-yielding rice[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2022, 174(1): e13638. |
| [22] | Wang K K, Zhu J, Xu X W, Li T J, Wang X, Warner T A, Cheng T, Zhu Y, Cao W X, Yao X, Zhang Z D. Quantitative monitoring of salt stress in rice with solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2023, 150: 126954. |
| [23] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| Jing X, Zhou M, Wang J, Wang Y, Wang W, Wang K, Guo B W, Hu Y J, Xing Z P, Xu K, Zhang H C. Effect of drought stress on root morphology and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of good taste japonica rice from late stage of panicle differentiation to early stage of grain filling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Kumar S, Tripathi S, Singh S P, Prasad A, Akter F, Abu Syed M, Badri J, Das S P, Bhattarai R, Natividad M A, Quintana M, Venkateshwarlu C, Raman A, Yadav S, Singh S K, Swain P, Anandan A, Yadaw R B, Mandal N P, Verulkar S B, Kumar A, Henry A. Rice breeding for yield under drought has selected for longer flag leaves and lower stomatal density[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(13): 4981-4992. |
| [25] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| Zhu W, Zhang X, Geng X Y, Zhang Z, Chen Y L, Wei H H, Dai Q G, Xu K, Zhu G L, Zhou G S, Meng T Y. Morphological and physiological characteristics of rice roots under combined salinity-drought stress and their relationships with yield formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Peng L R, Xiao H J, Li R, Zeng Y, Gu M, Moran N, Yu L, Xu G H. Potassium transporter OsHAK18 mediates potassium and sodium circulation and sugar translocation in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2023, 193(3): 2003-2020. |
| [27] | Ji K X, Wang Y Y, Sun W N, Lou Q J, Mei H W, Shen S H, Chen H. Drought-responsive mechanisms in rice genotypes with contrasting drought tolerance during reproductive stage[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2012, 169(4): 336-344. |
| [28] | 顾世梁, 朱庆森, 杨建昌, 彭少兵. 不同水稻材料籽粒灌浆特性的分析[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(1): 7-14. |
| Gu S L, Zhu Q S, Yang J C, Peng S B. Analysis on grain filling characteristic for different rice types[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(1): 7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Zheng C K, Zhou G H, Zhang Z Z, Li W, Peng Y B, Xie X Z. Moderate salinity stress reduces rice grain yield by influencing expression of grain number- and grain filling-associated genes[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40(3): 1111-1120. |
| [30] | 于美芳. 分蘖期干旱胁迫对寒地粳稻产量形成的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2017. |
| Yu M F. Effects of drought stress at tillering stage on yield formation of japonica rice in cold region Harbin: Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [31] | 王新鹏. 孕穗期干旱胁迫对寒地粳稻碳代谢及产量形成影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020. |
| Wang X P. Effects of drought stress at booting stage on carbon metabolism and yield formation of japonica rice in cold region[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Prathap V, Ali K, Singh A, Vishwakarma C, Krishnan V, Chinnusamy V, Tyagi A. Starch accumulation in rice grains subjected to drought during grain filling stage[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 142: 440-451. |
| [1] | LU Yezi, QIU Jiehua, JIANG Nan, KOU Yanjun, SHI Huanbin. Research Progress in Effectors of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [2] | WANG Chaorui, ZHOU Yukun, WEN Ya, ZHANG Ying, FA Xiaotong, XIAO Zhilin, ZHANG Hao. Effects of Straw Returning Methods on Soil Characteristics and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Fields and Their Regulation Through Water-fertilizer Interactions [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [3] | WANG Yaxuan, WANG Xinfeng, YANG Houhong, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, CAI Yubiao, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun. Recent Advances in Mechanisms of Adaptation of Planthoppers to Rice Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [4] | HUANG Tao, WEI Zhaogen, CHENG Qi, CHENG Ze, LIU Xin, WANG Guangda, HU Keming, XIE Wenya, CHEN Zongxiang, FENG Zhiming, ZUO Shimin. Gene Cloning and Broad-spectrum Disease Resistance Analysis of Rice Lesion Mimic Mutant lm52 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| [5] | MA Shunting, HU Yungao, GAO Fangyuan, LIU Liping, MOU Changling, LÜ Jianqun, SU Xiangwen, LIU Song, LIANG Yuyu, REN Guangjun, GUO Hongming. Functional Study of Rice Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor OseIF6.2 in Grain Size Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [6] | ZHANG Bintao, LIU Congcong, GUO Mingliang, YANG Shaohua, WU Shiqiang, GUO Longbiao, ZHU Yiwang. Evaluation of Blast Resistance and Identification of Superior Haplotype of OsDR8 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [7] | WEI Xinyu, ZENG Yuehui, XIAO Changchun, HUANG Jianhong, RUAN Hongchun, YANG Wangxing, ZOU Wenguang, XU Xuming. Cloning and Functional Verification of Rice-Blast Resistance Gene Pi-kf2(t) in Kangfeng B [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [8] | LI Wenqi, XU Yang, WANG Fangquan, ZHU Jianping, TAO Yajun, LI Xia, FAN Fangjun, JIANG Yanjie, CHEN Zhihui, YANG Jie. Development and Application of KASP Marker for Broad-Spectrum Resistance Gene PigmR to Rice Blast [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [9] | ZHANG Haiwei, GU Xinyi, CHEN Mingshuai, LI Fukang, SHI Yuecheng, YANG Ting, JIANG Shuochen. Effects of Nitrogen Type of Basal Fertilizer on Growth, Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 387-398. |
| [10] | SHEN Zhida, YU Qiuhua, ZHANG Bin, CAO Yudong, WANG Shaohua, WANG Hongfei, WU Yongqing, DAI Zhigang, LI Xiaokun. Effects of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rate on Grain Yield, Phosphorus Accumulation and Utilization of Direct-seeded Rice in Hubei Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [11] | HE Yong, ZHANG Shiqian, WANG Zhicheng, ZHAN Xiaokang, DING Yike, LIU Xiaorui, MA Susu, TIAN Zhihong. Synergistic Impact of Piriformospora indica and Compound Fertilizer on Rice Seedling Quality for Mechanical Transplanting [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| [12] | WU Jinshui, TANG Jiangying, TAN Li, GUO Zhiqiang, YANG Juan, ZHANG Xinzhen, CHEN Guifang, WANG Jianlong, SHI Wanju. Mechanisms of Arsenic Uptake and Transport in Rice and Agronomic Mitigation Strategies [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [13] | MA Weiyi, ZHU Jizou, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, DIAO Liuyun, WANG Lulu, MENG Tianyao, GAO Pinglei, CHEN Yinglong, DAI Qigen, WEI Huanhe. Research Progress in Effects of Salt and Drought Stresses on Rice Quality Formation and Associated Physiological Mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [14] | ZHANG Laitong, YANG Le, LIU Hong, ZHAO Xueming, CHENG Tao, XU Zhenjiang. Research Advances of Fragrance Substances in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| [15] | FENG Tao, ZHANG Zhaoyang, HUANG Xinni, WANG Yue, ZHONG Xuzhi, FENG Zhiming, LIU Xin, ZUO Shimin, OUYANG Shouqiang. Osa-miR166i-3 Positively Regulates Resistance to Sheath Blight Through Mediating the Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 187-196. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||